
Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency in Physical Count Processes:
Leveraging AI, IoT, and Automation for Real-Time Inventory
Management in Supply Chain
Prabhakaran Rajendran
1
, Nirmal Kumar Balaraman
2
and Hareesh Viswanathan
3
1
CSCS LLC, Alpharetta, Georgia, U.S.A.
2
Inframark LLC, Norcross, Georgia, U.SA.
3
prabhu@cscs.io, nbalaraman@inframark.com, hareesh.viswanathan@bsci.com
Keywords: AI, IoT, Automation, Inventory Management, Real-Time Tracking.
Abstract: This paper aims at studying how much AI, IoT, and automation play a crucial role in improving the calibration
and effectiveness of physical inventory count exercises. As supply chain networks become enhanced,
companies are using these technologies to counter issues that come with the use of enhanced inventory control
including but not limited to errors, slowness among others. About this, the present paper examines two
different case studies one, based on a well-known logistics company in Finland, and the other, Amazon’s
fulfillment centers exploring how the application of AI, IoT and automation enhance real-time inventory
management. The study informs that the adoption of these technologies greatly improves both the integrity
and efficiency of inventory data, accurate real-time monitoring, and less reliance on manual adjustments, and
streamlines warehouse logistics. This paper fills the existing literature gap in understanding technological
advancements in inventory management and provides valuable recommendations to companies that wish to
transform in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Overview
In today’s dynamic business world, inventory control
has emerged as one of the key aspects in determining
business effectiveness in delivering timely goods and
services that meet the customer’s expectations . Such
manual ways of conducting physical inventory counts
as a basic approach is a bit slow and can have a high
incidence of errors (Mermi, 2024). Below figure 1
illustrates the four industrial revolutions. The first
revolution (1784) was powered by steam engines,
revolutionizing manufacturing and transportation. The
second (1870) harnessed electricity, enabling mass
production. The third (1969) introduced information
technology, transforming communication and data
processing. The ongoing fourth revolution is driven by
artificial intelligence, shaping the future of
automation, innovation, and decision-making.
When organizations grow and there is a demand
for rapid data flow, the continuous utilization of
manual handling of inventory records is
counterproductive (Ugbebor, 2024). To deal with
these challenges
Figure 1: The industrial revolution (Dinh,2020).
Companies are seeking innovative solutions that are
AI, IoT and automation. All these technologies are
likely to bring about enhanced accuracy of the
inventory management processes coupled with
efficiency gains (Ayoola, 2024). The current research
aims at establishing how physical inventory count can
be improved using AI, IoT and automation to provide
real-time inventory updates thus minimizing costs
and improving the supply chain.
1.2 Background
Conventional physical inventory taking procedures
involve tasks such as estimating quantities via stock
Rajendran, P., Balaraman, N. K. and Viswanathan, H.
Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency in Physical Count Processes: Leveraging AI, IoT, and Automation for Real-Time Inventory Management in Supply Chain.
DOI: 10.5220/0013506000003944
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security (IoTBDS 2025), pages 493-500
ISBN: 978-989-758-750-4; ISSN: 2184-4976
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
493

counts which are done by employees; this is
unproductive, cumbersome and may lead to
inaccuracies. These manual techniques cause
inconsistencies in stock data thus causing stock out,
overstocking or incorrect records in the financial
accounts. In addition, the increasing scale of business
operational hampers the accuracy of inventories
records and the extent of its update. Hence, companies
are looking for ways of increasing accuracy of the
inventory and enhance the effectiveness of such a
procedure. Below figure 2 represents the key stages of
warehouse operations. It begins with unloading and
receiving goods, followed by the put-away process,
where items are stored in designated locations. Next,
goods are organized in storage until needed. When an
order is placed, the order-picking stage retrieves the
required items. Finally, products are packed and
loaded for shipment to their destination.
Figure 2: Warehouse operation process .
