
COSMOS: A Simulation Framework for Swarm-Based Orchestration in
the Edge-Fog-Cloud Continuum
Nadezhda Varzonova
1
and Melanie Schranz
2 a
1
University of Klagenfurt, Klagenfurt, Austria
2
Lakeside Labs, Klagenfurt, Austria
Keywords:
Agent-Based Simulation, Edge-Fog-Cloud Continuum, Swarm Intelligence.
Abstract:
The rapid expansion of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the increasing demand for data-intensive ap-
plications have driven research into distributed computing models such as the edge-fog-cloud continuum,
which integrates real-time edge processing, collaborative fog layer management, and highly scalable cloud
infrastructure. In this paper, we present COSMOS (Continuum Optimization for Swarm-based Multi-tier Or-
chestration System), a Python-based simulation framework built on the Mesa multi-agent library, designed for
implementing and evaluating self-organizing scheduling algorithms in distributed systems. The framework
provides modular components for swarm coordination dynamics, constraint-aware scheduling, and real-time
optimization, enabling flexible experimentation with various scheduling scenarios. We designed the system
architecture to be highly configurable and observable, allowing for flexible experiment setup and comprehen-
sive data collection. Its extensible API enables researchers to implement and evaluate alternative orchestration
strategies for resource allocation, facilitating the integration of both classical and learning-based schedul-
ing approaches. We demonstrate the effectiveness of COSMOS through case studies on diverse scheduling
paradigms, including nature-inspired approaches such as hormone-based orchestration and ant colony op-
timization. These studies showcase its capability to model and optimize real-world distributed computing
scenarios.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid expansion of Internet of Things (IoT) de-
vices and data-heavy applications has accelerated
research into the edge-fog-cloud continuum, which
unites low-latency edge, coordinated fog, and scalable
cloud resources (Palumbo et al., 2024). While this
model addresses cloud limitations like latency and
privacy, efficient workload scheduling across diverse,
dynamic layers remains a major challenge (Varghese
and Buyya, 2018). Current solutions still struggle to
balance responsiveness, resource use, and adaptabil-
ity in decentralized, fluctuating environments (Sri-
rama, 2024).
To address these challenges, we present COSMOS
(Continuum Optimization for Swarm-based Multi-
tier Orchestration System), a novel simulation frame-
work for evaluating self-organizing scheduling algo-
rithms in edge-fog-cloud ecosystems. Unlike conven-
tional schedulers that rely on centralized optimiza-
tion, COSMOS implements swarm intelligence prin-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0714-6569
ciples inspired by decentralized biological systems,
enabling emergent coordination across distributed
nodes. The framework extends Mesa’s agent-based
modeling toolkit (Kazil et al., 2020) to simulate:
• Multi-tier resource dynamics: Agent populations
representing edge devices, fog nodes, and cloud
servers with configurable behavioral policies.
• Constraint-aware scheduling: Integration of an-
swer set programming (ASP) for hard con-
straints and metaheuristic optimization for soft
constraints.
• Network-aware orchestration: Evaluation of com-
munication costs and dependencies across contin-
uum layers.
Building on these features, COSMOS serves as
a flexible tool for modeling distributed computing
systems as weighted graphs. It preserves the struc-
tural complexity of real-world networks while ab-
stracting away details that are unnecessary for evalu-
ating the performance of task scheduling algorithms.
A later section showcases an example of modeling
390
Varzonova, N., Schranz and M.
COSMOS: A Simulation Framework for Swarm-Based Orchestration in the Edge-Fog-Cloud Continuum.
DOI: 10.5220/0013645000003970
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH 2025), pages 390-397
ISBN: 978-989-758-759-7; ISSN: 2184-2841
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

a medium-sized network of computing devices with
COSMOS.
The paper is organized as follows: Related work is
shown in Section 2. We describe the system model of
the edge-fog-cloud continuum in Section 3 focusing
on resource and demand agents. Section 4 builds the
core of the paper in explaining the simulation archi-
tecture, configuration and implemented algorithms.
Additionally to that, we present in Section 5 an exam-
ple on the usage and data analysis when using COS-
MOS. The paper is concluded in Section 6.
2 RELATED WORK
Agent-Based Modeling (ABM) offers distinct advan-
tages over system dynamics or continuous differential
equation simulations for swarm algorithm develop-
ment, particularly when modeling decentralized sys-
tems with autonomous, interacting entities (Umlauft
et al., 2022). In ABM frameworks, swarms are rep-
resented as collections of individual agents that op-
erate through localized decision rules, interact dy-
namically with peers and their environment, and ex-
hibit emergent collective behaviors from simple in-
dividual behaviors. (Wilensky and Rand, 2015) out-
line specific guidelines for ABM applicability that
align particularly well with swarm systems. First,
ABM is well-suited when modeling medium-scale
systems containing dozens to thousands of interact-
ing agents—a range where traditional analytical so-
lutions become intractable yet statistical homogene-
ity assumptions remain invalid. Swarm systems in-
herently meet this criterion through their distributed
agent populations. Second, the localized interac-
tions essential for swarm implementations are cap-
tured through ABM’s capacity to model neighbor-
to-neighbor communication patterns and spatial con-
straints (Wilensky and Rand, 2015; Schranz et al.,
2021).
