
Real-Time Arabic Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv5
Zainab Abualhassan, Haidar Ramadhan, Mohammed Faisal Naji and Hajar Alsulaili
Computer Science and Engineering Department, Kuwait College of Science and Technology (KCST), Doha, Kuwait
Keywords:
Sign Recognition, YOLOv5, Machine Learning, Object Detection.
Abstract:
Sign language is a vital means of communication for the deaf and hard-of-hearing community, yet automatic
recognition still faces many challenges. While several sign languages have seen major advances in recogni-
tion systems, Arabic sign language (ArSL) remains underdeveloped and requires much more research. Object
detection models like YOLOv5 (You Only Look Once, Version 5) have revolutionized computer vision with
their high speed, accuracy, and ability to process data in real time. This paper introduces a recognition system
leveraging YOLOv5 , a leading object detection model, to classify the 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet. The
model was trained on a comprehensive dataset containing thousands of images representing each letter, achiev-
ing strong classification results with certain classes reaching perfect accuracy of 100%. To assess the model’s
performance, evaluation metrics such as precision, recall, and mean Average Precision (mAP) were employed,
demonstrating its practicality for real-world applications. Results indicate that YOLOv5’s architecture, with
its efficient feature extraction and real-time processing, reliably handles the complex hand gesture variations in
Arabic sign language. Its capability to distinguish subtle differences in hand positions makes it a valuable tool
for educational applications, accessibility solutions for the deaf and hard-of-hearing, and future advancements
in sign language translation systems. This study contributes a robust Arabic sign language recognition model,
addressing an essential need for improved accessibility and communication for Arabic-speaking users.
1 INTRODUCTION
Effective communication is essential for fostering
connection and understanding, yet it poses unique
challenges for the deaf community, particularly in
Arabic-speaking countries where Arabic Sign Lan-
guage (ArSL) plays a vital role. ArSL is not just a
means of communication; it is a cultural and linguis-
tic system that reflects the Arabic language and tra-
ditions. Unlike standardized languages like Ameri-
can Sign Language (ASL), ArSL is heavily influenced
by regional dialects. This influence leads to signifi-
cant variability, where the same word or phrase can
have different signs depending on the country or even
specific areas within a country (Al-Shamayleh et al.,
2020). This regional diversity complicates efforts to
create a unified recognition system, requiring mod-
els to adapt to specific dialectal differences and ad-
dress the lack of a standardized form of ArSL (Abdel-
Fattah, 2005).
The limited availability of high-quality ArSL
datasets has left research in this field relatively sparse
compared to studies on other sign languages. Most
existing datasets consist of static signs, often re-
stricted to the Arabic alphabet, lacking the continuity
needed for sentence-level or contextual gesture recog-
nition (Al-Qurishi et al., 2021). This scarcity of an-
notated data hinders the development of robust ma-
chine learning models capable of generalizing across
diverse gestures and limits their practical application
in real-world settings. Additionally, the absence of
a comprehensive recorded ArSL literature and incon-
sistent formal education for the Deaf in Arab coun-
tries increase these challenges (Abdel-Fattah, 2005).
To address these limitations, numerous efforts
have been made to automate sign language recog-
nition, employing both classical machine learning
techniques, such as Support Vector Machines (SVM)
(Almasre and Al-Nuaim, 2016), and advanced deep
learning methods like Convolutional Neural Net-
works (CNNs) (Suliman et al., 2021). Transfer learn-
ing has further improved detection accuracy by lever-
aging pre-trained models to adapt to the unique fea-
tures of ArSL (Alharthi and Alzahrani, 2023). More-
over, modern object detection models like YOLO
have achieved exceptional performance in real-time
recognition, offering precise detection of hand ges-
tures with high speed and accuracy.
ArSL recognition remains a challenging task due
Abualhassan, Z., Ramadhan, H., Naji, M. F. and Alsulaili, H.
Real-Time Arabic Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv5.
DOI: 10.5220/0013595200004000
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2025) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 181-187
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
181

to the limited availability of large-scale datasets, vari-
ability in hand gestures, and the need for real-time
processing capabilities. The contributions of this pa-
per are as follows:
• Utilizing YOLOv5 for Arabic Sign Language
(ArSL) Recognition: This study explores the
application of the YOLOv5 model for detecting
and classifying 28 Arabic sign language alphabet
gestures, addressing the challenge of recognizing
gestures within a small dataset.
