
Designing a Multimodal Interface for Text Simplification: A Case Study
on Deepfakes and Misinformation Mitigation
Francisco Lopes
1 a
, S
´
ılvia Ara
´
ujo
1 b
and Bruno Reynaud Sousa
2 c
1
School of Letters, Arts and Human Sciences, University of Minho, Braga, Portugal
2
School of Law, University of Minho, Braga, Portugal
Keywords:
Text Simplification, AI Literacy, Multimodal Learning, Graphical Abstract, Misinformation, Deepfakes.
Abstract:
The complexity of scientific literature often prevents non-experts from understanding science, limiting ac-
cess to scientific knowledge for a broader audience. This paper presents a proof-of-concept system designed
to enhance the accessibility of primary scientific literature through multimodal graphical abstracts (MGAs).
The system simplifies complex content by integrating textual simplification, visual elements, and interactive
components to support a broader range of learners. Using a case study on deepfake detection, the paper
demonstrates the system’s functionalities. Key features include automated text simplification, audio narration,
content summarization, and information visual representation. The example presented suggests the use of the
generated MGA to improve AI literacy and misinformation resilience by promoting direct engagement with
scientific content. Future work will focus on assessing the quality of text simplification and validating its
effectiveness through user studies.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital literacy equips individuals with competencies
necessary to critically interact with, evaluate, and
ethically utilize digital tools. It includes the ability
to find, evaluate, utilize, share, and create informa-
tion through digital technologies (Reddy et al., 2021).
Similarly, Artificial Intelligence (AI) literacy focuses
on understanding AI systems, enabling users to criti-
cally evaluate their implications, use them effectively,
and address ethical concerns surrounding their adop-
tion (Long and Magerko, 2020; Ng et al., 2021; Allen
and Kendeou, 2023). Promoting these skills align
closely with the United Nations’ Sustainable Devel-
opment Goal (SDG) number 4 (Quality Education),
which emphasizes the importance of ensuring equi-
table and inclusive education for all, and is recognized
as a catalyst for achieving broader SDGs. As digital
and AI literacy become increasingly essential, they
also offer opportunities to narrow the gap between
technical expertise and public understanding, poten-
tially improving scientific communication.
Challenges in scientific communication present
barriers to the dissemination and understanding of
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-0372-6257
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4321-4511
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0502-1305
knowledge, particularly due to the complexity of sci-
entific texts and the inaccessibility of technical lan-
guage (Borowiec, 2023). Overcoming technical and
complex language in scientific texts is a challenge
for communicating with the general public (Pruneski,
2018). The use of specialized vocabulary, complex
syntax, and jargon often alienates non-expert audi-
ences and contributes to misunderstanding and mis-
trust of science (Ivleva, 2022).
One potential approach to this challenge is text
simplification, which can reduce lexical and syntac-
tic complexity while preserving the core meaning
of scientific content, making it more accessible to
non-experts (Al-Thanyyan and Azmi, 2021). Sim-
plified texts have improved readability, making sci-
ence more understandable for individuals with low
literacy, non-native speakers, and those unfamiliar
with technical domains (Wan, 2018; Engelmann et al.,
2023). This is particularly relevant for those who
may have limited exposure to the terminology and
structure of specialized scientific texts (Engelmann
et al., 2023). Moreover, simplified scientific com-
munication enables broader public engagement with
research findings, which is essential for promoting
trust in science (Beks van Raaij et al., 2024). One
of the main challenges in simplifying scientific texts
is reducing both lexical (word-level) and syntactic
Lopes, F., Araújo, S. and Sousa, B. R.
Designing a Multimodal Interface for Text Simplification: A Case Study on Deepfakes and Misinformation Mitigation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013513100003932
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 1, pages 737-742
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
737

(sentence-level) complexity, without compromising
technical accuracy or losing essential meaning (Garuz
and Garc
´
ıa-Serrano, 2022; Ivleva, 2022).
The ongoing development of text simplification
technologies, particularly those based on generative
AI, presents significant potential for improving com-
munication between experts and non-experts (Sikka
and Mago, 2020). Recent advancements have enabled
the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) like T5,
PEGASUS, and ChatGPT to simplify complex sci-
entific content (Wan, 2018; Engelmann et al., 2023).