In the realm of distributed computing, particularly
within the edge-fog-cloud continuum, various simu-
lation frameworks and tools have emerged to support
the design, evaluation, and optimization of resource
allocation and scheduling strategies. While COSMOS
offers a unique combination of swarm intelligence
and modular design, other platforms provide distinct
strengths and focuses. Here is a brief overview of
some notable platforms similar to COSMOS, high-
lighting their pros and cons:
ENIGMA is suited for multi-tier resource man-
agement and provides detailed evaluation met-
rics for scheduling strategies, supporting large-
scale simulations with customizable configura-
tions (Zyskind et al., 2015). However, it lacks
COSMOS’s focus on swarm intelligence and
modular design patterns.
iFogSim a popular toolkit for fog computing envi-
ronments, boasts extensive documentation and a
strong emphasis on energy consumption and la-
tency analysis (Gupta et al., 2017). It effectively
models IoT devices, fog nodes, and cloud data
centers, but falls short in implementing swarm-
based self-organizing capabilities and lacks flex-
ibility for integrating custom scheduling algo-
rithms.
CloudSim a mature and widely-used framework for
cloud computing simulations, benefits from a
large user base and community support, offering
high extensibility for cloud-specific research (Cal-
heiros et al., 2011). Nevertheless, it doesn’t na-
tively support edge-fog-cloud continuum model-
ing and has limited support for real-time, decen-
tralized scheduling approaches.
EdgeCloudSim an extension of CloudSim tailored
for edge computing scenarios, provides features
for mobility modeling and network latency anal-
ysis in edge-cloud hybrid environments (Sonmez
et al., 2018). However, its focus on edge-cloud
interactions comes at the expense of limited sup-
port for intermediate fog layers, and it lacks incor-
poration of swarm intelligence or decentralized
decision-making mechanisms.
In comparison, COSMOS distinguishes itself
through its unique integration of swarm intelligence,
comprehensive modeling of the edge-fog-cloud con-
tinuum, and modular design using patterns like Fac-
tory and Strategy, which provide a unified API for
seamless integration of new scheduling algorithms,
promote code reusability, and enable flexible ex-
perimentation with different orchestration strategies.
It offers robust support for decentralized schedul-
ing and real-time simulation, making it particularly
well-suited for researchers exploring adaptive, self-
organizing systems in complex distributed environ-
ments.
3 SYSTEM MODEL
The edge-fog-cloud continuum contains two funda-
mental agent types (Wu et al., 2025): resource agents
and demand agents. Resource agents represent the
networked resource pools in the continuum, provid-
ing CPU and memory resources to fulfill incoming
requests. On the edge layer, these agents consist of
COSMOS: A Simulation Framework for Swarm-Based Orchestration in the Edge-Fog-Cloud Continuum
391

MEA 𝑣
1
MEA 𝑣
2
MEA 𝑣
3
MEA 𝑣
4
MEA 𝑣
5
MFA 𝑣
7
MFA 𝑣
6
MFA 𝑣
8
MCA 𝑣
9
MCA 𝑣
10
IoT Devices
IoT Devices
IoT Devices
IoT Devices
IoT Devices
EMDCs
EMDCs
EMDCs
Cloud Server
Cloud Server
Figure 1: Exemplary architecture of the considered edge-
fog-cloud continuum (Wu et al., 2025).
IoT devices such as smartphones, laptops, and mo-
bile robots, which have limited resource capabili-
ties. In contrast, the fog layer features micro data
centers, while the cloud layer comprises large-scale
data centers from cloud providers, capable of serv-
ing more requests but often plagued by latency and
privacy issues. Resource agents are interconnected,
allowing requests to be transferred not only verti-
cally between layers but also horizontally within the
same layer. This interconnections foster collabora-
tion points among resource agents across the contin-
uum. Considering M resource agents in the edge-
fog-cloud continuum, they form a connected graph
G = (V, E), where vertices V represent the resource
agents and edges E encode the communication links
between them (see Figure 1 exemplary).
Demand agents in the edge-fog-cloud continuum
represent incoming requests, analogous to “pods” in
the Kubernetes context (Kim et al., 2021). These
agents are categorized into small, medium, and large
pods based on their CPU and memory requirements.
The arrival of demand agents in the continuum fol-
lows a Poisson process, with inter-arrival times gov-
erned by an exponential distribution characterized by
parameter µ ∈ (0, 1]. This parameter µ determines the
frequency of pod arrivals, with smaller values indi-
cating less frequent arrivals and larger values repre-
senting more frequent pod entries into the system.
