
A Study of Multi-Objective Optimisation Algorithms
Peiqi Gao
a
Mathematics and Statistics, Xidian University, Xi`an, Shaanxi Province, 710071, China
Keywords: Multi-Objective Optimisation, AHP Combined with EWM, NSGA-II, PSO.
Abstract: In production activities, the problem often involves the optimisation of multiple objectives, and the traditional
single-objective problem-solving methods are unable to deal with optimisation problems with multiple
objectives. Traditional single-objective optimization methods usually focus on the optimal solution of one
objective function, while multi-objective optimization problems need to consider multiple objective functions
at the same time. This paper offers a comprehensive summary of the approaches to multi-objective
optimization problems and proposes recommendations for future development. Firstly, the development
history of multi-objective optimisation algorithms is reviewed, and then the related concepts of multi-
objective problems, such as pareto optimal solution set, are briefly explained. In this paper, multi-objective
optimisation algorithms are broadly classified into three categories: multi-objective weighting methods,
multi-objective population genetic algorithms, and multi-objective individual evolutionary algorithms. The
advantages and disadvantages of the three main types of methods are analysed by practical examples of the
methods, and suggestions for subsequent improvements are given based on limitations.
1 INTRODUCTION
In engineering and scientific contexts, it's common to
encounter optimisation problems where the goal is to
achieve optimality within a specific domain. These
are referred to as multi-objective optimisation
problems when multiple objectives are involved. For
example, when optimising the purchase of an item,
the decision maker usually has to balance price and
quality.
The solution to multi-objective optimisation
problems is very commonly used in production
activities, and researchers are constantly proposing
new ideas to deal with them. From 1896, Pareto
proposed the optimal solution of pareto to the
beginning of the 20th century, multi-objective
optimisation was introduced into finance and other
fields, marking the gradual formation of the
theoretical basis of multi-objective optimisation;
During the mid-to-late 20th century, scientists and
researchers primarily approached multi-objective
optimization problems by converting them into
single-objective problems, such as: the objective
function weighting method (Xiao, 2011). During the
transition from the 20th to the 21st century,
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-7480-8746
researchers applied population genetic algorithms in
the field of computational intelligence to multi-
objective optimisation. Later individual algorithms,
such as Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
(PSO) were applied to multi-objective optimisation.
Since then, new methods have been proposed, such as
Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithm based on
Decomposition (MOEA/D), but they are not
considered in this paper for the time being.
When dealing with multi-objective optimisation
problems, the main problem is how to make multiple
objectives reach the optimal solution. In the problem,
when one objective is optimized, the performance of
the other objectives usually decreases. This is because
a multi-objective optimization problem involves a
contradiction between the various sub-objectives.
Therefore, a compromise must be made to achieve the
best possible outcome. In other words, there are
solutions that cannot be compared in terms of their
advantages and disadvantages. Consequently,
solutions to multi-objective optimization problems
are not unique. Instead, there exists a set of optimal
solutions, which is referred to as the Pareto optimal
solution set.
Gao, P.
A Study of Multi-Objective Optimisation Algorithms.
DOI: 10.5220/0013680600004670
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Data Science and Engineering (ICDSE 2025), pages 175-181
ISBN: 978-989-758-765-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
175
This paper classifies multi-objective optimisation,
which is often used in scientific experiments, into
three categories, multi-objective weighting method
(which uses weighting to convert a multi-objective
problem into a single-objective problem.), multi-
objective population genetic algorithm (which
introduces multi-objective optimisation into the
framework of genetic algorithms), and multi-
objective individual evolutionary algorithms (which
applies an initial solution to generate a subsequent
solution). The corresponding computational
principles are analysed as well as specific
applications in scientific experiments. Ultimately and
give directions for improvement.
