
Generative Narrative-Driven Game Mechanics for Procedural Driving
Simulators
Nelson Bilber Rodrigues
1,2 a
, Ant
´
onio Coelho
1,2 b
and Rosaldo J. F. Rossetti
2,3 c
1
INESC TEC, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias s/n, 4200-465, Porto, Portugal
2
Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias s/n, 4200-465, Porto, Portugal
3
LIACC - Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science Lab, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias s/n, 4200-465, Porto, Portugal
{nrodrigues, acoelho, rossetti}@fe.up.pt, nelson.b.rodrigues@inesctec.pt
Keywords:
Procedural Content Generation, Inverse Procedural Modelling, Knowledge Graphs, Generative AI.
Abstract:
Driving simulators are essential tools for training, education, research, and scientific experimentation. How-
ever, the diversity and quality of virtual environments in simulations is limited by the specialized human re-
sources availability for authoring the content, leading to repetitive scenarios and low complexity of real-world
scenes. This work introduces a pipeline that can process text-based narratives outlining driving experiments
to procedurally generate dynamic traffic simulation scenarios. The solution uses Retrieval-Augmented Gen-
eration alongside local open-source Large Language Models to analyse unstructured textual information and
produce a knowledge graph that encapsulates the world scene described in the experiment. Additionally, a
context-based formal grammar is generated through inverse procedural modelling, reflecting the game me-
chanics related to the interactions among the world entities in the virtual environment supported by CARLA
driving simulator. The proposed pipeline aims to simplify the generation of virtual environments for traffic
simulation based on descriptions from scientific experiment, even for users without expertise in computer
graphics.
1 INTRODUCTION
Driving simulators are crucial for road safety and
behaviour studies, educational programs, and trans-
portation systems research. They provide a safe en-
vironment in which researchers can observe, analyse
the drivers and pedestrians’ behaviours under mul-
tiple parametrizable conditions (e.g., weather, high
traffic, unpredictable pedestrian reactions) without
risking human safety. Furthermore, the captured ex-
perimental data is useful for defining traffic policies or
improvements to road layouts that enhance safety. For
the aforementioned grounds, the necessity for design-
ing better methodologies and tools for driving simu-
lation are crucial.
However, the manually crafted virtual environ-
ments are repetitive and require intensive labour to
capture the diversity, complexity and uncertainty of
real-world driving, limiting their effectiveness in sim-
ulating authentic experiences. This gap emphasizes
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0519-7151
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7949-2877
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1566-7006
the necessity for research new methodologies to auto-
mate the generation and improve the diversity of sim-
ulated environments.
Addressing this challenge, the proposed solution
utilizes experiment description derived from ad-hoc
procedures in driving simulation to serve as founda-
tional model for procedurally generating game me-
chanics and imitating driving and pedestrian be-
haviours in driving simulators.
We propose a pipeline that combines Retrieval-
Augmented Generation (RAG) with Large Language
Models (LLMs) to structure the information, and in-
verse procedural modelling to generate a context-
based formal grammar to create the mechanics and
behaviours for driving scenarios. It is composed of
the following stages:
• Knowledge graph generation: Use RAG to extract
narrative elements from experiments description,
such as, entities, traffic signals, road topology, ge-
ographic information, weather conditions, traffic
patterns, and driver behaviours.
• Game mechanics mapping: Based on knowledge
graph data structure, procedural modelling tech-
Rodrigues, N. B., Coelho, A. and Rossetti, R. J. F.
Generative Narrative-Driven Game Mechanics for Procedural Driving Simulators.
DOI: 10.5220/0013311000003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 1: GRAPP, HUCAPP
and IVAPP, pages 339-346
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
339

niques are applied to generate and simulate driv-
ing action scenarios and behaviours.
• Visualization: Use Scenic language to define be-
haviours corresponding to the game mechanics
and inject them into CARLA driving simulator.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Open-Source Driving Simulators
This section presents a comprehensive overview of
open-source projects related to driving simulations,
categorized into two groups: photorealistic simulators
and traffic behaviour simulators.
CARLA (Dosovitskiy et al., 2017) is a photoreal-
istic simulator built on top of the Unreal Engine that
offers a virtual environment for complex multi-agent
dynamics at traffic intersections and sensory data to
train imitation and reinforcement learning. Neverthe-
less, it is limited by the number of 3D assets (e.g.,
buildings and pedestrians) that should be designed
and configured manually. VISTA 2.0 (Amini et al.,
2022), also under the photorealistic category, is based
on data-driven generated by sensors, builds up a sim-
ulation that can be used for full-scale autonomous ve-
hicles using accurate data.