Pods are successfully served when sufficient CPU and
memory resources are available on the selected re-
source agent. The decision regarding deployment on
edge, fog, or cloud resource agents is guided by the
self-organizing algorithm. Further information can be
found in (Wu et al., 2025).
4 COSMOS
In this paper, we present COSMOS (Continuum Op-
timization for Swarm-based Multi-tier Orchestration
System), a Python-based simulation framework built
on the Mesa multi-agent library, designed for im-
plementing and evaluating self-organizing scheduling
algorithms in distributed systems. The framework
provides modular components for swarm coordina-
tion dynamics, constraint-aware real-time optimiza-
tion. COSMOS is open-source available on Github
1
.
A key feature of COSMOS is its highly ex-
tensible API, allowing seamless integration of var-
ious scheduling strategies. The framework sup-
ports both rule-based algorithms and black-box ap-
proaches, where local decision rules can be encoded
using machine learning models.
4.1 Framework Architecture
COSMOS models the edge-fog-cloud continuum as
a dynamic environment populated by agents repre-
senting computational resources across different lay-
ers. These agents are designed to handle incoming
tasks, referred to as pods, which arrive with vary-
ing resource demands. Each resource agent belongs
to one of the three hierarchical levels: edge, fog, or
cloud, and offers a fixed amount of CPU cycles and
memory, according to its profile. At the same time,
the model is a dense connected network graph con-
sisting of a number of edge, fog and cloud devices (as
described in Section 3). Pods (i.e., demand agents)
enter this network dynamically with randomized ar-
rival times, controlled arrival density, and varying re-
source demands.
The COSMOS framework provides the capability
to generate diverse network topologies with customiz-
able load conditions and agent distributions, enabling
flexible experimentation with various scheduling sce-
narios. At the core of the framework’s hierarchy is the
Simulation class, which orchestrates the system’s
configuration, runtime flow, model initialization, de-
mand agent creation and distribution, as well as data
collection. Demand agent creation within the frame-
work is managed using the Factory design pattern, en-
suring modularity and scalability. The Model class
is responsible for constructing the network graph,
which consists of nodes representing resource agents
and edges connecting the three primary levels of the
edge-fog-cloud continuum. Resource agents are as-
signed to specific locations within the graph, while
communication costs are defined as edge weights.
This functionality is implemented using the Python
library Networkx, which facilitates graph-based mod-
eling and analysis. The behavior of demand agents
within the system is controlled by algorithms selected
1
COSMOS (Continuum Optimization for Swarm-
based Multi-tier Orchestration System): https://github.com/
Incomprehensible/COSMOS
SIMULTECH 2025 - 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
392
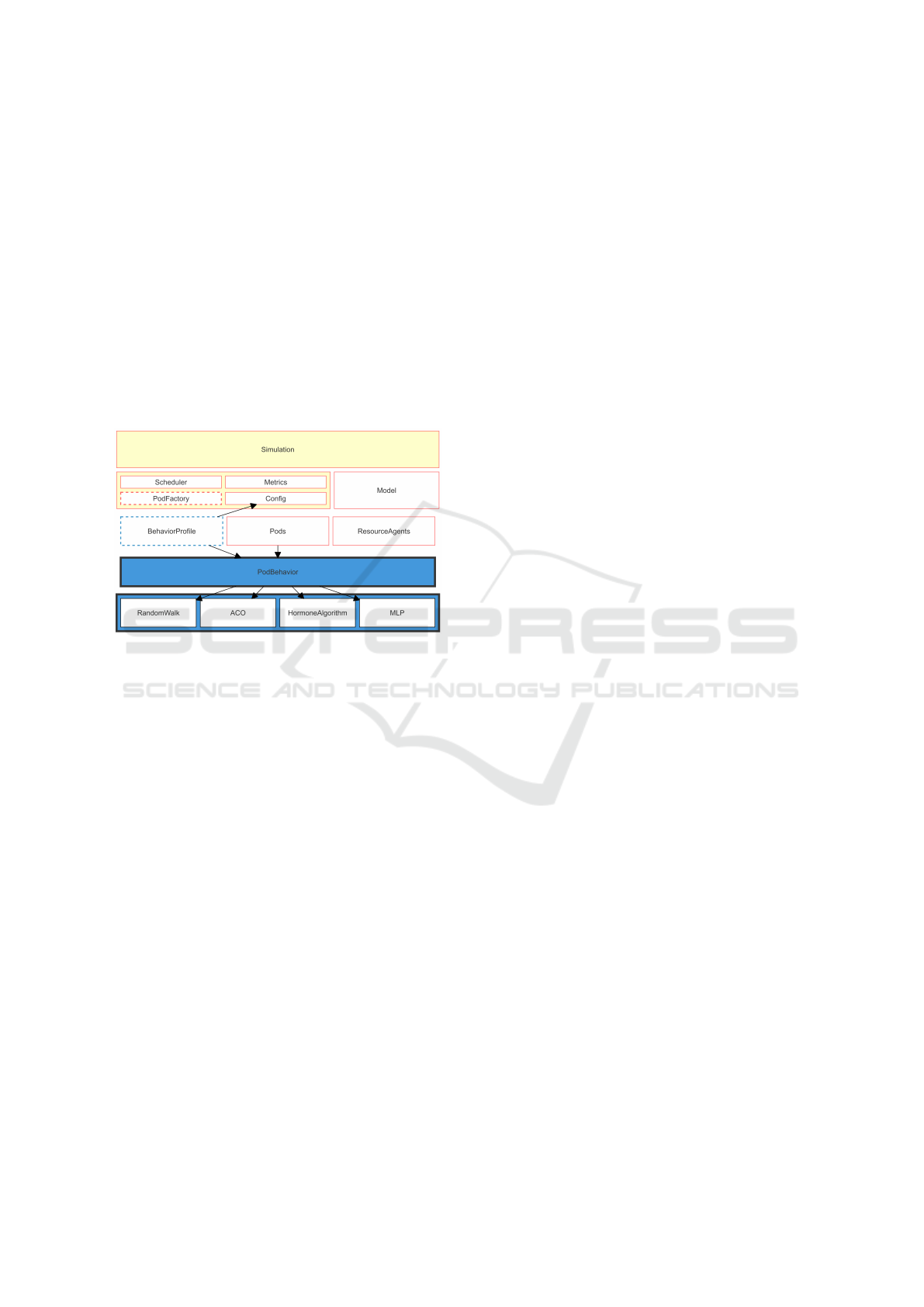
during configuration and activated via the Strategy de-
sign pattern. The BehaviorProfile class generates
a PodBehavior strategy and assigns it to individual
demand agents. The PodBehavior strategy class ini-
tializes specific scheduling algorithms based on the
configured parameters.
In our experiments, we evaluated results produced
by four distinct scheduling strategies: Random Walk,
Ant Colony Optimization (ACO), hormone-based al-
gorithm (HBA), and MLP (pretrained Multi-Layer