These models have been shown to be effective in sim-
plifying technical language across various contexts,
such as radiology reports (Doshi et al., 2023), dietary
supplement information (Tariq et al., 2023) and gov-
ernment communication (Beks van Raaij et al., 2024).
Building on these premises, this work presents a proof
of concept for a system designed to generate sim-
plified multimodal abstracts from primary literature.
The major contributions of this paper are:
• Designing a proof of concept system that simpli-
fies complex scientific content through the gener-
ation of multimodal graphical abstracts.
• Demonstrating the system’s functionality through
its application in simplifying a research paper on
deepfakes.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 re-
views related work on text simplification, multimodal
learning, and graphical abstracts. Section 3 details
the system design and implementation. Section 4
presents a case study focusing on deepfake detec-
tion, demonstrating the system’s capabilities. Section
5 discusses findings and implications. Finally, Sec-
tion 6 offers conclusions and directions for future re-
search.
2 RELATED WORK
This section reviews key concepts supporting the de-
velopment of the system, focusing on adapting pri-
mary literature, applying multimodal learning prin-
ciples, and integrating the concept of graphical ab-
stracts.
2.1 Adapting Primary Literature
Didactic transposition refers to the process of trans-
forming scientific knowledge from its original form
into a form that is suitable for teaching, ensuring it
is meaningful to learners in the classroom (Cheval-
lard and Bosch, 2020). As scientific knowledge is ini-
tially designed for use in its original context, not for
direct teaching, it must undergo transformations to fit
the goals of education (Kang and Kilpatrick, 1992).
This process involves adapting the content to ensure
it is both comprehensible and engaging, while main-
taining its integrity and core concepts. The result of
didactic transposition is the creation of learning ob-
jects, small, self-contained units of learning that en-
capsulate specific scientific knowledge in a format
that is easy for students to engage with (Chevallard
and Bosch, 2020). These objects could be textbooks,
teaching materials, online resources, or even interac-
tive models. The ability to adapt complex knowledge
into teaching-friendly formats is therefore essential
for cultivating scientific literacy.
2.2 Multimodal Learning
Multimodal learning refers to the use of multiple sen-
sory systems (e.g., visual, auditory, kinesthetic) in the
learning process, which can keep students more in-
terested and promote deeper understanding (Al-Jarf,
2024). This approach integrates various modes of
learning, such as text, images, video, audio, and
physical interaction, to create a holistic learning en-
vironment that engages learners on multiple levels
(Qushem et al., 2021). The combination of modalities
can help learners better understand complex explana-
tions and concepts by reducing cognitive load (Mayer,
2001, 2003).
Multimodal learning supports learner autonomy
by allowing students to interact with content in var-
ious ways and to select the modes of learning that
suit their preferences and needs (Al-Jarf, 2024). Mul-
timodal technologies like MOOCs, serious games,
and learning management systems employ multi-
ple modes of interaction to support diverse learn-
ing preferences and knowledge acquisition (Qushem
et al., 2021). These technologies create more inclu-
sive learning environments, allowing students to en-
gage with content in a flexible, interactive manner.
Neurodivergent learners (e.g., students with ADHD,
dyslexia) particularly benefit from multimodal learn-
ing, as it provides alternative means of engagement
and helps maintain their focus through diverse sen-
sory inputs (White, 2024).
2.3 Graphical Abstract
As scientific research becomes more specialized, tra-
ditional text-heavy abstracts often fail to engage non-
expert readers and even specialists from other fields.
Graphical abstracts (GA) provide an alternative by
offering concise, visual summaries of a study’s key
findings. These visual representations make research
EKM 2025 - 8th Special Session on Educational Knowledge Management
738

easier to understand, share, and remember, helping to
improve accessibility and engagement, allowing au-
diences to quickly grasp and retain essential informa-
tion (Lee and Yoo, 2023).
Graphical abstracts simplify complex ideas by
breaking them down into visually digestible elements,
making them accessible to both expert and non-expert
audiences. They transform dense, technical informa-
tion into easily understandable content, using images,
icons, and diagrams to represent key concepts, pro-
cesses, and results (Misiak and Kurpas, 2023). This
visual representation makes it easier for readers to un-
derstand the main ideas of a study without needing to
read through the entire paper. By creating a visually
compelling summary, researchers are more likely to
attract attention to their work, encouraging citations,
and greater engagement with their research.
