
SCRIPT-SAGE: An AI Chatbot that Helps You Learn Programming
Parth Wani, Aditya Dhonde, Aryabrat Pattanaik, Yash Ghuge and Vaishali Wangikar
MIT Academy of Engineering, Alandi, Pune, India
Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Chatbot, Coding Education, Programming Skills, Computational Thinking,
Learning Modules
Abstract:
This study presents SCRIPT-SAGE, an AI enhanced chatbot aimed at improving programming education,
primirarily in C language. SCRIPT-SAGE provides an engaging and interactive learning experience by com-
bining key features: a chatbot copilot for instant guidance, an integrated code editor for real-time practice,
and quizzes to assess and reinforce understanding. The platform aims to simplify complex programming con-
cepts, promote computational thinking, and support systematic learning through well-structured modules. By
bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and hands-on coding, SCRIPT-SAGE empowers learners to
develop confidence and proficiency in programming in a user-friendly and accessible environment.
1 INTRODUCTION
The emergence of AI has profoundly altered tech-
nological interactions, with chatbots being a promi-
nent advancement in this domain. Chatbots have con-
tributed to a wide range of industries, offering effi-
cient, automated solutions for tasks that once required
human intervention. From customer service to health-
care, e-commerce to finance, chatbots have made pro-
cesses faster, more accessible, and user-friendly.
Chatbots are now being used in various domains:
• Customer Support: Automating responses to fre-
quently asked questions and troubleshooting is-
sues in real-time.
• Healthcare: Assisting patients with symptom
checks, scheduling appointments, and providing
health-related information.
• E-commerce: Enhancing shopping experiences
by recommending products, guiding customers
through purchasing, and handling order queries.
• Banking and Finance: Facilitating transactions,
helping users track expenses, and offering finan-
cial advice.
Nevertheless, one of the most consequential ad-
vancements attributed to chatbots resides within the
domain of education, where they are fundamentally
transforming the educational experience. From a so-
ciocultural standpoint, chatbots seem to augment stu-
dents’ social presence by promoting emotional, trans-
parent, and cohesive discourse (P
´
erez et al., 2020).
Chatbots possess the capacity to provide uniform in-
formation to learners in real-time, incorporating criti-
cal elements such as evaluation standards, submission
deadlines, and the geographical sites of suggested
materials (Cunningham-Nelson et al., 2019). From
pedagogical perspective, unlike traditional methods
that rely on static resources and limited availability
of teachers, chatbots provide flexibility in use, and
are inexhaustibly available. Chatbots demonstrate the
capacity to reiterate material multiple times, thereby
supporting repetitive learning practices. Moreover,
chatbots that integrate both textual and speech-based
functionalities offer valuable assistance to students in
developing comprehensive reading, writing, and lis-
tening skills (Roos, 2018). From a technical stand-
point, the advent of transformer architecture has pro-
foundly transformed the domain through the imple-
mentation of attention mechanisms. These mech-
anisms facilitate large language models (LLMs) in
discerning contextual relationships within sentences
and throughout paragraphs, thus significantly enhanc-
ing their efficacy in tasks including translation, sum-
marization, and question-answering. (Abedi et al.,
2023).
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of
the SCRIPT-SAGE project, detailing its system archi-
tecture, core functionalities, and the rationale behind
its design choices. We explore how SCRIPT-SAGE’s
intuitive user interface, progress tracking capabilities,
Wani, P., Dhonde, A., Pattanaik, A., Ghuge, Y. and Wangikar, V.
SCRIPT-SAGE: An AI Chatbot That Helps You Learn Programming.
