
Broadcast Tree Construction for Shortest Path Finding with Secure
Data Aggregation Techniques in Wireless Sensor Networks
Vidya H. Deshmukh
1,2
, Pramod Jagan Deore
1,2
and S. B. Deosarkar
3
1
Dr. Babasahabe Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, India
2
R. C. Patel Institute of Technology, Shirpur, India
3
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, India
Keywords: WSN, Shortest Path Finding, Data Aggregation, HMAC, Broadcast Tree Generation, Routing Protocols,
Sensing Nodes, Optimization Techniques.
Abstract: A wireless sensor network (WSN) consists of a large number of deployed sensing devices that consume
little power and computing capabilities. Data packet switching in sensing devices is commonly achieved by
using multi-hop transmission due to the limited range of connectivity and the dense distribution of sensor
nodes. Dynamic routing in WSN has been increasingly popular in recent years. In modern times, sensor
networks extensively employ the multi-path data transmitting technique to optimize system performance by
using the available bandwidth. The main objective of this paper is to elucidate the concept of multi-path
routing, along with its inherent challenges and fundamental justifications for its application in sensor
networks. This study presents a method for finding the shortest path using the Broadcast Tree Construction
(BTC) algorithm, which incorporates data aggregation techniques to reduce network overhead during
communication. This method is suitable for both cluster networks and Wireless Sensor networks. The
suggested work was assessed utilizing the NS2 environment in a thorough experimental investigation. Four
alternative procedures were used to explore the system efficiency. Through rigorous experimental
investigation, the system is able to conserve 15% of energy while operating with 100 internal nodes.
Additionally, it improves network life by 7% when utilizing the SAODV routing protocol. This
performance is superior to the distance-based method of determining the shortest path in a WSN. It also
improves the data transfer rate and decreases the number of lost packets compared to previous methods of
identifying the shortest path in WSN’s.
1 INTRODUCTION
Restricted wireless sensor nodes have been
introduced in recent advancements in wireless
communication systems and the manufacturing of
cheap wireless devices. WSN has been used for
numerous applications, including medicine, target
detection, and surveillance systems, due to their
simplicity of deployment and non - linear and none
of the edge devices (Le, Chong, et al. , 2010). The
main function of sensor nodes in any application is
to detect the target area and send the collected data
to the base station for additional analysis. The lack
of efficiency in sensor node resources and the
unpredictable nature of limited wireless connections
The user's text is (Kenc and Boudec, 2008), along
with the varied throughput requirements of diverse
applications, offer many difficulties in developing
effective WSN communication protocols (Wang,
Niu, et al. , 2007). Meanwhile, finding appropriate
network algorithms to meet the varied performance
needs of various workloads is a critical problem in
wireless mesh networking. Several routing methods
have been suggested in this area to enhance the
efficiency needs of multiple applications via the
network topology of the distributed sensing protocol
stack.
The battery powers the sensor nodes, which in
many cases, these devices cannot be changed. When
the power goes out, and the network stops working,
they die. As a result, a routing method is critical for
extending the battery's life and effectively managing
the battery. This feature encourages the development
of energy-saving routing methods. Data is sent via
intermediary sensor nodes in a WSN, which is a
multi-hop infrastructure. The connections between
Deshmukh, V. H., Deore, P. J. and Deosarkar, S. B.
Broadcast Tree Construction for Shortest Path Finding with Secure Data Aggregation Techniques in Wireless Sensor Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0013600100004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 2, pages 685-693
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
685

iot devices are very vulnerable to failure. The
probability of connection failure directly impacts the
data packet transmission and the network's
dependability. This problem drives the development
of dependable routing methods. The movable sink
may be used to address the energy hole issue.
However, managing a transportable sink is a time-
consuming job. Several routing algorithms function
in the mobile sink context, but they have drawbacks
such as inefficient management, high power
consumption, and a lower data delivery ratio. To
extend the broadcaster's life, it's critical to control
the mobile sink effectively. The produced data
should approach the network device as soon as
possible in many instances. The later part latency is
increased by the lack of a routine route, the
placement of the sink, and the probability of
hardware failures. As a result, methods to decrease
latency must be included.
The primary goal of this study is to decrease
energy usage while also reducing delay. Some
methods may be used by the routing algorithm to
enhance energy consumption and network lifespan.
Below are a few smart energy methods that will be
explored:
Energy model: In any routing algorithm, the
energy storage system of the WSN nodes may assist
to enhance connection speeds (Le, Chong, et al. ,
2010). The precise definition of the energy balance
equation may provide a more accurate estimate of
the residual energy within every node. It simplifies
and clarifies observation. The network lifespan may
be increased by using a model with a comprehensive
perspective and a proper methodology.
Reduce the control packet overhead: A sensor
network uses the most energy during communication
systems (Kenc and Boudec, 2008). The shortest path
and preservation in the routing algorithm for
neighbour node identification need many control
signals to be sent between sensor nodes. The
proposed method must limit the network's
unnecessary circulation of control packets. The
volume of the received packets may have an impact
on the total amount of energy used.
Permit multi-hop communication:
Straightforward data transfer requires more energy
then multi-hop data transfer (Wang, Niu, et al. ,
2007). The sensor node must maximize the wireless
transmission capacity in direct connection, which
produces higher expenditure at each node. To cut
emissions, the routing algorithm must address these
problems.
