
The Role of Interaction Design in Narrative-Driven Games with a
First-Person Perspective in Fostering User Emotional Connection
Yingxi Cao
a
School of Information Science and Technology, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Game Interaction Design, Game Emotional Experience, Emotional Resonance, Story-Based Games.
Abstract: With the development of the gaming industry, video games have increasingly demonstrated emotional and
social functions, in addition to providing entertainment experiences for players. This shift has gradually
moved the focus from product-oriented design to a user-oriented approach centered on player emotional
experience. This study investigates the impact of interactive features in narrative-driven games on emotional
experiences. A questionnaire based on a Likert scale was used to survey and analyze players’ perceptions and
thoughts on existing game interaction features. The study found that players generally prefer interactive
features that offer autonomy in making choices and decisions, especially dialogue choices, branching
storylines, and moral choices. These features significantly enhance their sense of agency and emotional
experience within the game's narrative. Additionally, players hope that future games will provide more
authentic and nuanced choices, reduce the occurrence of pseudo-choices, and more finely reflect the impact
of player decisions on the direction of the story. However, complex interactive features, if poorly designed,
may cause players to lose interest in the main storyline. This suggests that game designers need to strike a
balance between enhancing player immersion and maintaining narrative clarity.
1 INTRODUCTION
Video games often provide players with a wide range
of emotional experiences. Tom Cole's study suggests
that, nowadays, players prefer to seek eudaimonic
experiences in addition to hedonistic experiences of
pleasure and hedonism when playing video games
(Tom&Marco, 2022). This conclusion suggests that
more and more players consider video games a means
of personal growth and meaningful engagement
rather than mere entertainment. For example, in the
game Journey, players can feel a sense of loneliness,
hope, and belonging as well as contemplate the
meaning of life by exploring the desert and
interacting with others. This study also concluded that
eudaimonic experience is a kind of game experience
that can bring deep emotional and cognitive
experiences, which can help players better understand
themselves, others, and the world, and promote self-
development. These experiences often challenge
players to confront difficult questions about
mortality, ethics, and human nature, leading to
personal growth and emotional maturity. Besides, by
analyzing the emotional experience in the interaction
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-0818-7000
design of the popular game League of Legends,
Zhang Yanlin and Zhang Tingxiang investigated the
impact of emotional factors on the interactive design
of internet games and proposed emotional interaction
design strategies tailored for online games
(Zhang&Zhang, 2016).
For the past few years, there has been an
increasing amount of discussion and research on
‘Game Emotional Experience’ and ‘Emotional
Interaction Design’, more and more people have
started to pay attention to the eudaimonic emotional
experience that games bring to players. This growing
academic interest reflects the gaming industry's
evolution toward more sophisticated emotional
storytelling and player engagement strategies.
However, more of these studies are based on specific
themes and types of video games. For example, when
designing a musical game, let players get more
diverse emotional experiences of the game by
changing the song's attributes (e.g., tempo, length),
designing different game modes and difficulties, or
adding multiplayer battle sessions, etc. Such as other
battle format RPG games can also use these ways to
enhance the player's emotional experience. For
154
Cao, Y.
The Role of Interaction Design in Narrative-Driven Games with a First-Person Perspective in Fostering User Emotional Connection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013680300004670
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Data Science and Engineering (ICDSE 2025), pages 154-160
ISBN: 978-989-758-765-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

narrative-driven games, the absence of combat
mechanics and diverse game modes raises critical
questions regarding the enhancement of player
emotional engagement. Investigating whether the
design of interactive features tailored to the narrative
or more creatively designed can strengthen user
emotional connections is of significant value for
future design and development of narrative games.
Drawing upon questionnaire data from ‘The
Impact of Interactive Functions in Story Games on
Emotional Experience’, this research investigates
public preferences and emotional responses to current
game interactive features. Players were prompted to
share insights and recommendations regarding the
design of prevalent game interactive functions,
informed by their gameplay experiences. This paper
analyzes the influence of interactive function design
on augmenting user emotional engagement and
identifies avenues for future refinement.
2 GAME INTERACTION DESIGN
AND EMOTIONAL
EXPERIENCE
2.1 Game Interaction Design
2.1.1 Concept
Game interaction design typically refers to the
process in game development where designers plan
and construct fundamental elements such as game
mechanics, interface styles, and operational methods
to facilitate effective interaction between players and
the game system. This approach aims to enhance
game playability while delivering rich emotional
experiences for players.
