
Comparative Analysis of Large Language Models for Automated Use
Case Diagram Generation
Nikhil Krishnan G S
a
, Ambadi S
b
and M G Thushara
c
Department of Computer Science and Applications, Amrita School of Computing, Amritapuri, India
Keywords:
UML, Use Case Diagram, LLM, Automating UML, Automation.
Abstract:
This study explores the use of Large Language Models in automating the process of generating use case
diagrams from software requirements written in natural language, ensuring both syntactic correctness and
semantic accuracy. The proposed methodology involves selecting a few prominent LLMs, preparing standard-
ized inputs, and assessing outputs based on their syntactic and semantic correctness, and relationship mapping.
Models were compared using a rigorous error analysis framework to identify strengths and limitations of the
models. Among the tested models, gemma2 achieved the best average performance. This research contributes
to advancing automated requirements processing, offering a scalable solution for software engineering work-
flows.
1 INTRODUCTION
Requirements engineering is the very first step in soft-
ware development which defines b oth the functional
and non-functio nal specifications of a software sys-
tem. These specification s are usually docu mented in
a Software Requirements Specifications (SRS) do c u-
ment. This document helps to translate stakehold er
expectations into the technical implementation of the
software and guides the development, testing, and val-
idation processes. I n the requirements, use case d ia -
grams play an important role. It visually represents
the interaction between users (actors) and the system
(use cases), makin g the requireme nts clear to both
technical and non-technical stakeholders and convey-
ing the software system’s expe cted behavior across
development teams.
Manually creating these use case diagrams is a
time-consuming task, particularly for complex soft-
ware systems with multiple actors and use ca ses
(Elallaoui et al., 2018). This of te n leads to inconsis-
tency issues, as high skill and attention to detail are re-
quired to m aintain uniformity in notations and struc-
tures in all the diagrams (Nair and T hushara, 2 024a).
In ad dition, manually created diagrams are prone to
human errors, such as n eglected relationships or mis-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-8538-2372
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-3839-5490
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8325-1491
interpreted use cases, w hich will affect the quality of
the SRS document (Nair an d Thushara, 2024b). Up-
dating the dia grams to add any new change in require-
ment is a labo r-intensive task and can introduce fur-
ther inconsistencies leading to scalability issues. D ue
to these drawbacks with the manual creation of dia-
grams, automating the proc e ss is gaining significant
attention, to streamline development and reduce error
(Elallaoui et al., 2018).
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a g ood
tool for automating the generation of use case
diagrams from natural language specifications
(Alessio et al., 2024) (Jeong, 2024). PlantUML
compiler allows for the generation of UML diagr ams
from PlantUML code. Bu t writing PlantUML code
manually is a time-consuming and error-prone
process (Alessio et al., 2024). LLMs when trained
on specific datasets containing both text and code,
become capable of generating PlantUML syntnax
from functional requirements (Soudani et al., 2024).
However, current LLMs, especially general-purpose
ones, often produce output with syntactic or semantic
errors, necessitating manual corrections for precise
executable code (Xie et al., 2023).
This study is motivated by the need for an auto-
mated and accurate generation of use case diagrams
from functional requirements, with minima l manual
intervention. By evaluating multiple base LLM s, this
research aims to identify which models perform be st
G S, N. K., S, A. and Thushara, M. G.
Comparative Analysis of Large Language Models for Automated Use Case Diagram Generation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013594700004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 2, pages 465-471
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
465

in generating error-free PlantUML code for use case
diagrams. This analysis will focus on error classi-
fication, particularly syntactic and sema ntic errors,
and determine the suitability of eac h model for fur-
ther fine-tuning. Identifying an optimal base model
with fewer initial errors will reduce the effort required
in post-genera tion correction and enhance the viabil-
ity of automated UML generation in both educ ational
and software development contexts.
The paper is structur ed as follows: Sectio n II re-
views related work in requirements engineering and
automated UML generation, focusing on advances in
LLM-driven code generation. Section III details the
methodology, includ ing environment setup, model se-
lection, input data preparation, a nd evaluation met-
rics. Section IV presents the results, analyzing mode l
performance based on error ra te s and code quality.