Transmission range modification: WSN is
several co networks in which data must pass via
intermediary nodes to reach its destination. During
implementation, it is common to discover that the
following accessible access points are almost always
near the sender node. As a result, instead of
transmitting data at full power, the RSSI (Xu, Liu, et
al. , 2010) may modulate the network throughput.
This method may assist in decreasing energy usage
and increasing network lifespan (Quang and
Miyoshi, 2010).
Data aggregation: At some time, comparable
data packets may be consolidated, and the collected
information can be sent to the sinkhole (Batwada,
Tripathi, et al. , 2012). Combining similar data
across the network reduces traffic on the web (Paul,
Nandi, et al. , 2008). Collisions and energy
consumption are decreased as a result of less traffic.
To extend the broadcaster's lifespan, the routing
algorithm must use the clustering algorithm.
Using MAC protocol: The node in the network
detects its surroundings, produces data, and sends it
to the reservoir (Karaki and Kamal, 2004). Sensor
networks must go into standby mode even when
they're not seeing or routing. As a result, for
networking energy saving, an appropriate Proposed
technique is needed.
Minimize the collision: Every data could reach a
wireless network device without even any
intervention in the packet forwarding (Chong and
Kumar, 2003). Each node must be capable of
communicating in a traffic delays atmosphere,
according to the standard. Alternatively, it may
result in data recapture, which directly impacts the
platform's fuel efficiency.
The primary contribution of our research is
outlined below.
The objective is to create an algorithm that finds
the shortest path from the source node to the base
station.
To provide a robust data aggregation technique
at the Cluster Heads' location.
To deploy the suggested solution across multiple
network protocols, including AODV, DSDV,
SOADV, and DSR.
The rest of the paper is divided into the
subsequent sections: Section II examines various
contemporary methodologies that previous
researchers have devised to uncover routes between
source and sink nodes. Part III demonstrates the
recommended system structure and execution, while
part IV outlines the proposed method specification
for implementation. The experimental configuration
for evaluating the proposed work and the results
obtained using our strategy, together with a
comparison study against various cutting-edge
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
686

methodologies, is detailed in section V. The
conclusion and potential future developments are
addressed in Section VI.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
Since the transmitted signal is dependent on
electricity, many studies have looked at the impact
of power in improving broadband services. The
maximum lifespan for the shortest route aggregation
tree was investigated by Luo et al.. The issue was
modified to a job scheduling scheme for each level
of a structure resembling a fat tree. The researchers
showcased the possibility of managing the problem
with a time complexity by using the min-cost max-
flow approach. They demonstrated the suitability of
their choice by showing that the produced shortest
route tree is superior, and their simulation confirmed
that it beats the random approach.
An efficient way for low latency data
transmission in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) is
the use of the lowest route routing, as described in
(Vetrivelan, 2019). A proposed routing system in
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) is LWSP
(Shortest path without Latency), which aims to
efficiently determine the shortest paths with
minimum command processing overhead time and
low latency. Based on performance tests and
simulation data, our proposed protocol demonstrates
superior performance compared to existing protocols
in terms of latency and additional processing time
for commands. The shortest path technique is used
for the establishment of a wireless sensor network
(Nakas, Christos, et al. , 2020). The purpose is to
implement the quickest route method in a wired
communication network, which will facilitate the
transmission of protocol and ensure real-time arrival
at the destination. This will include determining and
identifying the shortest path algorithm in a wireless
communication system.
An extensive examination of energy-conserving
techniques in wireless sensor networks (Kandris,
Dionisis, et al. , 2020). This paper provides an
analysis of both conventional and modern methods
proposed for attaining energy-efficient routing in
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs). The protocols
were classified into four main areas based on their
important structural or operational characteristics:
Customized System, Network Structure, Topology,
and Reliable Routing. They analyzed the pros and
cons of many common examples of the
aforementioned techniques. They have a same goal:
to save energy by optimizing their routing strategies.
Our investigation uncovered several variances in
both the structural and functional aspects.
A recent publication (Osamy, Walid, et al. ,
2019) has presented new findings on the uses of
wireless sensor networks. A comprehensive and
current survey of traditional and emerging
applications of Wireless Sensor Networks can
greatly enhance comprehension of this scientific
domain and the recognition of inventive uses. To
achieve this purpose, we outline the main categories
of applications in Wireless Sensor Networks and
analyze specific instances of each category. Their
distinctive characteristics are examined, along with
their benefits and drawbacks. Subsequently, there is
an examination of the many concerns linked to each
of these specific groups. Lastly, there are a few
concluding remarks.
The article titled "Tree building and scheduling
techniques based on simulated annealing decrease
duration in wireless sensor networks" discusses the
use of simulated annealing to reduce the duration in
wireless sensor networks (Zantalis, Fotios, et al. ,
2019). In order to gather data with a specific
schedule for node transmissions, the researchers
devised an innovative method for constructing trees
using simulated annealing, known as SATC. The
delivery time for aggregated data to the sink is
reduced by 50% utilizing SATC. The proposed
strategy utilizes the average time delay as the fitness
value for the simulated annealing (SA) process. This
fitness value is assessed using routing aware MAC
scheduling techniques. Simulation is used to
evaluate the efficiency of the proposed method and
compare it to current state-of-the-art techniques,
primarily by analyzing average delay and latency.