Perceptron), each implemented as separate strategy
classes. Figure 2 presents a block diagram illustrating
the architecture of the COSMOS framework, high-
lighting its modular components and interactions be-
tween classes.
Figure 2: The architecture of the COSMOS framework is
visually represented with key design patterns highlighted:
the Factory pattern is indicated by a red dashed line, the
Strategy pattern is marked with a blue dashed line, and the
specific implementations of the PodBehavior Strategy are
grouped within blue-filled blocks.
4.2 Algorithms
Scheduling in COSMOS is orchestrated at the highest
level of the class hierarchy. The Simulation class
maintains an instance of the scheduler, manages time
steps, controls agent activation within the environ-
ment, and monitors resource utilization and demand
agent movement across the network. The scheduling
process occurs within a single thread, where demand
agents are activated sequentially, each making an in-
dependent scheduling decision. This approach, with
its rapid context switching, effectively simulates an
asynchronous parallel model that closely resembles
real-world resource allocation environments.
The COSMOS framework implements four be-
havior profiles for scheduling: Random Walk, Ant
Colony Optimization (ACO), hormone-based algo-
rithm (HBA) as in (Wu et al., 2025), and the
neural-network-based encoded-rules algorithm (MLP
- Multi-Layer Perceptron). Since the positions of re-
source agents are fixed, only demand agents move
across the network graph. After completing a prede-
fined number of episodes, the framework collects and
processes performance metrics. The collected met-
rics include pods positions, execution success rate, re-
source utilization, and total communication costs.
In the simulation framework, the propagation of
the pods inside the network graph is an iterative pro-
cess governed by the programmed pods’ behavior. By
adjusting the simulation configuration, we define the
decision making procedure specific to the type of a
chosen scheduling algorithm. We implemented the
flexible behavior switching using the Strategy De-
sign Pattern. The behavior is initialized per demand
agent and depends on the said agent’s characteristics
only. The Behavior Profile base class definition
serves as a template for future algorithm implementa-
tions. Flexible and intuitive API of the framework al-
lows users to extend the collection of scheduling algo-
rithms and adopt new local rules-based strategies for
decentralized resource allocation. Automated evalua-
tion subsystem enables structured assessment of each
algorithm’s performance in diverse scenarios as well
as visualization of the results.
The Random Walk behavior profile provides a
baseline scheduling approach, where pods make ran-
domized movement decisions when selecting their
next node. If a pod meets its resource requirements
at its current node, it remains there. Otherwise, it
chooses randomly among its unvisited neighbors.
The most important parameter influencing deci-
sion making of the HBA scheduling algorithm is the
hormone level of each unvisited agent. The hormone
level of a resource agent is fixed at the time of cre-
ation and is assigned according to the provided com-
putational resources.
The behavior profile corresponding to the ACO
scheduling algorithm defines two key parameters:
evaporation rate and released pheromone intensity.
These parameters are dynamically computed based
on individual pod resource demands, influencing
scheduling behavior across the network. Algorithmic
details for the three algorithms can be found in (Wu
et al., 2025).