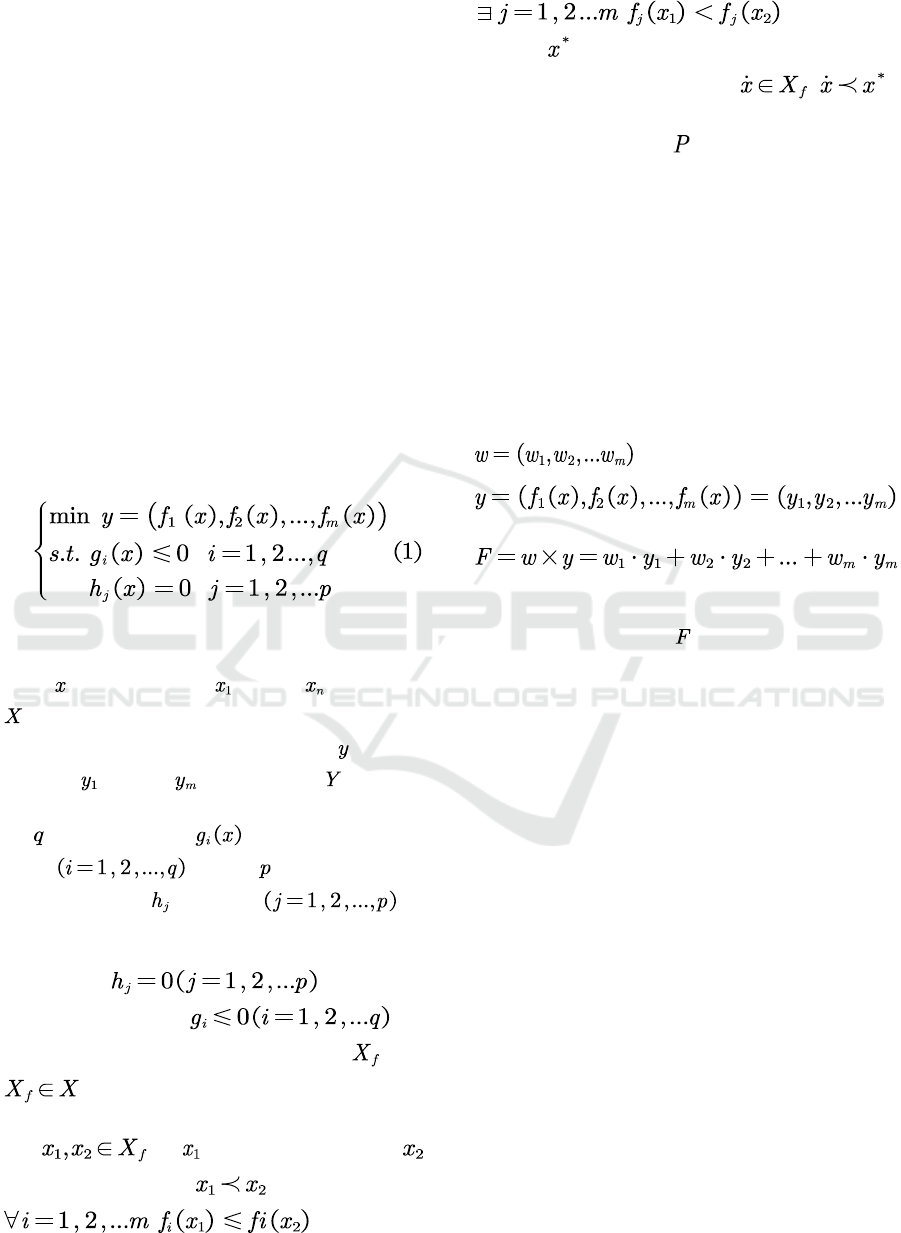
2 MATHEMATICAL
DESCRIPTION
The multi-objective problem can be described in the
following standard form
There are m objective functions, and the variables
involved in decision-making are n-dimensional. The
vector
, which includes through , belongs to
, an n-dimensional space for making decisions.
The variable representing objectives,
, which
includes
through , belongs to , the m-
dimensional space of objectives. Furthermore, there
are
constraints where is less than or equal to
zero
and constraints are
established where
equals zero .
Definition 1 (Feasible Solution) A solution is said
to be feasible if and only if it satisfies the equality
constraints
and the
inequality constraints
in .
The set of all feasible solutions, denoted as
, and
Definition 2 (pareto optimal solution) Assume
that
, is pareto dominated
(dominated as
, ) if
and
. A feasible
solution
is a pareto optimal solution (or non-
dominated solution) if there is no
.
and the set of all pareto optimal solutions is the set of
pareto optimal solutions
.
