
The Optimization Model and Algorithm of Emergency Logistics
Vehicle Routing Problem Considering Random Demand and
Robustness
Mei Li, Qian Li and Yan Lai
Shaanxi Fashion Engineering University, Shaanxi, 712046, China
Keywords: Random Demand, Genetic Algorithms, Emergency Logistics, Vehicle Path.
Abstract: The role of vehicle routing in emergency logistics is very important, but there is a problem of unreasonable
driving routes. Traditional methods cannot solve the problem of vehicle routing in emergency logistics, and
the route is irrational. Therefore, a genetic algorithm is proposed to optimize the analysis of vehicle paths.
Firstly, random demand is used to evaluate the route, and the index is divided according to the vehicle route
requirements to reduce the vehicle path in the interfering factor. Then, random demand for emergency
logistics vehicle path requirements, form a vehicle route scheme, and result on vehicle paths Conduct a
comprehensive analysis. MATLAB simulation shows that under certain evaluation criteria, the genetic
algorithm has a good effect on the accuracy and vehicle route
of emergency logistics The safety is superior
to traditional methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the field of logistics and transportation, route
optimization is an important issue. Path optimization
can effectively reduce the driving distance and time
of logistics vehicles, and improve the efficiency and
effectiveness of logistics transportation (Ahmed and
Al-Otaibi, et al. 2023). However, in practical
applications, the problem of logistics vehicle path
optimization is often affected by factors such as
random demand and robust characteristics, resulting
in increased complexity of route optimization (Alpos,
and Iliopoulou, et al. 2023). This article will explore
the impact of random demand and robust
characteristics on logistics vehicle path optimization
and how to optimize accordingly (Andersen, and
Belward, et al. 2023).
1.1 The Influence of Random Demand
and Robust Characteristics on
Logistics Vehicle Path
Optimization
In logistics and transportation, random demand refers
to the uncertainty of customer demand. This
uncertainty may be due to sudden changes in
customer demand, fluctuations in volume, or other
reasons (Andrade, and Usberti, 2023). The existence
of random demand will make the path optimization
problem of logistics vehicles more complicated. This
is because as demand changes, the routes and
distribution of logistics vehicles also need to change
to meet the needs of customers (Averbakh, and Yu,
2023).
In addition, robust properties also have an impact
on the routing optimization of logistics vehicles.
Robust characteristics refer to the ability of a system
to remain stable and reliable in the face of
uncertainty. In logistics, the realization of robust
characteristics can be achieved through proper
planning (Barauskas, and Brilingaite, et al. 2023).
However, the presence of random demand can
undermine the robustness of logistics vehicles,
resulting in a decrease in the quality of path
optimization (Becker, and Gauthier, et al. 2023).
In summary, random demand and robust
characteristics have the following effects on logistics
vehicle route optimization:
Difficult to predict demand: The existence of
random demand can make the data required for
logistics vehicle routing optimization more complex
and unpredictable (Bouleft, and Alaoui, 2023). This
Li, M., Li, Q. and Lai, Y.
The Optimization Model and Algor ithm of Emergency Logistics Vehicle Routing Problem Considering Random Demand and Robustness.
DOI: 10.5220/0013545800004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 1, pages 473-477
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
473

makes path planning more difficult, resulting in
increased complexity of path optimization problems.
Uncertainty in path planning: Due to random
demand, the path planning of logistics vehicles needs
to take into account possible future events (Caste,
Koch and Marenco, 2023), which makes path
planning more uncertain. This may lead to
adjustments and modifications to the path plan, which
will degrade the quality of the path plan (Chen, and
Zhou, et al. 2023).
Reduced robustness: The presence of random
requirements may lead to a decrease in the robustness
of path planning, which leads to a decrease in the
quality of path planning. This will make the
transportation efficiency and effectiveness of
logistics vehicles reduced (Chen, and Li, et al. 2023).
