
A Data-Driven Quest for Early Alzheimer’s Detection
Kiran Nandkumar Kasar and Maya Bembde
Information Technology Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering Pune, India
Keywords: Diagnose Alzheimer, Early Alzheimer’s Detection, AD Patients, Neuroimaging, MR Images.
Abstract: Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative condition that is a major cause of dementia globally,
impacting countless individuals and their families. Detecting Alzheimer’s early is essential for effective
management and treatment, as it can help slow symptom progression and enhance the quality of life for those
affected. Recent advancements in medical imaging and machine learning offer promising opportunities for
identifying Alzheimer’s in its early stages, enabling timely interventions. This research project was initiated
with the goal of leveraging cutting-edge image detection algorithms to analyze brain scan images for early
signs of Alzheimer’s disease. Employing a dataset comprising various brain scans, the methodology centered
around the development and validation of a machine learning model capable of distinguishing between scans
indicative of Alzheimer’s and those of healthy controls. Despite the meticulous design, the project
encountered significant challenges, notably data leakage and issues related to dataset quality, which have
served as valuable learning experiences. This document not only summarizes the work done and the obstacles
faced but also proposes a forward-looking plan aimed at overcoming these hurdles in future endeavors.
1 INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a prevalent cause of
dementia globally, characterized by progressive
memory loss and difficulties with concentration. As
the disease advances, individuals often face severe
complications like dehydration, malnutrition, or
infections, which can ultimately lead to death. Since
its initial identification in the early 1900s, there has
been no cure or treatment capable of halting the
disease’s progression. Nevertheless, early
intervention with various medications and supportive
non-drug therapies can positively influence the
disease’s trajectory, emphasizing the importance of
timely and effective care. MRI imaging has a high
potential for diagnosing brain injuries, tumors, and
lesions. In addition, it helps to eliminate symptoms
similar to AD caused by other causes or disorders
(Givin, 2024), (Sagheer, George et al. 2020).
AD affects more than just memory; it impacts
various aspects of an individual’s personality, life
experiences, and social interactions. The disease
typically starts with short-term memory impairment
and gradually affects long-term memory, leading to
challenges in maintaining orientation in time and
space. This deterioration is often depicted in the
works of artists who capture the cognitive decline and
spatial disorientation associated with AD, although
the emotional essence of their experiences remains
evident in their art. Diagnosing Alzheimer’s with
absolute certainty during a person’s lifetime remains
challenging. Diagnosis is generally based on
identifying characteristic symptoms while ruling out
other potential causes. Conditions such as depression,
meningitis, strokes, or brain hemorrhages can present
with similar symptoms, making careful diagnosis
crucial.
Effective clinical trials are essential for
monitoring the progression of AD and evaluating the
impact of treatments. Current diagnostic methods
include: Manual prediction by clinical experts using
patient history and visual analysis of brain scans.
Supervised Machine Learning (ML) techniques,
which have proven effective in differentiating AD
patients from cognitively healthy individuals by
analyzing MRI images and various biomarkers. (Zer,
et al. 2023), (Wiley, 2021)
Although the exact cause of Alzheimer’s remains
unknown, research indicates that a deficiency in the
neurotransmitter acetylcholine and the accumulation
of protein plaques in the brain may contribute to nerve
cell death. Several factors have been associated with
an increased risk of AD, including
568
Kasar, K. N. and Bembde, M.
A Data-Driven Quest for Early Alzheimer’s Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013596900004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd Inter national Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 2, pages 568-573
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

Age: The likelihood of developing AD doubles
approximately every five years after age 65. (Mielke,
2019)
Apolipoprotein E4 (APOE E4): Presence of this
gene increases the risk of AD by 10 to 30 times
compared to those without it, though the precise
mechanism remains unclear.
Gender: Women are statistically more likely to
develop AD than men, though the reasons are not
fully understood.
Medical Conditions: Type 2 diabetes, high blood
pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and depression are
known risk factors.
