
Portfolio Algorithm Based on Accounting Information System
Relevance
SuJuan Zhou
Yunnan College of Business Management, KunMing, 650000, China
Keywords: Combinatorial Algorithm, Investment Decisions, Accounting Information Management, Single Investment,
Invest More, Comprehensive Investment, Combination Rate, Relevance, Decision Accuracy.
Abstract: Accounting information management plays a crucial role in investment decision-making, but there is a
problem of inaccurate evaluation. The proportional estimation method cannot solve the accounting
information management problem in investment decision-making, and the decision-making plan is
unreasonable. Therefore, this article proposes a combination algorithm for investment risk accounting
information management analysis. Firstly, a combination of indicators is used to make decisions on
comprehensive investments, and indicators are divided according to accounting information management
requirements to reduce interference factors in accounting information management. Then, comprehensive
indicators are used to analyze investment risk accounting information, form an accounting information
management plan, and comprehensively analyze the results of accounting information management. The
accuracy of investment decision shows that under the condition that the decision analysis indicators are fixed,
the accuracy of the combination algorithm for accounting information management analysis of various
investment risks and the analysis time of accounting information management are better than the proportional
estimation method.
1 INTRODUCTION
The portfolio ratio is one of the important contents of
investment decision-making (Alsubaei, 2023), which
is of great significance for the accuracy of decision-
making (Bratfisch, Riar, et al. 2023). However, in the
process of accounting information management, there
is a problem of poor accuracy in accounting
information management plans (Cola, Mazza, et al.
2023), which affects the return on various
investments. Some scholars believe that applying
portfolio algorithm to investment decision analysis
can effectively analyze accounting information
management schemes and provide corresponding
support for accounting information management
(Dalloul, Ibrahim, et al. 2023). On this basis, this
article proposes a combination algorithm to optimize
accounting information management schemes and
verify the effectiveness of the algorithm (De, Ferreira,
et al. 2023).
1.1 Portfolio Algorithm for Accounting
Information Systems
The portfolio algorithm of the Accounting
Information System (AIS) is a mathematical method
that helps investors choose and balance their
portfolios. It helps people minimize risk and ensure
maximum returns by diversifying their portfolios
(Ferreira, Slavov, et al. 2023). In the portfolio
algorithm, there are three main components: asset
allocation, asset allocation, and asset restructuring
(Fredo, Motta, et al. 2023).
1.1.1 Asset Allocation
Asset allocation refers to the allocation of assets in a
portfolio to different asset classes to maximize returns
and minimize risk (Gyamera, Atuilik, et al. 2023).
Generally, asset classes include cash, bonds, stocks,
and real estate, among others. When allocating assets,
factors such as liquidity, risk, and return of assets
need to be considered (Hnatchuk, Hovorushchenko,
et al. 2023).
Zhou, S.
Portfolio Algorithm Based on Accounting Information System Relevance.
DOI: 10.5220/0013544100004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 1, pages 391-397
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
391

1.1.2 Asset Allocation
Asset allocation refers to the spread of assets in a
portfolio across different securities to diversify risk
and ensure maximum returns. Generally, security
options include stocks, bonds, and derivatives, among
others. In the process of asset allocation, investors
need to consider factors such as the risk level, return
expectations, liquidity and correlation of each
security (Hoelscher, and Shonhiwa, 2023).
1.1.3 Asset Restructuring
Asset restructuring refers to the re-evaluation of asset
allocation and asset allocation strategies over a period
of time to ensure that a portfolio always has the best
level of return and risk. Investors need to adjust their
asset allocation and asset allocation strategies at any
time to adapt to market changes and their own
investment goals (Jarah, Zaqeeba, et al. 2023).
1.2 Analysis of the Advantages and
Disadvantages of Portfolio
Algorithms
1.2.1 Advantages
(1) Risk reduction – Portfolio algorithms can
guarantee investment returns by diversifying assets
across different securities to minimize portfolio risk
(Kao, Yuan, et al. 2023).
