
Privacy-Preserving EEG Data Generation: A Federated Split Learning
Approach Using Privacy-Adaptive Autoencoders and Secure Aggregation
with GFlowNet
Shouvik Paul
a
and Garima Bajwa
b
Department of Computer Science, Lakehead University, 955 Oliver Road, Thunder Bay, Canada
Keywords:
Brain-Machine Interfaces, EEG, Hierarchical Autoencoder, Federated Split Learning, GFlowNet, Privacy.
Abstract:
EEG-based Brain-Machine Interfaces (BMI) are novel interaction paradigms used extensively in assistive
technologies and neurorehabilitation. However, these interfaces pose significant privacy risks as they rely
on unique neural patterns for their operation, which unintentionally reveal sensitive cognitive information
and biometric identifiers without consent. Unlike traditional data, EEG signals are challenging to anonymize
due to their complex, high-dimensional, and noise-sensitive nature. We present a novel approach to privacy-
preserving EEG data generation, combining Federated Split Learning (FSL) with hierarchical privacy-adaptive
autoencoders, secure aggregation, and Generative Flow Networks (GFlowNet). The hierarchical architecture
of the autoencoder enables multi-level feature extraction, effectively capturing both spatial and temporal de-
pendencies in the EEG signals. Using R
´
enyi Differential Privacy (RDP) and adaptive noise scaling, our model
anonymizes sensitive brain signals during data generation. The FSL architecture allows client-side process-
ing of raw EEG data, followed by server-side reconstruction and synthetic data generation using GFlowNet.
Secure aggregation further enhances privacy, ensuring that individual data contributions are protected even
during client and server communication. Evaluations of our approach under various privacy budgets demon-
strate a balanced privacy-utility trade-off.
1 INTRODUCTION
Brain-Machine Interfaces (BMIs) are new human-
computer interaction paradigms that directly interface
the brain with external devices. These systems har-
ness neural signals, notably Electroencephalography
(EEG), to be used for assistive technologies, neu-
rorehabilitation, or cognitive enhancement. How-
ever, EEG data are inherently sensitive as they in-
corporate unique and identifiable neural patterns that,
when made public, can lead to significant privacy
risks (Janapati et al., 2021; Torres et al., 2020; Li
et al., 2023). Adversaries may gain unauthorized ac-
cess to the data from EEG devices, which can be ex-
ploited both in secure and insecure manners. This ac-
cess could allow them to infer mental states, cogni-
tive health issues, or even personal traits of individu-
als (Douibi et al., 2021; Brocol et al., 2021).
To address these concerns, existing privacy-
preserving techniques, including differential privacy
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-2657-3225
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0659-4263
(DP) (Dwork, 2006), federated learning (FL) (Al-
shebli et al., 2024) and secure multiparty computa-
tion (SMPC) (Agarwal et al., 2018), have been intro-
duced. However, adapting these methods for EEG
data is substantial, especially considering the com-
plexity of high-dimensional, temporal-dependent, and
noise-sensitive features of EEG data (Popescu et al.,
2021; Debie et al., 2020). Most of the cutting-edge
privacy-preserving techniques relate to image or text-
type data and do not best fit the complexities of spatio-
temporal neural signals. In addition, most existing ap-
proaches employ a uniform privacy mechanism, lead-
ing to a substantial loss of data utility.
In this regard, we introduce the Federated Split
Learning (FSL) framework (Zhang et al., 2023) in-
tegrated with privacy-adaptive autoencoders (Singh
et al., 2023) and secure aggregation (SA) (Zhang
et al., 2021) for the generation of EEG data. We
propose a new model that utilizes R
´
enyi Differen-
tial Privacy (RDP) (Mironov, 2017) across hierarchi-
cal latent spaces to provide a dynamic trade-off be-
tween privacy and utility. Our method addresses a
common limitation of existing DP protections, i.e.,
638
Paul, S., Bajwa and G.
Privacy-Preserving EEG Data Generation: A Federated Split Learning Approach Using Privacy-Adaptive Autoencoders and Secure Aggregation with GFlowNet.
