
Integrating Conversational AI, Image Generation, and Code Generation:
A Unified Platform
Joylin Priya Pinto
a
, Mohammed Aqib, Osama Shakeel, Emad Habibi and Gagan S
Nitte Deemed to be University, NMAM Institute of Technology, Nitte, Karkala, Karnataka, India
Keywords:
DALL-E, OpenAI, API, StyleGAN, GPT-3.5-Turbo.
Abstract:
The new AI platform is designed and implemented by the software team at full-stack AI SaaS, which includes
conversational AI, image generation, and code generation. Powering for both conversation and code uses
OpenAI’s GPT-3.5- turbo and the platform will use DALL·E to generate images, thus offering a unified user
experience of these different AI villages through a single cohesive interface. Consumer-side routing is seen
in a number of technologies e.g. modern web technologies such as Next.js 13 and its App Router, thereby it
becomes possible to have smooth, fast and responsive user experience. The era in which we live is charac-
terized by user expectations that are always demanding, and this endeavor is related to vital user-experience,
developer-usability, and scalability tasks. An AI platform will only be useful if it involves the whole process
- integrating the listed elements to a solution that empowers users comprehensively across all the various do-
mains of activities will make it one. The discussion of the layout and those that use our platform is talked
about in this particular context which includes the scalability key aspect, the user interface design concern,
and the development treatment to the users. Next.js 13 together with API-s as well as the machine algorithms
of OpenAI presents the interlaid milieu of a technologic-creative realm which deals with today’s issues. Con-
sequently, we verify the efficiency of our system by load testing and collecting user reviews. These results not
only reaffirm the infallibility of our tool but also bring new areas for investigation and enhancement. In this
paper, we hope to stimulate some subtle debates on the probable of AI to make significant changes in the user
experience and enhance the productivity of the user, moving towards a scenario in which everyone has easy
access to AI tools covering a large variety of walks of life.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the period of highly competitive races within indus-
tries competing for more efficiency in operations and
innovation, AI becomes a transformative technology,
not an automation, but a creative and technical phe-
nomenon in today’s industry, greatly changing work-
flows and productivity in all sectors-from cus tomer
service with leading chatbots, content, and automated
code generation, transformed into simple applications
even for non-experts. With intuitive interfaces, to-
day’s users can unlock powerful AI tools without
requiring specialized programming or data science
knowledge, thus making technology more inclusive
than ever. This paper deals with the framework and
development process of an AI-powered SaaS that is
meant to bring together multiple AI functionalities to
one seamless user interface. The core AI tools in-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6742-7672
cluded in the platform would be conversational AI,
image generation, and code generation. We use Ope-
nAI’s GPT-3.5-turbo model for conversational AI and
code gener ation, which supports advanced natural
language processing to provide answers to questions,
give suggestions in decision- making scenarios, and
generate code upon prompts by the user. The fea-
ture of image generation is supported by OpenAI’s
DALL·E API on the platform, whereby unique im-
ages can be produced based on text descriptions;
therefore, it opens greater possibilities for artists, de-
signers, and general users on this creative front. The
platform architecture is based upon Next.js 13, which
is a new web framework with support for server-side
rendering and client-side routing, providing fine scal-
ability and responsive performance. This is the first
platform with fluent navigation due to the use of App
Router in Next.js 13, and simpler modular, scalable
development due to the nature of React with compo-
174
Pinto, J. P., Aqib, M., Shakeel, O., Habibi, E. and S, G.
Integrating Conversational AI, Image Generation, and Code Generation: A Unified Platform.
DOI: 10.5220/0013588800004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 2, pages 174-180
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

nents. Tailwind CSS enhances the looks of the plat-
form with responsive designs to create visually ap-
pealing and user- friendly interfaces across many de-
vices. We included Clerk to manage user authentica-
tion, thereby adding security and ensuring a seamless
login experience-an essential condition for trust and
engagement with users. This AI SaaS platform devel-
opment underlines the need for performance, acces-
sibility, and innovation in obtaining for de velopers,
creators, and even casual users, advanced AI models.
