
Optimizing Social Consensus: The Impact of Agent Selection and Topic
Strategy on Time to Reach Agreement
Johannes S Vorster
1 a
and Louise Leenen
1,2 b
1
Department of Computer Science, University of Western Cape, South Africa
2
CAIR, South Africa
Keywords:
Consensus, Consensus Simulation, Stochastic Simulation, Synchronization, Multi-Agent Simulation.
Abstract:
In the rapidly evolving landscape of organizational structures and project management, achieving timely con-
sensus among team members is crucial for maintaining agility and responsiveness. During the consensus
formation process, team members has the choice of who to talk to in an attempt to consolidate views on a
topic. In this paper we ask the question, to what extent do strategies for selecting team members affect the
speed of consensus formation? Similarly, once two team members engage in conversations on a specific set
of topics, the question we ask is, to what extent do different strategies for selecting the topics for discussion
affect the time to reach consensus within multi-agent systems. By simulating various strategies, we identify
methods that optimize consensus speed, specifically highlighting the benefits of prioritizing unaligned agents
and addressing contentious topics early in the process. Our findings reveal that these strategies significantly
enhance consensus efficiency, while approaches focusing on aligning with similar views tend to prolong the
process. Additionally, we observe that the initial distribution of agent views, provided the standard deviation
is constant, has negligible effects on consensus time, suggesting that diversity of opinion is more critical than
specific distribution patterns. These insights offer practical implications for improving decision-making pro-
cesses in organizational and project contexts.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Organizational Context
As technological innovation accelerates, businesses
must adapt their organizational structures and project
delivery methods to remain agile and responsive in
a constantly changing environment. Over the past
two decades, the evolution of organizational struc-
tures and project strategies has become a major topic
in both academia and industry. This discussion is
largely driven by technology companies navigating
the complex interplay of rapid technological advance-
ments, shifting competitive landscapes, and evolv-
ing customer expectations (Reagans et al., 2016;
Keupp et al., 2012; Chang and Harrington, 2000).
Evidence suggests that lateral structures and well-
connected networks offer greater economic value, re-
flected in faster project delivery and reduced resource
use, leading to better investment returns (Will et al.,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6452-4186
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9212-550X
2019). However, project complexity often hampers
consensus-building among team members, causing
delays and failures (Al-Ahmad et al., 2009; Whitney
and Daniels, 2013; Kian et al., 2016; Waheeb and An-
dersen, 2022).
1.2 Consensus Models
Consensus formation in Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
is a multifaceted challenge, intersecting fields such as
social sciences, economics, and computational mod-
eling. Traditional methods like the Delphi process
have been complemented by computational models
that simulate consensus dynamics (Yan et al., 2017).
These models draw from social science research on
crowd behavior and voter dynamics (Dunbar, 1998;
Stocker et al., 2001; Leishman et al., 2009). In MAS,
algorithms are designed for high-speed applications,
reflecting the need for rapid consensus in dynamic en-
vironments (Amirkhani and Barshooi, 2022).
Vorster, J. S., Leenen and L.
Optimizing Social Consensus: The Impact of Agent Selection and Topic Strategy on Time to Reach Agreement.
DOI: 10.5220/0013650900003970
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH 2025), pages 135-144
ISBN: 978-989-758-759-7; ISSN: 2184-2841
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
135

1.3 Social Settings
The topology and connectivity of social networks sig-
nificantly influence opinion dynamics and consen-
sus formation. Models such as Erd
˝
os-R
`
enyi, Watts-
Strogatz, and Barab
´
asi-Albert provide insights into
how network structures affect the speed and nature
of consensus formation (Erd
˝
os et al., 1960; Watts and
Strogatz, 1998; Barab
´
asi et al., 2000). These mod-
els highlight the importance of network design in fa-
cilitating or hindering consensus, with complete net-
works often leading to the fastest agreement (Michal-
ski et al., 2022).
1.4 Subversive Agents
The role of subversive agents in consensus processes
has been explored across various domains, reveal-
ing that even a small committed minority can signif-
icantly influence group dynamics (Xie et al., 2011;
Iacopini et al., 2022). In project teams, subversive
agents can delay consensus by introducing conflict-
ing views, underscoring the need for effective man-
agement of dissent and conflict (Vorster and Leenen,
2023b).
1.5 Organizational Structure
Organizational structure plays a critical role in con-
sensus formation. Polyarchies, characterized by fully
connected networks, facilitate quicker consensus
compared to hierarchical or hybrid structures (Will
et al., 2019; Vorster and Leenen, 2024a). The choice
of structure impacts not only the speed of decision-
making but also the quality of outcomes, particularly
in innovation and project selection (S
´
aenz-Royo and
Lozano-Rojo, 2023).
1.6 Our Earlier Work and Motivation
for this Paper
Our previous research has extensively explored the
dynamics of consensus formation within organiza-
tional settings, focusing on various factors that influ-
ence these processes. In Vorster and Leenen (2023a),
we introduced a simulator designed to investigate
consensus within organizations, emphasizing the role
of organizational structure, team dynamics, and arte-
facts. That study highlighted that for a fixed problem
size, consensus could be achieved within a maximum
time frame, independent of the number of agents in-
volved.
Building on that, Vorster and Leenen (2023b) ex-
amined the impact of subversive agents on consensus-
seeking processes. That work revealed how subver-
sive agents, whether engaging in industrial espionage
or acting as disgruntled employees, could subtly de-
lay consensus by influencing team dynamics without
raising suspicions.
Furthering this exploration, Vorster and Leenen
(2024b) delved into the influence of subversive agents
on project teams, demonstrating that even a small mi-
nority of such agents could significantly extend the
time to reach consensus. This study underscored the
potent influence of subversive agents in shaping deci-
sion outcomes.
In Vorster and Leenen (2024c), we investigated
the determinants of consensus processes, such as
group size and the role of artefacts. The study found
that artefacts significantly reduce consensus time, em-
phasizing their importance in streamlining communi-
cation and collaboration within teams.
Additionally, Vorster and Leenen (2024a) ex-
plored the effectiveness of artefacts and documenta-
tion in facilitating consensus. That research high-
lighted that while polyarchies are efficient at con-
sensus formation, smaller teams with well-structured
artefacts can achieve similar efficiency, particularly in
larger organizations where intra-team communication
may cause delays.