DOI: 10.5220/0013529100003979
In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2025), pages 638-643
ISBN: 978-989-758-760-3; ISSN: 2184-7711
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

not all features have to be protected equally, by as-
signing stronger protection to privacy-sensitive fea-
tures derived from EEG signal while reducing noise-
induced degradation in less sensitive features. In ad-
dition, GFlowNet (Lahlou et al., 2023) is employed to
improve the fidelity of synthetic EEG data while en-
suring that the structural and statistical properties of
real EEG signals are preserved.
2 BACKGROUND
EEG signals are commonly used for Brain-Machine
Interfaces (BMIs) because they are non-invasive, have
high temporal resolution, and are easy to obtain.
However, these personalized and biometric traits pose
risks in terms of privacy. EEG data have been used for
biometric authentication, mental state inference, and
even prediction of personality traits (Bidgoly et al.,
2022; Gui et al., 2016). Thus, unauthorized collec-
tion, storage, and sharing of EEG data leads to ethical
and security concerns, which call for effective privacy
preservation mechanisms. Conventional anonymiza-
tion methods such as data masking and encryption
are ineffective in safeguarding EEG data as attack-
ers can still restore identifying features through ma-
chine learning-based reconstruction attacks. Differ-
ential privacy (DP) is a key approach that provides
strong mathematical guarantees, as it introduces cal-
ibrated noise (Dwork, 2006). Depending on the con-
figuration of the direct DP for use with EEG signals,
a significant loss of information is often experienced,
limiting the utility of synthesized EEG data for down-
stream analysis.
Federated learning (FL) (Alshebli et al., 2024)
is a relatively decentralized machine learning algo-
rithm that allows a number of customers to collab-
oratively train a model without the exchange of raw
data. FL has been used as one of the potentials for
privacy-preserving healthcare applications, such as
EEG-based emotion recognition. However, standard
FL approaches involve continuous communication for
model updates, which suffers from a potential privacy
risk from gradient leakage attacks. To alleviate this,
Federated Split Learning (FSL) has been proposed in
which the model is split between the client and server,
minimizing the information leak as only intermediate
representations are communicated rather than the full
gradients (Zhang et al., 2023).
Until now, Generative Adversarial Networks
(GANs) have been widely implemented for EEG data
generation. However, conventional GANs depend on
adversarial learning between a generator and a dis-
criminator, which could face mode collapse and gra-
dient vanishing problems (Goodfellow et al., 2014).
Generative Flow Networks (GFlowNet) have recently
been introduced to provide an alternative generative
model that learns to produce structured outputs, by
optimizing a flow-based probability distribution. Re-
cent reports have shown that GFlowNets can produce
diverse and high-fidelity synthetic acts while main-
taining temporal consistency, making them ideal for
generating EEG signals (Lahlou et al., 2023).
Privacy and utility trade-offs are particularly
prominent in EEG data generated with privacy-
preserving approaches. Existing DP-based ap-
proaches introduce uniform noise across the entire
dataset, easily obliterating key spatial and temporal
patterns. Previous works, such as hierarchical pri-
vacy architectures, have incorporated multiple permu-
tations of differential privacy to ensure that while pri-
vacy is preserved, the essential features of the data are
also safeguarded. We extend these ideas by employing
R
´
enyi Differential Privacy (RDP) at multiple levels
of latent space, enabling the application of adaptive
privacy across layers of hierarchical representations
(Mironov, 2017).
3 METHODOLOGY
This section describes our approach for generating
privacy-preserving synthetic EEG data using Feder-
ated Split Learning (FSL) (Zhang et al., 2023) em-
ploying a hierarchical encoder-decoder architecture
inspired by (Lawhern et al., 2018; Cisotto et al., 2023)
and Generative Flow Networks (GFlowNet) (Lahlou
et al., 2023). To achieve a balance between high data
utility and strong privacy guarantees, we integrate
RDP (Mironov, 2017) and secure aggregation (Zhang
et al., 2021), protecting sensitive EEG data while en-
abling the generation of high-quality synthetic data.
3.1 Federated Split Learning (FSL)
Federated Split Learning (FSL) divides the learning
process between the client and the server. Clients
process raw EEG data locally, ensuring that the data
never leave the client’s device (Zhang et al., 2023).
Only anonymized latent representations are shared
with the server, which performs the remaining com-
putation without accessing the raw EEG data.