Reduction of optimization quality: The quality of
path optimization may degrade due to random
demand and robustness. Therefore, appropriate
methods and techniques are needed to address these
issues in order to optimize the path (Chirala, and
Sundar, et al. 2023).
1.2 Solution Scheme
In view of the impact of random demand and
robustness on the route optimization of logistics
vehicles, the following solutions can be adopted to
improve the quality and efficiency of route planning
(Fares, and Hassanien, et al. 2023).
Forecast demand: In logistics and transportation,
random demand can be predicted through historical
data and other relevant information. Through the
forecast of demand, the uncertainty of path planning
can be reduced, and the quality and efficiency of path
planning can be improved.
Increased resiliency: Due to the influence of
random demand and robustness, path planning needs
to take into account possible future events. Therefore,
it is necessary to increase the flexibility of path
planning so that it can be adjusted in time when
changes in the future.
Optimization algorithm: In the face of random
demand and robustness, path optimization algorithms
need to be more efficient, robust and flexible. Modern
optimization algorithms, such as genetic algorithms,
simulated annealing algorithms, and neural networks,
can be employed to improve the efficiency and
quality of path planning.
Optimization strategy: For the problems of
random demand and robustness, corresponding
optimization strategies can be formulated, such as
increasing spare resources and improving the
response speed to demand changes, so as to improve
the quality and efficiency of path planning.
In logistics, random demand and robustness have
a significant impact on route optimization. In order to
improve the quality and efficiency of path planning,
some corresponding solutions are required.
Specifically, the problems of random demand and
robustness can be dealt with by predicting demand,
increasing elasticity, optimizing algorithms and
optimization strategies, so as to improve the quality
and efficiency of route planning and realize the
efficient operation and effectiveness of logistics and
transportation.
In emergency logistics, the choice of vehicle path
is very important, and the environment of emergency
logistics also determines the complexity of the
vehicle routing problem. However, in the process of
vehicle route selection, there is a problem of poor
accuracy in the vehicle routing scheme, which brings
certain obstacles to emergency logistics
transportation. Some scholars believe that the
application of genetic algorithm to emergency
logistics analysis can effectively analyze the vehicle
route scheme and provide corresponding support for
vehicle route selection. On this basis, a genetic
algorithm is proposed to optimize the vehicle route
scheme and verify the effectiveness of the model.
2 RELATED CONCEPTS
2.1 Mathematical Description of the
Genetic Algorithm
The genetic algorithm uses computer simulation to
optimize the vehicle route scheme, and according to
the indicators in the vehicle route, find the unqualified
value in the emergency logistics, and integrate the
vehicle route scheme to make the final judgment
Feasibility of emergency logistics. Genetic
algorithms combine the advantages of computer
simulation calculations and quantify emergency
logistics, which can improve the rationality of vehicle
paths.
Hypothesis 1: The vehicle route requirement is
i
f
, the vehicle route scheme is
i
s
et
, the
satisfaction of the vehicle route scheme is
v
, and the
vehicle route scheme judgment function is
(0)
i
Uf≈
,As shown in Equation (1).
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
474

()
f
i
i
i
fv
v
Ufv U
U
σ
−
=+ ⋅
(1
)
2.2 Selection of Vehicle Routing
Scheme
Hypothesis 2: The emergency logistics function is
()
i
mf
, and the weight coefficient is
i
l
, then the
vehicle route requires unqualified emergency
logistics as shown in equation (2).
2
1
1
()= ( )
m
ii
i
i
mf m f m
m
=
→−+
(2
)
2.3 Analysis of Vehicle Routing
Schemes
Before the genetic algorithm is carried out, the
vehicle route scheme should be analyzed in multiple
dimensions, and the vehicle route requirements
should be mapped to the emergency logistics library,
and the unqualified vehicle route scheme should be
eliminated. First, emergency logistics is
comprehensively analyzed, and the threshold and
index weights of the vehicle route scheme are set to
ensure the accuracy of the genetic algorithm.