Section V explains how the models were evaluated
and the criteria that led to determining the best LLM
model. Finally, Section VI concludes with in sig hts
from this evaluation and discusses potential directions
for future research, including model fine-tuning for
improved accuracy in UML generation.
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Automated Requirements
Processing
The process of automating the generation of
UML diagrams and other structural formats
(Vemuri et al., 20 17) from software requirements
has been explored before. Previous works uti-
lized rule-based and NLP-based methods to
interpret the requirem ents (Veena et al., 2018)
(Veena et al., 2019). These approaches relied on
syntactic and semantic parsing to identify the
actors and use cases in the functional req uire-
ments. But the results generated often require
manual corrections (Nair and Thushara, 2024 b)
(Nair and Th ushara, 2024 a). More recent approaches
leverage machine learnin g models, but this requires
substantial doma in-specific training data to gen-
erate results with accuracy (Ahmed et a l., 2022).
Transforming UML diagrams from one type to
another has also been investigated, such as the work
on deriving activity diagrams from Java execution
traces (Devi Sree and Swaminathan, 2018) and trans-
forming sequ ence diagrams into activity diagram s
(Kulkarni and Srinivasa, 2021).
2.2 Use of Large Language Models in
Software Engineering
Studies (Alessio et al., 2024) have shown that LLMs
can translate descriptions in natural language into
code snippets and other meaningful structural rep-
resentations. Current LLMs like GPT and Codex
struggle with syntax accuracy and specific domain
requirements, often generating inconsistent results
(Xie et al., 2023). Research in this d omain shows a
need for fine-tuning LLMs to g enerate reliable re-
sults containing f ewer errors (Jeong, 2024). A ddi-
tionally, fram eworks leveraging retrieval-augmented
generation (RAG)-based approa ches have be e n ap-
plied to teaching U ML diagram generation effec-
tively (Ar dimento et al., 2024). Recent technical ad-
vancements also highlight efficient LLM models
that are capable of functioning on edge devices
(Abdin et al., 2024).
2.3 Error Analysis in LLM-Generated
Code
Identify ing errors and correcting them is a critical
step in evaluating the outputs genera te d by LLMs
for software e ngineering applications. Earlier stud-
ies have identified some common error types, such
as inconsistent semantics a nd misinterpreted require-
ments. Correction after generating results and fine-
tuning in the specific domain are two techniques that
have been proposed to address these issues. Recent
research de monstrates how graph transformation ap-
proach e s (Anjali et al., 2019) can mo del and analyze
UML diagrams effectively (Hachichi, 2022). Further-
more, evaluating the effectiveness of LLMs in gener-
ating UM L diagr ams has been explored, with notable
efforts in class diagram generation for comparative
analysis (De Bari, 2 024).
There is limited research on comparing LLMs
specifically for PlantUML syntax generation. This
gap stresses the need for comprehen sive error analysis
to determine the most suitab le model for auto mated
use case diagram generation.
ROUGE and BLUE are two conventional
referenc e -based metrics for evaluating LLMs. These
metrics are not preferred in this research as they have
relatively low correlation with human judg ements,
especially in open -ended generation task s. While
these metrics are good for evaluating shor t and
generic outputs, they fail to evaluate coherence and
relevance which are cr itical for human-like judge-
ments. On e solution to overcome these shortcomings
is to use LLM as a judge fo r evaluation. GEval
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
466

(Liu e t al., 2023) is a framework that uses LLM s
with chain-of-thoughts to evaluate the quality of
LLM-generated results. By taking natural language
instruction that defines the evaluation criteria as
prompt, G-Eval uses an LLM to generate a chain-
of-tho ughts of detailed evaluation steps. The prompt
along with the generated chain-of-thoughts is used to
evaluate the results.
2.4 Summary and Research Gap
While prior work has explored LLMs in requ ire-
ments processing and code generation, few studies
have focused on systematically comparing models for
use c ase diagram ge neration with PlantUML syntax
(Alessio et al., 2024). Our study addresses this gap b y
evaluating multiple lig htweight LLMs (low parameter
LLMs) installed in local ma c hines to identify those
with the lowest error rate s, aiming to reduce the need
for manual c orrections and enhance the automation
potential of UML generation tools in future works.
