
Enhanced Face Recognition Algorithm for Real-Time Applications
with Improved Accuracy
Raji Pandurangan, Lavanya C and Swetha C
Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Saveetha Engineering College, Chennai, India
Keywords: Face Recognition, Real-Time Detection, Feature Extraction, Accuracy, Precision, Robustness.
Abstract: Encouraging the development of safe and effective face recognition systems in applications such as
surveillance, access control, and identity verification, developing accurate and reliable algorithms has become
a significant focus in computer vision. Traditional methods like Dense U-Nets, Retina Face, and Hierarchical
Networks provide satisfactory results but often fall short in balancing accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and
specificity, especially in real-time scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose an enhanced face
recognition algorithm that leverages improved feature extraction and optimized classification techniques. Our
proposed method was evaluated alongside existing algorithms, achieving superior performance achieving an
overall accuracy of 89.50% while also achieving superior values for specificity, sensitivity, and precision.
These results demonstrate the method's effectiveness and suitability for high-stakes applications where
reliability is paramount. Future work will focus on adapting the model for diverse conditions such as low-
light and multi-angle environments to further improve robustness.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recognition of Faces is a Biometric Approach for
Detecting Faces. The challenge of verifying or
identifying a face from the multimedia images is
accomplished by employing a facial recognition
method. Recognising people by face has become
increasingly crucial as our civilisation has
progressed. Across the globe, face detection and
identification systems have been expanding (Shetty,
Rebeiro, et al. , 2021). Although the classroom
security camera is not fixed, the angle at which faces
are captured in the footage varies as well. This face
verification technique, which is based on deep
learning (DL), has demonstrated encouraging
outcomes in controlled settings, its performance in
uncontrolled environments might use a lot of
improvement. Both the network's output and the
dataset's diversity and quality affect the model's
performance (Li, Shen, et al. , 2023). Human people,
at birth, possess a distinctive feature that enables
them to recognise other persons, namely the "face."
In addition to speech and fingerprints, facial
recognition is a crucial component of biometrics, as
no two individuals possess identical facial features.
Myths that an individual may share facial
characteristics with seven different people, and face
detection and identification systems assist in
distinguishing among them. Facial expression
detection, face detection, and recognition have
significantly influenced the domain of image
processing (Wattamwar, Mate, et al. , 2021).
The development of algorithms for facial
recognition has been rapid and influenced by
numerous variables. Many approaches to veiled facial
recognition in light of the unexpected elements
encountered in actual life. Nevertheless, masked
facial recognition diverged from occluded face
recognition of the SarS-CoV2 pandemic (Neto, Pinto,
et al. , 2022). One thing that differentiates face
recognition algorithms is the fact that it uses a
confirmation or identification approach that assesses
personality. Two processes: facial recognition and
facial identification, form the backbone of the
method. Facial recognition is applicable to personal
computers with a few different ways that photos of
people's faces can be recognised. The "right" data
from frontal facial photos is typically used to
accomplish face recognition. Unblemished faces seen
on CCTV are a great example, even if there are many
contexts in which entire faces are not visible
(Shamrat, Majumder, et al. , 2022). Several research
214
Pandurangan, R., C, L. and C, S.
Enhanced Face Recognition Algorithm for Real-Time Applications with Improved Accuracy.
DOI: 10.5220/0013612400004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 3, pages 214-219
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

solutions have been proposed for the automatic
recognition of human emotional states. The World
Health Organisation reported that tragically, many
were unable to administer first aid in a timely manner
after falling on the road, leading to fatalities
(Bharathiraja, Sakthivel, et al. , 2023) By the age-
invariant face recognition, is a system that uses a
correlation between traits related to identity and age.
On the other hand, combining faces of varying ages,
face age synthesis (FAS) gets rid of age variance into
one group. On the other hand, FAS's artefacts hinder
downstream recognition, while face recognition
doesn't provide any visual findings to aid with model
interpretation (Huang, Zhang, et al. , 2022).
Nowadays, face recognition is much sought after
because of its practical use individual verification.
With just a little raw image or a glimpse, the
technology may aid in retrieving the person's
information from a database. Though not widely used
in India, biometric identification systems should use
facial recognition to render safer and without physical
contact, the system; this technology is urgently
needed (Saleem, Shiney, et al. , 2023).