2.4 Multimodal Graphical Abstract
Building on the ideas of text simplification, multi-
modal learning, and graphical abstracts, we intro-
duce the concept of the Multimodal Graphical Ab-
stract (MGA). It aims to support efforts to improve
the accessibility and comprehensibility of primary lit-
erature by combining visual elements, simplified text,
and multimodal principles into a cohesive format. A
traditional graphical abstract distills the key findings
of a research paper into a visual format. However,
for non-expert audiences, even these visual represen-
tations still pose challenges, as they are typically de-
signed with expert audiences in mind.
Combining interactive elements, dynamic visual-
izations, and simplified text creates a richer, more en-
gaging learning experience, making complex scien-
tific discourse more accessible to the general public’s
diverse learning needs. The simplified text ensures
that key concepts are communicated clearly, while the
graphical elements reinforce and expand on the text,
offering a more holistic understanding of the subject
matter. The interactive nature of the multimodal com-
ponents further encourages active learning, allowing
users to explore the content at their own pace.
Ultimately, the MGA serves as a means to democ-
ratize scientific knowledge, making it more accessi-
ble, engaging, and understandable for a wider audi-
ence.
3 SYSTEM DESIGN
The goal of this system is to automate the creation of
MGAs. The system’s main target users are individu-
als with varying levels of expertise in scientific top-
ics. Specifically, the system aims to support students
and educators who require simplified access to com-
plex academic research, as well as citizens interested
in gaining a deeper understanding of scientific con-
tent. To build the system, we conducted literature re-
views and analyzed existing graphical abstract guide-
lines and resources that focus on simplifying primary
scientific literature. We reviewed specialized journals
like Frontiers for Young Minds
1
, which focuses on
making complex science more accessible for younger
audiences. This research helped shape the system’s
goals and features, ensuring that it would meet the
needs of its target users.
The system was built using the OpenAI API for
text processing and simplification, the Narakeet API
for audio generation, and the Streamlit framework for
the user interface. Currently, in its initial version, the
system is still in the testing phase. As a proof-of-
concept prototype, only a subset of the functional re-
quirements has been implemented, with further devel-
opment planned for future versions. Non-functional
requirements, such as performance and scalability,
will also be addressed in subsequent iterations.
4 STUDY CASE: DEEPFAKES
