
Research on Source-Load Collaborative Planning Method of Active
Distribution Network Based on DG Initialization Site Selection
Xuan Yang
1
, Junhai Wang
1
, Gang Wang
1
, Mingchang Wang
1
, Lin Chen
1
and Chendan Dong
2
1
State Grid Hangzhou Power Supply Company, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
2
Hangzhou Guodian Electrical Power Technology Development Co., Ltd, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Keywords: Data Mining Theory, DG Initialization Site Selection, Collaborative Planning Approach, Distribution
Network, Mesh Load.
Abstract: At this critical juncture of the energy transition, distributed energy resources (DG) are springing up. DG
initialization and siting have become a major issue in power system planning. It involves not only the efficient
use of energy and the stability of the network, but also the balance between economic costs and environmental
impacts. Therefore, source-grid-load collaborative planning has become a key step in realizing the intelligence
of active distribution networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
First of all, we need to recognize that DG does not
exist in isolation, and its value is reflected in its
interaction with the grid (Zheng and Xuan, et al.
2023). The traditional power grid is a passive
transmission system, but when the DG is properly
initialized and situated (Zhou and Hu, et al. 2023), the
entire network is transformed into an intelligent
system that can proactively respond to changes in
demand and supply (Lin and Yan, et al. 2023). This
shift means greater energy efficiency, greater system
stability, and more flexibility in the market.
2 RELATED CONCEPTS
2.1 Mathematical Description of DG
Initialization Siting
Next, we need to explore how to do an effective DG
initial site selection. This process involves complex
data processing and model analysis, including but not
limited to load forecasting, variability assessment of
renewable energy (Liao and Zhang , et al. 2023),
analysis of network constraints, etc. With the support
of advanced algorithms and optimization techniques
(Jin, 2023), we can ensure that the layout of the DG
meets the economic, technical and environmental
requirements to the greatest extent.
(1
)
In addition, we need to consider social factors.
The location of DG should avoid densely populated
areas as much as possible to reduce the impact on
residents' lives.
(2
)
At the same time, considering that the
development of DG may change the local
employment structure and economic model, we need
to actively cooperate with local governments and
communities at the planning stage to ensure that the
project can be widely accepted and supported by the
society (Lei and Wu, et al. 2023).
Of course, technological innovation is the core
driving force for the development of DG (Liu Ying,
Song Limin, et al. 2023). Whether it is the
breakthrough of energy storage technology, the
application of cloud computing and big data, or the
combination of the Internet of Things and artificial
intelligence, it provides the possibility for the
efficient operation of DG (Zhu and Liu, et al. 2023).
lim( ) lim max( 2)
iij ij ij
xx
yt y t
→∞ →∞
⋅= ≥ ÷
2
max( ) ( 2 ) ( 4)
ij ij ij ij
y
tttmeant
x
Δ
=∂ + ⋅ +
Δ
Yang, X., Wang, J., Wang, G., Wang, M., Chen, L. and Dong, C.
Research on Source-Load Collaborative Planning Method of Active Distribution Network Based on DG Initialization Site Selection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013545500004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 1, pages 457-462
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
457

In the context of source-grid-load coordination, these
technologies not only optimize the allocation of
resources, but also improve the adaptive ability of the
system.
(3)
2.2 Selection of Collaborative Planning
Methods
Finally, let's look to the future. With the access of new
loads such as electric vehicles and smart homes, DG
and its distribution network will become more
complex and changeable (Guo, 2022). However, as
long as we adhere to the scientific source-grid-load
collaborative planning, and continue to explore and
innovate, we can ensure the sustainability, safety and
flexibility of the power system and welcome the
arrival of the smart grid era.
(4)
In summary, the active distribution network
source-grid-load collaborative planning of DG
initialization and site selection is a multi-dimensional
and interdisciplinary work, which requires us to
comprehensively consider technical, economic,
social and environmental factors (Zhang and Lei, et
al. 2022). Through careful planning and
implementation, we can ensure the optimal allocation
of DG resources and lay a solid foundation for
building an efficient, green and reliable future power
grid.
(5)
In today's fast-paced economic environment, the
initialization and siting of distributed generation
(DG) systems has become a key component of power
system planning. With the advancement of
technology and the rise of renewable energy, the
layout of DG projects is no longer a single-
dimensional decision-making process, but a
comprehensive task involving multi-factor
collaborative analysis.