Furthermore, the human brain has a special region
dedicated to face recognition called the fusiform face
area, which is crucial for our survival (Alankar,
Ammar, Kumar, 2020). Face recognition technology
relies on face detection, which entails identifying a
face in an initial image. Pandemic proportions have
been reached as the COVID-19 virus has spread to
over 200 countries. However, the virus is evolving at
a rapid pace, with new strains spreading via both
direct and indirect contact in areas where vaccines are
not yet available. Face masks and other social
distancing measures are necessary because many
infectious diseases spread through droplets, and
micro-droplets in particular (Deepa, Hariprasad, et al.
, 2022).
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
A person's face is the most distinctive feature that
allows others to recognise them. No two people are
exactly same, and that includes identical twins.
Therefore, distinguishing between them necessitates
facial recognition and identification. An example of a
biometric verification system is a facial recognition
system. A fresh collection of test cases is constructed
with extensive property information, and the face
recognition time constraint protocol. Also, for the
purpose of biometrics evaluation under COVID-19,
we have compiled a large-scale masked face subset.
There are three different types of recognition tasks:
conventional, masked, and impartial to ensure a
thorough evaluation of face matchers. An effective
method for training facial recognition models that
does not compromise performance is established
using a distributed architecture (Zhu, Huang, Kumar,
2022). The term "face" refers to the front portion of
an animal's or human's head that extends from the
jawline to the chin. Because it contains so many
crucial facts about a person or thing, face is the most
fundamental aspect of being human. It is believed that
humans can identify one another only by looking at
their faces. Class control for instructors at the
Technical Informatics College of Akre using facial
recognition technology to monitor student attendance
in a classroom setting (Mohammed, Zeebaree,
Kumar, 2021). Two methods, "Template Matching"
and "Local Binary Pattern Histogram (LBPH)," are
being compared. Python, the Raspberry Pi 3 Model
B+, OpenCV, and the LBPH algorithm were used to
build the prototype of the face recognition and
identity security system. This idea presents a method
for recognising random faces using the Haar
classifier. Instead than using databases, this method
compares individuals to a static collection and then
provides matches based on first, second, and third
results. Unlike biometric devices, it does not seek for
specific matches. It functions similarly to a CCTV in
that it can identify people, but it only stores a short
amount of footage (Chowdhury, Sakib, Kumar,
2022). The model can function in a wide range of
environments, including those with different lighting
and backgrounds, to Face mesh. Additionally, this
model can handle processing non-frontal images
containing both sexes, regardless of age or race.
images from the train the deep neural network of the
model, real-time images and the wild face dataset are
used. When testing, the model will report the person's
name if their facial landmarks match those in any of
the training images; else, it will output "unknown."
(Hangaragi, Neelima, et al. , 2023).
The process of creating altered or encrypted
versions of original biometric templates is known as
cancelable biometrics. Modern hacking tools can
retrieve the original biometric data stored in
databases, which led to the development of
cancellable biometrics. One workaround for this issue
is to replace the original biometric templates stored in
the database with cancellable ones. An approach to
cancellable face identification using a Fractional-
Order (FO) Lorenz chaotic system to encrypt facial
images is presented in this study. An individual's red,
green, and blue face image components can be
XORed with randomly generated keys that are
exclusive to that user. The Lorenz chaotic system
Enhanced Face Recognition Algorithm for Real-Time Applications with Improved Accuracy
215

with fractional orders generates these keys. The face
photos' encrypted colour components also undergo
some post-processing, including matrix rotation and
transposition. The last step is to combine the
decrypted and processed parts of the face image using
a wavelet fusion algorithm(Badr, Radwan, et al. ,
2021). The usage of face recognition systems for user
identification is widespread. It is a program that 3D
models utilise to accomplish a wide variety of
machine-based visual tasks, such as detecting edges
from various perspectives to minimise collisions. by
the incorporation of iris recognition into the face
recognition system. Python and OpenCV are utilised
to alter photographs of the face and iris (Srivastava,
Katiyar, et al. , 2022). Local binary pattern (LBP)
classifiers are invariant under different lighting
situations, making them ideal for face detection, and
Haar classifiers are highly accurate in this regard. To
enhance the identified faces, image processing
methods like quantisation, histogram equalisation,
bilateral filtering, and contrast correction are utilised.