3 MULTI-OBJECTIVE
WEIGHTING METHOD
3.1 Overview of the Weighting Method
The core idea of the weighting method is to convert a
multi-objective optimization problem into a single-
objective one by assigning weights to the various
objective functions. Let’s denote the weights as
and the objective functions as
. By calculating
, the multi-objective optimization problem is
effectively transformed into finding the feasible
solution that maximizes
, thereby identifying the
optimal solution.
The core of the weighting method lies in the
assignment of weights. There are three main
approaches to assigning weights: the subjective
weighting method, the objective weighting method,
and the integrated subjective and objective weighting
method. Among the commonly used subjective
weighting techniques, the Analytic Hierarchy Process
(AHP) and the Grey Analytic Hierarchy Process
(GAHP) are often utilized. However, these methods
are rather rough, and personal subjective factors have
a significant impact on the solution (Guo, 2008).
When it comes to problems requiring higher
precision, the results may not be consistent with the
actual situation.
Objective weighting techniques encompass
methods such as the Entropy Weight Method (EWM)
and Principal Component Analysis (PCA), among
others. This type of method is calculated based on the
data of the program (Wang, 2011). The results are
relatively objective, avoiding the influence of the
evaluator's subjective factors on the weight of the
indicators. Nevertheless, the Entropy Weight Method
(EWM) also has its drawbacks. The weights of the
indicators obtained through it only indicate the
relative intensity of the competition among the
ICDSE 2025 - The International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
176
indicators, rather than the true significance of the
metrics. Moreover, the determination of its weight
relies entirely on the relationship between the
objective data. When the objective data is more
special, the weight will differ from the actual
situation.
The subjective-objective comprehensive
weighting method usually combines the two
approaches mentioned above, such as the Analytic
Hierarchy Process-Entropy Weight Method (AHP-
EWM)(Fei, 2009). However, in the process of
seeking the integrated weights with this method, the
combination is merely a simple synthesis of the
results of the indicators after using each of the
subjective and objective methods to find the weights
of all the indicators.
3.2 Analytic Hierarchy Process-
Entropy Weight Method
Among all weighting methods, the most commonly
used in scientific research is (AHP-EWM) in the
subjective-objective integrated weighting method.
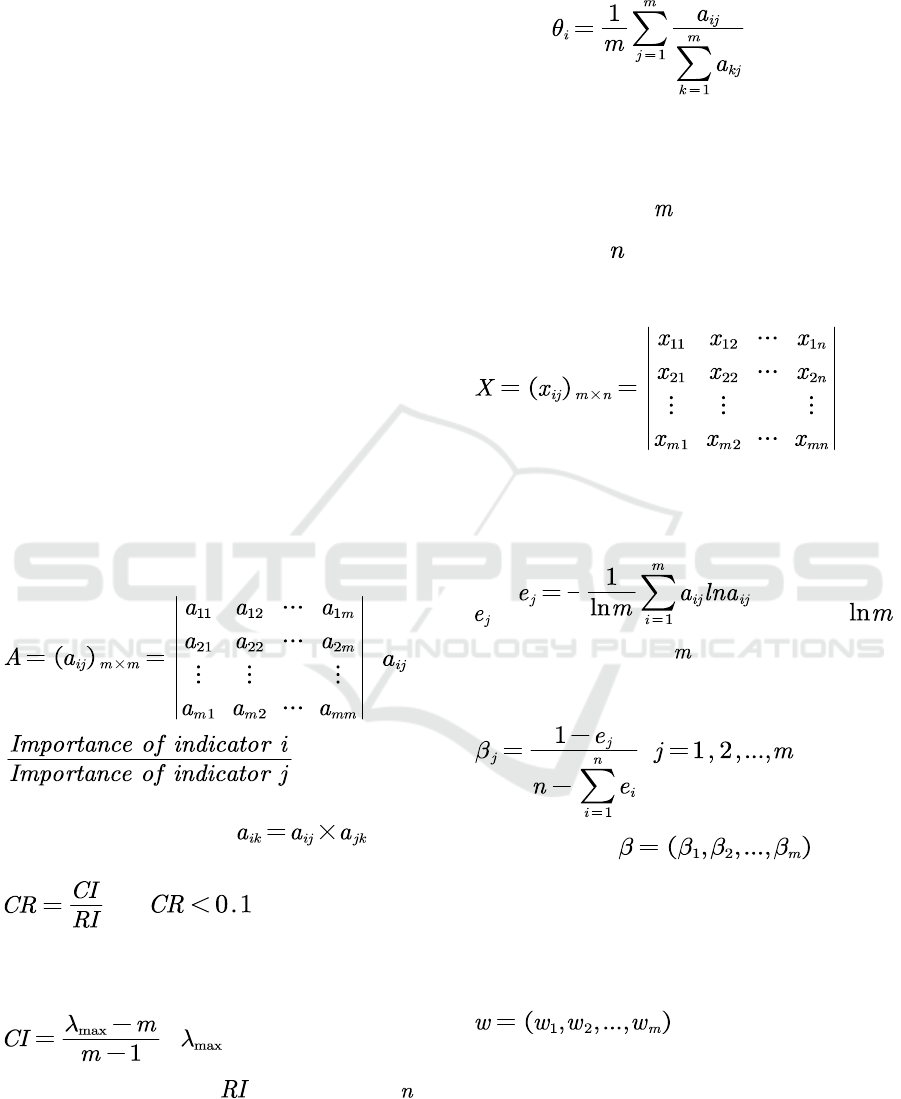
3.2.1 Calculation of Analytic Hierarchy
Process weights
Assume that the judgement matrix
is
1) Consistency test. Test whether the whole
judgement matrix meets
, by
judging the size of the consistency ratio coefficient
. If , the consistency of
the judgement matrix isn't acceptable, adjustments
are needed to ensure it meets the required
consistency. The consistency coefficient
, is the largest eigenvalue
of the judgement matrix.
is determined by ,
and the specific function value can be obtained
through the relevant table.