We show that sophisticated AI can civilize both tech-
nical and creative challenges in an accessible, user-
centered manner by combining OpenAI’s GPT-3.5-
turbo and DALL·E APIs with an efficient Next.js 13
framework. It sets a benchmark for bringing AI closer
to the mainstream and transforming the user experi-
ence in powerful and practical ways.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Rapid advances in artificial intelligence (AI) have
transformed industries by making it possible to
perform activities like natural language processing
(NLP), image generation, and code generation that
were previously thought to be the sole purview of hu-
man intelligence. A major factor in this change has
been the introduction of AI models such as GPT- 3
and DALL·E, which have features that mimic human-
like text comprehension and production as well as
incredibly life- like text-to-image synthesis. AI-
powered SaaS platforms are revolutionizing enter-
prises by increasing efficiency, fostering innovation,
and optimizing processes. This analysis highlights re-
search gaps and their implications for the future of
AI solutions by examining significant advancements,
integration difficulties, and user- focused design in
these platforms.
Harshil T. Kanakia et.al. (Kanakia and Nair, 2023)
suggested an approach that com-bines server-side and
client-side technology to create an application that
generates images using OpenAI’s Image GPT. The
React-built user interface lets users enter text to cre-
ate images, which are then handled by a server that
runs on Node.js and Express.js and processes the data
via an API. In order to create pixel values via a de-
coder utilizing autoregressive approaches, the server
communicates with OpenAI’s Image GPT, which to-
kenizes (using Byte Pair Encoding), embeds, and pro-
cesses through a Transformer network. A smooth
and effective system for text-to-image synthesis is en-
sured by storing the produced images, which are se-
mantically aligned with the input text, in a MongoDB
database for later retrieval. Following picture gener-
ation, the client receives an API response from the
server that contains the created image, which is sub-
sequently saved in a MongoDB database via Mon-
goose.js.
Amon Rapp et.al (Rapp et al., 2025) examined how
individuals react to images produced by a Gen-AI
text-to-image model, pay- ing particular attention
to the impressions, evaluations, and feelings they
arouse. It also aimed to investigate whether people
are capable of coming up with logical ”folk theories”
regarding how these technologies function internally.
Twenty participants in the study, who were given par-
ticular written prompts and twenty distinct visuals
produced by Stable Dif- fusion, participated in semi-
structured interviews. Heat maps were used to exam-
ine participant experiences and determine which input
features had the most impact on the visuals. The study
aimed to investigate how the general population views
AI-generated images outside of direct interaction with
the technology and emphasized the significance of
visual signals in comprehending Gen-AI’s behavior.
They looked at how individuals responded to Gen-AI-
generated photos, specifically how they evaluated the
images’ representation and aesthetic quality. The ma-
jority of participants thought the Gen- AI photos were
”strange” or ”prototypical,” which made them unset-
tling and made them consider the biases in the image
creation process. Participants reworked their percep-
tions and understandings by either overvaluing or un-
dervaluing the Gen- AI in an attempt to lessen their
experience of unfamiliarity. Many respondents cited
the themes of strangeness and self- overvaluation as
the most prevalent, even though some saw the images
as having utilitarian or epistemological worth.
Aditya Ramesh et al. (Ramesh et al., 2022) out-
lines a generative model that combines a prior and a
decoder to create visuals from text. The prior uses
diffusion and autoregressive (AR) techniques to cre-
ate CLIP image embedding’s zi from text captions y.
These embedding’s are converted into images by the
decoder using a modified diffusion model. In order
to enhance image quality during training, the authors
also cover the use of classifier- free guidance. Two
up samplers are utilized to produce high- resolution
images, and PCA is used to decrease the CLIP image
embedding’s in order to preserve important informa-
tion during training. The diffusion prior uses a Trans-
former model to directly predict the un-noised pic-
ture embedding, whereas the AR prior is conditioned
on both the text caption and the CLIP text embed-
ding. Contrastive models like CLIP have been shown
to learn robust representations of images that capture
both semantics and style. Moreover, the joint embed-
ding space of CLIP enables language-guided image
Integrating Conversational AI, Image Generation, and Code Generation: A Unified Platform
175
manipulations in a zero- shot fashion. We use diffu-
sion models for the decoder and experiment with both
auto-regressive and diffusion models for the prior,
finding that the latter are computationally more effi-
cient and produce higher-quality samples.