Emergency logistics is a systematic test of vehicle
routing schemes, which requires accurate analysis. If
the emergency logistics are in a nonnormal
distribution, their vehicle routing scheme will be
affected, reducing the accuracy of the overall vehicle
route. In order to improve the accuracy of the genetic
algorithm and improve the level of vehicle path, the
vehicle route scheme should be selected, and the
specific scheme selection is shown in Figure 1.
Vehicle
route
Driving route
Emergency
logistics
Path security
Path accuracy
Stochastic demand
Figure 1: The result of the selection of the vehicle routing
scheme
The survey of vehicle route scheme shows that the
vehicle route scheme presents a multi-dimensional
distribution, which is in line with objective facts.
Emergency logistics is not directional, indicating that
the vehicle route scheme has strong randomness, so it
is regarded as a high analytical study. Emergency
logistics meets the normal requirements, mainly
computer simulation operation adjusts emergency
logistics, eliminates duplicate and irrelevant schemes,
and supplements the default scheme, so that the
dynamic correlation of the entire vehicle route
scheme is strong.
3 OPTIMIZATION STRATEGIES
FOR EMERGENCY LOGISTICS
The genetic algorithm adopts the random
optimization strategy for emergency logistics, and
adjusts the vehicle route parameters to realize the
scheme optimization of emergency logistics. The
genetic algorithm divides the emergency logistics
into different vehicle route levels, and randomly
selects different schemes. In the iterative process, the
vehicle route scheme of different vehicle route levels
is optimized and analyzed. After the optimization
analysis is completed, the vehicle path levels of
different scenarios are compared to record the optimal
emergency logistics.
4 PRACTICAL EXAMPLES OF
EMERGENCY LOGISTICS
4.1 Vehicle Routing Profile
In order to facilitate vehicle paths, this paper takes
emergency logistics in complex situations as the
research object, with 12 paths and a test time of 12h
shown IN Table 1.
Table 1: Vehicle routing requirements
Scope of
application
Grade Accuracy Vehicle
p
ath
Path one ordinar
y
87.24 90.00
Hi
g
he
r
87.71 83.19
Path two ordinar
y
82.26 85.60
Hi
g
he
r
86.14 84.36
Path three ordinar
y
85.95 82.81
Hi
g
he
r
88.08 86.74
The vehicle routing process in Table 1 is shown in
Figure 2.
The Optimization Model and Algorithm of Emergency Logistics Vehicle Routing Problem Considering Random Demand and Robustness
475
Vehicle
route
Genetic
algorithm
Stochastic
demand
Path accuracyEmergency logistics
Figure 2: Analysis process of emergency logistics
Compared with traditional methods, the vehicle
routing scheme of genetic algorithm is closer to the
actual vehicle routing requirements. In terms of
random demand and distribution speed of emergency
logistics, genetic algorithms are superior to traditional
methods. From the change in vehicle routing scheme
in Figure 2, it can be seen that the genetic algorithm
has higher accuracy and faster delivery speed.
Therefore, the speed of the vehicle route scheme, the
rationality of the vehicle route scheme and the
summation stability of the genetic algorithm are
better.
4.2 Emergency Logistics Situation
The vehicle routing scheme of emergency logistics
contains non-structural information, semi-structural
information, and structural information. After the pre-
selection of genetic algorithm, the preliminary
vehicle path scheme of emergency logistics and the
vehicle path of emergency logistics are obtained
Analyze the feasibility of the scheme. In order to
more accurately verify the rationality of the
emergency logistics vehicle path, select the
emergency logistics with different vehicle route
levels, and the vehicle route scheme is shown in Table
2.