Smart transportation is increasingly being
influenced by the growing importance of machine
learning and the Internet of Things (Khedo,
Bissessur, et al. , 2020). Intelligent transportation
encompasses several aspects such as optimizing
routes, managing parking, improving street lighting,
preventing and detecting accidents, addressing road
imperfections, and implementing infrastructure
applications. The objective of this article is to
provide a comprehensive summary of machine
learning (ML) techniques and Internet of Things
(IoT) applications in Intelligent Transportation
Systems (ITS) in order to get a thorough
understanding of the advancements in these fields
and identify any possible areas that have not been
adequately addressed. The analyzed articles indicate
a possible deficiency in machine learning
applications for Smart Lighting Systems and Smart
Parking Applications. Furthermore, the prevailing
Broadcast Tree Construction for Shortest Path Finding with Secure Data Aggregation Techniques in Wireless Sensor Networks
687

ITS applications favored by scholars include route
optimization, parking management, and accident
detection.
The researchers in (Tasgaonkar, Pankaj, et al. ,
2020) developed an earthquake early warning
system with the aim of increasing the duration of
time available before an earthquake occurs, allowing
individuals to take precautionary measures. The
researchers established a Wireless Sensor Network
(WSN) on Mauritius, an island characterized by
significant seismic activity. The technique utilizes
primary waves to observe seismic activity. The
system determines the local velocity and hypocentre
location by analyzing the time delay between the
arrival of P-waves at the sensors. The paper titled
"Vehicle Search and Traffic Estimation for
Intelligent Transportation Systems Using Sensor
Technologies" is referenced as (Tasgaonkar, Pankaj,
et al. , 2020). Vehicle detection strategies include
both invasive and non-intrusive sensors. The
objective of this research is to provide a
comprehensive inventory of the sensors and
technologies used in vehicle identification and
traffic estimation. By establishing a connection with
the monitoring station on the vehicle's existence on
the road, these sensors will provide crucial
information. Sensors and communication
technologies are extensively used in intelligent
transportation systems. An assessment is conducted
to evaluate the most recent tools and techniques used
to determine the number of vehicles, their
classification, location, speed, traffic volume,
density, and traffic estimation. Sensor fusion enables
the seamless integration of data from several
sources, hence enhancing accuracy.
The Social Internet of Vehicles employs a Cross-
Layer Protocol for Traffic Management (Jain,
Bindiya, et al. , 2018). A considerable quantity of
sensors transmit data via wireless means in the
proposed Vehicular Social Networks that rely on the
VIoT. The wide range of hardware capabilities and
quality of service requirements for different
applications hinders the effectiveness of traditional
layered protocol solutions and modern cross-layer
solutions for wireless sensor networks. The
innovative Vehicular Social Network Protocol
(VSNP) based on Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN)
in the context of Vehicular Internet of Things
(VIoT) provides an optimal level of global
connectivity and outperforms current layered
systems. The introduction of the new SIoT cross-
layer module is the first phase in establishing
dependable vehicle-to-vehicle communication and
optimizing traffic management. We presented a
methodology for effectively handling traffic
congestion and enhancing road safety in the context
of VIoT.
Deep learning is used in data-driven pavement
imaging. An evaluation of analysis and automated
problem-solving ((Gopalakrishnan, Kasthurirangan.,
et al. , 2018). An exposition of recent research in
this field, highlighting present achievements and
challenges. The provided information includes a
comparison of deep learning software frameworks,
network architecture, hyper-parameters utilized in
each study, and the performance of crack detection.
This serves as a solid basis for future research in the
field of intelligent pavement and asset management
structures. The work continues by proposing future
research directions, including the use of deep
learning techniques to accurately identify and
classify various types, quantities, and severities of
distresses in both 2D and 3D pavement photos.
Utilizing GPS trace, autonomously detect traffic
signals, street intersections, and urban roundabouts
during the act of driving(Organero, Mario, et al. ,
2018). A novel approach is centered on the
automated identification of street elements such as
traffic signals, intersections, and circular junctions.
These elements may be used to generate street maps
and fill them with traffic-related infrastructure
characteristics such as traffic signals. The system
utilizes just the residual GPS data obtained from the
mobile device while driving to reduce system
demands and streamline data collecting from many
users with little effect. The GPS data is used to
construct time series for speed and acceleration. At
first, an outlier identification method is used (which
may be caused by infrastructure components or
specific traffic situations). Deep learning is used to
analyze speed and acceleration patterns at each
anomaly in order to extract essential characteristics,
which are identified as a traffic signal, pedestrian
crossing, urban roundabout, or another component.
The paper titled "Duty-Cycle Multi-hop Wireless
Sensor Network with Structure-Free Broadcast
Scheduling (Chen, Quan, et al. , 2021)" is being
referred to.
1. Instead of depending on a predetermined
structure, a two-step scheduling technique is
suggested to concurrently generate the broadcast tree
and calculate a timetable that avoids collisions. As
far as we know, this is the first endeavor to combine
these two types of processes.