Deepfakes refer to digital content, like images,
videos, and audio, created using AI tools that manip-
ulate reality, often producing content indistinguish-
able from authentic material (Kietzmann et al., 2020).
These technologies can be used to create fake media
that is harder to detect, posing serious risks to pri-
vacy, security, democracy, and trust (Nguyen et al.,
2019; Verdoliva, 2020). The creation and detection of
deepfakes require a sophisticated level of both AI and
media literacy. Without proper understanding, users
can become susceptible to misinformation and may
struggle to critically engage with this kind of content
(Sanchez-Acedo et al., 2024).
One of the primary barriers to addressing the chal-
lenges posed by deepfakes is the lack of AI literacy
among the general public. Simplifying and contex-
tualizing complex AI concepts can help individuals
understand how deepfakes are created, how they can
be detected, and why they are a problem in the first
place (McCosker, 2022). By breaking down the tech-
nical aspects of deep learning and AI algorithms used
to create deepfakes, it becomes possible to educate
the public in a way that makes these concepts more
accessible and meaningful (Nguyen et al., 2019). By
providing resources that demystify deepfake creation
1
https://kids.frontiersin.org/
Designing a Multimodal Interface for Text Simplification: A Case Study on Deepfakes and Misinformation Mitigation
739
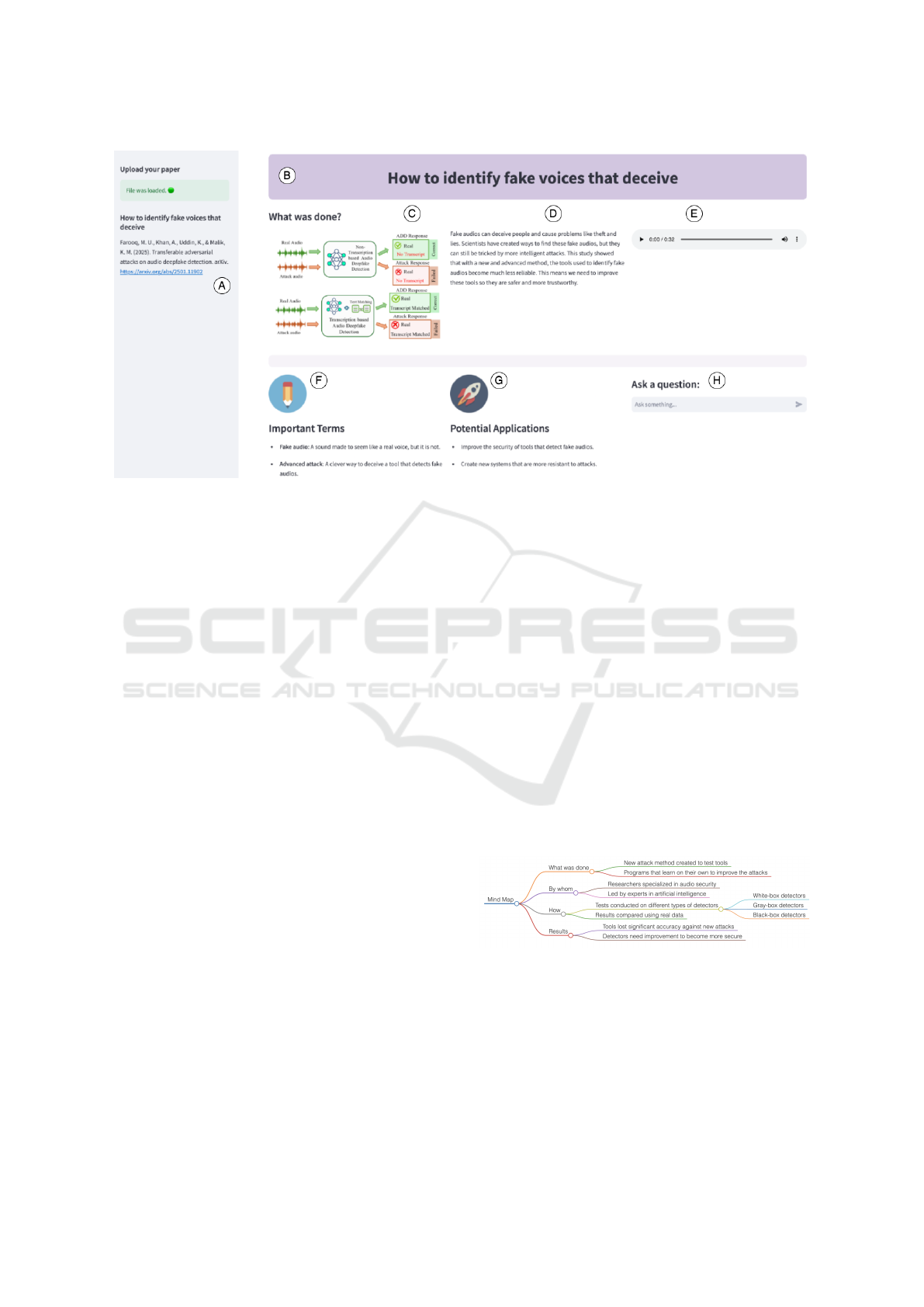
Figure 1: Screenshot of the system interface showcasing the main features (Content in Portuguese): (A) Uploaded scientific
paper reference, (B) Simplified title, (C) Extracted image from the study, (D) Simplified text summary, (E) Audio playback
of the summary, (F) Important terms glossary, (G) List of potential applications, and (H) Interactive chatbot.
and detection can help educate the public, enabling
them to identify and reject false media. It can also
enhance understanding of AI’s broader implications,
such as ethical concerns, algorithmic biases, and se-
curity threats (Verdoliva, 2020; Kian et al., 2024).
Programs designed to increase AI literacy can
equip individuals with the critical thinking skills
needed to recognize deepfake content, thereby en-
hancing societal resilience against misinformation
(Mokadem, 2023). Studies have shown that media lit-
eracy training significantly improves detection rates
for fake news, including deepfake videos (Mokadem,
2023).
For demonstration purposes, we use a study by
Farooq et al. (2025) on transferable adversarial at-
tacks to showcase the system’s capabilities. The
study investigates the robustness of audio deepfake
detection models against adversarial attacks, explor-
ing how these attacks can be transferred between dif-
ferent models.
