
Despeckeling Method for Ultrasound Thyroid Nodules Using
Innovative Wiener Filter
Vijaya S. Patil, Mayuresh B. Gulame, Aarti P. Pimpalkar, Priya Khune, Kanchan Wankhade
and
Komal Munde
Department of CSE, MIT School of Computing, MIT Art Design and Technology University, Loni-kalbhor, Pune, India
Keywords: Thyroid Nodule, Ultrasound Image, Despeckeling, Filter, Image Preprocessing.
Abstract: Ultrasound (US) imaging may analyze human bodies of different ages; nevertheless, speckle noise is produced
when a US image is obtained. A speckle noise removal technique is crucial technology since it prevents
doctors from accurately assessing lesions due to the speckle noise. Although there are several methods for
denoising thyroid images, an unfavorable over smoothing of the images results in the loss of structural edge
features, which impairs diagnosis. This paper explores a new Wiener filter-based method for noise reduction.
The suggested improved Wiener filter has the ability to locally modify itself in comparison to the traditional
Wiener filter. The proposed novel algorithm that takes advantage of speckle noise characteristics as well as
filtering techniques wiener filtering to improve the removal of speckle noise. An excellent balance between
the preservation of edges and details and efficient noise reduction can be achieved by automatically fine-
tuning its kernel. Moreover, we have got satisfactory performance with help of CQE i.e CQE value we have
got is 10.932 which is more as compared to other conventional methods. Moreover, FI is 0.948 which is nearer
to one. Thus our improved method can be used preprocessing of US images.
1 INTRODUCTION
Ultrasound (US) instruments have been used to check
the bodies of both young and old people; in fact, US
ultrasound is one of the most commonly used imaging
methods in the area of medical diagnostics. US
imaging equipment can be more affordable,
radiation-protected, and portable than other medical
imaging therapies like computed tomography,
magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray imaging. A
characteristic of US photos is speckle noise. The
speckle noise in medical US images is caused by
backscattered echo signals (Chen, and Lin, 2006),
(Chikui, Okamura, et al. 2006).Both multiplication
noise & Rayleigh distribution are characteristics of
speckle noise, which lowers the resolution of images
and contrast because of the granular pattern shown in
the photos. Doctors are unable to effectively identify
lesions since speckle noise on medical US images
make it more difficult to identify, analyse, and
recognize the features of lesions. One essential pre-
processing technique for achieving a trustworthy
lesion detection and analysis using US imaging is a
speckle noise reduction algorithm (Ciresan, Giusti, et
al. 2012).
Several methods for eliminating speckle noise
from digital and US images have been developed in
recent years. In this work, five different kinds of
speckle noise reduction strategies are compared: Lee
diffusion filter (LDF), anisotropic diffusion filters
(ADF), single filter, and nonlocal means (NLM)
algorithm.
To eliminate speckle noise from ultrasonic
images, a variety of single filter techniques have been
employed, including the Lee, Kuan, Frost, modified
Lee filter, improved Frost filter, and anisotropic
diffusion filtering. Because they often result in a
smoothing phenomenon at the margins, these filtering
methods are not the most effective at removing
speckle noise (Ciresan, Meier, et al. 2012).
OBNLM, or optimized Bayesian-based nonlocal
mean, is a strategy proposed by Coupe et al. (Boyat,
and Joshi, 2015) to reduce speckle noise. It was
combined with the OBNLM methodology and the
block-wise not local means (NLM) method. The
Pearson distance parameter in the OBNLM technique
Patil, V. S., Gulame, M. B., Pimpalkar, A. P., Khune, P., Wankhade, K. and Munde, K.
Despeckeling Method for Ultrasound Thyroid Nodules Using Innovative Wiener Filter.
DOI: 10.5220/0013606500004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 2, pages 885-889
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
885

was then used to determine how similar both patches
in the picture were in order to minimize speckle noise.
Using local statistics and the NLM filter, Yang et al.
developed an approach to reduce speckle noise.
Radlak and Smolka presented an adaptable solution
based on NLM filters.