Focus on simulations of behaviour, SUMO (Lopez
et al., 2018) focus on complex traffic simulations for
multiple vehicles and pedestrians instead of visual fi-
delity. The simulations can be microscopic such as
an individual pedestrian, and macroscopic, such vehi-
cle dynamics platooning and traffic density. UniNet
(Arppe et al., 2020) connects SUMO and the Unity
game engine to access the best of both worlds: high-
end graphics for visualization and industry-standard
traffic generator.
2.2 PCG in Driving Simulators
Procedural content generation (PCG) is a multidisci-
plinary approach in game development that automates
digital game content creation, requiring minimal man-
ual input. Multiple techniques can be applied, from
noise generation, formal grammars, and artificial in-
telligence, from evolutionary computing to deep rein-
forcement learning (Risi and Togelius, 2020).
PGDrive (Li et al., 2020) simulator was devel-
oped with the objective of generate multiple versions
of the simulation environment from the same base-
line. The authors used a search-based algorithm to
generate endless road networks to train artificial in-
telligence algorithms. MetaDrive (Li et al., 2022) is
an improvement of the previous work by extending
the simulation for multi-agent reinforcement learning
and providing an Open Gym environment to test the
agent’s interactions within simulated environment.
PCG techniques to automate were employed by
(Gambi et al., 2019a) for the generation of testing sce-
narios tailored for evaluating autonomous vehicle sys-
tems. The proposed solution generates multiple con-
figurations of virtual roads that expose self-driving
cars to safety-critical problems related to lane keep-
ing. (Gambi et al., 2019b) utilized of search-based
methods (genetic algorithms) that proved to be more
efficient and effective in generate road networks to-
wards safety-critical scenarios than random testing.
Although procedural content generation can cre-
ate complex structures automatically, configuring and
fine-tuning the underlying rules can be challenging
and prone to errors (Gieseke et al., 2021). A technique
called inverse procedural modelling (
ˇ
St’ava et al.,
2010) addresses these limitations by deriving rules
and structures directly from data rather than manually
defining them.
2.3 Narratives into Driving Simulations
Narrative-driven approaches enable the transforma-
tion of textual data into dynamic 3D scenarios. This
research topic focuses on defining and simulating
scene elements, character behaviours, and environ-
mental factors. However, translating narrative struc-
tures into functional game mechanics that present ac-
curate behaviours remains a crucial challenge.
A software artefact to recreate traffic accidents
from the analysis text-based data in the accident re-
ports into virtual worlds was developed by (Johans-
son et al., 2004). The authors built a linguistic model,
which extracts information from police reports about
traffic scene. (Gajananan et al., 2011) followed an-
other approach using a markup language called Sce-
nario Markup Language, to help the traffic engineers
to define key elements and complex transport do-
main scenarios. A framework for generating human-
autonomous vehicle interaction simulations based on
the plot concept present in narratives was proposed by
(Sun et al., 2021). The first stage involves gathering
real-world information to define key scenarios of user
interactions with autonomous vehicles. In the second
stage, scenario elements, such as environmental fac-
tors, infrastructure, non-player characters, and vehicle
interactions are categorized, with narrative attributes
guiding each element’s response to triggers. The fi-
nal stage involves constructing maps and connecting
scenarios through a cohesive storyline.
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
340

2.4 LLMs in Driving Simulations
LLMs can be applied to enhance driving simulations
by helping replicate human behaviours, contextual
understanding of urban environments, and generating
realistic, safety-critical scenarios. Integrating spatial
and semantic data is essential to the scene genera-
tion process. However, despite these advancements,
challenges still need to be addressed in achieving cus-
tomization accuracy, often requiring human valida-
tion and domain-specific model adaptations. LLMs
can decrease the gap between the real and virtual
world by helping reproduce the behaviours and habits
into agents, such as reproducing the driving behaviour
of human drivers as proposed (Gao et al., 2024).
CityGPT (Feng et al., 2024a) augments the power
of LLM to understand the urban environment by gen-
erating a model tailored to geospatial knowledge and
spatial and semantic task understanding. The model
was built with human movements and behaviours data
with a long temporal and spatial window.
A LLM to support the generation of realistic hu-
man behaviours for autonomous driving and pedes-
trian interactions was created by (Ramesh and Flohr,
2024). The authors collected information through
sensors plugged into the pedestrian’s garment and en-
coded the data into motion sequences to build a large
language model dataset. The behaviour of the pedes-
trians is translated into agents in the CARLA simu-
lated virtual environment.
ChatScene (Zhang et al., 2024) uses the LLMs to
generate safety-critical scenarios for autonomous ve-
hicles. The LLM agent translates the text into a prob-
abilistic domain-specific language, Scenic (Fremont
et al., 2023) that allows the descriptions and interac-
tion with CARLA simulator. Also, was built a re-
trieval database of Scenic code snippets that will be
used as a knowledge-base to interact with LLMs.