(6
)
2.3 Analysis of Collaborative Planning
Methodological Schemes
First of all, DG initialization refers to the start-up and
construction phases of a distributed generation
project, which involves an in-depth assessment of the
technical, environmental, economic, and social
impacts of the project. A successful DG initialization
plan not only ensures the smooth implementation of
the project, but also lays a solid foundation for stable
operation in the future.
(7
)
Site selection was a crucial step in the DG project.
Proper siting not only ensures efficient distribution
and use of energy, but also maximizes economic
benefits while minimizing social and environmental
costs. Therefore, the site selection process must take
into account multiple aspects such as geographical
location, environmental impact, policies and
regulations, market demand, network access, and
cost-effectiveness.
(8
)
In DG initialization and site selection,
collaborative analysis methods are particularly
important. Synergy means that the various elements
of decision-making are not considered in isolation,
but are interrelated and interactive. For example, an
environmental impact assessment should consider not
only the direct impact of the construction and
operation phases of the project, but also its potential
impact over its entire life cycle.
(9
)
Economic assessment is equally complex,
including not only initial investment, operating costs,
and earnings projections, but also policy incentives,
the time value of capital flows, and long-term market
dynamics. The social impact assessment takes into
account the direct and indirect impacts of the project
on the lives of local residents, such as noise,
landscape change and employment opportunities.
()
!
() 2 7
!!
iii
n
F
dty
rnr
ξ
=⋅→⋅
−
()= ( )
ii i i
dy
gt x z Fd w
dx
⋅−
∏
lim ( ) lim ( ) max( )
ii ij
xx
gt Fd t
→∞ →∞
+≤
() ( ) ( 4)
ii ij
gt Fd mean t+↔ +
2
() ( )
4
()
(4)2
ii
i
ij
gt Fd
bb ac
No t
mean t a
+
−± −
=
+
() [ () ( )]
iii
Z
ht gt F d=+
min[ ( ) ( )]
( ) 100%
2()()
ii
i
ii
gt Fd
accur t
gt Fd
+
=×
+
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
458

(10)
Another important aspect is technical analysis,
which involves the selection, performance, reliability
and impact of DG systems on the existing power
system. Technological advancements have provided
more options for DG projects, such as wind power,
solar photovoltaics, small-scale hydropower, and
biomass, each with its own unique advantages and
limitations.
3 OPTIMIZATION STRATEGIES
FOR COLLABORATIVE
PLANNING METHODS
Network access was another key factor in the location
of the DG. Since distributed generation often needs to
be connected to the main grid, the capacity, stability
and acceptability of the grid become technical
parameters that must be considered. A reasonable
network access scheme can ensure the smooth
connection of DG to the grid and avoid instability or
damage to the power grid.
4 PRACTICAL EXAMPLES OF
COLLABORATIVE PLANNING
APPROACHES
4.1 Introduction to Collaborative
Planning Methods
In conclusion, the synergistic analysis of DG
initialization and site selection requires us to adopt a
comprehensive and systematic way of thinking,
integrate various factors, and find the best solution
through accurate calculations and scientific decision-
making methods. This requires not only specialized
knowledge and skills, but also interdisciplinary
cooperation and efficient exchange of information.
As the energy landscape continues to change in
the future, DG projects will play an increasingly
important role.
Table 1: Collaborative planning approach requirements
Scope of
application
Grade Accuracy Collaborative
planning
a
pp
roach
Source-
network-load
collaborative
planning
al
g
orith
m
I 85.00 78.86
II 81.97 78.45
Source-
network-load
collaborative
planning
model
I 83.81 81.31
II 83.34 78.19
Source-
network-load
collaborative
planning
strate
gy
I 79.56 81.99
II 79.10 80.11
Data mining
theory
Analyse
Distribution
network
DG initialise
Collaborative
planning
Site selection
Net charge
Figure 1: The analysis process of the collaborative planning
method
Through effective synergistic analysis, we can
ensure that the initialization and site selection of DG
projects are more scientific, rational and efficient, so
as to promote the use of renewable energy, improve
energy security, reduce environmental impact, and
make positive contributions to the sustainable
development of social economy.