• Real-Time Model Implementation: The pro-
posed approach emphasizes real-time detection
and classification capabilities, making it suitable
for practical applications requiring instant recog-
nition.
The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 presents
a literature review of advances in ArSL recogni-
tion, Section 3 details methodology and implemen-
tation, Section 4 discusses results and comparisons
with state-of-the-art methods, and Section 5 con-
cludes with future research directions.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Early efforts in ArSL recognition primarily relied
on classical machine learning techniques, emphasiz-
ing image processing and feature extraction for ges-
ture classification. (Aly and Mohammed, 2014) de-
veloped an ArSL recognition system in 2014 using
Local Binary Patterns on Three Orthogonal Planes
(LBP-TOP) and SVM, which involved preprocessing
steps such as segmenting the hand and face through
RGB-to-color-space conversion. Similarly, (Tharwat
et al., 2021) proposed a system in 2021 focusing on
28 Quranic dashed letters, employing classifiers such
as K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN), Multilayer Perceptron
(MLP), C4.5, and Na
¨
ıve Bayes. Their approach uti-
lized a dataset of 9240 images captured under vary-
ing conditions and achieved a recognition accuracy of
99.5% for 14 letters using KNN. While these methods
demonstrated reasonable accuracy, they were con-
strained by limited scalability and the lack of real-
time implementation capabilities.
Researchers have increasingly adopted advanced
deep learning techniques for sign language recogni-
tion across various languages. For instance, (Tao
et al., 2018) utilized CNNs to address ASL recog-
nition, highlighting CNNs’ ability to effectively cap-
ture sign gestures. Similarly, (Suliman et al., 2021)
proposed a method for ArSL recognition, combin-
ing CNNs for feature extraction and Long Short-Term
Memory (LSTM) networks for classification. Their
approach employed the AlexNet architecture to ex-
tract deep features from input images and utilized
LSTMs to maintain the temporal structure of video
frames. The system achieved an overall recognition
accuracy of 95.9% in signer-dependent scenarios and
43.62% in signer-independent scenarios.
Pretrained models are widely used in sign lan-
guage recognition for leveraging knowledge from
large datasets. (Duwairi and Halloush, 2022) em-
ployed VGGNet, achieving 97% accuracy on the
ArSL2018 dataset, demonstrating the efficacy of pre-
trained architectures. (Zakariah et al., 2022) explored
the use of EfficientNetB4 on the ArSL2018 dataset,
achieving a training accuracy of 98% and a testing
accuracy of 95%. Their work incorporated extensive
preprocessing and data augmentation to enhance con-
sistency and balance within the dataset.
In addition, pre-trained YOLO-based approaches
have achieved remarkable results. (Ningsih et al.,
2024) applied YOLOv5-NAS-S to BISINDO sign
language, achieving a mAP of 97.2% and Recall
of 99.6%. (Al Ahmadi et al., 2024) introduced
attention mechanisms within YOLO for ArSL de-
tection, achieving a mAP@0.5 of 0.9909. Simi-
larly, (Alaftekin et al., 2024) utilized an optimized
YOLOv4-CSP algorithm for real-time recognition of
Turkish Sign Language, achieving over 98% preci-
sion and recall, further demonstrating YOLO’s effi-
cacy in high-speed and accurate sign language detec-
tion tasks.
A significant limitation in ArSL research remains
the lack of standardized datasets (refer Table 1). Most
studies rely on custom datasets with isolated signs,
such as ArSL2018, which is insufficient for compre-
hensive, continuous sign recognition (Al-Shamayleh
et al., 2020).