Text-to-Traffic Scene Generation framework de-
signed by (Ruan et al., 2024) is based on natural
language with descriptions to generate traffic scenes,
namely the road-network topology, and uses OpenAI
API to process the text describing from the scene
and compare with pre-defined trajectories, networks
topologies, and object’s positions, to generate the vir-
tual environment in CARLA. Nevertheless, compared
with ChatScene (Zhang et al., 2024), is more flexi-
ble related to customizations such as multiple agent
types, road signals, and objects. The solution is com-
posed of a group of LLM agents that have different re-
sponsibilities: translating the prompt text into Open-
DRIVE format (OpenDRIVE, 2024), converting it to
an intermediate format, and retrieving the most likely
plan according the user’s prompt. These plans are
manually pre-configured.
(Li et al., 2024) design a pipeline for traffic
simulation based on Simulation of Urban MObil-
ity (SUMO) and Large Language Models (Llama3
8B) that translate text in specific keywords to trigger
relevant scripts to generate the virtual environment.
The road-network topology is generated using Open-
StreetMap as a data source by converting specific re-
gions into coordinates to be visualised into SUMO.
Also, the pipeline has an analysis module that gen-
erates reports about traffic density, time analysis, and
emission of pollutants. LLMs are used to interpret the
text from the prompt and produce intermediate files to
support and analyse SUMO visualization.
City Bench (Feng et al., 2024b) a study about
the viability of the use of LLM in the urban do-
main. The authors concluded that open-source and
commercial LLMs perform poorly on several urban
tasks and point the LLMs tailored for urban do-
mains is necessary. Besides the study, they propose
a simulator named CitySim, that integrates multi-
source urban data with GIS and behavioural informa-
tion. The data is composed by integrating geospatial
data from OpenStreetMap (OpenStreetMap, 2024),
Google Maps, Baidu Maps and ERSI World Im-
agery and the behaviour data from Foursquare check-
ing dataset. This information was pre-processed and
stored to feed the multimodal LLMs.
Data gathered from police crash reports was used
by (Elmaaroufi et al., 2024) to generate the scenes
of the accidents. A dataset was built using NLP and
Scenic scripts to reproduce the accident scenes. The
OpenAI API was used to directly generate the Scenic
code (Fremont et al., 2023), and even with the ap-
plication of advanced prompting engineering tech-
niques, the syntactic correctness sometimes fails and
it was needed a Human-in-the-loop to manually fix
the generated specification.
2.5 Structuring Information in Graphs
Knowledge extraction is the discipline focused on
generating valuable insights and structured knowl-
edge from both structured and unstructured data
sources. Within this field, natural language pro-
cessing (NLP) offers a range of techniques to ac-
complish this task. This work specifically concen-
trates on Named Entity Recognition (NER) as a core
method for identifying and categorizing key informa-
tion within text, which is then utilized to construct a
knowledge graph.
A knowledge graph is a structured representation
that organizes real-world entities and their relation-
ships in a graph format, with a defined schema for
Generative Narrative-Driven Game Mechanics for Procedural Driving Simulators
341

types and relationships. The graph integrates infor-
mation from diverse sources and applies reasoning ca-
pabilities to generate new insights, enabling dynamic
knowledge creation beyond the initially stored data
(Ehrlinger and W
¨
oß, 2016).
Recent advances in generative AI can help to re-
trieve relevant information from unstructured data,
and the results can be further enhanced by the adop-
tion of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). This
technique is used for improving the labelling in
knowledge graphs, and support various applications
such as dataset question generation and summarized
Q&A. Nevertheless, while RAG is effective for re-
trieving specific answers found within specific text
regions, it struggles with answering global or ab-
stract queries, such as identifying overarching themes
within a dataset. This limitation is significant for
query-focused summarization tasks, which require
summarizing large amounts of text into meaningful
insights. The proposed approach, GraphRAG (Edge
et al., 2024), aims to bridge this gap by using a graph-
based knowledge representation that supports both
global and local query answering.
3 METHODS AND MATERIALS
A structured pipeline illustrated in (Fig. 1) was de-
signed to be composed of multiple stages: Knowl-
edge graph generation involves using unstructured
data to automatically create a graph that represents
entities and their relationships based on their semantic
meanings; Game mechanics generation by incorpo-
rating modelling techniques such as inverse procedu-
ral modelling; And, visualization using Scenic files, a
domain-specific probabilistic programming language
for modelling virtual environments and CARLA driv-
ing simulator.
Experiment description about scenes and events
were converted into small chunks of text, each de-
scribing a specific procedure to be replicated in the
virtual environment. The following text presents a
brief example of an experiment narrative representing
a scene in Paris, detailing interactions with pedestri-
ans.
”In Paris, a car and a bicycle move in the street,
the traffic light turns red, the car breaks, and five
pedestrians use the crosswalk.”