(2) Optimize returns – Portfolio algorithms can
optimize portfolio returns by selecting high-yield,
low-risk securities.
(3) Adapt to market changes – The portfolio
algorithm can adjust asset allocation and asset
allocation strategies at any time when the market
changes to adapt to market changes.
(4) Improve investment efficiency – Portfolio
algorithms can help investors use funds more
efficiently and improve investment efficiency
(Lamberton, Raschke, et al. 2023).
1.2.2 Disadvantages
(1) Rely on historical data – Portfolio algorithms
need to rely on historical data to predict future market
movements, which may lead to inaccurate algorithm
predictions (Loureiro, Milligan, et al. 2023).
(2) High algorithm complexity – The
implementation of the portfolio algorithm requires
the use of complex mathematical models and
algorithms, which may lead to investment failure if
not implemented correctly (Lukas, 2023).
(3) Human interference – Portfolio algorithms
need to artificially formulate asset allocation and
asset allocation strategies, and if investors' decisions
are irrational, it may affect the effectiveness of the
algorithm (Minbaleev, Berestnev, 2023).
(4) High capital threshold – Portfolio algorithms
require a large investment of capital in order to
achieve the best investment results, which may make
it difficult for small-scale investors to use the
algorithm (Mokhnacheva, 2023).
Portfolio algorithm is an effective investment
strategy that can reduce the risk of a portfolio to a
certain extent, improve investment returns and
efficiency (Poppe, Vrolijk, 2023). However, despite
the many advantages of portfolio algorithms, there
are still some limitations and disadvantages.
Therefore, investors should fully understand the
characteristics and limitations of the portfolio
algorithm, and use the algorithm appropriately when
formulating investment strategies, pay attention to the
uncertainty of the algorithm's predictions, and adopt
appropriate risk management strategies to ensure the
success of the portfolio (Qadri, Altass, 2023).
1.3 Optimization Indicators of
Accounting Information Systems
In order to assess the operation of accounting
information systems, it is necessary to consider the
indicators of the system in a comprehensive manner.
The following is an analysis of the relevant indicators
of the accounting information system (Qatawneh,
2023).
1.3.1 Efficiency Indicators
Data processing speed is one of the main indicators to
measure the efficiency of accounting information
systems. An efficient system should be able to
process large amounts of data quickly in a short
period of time to ensure fast response and response
time. Therefore, enterprises should continuously
optimize hardware equipment and software systems
to improve data processing speed.
Application response time is also an important
indicator of the efficiency of accounting information
systems. An efficient system should respond to a
user's request within 6 seconds, and this data is often
used as a reference value that can help enterprises
evaluate the responsiveness of the system. Fast
response times can improve user satisfaction and
bring higher revenue to the business.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
392

1.3.2 Task Completion Time
Task completion time is another important indicator
to measure the efficiency of accounting information
systems. An efficient system should be able to
complete data processing tasks in a short time and
provide timely results to users. Therefore, enterprises
should monitor the efficiency of system operation by
setting a reasonable task completion time, and
continuously optimize the system to improve
efficiency.
1.3.3 Security Metrics
Data confidentiality is one of the important indicators
to measure the security of accounting information
systems. A highly secure system should be able to
keep your organization's data safe from unauthorized
access and theft. Therefore, enterprises should take
appropriate measures, such as access control,
encryption technology, data backup, etc., to ensure
the confidentiality of data.
1.3.4 System Reliability
System reliability is another measure of the security
of accounting information systems. A highly reliable
system should guarantee system stability and prevent
system failure and data loss. Therefore, enterprises
should take appropriate measures, such as backup
systems, integrity verification, disaster recovery
plans, etc., to ensure the reliability of the system.