3 METHODOLOGY
This methodology aims to systematically evaluate and
compare the effectiveness of different Large Lan-
guage Models (LLMs) in generating accura te Plan-
tUML syntax directly from natural language require-
ments. Given the increasing use of LLMs in au-
tomating coding and diagramming tasks, understand-
ing their strength s and limitations in this specific con-
text is essential. This analysis seeks to identify which
models produce syntactically correct and semanti-
cally meanin gful use case diagrams, with minimal er-
rors, thus reducing the need for manual corrections.
By cond ucting a comparative analysis, we aim to de-
termine the m ost suitable LLM f or auto mating use
case diagram generation, particularly in terms of ac-
curacy, efficiency, and reliability.
The methodology is structured into key stages as
shown in figure 1: model selection, data preparation,
input specification , error classification, and evaluation
and analysis. E ach stage plays a vital role in ensur-
ing a comprehensive and fair comparison of the mod-
els. T his structured approach helps in identifying the
best-performing model and highlights common areas
where improvement is required.
3.1 Model Selection
The very first step in the methodology was to se-
lect a set of Large Language Models for evaluation.
We chose the models based on several factors includ-
ing their capability in generating struc tured code out-
puts, understanding natural language inputs, and ac-
cessibility. The focus was on selecting models tha t
were small in size, had smaller par ameters, and were
resource- efficient so that the mode ls could be run in
local machines. Each one of the selected models ha s
varied parameters and a rchitecture, which allows us
to observe the d ifferences in code quality, syntax ac-
curacy, and reliability across diverse configurations.
This selection process aims to ensure a well-round ed
compariso n of lightweight base mo del LLMs, to de-
termine which could best translate n atural language
requirements into accurate PlantUML syntax.
3.2 Data Preparation
To assess each model’s perfo rmance, a functional
requirements dataset that could efficiently test each
model’s capabilities had to be prepar e d. We prepared
a set of specifications based on common use case sce-
narios, including data processing, user administration,
and e-commerce. Th e requirements were annotated
wherever possible to emphasize specific components
such as actors, actions an d system interactions. This
gives the models a structured input. We pre-processed
the data before inpu tting it into the models to make the
wording more uniform and eliminate a mbiguities in
requirements caused by any technical jargon presen t
in the data, which th e model could potentially misin-
terpret. Because of this uniform formatting, it became
easier to evaluate each model’s answer correctness.
3.3 Input Specification
The LLM models receive a CSV file as input contain-
ing ten software fu nctional requirements, each rep-
resenting a software system. These functional re-
quirements are added as plain text with a standard-
ized prompt design e d to guide the mo del in gener-
ating PlantUML code for use case diagram s. The
prompt contains the desired output for mat, including
the proper semantics of ”include” and ”extend” rela-