1.3 Significance of the Study
Effective resource management is essential to meeting
consumer needs without overstocking or incurring
high operating costs (Kumar, 2024). Real-time
inventory tracking allows businesses to make
informed decisions on restocking, supply chain
management, and demand forecasting (Vinolyn
Vijaykumar, 2024). Inventory mismanagement can
directly impact customers, particularly in industries
reliant on tendering of products (Vaka, 2024).
Integrating AI, IoT, and automation presents a viable
solution for improving inventory accuracy and overall
business performance(Dash, 2019).
This study explores how these technologies
enhance traditional inventory management, offering
valuable insights into their impact on efficiency,
decision-making, and operational effectiveness in
modern supply chain processes.
1.4 Technological Context
Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things
(IoT), and automation are at the forefront of
technological advancements in inventory
management. AI uses machine learning algorithms to
analyze inventory data, predict demand, optimize
stock levels, and detect anomalies in real-time (Khan,
2024). IoT enables businesses to track inventory using
smart sensors and RFID (Radio Frequency
Identification) tags, allowing for seamless and real-
time updates on inventory levels (None Shivam,
2024). Automation, such as the use of drones or
robotic systems for physical counting, reduces human
intervention, increases speed, and minimizes the
chances of errors. These technologies work in tandem
to provide a more accurate, efficient, and automated
approach to managing inventory, making them crucial
for modern businesses looking to streamline their
operations (Vigneshwaran Gowrishankar, 2024).
1.5 Research Questions
• How can AI, IoT, and automation enhance the
accuracy of physical inventory count
processes?
• What efficiency improvements can be
achieved through real-time inventory
management using these technologies?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Inventory control has long been a crucial aspect of
supply chain and operations management,
emphasizing the importance of maintaining optimal
stock levels to meet customer demand efficiently and
cost-effectively. Traditionally, businesses relied on
manual processes such as Excel spreadsheets or
periodic stock counts, which proved error-prone and
inefficient (N. Kargah-Ostadi, 2020). Over time,
models like Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and
Just-in-Time (JIT) have been introduced to optimize
inventory while minimizing holding and ordering
costs. However, many industries still rely on manual
procedures. Today, advanced technologies such as AI,
IoT, and automation are beginning to transform
inventory management, enhancing accuracy and
efficiency (Soori, 2023).
AI, IoT, and automation have revolutionized
inventory management. Machine learning and
predictive analytics enhance demand forecasting by
identifying stock patterns. IoT enables real-time
inventory tracking through RFID tags and sensors,
providing instant stock updates (Mukherjee, 2021).
Automation technologies like drones and robotics are
increasingly adopted for stocktaking, reducing errors
and speeding up inventory counting processes
2.1 Technological Integration
Numerous studies highlight how AI, IoT, and
automation enhance inventory control. AI-driven
AI4EIoT 2025 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence for Emerging IoT Systems: Open Challenges and Novel Perspectives
494
predictive models analyze demand fluctuations,
optimizing inventory replenishment timing and
storage allocation (Kumar, 2024). For instance,
machine learning can process past sales data to
forecast future demand accurately, minimizing
stockouts and overstocking. IoT enables real-time
inventory tracking, offering a more efficient approach
to inventory and supply chain management. Research
indicates that RFID-based IoT systems provide
systematic, real-time stock updates while reducing
human errors in inventory control. These
technologies collectively improve accuracy,
efficiency, and decision-making, making them
essential for modern inventory management and
supply chain optimization (Dash, 2019).
Automation has significantly improved efficiency
in large-scale warehouses. Drones and robots
streamline stocktaking, reducing labor reliance while
enhancing speed and accuracy (Vigneshwaran
Gowrishankar, 2024). Research indicates that
automated systems improve inventory counting
accuracy by 40% over manual methods. These
technologies provide real-time inventory insights,
enabling better decision-making, optimizing
operations, and ultimately enhancing customer
satisfaction.
