
Exploring Artificial Intelligence's Function in Healthcare: Present
Uses and Prospects
Vaishali S. Katti
1 a
, Pramila R. Gadyanavar
1 b
and Swapnil Takale
2 c
1
Department of CSBS, Kolhapur Institute of Technology's College of Engineering (Autonomous), Kolhapur, India
2
Department of Electronics, SKN Sinhgad College of Engineering Korti, Pandharpur, India
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Reinforcement Learning (RL).
Abstract: By significantly enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of many procedures, artificial intelligence (AI) is
radically changing the healthcare industry. AI technologies are becoming essential to patient care by enabling
better diagnosis and the customization of treatment regimens. By utilizing the power of comprehensive
medical data analysis, these advanced tools enable medical personnel to identify trends, predict results, and
make data-driven decisions. In addition to improving the accuracy of care given, the application of AI in fields
like radiology, surgery, and patient management streamlines operational processes, which improves patient
outcomes. As AI technology develops, it has the potential to significantly alter healthcare procedures both
now and in the near future, creating opportunities for creativity and better health management.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recent advances in machine learning, data analytics,
and computing power have propelled the use of
artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare. AI is a
general term for a variety of technologies that can
mimic human intelligence, allowing systems to
evaluate intricate medical data and support medical
personnel in making defensible decisions. AI
integration is becoming more and more important as
healthcare institutions aim for increased effectiveness
and better patient outcomes.
From improving decision-making to expediting
procedures, artificial intelligence (AI) has profoundly
changed many facets of our life. The use of AI in
healthcare is one of its many uses that is particularly
significant and intimate. It helps with ailment
diagnosis, customized therapy planning, and even
patient survival rate prediction.
In this exploration, we will delve into the different
types of AI utilized in healthcare, their specific
applications, and the advantages they bring to the
field. Additionally, we will consider what the future
may hold for AI in healthcare. You will also find
information about relevant career opportunities and
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-4198-8171
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-0586-918X
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-3636-4450
online courses to help you begin your journey in
applying AI within the healthcare sector.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to improve
patient outcomes and expedite medical procedures,
high-performance medicine is a revolutionary
approach to healthcare. The integration of state-of-
the-art AI technologies in healthcare settings is
examined in this research, with especially given to
their uses in personalized medicine, therapy
optimization, and diagnostics. Across a range of
medical fields, the application of AI techniques, such
as machine learning and data analytics, has
demonstrated considerable promise in enhancing
precision, effectiveness, and predictive capacities. To
fully profit from these technologies, however, issues
like algorithmic bias, data privacy, and ethical
problems must be resolved. In order to create strong
AI-driven healthcare solutions, this analysis
highlights the future paths of AI in high-performance
medicine and promotes interdisciplinary
collaboration. E. J. Topol, (2019)
Katti, V. S., Gadyanavar, P. and Takale, S.
Exploring Artificial Intelligence’s Function in Healthcare: Present Uses and Prospects.
DOI: 10.5220/0013593100004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 2, pages 407-412
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4; ISSN: 3051-7680
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
407

This study utilizes deep learning to classify skin
cancer with accuracy comparable to that of
dermatologists. We trained the model on a sizable
dataset of dermatoscopic pictures using a
convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture in
order to recognize different skin lesions. In addition to
automating the classification process, the suggested
approach reduces human error, improving diagnosis
accuracy. Our findings show that the deep neural
network performs about as well as skilled
dermatologists and surpasses conventional image
processing techniques. The potential of AI-driven
technologies to enhance skin cancer diagnostics,
enable early detection, and eventually improve patient
outcomes is demonstrated in this paper. A. Esteva et
al., (2017).
The integration of big data and machine learning in
healthcare is covered in this paper, with an emphasis
on how these technologies could revolutionize medical
diagnosis and decision-making. It places a strong
emphasis on using deep learning techniques to increase
the predicted accuracy of illness management and
patient outcomes. Machine learning algorithms can
find patterns and insights in large datasets that improve
health monitoring and treatment plans. The report cites
a number of case studies that show how these
technologies not only expedite procedures but also
make it possible to identify illnesses early, which
eventually improves patient care. The results highlight
how crucial it is to implement AI-driven solutions in
order to handle the future complexity of healthcare. Z.
Obermeyer and E. J. Emanuel, (May 2020).