1.3.5 Quality Indicators
Data accuracy is one of the main indicators to
measure the quality of accounting information
systems. Data accuracy is directly related to the
correctness of business decisions, therefore,
enterprises should take appropriate measures, such as
data validation, data cleaning, etc., to ensure the
accuracy of data. Data integrity is also one of the
indicators to measure the quality of accounting
information systems. Enterprises should ensure the
integrity of data to guarantee the correctness and
integrity of data. Data integrity can be achieved by
employing measures such as data validation and data
backup.
1.3.6 User Satisfaction Metrics
User satisfaction is a key indicator to measure the
satisfaction of accounting information systems.
Through user surveys and feedback, enterprises can
understand the user's satisfaction with the system to
understand the advantages and disadvantages of the
system and further improve the system.
The user learning curve is also one of the
indicators to measure the satisfaction of accounting
information systems. Enterprises should provide
system interfaces and functions that are easy to learn
and use to help users quickly master the system and
improve work efficiency.
1.3.7 Cost Indicators
The overall development cost is one of the main
indicators to measure the cost of accounting
information systems. Companies should make a
reasonable budget before system development and
control system development costs to maximize
benefits.
Maintenance and operating costs are another
measure of the cost of accounting information
systems. Enterprises should control the operation and
maintenance costs of the system to ensure that the
system can operate stably for a long time and
minimize costs.
The above indicators can help enterprises
understand the operating status of the system and
continuously optimize the system to improve
efficiency and reduce costs. Enterprises should
choose and value these indicators according to their
actual situation to help enterprises make better
strategic decisions.
2 RELATED CONCEPTS
2.1 Mathematical Description of
Combinatorial Algorithms
The combination algorithm utilizes correlation to
optimize accounting information management plans,
and based on various indicators in accounting
information management, discovers unqualified
values in investment decisions, integrates accounting
information management plans, and ultimately
determines the feasibility of investment decisions.
The combination algorithm combines the advantages
of correlation to quantify investment decisions, which
can improve the direction of accounting information
management investment decisions.
Assumption I. Accounting Information
Management Requirements is