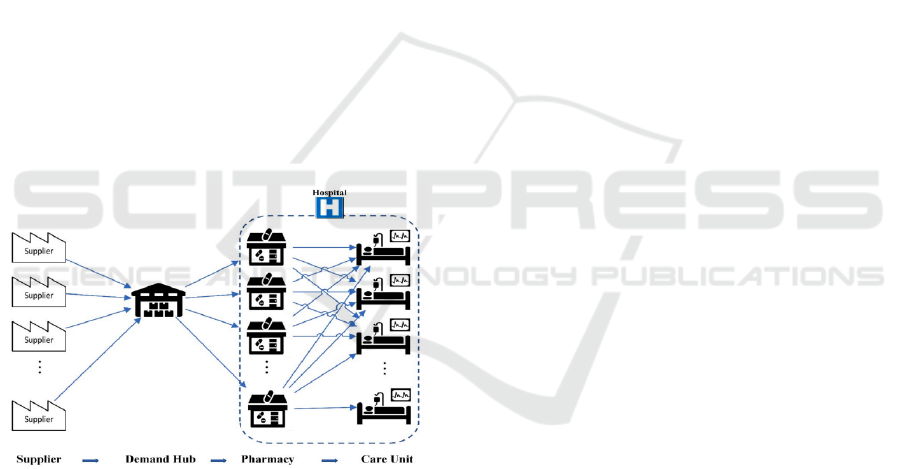
Figure 3: Flow of medical supplies (Mermi, 2024).
2.2 Gaps in Literature
Currently, there is a vast amount of literature that
discusses the individual technologies – AI, IoT, and
automation; however, theoretical research and case
studies on the application of these technologies are
abundant (Vaka, 2024). However, there is a lack of
published work presenting combined effects of both
on the physical inventory count processes, more so
from the perspective of real-time inventory count
(Ayoola, 2024). More literature reviews are confined
to single technology or existing sectors where
technological processes have been undertaken, while
a research gap exists regarding how these
technologies operate simultaneously to mitigate the
issues that arise with physical inventory counts
(Olugbenga Madamidola, 2024).
In addition, many studies examine IoT and
automation in manufacturing efficiency, few focus on
their impact on physical stock counting in inventory
management (Mukherjee, 2021). Existing literature
lacks insights into how these technologies enhance
accuracy and efficiency in near-real time, leaving
gaps in understanding their full potential for
inventory optimization.
Existing literature extensively examines AI, IoT,
and automation individually, with numerous
theoretical studies and case analyses on their
applications. However, there is a significant research
gap regarding their combined impact on real-time
physical inventory counting. Most studies focus on
single technologies or specific industries, offering
limited insights into their integrated potential. While
some research explores IoT and automation in
operational efficiency, few analyze their direct role in
improving stock counting accuracy. Additionally, the
absence of a proposed novel approach for real-time
inventory tracking restricts practical advancements.
These gaps hinder the development of actionable
insights needed to optimize inventory management
practices.
3 METHODOLOGY
Case Study (Dinh, 2020): AI in Inventory
Management at Finnish Logistics Company
This paper examines a Finnish logistics company that
has implemented AI in warehouse inventory
management, integrating Machine Learning (ML)
and Deep Learning (DL) to optimize supply chain
processes. AI has improved real-time inventory
tracking, replenishment accuracy, and efficiency.
Using a quantitative approach, data was collected
through employee interviews. The study evaluates
AI’s impact on inventory accuracy, efficiency, and
employee awareness while analyzing its strengths,
weaknesses, opportunities, threats, and future
prospects in inventory management.
Case Study
(Mermi, 2024): AI and Robotics in
Amazon’s Fulfilment Centres
Amazon’s use of AI in its fulfillment centers
exemplifies how technology can revolutionize
inventory management. The company employs
robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and
advanced automation for movement control, order
picking, restocking, and inventory tracking. By
Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency in Physical Count Processes: Leveraging AI, IoT, and Automation for Real-Time Inventory
Management in Supply Chain
495

maximizing operational capacity, Amazon has
achieved exceptional accuracy in handling vast
inventories, setting international supply chain
management standards. This case study, based on
secondary research from online databases, press
releases, industry reports, and academic journals,
highlights AI’s role in enhancing warehouse
efficiency. The study focuses on how robotics and
automation streamline inventory processes,
improving speed, accuracy, and real-time stock
control while reducing human dependency.