In our FSL setup, both the server and client com-
ponents were simulated on a personal computer, to
replicate a federated learning environment. We sim-
ulated 5 clients, each representing an independent
entity in the network, with each client handling its
unique subset of the EEG dataset. The raw EEG data
Privacy-Preserving EEG Data Generation: A Federated Split Learning Approach Using Privacy-Adaptive Autoencoders and Secure
Aggregation with GFlowNet
639

was divided into non-overlapping segments, ensuring
that each client processed a different portion of the
dataset. This configuration simulates real-world situ-
ations in which various devices gather data indepen-
dently.
Using the hierarchical encoder, each client pro-
cessed its local data to create latent variables l
1
, l
2
, l
3
that captured various temporal and spatial character-
istics of the EEG data. These latent variables were
then anonymized using RDP to ensure that they could
not be traced back to the original EEG signals. To
further improve privacy, each client added a random
mask, m
i
, to anonymized latent variables after imple-
menting RDP. After that, a centralized server received
the masked latent variables (l
′
i
+ m
i
) for aggregation.
The server, also simulated on the same machine, acted
as the central aggregator. It executed secure aggrega-
tion after receiving the masked latent variables from
each client to guarantee that no client’s data was re-
vealed. After aggregation, the server reconstructed
the EEG signals using the hierarchical decoder. Fi-
nally, the server used GFlowNet to create synthetic
EEG data while preserving the original EEG data’s
temporal and spatial structure.
3.2 Client-Side: Hierarchical Encoding
On the client side, raw EEG data is processed using a
hierarchical encoder architecture inspired by (Lawh-
ern et al., 2018; Cisotto et al., 2023), designed to cap-
ture both spatial and temporal features of EEG data
across multiple levels of abstraction.
The encoder processes the data in three stages,
producing latent variables l
1
, l
2
, l
3
, which capture dif-
ferent aspects of the EEG signals:
• First Block (temporal filter): The initial stage
captures basic temporal patterns using depth-wise
temporal convolution, producing the latent vari-
able l
1
, modeled as:
l
1
∼ N (µ
1
, σ
2
1
) (1)
where µ
1
and σ
1
are the mean and variance
learned from the data.
• Second Block (spatial filter): This stage applies
parallel convolutions to capture spatial features
across EEG channels, resulting in the latent vari-
able l
2
:
l
2
∼ N (µ
2
, σ
2
2
) (2)
• Third Block (separable convolution): The final
block refines both spatial and temporal features,
producing l
3
, which captures the remaining de-
pendencies in the EEG data:
l
3
∼ N (µ
3
, σ
2
3
) (3)
These hierarchical latent variables, l
1
, l
2
, l
3
, cap-
ture progressively more abstract representations of the
EEG data. These variables are then prepared for trans-
mission to the server after privacy mechanisms are ap-
plied. For details on the encoder configuration, refer
to Table 1.
3.3 Anonymization with RDP
To protect latent variables before transmission, R
´
enyi
Differential Privacy (RDP) (Mironov, 2017) is ap-
plied. RDP ensures that latent representations can-
not be traced back to the original EEG data by adding
controlled Gaussian noise. The privacy budget is dis-
tributed evenly across the latent spaces to balance pri-
vacy and utility. The total privacy budget ε
total
is di-
vided equally between the three latent spaces:
ε
1
= ε
2
= ε
3
=
ε
total
3
(4)
This approach ensures a consistent privacy guar-
antee across the different levels of feature abstrac-
tion. Noise is added to each latent variable l
i
(where
i = 1, 2, 3) as follows:
l
′
i
= l
i
+ N (0, σ
2
i
) (5)
where, N (0, σ
2
i
) represents Gaussian noise with
variance σ
2
i
. The noise scale σ
i
is determined by the
privacy budget ε
i
and the data sensitivity ∆ f :
σ
i
=
∆ f
ε
i
(6)
where, ∆ f represents the sensitivity of the data, en-
suring that each latent variable is protected while pre-
serving data utility.
3.4 Privacy with Secure Aggregation
To further enhance privacy, we implement Secure Ag-
gregation (Zhang et al., 2021), which ensures that in-
dividual client data remains protected during commu-
nication with the server. Each client applies a random
mask, m
i
, to anonymized latent variables before trans-
mission. The uniform distribution in the range [−1, 1]
was used to generate the random masks m
i
. This en-
sures that even if the server or an adversary attempts
to intercept the communication, it cannot access the
latent variables of any individual client.