3 METHODOLOGY AND
IMPLEMENTATION
This section outlines the workflow of training and
evaluating the YOLOv5 model for ArSL recogni-
tion, as illustrated in Figure 1. The dataset, is di-
vided into training, validation, and test sets. The
training and validation sets are utilized to train the
YOLOv5 model over 400 epochs, during which hy-
perparameters are fine-tuned to achieve optimal per-
formance. Following the completion of the training
process, the trained model is evaluated using the test
set based on evaluation metrics such as Accuracy,
Precision, Recall, F1 Score, Mean Average Precision
(mAP), mAP@50, mAP@50-95, Intersection over
Union (IoU), Logarithmic Loss, Confusion Matrix,
KDIR 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
182
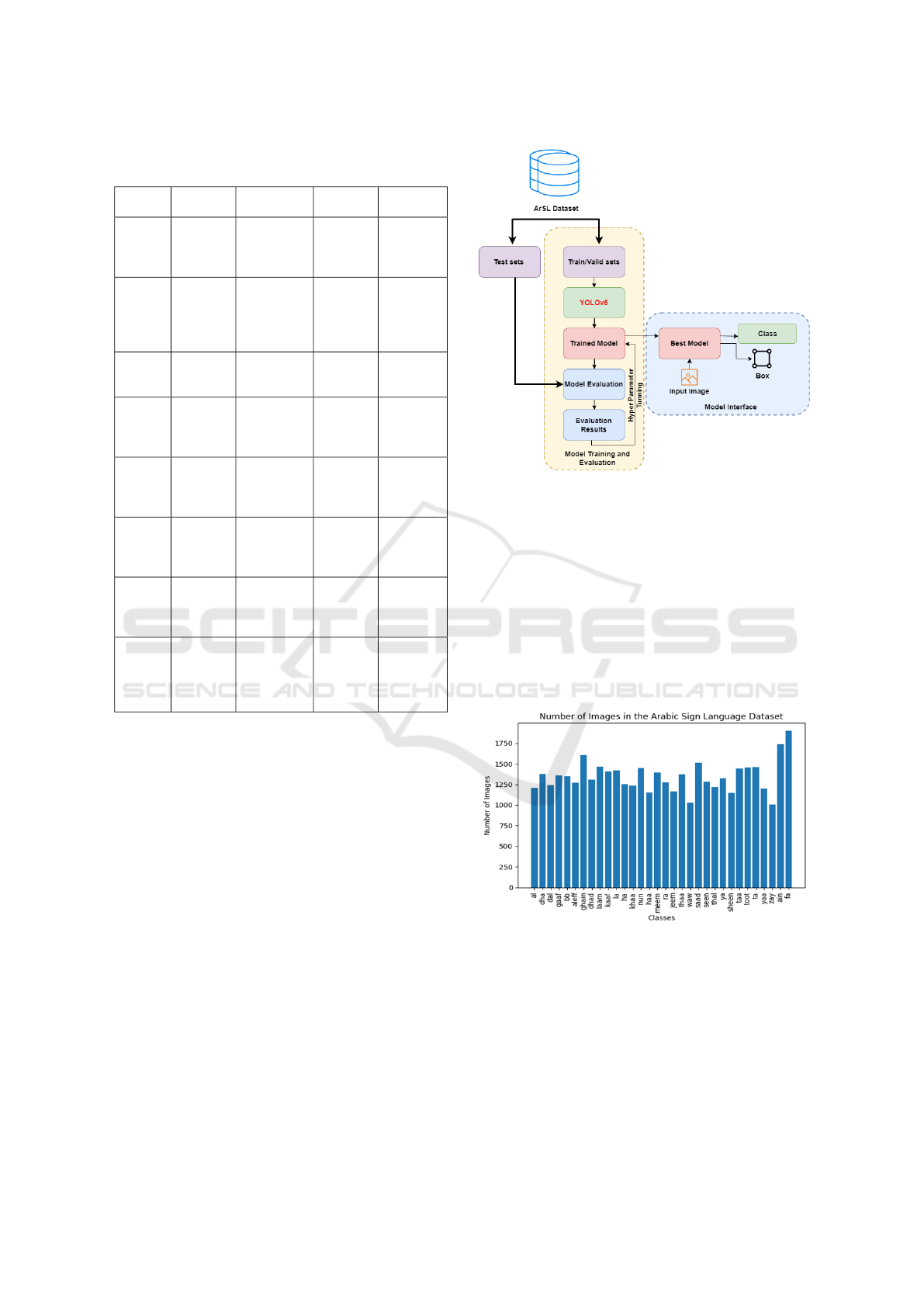
Table 1: Overview of Recent Advances in Sign Language
Recognition Techniques and Methodologies.