Paula Maddigan et. al. (Maddigan and Susnjak, 2023)
highlighted that the implementation of practical NLIs
has always been difficult because natural language is
inherently ambiguous and because badly written user
queries make it difficult for language models to de-
termine user intent. This paper suggests using the
devel- opments in pre-trained large language mod-
els (LLMs), like ChatGPT and GPT-3, to transform
free-form natural language straight into code for suit-
able visualisations, as an alternative to the conven-
tional approach of creating new language model itera-
tions. This study introduces Chat2VIS, a unique sys-
tem that leverages LLM capabilities and shows how
efficient rapid engineering can handle the challenging
challenge of language comprehension more quickly,
leading to simpler and more accurate in contrast to
the previous study.
Arghavan Moradi Dakhel et. al. (Dakhel et al., 2023)
presented an example of how the OpenAI Codex
might be used as an AI code assistant. It assists de-
velopers by suggesting lines or blocks of code in real
time, which makes the developers more productive
since they don’t have to write repetitive code. Nev-
ertheless, Copilot sometimes doesn’t have contex-
tual understanding especially when coding is complex
and needs a lot of clarification for recommendations.
Genius addresses all those shortcomings by combin-
ing conversational AI with code generation that has
been made more contextual and intuitive for coding as
needs and preferences of the developer are concerned.
Tero Karras at. el. (Karras, 2019) provided a dif-
ferent generator architecture for adversarial genera-
tive networks. The style-based architecture allows
for fine control over the images generated. Another
advancement is StyleGAN2, which further enhanced
image quality and resulted in very realistic outputs
with fewer artifacts. These developments have estab-
lished new standards for photorealism in the gener-
ation of AI-driven images. But, however, the mod-
els are extremely rigid with minimal in- teraction and
customizations. The authors Genius capitalize from
here, to add personalization in their version of DALL-
E’s image generation capabilities which allows users
to create images customized for any particular need-
an advantage that leaves every other technology to the
bench.
3 SYSTEM DESIGN AND
ARCHITECTURE
Our platform brings together three leading-edge AI
capability conversational AI, image generation, and
code generation within a single easy-to-use interface.
While each individually has strong performance, their
coming together in one unified platform provides a
one-of-a-kind seamless experience. Such an inte-
grated design enables diverse users - developers and
content creators, to entrepreneurs and casual users-
to use AI in wide-ranging applications without diffi-
culty. The result is intuitive, accessible, and powerful;
even the most complex AI conversations flow seam-
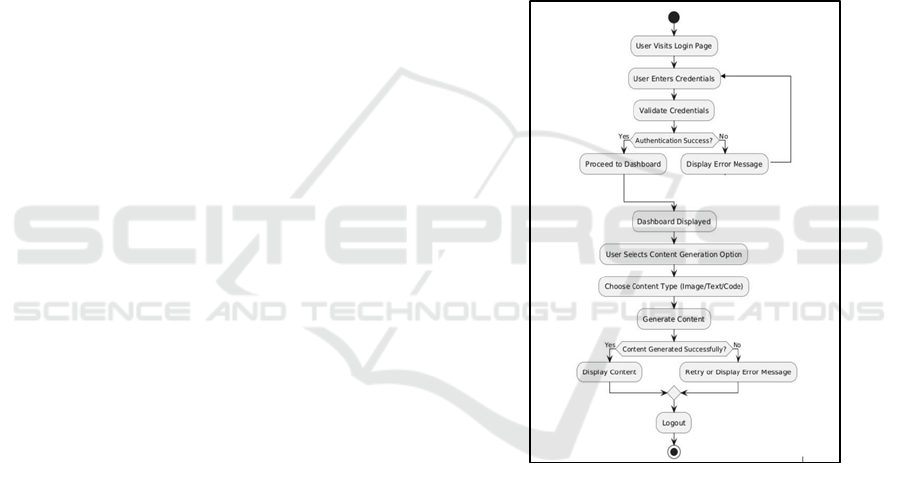
lessly. Figure 1 shows the architecture of the proposed
method.
Figure 1: Architecture of the Proposed Method
3.1 Conversational AI with
GPT-3.5-turbo
We have deployed OpenAI’s GPT-3.5-turbo model,
one of the leading cutting-edge language models
which guarantees human-like interactions. Unlike the
regular chatbot that uses already written response,
GPT-3.5-turbo relies on deep learn- ing to decipher
tricky prompts and respond with contextual richness.
This allows for a much more flexible and engaging in-
teraction where the AI can keep pace with varied user
inquiries, engage in back-and-forth exchanges, and
adjust responses based on the flow of conversation.