The masked latent variables are sent as:
l
′′
i
= l
′
i
+ m
i
(7)
Upon receiving the masked latent variables l
′′
i
from
all clients, the server aggregates the masked variables
and removes the masks using a process called mask
SECRYPT 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Security and Cryptography
640
cancellation (Zhang et al., 2021). This process en-
sures that the server cannot access individual client
data as it only deals with the aggregated results of the
masked latent variables, further enhancing the overall
privacy of the system.
3.5 Server-Side: Decoding and
Reconstruction
Once the anonymized latent variables are received by
the server, the hierarchical decoder, mirroring the en-
coder structure, reconstructs the original EEG signals.
The decoder is designed to ensure accurate recon-
struction of the temporal and spatial features.
• First Block (separable convolution): Uses sepa-
rable transposed convolutions to upsample the la-
tent variables and reconstruct the spatial-temporal
features.
• Second Block (spatial filter): Applies parallel
transposed convolutions to reconstruct spatial fea-
tures.
• Third Block (temporal filter): Reconstructs the
temporal dynamics in the EEG data using trans-
pose convolution.
The reconstruction loss is computed as:
L = L
recon
+ D
KL
(q(l|d)∥p(l)) (8)
where L
recon
measures temporal alignment using
Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) (Sakoe and Chiba,
1978), and D
KL
is the Kullback-Leibler (KL) Diver-
gence (Hershey and Olsen, 2007), ensuring that the
latent variables follow a Gaussian distribution.
3.6 Synthetic Data with GFlowNet
After verifying the quality of the latent variables, the
server uses Generative Flow Networks (GFlowNet)
(Lahlou et al., 2023) to generate synthetic EEG data.
GFlowNet models the generation process as a flow
through latent states, ensuring that the generated data
is spatially and temporally coherent. The generative
process for the entire sequence of EEG data points is
defined as (Sutskever et al., 2011; Graves, 2013):
P(y
1
, y
2
, . . . , y
n
|l
′
) = P(y
1
|l
′
)
n
∏
i=2
P(y
i
|y
i−1
, l
′
) (9)
where, the first data point y
1
is generated indepen-
dently based on latent variables l
′
, and each subse-
quent data point y
i
is generated conditionally based on
the previous point y
i−1
and the latent variables l
′
. This
structure ensures that the generative process begins
with the independent generation of y
1
and then fol-
lows a conditional sequence for the subsequent points.
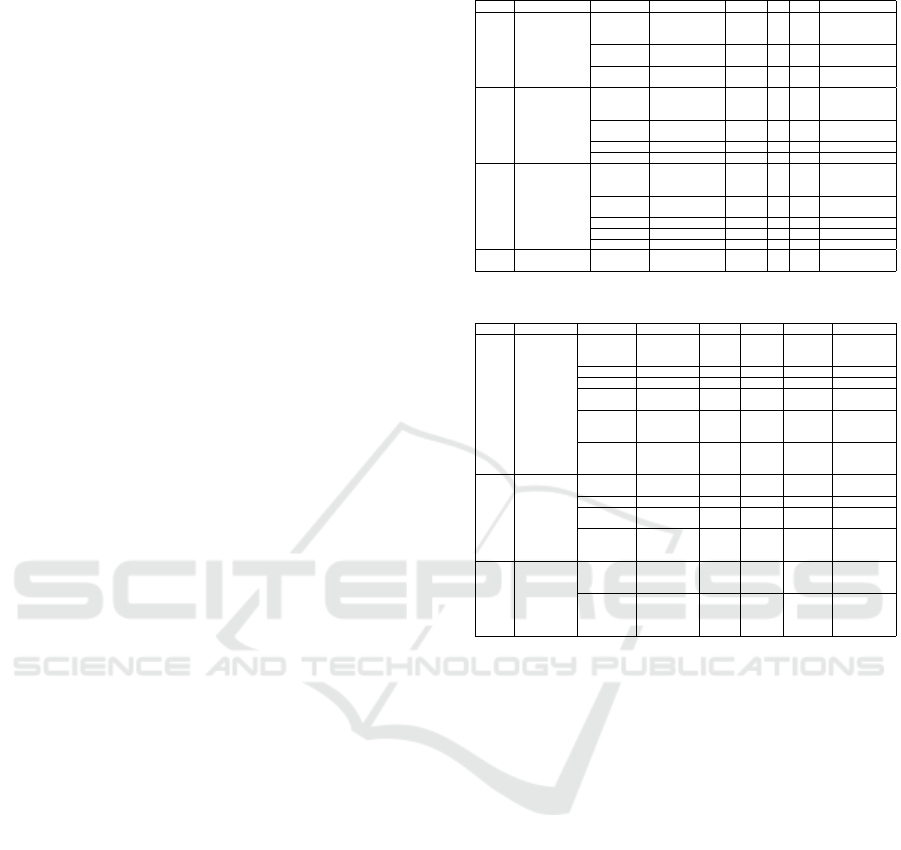
Table 1: Encoder Layer Configuration.