Ref. Model(s)
Used
Dataset Evaluation
Metrics
Evaluation
Method
(Aly
and Mo-
hammed,
2014)
LBP-TOP
+ SVM
ArSL
database
(23 words, 3
signers)
Accuracy -
(Tharwat
et al.,
2021)
KNN 9240 images
of Arabic sign
language ges-
tures for 28
letters
Accuracy,
RMSE,
Kappa
Statistic
10-fold
cross-
validation
(Suliman
et al.,
2021)
CNN-
LSTM
150 signs (50
repetitions
each)
Accuracy Train-test
split (70-
30)
(Duwairi
and Hal-
loush,
2022)
VGGNet,
AlexNet,
GoogleNet
ArSL2018
dataset
Accuracy
(97% for
VGGNet)
10-fold
cross-
validation
(Zakariah
et al.,
2022)
EfficientNetB4 ArSL2018
(54,049 im-
ages, 32
classes)
Accuracy
(95%)
Train-test
split (80-
20)
(Ningsih
et al.,
2024)
YOLOv5-
NAS-S
BISINDO (47
classes)
mAP
(97.2%),
Recall
(99.6%)
Not speci-
fied
(Al Ah-
madi
et al.,
2024)
YOLOv5
with At-
tention
ArSL21L
(14,202 im-
ages)
mAP@0.5
(0.9909)
Not speci-
fied
(Alaftekin
et al.,
2024)
YOLOv4-
CSP
Turkish Sign
Language
(numbers)
Precision
(>98%),
Recall
(>98%),
F1 Score
Not speci-
fied
and Area Under Curve (AUC-ROC). Subsequently,
the trained model is deployed within a user interface
framework, enabling real-time prediction capabilities.
Upon providing an input image, the model generates
the corresponding predicted class labels and bound-
ing boxes, effectively demonstrating its proficiency in
object recognition and localization.
3.1 Dataset
The Arabic Sign Language Dataset, hosted on Kag-
gle, consists of 5832 images representing 28 Arabic
letters (Arabic Sign Language ArSL dataset, 2022).
These images are divided into 4651 images for train-
ing, 891 for validation, and 290 for testing. Each
image has a resolution of 416 × 416 pixels, provid-
ing sufficient detail for machine learning applications.
The images were captured in various environments
using a cell phone camera, featuring diverse back-
grounds and varying hand angles, which adds natural
variation to the dataset.
As shown in Figure 2, the dataset exhibits an im-
Figure 1: Workflow for Training, Evaluation, and Deploy-
ment of YOLOv5 for Arabic Sign Language Recognition.
balance across the 28 classes, with certain classes,
such as ”fa” and ”ain,” containing significantly more
samples. This class imbalance poses challenges dur-
ing model training, emphasizing the importance of
preprocessing strategies like data augmentation or
class weighting to ensure fair and effective training.
Despite these challenges, the dataset is a valuable re-
source for advancing sign language recognition mod-
els, promoting accessibility and improved communi-
cation for the deaf and hard-of-hearing community.
Figure 2: Image count per class for the Arabic Sign Lan-
guage Unaugmented Dataset.
3.2 Proposed Model: YOLO
Framework
YOLO, introduced in 2015 (Redmon et al., 2015),
revolutionized object detection by providing a single-
stage system that processes an image in a single for-
ward pass for simultaneous bounding box and class
Real-Time Arabic Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv5
183

prediction. YOLO processes an entire image in a sin-
gle forward pass of the network, dividing it into a grid
and predicting bounding boxes and class probabilities
simultaneously. Its architecture, as illustrated in Fig-
ure 3, includes convolutional layers for feature extrac-
tion, upsampling for multi-scale detection, and an-
chor boxes to capture objects of different sizes. This
efficiency and adaptability make YOLO suitable for
a wide range of applications, from real-time surveil-
lance to medical imaging and autonomous systems.
YOLOv5, introduced in 2020 (Jocher et al., 2020),
is an open-source, PyTorch-based object detection
model known for its real-time performance and scal-
ability. Unlike earlier versions, YOLOv5 incor-
porates innovations like mosaic data augmentation,
auto-learning bounding box anchors, and enhanced
architecture. It offers scalability through variants like
YOLOv5s (small) to YOLOv5x (extra-large), cater-
ing to different resource and accuracy requirements.