3.1 Knowledge Graph
The first stage of pipeline is the extraction of Named
Entity Recognition (NER) to build a knowledge
graph supported by LLMs. The technique Retrieval-
Augmented Generation (RAG) was used to process
the small chunk of text and generate a file with corre-
sponding graph. The GraphRAG (Edge et al., 2024)
project is tailored for this task, however, it was nec-
essary to add extra configurations to enable running
open-source LLM models using Ollama tool (Ol-
lama, 2024). The chosen model for encoding was
Mistral, and for embeddings, it was nomic-embed-
text. The GraphRAG generates NER entities based
on these pre-defined labels: ORGANIZATION, PER-
SON, EVENT, GEO.
When starting a new GraphRAG project, a default
structure is provided to prompt the LLM and extract
the entities and their relations. The prompts were de-
fined to produce a description about the relation be-
tween the entities.
However, the default prompt’s structure was
changed to produce a small description of the action,
preferentially, a single verb representing an action be-
tween the entities. The prompt should have the entity
types, the input text, and the format of the correspon-
dent output.
The following prompt template (Fig. 2) was pro-
vided to the LLM to learn the relationship between a
car and light traffic.
3.2 Game Mechanics Mapping
The entities and relations in the knowledge graph
were mapped to specific game mechanics, facilitating
a coherent translation of narrative elements dynamic
behaviours.
The GraphRAG tool generates the knowledge
graph metadata exporting in tabular format the details
about the entities type (label) and descriptions:
Entity | Type | Description
The second table, describes the relationships and
the causality between the entities. This information
will be used to generate the rules associated with the
game mechanics.
Entity A | Entity B | Rule
Using the pandas library (pandas, 2024), it was
possible to merge the information from two tables
and produce a nested structure to be used as a foun-
dation to produce the context-based formal grammar
illustrated in Fig. 3. The mapping and generation of
game mechanics is based previous tabular data rep-
resenting the rules and relationships between entities
that are programmatically translated into a map-based
data structure (Fig. 4).
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
342
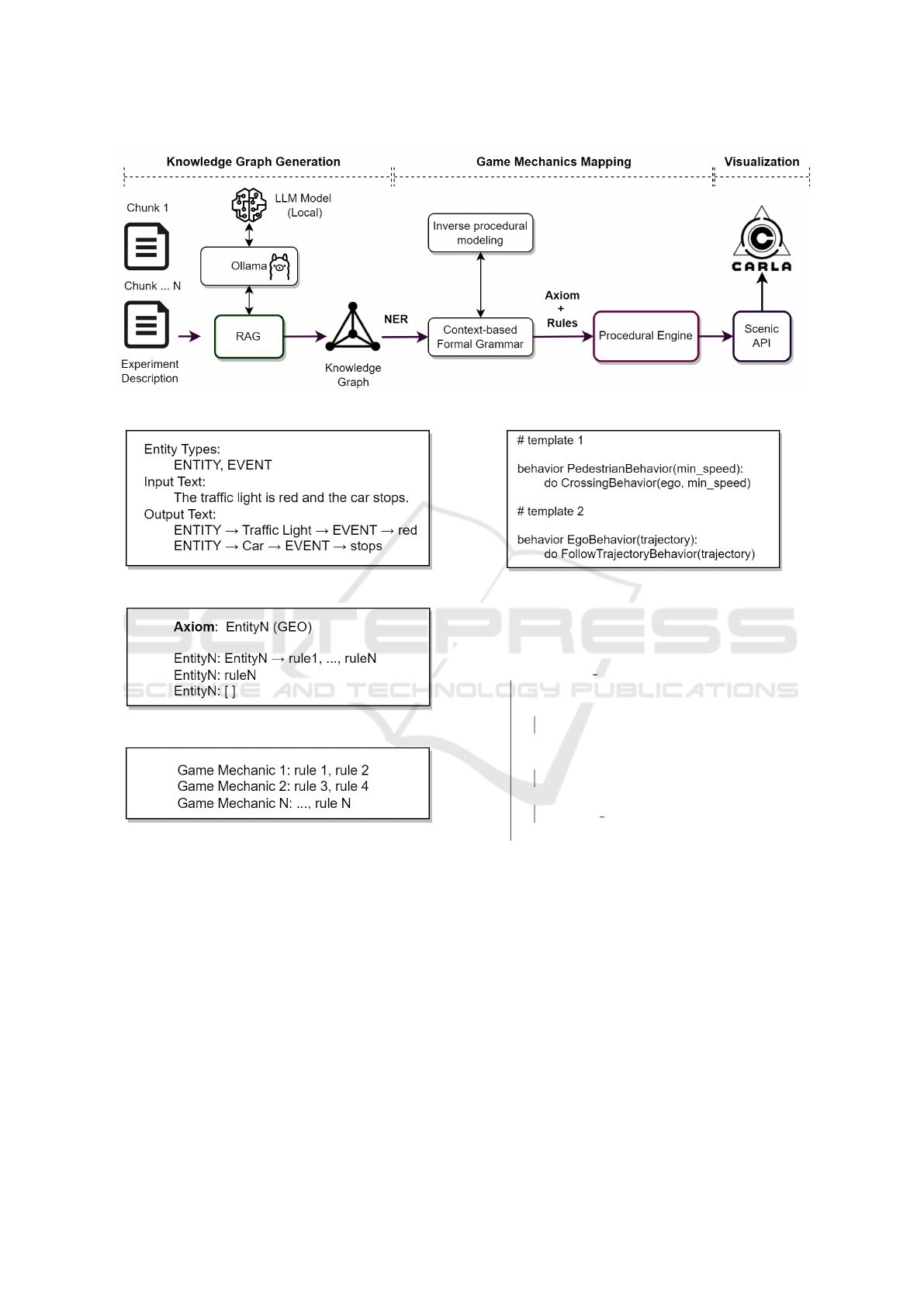
Figure 1: Pipeline from experiment description to game mechanics and visualize them in 3D driving simulations.