tionships and specifies tha t the output should contain
PlantUML code with valid syntax, without any ad di-
tional explanations or comments that could cause syn-
tax errors. The same prompt is used for every LLM
model and input set to guarantee uniformity in input
interpretation.
3.4 Evaluation Metrics
Answer correctness metric is used for evaluation. It is
a numeric a l scor e between 0 and 1, 0 being the least
Comparative Analysis of Large Language Models for Automated Use Case Diagram Generation
467
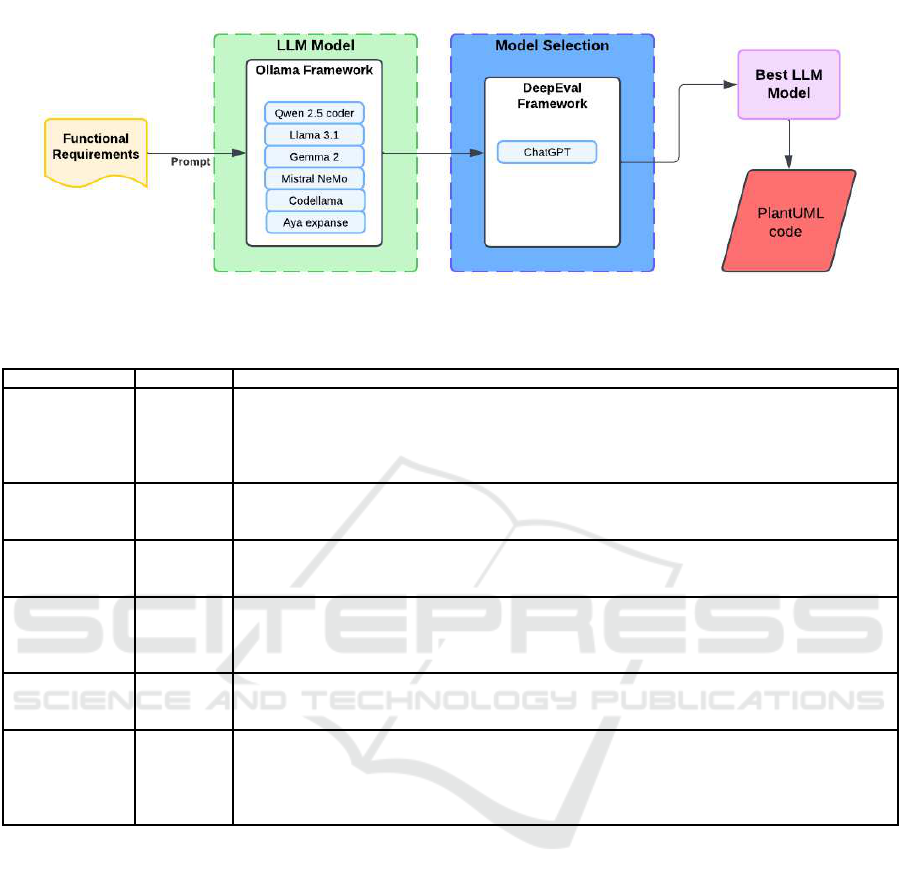
Figure 1: Structural Flow of the Proposed Model.
Table 1: Overview of Selected LLM Models for Use Case Diagram Generation.
Model Parameters Description
Qwen 2.5-coder 7B Qwen2.5-Coder (Hui et al., 2024) is an advanced version of the Qwen series of large language
models (formerly CodeQwen), offering notable improvements in code generation, r easoning,
and bug fixing over its predecessor, CodeQwen1.5. Built on the Qwen2.5 foundation, it is
trained on a vast dataset of 5.5 tri llion tokens, which includes source code, text-code grounding,
and synthetic data. It also supports long-context inputs of up to 128K tokens.
Gemma 9B Google’s lightweight Gemma2 (Team et al., 2024) models build on Gemini research, with en-
hanced capabilities in language understanding, suitable for tasks like question-answering, sum-
marization, and reasoning.
Llama 3.1 8B Meta’s Llama 3 (Dubey et al., 2024) improves over Llama 2 in coherence and contextual under-
standing, excelling in creative writing, coding, and conversational AI. Llama 3.1 is an upgraded
version that improves reasoning and context size.
Code Llama 7B Code Llama (Roziere et al., 2024) is a code generation model built on Llama 2, designed to
enhance developer workflows and assist in learning programming. It can generate both code
and natural language explanations, supporting popular programming languages like Python,
C++, Java, PHP, Typescript, C#, and Bash.
Mistral NeMo 12B A 12B model by Mistral AI with NVIDIA, NeMo offers a 128k token context window, support-
ing multilingual applications in English, French, German, and more. The model is optimized
for function calling and is similar to Mistral 7B.
Aya Expanse 8B Aya Expanse, developed by Cohere For AI, is a family of multili ngual large language mod-
els designed to close language gaps and improve global communication. It supports over 23
languages, including Arabic, Chinese, English, Hindi, and Spanish. The models use advanced
techniques like supervised fine-tuning, multilingual preference training, and model merging to
enhance performance across various linguistic tasks.
correct an d 1 being the most correct answer. Th e cor-
rectness metric involves comparing the LLM’s result
with the expected result based on any c ustom evalua-
tion criteria define d by the user. The evaluation crite-
ria involves:
• Syntax Correctness: This criter ia checks if the
generated PlantUML code has syntax errors and
if it will compile successfully.
• Comments and Descriptions: Any additional
comments o r descriptions included with the Plan-
tUML code will cause a syntax error. This criteria
checks if there are any comments or descriptions
in the result.
• Actor Count: To confirm that ther e ar e the same
number of actors in the exp ected and actual out-
puts.