2) Calculate the weights by performing column
normalisation followed by arithmetic mean to the
weights,
3.2.2 Calculation of Entropy Weighting
Method Weights
Let there be a total of data points, each data point
corresponds to
objective function values, the
corresponding objective function value of the data
points constitutes an evaluation matrix
The
operation procedure is as follows
Pre-processing of the above matrix such as data
regularisation, normalisation etc.
Calculate the entropy measure of the jth parameter
, , where
denotes the logarithm of
Calculate the entropy value corresponding to the
entropy weights
to get the
entropy weights.
3.2.3 The Final Weights
Multiply the weights of the hierarchical analysis and
entropy weighting methods and then normalise by
multiplication to get the final weights
3.3 Example of the Use of Hierarchical
Analysis-Entropy Weight Method
In practical applications, the hierarchical analysis-
entropy weight method is mainly used in the case of
A Study of Multi-Objective Optimisation Algorithms
177
limited decision-making methods, and Wang Huibin
and others applied this method to photovoltaic power
generation projects. The three main indicators in
photovoltaic power generation are scale, cost, and
benefit (Wang, 2022). The scale is determined by the
installed capacity, the number of hours of power
generation, and the amount of power generated. Cost
is determined by the averageised cost of electricity,
the investment per unit of electricity, and the time to
start earning. Benefits are determined by the internal
rate of return (IRR), which indicates profitability over
the entire operating period, and the net present value
(NPV), which measures net income per unit of
operating time. In this context, all indicators for scale
and benefit are maximizing. Indicators that are
maximized have larger corresponding values, while
those that are minimized have smaller values.
All indicators are normalised (all indicators are
converted into very large ones, which can be inverted)
and then dimensionless. Use Hierarchical Analysis-
Entropy Weighting to get the priority of each
scenario. The prioritisation results were compared
with the results obtained using only Hierarchical
Analysis and only Entropy Weights. The results
obtained were found to be superior.
4 MULTI-OBJECTIVE
POPULATION GENETIC
ALGORITHM
4.1 Overview of Multi-Objective
Population Genetic Algorithms
Over the past 30 years, genetic algorithms
have
developed rapidly. Scientists have applied genetic
algorithms to multi-objective optimisation problems
(Ma, 2007). This has been accompanied by the
introduction of concepts related to the Pareto optimal
solution set. As a result, the success rate of multi-
objective genetic algorithms has been further
guaranteed in terms of their computational results.
The Genetic Algorithm (GA) is a method for
finding optimal solutions, inspired by the biological
principle of "survival of the fittest." In this context,
the fitness value indicates the quality of a solution,
which is reflected by the final function value.
Additionally, GA involves encoding and decoding
operations, where feasible solutions are converted
into strings of characters, such as numbers or letters.