The paper introduces concurrent broadcasting, an
innovative transmission mechanism for wireless
networks, and investigates other methods to further
reduce the broadcast latency.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
688
3. The introduction of broadcasting algorithms
that may independently create a series of broadcast
schedules without a pre-determined tree was made
possible by taking into account collisions in both the
current and prior broadcast schedules, as well as the
broadcasting of simultaneous messages.
The most efficient path with risk management
for a malfunctioning wireless sensor network (Wang
and Na, 2019). Compromised Regions (CRs) consist
of a cluster of densely connected nodes (CNs) and
seem to provide a greater threat to networks
compared to individual CNs. In order to protect
against CR attacks, we have devised a Secure
Shortest Path Routing Algorithm (SPRA) that
redirects packets around, rather than through, CRs.
For instance, a source node computes the most direct
path to a sink node, avoiding any intersections with
CRs. It then identifies agent nodes along the route
indirectly by using a set of virtual locations.
Ultimately, a complex system using geographical
data is created to ensure that packages may be
passed via intermediary nodes until they are
successfully delivered to the final destination node.
In a series of experiments, we evaluate our strategy
by comparing it to the dynamically Greedy
Perimeter Stateless Routing (GPSR) and Directed
Diffusion (DD) methods.
The issue of transmitting data along the most
direct route (Younes, 2018). The problem of the
smallest broadcast tree was discussed and an
efficient genetic algorithm was shown to solve it.
The approach examines the connection, cost, and
bandwidth matrices of a network and constructs a
tree of least-cost routes. This tree is rooted at a
specific node s and takes into account bandwidth
limits. The construction of the tree is based on the
minimal broadcast tree algorithm. The genetic
algorithm (GA) was evaluated using three distinct
situations, and the results conclusively showed that
the proposed GA is very efficient. The paper WSN
(Sun, Xiao, et al. , 2019) proposes a method where
the integrated two-hop neighbourhood information
is used to create a transmission radius that is twice
as large, resulting in efficient code transmission. The
TNI-DBR technique is introduced to efficiently and
quickly provide codes in duty cycle-based WSNs by
using a Two-hop Neighbourhood Info with double
Broadcast Radius. Here are the most notable
breakthroughs discussed in the essay. The TNI-DBR
approach utilizes surplus energy to increase the
broadcast radius in the given region, enabling a
greater number of nodes to receive up-to-date code
via a continuous broadcast, hence decreasing the
latency in code dissemination. Unlike traditional
methods of distributing code, which choose
broadcasting nodes based on information from
nearby nodes within one hop.
3 PROPOSED SYSTEM DESIGN
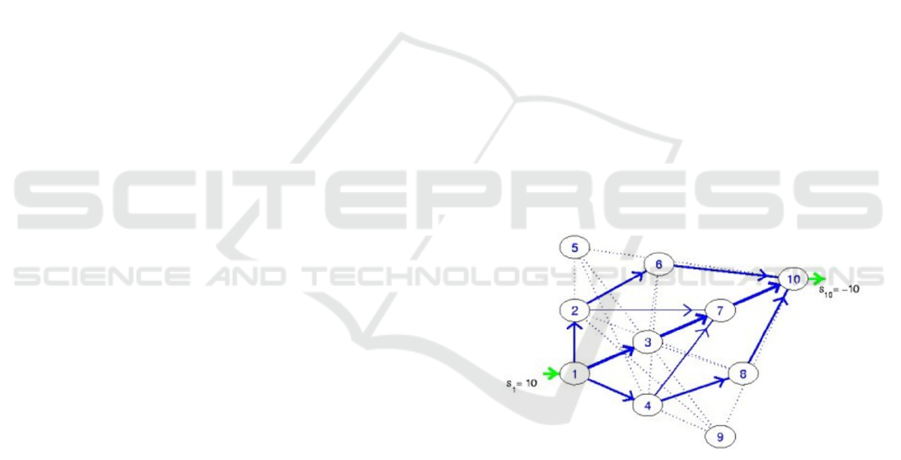
The below figure 1 describes the proposed system
architecture for secure pathfinding using a broadcast
reconstruction algorithm. During the execution of
the proposed system, first generate multiple clusters
in a network, each cluster having a cluster node that
contains at least one cluster head; others are cluster
members. The two basic algorithms have been
demonstrated for data aggregation and secure data
transmission between source to destination. In order
to the selection of source is the cluster head and
destination is the base station. The cluster head
eliminates data redundancy while BTC gives
assurance, that recommended channel or path is
stronger than other available resources. The major
benefit of the proposed BTC, that reduces the
network overhead and higher energy consumption. It
selects strong nodes which are having higher energy
from the neighbour's list. Based on that, BTC
constructs the entire path and transmit the data
security. As a result, both algorithms improve
quality of service of the entire simulation.
Figure 1: Proposed System Architecture using Minimal 10
Nodes by Minimal Spanning Tree
Existing hop-to-hop connectivity in wireless
sensor networks is thought to be exposed to data
transmission vulnerability. Due to the higher cost of
packet transmission of hop-by-hop communication,
the current system employs a security technique
known as broadcast tree construction and
authentication among network resources. The
identity of intermediary nodes may be compromised
from hop to hop, posing a security risk. They
employ trust computation of each node at the node
level for communication or packet transfer to
prevent security threats. Message transmission in the
Broadcast Tree Construction for Shortest Path Finding with Secure Data Aggregation Techniques in Wireless Sensor Networks
689

current architecture occurs selective neighbour node
using BTC algorithm between the source and
destination nodes, resulting it reduces the overhead
between nodes. In wireless sensor communication.