Additionally, it explores how other firms can
replicate Amazon’s AI-driven strategies to optimize
their own inventory management systems.
3.1 Comparison of Case Studies
The two case studies present different but
complementary perspectives on the integration of AI
into inventory management. While both companies
utilize AI, IoT, and automation, their approaches and
implementations vary significantly due to the
differences in scale, industry, and technological
infrastructure.
1. Technological Scope:
• Finnish Logistics Company: The focus is
primarily on AI-driven solutions like machine
learning and deep learning to enhance
inventory control. The case highlights the
challenges of adopting AI in a more traditional
logistics environment.
• Amazon: In contrast, Amazon has a much
broader implementation of AI, integrating
robotics, AGVs, and AI algorithms in its
fulfillment centers. This allows for more
advanced automation, enabling higher levels
of real-time tracking and inventory accuracy.
2. Impact on Inventory Management:
• Finnish Logistics Company: The integration
of AI has led to notable improvements in
inventory accuracy and operational efficiency.
However, challenges remain in the form of
employee adaptation to AI-driven changes,
which will likely improve over time.
• Amazon: AI has been successfully applied to
virtually all aspects of inventory management,
with a strong emphasis on robotics and
automation. The company’s fulfillment
centers represent a highly efficient and
scalable model for real-time inventory
management.
3. Scalability and Application:
• Finnish Logistics Company: While the
company’s adoption of AI is impressive, its
scale is smaller compared to Amazon, and
the focus is on improving efficiency and
accuracy within a single logistics operation.
• Amazon: Amazon’s global scale and use of
cutting-edge robotics and AI technologies
set it apart, with the company continuously
innovating in warehouse automation and
inventory management.
By comparing these cases highlights AI’s diverse
impact across companies. Both demonstrate AI’s role
in enhancing inventory precision and productivity,
but Amazon represents large-scale automation with
advanced robotics, a model difficult to replicate on a
smaller scale. In contrast, the Finnish logistics
company offers a more practical example of AI
integration, showcasing challenges in adoption.
Together, these cases illustrate how AI, IoT, and
automation are transforming inventory management,
improving accuracy, efficiency, and real-time
tracking across different business scales.
3.2 Potential Challenges in Adopting
IoT for Big Warehouses
Implementing IoT in large warehouses presents
several challenges affecting efficiency and
scalability. Latency and Connectivity Issues arise
from weak signal coverage and network congestion,
delaying inventory tracking. Scalability Constraints
occur when integrating thousands of sensors and
RFID tags across multiple warehouses, requiring
infrastructure upgrades. Data Overload demands
advanced cloud solutions and edge computing to
manage vast real-time inventory data. Cybersecurity
Risks increase with more IoT entry points,
necessitating robust security. Integration with Legacy
Systems poses compatibility challenges, hindering
seamless IoT adoption. Maintenance and Reliability
require continuous monitoring to ensure sensors and
automated systems function without disrupting
warehouse operations.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Findings of Case Study Results
Case Study (H. Dinh, 2020): AI-Driven Supply
Chain Enhancement
The data collected from the Finnish logistics
company reveal several key findings related to the
impact of AI on inventory management:
AI4EIoT 2025 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence for Emerging IoT Systems: Open Challenges and Novel Perspectives
496

• Improved Inventory Accuracy: The use of
AI in the form of machine learning and deep
learning has improved inventory accuracy
systems’ to a great extent. Some of the
improvements, which the company was able
to note after implementing the change
included; a marked decrease in the stock loss
differences and human mistake that were
prevalent during stock-take. Intelligent
systems offered features for real time
monitoring and prediction for physical
inventory as well as their digital counterpart.