These studies collectively contribute to a nuanced
understanding of the factors affecting consensus for-
mation, providing valuable insights for optimizing
decision-making processes in organizational contexts.
This paper investigates the impact of agent se-
lection strategies and topic prioritization on time
to reach consensus. By examining different strate-
gies for selecting discussion topics and agent align-
ment, we aim to identify methods that optimize con-
sensus speed. Our findings suggest that prioritiz-
ing unaligned agents and discussing topics with the
most differences in views first significantly improves
consensus efficiency. This research contributes to
the broader understanding of consensus dynamics in
organizational and computational contexts, offering
practical insights for enhancing decision-making pro-
cesses.
1.7 This Work: Agent and Topic
Selection Strategies
In this paper we want to investigate two aspects and
the interaction between them; agent selection and
topic selection.
In initial studies mentioned above, agents interact
with other agents at random and do not have a strat-
egy for how to select other agents. In this paper we
investigate two main strategies (a) prioritize selecting
SIMULTECH 2025 - 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
136
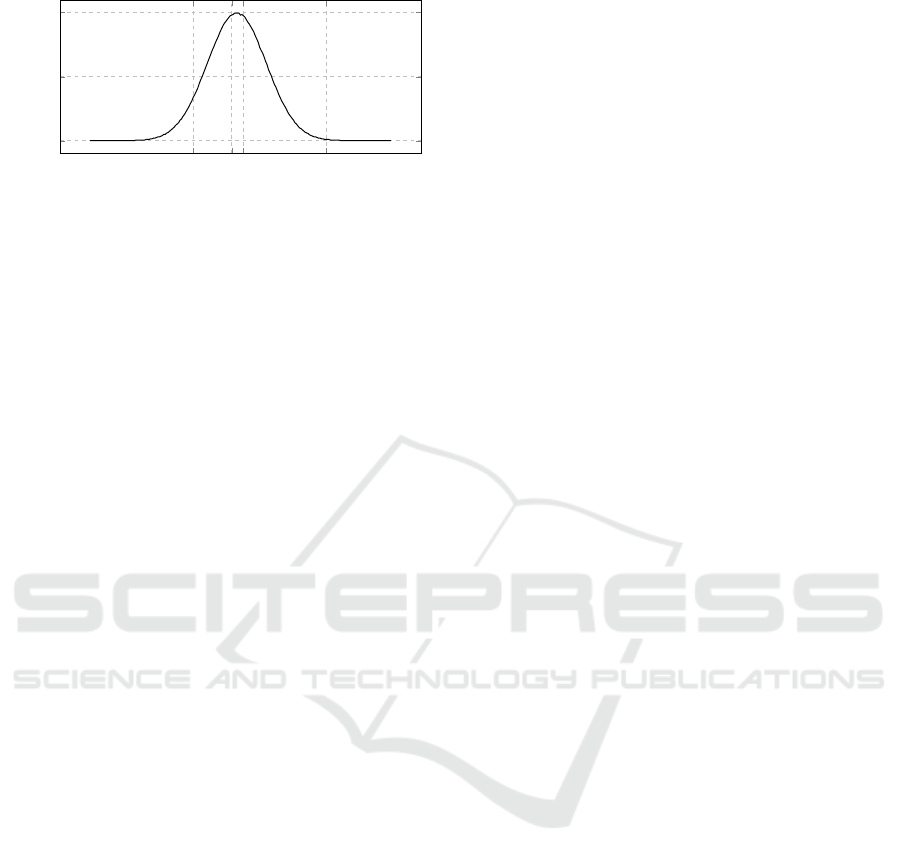
Topic selection Strategies
(a)
(b)(c) (d)
0
1
2
Frequency [%]
Figure 1: Topic selection strategies: (a) closest same side,
(b) furthest, same side, (c) closest, opposite side, and (d)
furthest, opposite side.
agents that have closely aligned views, and (b) priori-
tize selecting agents with conflicting views.
It can be argued that following the first strategy is
similar to first building a core of support, establish-
ing a large group of agents with a particular view to
portray that view to other agents.
On the other hand, the second strategy, to priori-
tize agents with the furthest views are more aligned
with a philosophy of trying to contain opposing views
and thus restrict the spread of these opposing views as
quickly as possible.
We are interested to see, using our simulation ap-
proach, what the effect of these two strategies are on
the time to reach consensus in a large group where it
is critical that consensus is reached, such as in project
execution (as opposed to social constructs such as
voter views).
An orthogonal aspect of investigation is topic se-
lection; is it better to (a) focus on similar topic, elim-
inating differences quickly and establishing a core of
mutual topics, or (b) focus on trying to address the
topics with highest difference in views first.
A second way to look at this variable is for an
agent to select topics based on the relative position
to the group view. Lets say agent i has a view to the
left (or right) of the group’s view on topic k. Would
it be better to first select topics where agent j is on
the same side of the issue or is it better to discuss op-
posing topics first? Here we identify and investigate
four strategies: (a) prioritise topics on the same side
of the issue and topics closest to the agents views first
(Close, same side topics); (b) prioritize topics on the
same side of the issue but with the biggest difference
in views first (Furthest, same side topics); (c) opposite
side but closest to the agents own view (Closest, op-
posite view); and (d) opposite view and furthest away
(Furthest, opposite view), see Figure 1 where agent i
has a view close to that of (a).
Here, option (c) aims to pull agents with oppos-
ing views but close to the median view over the line
to ’our side’. Strategy (b) tries to prevent this from
happening to agents on ’our team’. Strategy (d) aims
to address the ’radicals’ on the opposite side first and
strategy (a) aims to consolidate and build out the core
of support.
Our approach is to set up two sets; one with nine
experiments (three options on each axis of a two-
variable matrix). Axis one is the agent selection strat-
egy: Random strategy, agents with highest difference
in views first, and agents with lowest difference in
views first. On the second axis is the topic selection
strategy, with similar three options. And the other set
with twelve experiments, where the second axis cov-
ers the four options mentioned above.
2 METHODOLOGY AND
TERMINOLOGY
This section outlines the methodology and terminol-
ogy used in our study, focusing on the simulation
setup, agent interactions, and consensus measure-
ment. A detailed discussion of topics related to the
simulation and simulator can be found in Vorster and
Leenen (2023a).