Compared to other interaction design fields, game
interaction design necessitates consideration of
factors such as game type, gameplay mechanics, and
target player demographics. For instance, in First-
Person Shooter (FPS) games, inventory management
systems provide players with backpack functionality,
while timers are used when switching weapons or
skills to calculate time, thereby enhancing the realism
of the combat environment and immersing players in
the intense and thrilling atmosphere. In narrative-
driven games, the storytelling aspect means that
players must fully embody the game characters and
scenarios to fulfill the narrative function better and
convey the values the game intends to express.
Furthermore, in games, interaction design places
greater emphasis on how to enrich the effects and
changes brought about by each action, including
alterations in environmental sound effects and scene
lighting, the advancement of game plots and progress,
and the achievement of specific milestones.
2.1.2 Key Elements
The core elements of game interaction design
primarily encompass interface design, interaction
logic, and feedback systems. The interface serves as
the primary medium through which players perceive
game rules and states, encompassing the heads-up
display (HUD), menu systems, and informational
prompts. Interface design must ensure a rational and
legible layout, providing essential information and
assistance without compromising the player's
immersion.
Interaction logic encompasses fundamental
interactive mechanisms such as game controls, key
mappings, and input responses. When designing
interaction logic, it is crucial to ensure that the
interactive system is intuitive, easily understood, and
provides immediate responses, enabling players to
accurately interpret the designer's intent and execute
their desired actions.
A multi-channel, multi-layered feedback system
can facilitate the formation of a behavioral perception
loop for the player. For instance, visual dynamic
feedback displays changes in necessary data; auditory
feedback helps players differentiate between various
in-game scenarios or items; and haptic feedback, such
as that provided by VR controllers, simulates the
grasping effects of a real physical environment.
2.1.3 Types
Game interaction design can be broadly categorized
into three types: direct interaction, indirect interaction,
and environmental interaction. Direct interaction
involves players using explicit inputs to manipulate in-
game characters or objects, such as using a keyboard
and mouse to control character movement and
jumping. Indirect interaction requires players to
influence the game world through interface elements
or commands, exemplified by resource management
and unit deployment in strategy games.
Environmental interaction refers to players directly
engaging with the game environment itself, such as
scene exploration and item collection in puzzle games.
2.2 Game Emotional Experience
2.2.1 Concept
Game affective experience generally refers to the
various emotional responses and psychological
The Role of Interaction Design in Narrative-Driven Games with a First-Person Perspective in Fostering User Emotional Connection
155

feelings that players generate during the game, such
as excitement, curiosity, fear, tension, and sadness.
This emotional experience includes not only the
immediate emotional responses during the gameplay
but also the players' long-term emotions towards the
game, the sense of accomplishment gained after
achieving game achievements, and the overall
impression and memory of the game after clearing it.
2.2.2 Components
Donald Norman's "Emotional Design" posits three
levels of emotional experience: visceral, behavioral,
and reflective. Building on this framework, game
emotional experiences can be categorized into three
components: sensory triggers, interactive feedback,
and meaning construction. Sensory triggers extend
beyond the audiovisual impact of the game,
transforming primal responses into emotional
anchors, such as fear, excitement, or pleasurable
physiological memories. Interactive feedback
emphasizes the bidirectional emotional flow
generated during behavioral interactions, where
"action-response" dynamics render the behavior itself
an emotional carrier. Meaning construction involves
deepening emotional game experiences and mapping
them onto life experiences and social understanding
through mechanisms like narrative disruption or
metaphorical settings, elevating the game into a
vessel for philosophical contemplation.
2.2.3 Influencing Factors
The interactive mechanisms within a game directly
influence the player's emotional investment. As Will
Wright, the designer of The Sims, once stated,
‘Games can evoke emotional experiences that you
never feel when watching a movie, like pride or guilt’.
Compared to films or novels, the incorporation of
interactive mechanisms in games allows players to
experience a greater sense of agency, building upon
the emotional responses of the audience. While
simple dialogue choices often guide players through
the narrative as designed by the creators, choices
involving moral judgments and pivotal plot decisions
elicit deeper emotional resonance, prompting players
to contemplate the consequences of their actions and
their impact on the game's outcome, thereby fostering
a sense of responsibility.