• Efficiency Gains in Warehouse Operations:
Stock counting and replenishment has
benefited form the efforts made to automate
the processes that were once done manually.
Optimization of the supply picking and
replenishment routes has reduced the
durations taken and turnover rates hence faster
system operational rates.
• Employee Adaptation and Awareness: A
survey with the employees showed that there
was low to moderate understanding of AI
implementation. Some responses that stood out
include concerns about embracing change, and
thus adjusting to new technology that brings
improvement on the operational efficiency of
organizations by use of AI. But the company
ensured that employees undergo extensive
training; the effects of such aspect were
therefore reduced.
• Challenges and Future Prospects: In the
implementation part, integration problems
between new advanced AI technologies and
organizations’ existing systems were
mentioned as a problem. But for the present,
the company is hopeful about improving
predictive capabilities of AI and about
applying AI to more aspects of inventory
management in the future.
Case Study (Mermi, 2024): AI and Robotics in
Amazon's Fulfillment Centers
Amazon’s case study reveals a robust and advanced
application of AI in its fulfillment centers
• High-Level Automation and Accuracy: This
Company has embraced AI and robotics in
every process, from storage, replenishment of
stocks to picking of orders. Robotics has
helped enhance the rate and accuracy of
inventory with the support of AI to manage
real-time data integration throughout the
firm’s network of fulfillment centers globally.
• Scalability and Real-Time Inventory
Management: Robotics and automated
systems, as well as utilized AI algorithms,
help the company control significant amounts
of inventory at different locations. Other
outstanding features achieved through real-
time Inventory Management include reduction
of stockouts as well as cases of overstocking
since Amazon gets to track its demand and
supply levels in the most accurate manner
possible.
• Minimal Employee Interference: While the
AI and robots undertake most of the
responsibilities, employees are still in charge
of the running of the processes, monitoring,
repair, and decision making. Precision of work
whilst incorporating flexibility has been
boosted by the use of artificial intelligence
through adoption by Amazon.
• Challenges and Future Opportunities: It is
also essential to mention some of the problems
that Amazon faced in its AI/robotics journey,
namely, high initial expenses at the end of
which, the scaled-up value generated is
considered, and the difficulty of synchronizing
all the global centres of the company. The
company’s latest strategic direction in this
regard is to work on improving integration
between human employees and technology
tools to provide better quality and adaptability.
4.2 Answer to Research Questions
RQ 1: How can AI, IoT, and automation enhance
the accuracy of physical inventory count
processes?
These case studies confirm that AI, IoT, and
automation significantly enhance the precision of
physical inventory counting. Machine Learning
(ML) and Deep Learning (DL) improve inventory
tracking by eliminating human errors and ensuring
real-time stock data accuracy. The Finnish logistics
company experienced fewer discrepancies between
physical and virtual stock due to AI-based tracking.
Meanwhile, Amazon’s fulfillment centers leverage
robotics and AI to provide accurate real-time stock
updates, reducing errors associated with manual
labor. These technologies streamline replenishment,
picking, and order fulfillment, ensuring accurate
stock flow and optimal decision-making while
minimizing costly inventory mistakes. Figure 4
illustrates AI’s role in Amazon’s warehousing
operations. AI significantly enhances receiving, put-
away, storage, and fulfillment processes, improving
tracking and tracing to reduce errors. Robotics and
automation further optimize picking and packing
Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency in Physical Count Processes: Leveraging AI, IoT, and Automation for Real-Time Inventory
Management in Supply Chain
497

operations, resulting in faster, more precise
outcomes. Additionally, IoT devices provide real-
time shipping and delivery data, enhancing customer
experience and improving overall organizational
efficiency in inventory management.
Figure 4: AI Technologies in Amazon’s Warehouse.
RQ 2: What efficiency improvements can be
achieved through real-time inventory
management using these technologies?