Lifestyle Factors: Physical inactivity, smoking,
poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and head
injuries can also elevate the risk of developing
dementia.
Who Does Alzheimer’s Disease Affect:
Alzheimer’s disease predominantly affects
individuals over the age of 65, with the likelihood of
developing the condition increasing as people age.
Although less common, Alzheimer’s can also occur
in individuals younger than 65, usually in their 40s or
50s. This earlier onset form of the disease is known
as early-onset Alzheimer’s and accounts for fewer
than 10\% of all Alzheimer’s cases.
How common is Alzheimer’s disease:
Alzheimer’s disease is widespread, impacting
around 24 mil- lion individuals globally. About 10%
of those over the age of 65 are affected, and nearly
one-third of people over 85 are diagnosed with the
condition.
Current statistics on Alzheimer’s disease In India:
In 2019, India had an estimated 3.69 million active
cases of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
The reported prevalence rate for these conditions was
4.3 % However, the rate of Alzheimer’s disease
varies significantly across different states. Kerala,
Goa, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Himachal
Pradesh had the highest numbers of cases. This
distribution is closely related to the proportion of
elderly people within the populations of these states.
2 LITERATURE BACKGROUND
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in Alzheimer’s
dis- ease research and diagnosis has gained
significant attention in recent years. Early machine
learning approaches focused on analyzing clinical
and genetic data to identify patterns contributing to
early diagnosis.
Advancements in imaging technologies,
including MRI and PET, have facilitated the use of
AI in analyzing brain scans. Deep learning techniques
such as convolutional neural net- works (CNNs) have
proven effective in identifying biomarkers and
classifying Alzheimer’s disease. Integration of Multi-
Modal Data: Researchers began integrating multi-
modal data, including imaging, genomics, and
clinical information, to enhance the accuracy of
Alzheimer’s disease prediction models. (Livingston
Berger, 2020), (Draper et al. 2010), (O¨ zer, Koplay
et al. 2023). These integrative approaches showcased
the potential for comprehensive AI-based diagnostic
tools.4. Machine Learning in Early Detection: As the
importance of early detection became evident,
machine learning models were deployed to identify
subtle cognitive changes that precede clinical
symptoms. These models, utilizing diverse datasets,
demonstrated improved sensitivity and specificity in
distinguishing between cognitively normal
individuals and those with mild cognitive impairment
or early-stage Alzheimer’s disease.
Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs): In recent years, the advent of deep
learning, particularly CNNs, has revolutionized AI
applications in Alzheimer’s research. CNNs have
been employed to analyze brain imaging data,
automatically extracting features that contribute to
accurate disease classification.
Large-Scale Collaborative Initiatives:
Collaborative efforts, such as the Alzheimer’s
Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI),have played
a crucial role in advancing AI research. Large-scale
datasets from initiatives like ADNI have enabled the
training of robust machine learning models and the
development of predictive algorithms for
Alzheimer’s disease. (Rao, Bharath, et al. 3013).
3 PROPOSED IDEA
The goal of this project is to leverage the power of
artificial intelligence, specifically machine learning
and computer vision techniques, to analyze brain scan
images for the early detection and diagnosis of
Alzheimer’s disease. The expectation is that such a
tool could supplement existing diagnostic practices,
providing a more objective and potentially earlier
indication of these diseases.
Importance of Early Detection of Alzheimer’s
Disease: In 2006, Alzheimer's disease affected an
estimated 26.6 million people globally, and this
number is projected to quadruple by 2050. By that
time, approximately 1 in 85 individuals worldwide
could be living with the disease. A significant portion
of these cases, roughly 43%, will require intensive
A Data-Driven Quest for Early Alzheimer’s Detection
569
care equivalent to that provided in nursing homes.