For users, this conversational AI tool would behave
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
176

like a personal assistant, capable of handling techni-
cal questions, brainstorming new ideas, and providing
quick research insights or even managing customer
service inquiries. Businesses that wish to inject some
life into AI-powered assistants in customer support
could use this model towards creating a more natu-
ral and non-robotic feel for the conversational expe-
rience. Beyond that, the AI could prove useful for
developers and technical users by being a support-
ive tool for any project-related insights or code assis-
tance, making the conversational AI component one
of the most versatile tools available on the platform.
3.2 Use of DALL·E in Image Generation
Our platform features the AI model DALL·E, which
was trained to produce high-quality original images
from text- based prompts. DALL·E’s power is that it
can really decode complex and imaginative text de-
scriptions, allowing users to see what they want with-
out having design skills. Imagine describing the “sun-
set over a futuristic city skyline with neon-lit build-
ings,” and DALL·E brings it to life in seconds. This
has huge potential for digital marketers, content cre-
ators, visual artists, and anyone trying to produce cap-
tivating visuals speedily. Our platform makes possi-
ble access to such an advanced image-generating tool,
allowing for creative discovery as well as the ability
to quickly prototype ideas or create content for social
media, marketing campaigns, and so on. This capa-
bility further democratizes the creative process, where
people with ideas but perhaps less professional-level
design experience can create high-value visual con-
tent. DALL·E’s direct integration brings any abstract
ideas firmly into tangible, sharable formats- this both
amplifies productivity and creativity.
3.3 GPT-3.5-turbo for Code Generation
The final piece of our stack is code generation, driven
by GPT-3.5-turbo. Using this capability the end-
user types a natural-language command, and then the
model translates that into executable code in many
programming languages. This functionality goes a
long way toward really empowering developers to
quickly prototype and automate vast quantities of of-
ten tedious, hand-coding work. The ability to un-
derstand natural language also makes it accessible to
users who are not technically qualified, and one can
now create functional code without much program-
ming experience.
For the developers, it acts as an intelligent assistant
in coding; it absorbs repetitive tasks, generates boil-
erplate code, or even suggests more complex logic.
Suppose a user types in “write a Python function to
calculate the factorial of a number” and, in a matter
of seconds, has readable, efficient code. This is not
completing code; this tool will then respond to clari-
fying questions and provide options while it evolves
changes to the output in response to the user’s feed-
back. It relates the natural language to code and helps
transform users’ ideas into working code with a lot
of speed to achieve development and improve project
outcomes.
4 IMPLEMENTATION
Implementation of our platform will involve dif-
ferent layers ranging from the front end to the back
end through API integration. Such elements are inte-
gral for us to get the users using the technology with
as smooth a joyride as possible.
4.1 Front-End Development
The front-end was developed with a huge emphasis
put on user experience and functionality. With the
use of React, a component- based architecture allows
for the reusability of UI elements across the applica-
tion. Therefore, common components such as but-
tons, forms, and modals would be utilized efficiently
throughout sections of the platform, ensuring design
and functionality consistency. All of these AI mod-
els, in short, a conversational model, an image gener-
ation model, a code-generation model have their own
pages, all orchestrated through the powerful capabil-
ities of Next.js 13’s App Router. This has enhanced
routing. Not only this but has also reduced loading
times, so users can get just the functionalities they
need to use without waiting in vain. In order to easily
access our site, we made use of Tailwind CSS for the
responsive design. Using this ensures that the look
and functionality of our site look beautiful on any de-
vice. Our users can ensure a smooth experience using
their desktop computer at home or in a cafe´ while
running their office.
4.1.1 Conversational Model
In the proposed architecture, GPT-3.5-turbo model is
integrated to provide human-like conversations across
various use cases:
• Chatbot interactions: Assists users with real-time
responses and natural language processing.
• Customer support: Acts as a virtual assistant to an-
swer queries.
Integrating Conversational AI, Image Generation, and Code Generation: A Unified Platform
177
• Creative brainstorming: Helps users generate ideas,
summaries, and insights.
• Backend: The conversational API is handled
through a Next.js server that processes user inputs and
fetches responses from OpenAI.