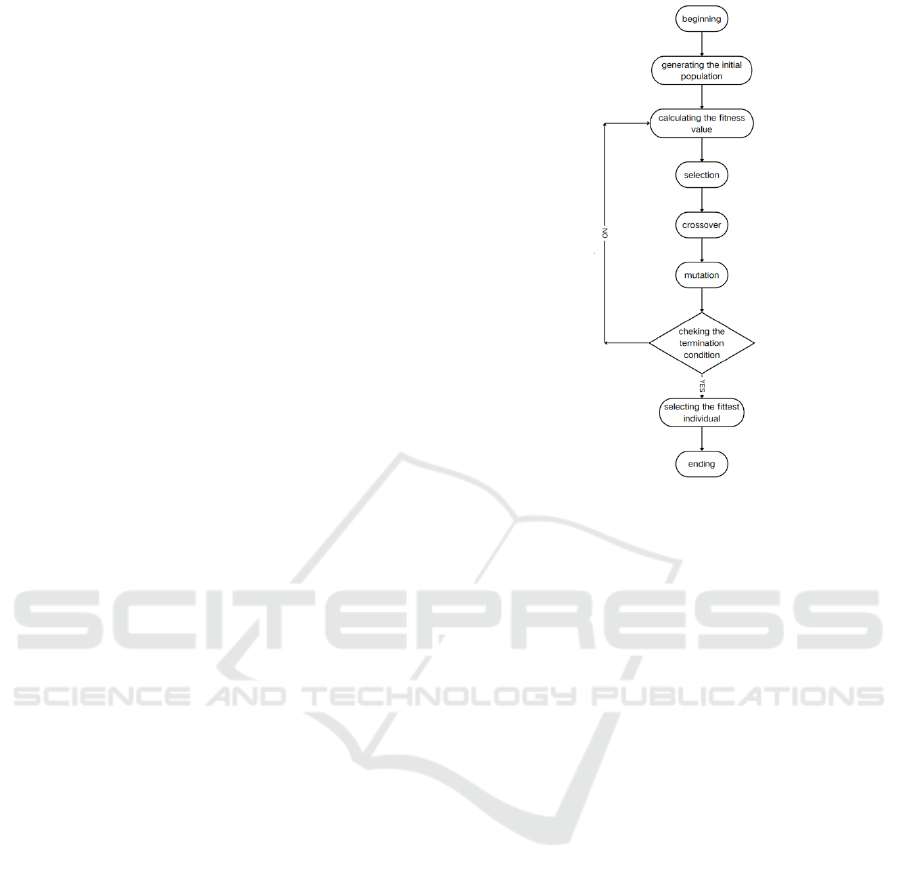
Figure 1: The flow of the genetic framework.(Picture credit :
Original)
The fundamental processes include selection,
recombination, and mutation, in figure 1.
Selection is used to choose better individuals from
the group. It increases the probability of these better
individuals being selected. This can ensure the
convergence of the algorithm. Common selection
methods include the roulette wheel selection method
(RWS). The individual's fitness value is directly
converted into the probability of being selected.
Crossover, where information is exchanged for
multiple parent individuals selected to produce new
child individuals. The diversity of solutions can be
ensured and local convergence due to too fast
convergence can be avoided to some extent. Common
crossover methods include single-point crossover, etc.
mutation, one of the selected parent individuals is
manipulated to produce a new child individual. It also
ensures the diversity of solutions and to some extent
avoids local convergence due to too fast convergence.
However, the difference with crossover is that
crossover requires at least two parent individuals,
while mutation can be achieved with only one parent
individual; at the same time, the probability of
crossover occurring is greater than the probability of
mutation occurring. A common method of mutation
is single point mutation.
ICDSE 2025 - The International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
178

4.2 Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic
Algorithm II (NSGA-II)
The common multi-objective genetic algorithms are
Vector Evaluated Genetic Algorithm (VEGA), Non-
dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm (NSGA), and
Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm
(SPEA)(Xu,2007). All of these methods use the
framework of genetic algorithms and also apply
pareto dominance relationships, which finally have
significant results in ensuring diversity. However,
although all of these methods employ the framework
of genetic algorithms, the specifics of each step are
different. In the following section, the commonly
used multi-objective genetic algorithm is described in
detail: Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II
(NSGA-II)(Gao, 2006)
Perform a fast non-inferiority stratification for the
population
. That is, according to the pareto
dominance relationship, individuals that do not have
dominance relationships with each other are in the
same non-inferiority stratum, where individuals that
are not dominated by any individual are in the first
stratum, those that are only dominated by individuals
in the first stratum are in the second stratum, and so
on until all individuals of the population have been
stratified. Individuals in the same stratum are also a
group of individuals, with the first stratum being the
first group and the second stratum being the second
group. According to the result of non-inferiority
stratification, the population
can be divided into
non-inferiority groups, i.e .,the first
group
is the optimal non-inferiority group of the
population.