4.2 Collaborative Planning Methods
In today's business environment, Data General (DG)
companies face stiff competition and ever-changing
market conditions. In this context, there is a subtle but
profound relationship between the DG initialization
process, i.e., the initial setup, configuration and start-
up of a company, and its location strategy.
min[ ( ) ( )]
() (
)
1
() ( )
2
ii
ii
ii
gt Fd
accur t randon t
gt Fd
+
=+
+
Research on Source-Load Collaborative Planning Method of Active Distribution Network Based on DG Initialization Site Selection
459
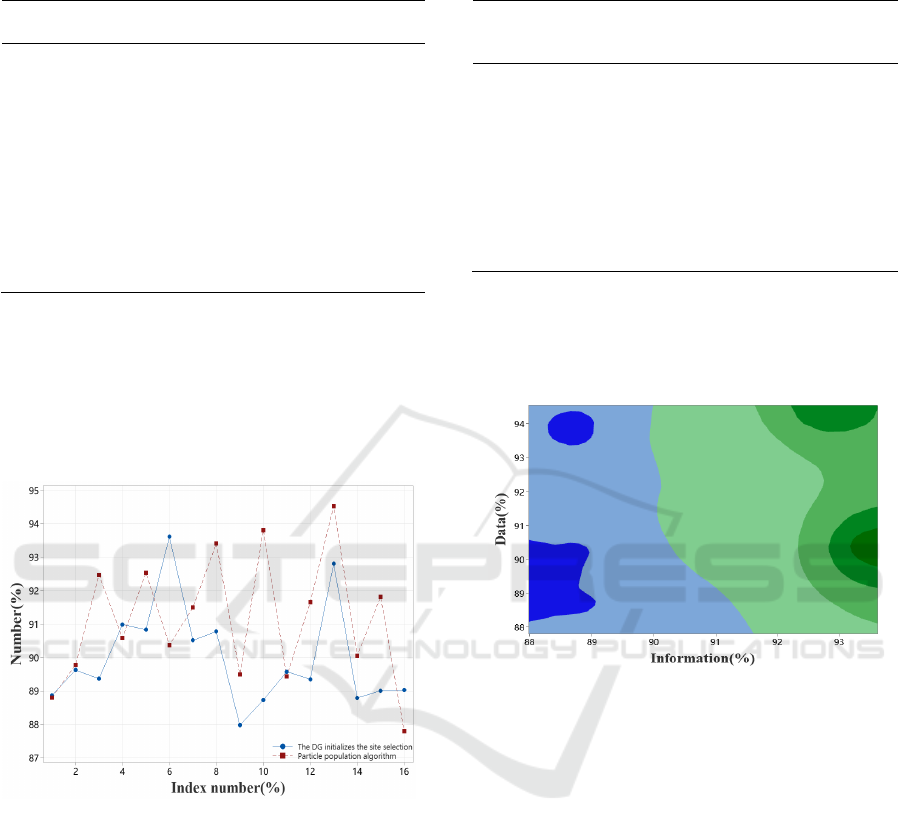
Table 2: Overall picture of the collaborative planning
approach scenario
Category Random
data
Reliability Analysi
s rate
Source-network-
load collaborative
p
lannin
g
al
g
orithm
85.32 85.90 83.95
Source-network-
load collaborative
p
lanning model
86.36 82.51 84.29
Source-network-
load collaborative
p
lannin
g
strate
gy
84.16 84.92 83.68
Mean 86.84 84.85 84.40
X6 83.04 86.03 84.32
P=1.249
4.3 Collaborative Planning Methods
and Stability
This relationship not only affects the operational
efficiency of the enterprise, but also directly relates to
many aspects such as enterprise cost management,
market expansion and even brand image.
Figure 2: Collaborative programming methods for different
algorithms
First of all, the core of DG initialization is to
ensure that the company's basic framework can be
adapted for future development. This involves
enterprise resource planning (ERP), supply chain
management, human resource allocation, and
technological innovation. In this process, site
selection became a decisive factor. A strategic
location can provide DG with easy access to logistics,
attract highly qualified talent, and access to a wider
network of customers and partners. Therefore, the
success of DG initialization depends to a large extent
on its ability to establish its own base of operations in
a favorable geographical location.
Table 3: Comparison of the accuracy of collaborative
planning methods of different methods
Algorith
m
Surve
y data
Collaborativ
e planning
approach
Magnitud
e of
change
Erro
r
DG
initialize
s site
selection
85.33 85.15 82.88 84.9
5
Particle
swarm
arithmeti
c
85.20 83.41 86.01 85.7
5
P 87.17 87.62 84.48 86.9
7
Furthermore, DG's location decision is closely
linked to its long-term development strategy. A
forward-looking site would provide DG with room to
expand, both physically and marketably.