2.1 Teams and Topics
The simulation involves two teams: the specification
team (team a) and the implementation team (team b).
Team a consists of
a
N agents, and team b consists of
b
N agents, with
a
N ≪
b
N. Each agent tracks a num-
ber of topics, with team a considering
a
B
max
topics
and team b considering
b
B
max
topics. The first
a
B
max
topics are common to both teams, requiring consensus
between both teams.
2.2 Artefacts
Topics are encoded in specification artefacts, which
map one-to-one with the topics tracked by team a.
The specification contains
a
C
max
topics. If an arte-
fact contains fewer topics than discussed by agents
(
a
C
max
<
a
B
max
), the first
a
C
max
topics coincide with
the artefact’s topics, allowing for the modelling of in-
complete artefacts.
2.3 Agent Connectivity and Meetings
Agents interact based on a connectivity graph mod-
elled as a directed graph. Each agent can only meet
with directly connected agents. Meetings last 30 min-
utes, allowing up to 16 meetings per day. The number
of topics discussed per meeting is determined stochas-
tically, ranging from one to ten. Outcomes for each
Optimizing Social Consensus: The Impact of Agent Selection and Topic Strategy on Time to Reach Agreement
137

topic include compromise consensus, one agent con-
vincing the other, or vice versa. The pseudo-Python
code for meetings between agents i and j is:
random.shuffle(topics)
issuesToDiscuss=randint(1,11)
for k in topics:
if agent[i].view[k]==agent[j].view[k]:
continue
rnd = randint(0,3)
if (rnd==0):
val = int((agent[i].view[k]
+ agent[j].view[k]))/2.0)
agent[i].view[k]=agent[j].view[k]=val
if (rnd==1):
agent[j].view[k] = agent[i].view[k]
if (rnd==2):
agent[i].view[k] = agent[j].view[k]
issuesToDiscuss-=1#
if issuesToDiscuss<=0:
break
2.4 Working on Artefacts
Agents can interact with artefacts within a 30-minute
time-slot, selecting a random number of topics, from
one to ten, where disagreement exists between agent’s
views and the artefacts position. Outcomes include
partial or full internalization of the artefact’s view or
modifying the artefact to reflect the agent’s view.
2.5 Measuring Consensus
Consensus is measured using absolute differences be-
tween views (b) on topics (k). For agents i and j, and
artefacts p, the consensus measure for a specific topic
(k) is:
u
k
i j
= δ
i j
|b
k
i
− b
k
j
|
u
k
ip
= δ
ip
|b
k
i
− c
k
p
|
where δ
i j
is a coefficient of understanding each other,
and is taken as δ
i j
= 1 here. The overall consensus for
an agent i over all agents (I
ν
) and all artefacts (I
A
) for
a specific topic k is:
u
k
i
=
∑
j∈I
ν
δ
i j
|b
k
i
− b
k
j
| +
∑
p∈I
A
δ
ip
|b
k
i
− c
k
p
|
The total difference in views between two agents
on all topics is given by
u
i j
=
B
max
∑
k=1
δ
i j
|b
k
i
− b
k
j
| (1)
The total consensus across all agents and artefacts
is:
u =
∑
i∈I
ν
∑
j∈I
ν
B
max
∑
k=1
δ
i j
|b
k
i
− b
k
j
| +
∑
i∈I
ν
∑
p∈I
A
C
max
∑
k=1
δ
ip
|b
k
i
− c
k
p
|
This measure (u) and its log is what will be used
to measure the level and extent to which a group has
reached consensus.
2.6 Time and Effort to Reach
Consensus
Agents record their actions in a diary. The effort e
max
to reach consensus is the sum of all actions taken:
e
max
=
t
max
∑
t=1
N
∑
i=1
busy(d
t
i
)
where busy(d
t
i
) = 1 if an action is taken, and 0 oth-
erwise. The simulation stops, after t
max
steps, when
no further actions are taken. We are interested in t
max
(averaged over may simulations) for the various sce-
narios under investigation.
2.7 Meeting Efficiency
Meeting efficiency is measured by the average num-
ber of topics discussed per meeting. If ¯z(t) is the ob-
served average and ¯z
max
is the maximum expected, ef-
ficiency at time t is:
e(t) =
¯z(t)
¯z
max
2.8 Strategy Notation
There are two dimensions to the strategy that an agent
(i) can follow. Firstly the selection of agents to meet
with, which we can denote as Strategy (Agents=far)
for the the strategy of prioritizing agents with over-
all views that are far from the current agent’s views,
that is, agents ( j) where the consensus measure (u
i j
,
eq. (1)) is relatively large. Three strategies are
considered namely Strategy (Agents=far), Strategy
(Agents=near), and Strategy (Agents=random).
Similarly and independently from the agent selec-
tion strategy an agent can also have a strategy for the
topics that will be discussed in a meeting. Such strate-
gies can be denoted with Strategy (topics=random),
Strategy (topics=Far), and Strategy (topics=Near) for
the three strategies we are considering, where top-
ics=Far denotes a strategy where agents will priori-
tize topics k where |b
k
i
− b
k
j
| is large relative to other
topics.