This study examines how machine learning and
artificial intelligence (AI) can be integrated into public
health, highlighting how they might improve medical
diagnosis and decision-making. It talks about how by
extracting patterns and insights from massive datasets,
deep learning algorithms might increase the predictive
accuracy of patient outcomes and illness treatment.
The study uses a number of case studies to show how
AI improves patient care by streamlining hospital
procedures and assisting in early disease identification.
The results highlight how urgently AI-driven solutions
must be implemented in order to handle public health's
growing complexity in the future. R. Shcherbina et al.,
(May 2020).
The integration of machine learning and artificial
intelligence (AI) in healthcare is examined in this
paper, with an emphasis on how these technologies
may improve medical diagnosis and decision-making.
It talks about how deep learning algorithms might
improve the predicted accuracy of patient outcomes
and treatment options by identifying patterns and
insights in massive datasets. A number of case studies
are provided to show how AI improves patient care by
streamlining healthcare procedures and assisting in the
early detection of illnesses. The results highlight the
pressing need for AI-driven solutions to successfully
handle the future complexities of public health while
also foreseeing the potential ethical and societal issues
that may result from their application. J. A. Alpaydin,
(2020).
The dual nature of artificial intelligence (AI) in
healthcare is examined in this essay, with an emphasis
on the possible risks as well as the benefits it offers. It
talks about how AI technology might improve patient
outcomes, expedite processes, and increase diagnostic
accuracy by analyzing massive information and
revealing insights that can be put to use. The study
does, however, also address important issues that could
affect patient care and healthcare access equity, such as
algorithmic bias, data privacy, and ethical
considerations. The conversation ends by urging a fair
approach to the incorporation of AI in healthcare,
stressing the necessity of strong rules and laws to
maximize its advantages while reducing related risks.
D. M. Topol, (2019).
The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI)
applications in healthcare presents a number of
complex issues, which are examined in this study. It
highlights important obstacles such the availability and
quality of data, integration with current healthcare
systems, and the requirement for workforce education
and training. Furthermore, the authors examine ethical
issues that may impede the fair use of AI technologies,
such as algorithmic prejudice and privacy concerns.
The study highlights the significance of tackling these
obstacles in order to fully achieve AI's promise to
improve healthcare delivery and outcomes through
case studies and expert views. The outcomes
demonstrate that in order to create successful plans for
deploying artificial intelligence in the healthcare
industry, stakeholders must work together. J. L. H.
Acar and H. J. Schaal, (2020).
This study investigates the possible effects of
artificial intelligence (AI) on the psychiatric
community, looking at the advantages and
disadvantages of implementing AI. It talks about how
AI can improve patient outcomes through
sophisticated data analysis, increase diagnosis
accuracy, and customize therapy regimens. The
availability and caliber of mental health data,
integration with current clinical procedures, and the
requirement for healthcare professionals to receive
training and education are major obstacles that are also
covered in the study. It also emphasizes the importance
of addressing ethical issues like algorithmic bias and
patient privacy in order to guarantee fair AI use in
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
408
mental health treatment. The results highlight how
crucial it is for stakeholders to work together to create
practical plans for incorporating AI into psychiatric
treatment in order to improve the standard of mental
health services. M. D. O'Reilly et al., (2020)"
3 METHODOLOGY
Artificial intelligence (AI) has greatly changed
various facets of our lives, streamlined processes and
improved the way we make decisions. Although these
systems are designed to replicate human cognitive
skills, they frequently exceed those abilities by
effectively processing large volumes of big data to
identify patterns, anomalies, and trends.