A number of techniques were employed in
(Fukushima, 1980), including as the enhanced
Wiener filter, fast Fourier transform (FFT), a Markov
random field (MRF). The upgraded Wiener filter
controls the mask size to accomplish each noise
reduction & detail conservation. The methodology
for speckle noise removal reduces the computational
cost of the program by using the MRF technique
method in the FFT domain.
In this paper improved wiener filter have been
implemented which will get good result as compared
to other conventional despekeling methods.
While images are formed utilising coherent
illumination, like acoustic imagery, Synthetic
Aperture Radar (SAR) data, etc., speckle noise is
discovered (Fukushima, 1980). It is created as a
result of the variation in backscatter from
heterogeneous cells. The received signal varies
arbitrarily due to the many echoes from image pixels'
constructive and destructive interference, and the
appearance of the image is distorted as a result.
The useable signal and the noise make up the two
components of the spekeled US image. Both
multiplicative and additive noise make up the noise.
While additive noise is noise produced by the sensor,
multiplicative noise is connected to the principle of
medical US imaging. The image generated by SRAD
has the following speckle noise model:
𝑓
(
𝑝,𝑞
)
=𝐼
(
𝑝,𝑞
)
∗𝑊
(
𝑝,𝑞
)
+𝐴
(𝑝,𝑞)
(1
)
Where the 𝐼
(
𝑝,𝑞
)
,𝑊
(
𝑝,𝑞
)
, and 𝐴
(𝑝,𝑞)
represents the initial signal, multiplicative noise, &
additive noise, respectively. Because its impact is
much smaller than that of the multiplicative noise
𝑊
(
𝑝,𝑞
)
, the additive noise 𝐴
(𝑝,𝑞) is left out of
the equation (He, Zhang, et al. 2015), (Michailovich,
and Tannenbaum, 2006).
The three items listed below comprise the
principal findings of this work:
1. We use an enhanced Wiener filter to despekel
ultrasound images. Additionally, an improved wiener
algorithm is used to improve the effectiveness of the
upgraded wiener filter.
2. We substituted mode parameter which
calculating the new pixel value approaches for
traditional Wiener filter.
3. Our suggested method got satisfactory result as
compared to conventional method.
We use the color quality enhancement (CQE) and
Noise index (NI) as performance metrics for
preprocessing technique evaluation. The experiment
demonstrates that Improved wiener filter, which
achieves good performance and preserve needed
information (Agaian, Lentz, et al. 2000), (Gao,
Panetta, et al. 2012).
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
2.1 Improved wiener filtering method
In order to diagnose thyroid nodules using the images
more effectively, we preprocessed the US images in
the dataset 1, using Improved Weiner filtering Model.
The improved Wiener filter's flow diagram is shown
in Fig. 1.
2.2 Image ultarsound dataset
and preprocessing
The scientific community can access the digitized
database of thyroid ultrasound images for free. There
are 134 snaps and 99 cases in the database (Do, and
Vetterli, 2005).
For images by additive noise and blur, the Wiener
filter is the MSE-optimal stationary linear filter.
Typically, Wiener filters are used in the frequency
domain. One uses the Discrete Fourier Transform
(DFT) to get
𝑋(𝑢,𝑣) from a degraded image, x(n,m). By
adding the Wiener filter 𝐺
(
𝑢,𝑣
)
to the product of
𝑋(𝑢,𝑣) , one can estimate the original image
spectrum:
𝑠
(
𝑢,𝑣
)
=𝐺
(
𝑢,𝑣
)
𝑋(𝑢,𝑣)
(2)
The Wiener filter is:
𝐺
(
𝑢,𝑣
)
=
𝐻
∗
(𝑢,𝑣)𝑃
(𝑢,𝑣)
|
𝐻
(
𝑢,𝑣
)|
𝑃
(
𝑢,𝑣
)
+𝑃
(𝑢,𝑣)
(3)
It is a method of filtering noise that is added. The
low pass wiener filters practice a pixel-wise adaptive
scheme to adjust their operation based on information
obtained from each pixel's immediate surroundings.
It computes the local average in addition to the
variance while filtering (Madsen, Ilavarasi, et al.