An agent’s overall strategy will consist of having
a strategy for agent selection and a strategy for topic
SIMULTECH 2025 - 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
138
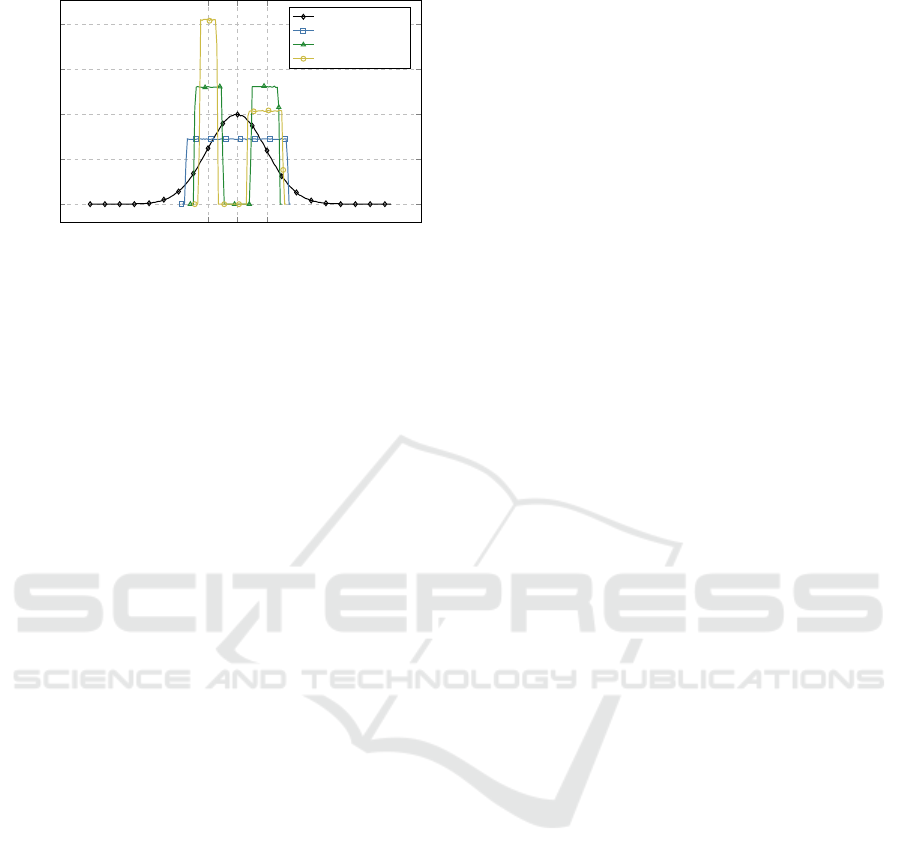
Initial View Histogram
µ − σ
µ
µ + σ
0
1
2
3
4
Frequency [%]
Normal
Uniform
Dual-Uniform
Asymetric-Uniform
Figure 2: The distributions used for initial views are: Nor-
mal, Uniform, Dual-Uniform, and Asymetric-Uniform as
shown in the figure. Each distribution is carefully selected
so that σ=constant=100, for all distributions.
selection, and the combination can therefore be indi-
cated using the same notation, for example Strategy
(agents=random, topics=random).
Next, we move on to the topic of strategies for
agent selection and topic selection. Equation (1) pro-
vide a mechanism for an agent to calculate a consen-
sus measure between it and another agent, and thus an
agent can select the agent with the smallest or largest
such value in order to implement the two strategies (a)
best aligned agent first, and (b) furthest aligned agent
first.
Similarly agent i can find a topic k, such that |b
k
i
−
b
m
i
| is the smallest (non-zero) value among the topics
m ∈ {1 to B
max
} for which they are not in agreement.
2.9 Mathematical Model Summary
Key concepts include:
• b
k
i
: The view that agent i has on a specific topic k.
• u
k
i
: Consensus on a specific topic k for agent i.
• u
i j
: Consensus between two agents i and j on all
topics.
• u: Overall consensus measure.
• t
max
: Time to reach consensus.
• e
max
: Effort to reach consensus.
• Strategy (agents=X, topics=Y): A strategy that
prioritizes agents using an agent selection strat-
egy X based on the consensus measure u
i j
, and
a strategy Y for selecting topics to discuss within
meetings based on the measure |b
k
i
− b
m
i
|.
This methodology provides a framework for
analysing consensus dynamics in multi-agent
systems.
3 SCENARIO CONFIGURATIONS
Agents are initialized with random views on each
of the topics using a specific distribution. Currently
Normal, Uniform, Dual-Uniform, and Asymmetric-
Uniform are supported, see Figure 2.
A simulation consists of agents meeting in 30
minute sessions where they discuss topics according
the the rules explained above. This continue until all
agents are satisfied that they have reached consensus
on all topics with all other agents in their connectiv-
ity network. The number of time-steps that it takes
to reach this state is noted. The exponential decrease
in the consensus measure (u) can be seen as one of
the grey plots in Figure 3. Over many such iterations
averages and standard deviations can be computed, as
shown in the figure.
Although not the primary focus of this study,
Vorster and Leenen (2023a), pointed out that the con-
sensus process may be dependent on the distribution
of initial views and in that work the mathematical
model was worked out based on a Normal distribution
of initial views. However, the question remained open
and in the first part of this work we want to address it
by modelling various initial distributions, see Figure
2. Through that work, it was assumed that the consen-
sus process, in particular how long it takes, is depen-
dent on the standard deviation of the distribution in
the absense of other information. Here we measure
the time to reach consensus for Normal, Uniform,
Dual-Uniform, and Asymmetric-Uniform as shown in
the future. In all these distributions we take care to use
the same mean and sigma in the initial view distribu-
tions.
For example to correctly compute the distribution
of the Asymmetric-Uniform distribution, we selected
the distribution width of the left portion (50 in this
case) and compute what the right-hand portion should
be to give the correct sigma (σ = 100). To ensure
we have not made mistakes in the mathematical cal-
culations or in the Python implementation we simu-
lated stochastically two million distribution calcula-
tions to ensure correctness, with results Normal (σ =
100.05, n=2M), Uniform (σ = 100.00, n=2M), Dual-
Uniform (σ = 99.98, n=2M), Asymmetric-Uniform
(σ = 100.03, n=2M).