To further assess the possibility of the approach for
successfully identifying faces in low-quality images,
have quantised raw face photographs at different
levels (Padmashree, Karunakar, et al. , 2022). A face
recognition program is a piece of technology that can
identify a person in a high-tech photo or video clip. A
safer and more user-friendly world can be discovered
with its help. Some instances include locating missing
people, detecting shoplifting, identifying security
personnel, locating social media profiles, and
recognising vehicle drivers. Detection, extraction,
and identification are the three main components of
face recognition. When it came time for face
detection, the algorithms used were Haar-Cascade,
Eigenfaces, Fisherfaces, and local binary pattern
histograms (Pandey, Yadav, et al. , 2022).
One viable
alternative for the day-to-day management of student
attendance systems is smart attendance with
instantaneous face detection. A facial recognition-
system that tracks attendance uses a person's likeness
to verify their identity. Nowadays, schools are facing
a big issue with the consistency of student attendance.
To take attendance, teachers employ face biometrics
that are based on a high-definition monitor to identify
each pupil. Both of them were more laborious and
demanding of time. media, in addition to several
kinds of digital technologies (Yadav, Sharma, et al. ,
2022). Intelligent technology that can recognise and
identify faces in order to collect attendance. the
attendance system more user-friendly, efficient, and
secure from proxy attacks. There was a possibility of
proxy in the previous manual-based attendance
system, but we will be able to fix it. This method can
clearly convey the idea to the computer as to whether
or not it is a valid proxy or legal attendance. This
system is less complicated and more secure(Bairagi,
Ahmed, et al. , 2021).
Smart city apps are becoming more popular in
many countries because they improve people's
quality of life, make better use of people's time and
resources, and decrease pollution. Because they
provide improved access management and space
allocation, multi-location parking garages are
ubiquitous in smart cities. This helps to alleviate
traffic and delays in densely populated commercial
areas. The IoT has the ability to connect billions of
devices and services throughout the globe, in real-
time, for many purposes. One of the hot topics in
internet of things research right now is smart parking.
Modern metropolitan cities have over one million
vehicles on the road, but there is a severe lack of
parking spaces to accommodate all of them.
3 METHODOLOGY
Modern parking garages are notoriously inefficient.
This means that drivers could waste a lot of time on
busy days just driving around a parking lot looking
for a spot. Better public service, less emissions and
pollutants, increased parking utilisation, improved
city tourist experience, and prevention of unneeded
capital investments are all possible outcomes of
implementing this system, which will also aid in
resolving the increasing problem of traffic
congestion, wasted time, and lost money. Facial
recognition technology finds extensive applications
in diverse security systems, ranging from physical
access control to computer user databases. All the
necessary software and hardware components of the
proposed system have been painstakingly designed.
Its primary objective is to introduce an automated
parking system that enhances the efficiency and
simplicity of parking for both drivers and
administrators.