Real-time inventory management, powered by AI,
IoT, and automation, significantly boosts
productivity. These technologies enhance stock
tracking speed, data accuracy, and minimize
downtime. Amazon’s real-time inventory tool
synchronizes global fulfillment centers, preventing
stockouts and overstocking. Similarly, the Finnish
logistics firm reduced costs through AI-driven
inventory automation. These improvements enable
faster decision-making, reduce manual labor reliance,
and enhance responsiveness to inventory fluctuations,
resulting in leaner operations and lower costs across
warehouse management and supply chain processes.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Interpretation of Results
From the analyzed case studies highlight the value of
AI, IoT, and automation in enhancing inventory
accuracy and efficiency. Both the Finnish logistics
company and Amazon demonstrate AI’s impact on
improving stock tracking. AI enables the Finnish firm
to implement real-time inventory tracking and receive
alerts for discrepancies between physical stock and
system records. Amazon, leveraging AI, machine
learning, and robotics, optimizes automation for
precise inventory synchronization. By minimizing
human intervention, these technologies ensure
accurate stock updates, reducing errors and enhancing
operational efficiency. Overall, AI-driven inventory
management improves accuracy, streamlines
operations, and enhances decision-making in modern
supply chains.
In both cases, AI adoption required employees to
adapt to new ways of working. Initially, Finnish
logistics company employees resisted AI integration,
but later developed a positive outlook. While AI
reduced manual stocktaking, employees transitioned
to strategic roles, such as monitoring AI systems and
addressing issues. Similarly, Amazon’s AI-driven
robotics now handle most physical tasks, while
human workers focus on system oversight and
maintenance. This demonstrates that AI and
automation do not replace human labor but redefine
roles, shifting employees toward managing AI
operations and making strategic decisions, ultimately
enhancing workforce efficiency and technological
collaboration.
5.2 Environmental Impact of IoT in
Warehouses
The IoT adoption in warehouses increases energy use
and e-waste. Continuous power is needed for sensors,
RFID tags, and automation, raising electricity
demand. High-powered data centers and cloud
computing for real-time tracking to elevate the carbon
footprint, while wireless networks and edge
computing add to energy consumption for data
processing and transmission.
IoT advancements lead to frequent device
upgrades, generating e-waste. Hard-to-recycle
sensors, batteries, and hardware contribute to
environmental contamination, while short product
lifecycles further intensify the challenge of
sustainable disposal in warehouses.
To minimize these impacts, warehouses can
implement energy-efficient IoT solutions, use
recyclable materials in devices, and adopt sustainable
e-waste management practices to reduce energy
consumption and manage waste effectively.
5.3 Limitations
Despite the realization of AI, IoT, and automations
lead to better inventory management, change
implementation is not easy. In general, both case
studies investigated the issues firms face when
incorporating new technologies with legacy systems,
which sometimes slows down the advantages that
such technologies offer. They indicate the use of AI-
based systems requires considerable time and
resources modalities to be imparted in human
resource dealing with them. Small companies will be
AI4EIoT 2025 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence for Emerging IoT Systems: Open Challenges and Novel Perspectives
498

unable to invest in such technology and training thus
putting them in a limited position as regards
implementing these innovations.
Both case studies focus on large companies with
the financial and organizational capacity to
implement AI, IoT, and automation. Amazon, as the
world’s largest e-commerce firm, leverages AI at
scale, benefiting from extensive technological
resources. However, these findings may not be
generalizable to smaller businesses with limited
resources, making them more applicable to large or
international firms rather than small and medium
enterprises (SMEs).