Figure 3: DG Initialization Site Selection Collaborative
Planning Method
For example, if DG chooses to set up its
headquarters in a science and technology park, it will
not only provide sufficient technical support and
talent for its R&D activities, but also enhance its
competitiveness and influence in the industry. In
addition, such a location can also bring preferential
policies to DG, such as tax exemptions, financial
support, etc., which are advantages that cannot be
ignored in the process of DG initialization.
4.4 Rationality of Collaborative
Planning Methods
However, site selection is not a simple decision-
making process. It requires a comprehensive
consideration of various factors, including
transportation accessibility, labor costs, local policy
environment, market demand analysis, etc. DG's in-
depth research and accurate judgment in these aspects
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
460
will directly affect the efficiency and cost of its
initialization.
Figure 4: Collaborative programming methods for different
algorithms
Finally, DG also needs to consider its brand
positioning and market image. A good location can
enhance the brand value of DG and attract more
customer attention.
4.5 The Effectiveness of Collaborative
Planning Approaches
In summary, the relationship between DG
initialization and site selection is complex and close.
A reasonable location strategy can provide a solid
foundation for the initialization of DG and help
enterprises occupy an advantageous position in a
highly competitive market.
Figure 5: Collaborative programming methods for different
algorithms
A missiting can lead to increased transportation
costs, brain drain, missed market opportunities, and
even legal risks for non-compliance with
environmental requirements. Therefore, the DG must
treat site selection as a strategic issue during the
initialization phase, rather than just as a simple
administrative task.
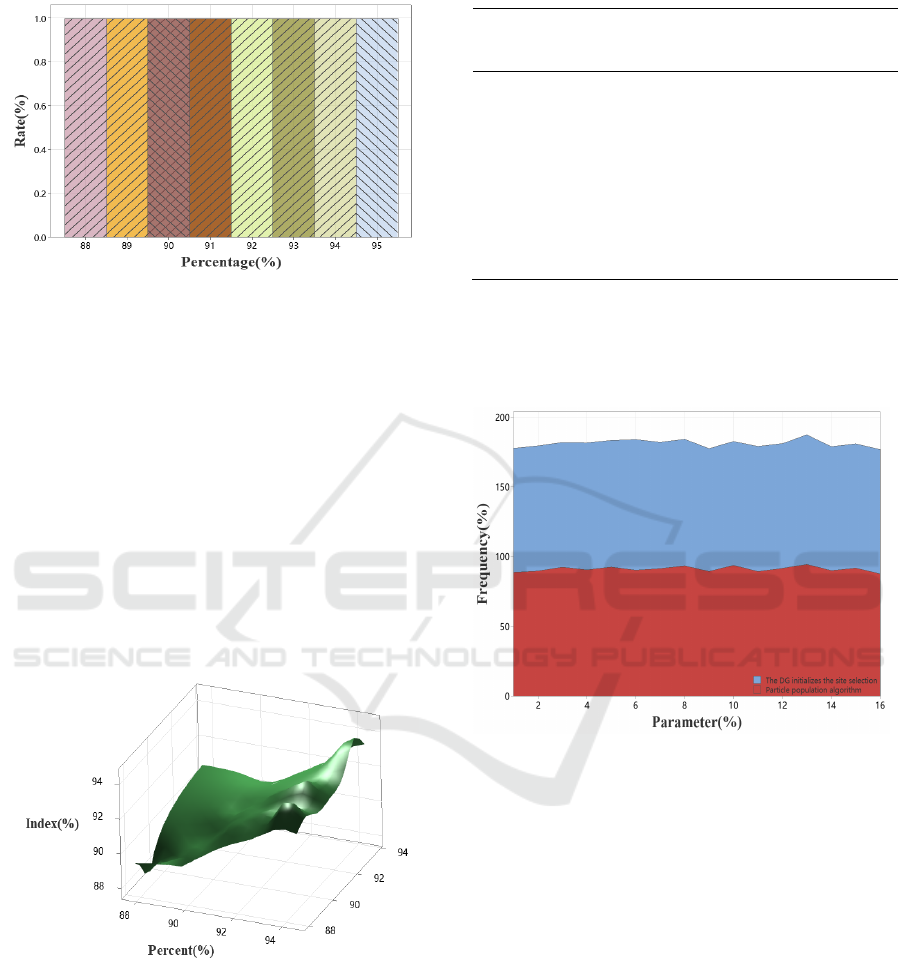
Table 4: Comparison of the effectiveness of collaborative
planning methods of different methods
Algorith
m
Surve
y data
Collaborativ
e planning
approach
Magnitud
e of
change
Erro
r
DG
initialize
s site
selection
82.21 85.92 84.59 82.8
5
Particle
swarm
arithmeti
c
83.73 84.23 84.41 83.5
5
P 84.20 87.39 84.76 83.9
0
For example, businesses located in economically
prosperous areas are often perceived as more dynamic
and innovative, which is extremely beneficial for DG
in the market and brand building.