4 ALGORITHM DESIGN
This section displays a data aggregation process
and a data transmission method that finds the
shortest route effectively. By reducing network
overhead and eliminating data redundancy, data
aggregation helps make data transfer between source
and sink nodes more efficient. Concurrently, internal
nodes that use a lot of power are reduced via tree
building. Together, the lists of internal nodes and
their neighbours allow this method to build a reliable
route up to the destination. Lightweight data
communication and the assurance that no data will
leak during transmission are both provided by this
approach.
4.1 Broadcast Tree Construction for
shortest path finding methods
Input: source node denoted as Src_node and sink
node Snk_node is a collection of adjacent nodes.
The neighbor node has an empty list, with the node's
identification as Node_id and its energy level. The
variable "Node_energy" is declared.
Output: Calculate the most efficient route from
the source node to the sink node or base station.
Step 1: Generate and initialize the network Src_node
and Snk_node with energy.
Step 2: Detect or choose the source file from the
Src_node.
Step 3: Check whether the value of file_data_values
is not null.
Step 4: Continuously read each byte, denoted as
'bytes', from the file data values until the
file_data_values is null.
Step 5: Transmit the data and initialize cost_filed_A,
cost_filed_B, parent_filed_A, parent_fileld_B
Step 6: Iterate over the nodes until the current node
is not null.
The value of cost_filed_A is equal to the value of
node[i].The variable "_energy" is assigned the value
of "node[i]" from the parent field
"parent_filed_A_values"._id cost_filed_B_values =
node[i+1]._id The energy parent field B values are
equal to the node ID of the next node in the
sequence.
Step 7: Check whether the value of
cost_filed_A_values is greater than the value of
cost_filed_B_values.
The value of cost_filed_B_values is nil.
The value of parent_filed_B_values is nil.
Otherwise, the values of parent_filed_A will be
equal to the values of parent_filed_B.
The values of cost_filed_B_values are assigned to
cost_filed_A_values. The values of
parent_filed_B_values are set to null.
The value of cost_filed_B_values is nil.
Step 8: Terminate the while loop.
Step 9: proceed check-out when reach to Snk_node
The method determines the next node by
considering possible neighboring nodes, using the
Parent_field as the node identifier and the cost_field
as the remaining energy of the chosen node. The
system develops routing and route based on energy
trust to ensure that no interruptions occur in
communication.
4.2 Data Aggregation Protocol
Input: The cluster head has received data in the
current stack, which is stored in the Rec_Data[]
array. The most recent packet received is stored in
the New_Rec_data[] array.
Output: true if data aggregation is feasible;
otherwise, false.
Step 1: Iterate over each read of data from
Rec_Data using the equation (1) below.
The equation (1) represents the sum of the values
in the array "Rec_Data" from index 0 to index n.
Step 2: Compute the cosine similarity between
the arrays Data[] and New_Rec_data. The result will
be a binary value (0 or 1) obtained by using the
function Calc_Cosine_Similarity on the elements
Data[k] and New_Rec_data.
Step 3: Terminate the for-loop