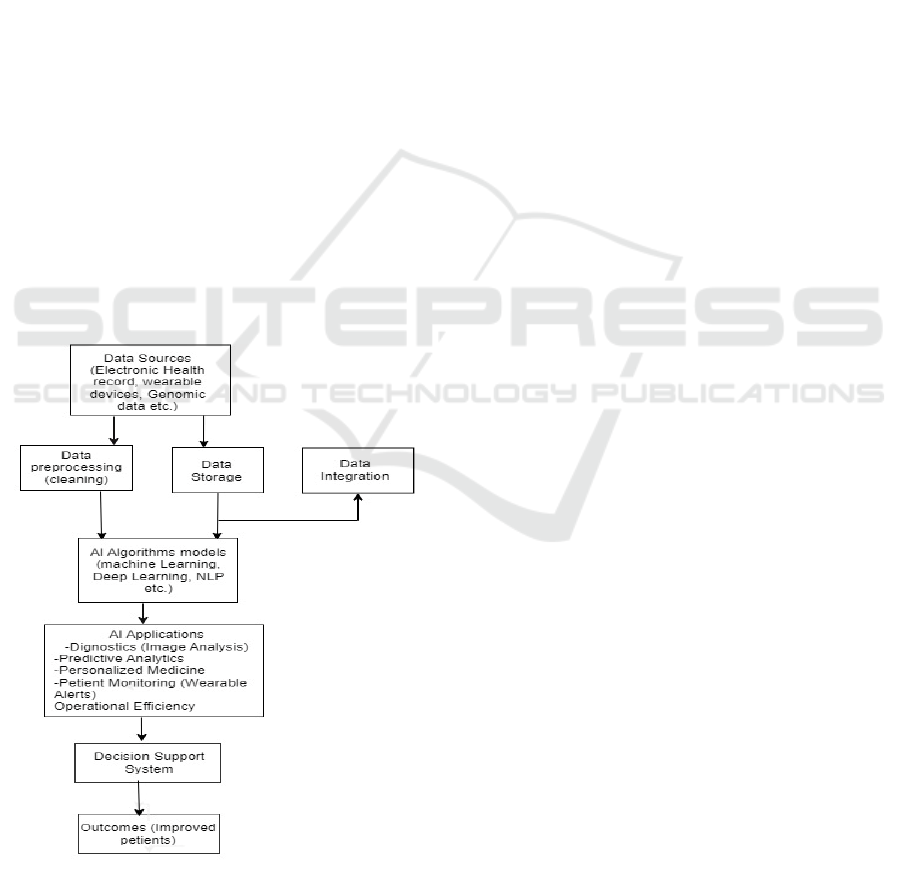
AI opens up numerous possibilities in healthcare,
enabling providers to enhance various medical
processes. For instance, it can assist in diagnosing
diseases and determining optimal treatment plans for
patients with critical conditions such as cancer.
Furthermore, AI-equipped robotic surgical tools can
aid surgeons by minimizing physical tremors and
offering real-time information during procedures.
Figure 1.
3.1 Artificial Intelligence Techniques
Without explicit programming, machine learning
methods allow computers to learn from data and
gradually get better at what they do. They fall into a
number of categories according to how they learn:
3.1.1 Learning Under Supervision
Definition: Labelled data, or input data combined with
the appropriate output, is used to train algorithms.
Typical Algorithms:
Blood pressure levels are one example of a
continuous outcome that can be predicted using linear
regression.
For binary classification tasks, such as identifying
if a patient has a particular disease, logistic regression
is utilized. Trees of Decision: a tree structure that
resembles a flowchart and is utilized for tasks
involving regression and classification. Random
Forests: An ensemble technique that increases
accuracy by combining several decision trees.
3.1.2 Learning Without Supervision:
Definition: Algorithms that recognize patterns or
groupings in data are trained on data that has no
labeled outputs.
Typical algorithms:
The K-means Clustering is a technique used to
segment patients that groups together comparable
data points.
Visualizing the links between data points is made
easier via hierarchical clustering, which creates a tree
of groups.
Analysis of Principal Components (PCA):
preserves variance while reducing the dimensionality
of the data, which aids in feature extraction.
Semi-Supervised Education:
In healthcare, where labelling data can be
expensive, this method improves learning efficiency
by combining a little bit of labelled data with a big
number of unlabelled data.
To increase diagnosis accuracy, for instance, a
small number of labelled patient records are used
alongside numerous unlabelled ones.
3.1.3 Reinforcement Learning
A type of machine learning called reinforcement
learning (RL) teaches an agent to make choices by
acting in a way that maximizes a concept of
cumulative reward. Here is a quick synopsis:
Important Ideas
Agent-A learner or decision-maker who interacts
with their environment is called an agent.
Environment: The setting in which the agent
functions and gets input.
Actions: The decisions the agent makes that have
an impact on the environment.
Exploring Artificial Intelligence’s Function in Healthcare: Present Uses and Prospects
409

State: An illustration of the surroundings at a
specific moment in time. The agent makes decisions
based on the state data.
Reward: A signal of feedback obtained following a
state of action. It shows how successful or unsuccessful
the action was in reaching the objective.
Policy: A method by which the agent decides what
to do next depending on the situation at hand. It may
be stochastic or deterministic.
The value function: which frequently reflects the
anticipated future benefits, calculates how good it is for
the agent to be in a specific state.