The narrative design of a game is a critical
element in shaping the emotional experience of the
player. By constructing the game's world-building,
fragmented narratives, multi-perspective structures,
and the use of metaphorical symbols, players can
establish emotional connections with game characters
throughout the gameplay. For instance, in the game
series The Rusty Lake, the non-linear narrative and
surrealistic symbols compel players to actively piece
together the complete story. In What Remains of
Edith Finch, the multi-character narrative of the
family allows players to explore the death scenes of
different family members, experiencing each
character's sense of helplessness in the face of
fatalism. These designs echo what game scholar Janet
Murray proposed in her classic work, Hamlet on the
Holodeck: The Future of Narrative in Cyberspace:
interactive narratives grant players "agency"—the
ability to influence the narrative's development
through choices and actions, making players not only
recipients of the story but also active interpreters of
the real-world significance behind the game.
The art style and sound design are equally
important sensory mediums for eliciting emotional
responses from players. The use of color, lighting,
and scene details in the visuals can convey specific
emotions under the environment and storyline. For
example, the game Journey uses minimalist desert
landscapes and dynamic lighting to create a sense of
solitude and sublimity; the game Inside uses cool
tones and oppressive scenes to convey a sense of
unease. In terms of sound effects, dynamic
soundtracks can respond to the player's actions in
real-time. For example, in the game Death Stranding,
low-pitched music accompanies the player's lonely
trek, while sudden silence or climactic melodies
suggest crisis or redemption.
Social behavior in multiplayer games also
significantly affects the emotional experience.
Cooperative mechanisms (such as the forced
collaboration in the game It Takes Two) build trust
through a sense of reliance, while competitive
mechanisms (such as team confrontation in Apex)
may stimulate a desire to win or a sense of frustration.
The richness of in-game social tools (emoticons, text)
also determines the efficiency of emotional
transmission: Animal Crossing uses cute actions to
promote relaxed social interaction, while Final
Fantasy 14 forms emotional communities through
virtual gatherings and player-created rituals (such as
weddings and funerals). Research shows that the
virtual interpersonal relationships established by
players in MMO games may produce real emotional
attachments and even affect real-world social
behavior. This "emotional migration" phenomenon is
a unique influence of games.
In addition, players' real-life experiences, cultural
backgrounds, and values will also filter the deep
involvement in the game experience, forming an
"emotional filter" - different players may trigger
completely different emotional responses when
facing the same game content, players from different
ICDSE 2025 - The International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
156

cultural backgrounds will have different
interpretations of the same game symbols, and
players' cognitive styles and preferences also affect
their investment in specific types of games.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
To comprehensively analyze the preferences,
emotional experiences, and affective resonance of the
public regarding interactive features in narrative
games, a survey titled "The Impact of Interactive
Features on Emotional Experience in Narrative
Games" was designed and disseminated. Player
feedback data was collected and analyzed to assess
the influence of various interactive features on
players' emotional responses and to identify specific
correlations between game interaction functionalities
and players' emotional experiences.
3.1 Questionnaire Design
The questionnaire for this study is divided into six
sections: basic information, the role of interactive
features in narrative, interactive features and player
emotional experience, interactive features and
immersion, suggestions for improvement, and cases
and preferences. The basic information section
collects the age and play frequency of the respondents
to facilitate cross-analysis of the differential impact
of players' personal experiences and backgrounds on
emotional experience. The questions in the section on
the role of interactive features in narrative use a
matrix scale (5-point rating) to ask respondents to rate
their preference for each interactive feature based on
their gaming experience and then evaluate the impact
of various interactive features on game narrative,
emotional investment, and story development. The
questions in the third and fourth sections use single-
choice and multiple-choice questions to record the
emotional experiences of the respondents during the
game. At the same time, they investigate whether
players have encountered situations where they have
lost interest in the game's theme due to overly
complex and cumbersome interactive features,
considering whether complex interactive design
harms the player's game experience. The last two
sections of the questionnaire collect the players'
suggestions for improvement of interactive features
based on their own gaming experience through open-
ended questions and ask the players to list the games
in which they believe the interactive features are
better combined with the story to provide more
supportive sample data for the study.