Figure 2: Prompt’s structure template.
Figure 3: PCG context-based grammar’s structure.
Figure 4: Game mechanics and rules association.
The translation of game mechanics from context-
based grammar to Scenic files was performed pro-
grammatically using predefined Scenic code tem-
plates, which represent the rules to be applied be-
tween two entities (Fig 5)
The context-based grammar is traversed, all re-
lationships between entities are verified and trans-
lated into the corresponding templates, representing
the rules and behaviours to be simulated. The algo-
rithm is described in the following pseudocode:
All templates are compiled into a single file and
syntactically validated using the Scenic API.
The formal grammar derives its structure from
the interconnected associations within the knowledge
Figure 5: Scenic templates modelling pedestrian and ego
car behaviour.
Data: grammar (graph)
Result: scenic file
while traverse grammar(Entity) do
(...);
if Entity and EntityN1 and rule 1 then
file += insert template 1;
else if EntityN and EntityN and rule N
then
file += insert template N;
else
traverse grammar(EntityN);
end
end
Algorithm 1: Context-based grammar to scenic file.
graph and contextual modelling of entity interactions.
This approach, known as inverse procedural mod-
elling, uses the input data to establish a structured and
context-dependent PCG grammar automatically.
3.3 Visualization
Scenic is a domain probabilistic programming lan-
guage that defines dynamic behaviours between
agents with a back-end that enables interaction with
CARLA. The transformation between the context-
based formal grammar to a Scenic file (plain text)
Generative Narrative-Driven Game Mechanics for Procedural Driving Simulators
343
is executed programmatically. The official CARLA
Docker image v0.9.15 was the baseline to visualize
the Scenic script invoked through the command line.
4 RESULTS
As a multi-stage pipeline, each step is designed with
specific objectives and results to be achieved.
4.1 Knowledge Graph Generation
Knowledge graph generated by GraphRAG identifies
the key entities along with their contextual associa-
tions, structuring the data as interconnected nodes and
relationships. Also, detects communities, which are
sub-structures within the larger graph that cluster sim-
ilar entities or those with frequent interactions. Fig. 6,
illustrates these connections between entities, where
the colour similarity indicates the proximity between
communities.
Figure 6: Knowledge graph corresponding to the text narra-
tive chunk.