Figure 1 illustrates a face recognition pipeline
utilizing the SSD (Single Shot Detector) algorithm to
achieve real-time detection and classification of
known individuals. The process is divided into three
primary stages such as Data Set Collection, Feature
Set Extraction and SSD Algorithm for Detection and
Classification. The SSD algorithm enables high-
speed, efficient face recognition, suitable for
applications that require rapid and accurate
identification of individuals. This setup is particularly
useful for security systems, attendance monitoring,
and other real-time identity verification systems.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
216
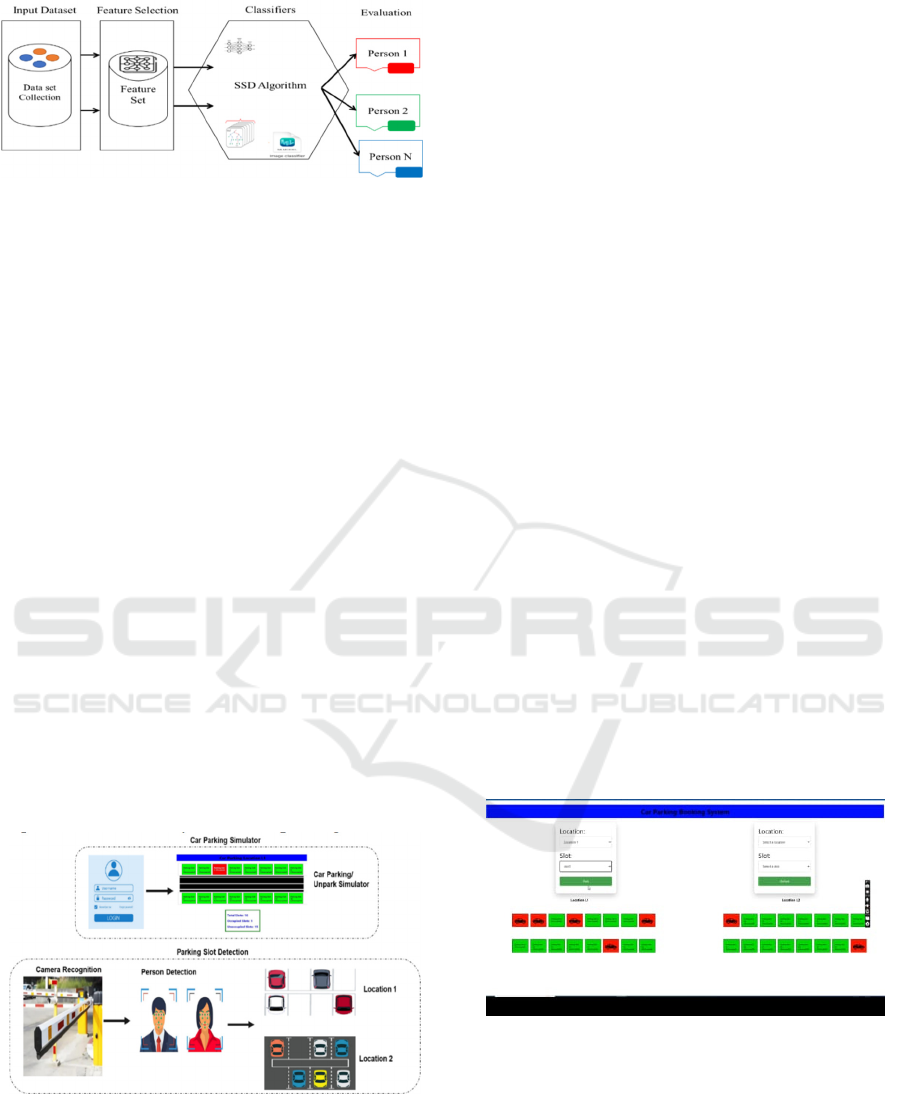
Figure 1: Proposed System Architecture
The system architecture integrates a camera for
real-time monitoring. The SSD algorithm is
employed for face detection. When a face is detected
at a parking slot, the toll gate will open. Multiple
parking slots are visualized using a graphical
interface. This system ensures efficient management
of parking spaces while providing a seamless
experience for users. It combines real-time image
processing with automated access control for an
optimized parking solution. Figure 2 describes the
proposed system block diagram. The system
architecture integrates a camera for real-time
surveillance and an SSD-based face detection
algorithm for efficient monitoring of car parking
areas. As vehicles approach the toll, the camera
captures live video feed. The SSD algorithm
processes the frames to detect faces in real-time,
ensuring precise identification. Simultaneously, the
system visualizes multiple parking slots across
different locations, indicating availability. Detected
faces are cross-referenced with a database to
authorize access to the parking area. If a recognized
face is associated with a valid parking permit, the toll
gate opens, allowing entry. This intelligent system
optimizes parking operations, enhancing user
experience and security at various parking locations.
Figure 2: Proposed System Block Diagram
3.1 Image Acquisition
Image acquisition refers to the process of
capturing a digital image from the physical world,
typically using a camera or some form of optical
sensor. This process involves converting analog
information from the real world into a digital format
that can be stored, processed, and manipulated by
computers.
3.2 Face Detection Module
The SSD is a DL algorithm for object detection,
including faces. Forecasts the classes of objects and
their bounding boxes at the same time, saving time.