The architecture integrates CSP (Cross Stage Partial)
layers for efficient feature extraction, PANet (Path
Aggregation Network) for feature aggregation, and
SPP (Spatial Pyramid Pooling) for expanded recep-
tive fields. These refinements enable YOLOv5 to de-
liver state-of-the-art performance while maintaining
computational efficiency, making it ideal for real-time
applications such as Arabic Sign Language gesture
detection.
Figure 3: YOLO model architecture (Redmon et al., 2015).
3.3 Evaluation Metrics
Evaluation metrics (Manning and Sch
¨
utze,
1999)(Shanmugamani, 2018) are critical in as-
sessing the performance of a machine learning
model, particularly for classification tasks such as
sign language recognition. These metrics provide
insights into the model’s ability to make accurate
predictions and generalize across unseen data. Accu-
racy is the most straightforward metric, measuring
the proportion of correct predictions among all
instances, as defined in Equation 1. However, it can
be misleading in imbalanced datasets. Precision,
defined in Equation 2, evaluates the accuracy of
positive predictions, making it important in scenarios
where false positives have significant consequences.
Recall, also known as sensitivity and shown in
Equation 3, measures the model’s ability to identify
all relevant instances, which is crucial for minimizing
false negatives. The F1 Score, defined in Equation 4,
provides a balanced measure by combining precision
and recall, especially when these metrics are in
trade-off.
For object detection tasks, Mean Average Preci-
sion (mAP) quantifies the precision-recall relation-
ship across various confidence thresholds, as de-
scribed in Equation 5. It provides a comprehensive
view of model performance across all classes. Fur-
thermore, Intersection over Union (IoU), defined in
Equation 6, assesses the spatial overlap between pre-
dicted and actual bounding boxes, making it vital for
evaluating localization accuracy. Together, these met-
rics offer a robust framework for understanding the
effectiveness of the model in recognizing and classi-
fying Arabic sign language gestures.
Accuracy =
TP + TN
TP + TN + FP + FN
(1)
Precision =
TP
TP + FP
(2)
Recall =
TP
TP + FN
(3)
F1 Score = 2 ·
Precision · Recall
Precision + Recall
(4)
mAP =
1
n
n
∑
i=1
AP
i
(5)
IoU =
Area of Overlap
Area of Union
(6)
4 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
This section presents the findings from implementing
the YOLOv5 model for classifying Arabic alphabets
in sign language.
4.1 Confusion Matrix
The confusion matrix, illustrated in Figure 4, serves
as a performance measurement tool for the Arabic
Sign Language recognition model. Each row repre-
sents the predicted labels, and each column represents
the true labels. Diagonal elements display the number
of correct predictions for each class, with most classes
achieving a perfect score of 1.00, indicating high ac-
curacy. The exception is the letter ”KHAA,” which
shows a minor misclassification rate, yielding an ac-
curacy of 0.97.
KDIR 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
184

Figure 4: Confusion matrix after training the model for 400
epochs.
4.2 Training and Validation
Performance
The training and validation performance metrics for
the Arabic Sign Language recognition model exhibit
considerable improvements over 400 epochs. The
graphs in Figure 5 illustrate decreasing trends in box,
object, and classification losses, suggesting effective
learning. Both precision and recall approach 1.0, indi-
cating high accuracy and completeness in predictions.
Mean average precision (mAP) metrics, calculated at
IoU thresholds of 0.5 and 0.5:0.95, indicate excellent
precision across a range of IoU values, further con-
firming the model’s reliability in recognizing Arabic
sign language gestures.
As shown in Table 2, the evaluation metrics for
the Arabic Sign Language Dataset demonstrate the
model’s robust performance across 28 classes. The
dataset contains 891 images per class, with an av-
erage precision of 0.981, recall of 0.998, mAP@50
of 0.980, and mAP@50-95 of 0.890. While most
classes, such as ”ALIF” and ”BAA,” achieved near-
perfect metrics, certain classes, such as ”QAAF,”
showed lower precision (0.596) and mAP@50-95
(0.540), highlighting areas for improvement. These
results indicate the model’s effectiveness in recogniz-
ing Arabic sign language gestures, though some chal-
lenges remain for specific classes with lower perfor-
mance.