Sl. No. Blocks SL Number Layers Kernel In. Out. Description
1 First block (tem-
poral filter)
1 Convolution 2d (1, 125) 1 8 Depth-wise con-
volution (tempo-
ral filter)
2 Batch Norm 2d - - - Default parame-
ters
3 Attention Layer - 8 8 Adds temporal
attention scores
2 Second block
(spatial filter)
4 Convolution 2d (1, 3) 8 16 Depth-wise con-
volution (spatial
filter)
5 Batch Norm 2d - - - Default parame-
ters
6 Activation - - - ELU
7 Dropout - - - p = 0.5
3 Third Block
(separable con-
volution)
8 Convolution 2d (1, 32) 16 16 Depth-wise con-
volution (separa-
ble conv.)
9 Convolution 2d (1, 1) 16 16 Pointwise convo-
lution
10 Activation - - - ELU
11 Average pooling (1, 8) - - -
12 Dropout - - - p = 0.5
4 Sample layer 13 Convolution 2d (1, 1) 16 32 Pointwise convo-
lution
Table 2: Decoder Layer Configuration.
Sl. No. Blocks SL Number Layers Kernel In. dep. Out. dep. Description
1 Third Block
(separable
convolution)
1 Dropout - - - p = 0.5
2 Upsample (1, 8) - - -
3 Activation - - - ELU
4 Batch Norm
2d
- - - Default pa-
rameters
5 Transpose
Convolution
2d
(1, 1) 32 16 Pointwise
convolution
6 Transpose
Convolution
2d
(1, 32) 16 16 Depth-wise
convolution
2 Second Block
(spatial filter)
7 Dropout - - - p = 0.5
9 Activation - - - ELU
10 Batch Norm
2d
- - - Default pa-
rameters
11 Transpose
Convolution
2d
(1, 3) 16 8 Depth-wise
convolution
(spatial filter)
3 First Block
(temporal
filter)
12 Batch Norm
2d
- - - Default pa-
rameters
13 Transpose
Convolution
2d
(1, 125) 8 8 Depth-wise
convolution
(temporal
filter)
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
4.1 Experimental Design
We used the BCI IV 2B dataset, which contains EEG
recordings of nine subjects identified as B1 through
B9, performing two motor imagery (MI) tasks with
and without feedback (Leeb et al., 2008). We used
recordings from all EEG channels (C3, Cz, and C4).
The signals were filtered using a bandpass filter be-
tween 0.5 and 100 Hz and a notch filter was applied
at 50 Hz. All subjects participated in five sessions.
Three sessions, S
III
through S
V
, had real-time feed-
back, while the first two, S
I
and S
II
, consisted of train-
ing data without any feedback. Each subject com-
pleted 60 trials for each MI class during the non-
feedback motor imagery sessions, for a total of 120
trials. During the feedback sessions, there were 80
trials for each MI class, for a total of 160 trials in a
session. The average duration of the trial was 4 sec-
onds. Each participant completed 720 tests in total,
although some were not completed due to differences
in the experiment. Signal data from each trial were
Privacy-Preserving EEG Data Generation: A Federated Split Learning Approach Using Privacy-Adaptive Autoencoders and Secure
Aggregation with GFlowNet
641
collected, with a focus on a segment of approximately
4 seconds. A 4-second frame sampled at a frequency
of 250 Hz corresponded to 1000 data points each trial.