DOI: 10.5220/0013591400004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 2, pages 301-308
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
301

and AI-powered interactions come together to create
a holistic learning environment. By examining the
intended outcomes and potential impact of SCRIPT-
SAGE, we aim to demonstrate its significance in the
field of computer science education and its potential
to make programming more accessible to a wider au-
dience. SCRIPT-SAGE, an AI-powered application,
leverages these advancements by integrating a built-
in chatbot specifically designed to help users learn the
C programming language. Through interactive con-
versations, SCRIPT-SAGE guides learners through
complex C programming concepts, offering real-time
code feedback, debugging support, and simplified ex-
planations to ensure that even beginners can navigate
the intricacies of the language.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
2.1 A Brief History of Chatbots
A literature review on current chatbot technologies
by (Caldarini et al., 2022) outlines the various types
of chatbots, including the Rule Based chatbots devel-
oped in the primary stages, and the most recenlty used
Deep Learning (DL) based chatbots, the databases
used to train the chatbots, the evaluation metrics used
for each type of chatbot, and their applications in
education and research. Techincal details, history,
and general architecture of chatbots are highlighted
in (Adamopoulou and Moussiades, 2020). Following
are the outline points of a generalized chatbot archi-
tecture:
1. User interface component
2. User message analysis component - A spell-
checker sentiment analysis and machine transla-
tion (multilingual chatbots).
3. Dialog management component - Data handling,
error handling, and ambiguity handling.
2.2 Chatbots in Different Domains
The growing trend in healthcare chatbot develop-
ment addresses the increasing demand for convenient,
at-home medical advice for common ailments like
colds, headaches, and abdominal pain. Research in-
dicates that 60% of doctor visits are for minor condi-
tions, 80% of which can be treated with simple home
remedies, often without needing professional medi-
cal intervention. While existing healthcare chatbots
can provide general advice through frequently asked
questions (FAQs), they lack the ability to offer the
nuanced, natural interaction expected in a human-
doctor consultation. (Gumusel, 2024) The banking
and finance sectors have rapidly embraced voice as-
sistants and chatbots to offer more responsive and ef-
ficient customer service. In order to improve cus-
tomer interactions, a recent study created a web-based
chatbot for online banking that makes use of artifi-
cial intelligence (AI) capabilities, including natural
language understanding (NLU). This chatbot enables
users to seamlessly access personal banking informa-
tion within the platform, improving the overall bank-
ing experience. (Doherty and Curran, 2019) Chat-
bot technology, often referred to as virtual assistants,
has gained significant prominence in the hospitality
industry.The viewpoints of users are not well under-
stood, despite the fact that user perspectives have been
thoroughly examined. A study that addressed this
knowledge gap examined the use of chatbots in the
hotel business using semi-structured interviews with
professionals in the field. The results emphasise the
main advantages chatbots offer the hotel sector, such
as enhanced visitor experiences and more efficient op-
erations (Buhalis and Cheng, 2020).
2.3 Chatbots in Education
The benefits of chatbots in the educational system are
discussed by (Adamopoulou and Moussiades, 2020),
noting that the learning support chatbots can preserve
information by replaying previous lessons for stu-
dents who miss them. The use of personal data by
conversational chatbots is covered in (Caldarini et al.,
2022). A security issue arises when chatbots use user
data and even ”learn” from it. Along with how the
backend manages user data on the server, the paper
also discusses security concerns related to data trans-
fers to the chatbot’s server. Some security-related top-
ics discussed in the paper include:
• Authentication and authorization - Malicious
chat-bots operating on crossplatforms, hazards of
sharing data on the internet.
• End-to-End Encryption - Usage of https proto-
col and public-key encryption is encourages.
• Self-destructing messages - Messages contain-
ing sensitive PII (Personally identifiable informa-
tion) are automatically erased after a set period of
time.
2.4 Computational Thinking in
Educational Landscape
1. The article (Papadakis, 2022), highlights the need
for developing appropriate applications. Compu-
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
302

tational Thinking is one of the fundamental skill
of 21st century. Despite the abundance of avail-
able apps, researchers have identified a critical
need for developmentally appropriate applications
specifically designed to promote CT concepts and
coding skills in young learners.
2. The literature (Lye and Koh, 2014) emphasizes
three key dimensions of CT: computational con-
cepts, practices, and perspectives. This review
underscores the need for more targeted research
in K-12 settings and highlights the importance of
developing comprehensive instructional strategies
to effectively integrate CT across various educa-
tional contexts.
3. The literature (Fagerlund et al., 2021) reveals a
significant challenge in defining clear educational
objectives for CT at the primary level, with cur-
ricula across various countries focusing on related
but distinct areas such as computer science, com-
puting, programming, or digital literacy. This lack
of specificity extends to the concrete operational-
ization of CT teaching, learning, and assessment
methods, even when using popular programming
environments like Scratch.