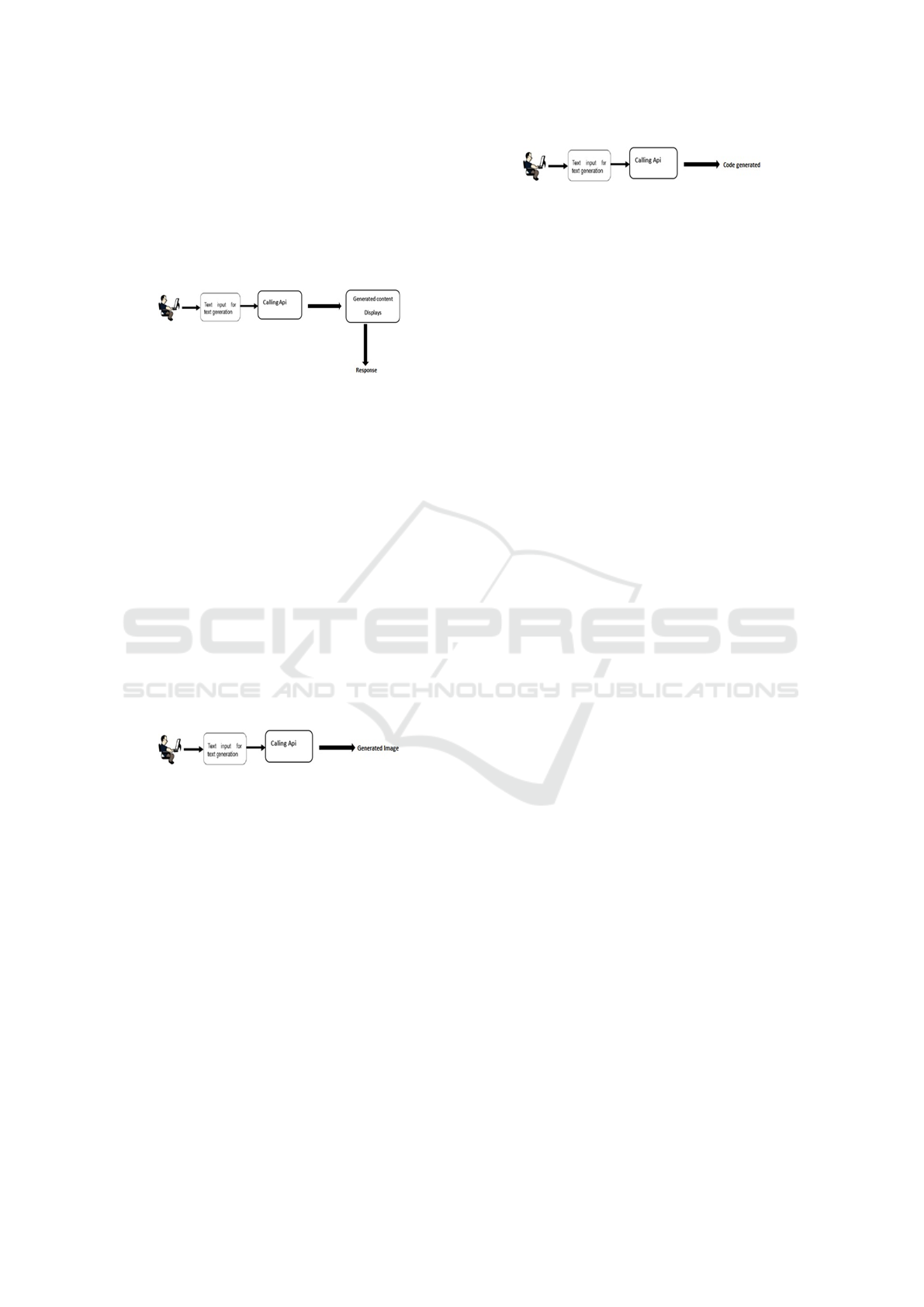
Figure 2 shows the working of the conversational
model of the proposed system.
Figure 2: Working of Conversational Model
4.1.2 Image Generation Model
• The platform integrates DALL·E API to generate
creative images from user-provided text prompts.
• Use cases: Designing custom artwork, generating
content visuals, or prototyping. Here, user inputs a
text prompt through the front-end UI. Backend routes
the request to the DALL·E API.
• The generated image is displayed to the user via the
front end.
• Performance: The system ensures quick responses
with proper error handling for invalid inputs.