The MLP-based behavior profile integrates a neu-
ral network as a black-box decision model for pod
scheduling. The model takes several input fea-
tures, including the difference between available
CPU/memory and the pod’s resource demands, the
communication cost of moving to a neighbor, and the
current CPU utilization of neighboring nodes. The
MLP model processes these inputs and produces an
activation score for each candidate node, determining
the pod’s next move.
COSMOS: A Simulation Framework for Swarm-Based Orchestration in the Edge-Fog-Cloud Continuum
393

The behavior profiles corresponding to the four
scheduling algorithms are parameterized within COS-
MOS, allowing users to adjust key decision parame-
ters such as pheromone decay, decision thresholds, or
learning rates to explore different orchestration strate-
gies.
5 EXEMPLARY SIMULATION
RESULTS
In this section, we present a case study demonstrating
the capabilities of the COSMOS framework for eval-
uating distributed scheduling algorithms in a highly
connected multi-tier computing environment. We per-
form a series of experiments evaluating four schedul-
ing strategies: Random Walk, ACO, HBA, and MLP-
based scheduling. Each algorithm is assessed based
on its efficiency in allocating computational resources
while optimizing task execution. We then analyze the
simulation results in detail for two representative al-
gorithms to highlight key performance differences.
5.1 Defining the Real-World Model
We establish a mapping between an exemplary indus-
trial plant and our simulation model. In our model,
we have a distribution of computational resources
as described in Table 1. Next, we approximate the
pod arrival frequency in our model. Task sources
at the edge layer include worker activity-dependent
sporadic data uploads or app usage as well as peri-
odic or event-driven data from sensor networks. At
the fog layer, industrial robots generate tasks at reg-
ular intervals, while workstations introduce randomly
distributed computational workloads (e.g., analytics,
processing). Finally, at the cloud layer, large-scale
computations, storage requests, or parallelization jobs
contribute to task arrivals. To model a busy network
scenario, we define a high task arrival rate by setting
µ = 0.8. We sum up these contributions to arrive at the
Table 1: Task arrival rates for different sources.
Task Source Count Interval (sec) Tasks/sec
Sensor Networks 100 10 10
Industrial Robots 40 5 8
Smartphones (Workers) 500 10 50
Workstations 100 20 5
Cloud Devices 10 60 0.17
Total - - 73.17
total estimated task arrival rate in Table 1. Although
the rounded arrival rate corresponds to 75 pods per
time step, we introduce controlled randomness into
the task injection process by sampling inter-arrival
intervals from an exponential distribution (µ = 0.8).
This results in slight variations in the number of pods
spawned at each step while preserving the expected
average rate over the simulation. This approach em-
ulates real-world fluctuations in workload and allows
us to evaluate the robustness of the scheduling strate-
gies under non-deterministic conditions.
5.2 Simulation Result Analysis
We compare four scheduling algorithms across a
range of performance metrics to illustrate the differ-
ences in scheduling behavior. Our analysis is based
on simulation results shown in Figures 3 and 4, as
well as in Tables 2 and 3. Each trajectory in the CPU
and memory utilization plots represents the average
activity across all computing nodes in the network un-
der the control of a given algorithm.
Resource utilization statistics in Figure 3 are col-
lected during simulation runtime using the parameters
detailed in Section 5.1. Layer dependency is calcu-
lated as D
layer
(t) =
N
layer
(t)
N
issued
, where D
layer
(t) is the de-
pendency on a given layer at time t, N
layer
(t) is the
number of pods currently on that layer and N
issued
is the total number of pods issued into the system.
Figure 4 shows the mean and maximum communica-
tion costs recorded across all pods, aggregated from
two independent simulation runs with 5500 and 6000
pods, respectively. The execution metrics in Tables
2 and 3 were obtained under varying simulation step
limits.
Our analysis focuses on three key performance
metrics:
• Communication costs – ideally, pods should
minimize their path to the target resource agent.
• Lower layer utilization – since computing
at the edge is more cost-efficient, scheduling al-
gorithms should prioritize utilizing this layer ef-
fectively.
• Execution ratio – the percentage of pods suc-
cessfully executed within the simulation time.
The execution ratio measures the efficiency of a
scheduling algorithm in completing tasks with ER =
N
executed
N
issued
, where N
executed
is the total number of pods
that have been successfully executed.
The comparative analysis highlights CPU and
memory utilization, communication costs, and execu-
tion efficiency, demonstrating how adaptive learning-
based scheduling outperforms stochastic allocation in
dynamic, multi-tier networks.
Random Walk, a baseline algorithm with no in-
telligent decision-making, incurs the highest commu-
nication costs among the four strategies (Figure 4).