However, delaying the onset and progression of
Alzheimer's by even a single year could prevent
nearly 9.2 million cases by 2050, significantly
reducing the burden on caregiving resources. Early
diagnosis is crucial, offering affected individuals the
opportunity to plan ahead, access early interventions,
and potentially slow disease progression:
Table 1: Summary of Literature survey:
No IEEE Paper Name Authors Publis
hed
Year
Related Work Methodology
Used
Future Scope Technology
Used/(Accuracy
Rate)
1 Deep Learning-
Based Early
Alzheimer's Disease
Detection
(Abrol, Bhattarai, et
al. 2020
)
John Smith,
Emily
Johnson
2020 -Utilized deep learning
for Alzheimer's
detection
- Convolutional
Neural Networks
(CNN) for
feature
extraction and
classification
-
Implementation
in clinical
settings
Deep Learning,
MRI data(85%)
2 "Blood Biomarkers
for Early
Alzheimer's
Diagnosis" (Chima,
Emmanuel et al.
2021)
Xinzhong Li
, Camille
Carroll ,
Stephen
Pearson
2021 - Previous studies on
blood
Biomarkers for
Alzheimer's diagnosis
- Analysis of
blood samples
for specific
biomarkers
-Large-scale
clinical trials
Blood biomarker
analysis(78%)
3 " Evaluation of
neuro images
diagnosis of
Alzheimer’s disease
using Deep learning
" (Hamdi, Mounir et
al. 2022
)
Hamdi,
Mounir;et al
2022 -Studies investigating
cerebrospinal fluid
(CSF) biomarkers for
Alzheimer's diagnosis
- Analysis of
CSF samples for
specific
biomarkers
-
Standardization
of CSF
biomarker
measurement
Deep Learning
(81%)
4 "Neuroimaging
Markers for Early
Alzheimer's
Prediction" ( Abrol,
et al. 2020
)
Wei Chen,
Pedro
Rodriguez
2020 Previous neuroimaging
studies identifying
biomarkers for early
Alzheimer's
p
rediction
-Utilization of
advanced
neuroimaging
techniques
-Integration
with AI-based
diagnostic
systems
Neuroimaging, AI
algorithms(82%)
5 "LeNet-deep neural
network model for
Alzheimer"
(Hazarika et al.
2021)
Hazarika,
Rahul Amin
2021 - Previous studies on
metabolomic profiling
for Alzheimer's disease
diagnosis
- 2D
functional MRI
-Integration
with AI-based
diagnostic
systems
CNN(90.1)
6 " Alzheimer’s
Stages Classification
Functional Brain
Changes in
Magnetic Resonance
Images " (Shamrat,
et 2023)
M. J. M.
Shamrat et
al.,
2023 - Introduction of novel
imaging techniques for
early Alzheimer's
detection
- Evaluation of
advanced
Magnetic
Resonance
Image
-Clinical
validation in
community
healthcare
Advanced
neuroimaging
techniques(87
%)
7 “A early detection
of Alzheimer using
ML” (Kabir, Md
Sharia
r
2023)
Kabir, Md
Shariar,e t al
2023 - Previous studies on
proteomic biomarkers
for Alzheimer's
diagnosis
- Analysis of
protein
expression
p
atterns
- Accurate
prediction for
Alzheimer
Proteomic
analysis, Machine
learning
algorithms(99%)
8 A review on medical
image denoising
algorithms "
(Sagheer, George et
al. 2020)