6 CONCLUSION
6.1 Summary of Findings
The study focuses on AI, IoT, and automation as key
factors that have revolutionized physical inventory
count through their ability to improve the precision
and speed of the processes in question. The proposed
studies, based on the experience of a Finnish logistics
company and Amazon, show that the use of AI and
automation strengthens the efficiency of inventory
management in terms of both precision and
productivity. They facilitate real time tracking of
products, minimize error and enhance efficiency of
the warehouse through repetitive tasks to these
technologies. This change of technology posed some
barriers to development since the initial employees
struggled to handle new systems, only to change their
roles to managers of these complex solutions once
they were able to adapt. Furthermore, both firms
demonstrate that large organizations can find scalable
solutions and that their success depends on these
organizations’ size and available resources.
6.2 Recommendations
Based on the findings, the following
recommendations are made for organizations
considering the integration of AI, IoT, and
automation into their inventory management
processes:
• Gradual Integration: To avoid the risks
mentioned above, organizations should take a
gradual approach when integrating AI and
automation, beginning with using them in
pilot projects or in some specific segments of
company activity. It enables assessment and
modeling depending on performance
outcomes to incorporate changes to meet new
demands.
• Employee Training and Reskilling: While
deploying intelligence and automation
technologies, organizations should ensure an
adequate training plan to create staff ready to
manage, operate and upkeep the technologies.
The utilization of these tools will be easier and
immediate if a workforce is already familiar
with them.
• Adaptation of Legacy Systems: IT
departments with legacy technologies already
in place should think through how AI and
automation will live alongside current
inventory management systems. Perhaps
instead of implementing completely new
systems of working, replacement could come
in a more integrated form where new
technologies build upon and improve the
existing structures.
6.3 Future Research
Future research should explore several avenues to
deepen our understanding of AI, IoT, and automation
in inventory management:
• Broader Industry Exploration: Engaging
different industries and organization sizes to
provide real-life case studies will give a
clearer understanding of the opportunities and
issues that revolve around AI and automation.
In particular, more effort dedicated to
scientific study of SMEs could offer means
that such companies can use to overcome
challenges related to implementing such
technologies.
• IoT’s Role in Real-Time Inventory
Management: Even though this research
provides a connection to IoT, it can be seen
that further potential of IoT in real-time stock
management was not investigated in this
study. Subsequent research must explore the
potential of IoT in creating bi-directional
visibility of inventory across various systems
and platforms to improve operational
inventory flexibility.
• Advanced AI Models and Predictive
Analytics: As artificial intelligence
progresses there is opportunity to enhance
inventory analytics through more advance
predictive methods. Future research could
aimed at how accurate demand forecasting
models are and the application of these models
Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency in Physical Count Processes: Leveraging AI, IoT, and Automation for Real-Time Inventory
Management in Supply Chain
499

to enhance demand and supply management
and hence minimize wastage.
Thus, extended investigation of these three
prospective areas will allow researchers and
practitioners to advance further the use of AI, IoT,
and automation in inventory management,
contributing to greater businesses opportunities in
different industries.
REFERENCES
Ayoola V. B., Osam-Nunoo G., Chima Umeaku, and
Babatunde Olusola Awotiwon, “IoT-driven Smart
Warehouses with Computer Vision for Enhancing
Inventory Accuracy and Reducing Discrepancies in
Automated Systems,” Nov. 26, 2024.
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/George-Osam-
Nunoo/publication/386110610
Dash R., McMurtrey M., Rebman C., and Kar U. K.,
“Application of Artificial Intelligence in Automation of
Supply Chain Management,” Journal of Strategic
Innovation and Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 3, Jul. 2019,
Available: https://articlearchives.co/index.php/JSIS/
article/view/4867
Dinh H., “The Revolution of Warehouse Inventory
Management by Using Artificial Intelligence: Case
Warehouse of Company X,” www.theseus.fi, 2020.
https://www.theseus.fi/handle/10024/346144
Kargah-Ostadi N., Waqar A., and Hanif A., “Automated
Real-Time Roadway Asset Inventory using Artificial
Intelligence,” Transportation Research Record: Journal
of the Transportation Research Board, p.
036119812094492, Aug. 2020, doi: https://doi.org/
10.1177/0361198120944926.
Khan, N. Jhanjhi Z., Hamid D. H. T. B. A. H., and Omar H.