The system interface, as shown in Figure 1, inte-
grates several features to provide users with a inter-
active experience when exploring research on deep-
fake detection. The interface begins with (A) the up-
loaded scientific paper reference, which allows users
to quickly trace the original study. The (B) simpli-
fied title offers a concise overview of the research,
while (C) displays an example of an image extracted
from the paper, illustrating the type of visual con-
tent included in the study. The system also provides
a simplified text summary (D), breaking down intri-
cate concepts into digestible information. Addition-
ally, (E) enables audio playback of the summary, of-
fering support for those who prefer auditory learning.
To support understanding of technical jargon, (F) in-
cludes a glossary of important terms relevant to deep-
fake detection. Users can also explore (G) a list of
potential applications, showcasing how the findings
can be practically implemented in various real-world
scenarios. Finally, (H) offers an interactive chatbot,
allowing users to engage directly with the content by
asking questions or seeking additional information,
thus enhancing the overall accessibility and usability
of the system.
The system also generates a mind map that sum-
marizes key aspects of the study (Figure 2). It vi-
sually organizes the research objectives, contributors,
methodology, and findings, providing a clear and con-
cise overview.
Figure 2: Mind map generated by the system, summarizing
key aspects of the study. Originally in Portuguese, trans-
lated into English for easier comprehension.
As shown in Figure 3, the system features a gami-
fied quiz designed to reinforce key concepts from the
study. By answering questions related to the research,
users can engage interactively while earning points
based on their accuracy.
EKM 2025 - 8th Special Session on Educational Knowledge Management
740
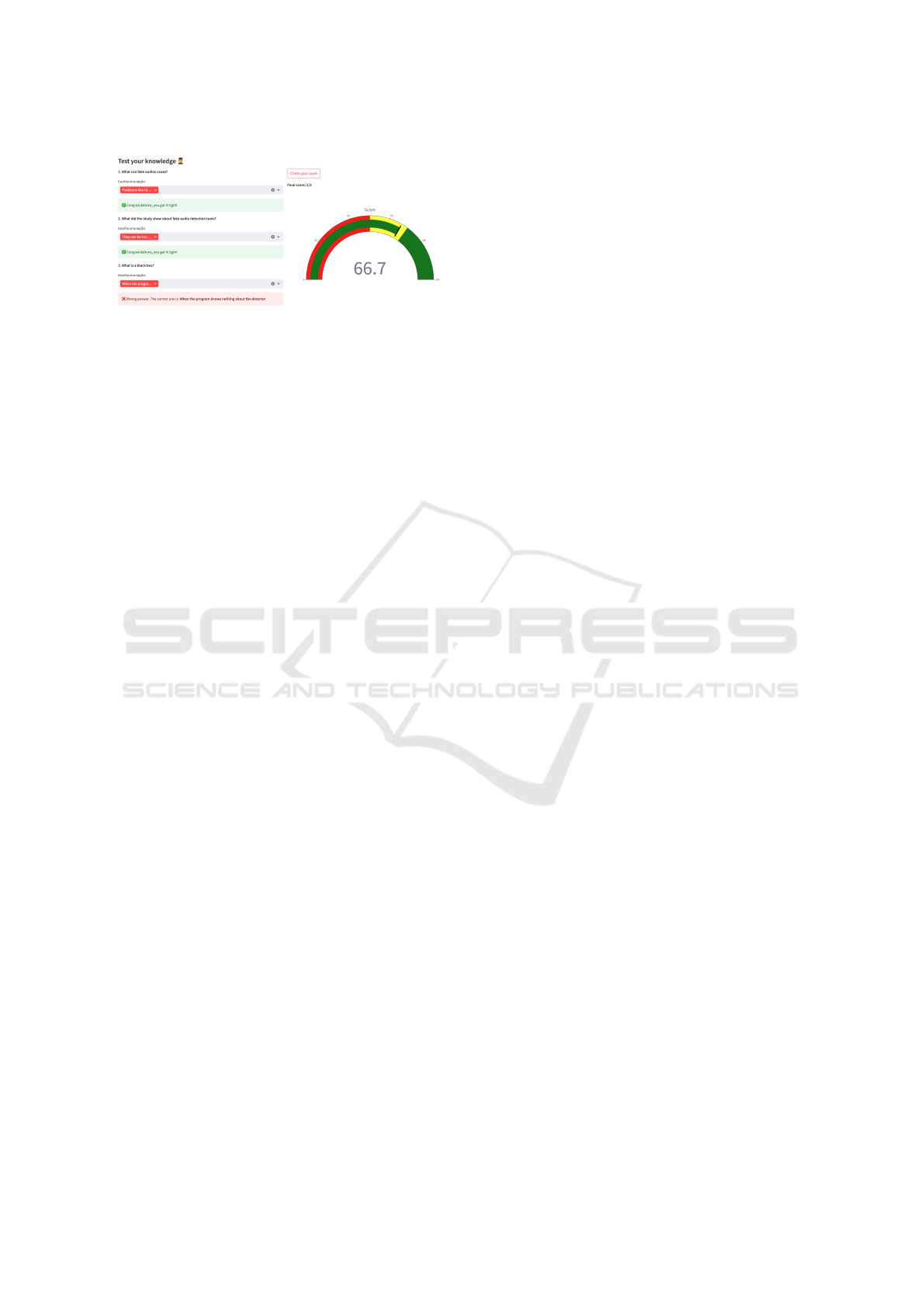
Figure 3: Screenshot of the gamified quiz feature, where
users answer questions related to the study to earn points.
The quiz features multiple-choice questions, with
correct answers highlighted in green and incorrect
ones marked in red, along with feedback on the cor-
rect response. A gauge-style score visualization pro-
vides a overview of the user’s performance.
5 CONCLUSION
This paper presents a proof-of-concept prototype
designed to make complex scientific content more
accessible, demonstrated through its application in
deepfake research. The system implements the con-