2.5 Pedagogical Approaches: Chatbot
Case Study
1. A comprehensive study (Kim and Ko, 2017) an-
alyzing 30 diverse and widely-used online cod-
ing tutorials against dimensions derived from
learning sciences and education literature reveals
both strengths and weaknesses in their approach.
The research indicates that most tutorials share
commonalities in content coverage and employ
a bottom-up organizational structure, providing
goal-directed practice opportunities with immedi-
ate feedback. (Labadze et al., 2023) However, the
study highlights critical shortcomings, notably the
lack of personalization to learners’ prior coding
knowledge and insufficient guidance on knowl-
edge transfer and application.
2. The literature (Bers, 2019) highlights a signifi-
cant gap in pedagogical approaches specifically
tailored for teaching computer science to young
children. Traditional STEM-based instructional
methods, originally designed for older students,
are often inadequate for early childhood educa-
tion. (Peteranetz et al., 2018) Researchers have
come up with creative solutions to this prob-
lem, like ”Coding as Another Language” (CAL),
which views coding as a new symbolic repre-
sentation system for expressive and communica-
tive purposes. This method, which is based
on principles of language and literacy education,
stresses play, exploration, socialization, and cre-
ativity while acknowledging the distinct devel-
opmental phases of young children. The lit-
erature also introduces the concept of six cod-
ing stages or learning trajectories that children
progress through when exposed to CAL curricu-
lum. Case studies utilizing tools like the KIBO
robot and ScratchJr app have been conducted
to characterize these stages and demonstrate the
practical application of CAL instructional prac-
tices.
3. Study in (Scott et al., 2007) have identified several
key issues that contribute to student demotivation,
including difficulties with programming language
syntax and semantics, underdeveloped problem-
solving and program design skills, and the com-
plexity of development environments. (Popat and
Starkey, 2019) In response to these challenges,
researchers have explored various approaches to
support novice programmers. One such inno-
vative approach involves the use of interactive,
visual problem-solving tools. This paper con-
tributes to this body of research by proposing an
interactive flowchart-based tool that not only aids
in visual problem-solving but also generates syn-
tactically correct program code. The literature
emphasizes the importance of visual representa-
tions in enhancing student understanding, and this
tool builds on that principle by providing ani-
mation features and establishing a clear connec-
tion between visual solutions and code represen-
tations.
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
To address the challenges of teaching programming
through chatbots, we propose SCRIPT-SAGE, an AI-
driven chatbot designed to facilitate coding education.
SCRIPT-SAGE offers an integrated platform where
students can engage in interactive coding lessons, re-
ceive real-time feedback, and improve their coding
skills in a supportive environment. By leveraging AI,
SCRIPT-SAGE aims to enhance the learning experi-
ence by providing personalized assistance, answering
questions, and guiding learners through programming
concepts and practical exercises.
3.1 System Architecture
SCRIPT-SAGE is structured to provide comprehen-
sive experience to the users. Layered architecture in
SCRIPT-SAGE: An AI Chatbot That Helps You Learn Programming
303

Figure 1: Script-Sage: Layered Architecture.
Figure 1 pans out the components of the system: Cod-
ing Playgound, Chatbot, and Quiz Section. User di-
rectly interacts with the top layer consisting of Code
Editor, Code Evaluator, Prompts, Inputs, Questions
and Reviews. All of the components interact with the
core LLM - Gemini by Google. The details of the
interaction are shown in Figure 2. Each data point
generated by user is passed through LLM to convert
the metric data into natural language. This approach
condenses the data and provides user the compact in-
formation. User directly interacts with Code Engine,
Quiz Engine and Chatbot Engine which interacts with
respective utility engines which, in-turn interacts with
Gemini LLM. The approach allows only required in-
formation to flow into the LLM, get the information
from LLM and send it back to the user.
3.2 Technical Aspects
The underlying system mechanism of SCRIPT-SAGE
includes a transformer based chatbot that works based
on attention mechanism. (Vaswani, 2017)
• Self Attention Mechanism: An essential part of
transformer models is the Self-Attention Mecha-
nism. It is essential for comprehending the con-
nections between words in a sentence, which en-
ables the model to successfully capture contextual
meanings. In a sentence, each word’s meaning
can depend on other words in the sentence. Self-
attention calculates how much each word should
pay attention to every other word, helping the
model understand their contextual relationships.