The outcome of these simulations are shown in
Figure 4. The effect of initial views are negligible
as can be seen from the (bottom) graphs showing the
difference between the outcome of these distributions
relative to the Normal distribution. This is somewhat
of a surprising results since it then implies that the
time to reach consensus is independent of the dis-
tribution of initial views, but only dependent on the
Optimizing Social Consensus: The Impact of Agent Selection and Topic Strategy on Time to Reach Agreement
139
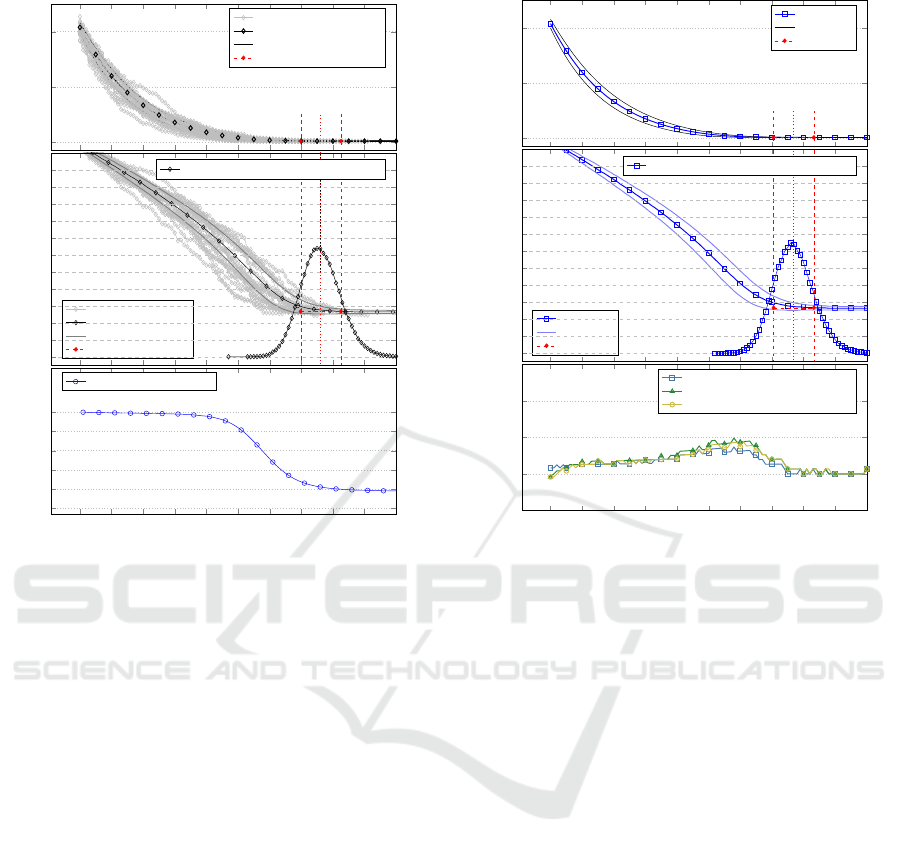
Consensus-reaching processes
0
1
2
·10
5
Consensus (u)
Consensus for 20 simulations
Averaged Consensus
1σ
t
max
1σ
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Consensus (logu)
logu for 20 simulations
logu averaged
1σ
t
max
1σ
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Histogram [%]
Histogram of t
max
(IV=Normal) N (76.2, 6.36)
0 10 20 30 40
50 60
70 80 90 100
0
20
40
60
80
100
Time (t
max
)
Meeting efficiency [%]
Topics discussed per meeting
Figure 3: (Top) Various simulations of the 10-group show-
ing the consensus measure (u) over time. (Middle) The same
data as in top graph, but now using log
e
(consensus). His-
togram of the time it takes to reach consensus over many
such runs (µ = 76.2, σ = 6.36, n=200000). (Bottom) Meet-
ing effectiveness graphs for the two groups.
standard-deviation of views, rather than the type of
distribution, at least for the set of distributions we
have used. This was not predicted in the construction
of the initial mathematical model published in Vorster
and Leenen (2023a) and in future work it would be
worth re-visiting that model and simplifying it using
the findings from this study.
The simulator is written in Python, and the general
architecture is such that a scenario consisting of a set
of parameters is registered with the simulation class
which manages the execution of scenarios. Many sce-
narios can be registered in sequence before the simu-
lations start.
The scenario parameters include the number of
agents involved, artefacts involved, team structure and
communications channels between agents, the num-
ber of topics under discussion, the distributions used
for initial views of agents, and the agent and topic se-
lection strategies that will be used. Finally, the total
number of simulations that will be executed per sce-
nario parameter is specified (n=20000 in this case).
The simulator is multi-threaded, each threat ex-
ecutes a specific scenarios repeatedly for a set time
Effect of Distributionss
0
1
2
·10
5
Consensus (u)
IV=Uniform
1σ
t
max
1σ
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Consensus (logu)
IV=Uniform
1σ
t
max
1σ
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Histogram [%]
Histogram of t
max
(IV=Uniform) N (76.9, 6.37)
0 10 20 30 40
50 60
70 80 90 100
−1
0
1
2
3
Time (t
max
)
Log(u) difference [%]
Uniform vs Normal (diff.%)
Dual-Uniform vs Normal (diff.%)
Asymetric-Uniform vs Normal (diff.%)
Figure 4: (Top) Various simulations of the 10-group show-
ing the consensus measure over time when the initial dis-
tribution of views are Uniform. (Middle) The same data as
in top graph, but now using log
e
(consensus). Histogram of
the time it takes to reach consensus over many such runs
(µ = 76.9, σ = 6.37, n=200000). (Bottom) A difference plot
to highlight the impact of initial view on the consensus pro-
file.
(usually 60 seconds) and once that time is reached the
thread terminates after the current scenario has fin-
ished execution. Results are appended to various logs.
Every few minutes (30 in the default configuration)
the logs are processed and statistics are calculated for
the results files. The results files are such that they
can be directly processed in this L
A
T
E
Xdocument.
Various progress files are kept up to date so that
simulations can be stopped at any time and re-started
later without the loss of data and very importantly
time.