Step 4: Retrieve the Result_state and return it.
The method mentioned above performs data
aggregation and validates the received data by
comparing it with the presently received data. This
approach mitigates the duplication of data by
consolidating the information collected from various
sensor nodes. Additionally, it reduces the network
overhead involved in communication and conserves
energy.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
An analysis of the current system as well as its
potential successors is provided in this section. After
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
690
outlining our experimental methodology and making
use of several measures including throughput,
packet delivery ratio, cost, and time, the
quantitatively evaluates the study. Many methods
exist for processing, filtering, and displaying vector
and scalar data. We are located in the project folder's
results directory. The findings of the simulation are
stored in the Tr file. Our graph tool will be used by
the mechanism. This file will display the result
parameters in relation to the x and y-axis
parameters. Any graphing program should be able to
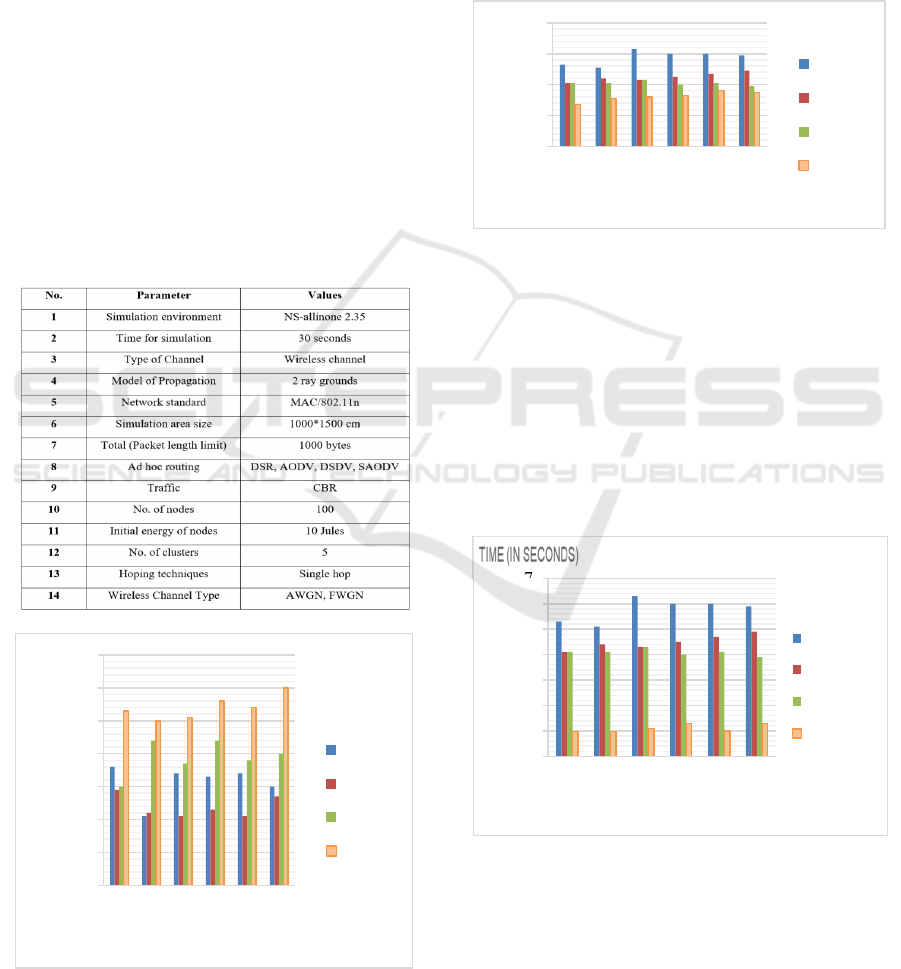
plot files with the awk extension. In Table 1 below,
you can see the NS2 setup settings established for
the suggested Ubuntu open-source simulation.
The setup environment for the proposed IEEE
802.11n implementation is described in Table 1.
Using the SAODV Protocol, the findings shown in
Figures 2–6 below show how the proposed system
calculates quality-of-service parameters.
Table 1: Parameters and Values in wireless network with
100 nodes in NS2.
Figure 2: The suggested SAODV system's throughput
compared to other protocols.
The suggested simulation's throughput as a
function of simulation time is shown in Figure 2,
which is located above. In accordance with Table 1,
the network setup settings have been fine-tuned.
With IEEE 820.11n, which offers bandwidth of up
to 600 MB, the starting input nodes have been set at
100. Even while simulation time has grown with
SAODV, throughput has declined with DSR,
DSDV, and AODV, but it has improved with
SAODV.
Figure 3: The suggested SAODV system's end-to-end
delay SAODV metric in contrast to competing methods
Finding the logarithm of the time delay as shown
in Figure 3 provides the basis for calculating the
end-to-end latency. A packet's success rate is
determined by two factors: the amount of packets
transmitted by the internal load and the number of
packets received by the destination node. The
reduced packet overhead experienced by SAODV
producers during communication is also shown in
this experiment.
Figure 4: Packet drop rate vs simulation time
An example of how the packet drop rate is
determined is shown in figure 4, which is the result
of subtracting the number of packets successfully
received by the destination node from the number of
packets sent by the sensor node. During connection
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
5 1015202530
THROUGHPUT
TIME (IN SECONDS)
DSDV
DSR
AODV
SAODV
0
2
4
6
8
5 1015202530
END TO END DELAY
TIME (IN SECONDS)
DSDV
DSR
AODV
SAODV
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
5 1015202530
packet drop rate
time (in seconds)
DSDV
DSR
AODV
SAODV
Broadcast Tree Construction for Shortest Path Finding with Secure Data Aggregation Techniques in Wireless Sensor Networks