SSD uses a multi-scale feature map to detect objects
of different sizes, enhancing its accuracy and speed.
In the SSD algorithm, face alignment typically
involves a preprocessing step before face detection.
This step aims to ensure that facial features within the
detected bounding boxes are consistently positioned.
Common techniques for face alignment include using
facial landmarks or pose estimation to adjust the
orientation and alignment of the detected faces. This
helps improve the accuracy of subsequent face
recognition or analysis tasks.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Parking systems are only one area where the IoT has
revolutionised contemporary living by capitalising on these
enormous technological advances. These potential
prompted the development of a smart parking system,
which uses an integrated multiple-slot approach to
automatically notify cars of available parking spots, saving
both time and money by reducing the need to staff parking
lots.
Figure 3: Car Parking Booking System Interface for Multi-
Location Slot Selection and Availability
Figure 3 depicts the user interface of a car parking
booking system, designed to allow users to select a
parking location and view the availability of parking
slots. The interface includes two main sections, each
representing a different location (Location L1 on the
left and Location L3 on the right). Each section
Enhanced Face Recognition Algorithm for Real-Time Applications with Improved Accuracy
217
displays a form for selecting a location and a parking
slot, along with a "Park" or "Unbook" button. Red
Slots: represents occupied parking spaces. An icon of
a car is displayed within each red slot to indicate that
it is currently in use. Green Slots represents available
parking spaces, which users can select for booking.
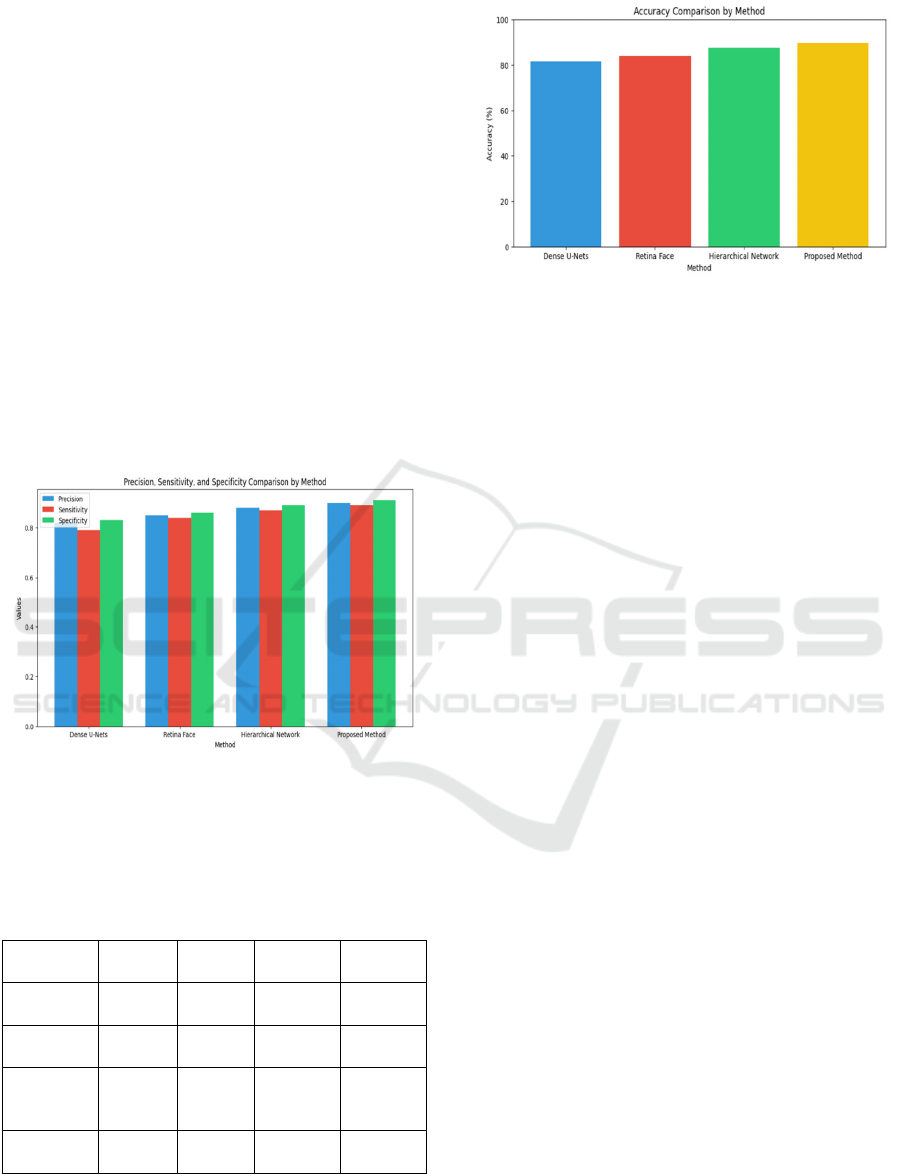
Figure 4 shows the precision, Sensitivity, and
Specificity Comparison by Method, with grouped
bars representing each metric for the algorithms. In
this chart, the Proposed Method consistently
outperforms other methods across all three metrics:
precision, sensitivity, and specificity, indicating its
balanced and robust performance in face recognition
tasks. Table I presents the performance indicators—
specificity, sensitivity, accuracy, and precision —for
four face recognition algorithms: Dense U-Nets,
Retina Face, Hierarchical Network, and the Proposed
Method. The Proposed Method demonstrates the
highest values across all metrics, indicating superior
performance in face recognition tasks.
Figure 4: Performance Comparison of Face Recognition