2007). De-convolution is produced by inverse
filtering, and noise is removed using compression.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
886
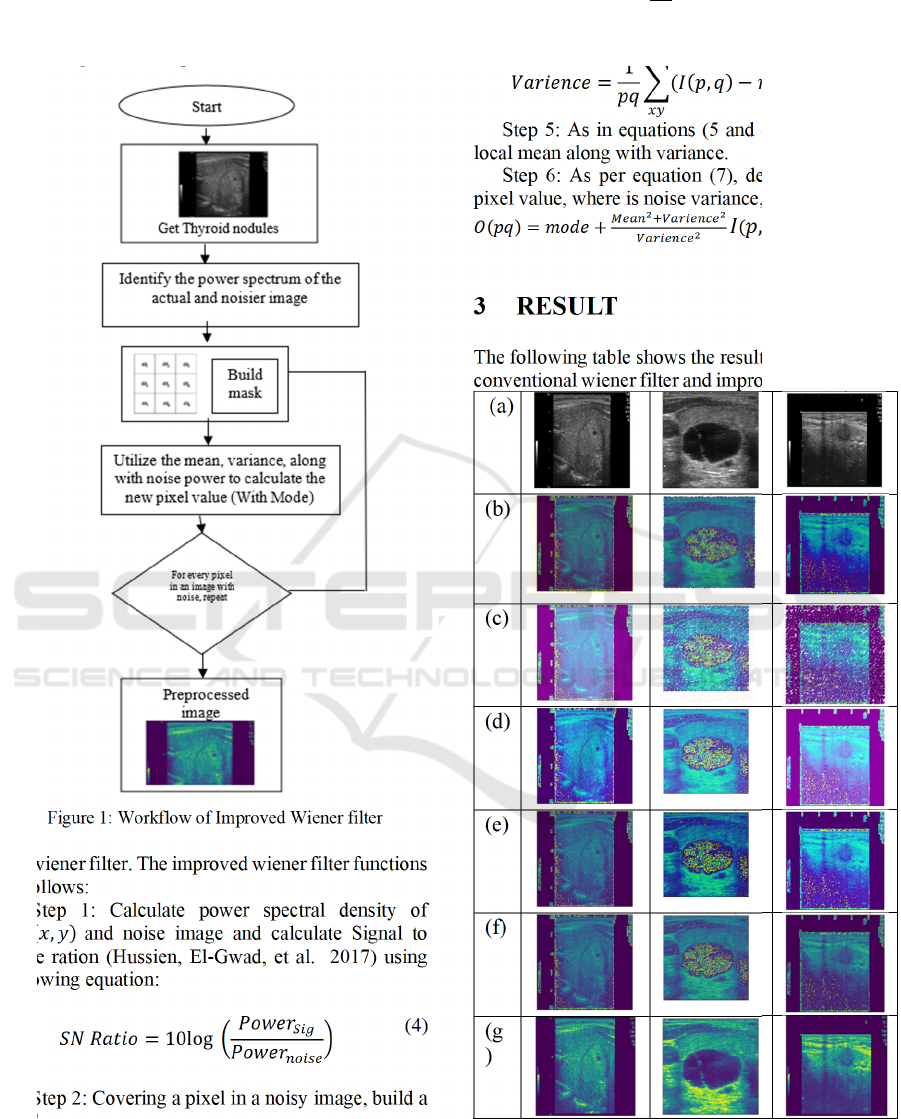
The improved Wiener filter utilizes a 3 × 3 filter in
order to determine the median value of every pixel.
The resulting matrix is then subjected to further
processing that is comparable to
Figure 1: Workflow of Improved Wiener filter
the wiener filter. The improved wiener filter functions
as follows:
Step 1: Calculate power spectral density of
𝐼
(
𝑥,𝑦
)
and noise image and calculate Signal to
noise ration (Hussien, El-Gwad, et al. 2017) using
following equation:
𝑆𝑁 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜 = 10log
𝑃𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟
𝑃𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟
(4
)
Step 2: Covering a pixel in a noisy image, build a
mask
Step 3: Filter all of the pixels that are covered by
the mask by pixel intensity.
Step 4: Set the median to the mask's central pixel
by finding it.