The mechanism computes scores that indicate the
importance of each word in relation to the cur-
rent word being processed. These scores help the
model focus on the relevant words while generat-
ing a response.
• Multiple layers of Attention: Transformers can
recognise the relationships between words in a
sentence regardless of where they are in the sen-
tence thanks to layered layers of self-attention
processes. Each layer refines the understand-
ing of word connections, allowing the model
to interpret complex dependencies in language.
This layered approach helps the model build a
more detailed representation of the input text.
Unlike older architectures like Recurrent Neural
Networks (RNNs) or Long Short-Term Memory
(LSTM) networks, which process words sequen-
tially, transformers handle all tokens (words or
subwords) in parallel. This parallelism greatly im-
proves the speed of computation, making trans-
formers much more efficient and suitable for pro-
cessing large datasets. It enables the model to bet-
ter manage long-range dependencies.
• Cross Attention Mechanism: The Cross-
Attention Mechanism in multimodal models al-
lows the model to process and relate informa-
tion from different data types (modalities), such
as text, images, audio, and video, to create a uni-
fied understanding of the data. Cross-attention
links information from one data type to another,
allowing the model to interpret the relationships
between them. For example, when processing an
image with a caption, the model can relate specific
words to particular parts of the image.
Pseudocode for Attention based mechanisms:
1. Tokenization: Convert the input text into tokens.
2. Embedding: Map tokens to vectors using an em-
bedding matrix.
3. For each token in the sequence:
(a) Apply Self-Attention mechanism:
i. Calculate Query, Key, and Value matrices.
ii. Compute attention scores.
iii. Generate a weighted representation of the to-
kens.
(b) Apply Feed-Forward Neural Network to pro-
cess the attended output.
(c) Add Residual Connection and Layer Normal-
ization.
4. Repeat step 4 for each layer in the transformer
(stacked layers).
5. Generate the output token probabilities using a
Softmax function.
6. Use Beam Search or Sampling to generate the
most probable response.
7. Convert tokens back to human-readable text.
8. Output: Return the generated response to the user.
Query, Key, Value: These matrices are derived
from the input tokens and help in computing the at-
tention scores.