Diagram
Initialization of the Learning Process: The agent
begins with a starting policy and may operate
randomly or with prior knowledge.
Interaction: The agent keeps an eye on the
environment's present state or states.
It chooses action (a) based on its policy. The
activity results in a new state (s') for the environment
and a reward (r) for the agent.
Comments: By reinforcing the importance of the
action performed in the particular state, the reward
directs the agent to revise its strategy for subsequent
choices.
3.2 Different Algorithm’s used in
Healthcare Domain
3.2.1 Random Forest Algorithm
A machine learning technique called the Random
Forest Algorithm creates and combines several
decision trees to produce precise forecasts. In a
random forest, each decision tree generates its own
forecast, which is then added together to produce the
outcome. Both classification (category identification)
and regression (number prediction) activities employ
this technique.
Figure 2.
3.2.2 Support vector Machine
Support vector machines, or SVMs, are among the
most popular supervised learning methods for both
regression and classification problems. However, its
primary use is in machine learning to address
categorization issues.
The SVM approach seeks to determine the best line
or decision boundary that might separate n-
dimensional space into classes so that it will be easy to
categorize more data points in the future. This ideal
decision boundary is known as a hyperplane.
SVM chooses the extreme points and vectors in
order to construct the hyperplane. Since these extreme
circumstances are referred to as support vectors, the
technique is called a Support Vector Machine. Look at
the diagram below, which uses a decision boundary or
hyperplane to categorize two different groups.
An example can help explain how the SVM
algorithm operates. Assume we have a dataset with two
features (x1 and x2) and two tags. Examine the picture
below:
Figure 3.
We can easily split these two classes with a
straight line because it is a two-dimensional space.
These classes, however, might be separated by
multiple lines. Examine the picture below:
Figure 4.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
410
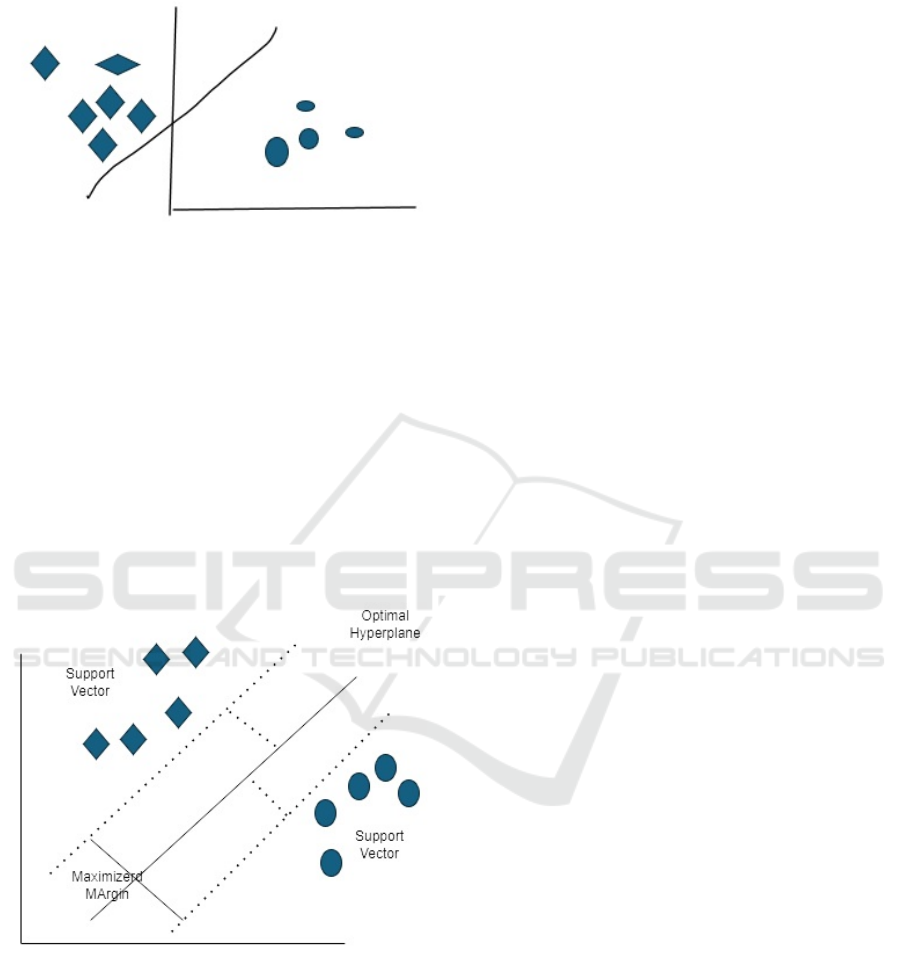
As a result, the SVM method aids in identifying
the optimal line or decision boundary, which is
referred to as a hyperplane. The SVM algorithm
determines the line's closest point between the two
classes. We refer to these sites as support vectors.