4 RESULTS
Figure 5 shows the results from the simulations. The
top left plot shows that scenario where agent and topic
selection is completely random and this scenario also
acts as the baseline to compare the other scenarios
against. For this scenario it takes on average 498.32
(σ = 59.80, n = 400000) time steps to reach consen-
SIMULTECH 2025 - 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
140
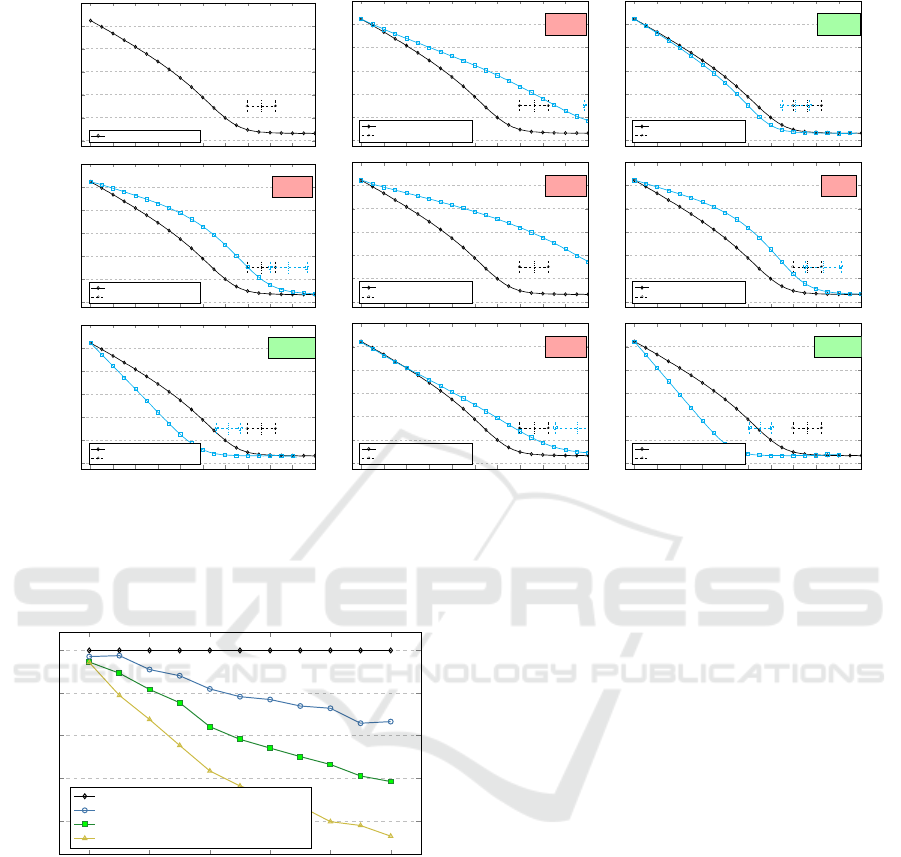
Strategy (agents=random) Strategy (agents=near) Strategy (agents=far)
(topics=random)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Consensus (logu)
agents=random, topics=random
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
44,5%
agents=random, topics=random
agents=near, topics=random
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−6,7%
agents=random, topics=random
agents=far, topics=random
(topics=near)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
15,9%
Consensus (logu)
agents=random, topics=random
agents=random, topics=near
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
62,9%
agents=random, topics=random
agents=near, topics=near
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
9,2%
agents=random, topics=random
agents=far, topics=near
(topics=far)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−19,3%
Consensus (logu)
agents=random, topics=random
agents=random, topics=far
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
25,1%
agents=random, topics=random
agents=near, topics=far
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−27,1%
agents=random, topics=random
agents=far, topics=far
Figure 5: Agent selection strategies are presented on the horizontal axis and topic selection strategies on the vertical axis. The
black (diamond) plots are the baseline (random agent selection and random topic selection) against which the other strategies
are measured. Each strategy combination also shows the percentage improvement as measured against this baseline. Green
(negative percentage) indicate faster time to reach consensus and a red (positive percentage) indicate longer time to reach
consensus.
% of agents following strategy
0 20 40
60
80 100
−40
−30
−20
−10
0
Time to reach Consensus
Strategy: random agents, random topics
Strategy unaligned agents, random topics
Strategy random agents, opposing views first
Strategy unaligned agents, opposing views first
Figure 6: The effect of number of agents in the group on
the time to reach consensus relative to the random agents,
random topics strategy.
sus. The specific number of time-steps are not rele-
vant, but the relative difference as shown in the graphs
are the measure we employ for comparison.
First let us discuss the strategies where agents opt
to first align with agents that are already close in terms
of their views, Strategy (agents=near), middle col-
umn of Figure 5). All these strategies show a sig-
nificant increase in time to reach consensus Strategy
(topics=random) +44,5%, (topics=near) +62,9 %, and
(topics=far) +25,1%.
Similarly, Strategies (topics=near), middle row
in figure Figure 5, show increases in time to reach
consensus of +15,9 %, +62,9%, and +9,2 % for
(agents=random), (agents=near), and (agents=far) re-
spectively.
The strategies that lead to improvements in time
to reach consensus are to prioritize unaligned agent
(agents=far), opposing views (topics=far), or both,
with 6,7%, 19,3%, and 27,1 % improvements respec-
tively.
To understand how these results change with the
percentage of agents following the strategy (as op-
posed to random), we ran a large number of exper-
iments (n=400000 per point) with 100 agents in the
group, and varying the number of agents that follow a
specific strategy. We report here only on the strategies
that improve time to reach consensus.
There results are shown in Figure 6 and from in-
spection of these graphs, are only approximately lin-
ear. It shows that the more agents follow the strategy
the bigger the results, as expected.
Finally, we want to further explore the topic selec-
tion strategy and in particular if there is a difference
in prioritizing members on the same side of an issue
first versus the above strategy of far and near classi-
fications. To do this we define four topic-selection
strategies based on if the two agents are one the ’same
side’ of an issue versus on the opposite side and if
their views are near or far from each other.