Crowding degree calculation, Crowding degree
can indicate the density of individuals in the space.
Assume that the jth non-inferiority group consists of
m individuals. After the jth non-inferiority group is
desorted for the mth objective function value, an
infinite distance is assigned between the first and last
points, and the congestion degree distance for the ith
individual is calculated as
denoting the maximum and minimum values,
respectively
The dominance relation can be further extended
by the crowding degree calculation in step 2). That is,
, i.e., it means that when two solutions belong to the
same non-inferior group, the solution with greater
crowding degree is preferred.
Add the elite strategy in selecting the best
individual. That is, the selection range of individuals
is increased to the concatenation of parents and
children, expanding the search range and making the
algorithm less likely to fall into local optimal
solutions.
4.3 Application of NSGA-II Algorithm
Wang Xi employed the NSGA-II algorithm to tackle
the issue of connecting wind farms to the grid and
expanding the grid, with the aim of reducing costs,
minimizing grid expansion, and lowering pollutant
emissions (Wang, 2011). The final objective is
reached by adjusting the independent variables wind
farm access location, access capacity, and the scheme
of grid expansion.
By comparing the other algorithms, it is
concluded that the NSGA-II ensures the stability of
the algorithm results, i.e., it works well for most of
the cases. At the same time, it does not need a priori
knowledge to get the weights, and the calculation
process is more intelligent.
5 MULTI-OBJECTIVE
INDIVIDUAL EVOLUTIONARY
ALGORITHMS
5.1 Brief Description of Multi-
Objective Individual Evolutionary
Algorithms
In the last fifteen years, population-based algorithms
such as genetic algorithms have not developed
significantly, but some optimisation algorithms based
on individual search mechanisms have developed
rapidly, such as Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
(Zhang, 2004), Ant Colony Optimization (ACO)
(Duan, 2004). These algorithms are different from the
mechanism of eliminating individuals in genetic
algorithms, but update and iterate each individual in
the population based on the optimal solution of the
current individual and population. Therefore, this
type of algorithm has more interaction of information
between individuals, and has memory and
consistency for the update route. At the same time,
the update is more flexible and less likely to fall into
local optimal solutions.
A Study of Multi-Objective Optimisation Algorithms
179
5.2 Multi-Objective Particle Swarm
Algorithm
Among the individual-based search mechanism
optimisation methods, the particle swarm algorithm is
more frequently utilized. In this study, we will first
introduce the particle swarm algorithm, and then
describe how to apply the particle swarm algorithm to
multi-objective optimisation problems.