𝑀𝑒𝑎𝑛 =
1
𝑝𝑞
𝐼(𝑝,𝑞)
(5)
𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 =
1
𝑝𝑞
(𝐼
(
𝑝,𝑞
)
𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑛)
(6)
Step 5: As in equations (5 and (6), calculate the
local mean along with variance.
Step 6: As per equation (7), determine the new
pixel value, where is noise variance, is median value.
𝑂
(
𝑝𝑞
)
=𝑚𝑜𝑑𝑒+
𝐼
(
𝑝,𝑞
)
𝑚𝑜𝑑𝑒)(7)
3 RESULT
The following table shows the result of US images of
conventional wiener filter and improved wiener filter.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(g
)
Figure 2: Images after filtering a) Sample US image b)
NLM filter c) LDF filter d)ADF filter e) Hybrid method f)
b) Convention wiener filter c) Improved wiener filter
Despeckeling Method for Ultrasound Thyroid Nodules Using Innovative Wiener Filter
887
As there is no noise free image available in real
time ultrasound images we have used no reference
image quality measures like CQE and noise index and
full reference like PSNR and SSIM for measuring the
quality of our novel algorithm.
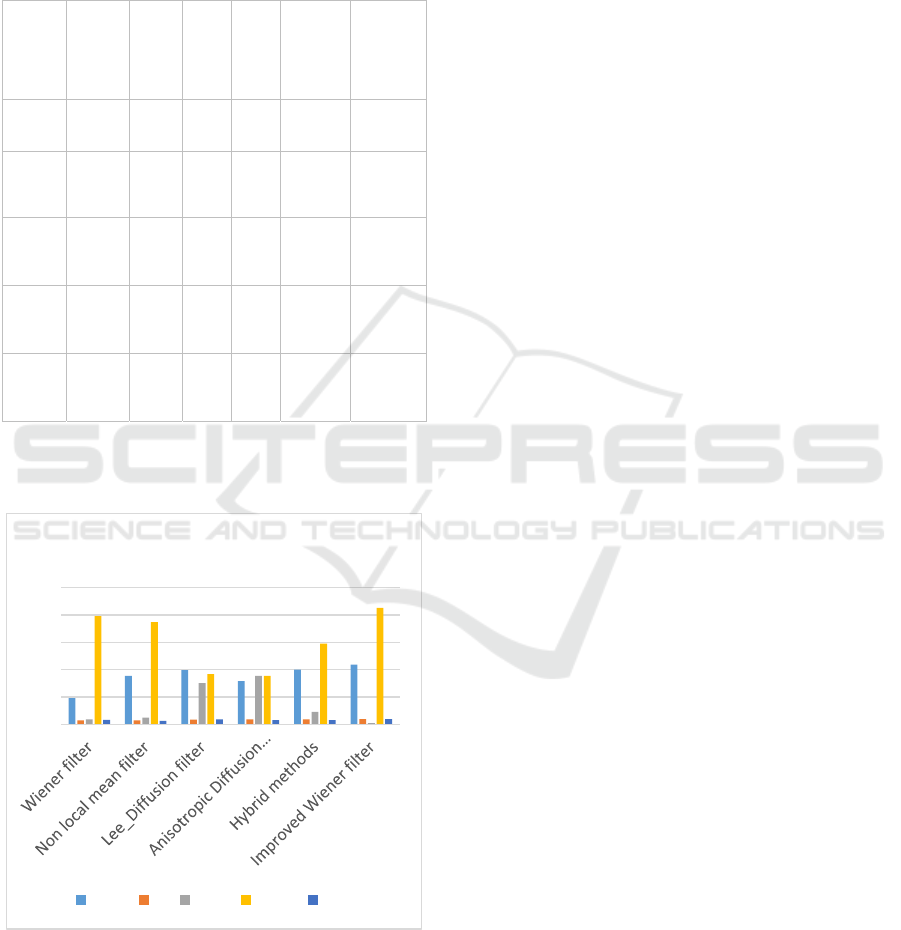
Table 1: Performance Measures For Denoisisng
Quali
ty
Metri
c
Wien
er
filter
NL
M
LD
F
AD
F
Hybri
d
metho
ds
Improv
ed
Wiener
filter
CQE 4.82
8.8
6
9.9
3
7.9
0
10.01 10.9
FI 0.76
0.7
5
0.8
9
0.9
2
0.90 0.94
MSE 0.90
1.2
3
7.5
6
8.8
9
2.30 0.23
PSN
R
19.80
18.