Optimizing Social Consensus: The Impact of Agent Selection and Topic Strategy on Time to Reach Agreement
141
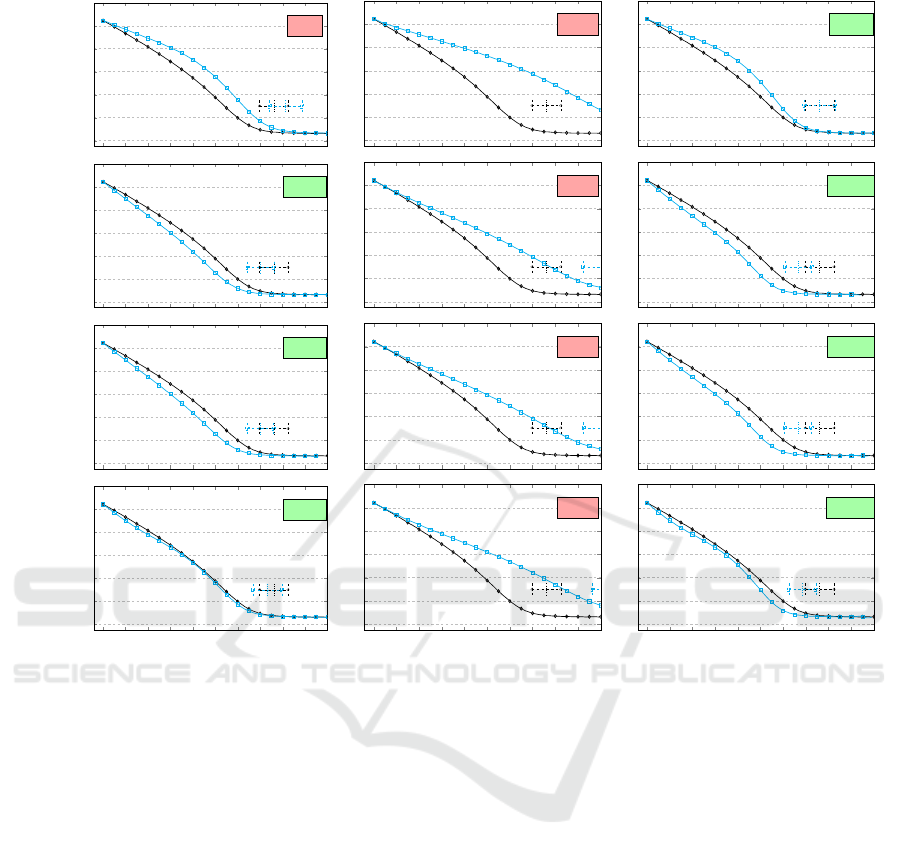
Strategy (agents=random) Strategy (agents=near) Strategy (agents=far)
topics=near,
same side
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
7,0%
Consensus (logu)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
53,7%
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−0,1%
topics=far,
opposite side
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−7,8%
Consensus (logu)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
35,3%
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−12,5%
topics=far,
same side
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−7,9%
Consensus (logu)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
35,3%
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−12,6%
topics=near,
opposite side
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−3,8%
Consensus (logu)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
41,9%
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
−1 0,0 %
Figure 7: Agent selection strategies are presented on the horizontal axis and topic selection strategies on the vertical axis. The
black (diamond) plots are the baseline (random agent selection and random topic selection) against which the other strategies
are measured. Each strategy combination also shows the percentage improvement as measured against this baseline. Green
(negative percentage) indicate faster time to reach consensus and a red (positive percentage) indicate longer time to reach
consensus.
The results are shown in Figure 7 and indicate that
(agents=far) Strategies dominate any other agent se-
lection strategy.
However, the interesting part is comparing the re-
sults from Figure 7 to that of Figure 5. In particular it
seem that broadly prioritizing far agents irrespective
of perceptions of ’side’ (topics=far, agents=random,
−19,3% in Figure 5) is better than selecting agents
based on perceptions of side (topics=far opposite side,
−7,8%, and topics=far same side, −7,9% in Figure
7).
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Interpretation of Results
Our findings indicate that strategies prioritizing un-
aligned agents and opposing views significantly en-
hance consensus efficiency. Specifically, the strategy
of selecting agents with the most divergent views and
discussing topics with the greatest differences first re-
sulted in the most improvement in time to reach con-
sensus compared to random strategies. This suggests
that addressing the most contentious issues early can
streamline the consensus process by preventing the
entrenchment of opposing views and is a superiour
strategy to first building a core of support. Strategies
that focused on aligning with agents already close
in views or discussing similar topics first led to in-
creased time to reach consensus. This outcome high-
lights the potential inefficiency of reinforcing existing
agreements without addressing underlying conflicts.
It is important to address issues that have a high
difference in views early irrespective of perceptions
of ’side’. The results clearly show that ignoring far
from the norm views within perceived ’same’ side
team members can still extend the time to reach con-
sensus and a better strategy is to address issues irre-
SIMULTECH 2025 - 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
142

spective of perceived membership sides.
5.2 Implications for Organizational
Practice
These results have practical implications for project
management and organizational decision-making. In
environments where rapid consensus is critical, such
as in project execution, prioritizing engagement with
dissenting opinions and contentious topics can expe-
dite decision-making processes. This approach may
also foster a more inclusive environment by ensur-
ing that diverse perspectives are considered and in-
tegrated early in the decision-making process.
5.3 The Role of Initial View
Distributions
Interestingly, our study found that the initial distribu-
tion of agent views (whether normal, uniform, dual-
uniform, or asymmetric-uniform) had negligible ef-
fects on the time to reach consensus, provided the
standard deviation was constant. This suggests that
the diversity of initial opinions, rather than their spe-
cific distribution, is a more critical factor in consen-
sus dynamics. This finding challenges traditional as-
sumptions and suggests new avenues for simplifying
mathematical models of consensus processes.
5.4 Limitations and Future Research
While our study provides valuable insights, it is not
without limitations. The simulations were conducted
in a controlled environment with specific assump-
tions about agent behaviour and interaction. Future
research could explore more complex models incor-
porating factors such as dynamic network topologies,
varying levels of agent influence, and real-world con-
straints.
Additionally, the impact of subversive agents on
consensus processes warrants further investigation.
Understanding how these agents can be managed or
mitigated could provide further improvements in con-
sensus efficiency.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Earlier research on the causes of project failures, de-
lays, and cost overruns have identified lack of con-
sensus as one of the key contributing factors. The
consensus formation process is time-consuming, and
often left out of project planning or its effort is under-
estimated.
In this study, we explored the impact of agent se-
lection and topic prioritization strategies on the ef-
ficiency of consensus formation within multi-agent
systems. Our findings indicate that strategies prior-
itizing unaligned agents and contentious topics en-
hance the speed of reaching consensus. Specifically,
engaging with agents holding divergent views and ad-
dressing the most contentious issues early in the pro-
cess can streamline consensus-building by prevent-
ing the entrenchment of opposing views. Conversely,
strategies focusing on aligning with agents already
close in views or discussing similar topics first tend
to prolong the consensus process and is a less efficient
strategy.
These insights have practical implications for or-
ganizational decision-making and project manage-
ment. By prioritizing engagement with dissenting
opinions and contentious topics, organizations can ex-
pedite decision-making processes and foster a more
inclusive environment that integrates diverse perspec-
tives early on. Furthermore, our study reveals that the
initial distribution of agent views, provided the stan-
dard deviation remains constant, has negligible effects
on the time to reach consensus. This suggests that the
diversity of initial opinions is more critical than their
specific distribution, challenging traditional assump-
tions and offering new avenues for simplifying math-
ematical models of consensus processes.