• Use Case Correspondence: This criterion en -
sures that the generated output matches the ex-
pected output.
• Extend and Include Relationships: To confirm
that the relationships are accurately implemented
and positioned in the diagram.
• Hallucination Detection: To look for any extra
created content that does not fit the specified func-
tional requirements.
These me trics provided a balanced assessment
framework, helping to capture both the precision and
usability of each model’s output.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
468
4 RESULTS
Figure 2: Evaluation results.
The identical set of carefully chosen requirements
was fed into each model for testing, and the output
produced by PlantUML was compared to our pre-
determined metrics. We ensur ed that every output
complied with PlantUML requirements by using au-
tomated methods to verify synta x accuracy. In or-
der to confirm semantic accuracy, we also carried out
a manual examination in wh ich we evaluated if the
relationships and elements were a ppropriately repr e-
sented by compar ing the created diagrams with the
original cr iteria.
After testing, we ranked th e models accordin g to
how well th ey perfo rmed across all measu res. The
inputs, actual outputs, expecte d outputs, correctness
scores and corr ectness reasons for each LLM can
be viewed here - https://github.com/Mandalorian-
way/Comparative-Analysis-of-Large-Language-
Models-Result. As seen in table 2, models with
frequent errors or ambiguou s outputs were scored
worse, whereas those with higher syntax and se-
mantic accuracy and lower err or rates were ranked
favorably. We were able to determine each model’s
advantages and disadvantages as well as which
LLMs are best at producing pre cise UML dia grams
straight from requirements thanks to this comparative
analysis.
5 EVALUATION
The G-Eval correctness score is calculated by using a
scoring fu nction that combines the prompt, a chain-
of-tho ught and the input context, along with the gen-
erated plantUML code. The evaluation process in-
volves generating a set of scores based on the evalu-
ation criteria we provide. The LLM evaluates the re-
sults and produces a probability for each score, and
the final score is calculated as a weig hted sum of
the probabilities and their corresponding score values.
This approach normalizes the scores and provides a
more continuous, fine-grained score.
The G-Eval correctness score is calculated as:
score =
n
∑
i=1
p(s
i
) × s
i
Where:
• p(s
i
) is the probability of the score s
i
being as-
signed by the LLM.
• s
i
is one of the possible discrete scores in the pre-
defined set of scores for evaluation criteria.
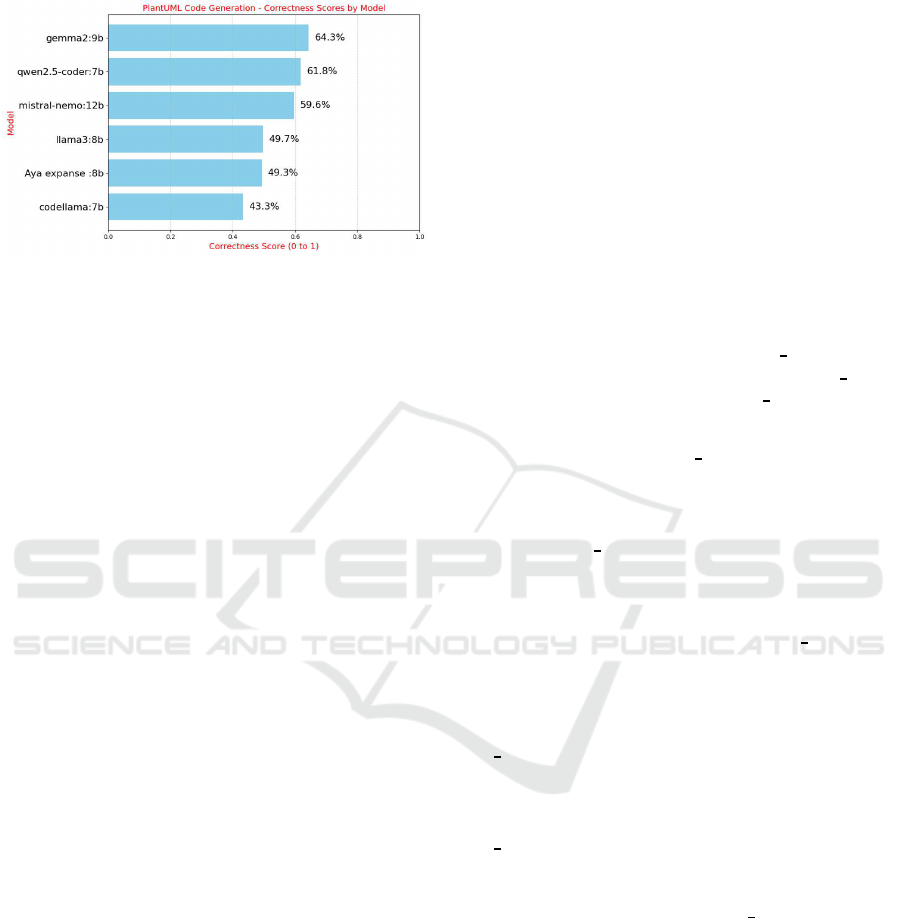
On examining the evaluation results, it is ob-
served that Gemma2:9b-instruct-q6
K performed
the best with Qwen2.5 -coder:7b-instruct-q6
K and
Mistral-Nemo:12b-instruct-2407-q6 K right behind
the model, having comp arable scores.