cept of multimodal graphical abstracts, combining el-
ements of text simplification, multimodal learning,
and visual elements to enhance comprehension of
complex scientific topics. We outlined the system’s
design process, and demonstrated its capabilities by
applying it to simplify a paper on deepfake detection.
The system illustrates the capacity of combining text
simplification with multimodal tools to support non-
expert communities in understanding scientific infor-
mation. This allows users to directly interact with
original research, helping them develop a more accu-
rate and trustworthy understanding of scientific con-
tent.
Future work will focus on ensuring that the sim-
plified information remains technically accurate and
does not oversimplify key concepts. This will in-
volve validating text simplification using computa-
tional metrics, along with incorporating feedback
from both experts and end-users to enhance the sys-
tem’s reliability and effectiveness.
REFERENCES
Al-Jarf, R. (2024). Multimodal teaching and learning in the
efl college classroom. Journal of English Language
Teaching and Applied Linguistics.
Al-Thanyyan, S. and Azmi, A. (2021). Automated text sim-
plification. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 54:1–
36.
Allen, L. and Kendeou, P. (2023). Ed-ai lit: An interdis-
ciplinary framework for ai literacy in education. Pol-
icy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain Sciences,
11:3–10.
Beks van Raaij, N., Kolkman, D., and Podoynitsyna, K.
(2024). Clearer governmental communication: Text
simplification with chatgpt evaluated by quantitative
and qualitative research. In Di Nunzio, G. M., Vez-
zani, F., Ermakova, L., Azarbonyad, H., and Kamps,
J., editors, Proceedings of the Workshop on DeTermIt!
Evaluating Text Difficulty in a Multilingual Context
@ LREC-COLING 2024, pages 152–178. ELRA and
ICCL.
Borowiec, B. (2023). Ten simple rules for scientists engag-
ing in science communication. PLOS Computational
Biology, 19.
Chevallard, Y. and Bosch, M. (2020). Didactic transposi-
tion in mathematics education. In Proceedings of the
2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Comput-
ing Systems, pages 214–218.
Doshi, R., Amin, K., Khosla, B., Bajaj, S., Chheang, S., and
Forman, M. (2023). Utilizing large language models
to simplify radiology reports: A comparative analy-
sis of chatgpt-3.5, chatgpt-4.0, google bard, and mi-
crosoft bing.
Engelmann, B., Haak, F., Kreutz, C., Nikzad, N., and
Schaer, P. (2023). Text simplification of scientific
texts for non-expert readers. ArXiv.