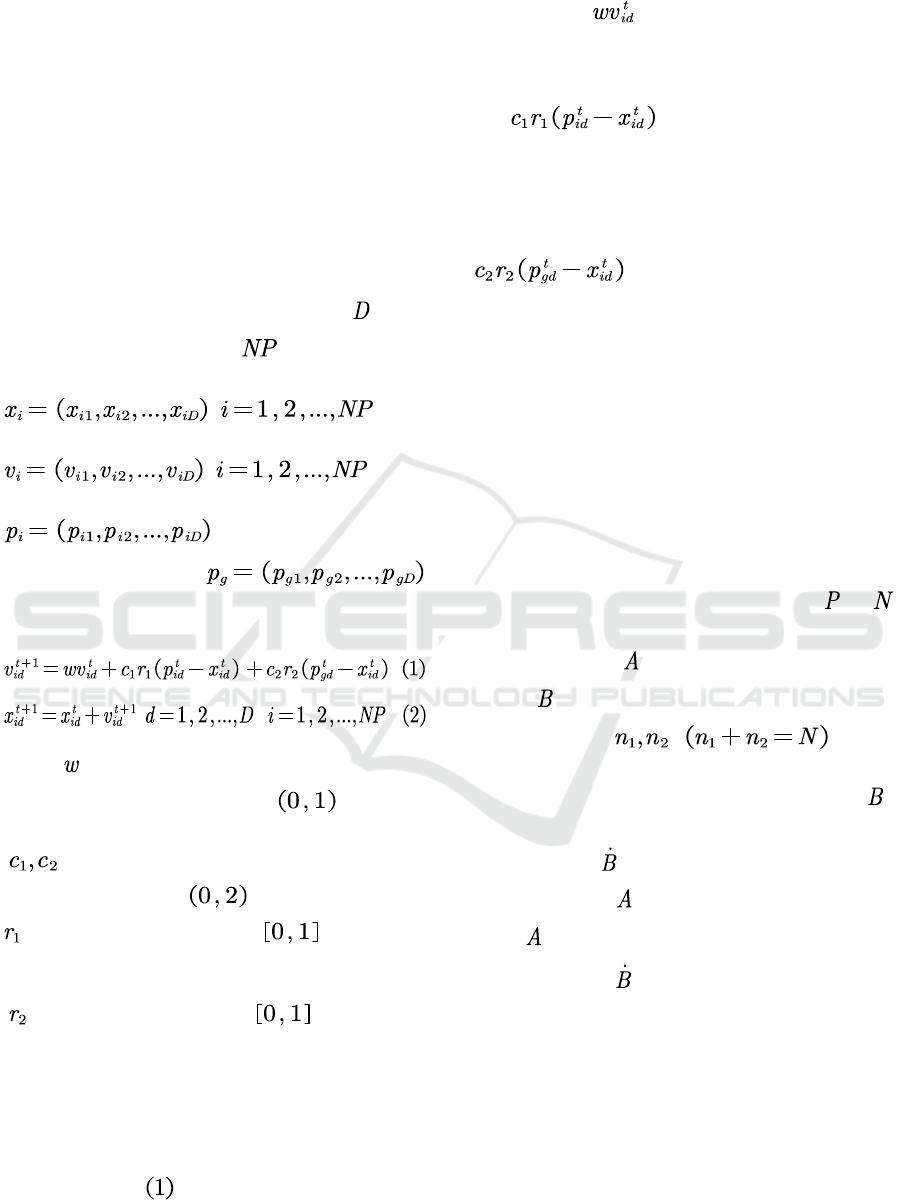
5.2.1 The Particle Swarm Algorithm
The basic particle swarm algorithm is mainly for
single-objective optimisation problems, let
be the
size of the parameter space,
be the size of the
population, and the particle is ,
.The
corresponding velocity
The
best position for this particle so far is
, and the best position for
the whole population is.
According to the iterative formula
where
is the inertia index and is a number
generated by a random process in
. reflecting
the dependence on the previous speed
is the acceleration weight, a number generated
by a random process in
is the stochastic number in is called the
cognitive factor. Reflects dependence on one's own
experience
is the random number in is the social
factor. Reflects the degree of dependence on group
experience
The coordinates of the particles in the population are
updated iteratively until the requirements of the
question are met (either the number of iterations
required or the accuracy required). By observing the
iteration formula
, we can find that the velocity
iteration formula is roughly divided into three parts,
the first part
indicates that it receives the
influence of the last velocity vector, i.e., it is
influenced by its own velocity at the last moment,
which is also known as the memory term. The second
part
Indicates that the velocity of
the particle receives the influence of the vector from
the current position to the particle's optimal point, i.e.,
it indicates that it receives the influence of the
particle's optimal point, which is also known as the
self-cognition term. The third part
indicates that the velocity receives
the influence of the vector from the current individual
position to the group optimal position, which can
reflect the influence of receiving the group optimal
point, also known as the group cognitive term. Also
All are random numbers, which can increase the
diversity of the solution.
5.2.2 Applications of Multi - Objective PSO
For the multi-objective particle swarm algorithm,
since there is no single optimal solution, only the
optimal solution set exists, i.e., The ultimate objective
is to achieve the best possible solutions. Based on the
pareto dominance relation, the population
of
is divided into two populations, one is the non-
dominated subset
, the other is the dominated
subset
, and the corresponding numbers of
individuals are
. Each
update of the individual coordinates of the particle
population is only for the dominant subset
.