A. H. B. H., “Internet of Things (IoT) Impact on
Inventory Management: A Review,” www.igi-
global.com, 2024. https://www.igi-global.com/chapter/
internet-of-things-iot-impact-on-inventory-
management/339252
Kumar P., Choubey D., Raimat Amosu O., and Mariam
Ogunsuji Y., “AI-enhanced inventory and demand
forecasting: Using AI to optimize inventory
management and predict customer demand,” World
Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, vol. 23,
no. 1, pp. 1931–1944, Jul. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/
10.30574/wjarr.2024.23.1.2173.
Ma X., Wang Zeyu, Ni X., and Ping G., “Artificial
intelligence-based inventory management for retail
supply chain optimization: a case study of customer
retention and revenue growth,” Journal of Knowledge
Learning and Science Technology ISSN 2959-6386
(online), vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 260–273, Oct. 2024, doi:
https://doi.org/10.60087/jklst.v3.n4.p260.
Mermi M., “Applications of Artificial Intelligence in
Warehouse Management: Case Study of Amazon,”
ﺔﻣﺍﺪﺘﺴﻤﻟﺍ ﺔﻴﻤﻨﺘﻟﺍﻭ ﺭﺎﻤﺜﺘﺳﻻﺍﻭ ﻞﻳﻮﻤﺘﻟﺍ ﺔﻠﺠﻣ , vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 30–
45, Dec. 2024, Accessed: Dec. 15, 2024. [Online].
Available: https://asjp.cerist.dz/index.php/en/article/
256756
Mukherjee A., “Robotic process automation with Blue
Prism to optimize inventory management,”
opus4.kobv.de, Aug. 01, 2021. https://opus4.
kobv.de/opus4-haw/frontdoor/index/index/docId/3661.
None Shivam and Gupta M., “Inventory and warehouse
management in industry 4.0: a BPR perspective,”
Journal of Information Technology Case and
Application Research, pp. 1 –36, Nov. 2024, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1080/15228053.2024.2433926.
Olugbenga Madamidola, Daramola O., Kolawole Akintola,
and Olawale Adeboje, “A Review of Existing Inventory
Management Systems,” International Journal of
Research in Engineering and Science, vol. 12, no. 9, pp.
40–50, Sep. 2024, Available:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Olugbenga-
Madamidola/publication/383947700
Soori M., Arezoo B., and Dastres R., “Internet of things for
smart factories in industry 4.0, a review,” Internet of
Things and Cyber-Physical Systems, vol. 3, no. 1, pp.
192–204, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.iotcps.2023.04.006.
Ugbebor F., Adeteye M., and Ugbebor J., “Automated
Inventory Management Systems with IoT Integration to
Optimize Stock Levels and Reduce Carrying Costs for
SMEs: A Comprehensive Review,” Deleted Journal,
vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 306–340, Nov. 2024, doi:
https://doi.org/10.60087/jaigs.v6i1.257.
Vaka D. K., “Integrating inventory management and
distribution: A holistic supply chain strategy,”
International Journal of Managing Value and Supply
Chains, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 13–23, Jun. 2024, doi:
https://doi.org/10.5121/ijmvsc.2024.15202.
Vigneshwaran Gowrishankar, Arunkumar Jagadeesan, Raj
K., Gupta K., and Kiruthiga T., “Process Automation
for Enhanced Supply Chain Management with Internet
of Things (IoT),” pp. 1272–1278, Jul. 2024, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1109/aic61668.2024.10731110.
Vinolyn Vijaykumar, Mercy P., Agnes L., Leena H. M., and
Savarimuthu C., “Convergence of IoT, Artificial
Intelligence and Blockchain Approaches for Supply
Chain Management,” Apress eBooks, pp. 45–89, Jan.
2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/979-8-8688-0315-
4_2.
AI4EIoT 2025 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence for Emerging IoT Systems: Open Challenges and Novel Perspectives
500