SIMULTECH 2025 - 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
394
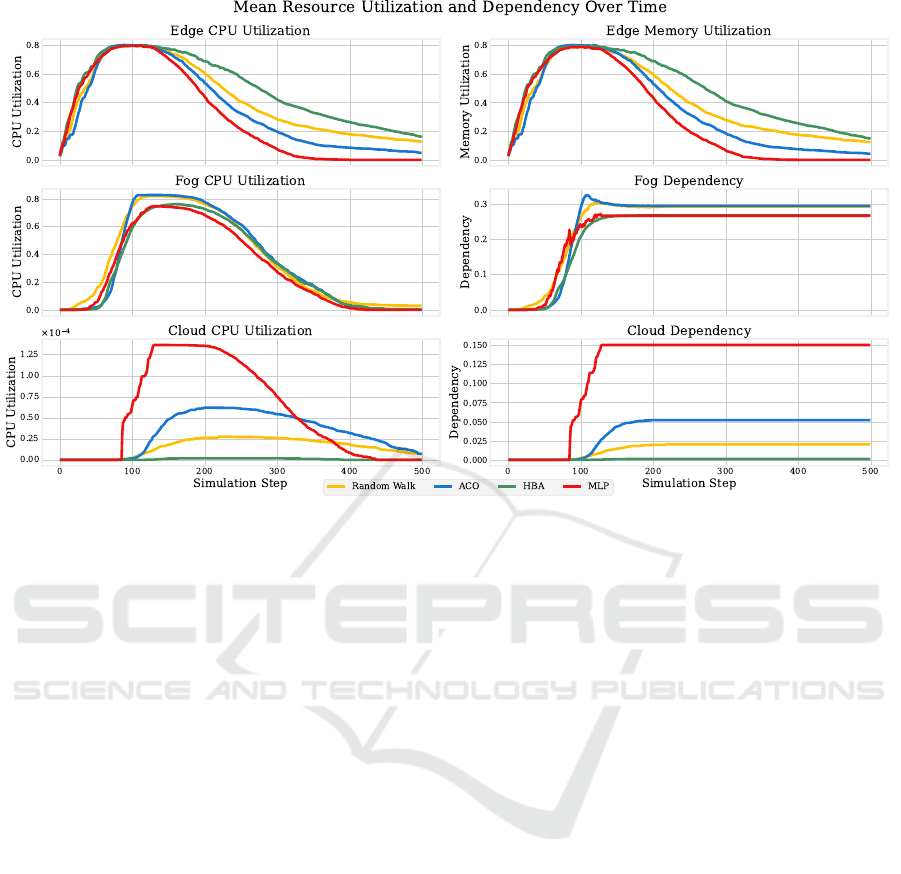
Figure 3: Resources utilization for four scheduling algorithms with fixed number of pods (500).
This is because it follows an exploratory approach,
where pods traverse the network extensively before
reaching their execution nodes. As a result, tasks ac-
cumulate in the lower layers, leading to a delayed ex-
ecution process. Although Figure 3 shows that Ran-
dom Walk uses the cloud and fog slightly more than
HBA, it still primarily relies on the edge layer. This
makes Random Walk a viable strategy in scenarios
where resource utilization across all layers (with ac-
cent on lower layers) is prioritized over execution
speed. However, in larger networks with high ini-
tial loads, this approach risks causing congestion, as
pods remain in the system for an extended period. We
can observe the effects of the ’wandering’ behavior
of the pods on accumulated communication costs of
Random Walk in Figure 4 where the overhead is the
highest among all algorithms.
On the other hand, the MLP-based scheduler takes
a more structured approach, resulting in faster exe-
cution times, lower peak communication costs, and
more balanced resource utilization across layers. As
shown in Figure 4, MLP achieves the lowest mean
and maximum communication costs among all tested
algorithms. We observed that communication costs
per pod follow a logarithmic growth pattern, which
stabilizes earlier under MLP compared to other meth-
ods -particularly Random Walk. As seen in Tables 2,
MLP completes all executions by step ≈440, whereas
Random Walk and other classical algorithms still have
unfinished tasks beyond step 600. To observe a 100%
task execution rate across most algorithms, the num-
ber of simulation steps had to be extended to 700.
MLP’s faster convergence is also reflected in the CPU
and memory utilization plots (Figure 3) for 500 steps
and 5500 pods, where layers utilization is shown as
a multiple time series, and fog/cloud dependency is
presented as cumulative overhead.