Table 2: The overall picture of the vehicle routing scheme
Categor
y
Rationalit
y
Analysis rate
Path one 88.78 90.69
Path two 87.53 88.86
Path three 92.96 90.47
mean 87.68 87.90
X
6
89.89 88.64
P=2.13
4.3 Vehicle Routing and Stability of
Vehicle Paths
In order to verify the accuracy of the genetic
algorithm, the vehicle routing scheme is compared
with the traditional method, and the vehicle routing
scheme is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Vehicle routing with different algorithms
It can be seen from Figure 3 that the vehicle path
of the genetic algorithm is higher than that of the
traditional method, but the error rate is lower,
indicating that the vehicle path of the genetic
algorithm is relatively stable, while that of the
traditional method Vehicle paths are uneven. The
average vehicle routing scheme of the above three
algorithms is shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Comparison of vehicle route accuracy of different
methods
Algorithm Vehicle
p
ath
Magnitude
of chan
g
e
Error
Genetic
algorith
m
91.77 93.96 93.51
Traditional
methods
90.65 88.97 90.69
P 88.26 87.72 89.06
It can be seen from Table 3 that the traditional
method has shortcomings in the rationality of vehicle
routes in emergency logistics, and emergency
logistics has changed significantly, and the error rate
is high. The general result of the genetic algorithm is
that the vehicle path is closer and better than
traditional methods. At the same time, the vehicle
path of the genetic algorithm is greater than 91%, and
the accuracy does not change significantly. To further
verify the superiority of genetic algorithms. In order
to further verify the effectiveness of the proposed
method, the genetic algorithm was generally analyzed
by different methods, as shown in Figure 4.
It can be seen from Figure 4 that the vehicle path
of the genetic algorithm is significantly better than the
traditional method, and the reason is that the genetic
algorithm increases the adjustment coefficient of
emergency logistics and sets the vehicle path
threshold, rejecting non-compliant vehicle routing
schemes.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
476
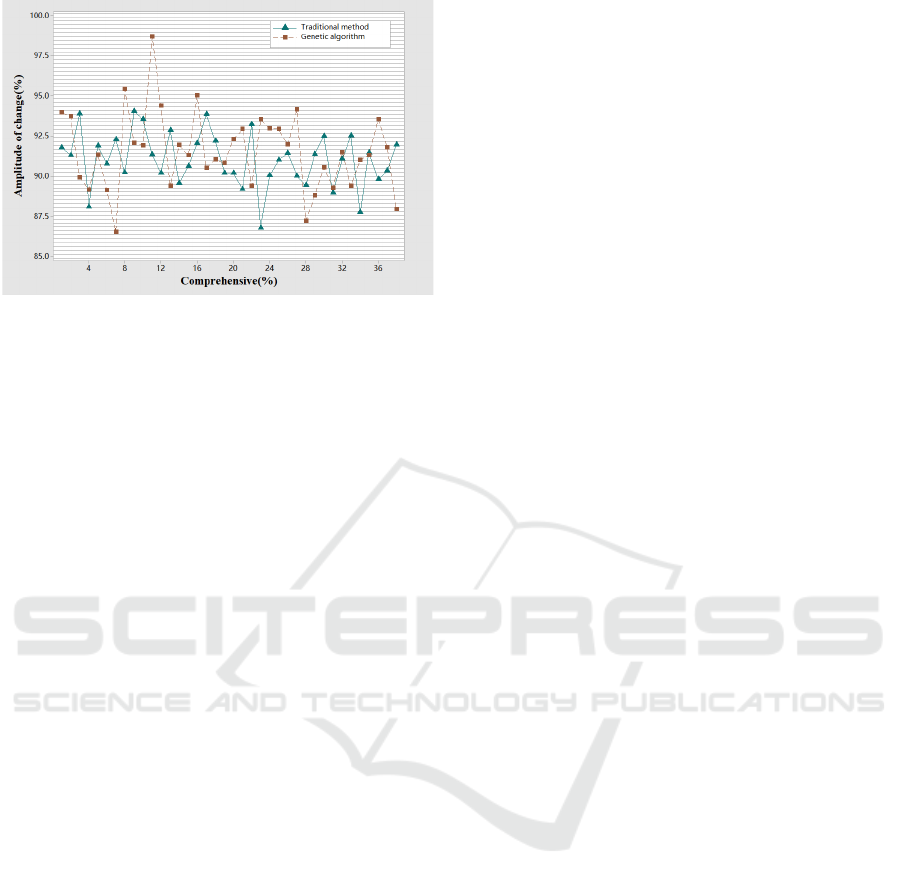
Figure 4: The vehicle path of the genetic algorithm vehicle
path
5 CONCLUSIONS
Aiming at the problem that the path of emergency
logistics vehicles is not ideal, this paper proposes a
genetic algorithm and combines computer simulation
to optimize emergency logistics. At the same time,
the vehicle path distance and rationality of selection
are analyzed in depth, and the vehicle route collection
is constructed. Studies show that genetic algorithms
can improve the accuracy and stability of emergency
logistics, and can carry out general vehicle routes for
emergency logistics. However, in the process of
genetic algorithm, too much attention is paid to the