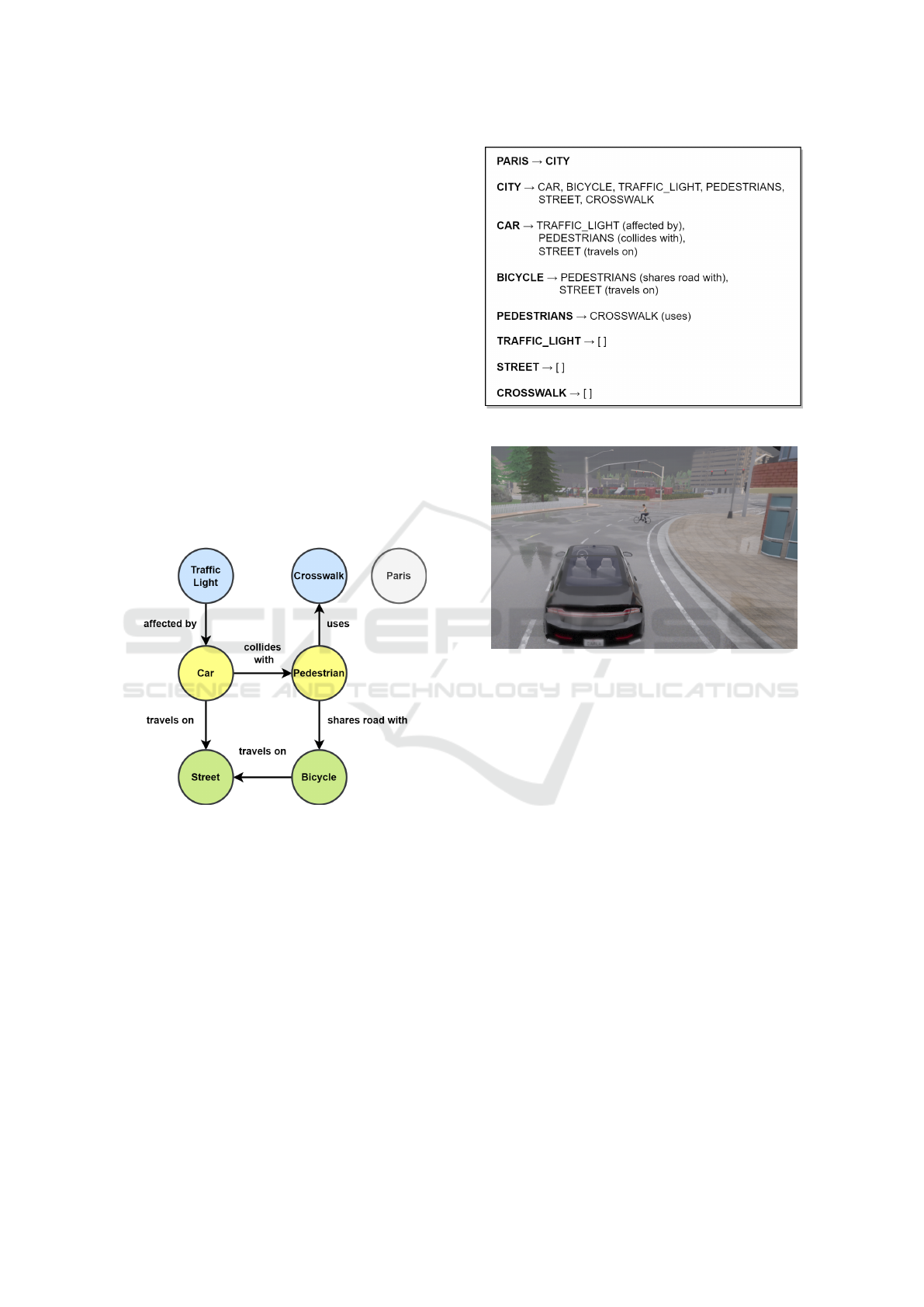
4.2 Game Mechanics Mapping
The mapping process described in subsection 3.2,
produces the following grammar, which is compiled
into a Scenic file. The axiom is the high-level GEO
entity (”Paris”) and rules translate the relationships
between entities (Fig. 7).
4.3 Visualization
The visualization is provided through the CARLA
open-source simulator (Fig. 8). The virtual scene is
the result of the rendering of the Scenic file correspon-
dent to the PCG grammar.
Figure 7: PCG generated context-based grammar.
Figure 8: Intersection between a car and a bicycle.
5 DISCUSSION
The proposed pipeline is effective to generate virtual
scenes from narratives, highlighting the potential of
using RAG with LLMs to detect entities and infer se-
mantic and contextual information.
5.1 Advantages of the Pipeline
Using LLMs proves advantageous, as they can rec-
ognize key entities and enhance the knowledge graph
with semantic and contextual data, laying the ground-
work for more automated and responsive simulation
environments.
Inverse procedural modelling addresses the prob-
lem of requiring specialized knowledge to gener-
ate PCG grammars. Combining LLMs and knowl-
edge graphs, it was possible to automatically generate
grammars influenced by contextual data, where LLMs
interpret and structure narrative input, and knowledge
graphs provide the interconnected associations that
shape grammar rules.
This approach aims to overcome the use of
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
344

complex prompt engineering, and unpredictable be-
haviour, by introducing a context-based formal gram-
mar to structure the final Scenic file. Overcome, the
limitations stated by (Elmaaroufi et al., 2024) that ex-
plored various prompt engineering techniques to gen-
erate directly Scenic files but concluded that was in-
sufficient for accurately producing always a valid out-
put. Comparing with the work of (Ruan et al., 2024),
which used pre-defined scenes that match with the
text on narratives, this work uses RAG within LLM
can semantically identify and structure multiple ob-
jects in the scenes that can be combined into final
Scenic file.
In contrast to solutions that require commercial
LLMs, as presented in the work of (Ruan et al., 2024),
the proposed pipeline is based on open-source LLMs
that can run on the local computer and be shared
on public hubs. The objective is to promote the re-
peatability of scientific experiments and procedures
because the solution is not dependent on third-party
software and expensive hardware.