Attention Calculation: This step determines
which words in the sentence should be focused on
more heavily to generate the response.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
304
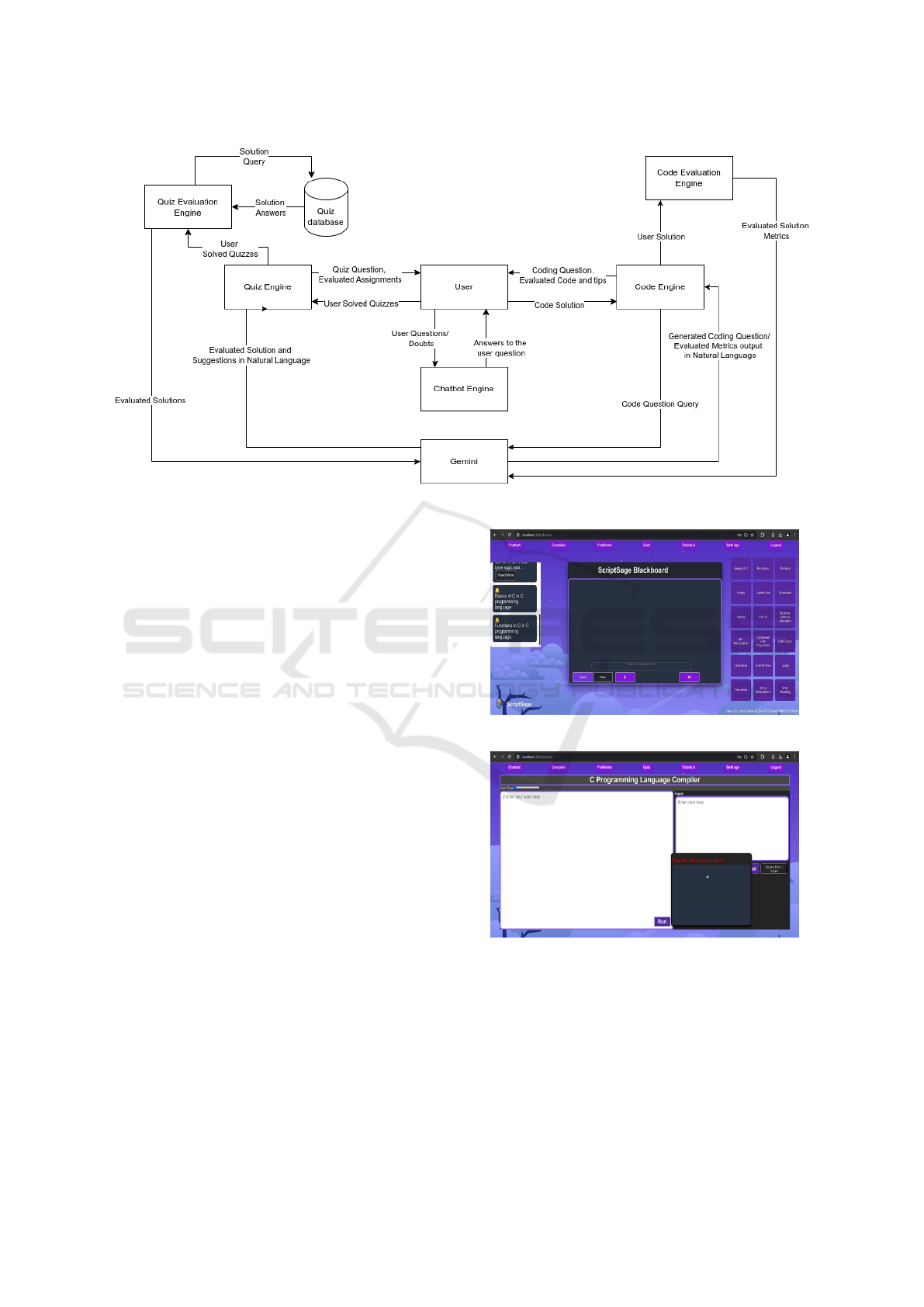
Figure 2: Script-Sage: Working Flow Diagram (DFD).
Softmax Function: Converts raw scores into
probabilities to select the best token for the response.
Feed-Forward Neural Network: Applies trans-
formations to the attended output for deeper process-
ing.
Beam Search/Sampling: Used to generate a co-
herent response by choosing the best possible se-
quence of words.
3.3 UI and Features
Script Sage is designed as an intelligent and inter-
active platform aimed at teaching programming lan-
guages, specifically focusing on C. Its architecture
revolves around integrating AI-driven chatbot func-
tionalities, real-time coding environments, and user
progress tracking to create a seamless learning expe-
rience. (Tlili et al., 2023)
3.3.1 UI
1. The core of SCRIPT-SAGE in Figure 3, is Google
Gemini 1.5 pro latest, which is tuned to answer
user queries related to coding. The chatbot is
trained on a large corpus of programming knowl-
edge. By providing clear explanations and step-
by-step guidance, it enhances the learning process
for both beginners and intermediate users.
2. SCRIPT-SAGE integrates a real-time code editor
as shown in 4 that supports C programming. This
editor allows users to write and run code directly
within the chatbot interface, offering immediate
Figure 3: Script-Sage: Home.
Figure 4: Script-Sage: Code Editor.
feedback on syntax and logic errors. It also in-
cludes features like syntax highlighting and error
detection, which enhance the learning experience
by providing useful insights into the coding pro-
cess.
3. SCRIPT-SAGE includes interactive quizzes that
evaluate the user’s grasp of programming con-
cepts. The learning module is adaptive, which
SCRIPT-SAGE: An AI Chatbot That Helps You Learn Programming
305

Figure 5: Script-Sage: Question Generator.
Figure 6: Script-Sage: Quiz.
means that it presents content tailored to the user’s
skill level and progress. As users complete the
quizzes (Figure 5), the system generates feedback,
helping them focus on areas that need improve-
ment.
4. A key feature of SCRIPT-SAGE is its ability to
track user progress over time. The system records
the modules completed, quiz scores , and cod-
ing exercises, allowing users to monitor their im-
provement. This data can also be used to person-
alize future learning materials.