S. V.
Mohd
Sagheer and
S. N. George
2020 -Studies integrating
genetic and
neuroimaging markers
for Alzheimer's
prediction
- Integration of
genetic risk
Factors with
neuroimaging
data
-Long-term risk
prediction and
personalized
medicine
Genetic analysis,
Neuroimaging
data(89%)
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
570
9 Machine Learning
for Early
Alzheimer's
Progression (Givin,
2024)
Sophia
Gonzales,
Daniel White
2024 - Previous machine
learning studies for
disease progression
prediction in
Alzheimer's patients
- Utilization of
longitudinal data
for machine
learning models
- Prediction of
disease
accuracy
Machine learning,
Longitudinal
data(93%)
Medical Benefits:
Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease provides
access to a wider range of treatment options and
creates opportunities for participation in clinical trials
that could benefit patients and advance research. It
empowers individuals to proactively manage their
health, offering emotional relief by addressing
symptoms early. Families gain time to strengthen
their bonds and explore available resources and
support systems. Planning ahead for legal, financial,
and end-of-life decisions ensures that personal wishes
are honored. Economically, early detection can
significantly reduce long-term care and medical
costs. If Alzheimer’s were diagnosed during the mild
cognitive impairment stage for all affected
individuals, healthcare systems could collectively
save trillions of dollars, alleviating financial burdens
on families and society.
3.1 Methodology
The research work aimed to detect Alzheimer’s
Disease (AD) at an early stage. Data from platforms
such as the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging
Initiative (ADNI) dataset and National Alzheimer’s
Coordinating Center (NACC) dataset were used for
this research work consists of MRI images. The data
has four classes of images both in training as well as
a testing set:
1. Mild Demented.
2. Moderate Demented.
3. Non Demented.
4. Very Mild Demented
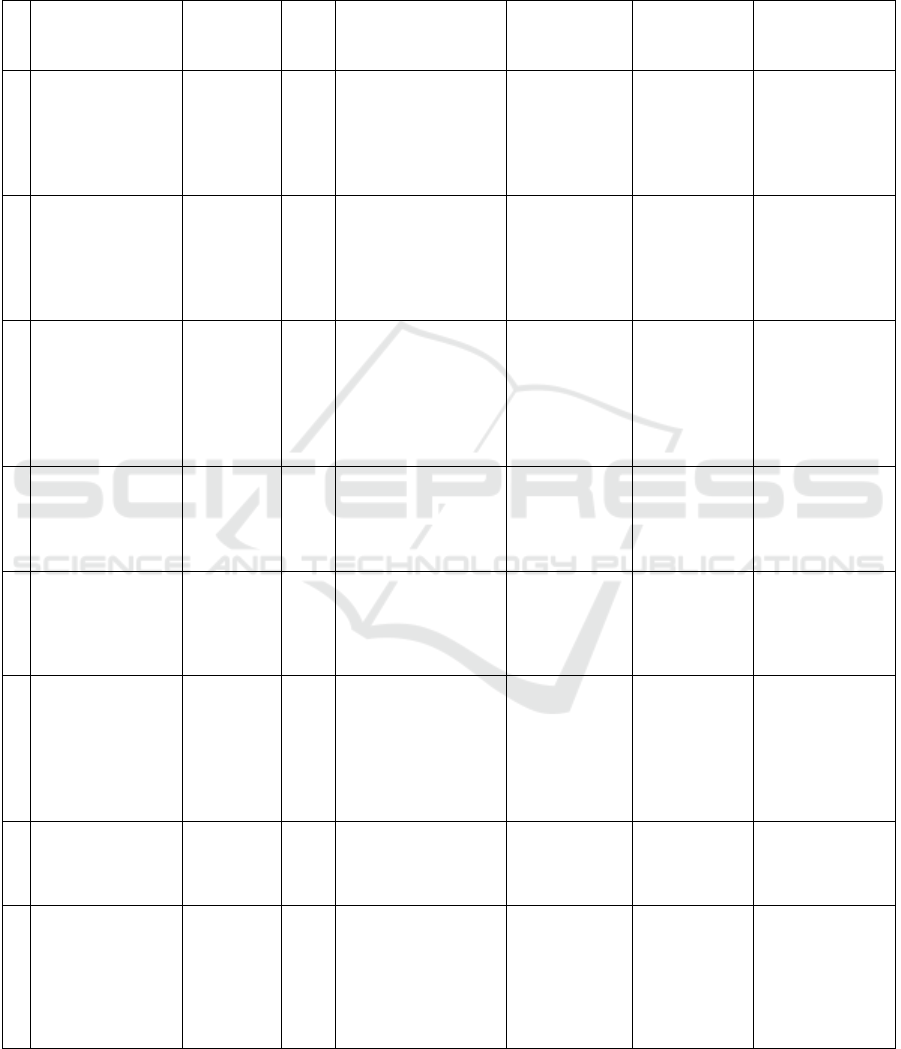
Figure 1: Process Overview.