A key factor behind this improvement is how MLP
schedules workload distribution early in the simula-
tion. As shown in Figure 3, MLP utilizes the edge
and fog layers at a rate comparable to other algo-
rithms during the initial phase but begins leverag-
ing the cloud layer earlier. It continues executing
pods at the cloud layer for approximately one-fifth
of the simulation duration before gradually reducing
cloud usage over time. This approach ensures that
tasks are completed faster while keeping communi-
cation costs low enough to maintain efficiency. Al-
though the differences in execution ratio depicted in
Table 2 are numerically small (largest difference be-
ing ≈ 0.035), they are meaningful due to the large
number of pods and simulation steps. MLP com-
pletes tasks several iterations earlier than other algo-
rithms, indicating faster convergence. Given the non-
linear behavior of the system, this performance gap is
likely to widen as the graph or workload scales. We
demonstrate this scalability by increasing the number
of pods from 5500 to 6000 and observing that MLP
continues to maintain lower communication costs, as
shown in Table 3 and Figure 4. The observed execu-
COSMOS: A Simulation Framework for Swarm-Based Orchestration in the Edge-Fog-Cloud Continuum
395
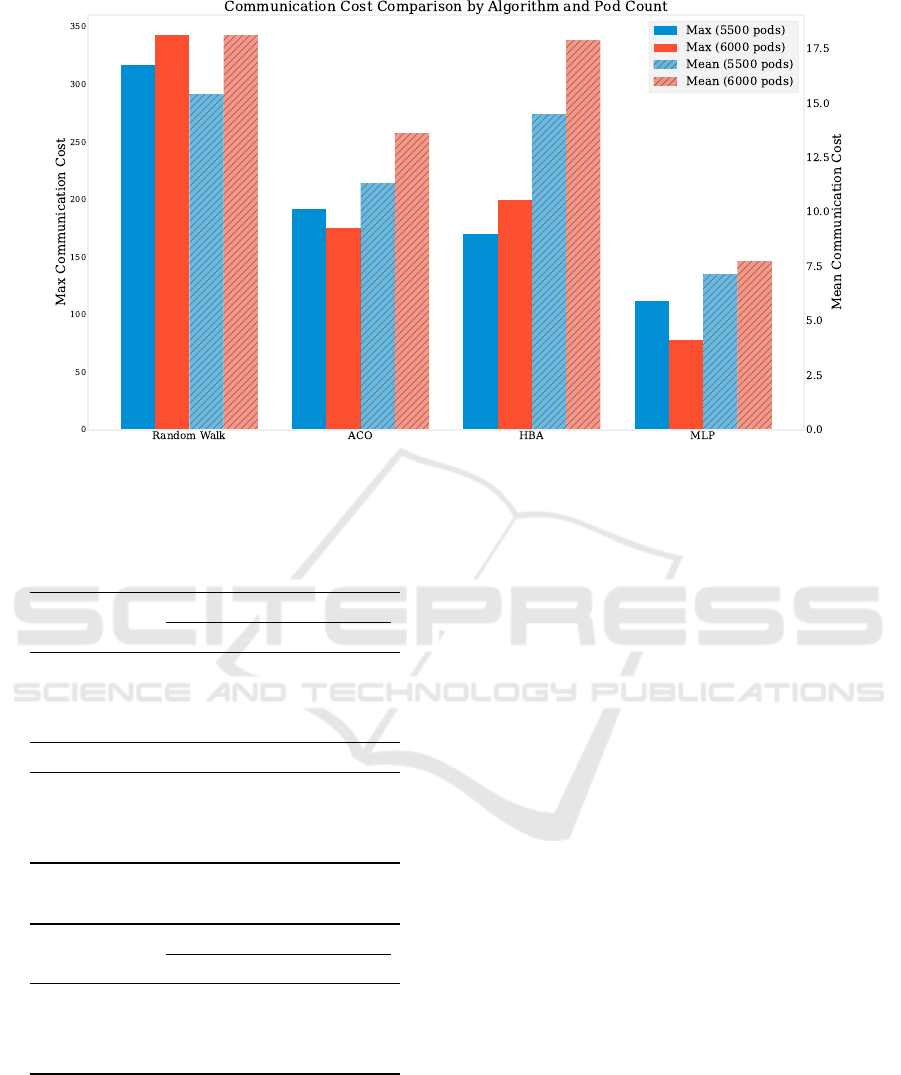
Figure 4: Communication costs for four scheduling algorithms with different number of pods.
Table 2: Execution statistics for 5500 pods. A dash (–) in
the last column indicates incomplete task execution by the
end of the simulation.
Algorithm
500 steps
Exec. ratio Completion step
Random Walk 0.965 —
ACO 0.987 —
HBA 0.97 —
MLP 1.00 427
700 steps
Random Walk 0.998 —
ACO 1.00 666
HBA 0.999 —
MLP 1.00 429
Table 3: Execution statistics for 6000 number of pods.
Algorithm
700 steps
Exec. ratio Completion step
Random Walk 0.995 —
ACO 1.00 690
HBA 1.0 696
MLP 1.00 434
tion pattern also suggests that the MLP model gener-
alizes well to more complex scenarios than those seen
during training, demonstrating its adaptability to dy-
namic conditions.
Two additional observations from our analysis
highlight the scheduling performance of the HBA and
ACO algorithms. HBA maintains relatively low com-
munication costs, completes the majority of tasks on
time, and successfully shifts most of the workload
toward the preferred edge layer. These characteris-
tics make HBA a strong candidate for deployment
in resource-constrained systems. ACO, on the other
hand, demonstrates adaptability to varying workloads
and combines consistent task execution with a priori-
tization of edge and fog layers, resulting in stable per-
formance across varying scenarios. It may therefore
be considered a “best-of-both-worlds” strategy, bal-
ancing task completion effectiveness with lower-layer
resource preference.