3.3.2 Features
Key components of the system include the following:
1. The core of Script Sage is a generative AI chatbot
that helps users learn programming by answering
questions, explaining code, and debugging prob-
lems. The chatbot leverages a large dataset of
programming-related content, enabling it to of-
fer context-aware responses based on the user’s
queries.
2. The system integrates a code editor within the in-
terface where users can write and execute C pro-
gramming code. This editor provides immediate
feedback on syntax errors, logic issues, and per-
formance, making the learning process more prac-
tical and hands-on.
3. A dynamic learning module that adapts to the
user’s knowledge level, providing interactive
quizzes to assess and reinforce their understand-
ing of programming concepts. Based on perfor-
mance, the module adjusts the difficulty of subse-
quent questions and provides detailed feedback.
4. Script Sage tracks user activities, including quiz
scores, completed modules, and coding time
spent. This data is analyzed to create personalized
learning paths, ensuring that users focus on areas
that require improvement while encouraging con-
tinuous engagement.
5. The system incorporates elements of casual con-
versation designed to support the mental well-
being of the user. These include reminders to take
breaks during long coding sessions and motiva-
tional feedback to encourage consistent learning
without causing burnout.
6. The NLP component of Script Sage is crucial for
understanding user input and delivering appropri-
ate responses. The model is fine-tuned for pro-
gramming education, ensuring that the chatbot
can handle queries related to:
(a) Syntax explanation and logic-building.
(b) Debugging and error handling.
(c) Programming best practices.
The chatbot can interpret user intent, regardless of
the query’s complexity, and provide personalized
assistance. Over time, the model can be improved
using user data to enhance response accuracy and
engagement.
4 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
4.1 Detailed Insights
• Zendesk’s Answer Bot (Customer Service):
– Functionality: Focuses on automating cus-
tomer service interactions by providing instant
answers to frequently asked questions.
– Strengths: Significantly reduces response
times, enhancing customer satisfaction.
• Woe-bot (Healthcare):
– Functionality: Offers mental health support
using cognitive behavioral therapy techniques.
– Strengths: Provides accessible emotional sup-
port in a friendly manner.
• Duolingo (Education):
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
306

Table 1: Domains and their corresponding chatbot functionalities. The final sentence of a caption should end with a period.
Domain Chatbot Functionality
Programming Script Sage C programming queries, code snippets, debugging
assistance.
Customer Service Zendesk’s Answer Bot Automates responses to customer queries.
Healthcare Woebot Mental health support and CBT techniques.
Education Duolingo Language learning through interactive conversa-
tions.
Finance Cleo Personal finance management and budgeting ad-
vice.
Entertainment AI Dungeon Interactive storytelling and creative writing.
– Functionality: Engages users in language
learning through games and quizzes.
– Strengths: Its gamified approach keeps users
motivated and enhances language retention.
• Cleo (Finance):
– Functionality: Acts as a personal finance as-
sistant, offering insights on spending and bud-
geting.
– Strengths: Provides users with a clear picture
of their financial health.
• AI Dungeon (Entertainment):
– Functionality: Allows users to create and navi-
gate through interactive storytelling adventures.
– Strengths: The open-ended nature of interac-
tions fosters creativity.
• SCRIPT-SAGE:
– Specialization: Designed specifically for C
programming, it excels in providing targeted
support for coding-related queries.
– Strengths: Offers deep insights into C lan-
guage features, including memory management
and data structures.
5 CONCLUSION
The SCRIPT-SAGE project exemplifies how modern
technology, particularly AI, can be used to create a
dynamic and engaging learning environment. Us-
ing generative AI to power its conversational chat-
bot, SCRIPT-SAGE provides contextually relevant
personalized support to learners. The integration of
a real-time code editor, quizzes, and user progress
tracking ensures that users receive immediate feed-
back and can monitor their learning journey effec-
tively.
The technology stack, consisting of React JS for
the frontend and AWS cloud services for deployment,
enables scalability, performance, and a seamless user
experience. The use of CI/CD pipelines ensures that
updates to chatbot and learning modules are deployed
efficiently, maintaining the quality and availability of
the application.
In future phases, the deployment of SCRIPT-
SAGE in the cloud will allow continuous improve-
ments in system performance, scalability, and user
interaction, laying the groundwork for a long-lasting
and impactful tool in the world of programming edu-
cation.