5.2 Limitations
Nevertheless, not all entities have direct relationships
with other entities. For instance, while ”Paris” (a ge-
ographical entity) appears within the narrative struc-
ture, it is not directly associated with entities such as
”street.” This highlights how communities are related
to their contextual meaning, e.g., ”street” is closer to
”car” than ”Paris”. The generated knowledge graph
is context-based and semantically valid. Also, some
limitations were detected such as the quantifier (”five
pedestrians”) and traffic lights adjective (”red”) were
not detected.
As described in subsection 3.2 the mapping be-
tween the game mechanics and the Scenic file is done
programmatically, underscoring a need for automa-
tion to streamline this integration in future iterations.
This manual process is a limitation of the proposed
pipeline because the knowledge graph can have ac-
tions that are not directly present in the coded data
structure.
The experimental trials and data demonstrate that
prompt results are also sensitive to prompt engineer-
ing, as the quality of generated scenarios heavily re-
lies on well-crafted prompts to guide the model.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
CHALLENGES
This work presents a pipeline for generating virtual
scenes for driving simulators using narrative-oriented
techniques using LLM. GraphRAG, was the tool to
generate a structured knowledge graph that identifies
the entities and their relationships.
Incorporating techniques, such as inverse proce-
dural modelling, presents an innovative solution for
automatically generating context-based formal gram-
mar from narrative chunks using generative AI and
RAG. This approach addresses challenges associated
with relying on predefined scenes or handling inac-
curate results from direct prompt results, even when
employing complex prompt engineering techniques.
The initial results in automating context-based
formal grammar generation supported by LLM rep-
resent an important step in the process of automat-
ing content authoring for driving simulators. How-
ever, certain pipeline stages, such as mapping context-
based grammar to the Scenic file, require further au-
tomation for more efficient scenario generation and
visualization.
As future work will be also explored the fine-
tuning of LLM with geospatial data (e.g. maps such
OpenStreetMap), to work in conjunction with already
detected capabilities of detecting city names, to help
to recreate specific environments in the CARLA sim-
ulator. Also, the RAG will be enhanced by NLP toolk-
its to detect quantifiers in the relations between enti-
ties (e.g.”five pedestrians”).
The current validation method is based on syntac-
tic validation of final Scenic file provided by Scenic
API. Nevertheless, to validate the actor’s behaviours
in the simulation will be performed a focus-group
composed by experts (e.g. traffic engineers) to access
the correct representation of the description of the ex-
periment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is co-financed by Component 5 - Capital-
ization and Business Innovation, integrated in the Re-
silience Dimension of the Recovery and Resilience
Plan within the scope of the Recovery and Resilience
Mechanism (MRR) of the European Union (EU),
framed in the Next Generation EU, for the period
2021 - 2026, within project FAIST, with reference 66.
REFERENCES
Amini, A., Wang, T.-H., Gilitschenski, I., Schwarting, W.,
Liu, Z., Han, S., Karaman, S., and Rus, D. (2022).
Vista 2.0: An open, data-driven simulator for multi-
modal sensing and policy learning for autonomous ve-
hicles. In 2022 International Conference on Robotics
and Automation (ICRA), pages 2419–2426.
Generative Narrative-Driven Game Mechanics for Procedural Driving Simulators
345

Arppe, D. F., Zaman, L., Pazzi, R. W., and El-Khatib, K.
(2020). Uninet: A mixed reality driving simulator.
In Proceedings of Graphics Interface 2020, GI 2020,
pages 37 – 55. Canadian Human-Computer Commu-
nications Society / Soci
´
et
´
e canadienne du dialogue
humain-machine.
Dosovitskiy, A., Ros, G., Codevilla, F., Lopez, A., and
Koltun, V. (2017). CARLA: An open urban driving
simulator. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Confer-
ence on Robot Learning, pages 1–16.
Edge, D., Trinh, H., Cheng, N., Bradley, J., Chao, A., Mody,
A., Truitt, S., and Larson, J. (2024). From local to
global: A graph rag approach to query-focused sum-
marization.
Ehrlinger, L. and W
¨
oß, W. (2016). Towards a definition
of knowledge graphs. SEMANTiCS (Posters, Demos,
SuCCESS), 48(1-4):2.
Elmaaroufi, K., Shanker, D., Cismaru, A., Vazquez-
Chanlatte, M., Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A., Zaharia,
M., and Seshia, S. A. (2024). ScenicNL: Generat-
ing probabilistic scenario programs from natural lan-
guage. In First Conference on Language Modeling.
Feng, J., Du, Y., Liu, T., Guo, S., Lin, Y., and Li, Y. (2024a).
Citygpt: Empowering urban spatial cognition of large
language models.
Feng, J., Zhang, J., Yan, J., Zhang, X., Ouyang, T., Liu,
T., Du, Y., Guo, S., and Li, Y. (2024b). Citybench:
Evaluating the capabilities of large language model as
world model.
Fremont, D. J., Kim, E., Dreossi, T., Ghosh, S., Yue,
X., Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A. L., and Seshia, S. A.