691
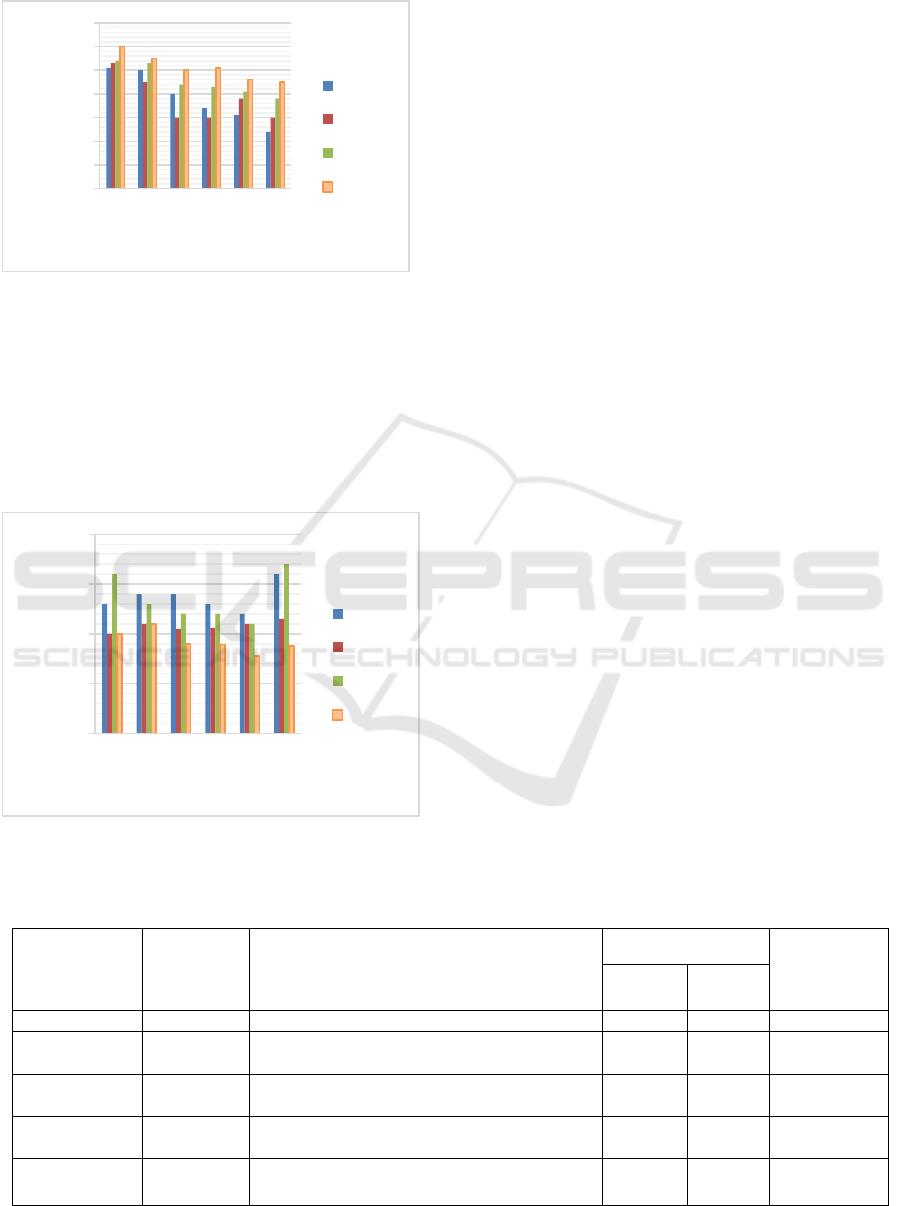
between heterogeneous nodes, DSDV causes a high
packet loss rate but SAODV causes a lower one.
Figure 5: Evaluation of the suggested SAODV system's
packet delivery ratio relative to competing protocols
Figure 5 shows the communication packet
delivery ratio vs simulation time. The packet
delivery rate is based on the number of successfully
delivered packages sent by the source node. Both
internal node communication and source-to-sink
node communication may benefit from a comparable
strategy.
Figure 6: Compared to competing protocols, the suggested
SAODV system's packet control overhead
Figure 6 displays the results of the entire
experiment analysis, which includes a number of
elements and a system performance analysis using
several methods. Compared to other alternative
Quality of Service (QoS) criteria, SAODVs deliver
superior outcomes. Across all trials, SAODV
outperformed AODV, DSDV, and DSR by an
average of 3-5%.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This article introduces the method, which helps
reduce power consumption and find the shortest path
for data transmission in a wireless sensor network.
Parent filed cost field and neighbour nodes.
Identification is an important factor of the BTC
algorithm. Before data transmission, we applied the
data aggregation technique protocol at the cluster
head level, which eliminates the data redundancy.
Both algorithms provide different advantages to
effective simulation. IT systems also skip the
distributed path selection problem and cut
generation during the data transmission. Data
aggregation reduce the commutation cost and reduce
memory and power consumption, respectively. We
have conducted four separate tests using the AODV,
SAODV, DSR, and DSDV procedures in our
experimental research. From what we can tell, when
it comes to SAODV, the system manages to keep
internal nodes' energy consumption at 15% while
improving the network life at 7%. Improve this
study in the future by including packet scheduling
and other methods for detecting and preventing
network assaults.
Table 2: Performance evaluation of proposed system for IEEE 802.11
Details of
technical
parameters
Output
achieved
Outcome inferred from output Impact Improvement
Without
BTC
With
BTC
Throu
g
h
p
ut 4.1 bit/s Hi
g
h throu
g
h
p
ut even hi
g
h traffic
g
enerate
d
3.5 bit/s 4.1 bit/s 0.6 bit/sec
E2E delay 0.019 sec Reduce E2E delay by using BTC based data
transmission
0.028sec 0.019
sec
0.09 bit/sec
Packet Drop 1.9 Low packet drop rate than traditional WSN
and cluster networking
4.7 1.9 3.8
Packet
Deliver
y
99.2 Achieve good packet delivery rate even we
chan
g
ed no. of nodes and size of data
95.20 99.2 4.0
Overhead 0.75 Packet overhead is almost noting. 1.85 0.75 1.10
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
5 1015202530
PACKET DELIVERY
TIME (IN SECONDS)
DSDV
DSR
AODV
SAODV
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
5 1015202530
PACKET OVERHEAD
TIME (IN SECONDS)
DSDV
DSR
AODV
SAODV
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
692

REFERENCES
T. N. Le, P. H. J. Chong, X. J. Li, and W. Y. Leong, “A
Simple Grid-Based Localization Technique in
Wireless Sensor Networks for Forest Fire Detection,”
In 2nd International Conference on Communication
Software and Networks, Pages 93 – 98, February
2010.