3.2 Hypotheses
Based on the current research status and questionnaire
design, the following hypotheses are proposed:
Players' ratings for "dialogue choices,"
"branching narratives," and "moral choices" are
significantly higher than other common interactive
features (such as time management). They are more
inclined towards options that provide players with
autonomy and decision-making power. Furthermore,
they believe that "moral choices" and "environmental
storytelling" have a stronger effect on eliciting
emotional resonance in players than operational
functions (such as QTEs). However, while
"branching narratives" and "multiple character
perspectives" enhance story depth and ending
diversity, overly complex designs or an excessive
number of branching choices may cause some players
to lose interest in the main storyline. In addition,
players perceive the existence of "pseudo-choices"
and "moral dualism" in some current story-driven
games, which deviate significantly from the impact of
similar choices or situations in reality. They
anticipate more realistic and dynamic narrative
feedback mechanisms.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Initially, players' preference levels for diverse
interactive features were assessed using a 1-5 Likert
scale (1 representing strong disfavor, 5 representing
strong favor). The mean scores for each interactive
feature are presented as follows in Table 1:
Table 1: players' preference levels for diverse interactive
features
Types of Interactive
Features
Average
Value
Dialogue Choices 4.21
Branching Storylines 3.95
Fast Response Time 4.06
Item Interaction 4
Character Customization 4.12
Exploration and Puzzle-
Solving
4.08
Moral Choices 3.97
Time Management 3.88
Multiple Character
Perspectives
3.92
Dynamic World 4.09
Hidden Plot and Easter
Eggs
4.16
The Role of Interaction Design in Narrative-Driven Games with a First-Person Perspective in Fostering User Emotional Connection
157
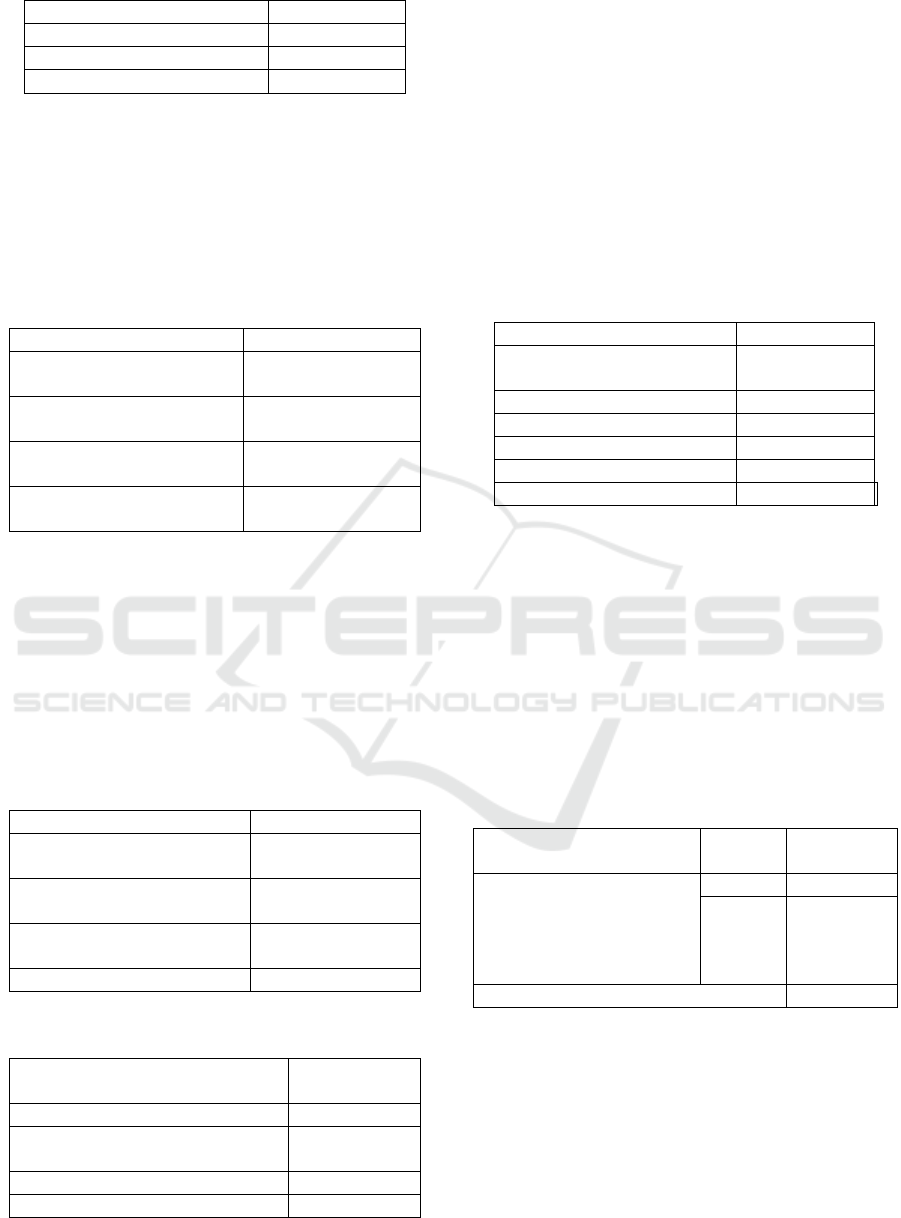
Social Interaction 4.07
Combat and Strategy 4.2
Environmental Storytelling 4.14
Loading and Saving 3.95
Players exhibit increased engagement with games
that incorporate dialogue choices, hidden plot and
easter eggs, and environmental storytelling elements.
Simultaneously, compared to assumptions, players do
not have a high preference for moral choices, as
shown in the data below in Table 2:
Table 2: players believe that dialogue choices play the
following roles:
Variables Average Value
Prompt players' moral
reflection
4.19
Enhance the authenticity of
character development
3.84
Leads to increased plot
complexity
3.97
Affect players' emotional
resonance
4.09
Data shows that while players believe moral
choices can provoke moral reflection and enhance
character development, they also bring an equal
degree of negative effects, such as increased plot
complexity and reduced emotional resonance.
Additionally, regarding the perceived roles of
dialogue choices and environmental storytelling in
games, the data is as follows in Table 3 and 4:
Table 3: players believe that moral choices play the
following roles:
Variables Average Value
Drive the narrative
forward
3.88
Enhance character
immersion
3.51
Influence the story's
outcome
3.64
Increase replay value 3.74
Table 4: players believe that environmental storytelling
plays the following roles:
Variables
Average
Value
Supplement the main storyline 4.08
Enhance the authenticity of the
game world
3.77
Boost the motivation to explore 3.88
Distract players' attention 3.95
Data shows that players believe dialogue choices
can not only drive the narrative forward but also
significantly increase the game's replay value.
Similarly, environmental storytelling can supplement
the main storyline and enhance players' exploration
motivation. However, players also think that
environmental storytelling can, to some extent,
distract attention.
The “sense of agency” that games provide to
players is closely related to their emotional
experience. The data in Table 5 shows that:
Table 5: Which interactive mechanic most effectively
fosters a sense of narrative agency?
Variables Percentage(%)
Multiple Character
Perspectives
23
Moral Choices 22
Branching Storylines 21
Dialogue Choices 19
Dynamic World 15
Aggregate 100.000
The use of multiple character perspectives, which
allows players to experience the game's narrative
from a more macroscopic viewpoint, enhances
players' perception that the game's story is being
driven by their actions.
Additionally, moral choices and branching
storylines, which are exploratory interactive features,
also enable players to feel that they are actively
guiding the development of the game's plot. The data
in Table 6 shows that:
Table 6: players' opinions on whether interactive features
affect their interest in the main storyline of a game
question attitude
Percentage
(%)
Have you ever lost interest in
the main storyline due to overly
complex interactive features,
such as too many branching
storylines?
yes 67
no 33
Aggregate 100.000
It is worth considering that players generally
believe that overly complex interactive features can
cause them to lose interest in the main storyline of a
game. This requires game developers to carefully
consider how to design interactive features to achieve
a better emotional experience for players.
In the open-ended questions, this study collected
players' views on the existing issues with interactive
features in current games and their suggestions for
improvement. Through frequency analysis, it was
ICDSE 2025 - The International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
158
found that players believe the logic behind the various
choices and branching storylines in current game
interactions is often unreasonable. They frequently
encounter binary choices that lack substantial impact
and are essentially "pseudo-choices." Players argue
that choices in games should be more nuanced and
layered, with impacts that are more direct and clear
and should be fully reflected in the direction of the
storyline.