4.3 Evaluation Curves
The model’s classification performance is detailed
through several evaluation curves, as depicted in Fig-
ure 6:
• (a) Recall-Confidence Curve: Recall remains
high across all confidence levels, suggesting
Table 2: Performance Metrics for Arabic Sign Language
Classes.
Class Images Instan-
ces
Preci-
sion
Recall mAP@
50
mAP@
50-95
all 891 870 0.981 0.998 0.980 0.890
ALIF 891 29 1.000 0.964 0.995 0.802
BAA 891 28 0.997 1.000 0.995 0.882
TA 891 30 0.996 1.000 0.995 0.896
THA 891 30 0.995 1.000 0.995 0.924
JEEM 891 30 0.996 1.000 0.995 0.872
HAA 891 30 0.997 1.000 0.995 0.869
KHAA 891 30 0.965 0.967 0.948 0.812
DELL 891 30 0.996 1.000 0.995 0.897
DHELL 891 32 0.996 1.000 0.995 0.910
RAA 891 32 0.999 1.000 0.995 0.915
ZAY 891 31 0.997 1.000 0.995 0.914
SEEN 891 33 0.995 1.000 0.995 0.935
SHEEN 891 34 0.998 1.000 0.995 0.931
SAD 891 35 0.998 1.000 0.995 0.862
DAD 891 35 0.997 1.000 0.995 0.942
TAA 891 33 0.997 1.000 0.995 0.951
DHAA 891 31 0.997 1.000 0.995 0.954
AYN 891 30 1.000 1.000 0.995 0.900
GHAYN 891 31 0.997 1.000 0.995 0.936
FAA 891 31 0.996 1.000 0.995 0.916
QAAF 891 31 0.596 1.000 0.613 0.540
KAAF 891 31 0.996 1.000 0.995 0.917
LAAM 891 31 0.995 1.000 0.995 0.936
MEEM 891 31 0.995 1.000 0.995 0.922
NOON 891 30 0.998 1.000 0.995 0.903
HA 891 30 0.996 1.000 0.995 0.874
WAW 891 31 0.996 1.000 0.995 0.918
YA 891 30 0.997 1.000 0.995 0.900
Avg. 891 60 0.981 0.998 0.980 0.890
Figure 5: Training and validation metrics over 400 epochs.
that the model consistently identifies relevant in-
stances.
• (b) F1-Confidence Curve: The high F1 score in-
dicates a balanced performance between precision
and recall across various confidence thresholds.
• (c) Precision-Confidence Curve: Precision is
maintained at high levels for most confidence val-
ues, indicating that the model’s predictions are
highly accurate.
• (d) Precision-Recall Curve: A strong relation-
ship between precision and recall is observed,
with an mAP of 0.980 at IoU=0.5, demonstrating
the model’s effectiveness in accurately detecting
Real-Time Arabic Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv5
185

Figure 6: Evaluation curves for the Arabic Sign Language
recognition model, showing (a) Recall-Confidence, (b) F1-
Confidence, (c) Precision-Confidence, and (d) Precision-
Recall.
and classifying Arabic sign language gestures.
4.4 Model Interface
The Arabic Sign Language recognition model, trained
using Python programming, is designed to detect and
classify gestures from both hands simultaneously, as
illustrated in Figure 7. The interface of the model
emphasizes the need for adequate lighting and high-
quality camera resolution to ensure precise detection
and classification of hand gestures. These factors
are crucial for capturing clear and detailed images,
which significantly enhance the model’s accuracy, as
reflected in the confusion matrix and other evaluation
metrics.
Figure 7: Model Interface.
5 CONCLUSION
This study developed an Arabic Sign Language
recognition model using the YOLOv5 architecture,
made for real-time classification of Arabic alphabets
through hand gestures. The model achieved high ac-
curacy, by achieving nearly 100% on precision, recall,
and mAP metrics, particularly at an IoU threshold of
0.5. The evaluation curves, confusion matrix, and
training metrics further support the model’s robust-
ness and reliability in recognizing Arabic sign lan-
guage.