This feature provides users with creative image gen-
eration capabilities, making it useful for content cre-
ators and designers. Figure 3 shows the working of
the image generation model of the proposed system.
Figure 3: Working of Image Generation Model
4.1.3 Code Generation Model
• The GPT-3.5-turbo model powers the code genera-
tion feature to assist developers with code snippets.
Generating ready-to-use code for specific tasks (e.g.,
sorting algorithms, API calls). Bug fixes and sugges-
tions help users debug code or optimize logic.
• Language support: Covers multiple programming
languages such as Python, Java, and JavaScript.
• Front-end input fields where users describe the re-
quired code. API requests sent to the GPT-3.5-turbo
backend to generate the corresponding code snippet.
• The result is displayed with syntax highlighting for
better readability. This feature improves productiv-
ity by giving developers quick access to relevant code
solutions. Fig. 4 shows the working of the conversa-
tional model of the proposed system.
Figure 4: Working of Conversational Model
4.2 Back-End Development
We’ve used Node.js and Express for the back-end
part of our application. Pretty much everything that
was required in order to handle API requests on
the OpenAI advanced models being GPT-3.5-turbo
and DALL·E was given. Another point made on
the performance-oriented back-end structure was the
data fetching provided by Next.js 13 for real-time re-
sponses in front- end components.
It goes a long way in ensuring that as soon as users
send in their requests-whether it is generating text,
images, or code- the responses are served fast and cor-
rect. Our back-end architecture is optimized to take
simultaneous requests just in case users will be mak-
ing loads of requests at one time, thereby making the
interaction more responsive.
4.3 Performance Review
To measure our system, we carried out thorough per-
formance testing, which involved test cases on load
strength, quality of the response served by the AI,
and user experience generally. User experience is
exactly what we measure at the heart. From experi-
ments and through feedback from users, we gathered
information on how people interact with our web-
site. Users were clearly satisfied with our website.
However, they were most satisfied with the conversa-
tional AI feature. Users opined that the answers re-
ceived from the system were always very specific and
relevant. Interacting with the system remained both
funny and informative. What was most pleasantly
surprising was that in the case of image generation
through DALL·E, the feedback was highly positive.
Users were astonished at the capacity of the model
to generate visual images on text prompts that var-
ied incredibly and even exceeded their expectations.
This ability not only enhances the creative process but
also opens new avenues for the generation of digital
content. The code generation feature also left devel-
opers a game- changer, as users pointed out how it
streamlined their workflow in terms of avoiding a lot
of redundant coding. Saves time, as well as increases
productivity, letting developers look at more complex
and innovative aspects of a project rather than getting
bogged down with nitty-gritty coding issues. Overall,
the performance review confirms our platform’s suc-
cessful fulfillment of all necessary user needs since it
is a combination of state-of- the-art technology and a
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
178

user-friendly design to constitute a powerful tool for
quite a diversified range of applications.
5 CHALLENGES FACED AND
SOLUTIONS
5.1 Integration of AI Tools
Challenge: Integrating the GPT-3.5-turbo and
DALL·E APIs into a single platform presented com-
patibility issues. Each API had its own authentication
methods, rate limits, and data handling requirements,
complicating the seamless interaction needed for real-
time user experiences.
Solution: To address this challenge, a unified back-
end service was developed using Node.js and Express,
which streamlined API interactions. A middleware
layer was created to handle authentication and re-
quests to the OpenAI APIs. This abstraction layer
simplified the process of communicating with both
tools, allowing for efficient data management and er-
ror handling. Furthermore, extensive testing was per-
formed to optimize API call efficiency and minimize
latency.
5.2 User Authentication and Security
Challenge: Secure user authentication was a key re-
quirement to safeguard user data and ensure a safe
user experience. The system design was complex as
it had to manage user sessions, authentication tokens,
and sensitive data without compromising security.
Solution: Clerk’s authentication solution was inte-
grated to the platform, providing a solid framework
for user management. Secure sign-up and login were
provided, along with token-based authentication for
session management. Best practices for securing API
endpoints and encrypting sensitive information were
followed to ensure that user data were secure.
5.2.1 Performance Optimization
Challenge: This made performance and response
times significant issues since the multiple functional-
ities on the platform also comprised various AI tools.
Sloppy loading and sluggish response could be disas-
trous for users, especially on live applications.