We used three sessions (S
I
through S
III
), denoted
as Tr, consisting of a mix of real data trials collected
with and without feedback. We removed the artifact-
containing trials and finally created synthetic data, Sy,
equal to the training data samples in Tr.
4.2 Classification Performance
The computational evaluation is broken down into
two distinct scenarios: Tr → Sy: (Train
(Tr)
, Test
(Sy)
)
and Sy → Tr: (Train
(Sy)
, Test
(Tr)
).
• Tr → Sy: (Train
(Tr)
, Test
(Sy)
): Deep learning
models are first trained on Tr (real EEG train sub-
set), and then tested on the corresponding Sy (gen-
erated synthetic EEG). This scenario provides in-
sights into how well the model generalizes from
real-world samples to synthetic ones, which is
critical to understanding the effectiveness of syn-
thetic data for inference tasks when training is
done on real datasets.
• Sy → Tr: (Train
(Sy)
, Test
(Tr)
): This scenario in-
volves training the same models using Sy data and
testing them with Tr data. This test is particularly
important because it shows whether the synthetic
data are robust enough to be useful for training
models that can later perform well on real-world
data.
A comprehensive understanding of the performance
of models trained with synthetic and real data was
achieved by examining the results in various set-
tings. These evaluations provide valuable informa-
tion on the practical applicability of synthetic data,
Sy, in a real world situation, and the dependability of
our proposed privacy-preserving method. In all in-
stances, the ShallowNet model (Schirrmeister et al.,
2017) was utilized for classification tasks. The per-
formance of the models was compared with two state-
of-the-art methods; DP-GAN (Debie et al., 2020) and
RDP-CGAN (Torfi and Fox, 2022). To ensure a fair
comparison of all techniques, we used 500 rounds
(
¯
R) for our method and 500 total epochs for the
other models, along with an identical clipping norm
C = 0.5, ∆ f = C, α = 10, and the privacy parame-
ter δ = 10
−3
. Table 3 shows the test accuracy for
the two evaluation scenarios - (Train
(Tr)
, Test
(Sy)
) and
(Train
(Sy)
, Test
(Tr)
) - across different subjects and
methods with ε = 3.
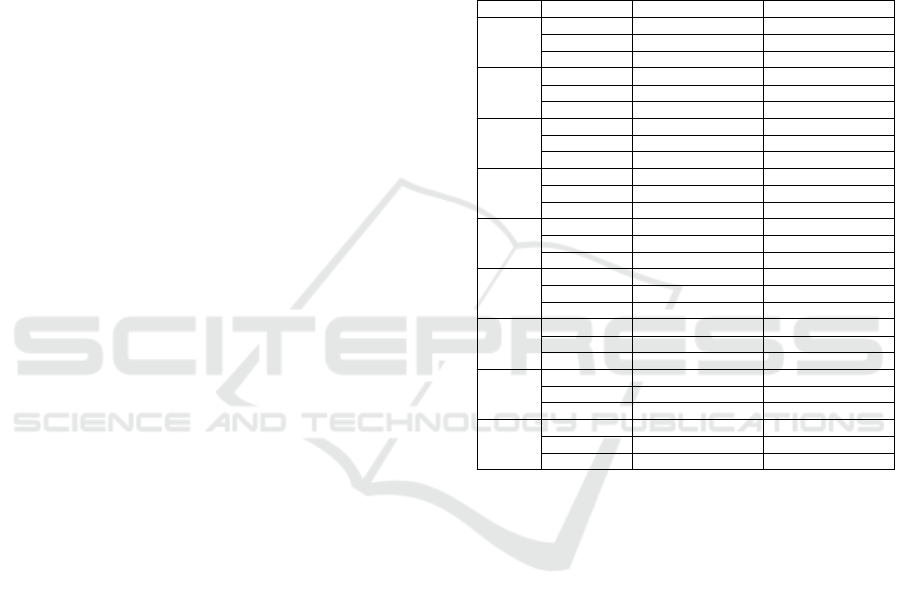
Our method achieves higher accuracy in both sce-
narios compared to the popular methods; DP-GAN
and RDP-GAN. Furthermore, we observed a compa-
rable decline in accuracy in the second scenario in
which Sy was used as training data, which was con-
sistent with the literature, DP-GAN and RDP-CGAN
models. However, the percentage drop of our model
was significantly lower, particularly for four subjects
- B4, B5, B7 and B9. This reduced impact on accu-
racy indicates that the synthetic data generated in our
study exhibits enhanced usability for applications that
have limited access to real EEG data.