Algorithms
Table 1: Performance Metrics of Face Recognition
Algorithms
Method Accura
cy
Precisi
on
Sensitivi
ty
Specifici
ty
Dense U-
Nets
81.43% 0.82 0.79 0.83
Retina
Face
83.87% 0.85 0.84 0.86
Hierarchi
cal
Networ
k
87.36% 0.88 0.87 0.89
Proposed
Metho
d
89.50% 0.90 0.89 0.91
Figure 5: Accuracy Comparison of Face Recognition
Algorithms
Figure 5 shows the Accuracy Comparison by
Method, where each algorithm's accuracy is
displayed as a percentage. The Proposed Method
exhibits the highest accuracy at 89.50%, followed by
the Hierarchical Network at 87.36%, Retina Face at
83.87%, and Dense U-Nets at 81.43%. This indicates
the overall improved performance of the Proposed
Method over existing approaches.
5 CONCLUSION
The comparative analysis of face recognition
algorithms demonstrates that the Proposed Method
outperforms the Dense U-Nets, Retina Face, and
Hierarchical Network approaches across all key
metrics: accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and
specificity. With an accuracy of 89.50% and
consistently higher precision, sensitivity, and
specificity values, the Proposed Method proves to be
more reliable and effective for face recognition tasks.
These results suggest that the enhancements
introduced in the Proposed Method lead to more
accurate detection and classification, making it a
suitable choice for uses necessitating exact
measurements and reliability, such as security
systems and identity verification solutions. Future
work could focus on further optimizing the Proposed
Method for faster real-time processing and testing it
across diverse datasets to enhance its robustness and
adaptability in various real-world environments.
REFERENCES
Shetty AB, Rebeiro J. Facial recognition using Haar
cascade and LBP classifiers. Global Transitions
Proceedings. 2021 Nov 1;2(2):330-5.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
218

Li N, Shen X, Sun L, Xiao Z, Ding T, Li T, Li X. Chinese
face dataset for face recognition in an uncontrolled
classroom environment. IEEE Access. 2023 Aug 7.
Wattamwar S, Mate R, Rainchwar P, Mantri S, Sorate G.
Optimal Face Recognition System using Haar
Classifier. In2021 International Conference on Smart
Generation Computing, Communication and
Networking (SMART GENCON) 2021 Oct 29 (pp. 1-
7). IEEE.
Neto PC, Pinto JR, Boutros F, Damer N, Sequeira AF,
Cardoso JS. Beyond masks: On the generalization of
masked face recognition models to occluded face
recognition. IEEE Access. 2022 Aug 16;10:86222-33.
Javed Mehedi Shamrat FM, Majumder A, Antu PR,
Barmon SK, Nowrin I, Ranjan R. Human face
recognition applying haar cascade classifier.