Gemma2:9b-instruct-q6
K perform ed well in
modeling use cases but some relationships were
mapped incorrectly, missed some functional require-
ments, and had mismatched u se case names. Aya-
Expanse:8 b-q6
K received its score due to the misuse
of
<include>
and
<extend>
relationships, logical in-
consistencies in connecting actors and use cases, and
inclusion of unnecessary text and comments that com -
promises syntax . Llama3:8b-instruct-q6
K correctly
modeled most use cases but had u sed relationships in-
correctly, added unnece ssary comments, and omitted
or misrepresented requireme nts, with occasional hal-
lucinated conten t. Mistral-Nem o:12b-instruct-2407-
q6
K followed basic syntax well, but had issues with
<include>
and
<extend>
relationships, missing or
misrepresented requiremen ts, and logical errors in
mapping r e la tionships. Qwen2.5-cod e r:7b-instru ct-
q6
K did well in modeling use cases but faced sim-
ilar issues with incorrect relationship usage, miss-
ing connections, and redundant labels in relation-
ships. Codellama:7b-instruct- q6
K struggled with
similar issues, including incorrect use of relation-
ships, logical errors in actor-to-use case connections,
and extra text before or after the PlantUML code.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Automating the generation of UML diagrams holds a
significant importance in reducing manual effort and
improving the accuracy of the diagrams. Using Large
Comparative Analysis of Large Language Models for Automated Use Case Diagram Generation
469
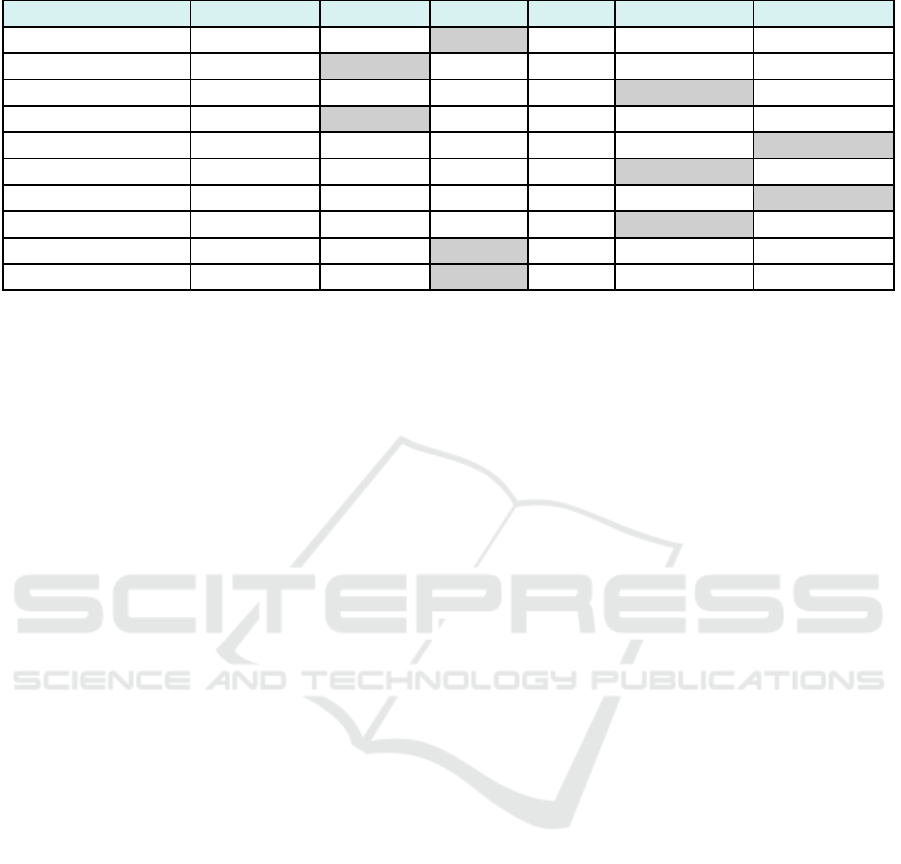
Table 2: Answer correctness score.