Figure 6: DG initializes the collaborative planning method
of site selection
As a result, companies need to invest in data
management and cleaning to ensure data reliability.
Second, algorithm design and parameterization
require specialized knowledge, which requires the
finance team to have some data analysis capabilities
or work closely with data scientists.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Conversely, a wrong location decision can have a
series of negative impacts on DG, and even affect the
long-term development of the company. As a result,
DG must place a high priority on its site selection
strategy during the initialization process, ensuring
that every decision step supports its business goals
and growth vision. Only in this way will DG be able
Research on Source-Load Collaborative Planning Method of Active Distribution Network Based on DG Initialization Site Selection
461

to establish a strong foothold and succeed in the ever-
changing business world.
REFERENCES
Zheng Jieyun, Xuan Juqin, Zhang Linyao, Chen Bo, Chen
Yuanwei,&Chen Xiaobin, etc (2023) An active
distribution network source network load storage
coordination planning method considering electric
vehicle charging stations Journal of Wuhan University:
Engineering Edition, 56 (1), 11
Zhou Yu, Hu Weifeng, Ma Ruxiang, Wang Sheng, Shi
Hongbing,&Xu Zheng (2022) An active distribution
network source load elastic control system
CN201811367045.7
Lin Junhao, Yan Hao,&Wang Junxiang (2023) Based on
Monte Carlo tree search and ε Optimization method for
load storage collaborative operation of distribution
network source network based on constrained
algorithm Electricity and Energy, 44 (2), 179-186
Liao Xiaobing, Zhang Min, Le Jian, Li Zicheng,&Gong
Chao (2023) An affine tunable robust optimization
method for active distribution networks considering
cyclic life loss Power System Protection and Control,
51 (8), 37-49
Jin Haitao (2023) A multi-objective collaborative planning
method for load storage in distribution networks
CN115689034A
Dong Lei, Wu Yi, Zhang Tao, Wang Xinying, Hao
Yi,&Guo Lingxu (2023) A two-layer optimization
method for active distribution networks with intelligent
soft switches based on reinforcement learning Power
System Automation, 47 (6), 10
Liu Ying, Song Limin, Gong Qiang, Lv Sen, Chen
Sen,&Xie Ning (2023) Research on the coordinated
planning model of rural comprehensive energy system
source network load storage considering demand
response Hunan Electric Power, 43 (3), 21-28
Zhu Anming, Liu Chao, Wang Chengmin,&Chen Wanxi
(2023) A collaborative planning method for active
distribution network source network load Electrical
automation, 45 (2), 68-70
Guo Xiaocheng (2022) Active distribution network
framework planning based on source network load
storage coordination optimization Communication
Power Supply Technology, 39 (14), 6-9
Zhang Zhonghui, Lei Dayong, Li Jun, Xu Yanyu,&Luo
Junwei (2022) Based on adaptive ε- A source network
load storage dual level collaborative programming
model with SOP for active distribution networks that
dominates multi-objective particle swarm optimization
algorithm Grid Technology (006), 046
Liu Kinkinson, Luo Ning, Wang Jie, Xu Chang, Cao
Yi,&Liu Zhiwen (2022) Collaborative planning of load
storage in distribution network based on massive scene
dimensionality reduction China Electric Power, 55
(12), 8
Liao Jianbo, Wu Kailin, Liu Peng (2022) A power balance
method for source network load storage collaboration
in new power systems Electrical Technology (10), 132-
138
Yu Ziheng, Zhou Bowen, Yang Dongsheng, Zhang
Huaguang, Liu Xinrui,&Luo Yanhong, et al (2022) An
Active Distribution Network Source Load Interaction
Decision Method Based on Consistency Algorithm
CN201910862396.3
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
462