Farooq, M. U., Khan, A., Uddin, K., and Malik, K. M.
(2025). Transferable adversarial attacks on audio
deepfake detection. arXiv.
Garuz, A. and Garc
´
ıa-Serrano, A. (2022). Controllable sen-
tence simplification using transfer learning. Journal
of Computational Linguistics, pages 2818–2825.
Ivleva, N. (2022). Scientific text language code complex-
ity as a factor of communication difficulties. Bulletin
of Udmurt University. Series History and Philology,
32(3):537–545.
Kang, W. and Kilpatrick, J. (1992). Didactic transposition
in mathematics textbooks. For the Learning of Math-
ematics, 12:2–7.
Kian, L. S., Mamat, N., Abas, H., Hamiza, W., and Ali, W.
(2024). Ai integrity solutions for deepfake identifi-
cation and prevention. Open International Journal of
Informatics.
Kietzmann, J., Lee, L., McCarthy, I., and Kietzmann, T.
(2020). Deepfakes: Trick or treat? Business Horizons.
Lee, J. and Yoo, J. (2023). The current state of graphical
abstracts and how to create good graphical abstracts.
Science Editing.
Long, D. and Magerko, B. (2020). What is ai literacy?
competencies and design considerations. In Proceed-
ings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors
in Computing Systems.
Mayer, R. (2001). Multimedia Learning: The Promise of
Multimedia Learning. Cambridge University Press.
Mayer, R. (2003). The promise of multimedia learning: us-
ing the same instructional design methods across dif-
ferent media. Learning and Instruction, 13:125–139.
Designing a Multimodal Interface for Text Simplification: A Case Study on Deepfakes and Misinformation Mitigation
741

McCosker, A. (2022). Making sense of deepfakes: So-
cializing ai and building data literacy on github and
youtube. New Media & Society, 26:2786–2803.
Misiak, M. and Kurpas, D. (2023). In a blink of an eye:
Graphical abstracts in advances in clinical and experi-
mental medicine.
Mokadem, S. (2023). The effect of media literacy on misin-
formation and deep fake video detection. Arab Media
& Society.
Ng, D. T. K., Leung, J. K. L., Chu, S. K. W., and Qiao, M. S.
(2021). Conceptualizing ai literacy: An exploratory
review. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelli-
gence, 2.
Nguyen, T., Nguyen, Q., Nguyen, D., Nguyen, D., Huynh-
The, T., Nahavandi, S., Nguyen, T., Pham, V., and
Nguyen, C. (2019). Deep learning for deepfakes cre-
ation and detection: A survey. Comput. Vis. Image
Underst., 223.
Pruneski, J. (2018). Introducing students to the challenges
of communicating science by using a tool that em-
ploys only the 1,000 most commonly used words.
Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education, 19.
Qushem, U., Christopoulos, A., Oyelere, S., Ogata, H., and
Laakso, M. (2021). Multimodal technologies in preci-
sion education: Providing new opportunities or adding
more challenges? Education Sciences.
Reddy, P., Sharma, B., and Chaudhary, K. (2021). Digi-
tal literacy: A review in the south pacific. Journal of
Computing in Higher Education, 34(1):83–108.
Sanchez-Acedo, A., Carbonell-Alcocer, A., G
´
ertrudix, M.,
and Rubio-Tamayo, J. (2024). The challenges of me-
dia and information literacy in the artificial intelli-
gence ecology: Deepfakes and misinformation. Com-
munication & Society, 37(4):223–239.
Sikka, P. and Mago, V. (2020). A survey on text simplifica-
tion. ArXiv.
Tariq, R., Malik, S., Roy, M., Islam, M., Rasheed, U., Bian,
J., Zheng, K., and Zhang, R. (2023). Assessing chat-
gpt for text summarization, simplification, and extrac-
tion tasks. In 2023 IEEE 11th International Confer-
ence on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), pages 746–
749.
Verdoliva, L. (2020). Media forensics and deepfakes: An
overview. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal
Processing, 14:910–932.
Wan, X. (2018). Automatic text simplification. Computa-
tional Linguistics, 44(4):659–661.
White, J. (2024). Unlocking potential with multimodal
learning and assessment. GILE Journal of Skills De-
velopment.
EKM 2025 - 8th Special Session on Educational Knowledge Management
742