The model employs convolutional layers with
max-pooling, batch normalization, dropout, and
dense layers. Bayesian Optimization was used for
hyperparameter tuning to achieve high accuracy.
Input Data: The input to the model consists of
neuroimaging data, such as structural MRI scans, that
capture brain images of individuals (Ajay, Manu, et
al. 2023). These images serve as the primary source
of information for the diagnosis. As shown in Fig1.
Hyperparameter Optimization using Keras
Tuner: In our endeavour to detect Alzheimer’s
disease from brain scan images, we constructed a
model with a straightforward yet effective
architecture tailored to process 176x176 images.
The architecture comprised several key components
designed to capture the intricate patterns
characteristic of Alzheimer’s pathology in brain scans
Convolutional Layers with Max-Pooling:
These layers are fundamental in extracting spatial
hierarchies of features from the images. Max- pooling
was utilized to reduce dimensionality and to enhance
the detection of features by summarizing the presence
of features in patches of the input image. As shown in
Fig2
Figure 2: CNN Architecture
Activation Function
ReLU formula is :
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑚𝑎𝑥(0, 𝑥) (1)
Both the ReLU function and its derivative are
monotonic. If the function receives any negative
input, it returns 0; however, if the function receives
any positive value x, it returns that value. As a result
in equation 1, the output has a range of 0 to infinite.
Convolutional Layer Output:
Let’s assume we have a 2D convolutional layer
with a filter W and an input X. The output of a
convolution is a feature map as shown in equation 2,
denoted as Z,
𝑍 = 𝑊𝑋 + 𝑏 (2)
Where:
*Represents the convolution operation. W is the
filter (or kernel).
A Data-Driven Quest for Early Alzheimer’s Detection
571
X is the input matrix (e.g., an image or feature
map from the previous layer).
b is the bias term.
Z is the pre-activation output.
ReLU in CNN:
The ReLU function is applied element-wise to the
output Z from the convolutional layer, resulting in
equation 3:
𝐴 = 𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈(𝑍) (3)
Where:
A is the output after applying the ReLU function.
Z is the pre-activation input (i.e., the output of the
convolution).
Thus, for an input matrix X, the convolution
operation followed by the ReLU activation can be
written as equation 4:
𝐴 = 𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈(𝑊𝑋 + 𝑏) (4)
Batch Normalization and Dropout: To mitigate
the risk of overfitting and to improve model
generalization, batch normalization and dropout
techniques were incorporated. Batch normalization
standardizes the inputs to a layer, ensuring the model
trains efficiently and stably. Dropout, on the other
hand, randomly ignores a subset of neurons during
training, thus preventing the model from becoming
overly reliant on any specific set of neurons
Dense Layers: The model included three fully
connected (dense) layers that further processed
features extracted by the convolutional layers,
facilitating the learning of non-linear combinations of
these features.
Output Layer: The final layer of the model
consisted of four neurons, corresponding to the
multi-class classification task. This layer utilized a
softmax activation function to output a probability
distribution over the four classes, enabling the model
to predict the class of each input image.