Table 7: Which type of narrative-driven interactive design
do you prefer?
Variables Percentage(%)
Limited Freedom: The main
storyline is fixed, but side quests
are explorable.
48
High Freedom: Player choices can
completely change the story.
29
Linear Narrative: Interaction is
used solely to enhance immersion.
23
Aggregate 100.000
In addition to this, Table 7 shows that players'
preference for a narrative structure with a fixed main
storyline but explorable side quests also reflects that
there is a limit to the degree of freedom they are
willing to accept in terms of exploration and
interactive features. Only by designing and
integrating narrative and interactive elements
reasonably can players better and more fully
experience the emotional resonance and deep
reflection that games offer.
The games that players highlighted as examples
of excellence in the survey, such as What Remains of
Edith Finch and Red Dead Redemption, are notable
for their seamless integration of interactive features
and narrative. These examples provide valuable
lessons for future game developers.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study reveals that the design of interactive
features significantly influences players' emotional
experiences within narrative-driven games.
Specifically, interactive elements such as dialogue
choices, branching narratives, and moral dilemmas
not only enhance player immersion and emotional
investment but also increase a game's replay ability.
Consequently, optimizing these interactive features
can better satisfy players' desires for emotional
engagement and resonance in today's fast-paced
society, thereby improving a game's overall appeal
and sense of immersion. This research addresses a
gap in previous studies by exploring the emotional
impacts of various interactive features in narrative
games, providing insights for future game interaction
design. Furthermore, this study underscores the
critical role of player emotional experience in game
design, offering research support for future game
developers in prioritizing content and features. Future
research and game interaction design should
emphasize the tangible consequences of "player
choice," refine branching narrative logic and enrich
the complexity of moral choices. Simultaneously,
exploring integrations with technologies like VR and
AR could unlock diverse possibilities, fostering richer
and more profound emotional experiences in future
games.
REFERENCES
Chen, W. W. 2019. Emotional interaction design in mobile
games: A case study of Florence. Design Research, 11,
31–33.
Corcos, A. 2018. Being enjoyably challenged is the key to
an enjoyable gaming experience: an experimental
approach in a first-person shooter game. Socioaffective
Neuroscience & Psychology, 8(1).
Croissant, M., Frister, M., Schofield, G., & McCall, C.
2024. Advancing Methodological Approaches in
Affect-Adaptive Video Game Design: Empirical
Validation of Emotion-Driven Gameplay
Modification. International Journal of Human –
Computer Interaction, 1–15.
Edirlei, S. L., Bruno, F., Antonio, L. F. 2018. Player
behavior and personality modeling for interactive
storytelling in games.
Katherine, I. 2016. How Games Move Us: Emotion by
Design.
Norman, D. A. 2005. Emotional Design: Why We Love (or
Hate) Everyday Things. New York, NY: Basic Books.
Oliveira, I., Carvalho, V., Soares, F., Novais, P., Oliveira,
E., & Gomes, L. 2023. Development of a Virtual
Reality Escape Room Game for Emotion
Elicitation. Information, 14(9), 514.
Tom, C., & Marco, G. 2022. Emotional Exploration and the
Eudaimonic Gameplay Experience: A Grounded
Theory.
Wang, F. Y. T. 2024. Interactive design strategy for music
games based on emotional experience. Footwear
Technology and Design, 17, 102–104.
Wang, Z. 2017. Research on mobile game design based on
emotional interaction theory. Art and Design
(Theory), 7(7), 75–77.
Wu, Y. 2022. Research on the interactive design of "meta-
game" based on emotional experience (Master's thesis).
Nanjing University of the Arts. CNKI.
Xu, C., & Wu, Y. X. 2020. Interactive design of mobile
games based on emotional experience. Popular Art and
Literature, 118–119.
The Role of Interaction Design in Narrative-Driven Games with a First-Person Perspective in Fostering User Emotional Connection
159

Zhang, Y. L., & Zhang, T. X. 2016. Exploring emotional
factors affecting interactive design in online
games. Design Research, 21, 144–145.
ICDSE 2025 - The International Conference on Data Science and Engineering
160