L. Kenc and J. Y. L. Boudec, “Adaptive Load Sharing for
Network Processors,” IEEE/ACM Transactions on
Networking, Vol. 16, No. 2, Pages 293 – 309, April
2008.
J. Wang, Y. Niu, J. Cho, and S. Lee, “Analysis of Energy
Consumption in Direct Transmission and Multi-hop
Transmission for Wireless Sensor Networks,” In 3rd
International IEEE Conference on Signal-Image
Technologies and Internet-Based System (SITIS ’07),
Pages 275 – 280, 2007.
J. Xu, W. Liu, F. Lang, Y. Zhang, and C. Wang, “Distance
Measurement Model Based on RSSI in WSN,”
Wireless Sensor Network, Vol. 2010, No. 2, Pages
606 – 611, August 2007.
V. T. Quang and T. Miyoshi, “A Transmission Range
Adjustment Algorithm to Avoid Energy Holes in
Wireless Sensor Networks,” In 8th Asia-Pacific
Symposium on Information and Telecommunication
Technologies (APSITT ’10), Pages 1 – 6, June 2010.
R. K. Batwada, M. Tripathi, M. S. Gaur, and V. Laxmi,
“An Approach for Prolonging the Life Time of
Wireless Sensor Network,” In 2nd International
Conference on Information and Network Technology
(ICINT ’12), Vol. 27, Pages 264 – 268, 2012.
S. Paul, S. Nandi, and I. Singh, “A Dynamic Balanced-
Energy Sleep Scheduling Scheme in Heterogeneous
Wireless Sensor Network,” In 16th IEEE International
Conference on Networks (ICON ’08), Pages 1 – 6,
December 2008.
J. N. A. Karaki and A. E. Kamal, “Routing Techniques in
Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey,” IEEE Wireless
Communications, Vol. 11, No. 6, Pages 6 – 28,
December 2004
C. Y. Chong and S. P. Kumar, “Sensor Networks:
Evolution, Opportunities, and Challenges,”
Proceedings of the IEEE, Vol. 91, No. 8, Pages 1247 –
1256, August 2003.
Vetrivelan, N. "An Efficient LWSP Technique in WSN
with Shortest Path Routing for Less Latency in Data
Transmission." (2019).
Aijaz Magray, Mudasir Younis,Chitaranjan sharma "
Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Shortest Path
Algorithms" International Journal of Advanced
Scientific Research and Management, Volume 4 Issue
1, Jan 2019
Nakas, Christos, Dionisis Kandris, and Georgios
Visvardis. "Energy efficient routing in wireless sensor
networks: a comprehensive survey." Algorithms 13.3
(2020): 72.
Kandris, Dionisis, et al. "Applications of wireless sensor
networks: an up-to-date survey." Applied System
Innovation 3.1 (2020): 14.
Osamy, Walid, Ahmed A. El-sawy, and Ahmed M. Khedr.
"SATC: A simulated annealing-based tree
construction and scheduling algorithm for minimizing
aggregation time in wireless sensor networks."
Wireless Personal Communications 108.2 (2019):
921-938.
Zantalis, Fotios, et al. "A review of machine learning and
IoT in smart transportation." Future Internet 11.4
(2019): 94.
Khedo, K.K.; Bissessur, Y.; Goolaub, D.S. An inland
Wireless Sensor Network system for monitoring
seismic activity. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020,
105, 520–532.
Tasgaonkar, Pankaj P., Rahul Dev Garg, and Pradeep
Kumar Garg. "Vehicle detection and traffic estimation
with sensors technologies for intelligent transportation
systems." Sensing and Imaging 21.1 (2020): 1-28.
Jain, Bindiya, et al. "A cross layer protocol for traffic
management in Social Internet of Vehicles." Future
Generation computer systems 82 (2018): 707-714.
Gopalakrishnan, Kasthurirangan. "Deep learning in data-
driven pavement image analysis and automated
distress detection: A review." Data 3.3 (2018): 28.
Munoz-Organero, Mario, Ramona Ruiz-Blaquez, and Luis
Sánchez-Fernández. "Automatic detection of traffic
lights, street crossings and urban roundabouts
combining outlier detection and deep learning
classification techniques based on GPS traces while
driving." Computers, Environment and Urban Systems
68 (2018): 1-8.
Chen, Quan, et al. "Structure-Free Broadcast Scheduling
for Duty-Cycled Multihop Wireless Sensor
Networks." IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing
(2021).
Wang, Na, and Jian Li. "Shortest path routing with risk
control for compromised wireless sensor networks."
IEEE Access 7 (2019): 19303-19311.
Younes, A., et al. "The Shortest-Path Broadcast Problem."
International Journal of Applied Engineering Research
13.10 (2018): 7580-7584.
Sun, Xiao, et al. "Two-hop neighborhood information
joint double broadcast radius for effective code
dissemination in WSNs." IEEE Access 7 (2019):
88547-88569.
Broadcast Tree Construction for Shortest Path Finding with Secure Data Aggregation Techniques in Wireless Sensor Networks
693