4 RESULT
To optimize the model’s performance, Bayesian
Optimization was employed, allowing us to fine-tune
hyperparameters such as the number of convolutional
layers, filters, dense layers, and learning rates. This
method of hyperparameter optimization seeks to find
the set of parameters that maximizes the model’s
accuracy through a principled approach that models
the performance function
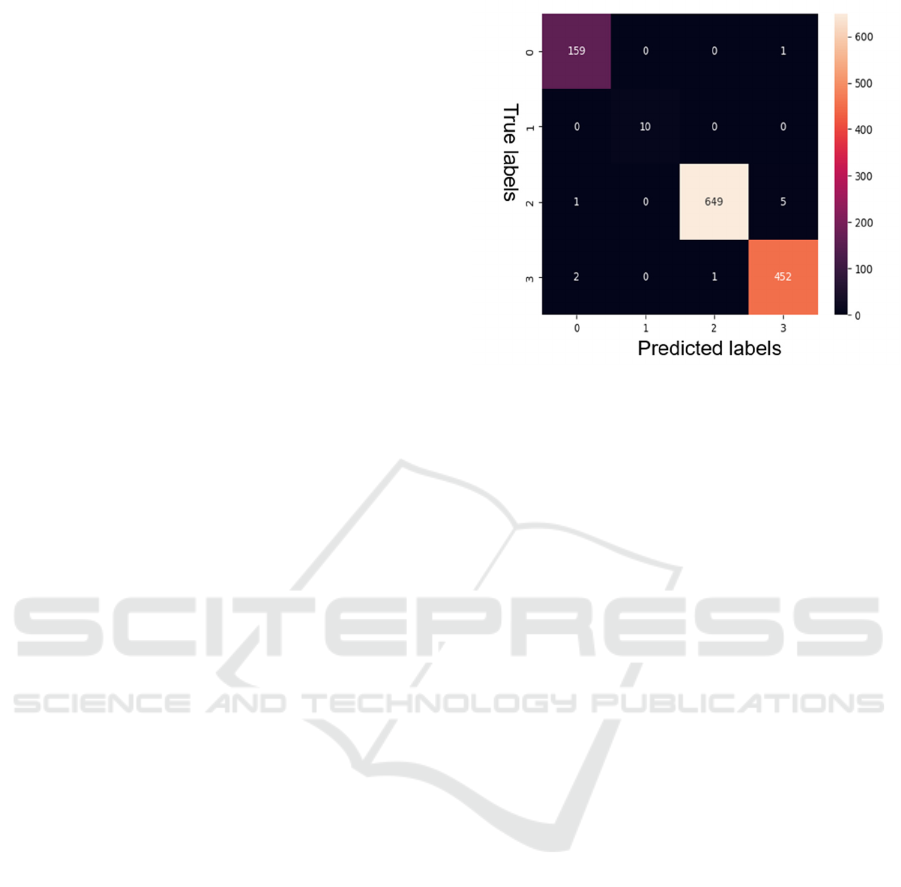
Figure 3: Confusion Matrix
The application of Bayesian Hyperparameter
Optimization yielded remarkable results. Keras Tuner
was used to optimize hyperparameters such as the
number of convolutional layers, filters, dense layers,
and learning rates. Summary of the Keras CNN model
is as shown in the fig 2. The proposed model will train
for detection of the Alzheimer for the input MRI
image. The expecting confusion matrix of the
proposed model represented in the fig 3.
5 CONCLUSION
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease through AI-
based methods shows immense potential in reducing
the global burden of this disease. The findings
emphasize the importance of using advanced AI
techniques for robust and scalable solutions.
REFERENCES
A. Abrol, et al., “Deep residual learning for neuroimaging:
An applica- tion to predict progression to Alzheimer’s
disease,” J. Neurosci. Methods, 2020.
H.O¨ zer, et al., “Texture analysis of multiparametric
magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating
clinically significant prostate cancer,” Turkish J. Med.
Sci., 2023.
Wiley J. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers
Dement. 2021 Mar;17(3).
Nichols E, Steinmetz JD, Vollset SE, Fukutaki K, Chalek J,
Abd-Allah F, Abdoli A, Abualhasan A, Abu-Gharbieh
E, Akram TT, Al Hamad H. Estimation of the global
prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted
prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the Global Burden
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
572

of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet Public Health. 2022
Feb 1;7(2):e105-25.