Margin is the distance between the vectors and the
hyperplane. And maximizing this margin is SVM's
objective. The ideal hyperplane is the one with the
largest margin.
Algorithm for Support Vector Machines
Since it is a two-dimensional space, we can
simply divide these two classes with a straight line.
However, these classes may be divided by several
lines. Examine the picture below:
Figure 5.
3.3 Current Applications of AI in
Healthcare
3.3.1 Diagnostics
The diagnostic procedure is greatly aided by AI,
especially in fields like medical imaging. Compared
to conventional techniques, deep learning algorithms
are more accurate in identifying abnormalities like
cancer in radiological scans. For example, under
certain situations, AI systems have been
demonstrated to match or even exceed the diagnosis
precision of skilled radiologists (Shcherbina et al.,
2020).
Diagram
Graph TD
A [Patient Data] -->|Input| B [AI Model]
B --> |Analyzes| C [Medical Imaging]
B --> |Analyzes| D [Genetic Data]
B --> |Analyzes| E [Electronic Health Records]
C --> |Real-Time Analysis| F [Diagnosis]
D --> |Real-Time Analysis| F [Diagnosis]
E --> |Real-Time Analysis| F [Diagnosis]
F --> |Feedback| B
Real-time inputs from genetic information,
electronic health records, and medical imaging are
all included in patient data.
Real-time analysis of the input data is done by the
AI model to find trends and abnormalities.
Diagnosis: Based on the analysis, the AI model
offers a diagnosis in real time.
Feedback: The diagnosis is utilized to keep
improving the accuracy of the AI model.
3.3.2 Personalized Medicine
AI plays a key role in creating individualized
treatment plans. AI can assist clinicians in creating
treatment plans that maximize effectiveness and
minimize side effects by analysing data from multiple
sources, such as genetic information, medical history,
and lifestyle factors. In disciplines like oncology,
where therapies can be tailored according to a
patient's tumour’s genetic profile, this strategy has a
particularly significant influence. .
3.3.3 Patient Monitoring and Management
Healthcare professionals can better monitor patients
thanks to AI technologies. Vital signs can be tracked
by wearable technology with AI algorithms, which
can also notify medical professionals of possible
problems before they become serious. In the end, this
proactive monitoring improves patient care by
enabling prompt actions.
3.3.4 Operational Efficiency
Additionally, AI is advancing the simplification of
administrative duties in healthcare facilities.
Healthcare workers can devote more of their attention
to patient care by using automated technologies to
handle patient data administration, billing, and
appointment scheduling more effectively.
3.4 Benefits of AI in Healthcare
1 Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy:
AI increases the accuracy of diagnosis, especially
in complicated cases involving big data sets
2 Increased Efficiency: AI lessens the workload
for healthcare professionals by automating
Exploring Artificial Intelligence’s Function in Healthcare: Present Uses and Prospects
411
repetitive tasks, freeing up more time for patient
care.
3 Bespoke Treatment: Healthcare professionals
can give individualized care plans that are suited
to each patient's needs by using AI-driven
analysis.
3.4.1 Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Notwithstanding its potential, there are several
obstacles to overcome before AI may be used in
healthcare. Data privacy concerns are paramount, as
sensitive patient information must be protected against
breaches. Additionally, the risk of algorithmic bias—
where AI systems may reflect existing biases in the
data—poses ethical dilemmas that need to be
addressed. Furthermore, the integration of AI
technologies requires appropriate regulatory
frameworks to ensure safety and efficiency.