The developed system holds potential for applica-
tions in sign language translation, educational tools,
and accessibility technologies for the deaf and hard-
of-hearing community. Future improvements may
involve augmenting the dataset with more diverse
hand shapes and backgrounds to further enhance the
model’s generalizability. Additionally, exploring ad-
vanced versions of YOLO or other deep learning ar-
chitectures could further optimize performance for
real-world applications. This work marks a signif-
icant step in developing accessible tools for Ara-
bic sign language communication, enhancing under-
standing and fostering better connections within the
community.
REFERENCES
Abdel-Fattah, M. A. (2005). Arabic sign language: A per-
spective. The Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Edu-
cation, 10(2):212–221.
Al Ahmadi, S., Mohammad, F., and Al Dawsari, H. (2024).
Efficient yolo based deep learning model for arabic
sign language recognition. Unpublished Manuscript
or Add Specific Journal.
Al-Qurishi, M., Khalid, T., and Souissi, R. (2021). Deep
learning for sign language recognition: Current tech-
niques, benchmarks, and open issues. IEEE Access,
9:126917–126951.
Al-Shamayleh, A. S., Ahmad, R., Jomhari, N., and
Abushariah, M. A. M. (2020). Automatic arabic
sign language recognition: A review, taxonomy, open
challenges, research roadmap and future directions.
Malaysian Journal of Computer Science, 33(4):306–
343.
Alaftekin, M., Pacal, I., and Cicek, K. (2024). Real-time
sign language recognition based on yolo algorithm.
Neural Computing and Applications, 36:7609–7624.
Alharthi, N. M. and Alzahrani, S. M. (2023). Vision
transformers and transfer learning approaches for ara-
bic sign language recognition. Applied Sciences,
13(21):11625.
Almasre, M. A. and Al-Nuaim, H. (2016). Recognizing
arabic sign language gestures using depth sensors and
KDIR 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
186

a ksvm classifier. In 2016 8th Computer Science and
Electronic Engineering (CEEC), pages 146–151.
Aly, S. and Mohammed, S. (2014). Arabic sign language
recognition using spatio-temporal local binary pat-
terns and support vector machine. In Hassanien, A. E.,
Tolba, M. F., and Azar, A. T., editors, Advanced Ma-
chine Learning Technologies and Applications, vol-
ume 488 of Communications in Computer and Infor-
mation Science, pages 95–102. Springer, Cham.
Arabic Sign Language ArSL dataset (2022). Arabic sign
language arsl dataset. Kaggle.
Duwairi, R. M. and Halloush, Z. A. (2022). Automatic
recognition of arabic alphabets sign language using
deep learning. International Journal of Electrical &
Computer Engineering, 12(3).
Jocher, G. et al. (2020). Yolov5 by ultralytics. https://github.
com/ultralytics/yolov5.
Manning, C. and Sch
¨
utze, H. (1999). Foundations of Statis-
tical Natural Language Processing. MIT Press.
Ningsih, M. R., Nurriski, Y. J., Sanjani, F. A. Z., Al Hakim,
M. F., Unjung, J., and Muslim, M. A. (2024). Sign
language detection system using yolov5 algorithm to
promote communication equality people with disabili-
ties. Scientific Journal of Informatics, 11(2):549–558.
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., and Farhadi, A.
(2015). You only look once: Unified, real-time ob-
ject detection.
Shanmugamani, R. (2018). Deep Learning for Computer
Vision. Packt Publishing.
Suliman, W., Deriche, M., Luqman, H., and Mohandes, M.
(2021). Arabic sign language recognition using deep
machine learning. In 2021 4th International Sym-
posium on Advanced Electrical and Communication
Technologies (ISAECT), pages 1–4.
Tao, W., Leu, M. C., and Yin, Z. (2018). American sign lan-
guage alphabet recognition using convolutional neural
networks with multiview augmentation and inference
fusion. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelli-
gence, 76:202–213.
Tharwat, G., Ahmed, A. M., and Bouallegue, B. (2021).
Arabic sign language recognition system for alphabets
using machine learning techniques. Journal of Elec-
trical and Computer Engineering, 2021(1):2995851.
Zakariah, M., Alotaibi, Y. A., Koundal, D., Guo, Y.,
and Elahi, M. M. (2022). Sign language recogni-
tion for arabic alphabets using transfer learning tech-
nique. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience,
2022(1):4567989.
Real-Time Arabic Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv5
187