Singh G, Sharma M, Kumar GA, Rao NG, Prasad K,
Mathur P, Pandian JD, Steinmetz JD, Biswas A, Pal
PK, Prakash S. The burden of neurological disorders
across the states of India: the Global Burden of Disease
Study 1990–2019. The Lancet Global Health. 2021
Aug 1; 9(8):e1129-44.
Hamdi, Mounir;et al. “Evaluation of neuro images for the
diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using Deep learning
“2022:834032
Ravindranath V, Sundarakumar JS. Changing demography
and the challenge of dementia in India. Nature Reviews
Neurology. 2021 Dec;17(12):747-58.
Rao GN, Bharath S. Cost of dementia care in India:
delusion or reality?. Indian journal of public health.
2013 Apr 1;57(2):71.
Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease with Blood Plasma
Proteins Using Support Vector Machines Chima S. Eke
, Emmanuel Jammeh , Xinzhong Li , Camille Carroll ,
Stephen Pearson , and Emmanuel Ifeachor 2021
M. J. M. Shamrat et al., "AlzheimerNet: An Effective Deep
Learning Based Proposition for Alzheimer’s Disease
Stages Classification From Functional Brain Changes
in Magnetic Resonance Images," in IEEE Access, vol.
11, pp. 16376-16395, 2023.
Hazarika, Rahul Amin,et al.”An improved LeNet-deep
neural network model for Azheimer;s disease
classification using brain magnetic resonance images”
IEEE Access 9 (2021): 161194-161207.
Mielke MM. Sex and gender differences in Alzheimer’s
disease demen- tia. The Psychiatric times.2019
Nov;35(11):14.
Livingston G, Huntley J, Sommerlad A, Ames D, Ballard
C, Banerjee S, Brayne C, Burns A, Cohen-Mansfield J,
Cooper C, Costafreda SG. Dementia prevention,
intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet
Commission. The Lancet. 2020 Aug
8;396(10248):413-46.
Draper B, Peisah C, Snowdon J, Brodaty H (2010) Early
dementia diagnosis and the risk of suicide and
euthanasia. Alzheimers Dement 6, 75-82
H.O¨ zer, M. Koplay, A. Baytok, N. Seher, L. S. Demir, A.
Kilinc¸er, M. Kaynar, and S. Go¨ktas¸, “Texture
analysis of multiparametric magnetic resonance
imaging for differentiating clinically significant
prostate can- cer in the peripheral zone,” Turkish J.
Med. Sci., vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 701– 711, Jan. 2023
A. Abrol, M. Bhattarai, A. Fedorov, Y. Du, S. Plis, and V.
Calhoun, “Deep residual learning for neuroimaging: An
application to predict progression to Alzheimer’s
disease,” J. Neurosci. Methods, vol. 339, Jun. 2020,
Art. no. 108701
A Review on Machine Learning Approaches for Diagnosis
of Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment
Based on Brain MRI. Hella Givin and Jean-Paul
Calbimonte Institute of Informatics, University of
Applied Sciences and Arts Western Switzerland (HES-
SO), 3960 Sierre, Switzerland The Sense Innovation
and Research Center, 1007 Lausanne, Switzerland.
S. V. Mohd Sagheer and S. N. George, “A review on
medical image denoising algorithms,” Biomed. Signal
Process. Control, vol. 61, Aug. 2020, Art. no. 102036.
Kabir, Md Shariar, et al. “A early detection of Alzheimer
using Machin Learning Approach” 2023 (ICCCI).
Ajay B N , Manu K.S, Preethi M, A Comprehensive
Overview of the Novel Approach to Detect Alzheimer’s
Disease using Deep Learning and Convolutional Neu-
ral Network.2023.
A Data-Driven Quest for Early Alzheimer’s Detection
573