7
9.2
8.9
0
14.78 21.3
SSIM 0.82
0.6
7
0.9
2
0.7
8
0.80 0.98
The graphical representation of performance is
shown below:
Figure 3: Performance Analysis of Improved wiener
filtering Method
4 CONCLUSION
The granularity of speckled images makes them
challenging to interpret for both the human eye and
computer segmentation and classification techniques.
Despeckling is crucial to do as a pre-processing step
before moving on to the feature withdrawal,
investigation, and recognition phases of image
handling jobs. Despeckling's main objective is to cut
down on speckle noise without losing any of the
information. In order to reduce speckle, a improved
Wiener filter is applied. Comparing the suggested
approach, the speckle noise can be greatly reduced,
and the new method finds use in remote sensing. Our
innovative approach has been contrasted with five
filtering ways, and the results have been examined
using both full reference quality metrics and results
without reference. Moreover, we have got good result
to parameters like CQE and Filter index and SSIM. In
our ongoing research, we will concentrate on
processing darkened areas in ultrasound images of
thyroid nodules.
REFERENCES
Chen YW, Lin CJ (2006) Combining SVMS with various
feature selection strategies. In: Guyon I, Nikravesh M,
Gunn S, Zadeh LA (eds) Feature extraction. Studies in
Fuzziness and Soft Computing, vol 42. Springer,
Berlin, pp 315–324
Chikui T, Okamura K, Tokumori K, Nakamura S, Shimizu
M, Koga M, Yoshiura K (2006) Quantitative analyses
of sonographic images of the parotid gland in patients
with sjögrens syndrome. Ultrasound Med Biol
32(5):617–622
Ciresan D, Giusti A, Gambardella L M, Schmidhuber J
(2012) Deep neural networks segment neuronal
membranes in electron microscopy images. In:
Advances in neural information processing systems, pp
2843–2851
Ciresan D, Meier U, Schmidhuber J (2012) Multi-column
deep neural networks for image classification. In: 2012
IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 3642–3649
A Review Paper: Noise Models In Digital Image
Processing. Signal Image Process. an Int. J, 6 (2)
(2015), pp. 63-75
Fukushima K (1980) Neocognitron: a self-organizing
neural network model for a mechanism of pattern
recognition unaffected by shift in position. Biol Cybern
36(4):193–202
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Delving deep into
rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on
imagenet classification. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1502.01852
0
5
10
15
20
25
Performance Analysis
CQE FI MSE PSNR SSIM
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
888

O. Michailovich, A. Tannenbaum De-speckling of medical
ultrasound images IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr
Freq Control, 53 (1) (2006), pp. 64-78 M.T. Madsen
S. S. Agaian, K. P. Lentz, and A. M. Grigoryan, "A new
measure of image enhancement," in IASTED
International Conference on Signal Processing &
Communication, 2000, pp. 19-22.
C. Gao, K. Panetta, and S. Agaian, "A new color contrast
enhancement algorithm for robotic applications,” in
IEEE conference on Technologies for Practical Robot
Applications, 2012.
M.N. Do, M. Vetterli The contourlet transform: an efficient
directional multiresolution image representation IEEE
Trans. Image Process., 14 (2005), pp. 2091-2106 View
in ScopusGoogle Scholar
Recent advances in SPECT imaging J. Nucl. Med., 48
(2007), pp. 661-673 View article CrossRefView in
ScopusGoogle Scholar
G.N. Hussien, El-Gwad and Y.M.K. Omar. (2017)
“Selection of the best despeckle filter of ultrasound
images.” Proc. - 2017 2nd Int. Conf. Multimed. Image
Process. ICMIP 2017 2017: 245–249.
Despeckeling Method for Ultrasound Thyroid Nodules Using Innovative Wiener Filter
889