Determine the dominance relationship between the
updated subset
and the individuals in the non-
dominated subset
, if there is an individual in the
subset
that is dominated by an individual in the
dominated subset
, then replace the corresponding
individual. The update is iterated until the termination
condition (accuracy or number of iterations) is met.
5.3 Application of Multi-Objective
Particle Swarm Algorithm
Gu applied particle swarm optimisation (PSO)to a
Combined Heat and Power (CHP)-based Microgrid
system (Gu, 2012). A Combined Heat and Power
(CHP)-based Microgrid system mainly refers to a
ICDSE 2025 - The International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
180

system that can control the simultaneous production
of electricity and heat. The final objective function is
to minimise the operating cost, carbon monoxide
emission and nitrogen oxide emission. Meanwhile,
the constraints are: battery charging and discharging
balance and surplus supply of heat energy. The
particle swarm algorithm was applied to optimisation
in two cases: a hospital and a school. The final
calculation results were found to be reasonable. It was
concluded that the particle swarm algorithm is widely
used in the field of combined heat and power supply.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, the existence of multi-objective
problems is firstly introduced widely, after which the
basic concepts about multi-objective problems, such
as feasible solution sets, are introduced. After that, the
common methods for solving multi-objective
problems are classified into three categories,
describing their mathematical principles and
applications in real life, and comparing the
advantages and disadvantages between different
methods. All three types of methods can be improved.
The main element involved in the weighting
method is the determination of the weight vectors, a
part that is difficult to improve if one wants to make
innovations in the mathematical theory. In addition to
the determination method can be improved, the
weights can be made adaptive, that is, the weights are
not fixed in the arithmetic process, and do not need
human intervention to improve. Multi-objective
population genetic algorithms are also relatively well-
developed at the structural level of the algorithm.
However, the determination of some parameters can
utilize emerging computational methods in recent
years, such as surrogate models and machine
learning. Yet, the choice of specific methods still
needs to be tailored to the specific application
scenario. For the recently emerged multi-objective
individual evolutionary algorithms, there are many
innovations, such as the introduction of the farthest
point from the point and the nearest point in the
iterative formula to avoid the local optimal solution,
as well as the introduction of other particles in the
population to improve the iterative formula and so on.
REFERENCES
Duan, H., Wang, D., Zhu, J., et al., 2004. Progress in the
theory and application research of ant colony algorithm.
Control and Decision Making, (12), pp.1321-
1326+1340.
Fei, Z., 2009. Research on entropy right-hierarchical
analysis method and grey-hierarchical analysis method.
Tianjin University.
Gao, Y., 2006. Research and application of non-dominated
sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA). Zhejiang
University.
Gu, W., Wu, Z., WANG, R., 2012. Multi-objective
operation optimisation of cogeneration-type microgrid
considering pollutant gas emission. Power System
Automation, 36(14), pp.177-185.
Guo, J., Zhang, Z., Sun, Q., 2008. Research and application
of hierarchical analysis. Chinese Journal of Safety
Science, (05), pp.148-153.
Ma, Y., Yun, W., 2012. Research progress of genetic
algorithm. Computer Application Research, 29(04),
pp.1201-1206+1210.
Wang, Y., 2011. Comprehensive evaluation of professional
journals of library and intelligence in mainland China -
A comparative study based on entropy weighting,
principal component analysis and simple linear
weighting. Intelligence Science, 29(06), pp.943-947.
Wang, H., Hu, F., Liu, Y., 2022. Research on multi-
objective decision analysis of photovoltaic power
generation project. Hydropower Generation, 48(10),
pp.99-103.
Wang, X., Zhang, P., 2011. Multi-objective grid planning
for wind farms using NSGA-II hybrid intelligent
algorithm. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering,
31(19), pp.17-24.
Xiao, X., Xiao, D., Lin, J., et al., 2011. Research overview
of multi-objective optimisation problems. Computer
Application Research, 28(03), pp.805-808+827.
Xu, L., 2007. Research and application of multi-objective
optimisation problem based on genetic algorithm.
Central South University.
Zhang, L., Zhou, C., Ma, M., et al., 2004. Solving multi-
objective optimisation problems based on particle
swarm algorithm. Computer Research and
Development, (07), pp.1286-1291.
A Study of Multi-Objective Optimisation Algorithms
181