Despite the valuable insights gained, this study is
not without limitations. The simulations were con-
ducted in a controlled environment with specific as-
sumptions about agent behavior and interaction. Fu-
ture research could explore more complex models in-
corporating dynamic network topologies, varying lev-
els of agent influence, and real-world constraints. Ad-
ditionally, the role of subversive agents in consensus
processes warrants further investigation. Understand-
ing how these agents can be managed or mitigated
could provide further improvements in consensus ef-
ficiency.
Future work could also focus on developing adap-
tive strategies that dynamically adjust agent and topic
selection based on real-time feedback from the con-
sensus process. Exploring the integration of machine
learning techniques to predict and optimize consensus
pathways could offer significant advancements in the
field.
Optimizing Social Consensus: The Impact of Agent Selection and Topic Strategy on Time to Reach Agreement
143

REFERENCES
Al-Ahmad, W., Al-Fagih, K., Khanfar, K., Alsamara, K.,
Abuleil, S., and Abu-Salem, H. (2009). A taxonomy
of an it project failure: root causes. International
Management Review, 5(1):93.
Amirkhani, A. and Barshooi, A. H. (2022). Consensus in
multi-agent systems: a review. Artificial Intelligence
Review, 55(5):3897–3935.
Barab
´
asi, A.-L., Albert, R., and Jeong, H. (2000). Scale-
free characteristics of random networks: the topology
of the world-wide web. Physica A: statistical mechan-
ics and its applications, 281(1-4):69–77.
Chang, M.-H. and Harrington, J. E. (2000). Centralization
vs. decentralization in a multi-unit organization: A
computational model of a retail chain as a multi-agent
adaptive system. Management Science, 46(11):1427–
1440.
Dunbar, R. I. (1998). The social brain hypothesis. Evo-
lutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews:
Issues, News, and Reviews, 6(5):178–190.
Erd
˝
os, P., R
´
enyi, A., et al. (1960). On the evolution of
random graphs. Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. Sci,
5(1):17–60.
Iacopini, I., Petri, G., Baronchelli, A., and Barrat, A.
(2022). Group interactions modulate critical mass
dynamics in social convention. Communications
Physics, 5(1):64.
Keupp, M. M., Palmi
´
e, M., and Gassmann, O. (2012). The
strategic management of innovation: A systematic re-
view and paths for future research. International jour-
nal of management reviews, 14(4):367–390.
Kian, M. E., Sun, M., and Bosch
´
e, F. (2016). A consistency-
checking consensus-building method to assess com-
plexity of energy megaprojects. Procedia-social and
behavioral sciences, 226:43–50.
Leishman, T. G., Green, D. G., and Driver, S. (2009).
Self-organization in simulated social networks. In
Computer-Mediated Social Networking: First Inter-
national Conference, ICCMSN 2008, Dunedin, New
Zealand, June 11-13, 2008, Revised Selected Papers,
pages 150–156. Springer.
Michalski, R., Serwata, D., Nurek, M., Szymanski, B. K.,
Kazienko, P., and Jia, T. (2022). Temporal network
epistemology: On reaching consensus in a real-world
setting. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Non-
linear Science, 32(6).
Reagans, R., Miron-Spektor, E., and Argote, L. (2016).
Knowledge utilization, coordination, and team perfor-
mance. Organization Science, 27(5):1108–1124.
S
´
aenz-Royo, C. and Lozano-Rojo, A. (2023). Authoritar-
ianism versus participation in innovation decisions.
Technovation, 124:102741.
Stocker, R., Green, D. G., and Newth, D. (2001). Consensus
and cohesion in simulated social networks. Journal of
Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 4(4).
Vorster, J. and Leenen, L. (2023a). Consensus simulator for
organisational structures. In Proceedings of the 13th
International Conference on Simulation and Modeling
Methodologies, Technologies and Applications, pages
15–26.
Vorster, J. and Leenen, L. (2023b). Exploring the effects of
subversive agents on consensus-seeking processes us-
ing a multi-agent simulator. In Proceedings of the 13th
International Conference on Simulation and Modeling
Methodologies, Technologies and Applications, pages
104–114.
Vorster, J. and Leenen, L. (2024a). The unreasonable ef-
fectiveness of artefacts and documentation: An explo-
ration of consensus using multi-agent simulations in
a two-team configuration. In Proceedings of the 14th
International Conference on Simulation and Model-
ing Methodologies, Technologies and Applications –
SIMULTECH, pages 313–323.
Vorster, J. S. and Leenen, L. (2024b). Exploring the im-
pact of subversive agents on consensus processes in
project teams: Multi-agent simulations. In Wagner,
G., Werner, F., and De Rango, F., editors, Simula-
tion and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and
Applications, pages 29–60, Cham. Springer Nature
Switzerland.
Vorster, J. S. and Leenen, L. (2024c). Stochastic consen-
sus simulation fororganizational cooperation. In Wag-
ner, G., Werner, F., and De Rango, F., editors, Simula-
tion and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and
Applications, pages 139–173, Cham. Springer Nature
Switzerland.
Waheeb, R. A. and Andersen, B. S. (2022). Causes of prob-
lems in post-disaster emergency re-construction pro-
jectsiraq as a case study. Public Works Management
& Policy, 27(1):61–97.
Watts, D. J. and Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynamics
of small-world networks. Nature.
Whitney, K. M. and Daniels, C. B. (2013). The root cause
of failure in complex it projects: Complexity itself.
Procedia Computer Science, 20:325–330.
Will, M. G., Al-Kfairy, M., and Mellor, R. B. (2019). How
organizational structure transforms risky innovations
into performance–a computer simulation. Simulation
Modelling Practice and Theory, 94:264–285.
Xie, J., Sreenivasan, S., Korniss, G., Zhang, W., Lim,
C., and Szymanski, B. K. (2011). Social consensus
through the influence of committed minorities. Phys-
ical Review E, 84(1):011130.
Yan, H.-B., Ma, T., and Huynh, V.-N. (2017). On qualitative
multi-attribute group decision making and its consen-
sus measure: A probability based perspective. Omega,
70:94–117.
SIMULTECH 2025 - 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
144