REFERENCES
Abedi, M., Alshybani, I., Shahadat, M. R. B., and Murillo,
M. (2023). Beyond traditional teaching: The poten-
tial of large language models and chatbots in graduate
engineering education. Qeios.
Adamopoulou, E. and Moussiades, L. (2020). An overview
of chatbot technology. In IFIP international confer-
ence on artificial intelligence applications and inno-
vations, pages 373–383. Springer.
Bers, M. U. (2019). Coding as another language: A ped-
agogical approach for teaching computer science in
early childhood. Journal of Computers in Education,
6(4):499–528.
Buhalis, D. and Cheng, E. S. Y. (2020). Exploring the use of
chatbots in hotels: technology providers’ perspective.
In Information and Communication Technologies in
Tourism 2020: Proceedings of the International Con-
ference in Surrey, United Kingdom, January 08–10,
2020, pages 231–242. Springer.
Caldarini, G., Jaf, S., and McGarry, K. (2022). A literature
survey of recent advances in chatbots. Information,
13(1):41.
Cunningham-Nelson, S., Boles, W., Trouton, L., and Marg-
erison, E. (2019). A review of chatbots in education:
practical steps forward. In 30th annual conference
for the australasian association for engineering ed-
ucation (AAEE 2019): educators becoming agents of
change: innovate, integrate, motivate, pages 299–306.
Engineers Australia.
SCRIPT-SAGE: An AI Chatbot That Helps You Learn Programming
307

Doherty, D. and Curran, K. (2019). Chatbots for online
banking services. In Web Intelligence, volume 17,
pages 327–342. IOS Press.
Fagerlund, J., H
¨
akkinen, P., Vesisenaho, M., and Viiri,
J. (2021). Computational thinking in programming
with scratch in primary schools: A systematic re-
view. Computer Applications in Engineering Educa-
tion, 29(1):12–28.
Gumusel, E. (2024). A literature review of user privacy con-
cerns in conversational chatbots: A social informatics
approach: An annual review of information science
and technology (arist) paper. Journal of the Associa-
tion for Information Science and Technology.
Kim, A. S. and Ko, A. J. (2017). A pedagogical analy-
sis of online coding tutorials. In Proceedings of the
2017 ACM SIGCSE Technical Symposium on Com-
puter Science Education, pages 321–326.
Labadze, L., Grigolia, M., and Machaidze, L. (2023). Role
of ai chatbots in education: systematic literature re-
view. International Journal of Educational Technol-
ogy in Higher Education, 20(1):56.
Lye, S. Y. and Koh, J. H. L. (2014). Review on teaching and
learning of computational thinking through program-
ming: What is next for k-12? Computers in human
behavior, 41:51–61.
Papadakis, S. (2022). Apps to promote computational
thinking and coding skills to young age children:
A pedagogical challenge for the 21st century learn-
ers. Educational Process: International Journal
(EDUPIJ), 11(1):7–13.
P
´
erez, J. Q., Daradoumis, T., and Puig, J. M. M. (2020). Re-
discovering the use of chatbots in education: A sys-
tematic literature review. Computer Applications in
Engineering Education, 28(6):1549–1565.
Peteranetz, M. S., Wang, S., Shell, D. F., Flanigan, A. E.,
and Soh, L.-K. (2018). Examining the impact of com-
putational creativity exercises on college computer
science students’ learning, achievement, self-efficacy,
and creativity. In Proceedings of the 49th ACM techni-
cal symposium on computer science education, pages
155–160.
Popat, S. and Starkey, L. (2019). Learning to code or coding
to learn? a systematic review. Computers & Educa-
tion, 128:365–376.
Roos, S. (2018). Chatbots in education: A passing trend or
a valuable pedagogical tool?
Scott, A., Watkins, M., and McPhee, D. (2007). A step back
from coding–an online environment and pedagogy for
novice programmers. In Proceedings of the 11th Java
in the Internet Curriculum Conference, volume 2007,
pages 35–41. Citeseer.
Tlili, A., Shehata, B., Adarkwah, M. A., Bozkurt, A.,
Hickey, D. T., Huang, R., and Agyemang, B. (2023).
What if the devil is my guardian angel: Chatgpt as
a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart
learning environments, 10(1):15.
Vaswani, A. (2017). Attention is all you need. Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
308