c
i
,The accounting
information management plan is
lim
,The
combination rate of accounting information
management solutions is
w
,The judgment function
Portfolio Algorithm Based on Accounting Information System Relevance
393
of accounting information management plan is
U(g > 0)
,As shown in formula (1)。
21
1
1
lim (c w) cos
n
n
ii
x
i
i
FV g
θ
−
→∞
=
=
=−
(1
)
2.2 Selection of Investment Decision
Direction Plans
Assumption II The investment decision function is
()
i
g
x
,The weight coefficient is
l
,So, there are
unqualified investment decisions in accounting
information management, as shown in formula (2):
2
1
11
1
() ,,
n
nn
iniii
ii
i
gl g g glXl
==
=
−≈
(2
)
2.3 Analysis of Accounting Information
Management Plan
Before conducting a combination algorithm, it is
necessary to conduct a multidimensional analysis of
the accounting information management plan and
map the accounting information management
requirements to the investment decision database,
eliminating unqualified accounting information
management plans. Conduct a comprehensive
analysis of investment decisions and set thresholds
and indicator weights for accounting information
management plans to ensure the accuracy of the
combination algorithm. The investment decision is a
system testing accounting information management
plan that requires correlation analysis. If the
investment decision is in a non normal distribution,
its accounting information management plan will be
affected, reducing the accuracy of the overall
accounting information management. In order to
improve the accuracy of the combination algorithm
and improve the level of accounting information
management, it is necessary to select accounting
information management schemes, and the specific
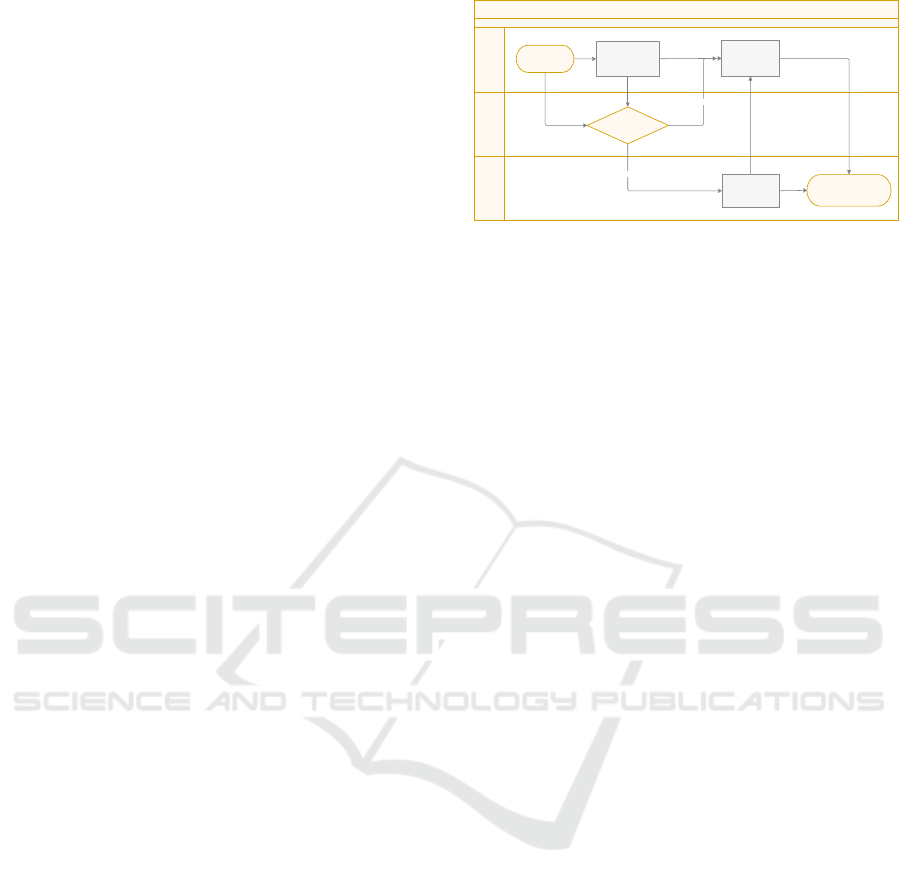
scheme selection is shown in Figure 1.
conclusion2 conclusion1conclusion3
Accounting
information
portfolio ratio
investment type
correlation
Scheme
calculation
是
decision-making
accuracy
否
Figure 1: Selection Results of Investment Decision
Direction Schemes
The investigation of the accounting information
management plan shows that the investment decision-
making direction plan presents a multidimensional
graph distribution, which is in line with objective
facts. Investment decisions have no directionality,
indicating that the investment decision direction
scheme has strong randomness, so it is considered as
a higher level of analytical research. Investment
decisions comply with normal requirements, mainly
by adjusting investment decisions based on
correlation, removing duplicate and irrelevant plans,
and supplementing default plans, making the dynamic
correlation of the entire accounting information
management plan strong.