Functional Requirements Aya expanse :8b codellama:7b gem ma2:9b llama3:8b mistral- nemo:12b qwen2.5-cod er:7b
Application 1 0.524 0.314 0.864 0.003 0.577 0.722
Application 2 0.379 0.77 0.76 0.617 0.74 0.747
Application 3 0.656 0.647 0.448 0.655 0.732 0.624
Application 4 0.644 0.786 0.627 0.78 0.665 0.699
Application 5 0.387 0.308 0.47 0.517 0.469 0.646
Application 6 0.461 0.136 0.447 0.54 0.665 0.575
Application 7 0.465 0.271 0.406 0.397 0.366 0.625
Application 8 0.436 0.36 0.653 0.373 0.763 0.405
Application 9 0.479 0.382 0.865 0.484 0.532 0.665
Application 10 0.495 0.351 0.889 0.602 0.455 0.475
Language Models f or code generation is a growing
area of research in recent times. In this research, we
have explored the capability of LLMs to create these
UML diagrams. The objective of this research was to
compare a few base LLMs to find out which one of
them performed be st fo r generating PlantUML code
for use case diagrams.
From this research, we have identified that on
average, gemma2 outperformed the other models in
generating PlantUML cod e with least errors. How-
ever, from our ob servations, we see that even though
gemma2 has the be st average score, it did no t perform
the best for every input. T he results produced still has
a few syntactic and semantic inaccurac ie s. This is be-
cause base LLMs do not have any understanding of
the domain and will generate inconsistent r esults.
In order to improve the pe rformance of these mod-
els in this domain, extensive fine- tuning is required.
A set of diverse functional require ments can be used
for fin e-tuning to create a robust mo del capable of
handling complex functional requirements. Retirieval
Augmente d Generation can also be used to provide
context on UML syntax to the LLM. Future works
can use human feedback loops to iteratively refine the
results and improve the semantic quality of the gener-
ated results. Using com plex inputs for testing, includ-
ing ambiguous a nd incomplete inputs, can help assess
the model’s adaptability to d ifferent patters of inputs.
This refined model can reduce the human effort re-
quired in the generation of UML diagrams. The final
version of this improved model can be integrated into
software development pipelines to save the time an d
effort of software analysts and architects.
REFERENCES
Abdin, M., Aneja, J., Awadalla, H., Awadallah, A., Awan,
A. A., Bach, N., Bahree, A., Bakhtiari, A., Bao, J.,
Behl, H., et al. (2024). Phi-3 technical r eport: A
highly capable language model locally on your phone.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.14219.
Ahmed, S., Ahmed, A., and Eisty, N. U. (2022). Auto-
matic transformation of natural to unified modeling
language: A systematic review. In 2022 IEEE/ACIS
20th International Conference on Software Engineer-
ing Research, Management and Applications (SERA),
pages 112–119. I EEE.
Alessio, F., Sallam, A., and Chetan, A. (2024). Model gen-
eration from requirements with llms: an exploratory
study-replication package.
Anjali, S., Meera, N. M., and T hushara, M. (2019). A
graph based approach for keyword extraction from
documents. In 2019 Second International Confer-
ence on Advanced Computational and Communica-
tion Paradigms (ICACCP), pages 1–4. IEEE.
Ardimento, P., Bernardi, M. L ., and Cimitile, M. (2024).