These results illustrate the advantages of intelli-
gent scheduling in distributed computing and high-
light the practical applicability of self-optimizing or-
chestration methods. The visualization tools within
the simulation framework significantly aid in inter-
preting results, especially in large, highly intercon-
nected networks, by enabling layer-based analysis of
performance metrics.
6 CONCLUSION
This study presented the COSMOS framework, de-
signed to enhance accessibility and observability in
swarm and agent-based orchestration systems. We
demonstrated its capabilities by simulating multiple
self-organizing scheduling algorithms in a highly con-
nected edge–fog–cloud computing environment. The
SIMULTECH 2025 - 15th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
396

framework’s flexibility was showcased through its
support for diverse scheduling strategies and con-
figurable experiment setups. To validate COSMOS,
we analyzed the performance of four scheduling
algorithms. Our findings highlighted the impor-
tance of intelligent scheduling, showing that artificial
intelligence-based methods are both realizable and ef-
fective within the framework.
Future work on COSMOS may focus on per-
formance optimizations, such as parallelized simula-
tions, as well as the development of an intuitive user
interface, enhanced visualization tools, and a robust
data logging and storage pipeline.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Funded by the European Union, project MYRTUS, by
grant No. 101135183. Views and opinions expressed
are however those of the author(s) only and do not
necessarily reflect those of the European Union. Nei-
ther the European Union nor the granting authority
can be held responsible for them.
REFERENCES
Calheiros, R. N., Ranjan, R., Beloglazov, A., De Rose, C.
A. F., and Buyya, R. (2011). Cloudsim: a toolkit for
modeling and simulation of cloud computing environ-
ments and evaluation of resource provisioning algo-
rithms. Software: Practice and Experience, 41(1):23–
50.
Gupta, H., Vahid Dastjerdi, A., Ghosh, S. K., and Buyya,
R. (2017). ifogsim: A toolkit for modeling and
simulation of resource management techniques in
the internet of things, edge and fog computing en-
vironments. Software: Practice and Experience,
47(9):1275–1296.
Kazil, J., Masad, D., and Crooks, A. (2020). Utilizing
python for agent-based modeling: The mesa frame-
work. In Proceedings of the 13th International Con-
ference on Social, Cultural, and Behavioral Modeling,
pages 308–317. Springer.
Kim, E., Lee, K., and Yoo, C. (2021). On the resource man-
agement of kubernetes. In Proceedings of the 2021
International Conference on Information Networking,
pages 154–158.
Palumbo, F., Zedda, M. K., Fanni, T., Bagnato, A., Castello,
L., Castrillon, J., Ponte, R. D., Deng, Y., Driessen, B.,
Fadda, M., et al. (2024). Myrtus: Multi-layer 360 dy-
namic orchestration and interoperable design environ-
ment for compute-continuum systems. In Proceedings
of the 21st ACM International Conference on Comput-
ing Frontiers: Workshops and Special Sessions, pages
101–106.
Schranz, M., Di Caro, G. A., Schmickl, T., Elmenreich,
W., Arvin, F., ¸Sekercio
˘
glu, A., and Sende, M. (2021).
Swarm intelligence and cyber-physical systems: con-
cepts, challenges and future trends. Swarm and Evo-
lutionary Computation, 60:100762.
Sonmez, C., Ozgovde, A., and Ersoy, C. (2018). Edge-
cloudsim: An environment for performance eval-
uation of edge computing systems. Transac-
tions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies,
29(11):e3493.
Srirama, S. N. (2024). Distributed edge analytics in edge-
fog-cloud continuum. Internet Technology Letters,
8(3).
Umlauft, M., Schranz, M., and Elmenreich, W. (2022).
Simulation of swarm intelligence for flexible job-shop
scheduling with swarmfabsim: Case studies with ar-
tificial hormones and an ant algorithm. In Proceed-
ings of the International Conference on Simulation
and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Ap-
plications, pages 133–155. Springer.
Varghese, B. and Buyya, R. (2018). Next generation cloud
computing: New trends and research directions. Fu-
ture Generation Computer Systems, 79:849–861.
Wilensky, U. and Rand, W. (2015). An Introduction to
Agent-Based Modeling: Modeling Natural, Social,
and Engineered Complex Systems with NetLogo. MIT
Press.
Wu, K., Ghasemi, A., and Schranz, M. (2025). Swarm
intelligence-based algorithm for workload placement
in edge-fog-cloud continuum. In Proceedings of the
17th International Conference on Agents and Artifi-
cial Intelligence.
Zyskind, G., Nathan, O., and Pentland, A. (2015). Enigma:
Decentralized computation platform with guaranteed
privacy. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.03471.
COSMOS: A Simulation Framework for Swarm-Based Orchestration in the Edge-Fog-Cloud Continuum
397