3 OPTIMIZATION STRATEGIES
FOR INVESTMENT DECISIONS
The combination algorithm adopts a combination
correlation optimization strategy for investment
decisions and adjusts comprehensive investment
parameters to achieve optimization of investment
decisions. The combination algorithm divides
investment decisions into different levels of
accounting information management and randomly
selects different plans. During the iteration process,
optimize and analyze accounting information
management plans at different levels of accounting
information management. After the optimization
analysis is completed, compare the accounting
information management levels of different schemes
and record the best investment decisions.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
394
4 PRACTICAL CASES OF
INVESTMENT DECISIONS
4.1 Introduction to Accounting
Information Management
In order to facilitate accounting information
management, this article focuses on investment
decisions in complex situations, with 3 categories and
a testing period of 1 year. The specific accounting
information management plan for investment
decisions is shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Requirements for Accounting Information
Management in Universities
Category Level Portfolio
Ratio
Correlation
Single Investment I 63.65% 93.07%
II 54.28% 84.65%
Multiple
Investments
I 63.23% 94.47%
II 59.87% 85.16%
Comprehensive
Investments
I 65.61% 94.67%
II 53.82% 82.79%
The accounting information management process
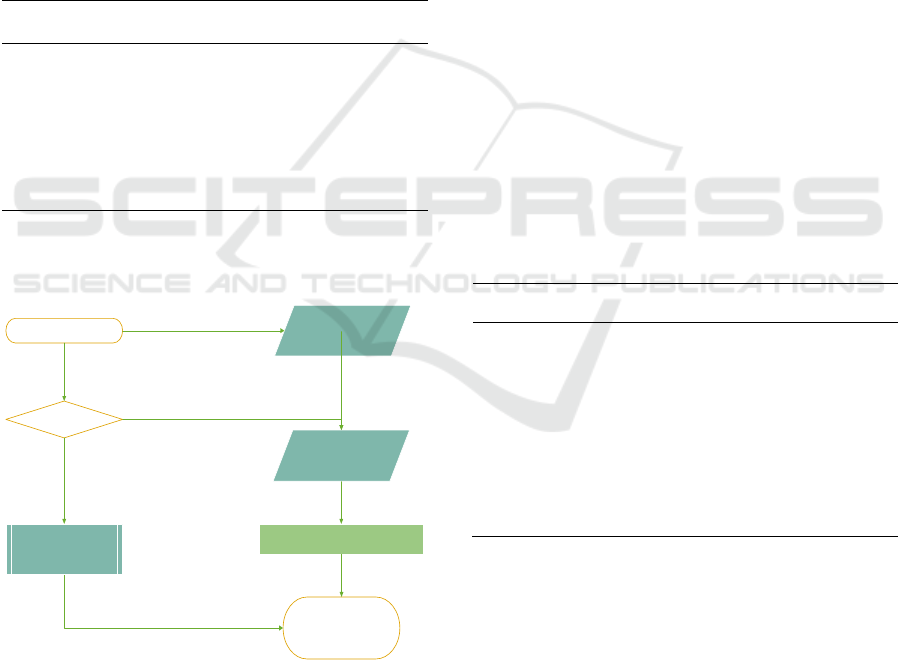
in Table 1. is shown in Figure 2.
optimization
Genetic algorithm
Overall
scheduling
Scheduling accuracy
Process simplification
rate
Local scheduling;
Dosiyoution
Figure 2: Analysis Process of Investment Decision
Compared with the proportional estimation
method, the accounting information management
scheme of the combination algorithm is closer to the
actual accounting information management
requirements. In terms of rationality and volatility of
investment decisions, combination algorithms and
proportional estimation methods are used. From the
changes in the accounting information management
scheme in Figure 2, it can be seen that the
combination algorithm has higher decision-making
accuracy. Therefore, the combination rate of
accounting information management solutions based
on the combination algorithm is more optimized and
the correlation is more reasonable.
4.2 Investment Decision-Making
Situation
The accounting information management plan for
investment decisions includes unstructured
information, semi structured information, and
structured information. After preselection of the
combination algorithm (Rosmawati, Apandi 2023), a
preliminary accounting information management
plan for investment decisions was obtained, and the
feasibility of the accounting information management
plan for investment decisions was analyzed. In order
to more accurately verify the innovation effect of
investment decisions, investment decisions with
different levels of accounting information
management were selected, and the accounting
information management plan is shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Overall Situation of Investment Decision Direction
Plan
Category Risk Rate Return Rate
Single Investment 74.75% 76.05%
Multiple Investments 73.62% 75.86%
Comprehensive
Investments
73.54% 76.49%
Mean 76.17% 74.74%
X 74.20% 75.78%
P=75.01%
4.3 Investment Decision Direction and
Stability of Accounting Information
Management
To verify the accuracy of the combination algorithm,
the accounting information management scheme was
compared with the proportional estimation method, as
shown in Figure 3.