InPervasive Computing and Social Networking:
Proceedings of ICPCSN 2021 2022 (pp. 143-157).
Springer Singapore.
Bharathiraja N, Sakthivel M, Deepa T, Hariprasad S,
Ragasudha N. Design and implementation of selection
algorithm based human emotion recognition system.
In2023 7th International Conference on Trends in
Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI) 2023 Apr 11 (pp.
1348-1353). IEEE.
Huang Z, Zhang J, Shan H. When age-invariant face
recognition meets face age synthesis: a multi-task
learning framework and a new benchmark. IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence. 2022 Oct 28;45(6):7917-32.
Saleem S, Shiney J, Shan BP, Mishra VK. Face recognition
using facial features. Materials Today: Proceedings.
2023 Jan 1;80:3857-62.
Alankar B, Ammar MS, Kaur H. Facial emotion detection
using deep learning and Haar Cascade Face
Identification algorithm. InAdvances in Intelligent
Computing and Communication: Proceedings of ICAC
2020 2021 (pp. 163-180). Springer Singapore.
Deepa T, Hariprasad S, Bharathiraja N, Chokkalingam A.
A Real Time Face Mask Detection and Health Status
Monitoring using Deep Learning after Pandemic.
In2022 International Conference on Augmented
Intelligence and Sustainable Systems (ICAISS) 2022
Nov 24 (pp. 430-435). IEEE.
Zhu Z, Huang G, Deng J, Ye Y, Huang J, Chen X, Zhu J,
Yang T, Du D, Lu J, Zhou J. Webface260M: A
benchmark for million-scale deep face recognition.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence. 2022 Apr 26;45(2):2627-44.
Mohammed MA, Zeebaree DQ, Abdulazeez AM, Zebari
DA, Fadhil ZD, Ahmed FY, Rashed EM. Machine
learning algorithm for developing classroom
attendance management system based on haar cascade
frontal face. In2021 IEEE Symposium on Industrial
Electronics & Applications (ISIEA) 2021 Jul 10 (pp. 1-
6). IEEE.
Chowdhury MI, Sakib NM, Masum Ahmed SM, Zeyad M,
Walid MA, Kawcher G. Human face detection and
recognition protection system based on machine
learning algorithms with proposed AR technology.
Advances in Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality.
2022:177-92.
Hangaragi S, Singh T, Neelima N. Face detection and
Recognition using Face Mesh and deep neural network.
Procedia Computer Science. 2023 Jan 1;218:741-9.
Badr IS, Radwan AG, El-Rabaie ES, Said LA, El Banby
GM, El-Shafai W, Abd El-Samie FE. Cancellable face
recognition based on fractional-order Lorenz chaotic
system and Haar wavelet fusion. Digital Signal
Processing. 2021 Sep 1;116:103103.
Srivastava SK, Katiyar S, Kumar S. Pattern matching using
face recognition system. InSoft Computing: Theories
and Applications: Proceedings of SoCTA 2020,
Volume 1 2022 (pp. 161-171). Springer Singapore.
Padmashree G, Karunakar AK. Improved LBP face
recognition using image processing techniques.
InInformation and Communication Technology for
Competitive Strategies (ICTCS 2021) ICT:
Applications and Social Interfaces 2022 Jun 23 (pp.
535-546). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
Pandey N, Yadav PK, Arjun KP. Face recognition system
using computational algorithms. In2022 2nd
International Conference on Advance Computing and
Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE)
2022 Apr 28 (pp. 1739-1744). IEEE.
Yadav A, Sharma A, Yadav SS. Attendance Management
System Based on Face Recognition Using Haar-
Cascade. In2022 2nd International Conference on
Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in
Engineering (ICACITE) 2022 Apr 28 (pp. 1972-1976).
IEEE.
Bairagi R, Ahmed R, Tisha SA, Sarder MS, Islam MS,
Islam MA. A real-time face recognition smart
attendance system with haar cascade classifiers. In2021
third international conference on inventive research in
computing applications (ICIRCA) 2021 Sep 2 (pp.
1417-1425). IEEE.
Enhanced Face Recognition Algorithm for Real-Time Applications with Improved Accuracy
219