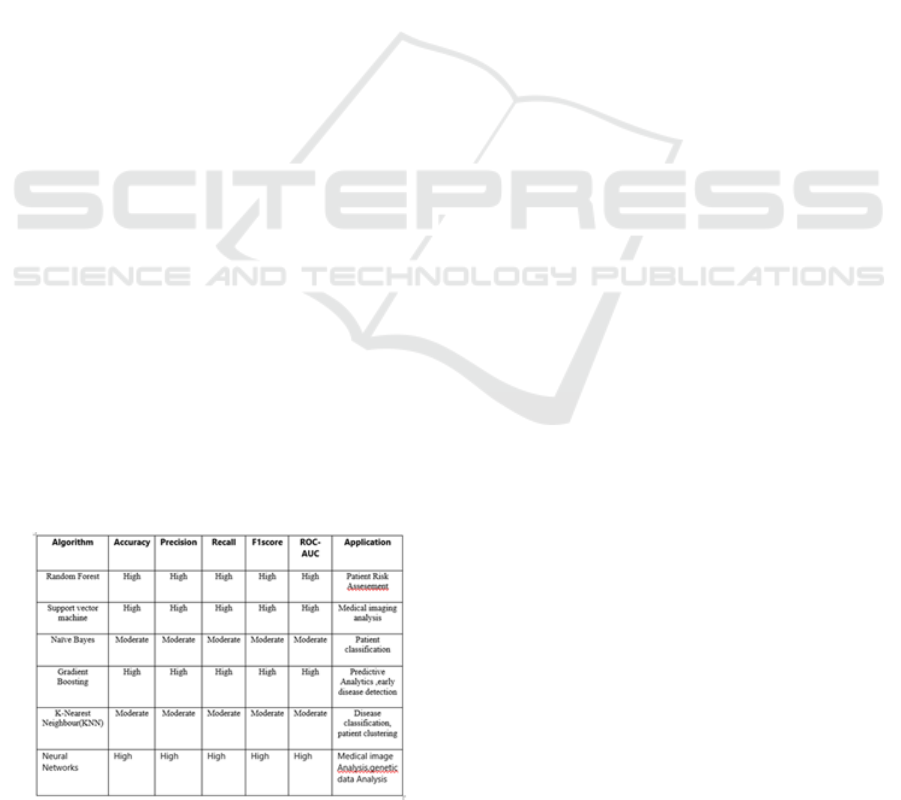
4 RESULTS
Table shows various algorithms used in Health care
domain.
Table 1: This provides an overview of the listed machine
learning algorithms' capabilities and uses.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Although it may improve operational efficiency,
personalize therapy, and improve diagnostic skills,
artificial intelligence has the potential to
revolutionize the healthcare industry. Even while
there are still issues, especially with ethics and data
privacy, the possible advantages greatly exceed the
dangers. A bright future for healthcare is provided by
ongoing advancements in AI technologies, which will
eventually result in better patient care and results.
REFERENCES
Z. Obermeyer and E. J. Emanuel, (May 2020) "Predicting
the Future—Big Data, Machine Learning, and Health
Care," New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 375, no.
13, pp. 1216-1219.
R. Shcherbina et al., (May 2020)"COVID-19: The Role of
Artificial Intelligence in Public Health," IEEE Signal
Processing Magazine, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 98-107.
J. A. Alpaydin, (2020) "Artificial Intelligence in Health
Care: Anticipating Challenges to Ethics and
Society," International Journal of Health Policy and
Management, vol. 9, no. 10, pp. 419-424,
J. L. H. Acar and H. J. Schaal, (2020) "Challenges in
Implementing Artificial Intelligence Applications in
Healthcare," European Journal of Health Economics,
vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 3-5.
M. D. O'Reilly et al., (2020)"Artificial Intelligence in
Healthcare: A Comprehensive Review," Journal of
Healthcare Informatics Research, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1-
24,
M. R. Cheng et al. (2019), "Artificial Intelligence and the
Future of Psychiatry," International Journal of
Psychiatry in Medicine, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 75-85
Jiang, F., Jiang, Y., Zhi, H., et al. (2019)"Artificial
Intelligence in Healthcare: Anticipating Challenges to
Ethics and Society." Nature Medicine, vol. 25, no. 1,
pp. 3-4, 2019.
A. M. M. G. H. A. M. A. A. J. K. A. M. A. Alshahrani et al.
(2018), "The Role of Artificial Intelligence in
Improving Healthcare Services: A Systematic
Review," Healthcare, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 1-14, 2020.
DOI: 10.3390/healthcare8040455. of the CheXNeXt
Algorithm to Radiologists." PLOS Medicine, vol. 15,
no. 11, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002686.
Kumar, A., & Singh, R. (2018) "Artificial Intelligence in
Healthcare: Overview and Future
Directions." Innovations in Pharmacy, vol. 9, no. 1, .
DOI: 10.24926/iip.v9i1.3922
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
412