Portfolio Algorithm Based on Accounting Information System Relevance
395
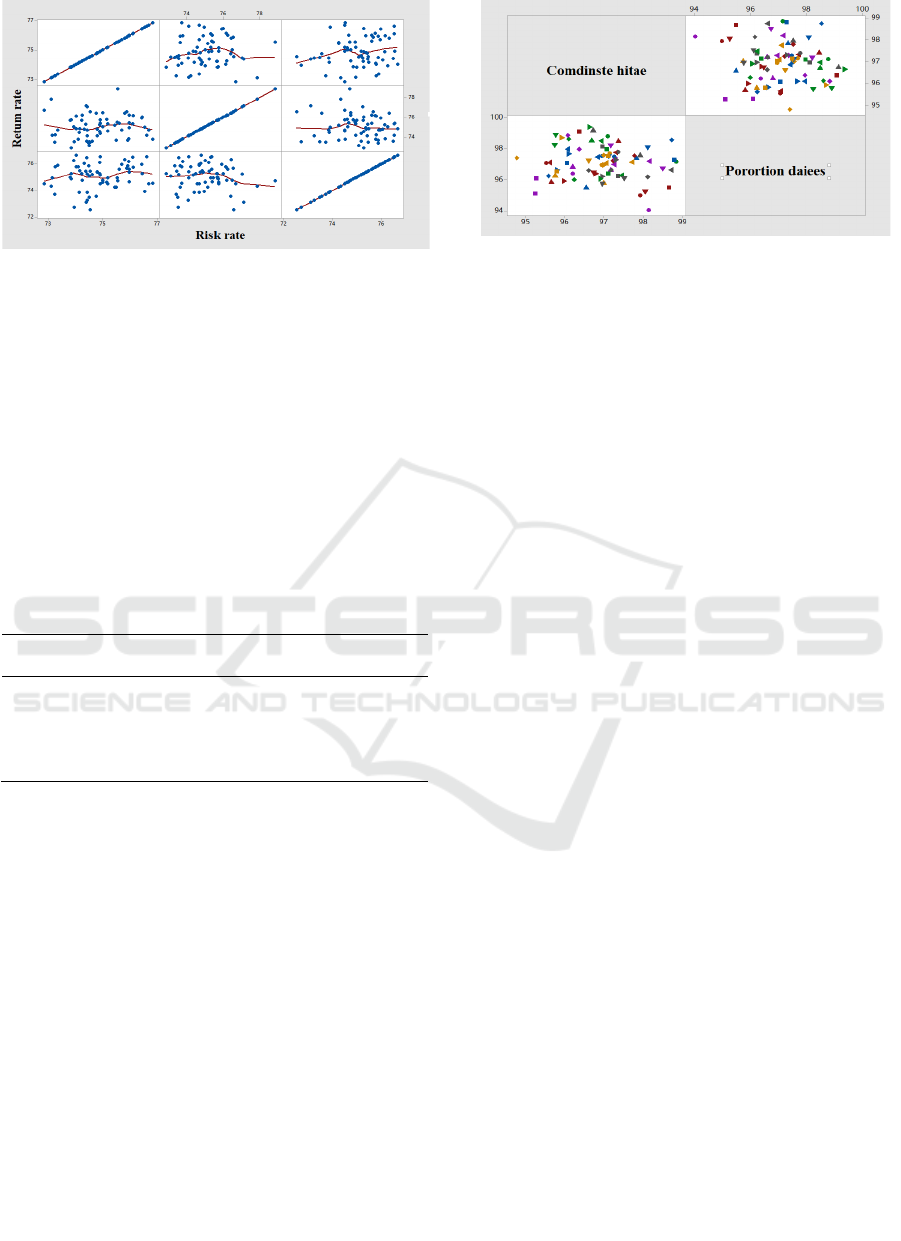
Figure 3: Investment Decision Directions for Different
Algorithms
As shown in Figure 3, the investment decision-
making direction of the combination algorithm is
higher than that of the proportional estimation
method, but the error rate is lower, indicating that the
accounting information management of the
combination algorithm is relatively stable, while the
accounting information management of the
proportional estimation method is uneven. The
average accounting information management scheme
for the above three algorithms is shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Comparison of Accounting Information
Management Accuracy by Different Methods
Method Combinatio
n
Correlatio
n
Decisio
n
Combinatoria
l
97.31% 97.73% 95.98%
Proportion
Ales
98.11% 98.08% 95.49%
P 97.93% 97.52% 95.55%
It can be seen from Table 3. that in terms of
investment decision-making, the proportional
estimation method has shortcomings in investment
decision-making direction and combinatorial
optimization, and investment decision-making has
undergone significant changes with a high error rate.