(2023). Scenic: a language for scenario speci-
fication and data generation. Machine Learning,
112(10):3805–3849.
Gajananan, K., Doirado, E., Nakasone, A., Cuba, P.,
Prendinger, H., and Miska, M. (2011). Creating in-
teractive driver experiences with the scenario markup
language. In Proceedings of the 8th International
Conference on Advances in Computer Entertainment
Technology, ACE ’11, New York, NY, USA. Associa-
tion for Computing Machinery.
Gambi, A., Mueller, M., and Fraser, G. (2019a). Asfault:
Testing self-driving car software using search-based
procedural content generation. In 2019 Ieee/Acm 41st
International Conference On Software Engineering:
Companion Proceedings, pages 27–30. IEEE.
Gambi, A., Mueller, M., and Fraser, G. (2019b). Automat-
ically Testing Self-Driving Cars with Search-Based
Procedural Content Generation, page 318–328. As-
sociation for Computing Machinery, New York, NY,
USA.
Gao, C., Lan, X., Li, N., Yuan, Y., Ding, J., Zhou, Z., Xu, F.,
and Li, Y. (2024). Large language models empowered
agent-based modeling and simulation: a survey and
perspectives. Humanities and Social Sciences Com-
munications, 11(1):1259.
Gieseke, L., Asente, P., M
ˇ
ech, R., Benes, B., and Fuchs,
M. (2021). A survey of control mechanisms for cre-
ative pattern generation. Computer Graphics Forum,
40(2):585–609.
Johansson, R., Williams, D., Berglund, A., and Nugues, P.
(2004). Carsim: A system to visualize written road ac-
cident reports as animated 3d scenes. In Proceedings
of the 2nd Workshop on Text Meaning and Interpreta-
tion, TextMean ’04, USA. Association for Computa-
tional Linguistics.
Li, Q., Peng, Z., Feng, L., Zhang, Q., Xue, Z., and Zhou, B.
(2022). Metadrive: Composing diverse driving sce-
narios for generalizable reinforcement learning. IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intel-
ligence.
Li, Q., Peng, Z., Zhang, Q., Qiu, C., Liu, C., and Zhou,
B. (2020). Improving the generalization of end-to-end
driving through procedural generation. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2012.13681.
Li, S., Azfar, T., and Ke, R. (2024). Chatsumo: Large lan-
guage model for automating traffic scenario genera-
tion in simulation of urban mobility.
Lopez, P. A., Behrisch, M., Bieker-Walz, L., Erdmann, J.,
Fl
¨
otter
¨
od, Y.-P., Hilbrich, R., L
¨
ucken, L., Rummel,
J., Wagner, P., and Wiessner, E. (2018). Microscopic
traffic simulation using sumo. In 2018 21st Interna-
tional Conference on Intelligent Transportation Sys-
tems (ITSC), pages 2575–2582.
Ollama (2024). Get up and running with large language
models. https://github.com/ollama/ollama. Accessed:
2024-10-20.
OpenDRIVE, A. (2024). Asam opendrive. https://www.
asam.net/standards/detail/opendrive. Accessed: 2024-
10-26.
OpenStreetMap (2024). Openstreetmap. https://www.
openstreetmap.org/about. Accessed: 2024-10-26.
pandas (2024). pandas - python data analysis library. https:
//pandas.pydata.org. Accessed: 2024-10-20.
Ramesh, M. and Flohr, F. B. (2024). Walk-the-talk: Llm
driven pedestrian motion generation. In 2024 IEEE In-
telligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), pages 3057–3062.
IEEE.
Risi, S. and Togelius, J. (2020). Increasing generality in ma-
chine learning through procedural content generation.
Nature Machine Intelligence, 2(8):428–436.
Ruan, B.-K., Tsui, H.-T., Li, Y.-H., and Shuai, H.-H. (2024).
Traffic scene generation from natural language de-
scription for autonomous vehicles with large language
model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.09575.
Sun, X., Zhang, Y., and Zhou, W. (2021). Building narrative
scenarios for human-autonomous vehicle interaction
research in simulators. In Cassenti, D. N., Scataglini,
S., Rajulu, S. L., and Wright, J. L., editors, Advances
in Simulation and Digital Human Modeling, pages
150–156, Cham. Springer International Publishing.
ˇ
St’ava, O., Bene
ˇ
s, B., M
ˇ
ech, R., Aliaga, D. G., and Kri
ˇ
stof,
P. (2010). Inverse procedural modeling by automatic
generation of l-systems. Computer Graphics Forum,
29(2):665–674.
Zhang, J., Xu, C., and Li, B. (2024). Chatscene:
Knowledge-enabled safety-critical scenario genera-
tion for autonomous vehicles. In 2024 IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recog-
nition (CVPR), pages 15459–15469.
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
346