Table 3: Performance comparison of the models for each
subject using ShallowNet architecture in two scenarios.
Bold values indicate the highest performance for each row.
Subject Methods (Train
(Tr)
, Test
(Sy)
) (Train
(Sy)
, Test
(Tr)
)
B1
Our Method 85.54 82.47
DP-GAN 75.21 70.82
RDP-CGAN 72.74 67.19
B2
Our Method 80.42 77.53
DP-GAN 68.26 62.40
RDP-CGAN 70.93 58.74
B3
Our Method 78.71 74.85
DP-GAN 66.15 59.31
RDP-CGAN 61.76 56.94
B4
Our Method 91.39 90.51
DP-GAN 79.22 69.75
RDP-CGAN 74.87 66.52
B5
Our Method 85.61 82.82
DP-GAN 76.20 66.59
RDP-CGAN 73.12 69.83
B6
Our Method 80.52 77.29
DP-GAN 63.39 59.77
RDP-CGAN 62.71 56.88
B7
Our Method 81.43 80.89
DP-GAN 66.94 62.62
RDP-CGAN 63.86 58.55
B8
Our Method 80.82 76.67
DP-GAN 67.65 64.30
RDP-CGAN 66.29 60.54
B9
Our Method 86.57 81.41
DP-GAN 72.64 63.93
RDP-CGAN 68.18 59.53
5 CONCLUSION
We introduced a federated split learning framework
to generate synthetic EEG data, integrating hierar-
chical privacy adaptive autoencoders, secure aggrega-
tion, and GFlowNet with RDP to balance data utility
with strong privacy. The hierarchical architecture of
the autoencoders enabled efficient extraction of multi-
level spatial and temporal characteristics from EEG
signals, essential for preserving the quality of the gen-
erated synthetic EEG data. The client-side feature
extraction and server-side data generation was split
using FSL, thus reducing the client’s computational
demand and keeping raw EEG data on the device.
Adaptive autoencoders and RDP enhanced privacy by
dynamically adding noise based on data sensitivity,
while secure aggregation helped keep client contri-
butions private during server communication. Our
results showed that the proposed method effectively
SECRYPT 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Security and Cryptography
642

balances privacy and utility across different privacy
budgets, making it ideal for privacy-sensitive appli-
cations such as medical diagnostics, brain-computer
interfaces, and other EEG-based systems.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, A., Dowsley, R., McKinney, N. D., Wu, D.,
Lin, C.-T., De Cock, M., and Nascimento, A.
(2018). Privacy-preserving linear regression for brain-
computer interface applications. In 2018 IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Big Data (Big Data), pages
5277–5278. IEEE.
Alshebli, S., Alshehhi, M., and Yeun, C. Y. (2024). Inves-
tigating how data poising attacks can impact an eeg-
based federated learning model. In 2024 2nd Interna-
tional Conference on Cyber Resilience (ICCR), pages
1–6. IEEE.
Bidgoly, A. J., Bidgoly, H. J., and Arezoumand, Z. (2022).
Towards a universal and privacy preserving eeg-based
authentication system. Scientific Reports, 12(1):1–12.
Brocol, X. et al. (2021). Brain-computer interfaces in safety
and security fields: Risks and applications. Journal of
Neuroscience, 40:123–135.
Cisotto, G., Zancanaro, A., Zoppis, I. F., and Manzoni,
S. L. (2023). hveegnet: exploiting hierarchical vaes on
eeg data for neuroscience applications. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2312.00799.
Debie, E., Moustafa, N., and Whitty, M. T. (2020).
A privacy-preserving generative adversarial network
method for securing eeg brain signals. In 2020
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks
(IJCNN), pages 1–8. IEEE.
Douibi, K. et al. (2021). Toward eeg-based bci applications
for industry 4.0: Challenges and possible applications.
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 15:705064.
Dwork, C. (2006). Differential privacy. automata, lan-
guages and programming. In 33rd International Col-
loquium, ICALP.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., and Courville, Aaron
& Bengio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial nets.