analysis of vehicle path, resulting in irrationality in
the selection of vehicle route indicators.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This subject originates from the 2021 Scientific
Research Plan of Shaanxi Provincial Department of
Education. Research on Emergency Logistics for
Uncertain Demand and Road Section Failure,No.:
21JK0037
REFERENCES
Ahmed, Z. H., Al-Otaibi, N., Al-Tameem, A., & Saudagar,
A. K. J.(2023) Genetic Crossover Operators for the
Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem. Cmc-
Computers Materials & Continua, 74(1): 1575-1605.
Alpos, T., Iliopoulou, C., & Kepaptsoglou, K.(2023)
Nature-Inspired Optimal Route Network Design for
Shared Autonomous Vehicles. Vehicles, 5(1): 24-40.
Andersen, T., Belward, S., Sankupellay, M., Myers, T., &
Chen, C. R.(2023) Reoptimisation strategies for
dynamic vehicle routing problems with proximity-
dependent nodes. Top.
Andrade, M. D., & Usberti, F. L.(2023) A theoretical and
computational study of green vehicle routing problems.
Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 45(5).
Averbakh, I., & Yu, W.(2023) The probabilistic
uncapacitated open vehicle routing location problem.
Networks, 82(1): 68-83.
Barauskas, A., Brilingaite, A., Bukauskas, L., Ceikute, V.,
Civilis, A., & Saltenis, S.(2023) Test-data generation
and integration for long-distance e-vehicle routing.
Geoinformatica.
Becker, C., Gauthier, J. B., Gschwind, T., & Schneider,
M.(2023) In-depth analysis of granular local search for
capacitated vehicle routing. Discrete Applied
Mathematics, 329: 61-86.
Bouleft, Y., & Alaoui, A. E.(2023) Dynamic Multi-
Compartment Vehicle Routing Problem for Smart
Waste Collection. Applied System Innovation, 6(1).
Caste, J., Koch, I., & Marenco, J.(2023) Implementing a
multi-user framework for vehicle routing problems: a
chronicle. Central European Journal of Operations
Research.
Chen, J. Y., Zhou, R., Sun, G. B., Li, Q. W., & Zhang,
N.(2023a) Distributed formation control of multiple
aerial vehicles based on guidance route. Chinese
Journal of Aeronautics, 36(3): 368-381.
Chen, X. T., Li, Q., Li, R. H., Cai, X. Y., Wei, J. N., &
Zhao, H. Y.(2023b) UAV Network Path Planning and
Optimization Using a Vehicle Routing Model. Remote
Sensing, 15(9).
Chirala, V. S., Sundar, K., Venkatachalam, S., Smereka, J.
M., & Kassoumeh, S.(2023) Heuristics for Multi-
Vehicle Routing Problem Considering Human-Robot
Interactions. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles,
8(5): 3228-3238.
Fares, I., Hassanien, A. E., Rizk-Allah, R. M., Farouk, R.
M., & Abo-donia, H. M.(2023) Solving capacitated
vehicle routing problem with route optimisation based
on equilibrium optimiser algorithm. International
Journal of Computing Science and Mathematics, 17(1):
13-27.
The Optimization Model and Algorithm of Emergency Logistics Vehicle Routing Problem Considering Random Demand and Robustness
477