The general result of the combination algorithm has a
higher accuracy rate in investment decision-making
direction, which is superior to the proportional
estimation method. At the same time, the accuracy of
the investment decision direction of the combination
algorithm is greater than 90%, and there has been no
significant change in accuracy. To further verify the
superiority of the combination algorithm. To further
validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in
this article, different methods were used for general
analysis of the combined algorithm, as shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 4: Investment Decision Direction of Combination
Algorithm Accounting Information Management
From Figure 4., it can be seen that the investment
decision direction of the combination algorithm is
significantly superior to the proportional estimation
method. The reason for this is that the combination
algorithm increases the investment decision
adjustment coefficient and sets a threshold for
comprehensive investment, eliminating accounting
information management schemes that do not meet
the requirements.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In response to the problem of unsatisfactory
investment decision-making direction, this article
proposes a combination algorithm and optimizes
investment decisions by combining the correlation of
combination rates. At the same time, conduct in-depth
analysis on innovation in accounting information
management and threshold innovation, and construct
a comprehensive investment portfolio. Research has
shown that combination algorithms can improve the
accuracy and stability of investment decisions and
can be used for general accounting information
management of investment decisions. However, in
the process of combining algorithms, excessive
emphasis is placed on the analysis of accounting
information management, resulting in unreasonable
selection of accounting information management
indicators.
REFERENCES
Alsubaei, F. S.(2023) Detection of Inappropriate Tweets
Linked to Fake Accounts on Twitter. Applied Sciences-
Basel, 13(5):3.
Bratfisch, C., Riar, F. J., & Bican, P. M.(2023) When
entrepreneurship meets finance and accounting: (non-
)financial information exchange between venture
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
396

capital investors, business angels, incubators,
accelerators, and start-ups. International Journal of
Entrepreneurial Venturing, 15(1): 63-90.
Cola, G., Mazza, M., & Tesconi, M.(2023) Twitter
Newcomers: Uncovering the Behavior and Fate of New
Accounts Through Early Detection and Monitoring.
Ieee Access, 11(3): 55223-55232.
Dalloul, M. H. M., Ibrahim, Z. B., & Urus, S. T.(2023)
Financial Crises Management in Light of Accounting
Information Systems Success: Investigating Direct and
Indirect Influences. Sustainability, 15(10):89.
De Aguiar, R. F., Ferreira, P. L., & Gomes, M. Z.(2023)
Competencies in technology and information system
demanded in accounting sciences: the national student
performance exam (ENADE). Revista Ambiente
Contabil, 15(1): 47-66.
Ferreira, T. J., Slavov, T. N. B., Parisi, C., & Russo, P.
T.(2023) Case study of accounting automation from the
perspective of institutional theory. Revista De Gestao E
Secretariado-Gesec, 14(3): 3469-3491.