Advances in neural information processing systems,
27:2672–2680.
Graves, A. (2013). Generating sequences with recurrent
neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1308.0850.
Gui, Q., Yang, W., Jin, Z., Ruiz-Blondet, M. V., and Las-
zlo, S. (2016). A residual feature-based replay attack
detection approach for brainprint biometric systems.
In 2016 IEEE International Workshop on Information
Forensics and Security (WIFS), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Hershey, J. R. and Olsen, P. A. (2007). Approximating the
kullback leibler divergence between gaussian mixture
models. In 2007 IEEE International Conference on
Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing-ICASSP’07,
volume 4, pages IV–317. IEEE.
Janapati, R., Dalal, V., and Sengupta, R. (2021). Advances
in modern eeg-bci signal processing: A review. Mate-
rials Today: Proceedings, 80:2563–2566.
Lahlou, S., Deleu, T., Lemos, P., Zhang, D., Volokhova, A.,
Hern
´
andez-Garcıa, A., Ezzine, L. N., Bengio, Y., and
Malkin, N. (2023). A theory of continuous generative
flow networks. In International Conference on Ma-
chine Learning, pages 18269–18300. PMLR.
Lawhern, V. J., Solon, A. J., Waytowich, N. R., Gordon,
S. M., Hung, C. P., and Lance, B. J. (2018). Eeg-
net: a compact convolutional neural network for eeg-
based brain–computer interfaces. Journal of neural
engineering, 15(5):056013.
Leeb, R., Brunner, C., M
¨
uller-Putz, G., Schl
¨
ogl, A., and
Pfurtscheller, G. (2008). Bci competition 2008–graz
data set b. Graz University of Technology, Austria,
16:1–6.
Li, J. et al. (2023). Meta-learning for fast and privacy-
preserving source knowledge transfer of eeg-based
bcis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Re-
habilitation Engineering, 31:123–134.
Mironov, I. (2017). R
´
enyi differential privacy. In 2017
IEEE 30th Computer Security Foundations Sympo-
sium (CSF), pages 263–275. IEEE.
Popescu, D., Voicu, R., and Bichindaritz, I. (2021). Privacy-
preserving classification of eeg data using machine
learning and homomorphic encryption. IEEE Access,
9:25979–25989.
Sakoe, H. and Chiba, S. (1978). Dynamic programming
algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition.
IEEE transactions on acoustics, speech, and signal
processing, 26(1):43–49.
Schirrmeister, R. T., Springenberg, J. T., Fiederer, L. D. J.,
Glasstetter, M., Eggensperger, K., Tangermann, M.,
Hutter, F., Burgard, W., and Ball, T. (2017). Deep
learning with convolutional neural networks for eeg
decoding and visualization. Human brain mapping,
38(11):5391–5420.
Singh, G., Patel, P., Asaduzzaman, M., and Bajwa, G.
(2023). Selective eeg signal anonymization using
multi-objective autoencoders. In 2023 20th Annual In-
ternational Conference on Privacy, Security and Trust
(PST), pages 1–7. IEEE.
Sutskever, I., Martens, J., and Hinton, G. E. (2011). Gener-
ating text with recurrent neural networks. In Proceed-
ings of the 28th international conference on machine
learning (ICML-11), pages 1017–1024.
Torfi, A. and Fox, Edward A & Reddy, C. K. (2022).
Differentially private synthetic medical data genera-
tion using convolutional gans. Information Sciences,
586:485–500.
Torres, E. P., Torres, E. A., Hern
´
andez-
´
Alvarez, M., and
Yoo, S. G. (2020). Eeg-based bci emotion recognition:
A survey. Sensors, 20(18):5083.
Zhang, Z., Li, J., Yu, S., and Makaya, C. (2021). Safe-
learning: Enable backdoor detectability in federated
learning with secure aggregation. arXiv:2102.02402.
Zhang, Z., Pinto, A., Turina, V., Esposito, F., and Matta,
I. (2023). Privacy and efficiency of communications
in federated split learning. IEEE Transactions on Big
Data, 9(5):1380–1391.
Privacy-Preserving EEG Data Generation: A Federated Split Learning Approach Using Privacy-Adaptive Autoencoders and Secure
Aggregation with GFlowNet
643