Solution: Different approaches are also used for per-
formance optimization. The server-side rendering in
Next.js reduces the initial load times while using the
application front end. Other than that, the response
from the APIs is also cached which prevents their call.
Loads have been tested so that gives more room for
refinement on both the front and the back-end.
5.3 User Interface Design
Challenge: The key was to make it easy to understand
and intuitive and communicate the potential of the
platform. Balancing functionality with aesthetics in
order to satisfy many varied user needs required very
careful design considerations. Solution: With this
progression, user feedback was asked to be included
throughout the process; hence, usability testing intro-
duced iterative refinements in that design. For lay-
outs, Tailwind CSS has been adopted, making the de-
signs re- sponsive as well as attractive by applying a
modular, easier interface using React components to
develop it. Always having access standards in mind
so as to make it possible to the wider Audience’s us-
ability also applied.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Conclusively, our Software as a Service (SaaS) plat-
form has reached all the targets set out in its roadmap
version. It is a very successful platform that inte-
grates the GPT-3.5- turbo technology of OpenAI and
the DALLE API, which is the most recent invention of
the GPT family. The platform, moreover, not only en-
sures real-life conversations mimicking the users but
also through this facilitates the process of image gen-
eration through textual descriptions and code creation
from specific prompts. From the beginning, our main
goal was to create a comprehensive solution for de-
velopers, content creators, and businesses. As a re-
sult of our careful planning and execution, we have
turned our vision into a reality. The user-centric expe-
rience that was offered through the use of Next.js 13
for server-side rendering and the implementations of
React and Tailwind CSS in the front end has enabled
us to accomplish this task. Additional security mea-
sures such as the use of Clerk for user authentication
have increased the reliability of the platform, thereby
protecting data while creating a feeling of trust among
users.
In addition, the modular architecture that made the
platform easy to extend and adapt to user needs
and technological advancement were the other advan-
tages. Adding extra features with AI capabilities such
as sentiment analysis and advanced NLP tools can
greatly be of benefit to the users. Sentiment analy-
sis would enable us to look at the interactions on a
much more granular level, while advanced NLP tools
Integrating Conversational AI, Image Generation, and Code Generation: A Unified Platform
179

could also allow for context awareness and nuance in
conversation to further enhance user engagement and
satisfaction. The main expansion of use cases is sig-
nificant to the growth of the platform, as the poten-
tial areas of application involve personalized educa-
tion tools that use conversational AI for tutoring, cre-
ative design applications for collaborative image gen-
eration, or automated coding assistants for develop-
ers. That means in order to increase market relevance
and adoption, we tailor the platform to specific indus-
tries, including e-commerce, healthcare, and enter-
tainment. An effective feedback mechanism will help
induce the users to share their experience and provide
suggestions directly through the platform. In such a
user- driven approach, it might be possible to guide
updates and development of future features so that the
platform develops accordingly considering the needs
and expectations of users. We believe that dedication
to continuous improvement and a focus on user expe-
rience will make a powerful tool to empower users in
creative or professional endeavors.
REFERENCES
Dakhel, A. M., Majdinasab, V., Nikanjam, A., Khomh, F.,
Desmarais, M. C., and Jiang, Z. M. J. (2023). Github
copilot ai pair programmer: Asset or liability? Jour-
nal of Systems and Software, 203:111734.
Kanakia, H. T. and Nair, S. P. (2023). Designing a user-
friendly and responsive ai based image generation
website and performing diversity assessment of the
generated images. In 2023 4th International Confer-
ence on Electronics and Sustainable Communication
Systems (ICESC), pages 1090–1097. IEEE.
Karras, T. (2019). A style-based generator architecture
for generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1812.04948.
Maddigan, P. and Susnjak, T. (2023). Chat2vis: generating
data visualizations via natural language using chatgpt,
codex and gpt-3 large language models. Ieee Access,
11:45181–45193.
Ramesh, A., Dhariwal, P., Nichol, A., Chu, C., and
Chen, M. (2022). Hierarchical text-conditional im-
age generation with clip latents. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2204.06125, 1(2):3.
Rapp, A., Di Lodovico, C., Torrielli, F., and Di Caro, L.
(2025). How do people experience the images cre-
ated by generative artificial intelligence? an explo-
ration of people’s perceptions, appraisals, and emo-
tions related to a gen-ai text-to-image model and its
creations. International Journal of Human-Computer
Studies, 193:103375.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
180