Fredo, A. R., Motta, M. E. V. d., Camargo, M. E., &
Priesnitz, M. C.(2023) Digital transformation: the
digitization of accounting. Revista De Gestao E
Secretariado-Gesec, 14(1): 681-714.
Gyamera, E., Atuilik, W. A., Eklemet, I., Matey, A. H.,
Tetteh, L. A., & Apreku-Djan, P. K.(2023) An analysis
of the effects of management accounting services on the
financial performance of SME: The moderating role of
information technology. Cogent Business &
Management, 10(1):89.
Hnatchuk, Y., Hovorushchenko, T., Shteinbrekher, D.,
Boyarchuk, A., & Kysil, T.(2023) MEDICAL
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY FOR DECISION-
MAKING TAKING INTO ACCOUNT THE NORMS
OF CIVIL LAW. International Journal on Information
Technologies and Security, 15(1): 77-88.
Hoelscher, J., & Shonhiwa, T.(2023) J&S Publisher
Problems: A Diagnostic Analytics Case Exploring
Employee Expense Reimbursement. Journal of
Emerging Technologies in Accounting, 20(1): 213-221.
Jarah, B. A. F., Zaqeeba, N., Al-Jarrah, M. F. M., Al
Badarin, A. M., & Almatarneh, Z.(2023) The Mediating
Effect of the Internal Control System on the
Relationship between the Accounting Information
System and Employee Performance in Jordan Islamic
Banks. Economies, 11(3):90.
Kao, M. C., Yuan, Y. H., & Wang, Y.-X.(2023) The study
on designed gamified mobile learning model to assess
students? learning outcome of accounting education.
Heliyon, 9(2):89.
Lamberton, B. A., & Raschke, R. L.(2023) Using Backward
Design to Incorporate Technology into a Non-AIS
Course. Journal of Emerging Technologies in
Accounting, 20(1): 259-267.
Loureiro, T. G., Milligan, B., Gacutan, J., Adewumi, I. J.,
& Findlay, K.(2023) Ocean accounts as an approach to
foster, monitor, and report progress towards sustainable
development in a changing ocean-The Systems and
Flows Model. Marine Policy, 154(2):89.
Lukas, C.(2023) On interim performance evaluations and
interdependent period outcomes. Journal of
Management Control, 34(1): 67-108.
Minbaleev, A. V., Berestnev, M. A., & Evsikov, K.
S.(2023) ENSURING INFORMATION SECURITY
OF MINING EQUIPMENT IN THE QUANTUM
ERA. Proceedings of the Tula States University-
Sciences of Earth, 1(3): 567-584.
Mokhnacheva, Y. V.(2023) Document Types Indexed in
WoS and Scopus: Similarities, Differences, and Their
Significance in the Analysis of Publication Activity.
Scientific and Technical Information Processing, 50(1):
40-46.
Poppe, K., Vrolijk, H., & Bosloper, I.(2023) Integration of
Farm Financial Accounting and Farm Management
Information Systems for Better Sustainability
Reporting. Electronics, 12(6):87.
Qadri, F. A., Altass, S., & Aman, Q.(2023) Examining the
perceptions of executives regarding accounting
information system (AIS). Evidence from listed
companies in Saudi stock exchange (TADAWUL).
Amazonia Investiga, 12(61): 184-192.
Qatawneh, A. M. M.(2023) The Role of Employee
Empowerment in Supporting Accounting Information
Systems Outcomes: A Mediated Model. Sustainability,
15(9):16.
Rosmawati, R. I. D. A., Apandi, N. n., Widarsono, A. G. U.
S., & Sugiharti, H. A. R. P. A.(2023) ACCOUNTING
INFORMATION SYSTEMS FOR INTERNAL
AUDITOR'S PERCEPTION: CASE STUDY AT
HIGHER EDUCATION INSTITUTION WITH
LEGAL STATUS. Journal of Engineering Science and
Technology, 18(2): 1309-1322.
Portfolio Algorithm Based on Accounting Information System Relevance
397