Teaching uml using a rag-based llm. In 2024 Interna-
tional Joint Conference on Neural Networks ( IJCNN),
pages 1–8. IEEE.
De Bari, D. (2024). Evaluating large language models
in software design: A comparative analysis of uml
class diagram generation. PhD thesis, Politecnico di
Torino.
Devi Sree, R. and Swaminathan, J. (2018). Construction of
activity diagrams from java execution traces. In Am-
bient Communications and Computer Systems: RAC-
CCS 2017, pages 641–655. Springer.
Dubey, A., Jauhri, A ., Pandey, A., Kadian, A ., Al-Dahle,
A., Letman, A., Mathur, A., Schelten, A., Yang, A.,
Fan, A., et al. (2024). The llama 3 herd of models.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.21783.
Elallaoui, M., Nafil, K., and Touahni, R. (2018). Automatic
transformation of user stories into uml use case dia-
grams using nlp techniques. Procedia computer sci-
ence, 130:42–49.
Hachichi, H. (2022). A graph transformation approach
for modeling uml diagrams. International Journal of
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
470

Systems and Service-Oriented Engineering (IJSSOE),
12(1):1–17.
Hui, B., Yang, J., Cui, Z., Yang, J., Liu, D., Zhang, L .,
Liu, T., Zhang, J., Yu, B., Lu, K., et al. (2024).
Qwen2. 5-coder technical report. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2409.12186.
Jeong, C. (2024). Fine-tuning and util ization meth-
ods of domain-specific llms. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2401.02981.
Kulkarni, D. R. and Srinivasa, C. (2021). Novel approach
to transform uml sequence diagram to activity dia-
gram. Journal of University of Shanghai f or Science
and Technology, 23(07):1247–1255.
Liu, Y., Iter, D., Xu, Y., Wang, S., Xu, R., and Z hu, C.
(2023). G-eval: Nlg evaluation using gpt-4 with better
human alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.16634.
Nair, R. P. and Thushara, M. (2024a). Hybrid actor-action
relation extraction: A machine learning approach.
Procedia Computer Science, 233:401–410.
Nair, R. P. and Thushara, M. (2024b). Investigating nat-
ural language techniques for accurate noun and verb
extraction. Procedia Computer Science, 235:2876–
2885.
Roziere, B., Gehring, J., Gloeckle, F., Sootla, S., Gat, I.,
Tan, X. E., Adi, Y., Liu, J., Sauvestre, R., Remez, T.,
et al. (2024). Code llama: Open foundation models
for code.
Soudani, H., Kanoulas, E., and Hasibi, F. (2024). Fine tun-
ing vs. retrieval augmented generation for less popular
knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2024 Annual In-
ternational ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and
Development in Information Retrieval in the Asia Pa-
cific Region, pages 12–22.
Team, G., Riviere, M., Pathak, S., Sessa, P. G. , Hardin, C.,
Bhupatiraju, S., Hussenot, L., Mesnard, T., Shahri-
ari, B., Ram´e, A., et al. (2024). Gemma 2: Improv-
ing open language models at a practical size. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2408.00118.
Veena, G., Gupta, D., Lakshmi, S., and Jacob, J. T. (2018).
Named entity recognition in text documents using a
modified conditional random field. In Recent Find-
ings in Intelligent Computing Techniques: Proceed-
ings of the 5th ICACNI 2017, Volume 3, pages 31–41.
Springer.
Veena, G., Hemanth, R., and Hareesh, J. (2019). Relation
extraction in clinical text using nlp based regular ex-
pressions. In 2019 2nd International Conference on
Intelligent Computing, Instrumentation and Control
Technologies (ICICICT), volume 1, pages 1278–1282.
IEEE.
Vemuri, S., Chala, S., and Fathi, M. (2017). Automated
use case diagram generation from textual user re-
quirement documents. In 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian
Conference on Electrical and Computer E ngineering
(CCECE), pages 1–4. IEEE.
Xie, D., Yoo, B., Jiang, N., Kim, M., Tan, L ., Zhang, X.,
and Lee, J. S. (2023). Impact of large language models
on generating software specifications. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2306.03324.
Comparative Analysis of Large Language Models for Automated Use Case Diagram Generation
471
