Large Language Model-Informed Geometric Trajectory Embedding for
Driving Scenario Retrieval
Tin Stribor Sohn
1,∗
, Maximilian Dillitzer
1,2,∗
, Tim Br
¨
uhl
1
, Robin Schwager
1
,
Tim Dieter Eberhardt
1
, Michael Auerbach
2
and Eric Sax
3
1
Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, Weissach, Germany
2
Hochschule Esslingen, Esslingen, Germany
3
Karlsruher Institut f
¨
ur Technologie, Karlsruhe, Germany
Keywords:
Geometric Trajectory Embedding, Large Language Model, Scenario Retrieval, Behavioural Scenario.
Abstract:
This paper introduces a Large Language Model-informed geometric embedding for retrieving behavioural
driving scenarios from unlabelled trajectory data, aimed at improving the search of real driving data for
scenario-based testing. A Variational Recurrent Autoencoder with a Hausdorff Distance-based loss generates
trajectory embeddings that capture detailed spatial patterns and interactions, offering enhanced interpretability
over traditional mean squared error-based models. The embeddings are further organised through unsuper-
vised clustering using HDBSCAN, grouping scenarios by similarities at the scene, infrastructure, behaviour,
and interaction levels. Using GPT-4o for describing scenarios, clusters, and inter-cluster relationships, the
approach enables targeted scenario retrieval via a Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation pipeline, enabling a
natural language search of unlabelled trajectories. Evaluation demonstrates a retrieval precision of 80.2% for
behavioural queries involving infrastructure, multi-agent interactions, and diverse traffic conditions.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Safety of the Intended Functionality (SOTIF)
standard provides guidance for the validation and ver-
ification (V&V) process of automated driving systems
(ADS). According to SOTIF, driving functions must
not only ensure safety under typical operating condi-
tions, but must also be able to deal with hazardous
and unforeseen scenarios that pose the highest safety
risks (International Organization for Standardization,
2022). This standard emphasises the need for an ADS
not only to behave safely on its own, but also to antic-
ipate and handle potential faults and misbehaviour of
other road users, emphasising that driving functions
need to be evaluated at a behavioural level to ensure
robust fault anticipation.
In real-world driving data, road user behaviour is
often represented by object lists with associated tra-
jectories that serve as indicators of driving scenar-
ios. However, mapping scenarios and their associ-
ated trajectories to each other remains a significant
challenge for V&V tasks. Existing manoeuvre-based
∗
Equal contribution
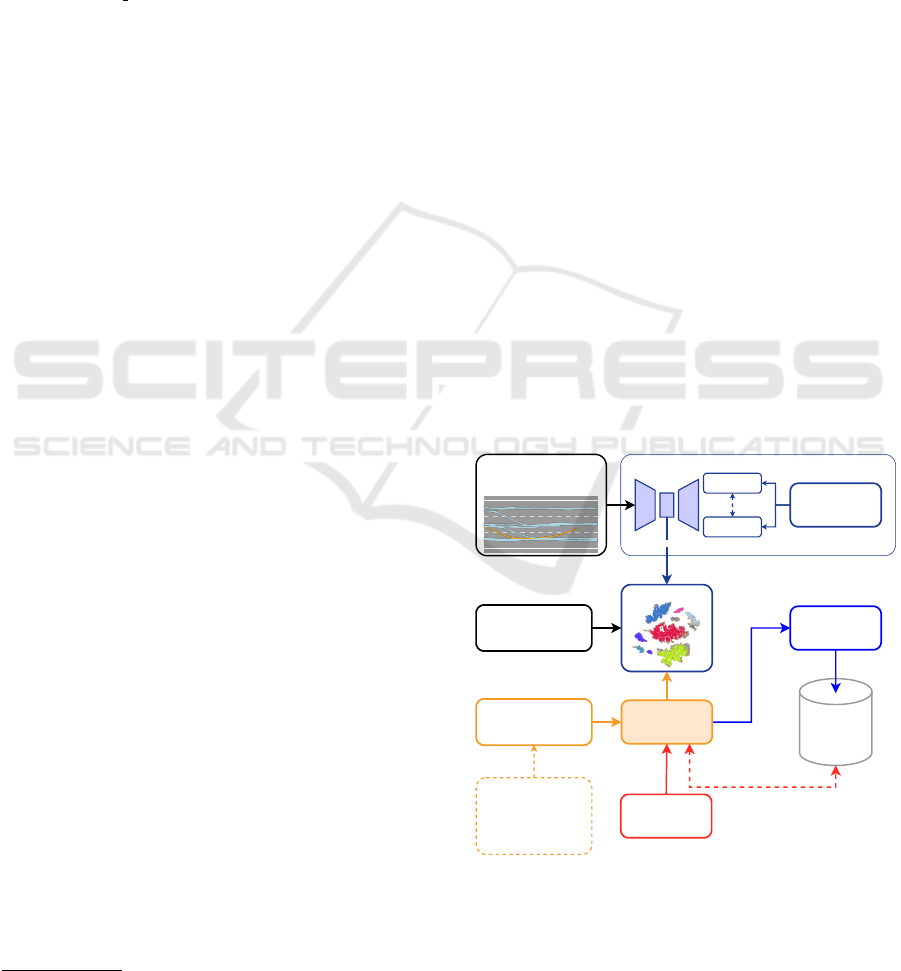
Ego Trajectory
& Trajectories of other
Road Users
VRAE
Latent Space
Geometric Embedding
LLM
Trajectory and Cluster
Description with
Prompts
Cluster Embedding
(HDBSCAN)
GraphRAG
Indexing
Graph
Database
Natural Language
Query
queried Output
Reconstructed
Ground Truth
Hausdorff
Distance
1. Describe Sample Scene
2. Compare to neighbouring
Samples in same Cluster
3. Compare to random
Samples of other Clusters
Figure 1: Method for generating geometric trajectory em-
beddings and mapping them to textual descriptions, en-
abling scenario retrieval and searchability at a behavioural
level through natural language queries.
approaches often rely on pre-defined rules, which
66
Sohn, T. S., Dillitzer, M., Brühl, T., Schwager, R., Eberhardt, T. D., Auerbach, M. and Sax, E.
Large Language Model-Informed Geometric Trajectory Embedding for Driving Scenario Retrieval.
DOI: 10.5220/0013276500003941
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems (VEHITS 2025), pages 66-75
ISBN: 978-989-758-745-0; ISSN: 2184-495X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

may not be sufficient to capture the full range of be-
havioural complexity.
This paper proposes a novel method to enhance
the searchability of unlabelled trajectory-based sce-
narios found in naturalistic driving data through the
integration of geometric trajectory embeddings and
Large Language Models (LLMs) (Fig. 1). By ad-
dressing existing limitations in the searchability of be-
havioural scenarios in scenario-based testing (SBT),
the proposed method contributes to the state of the art
in five key ways:
• Fine-Grained Clustering of Unlabelled Trajec-
tories: Using a variational recurrent autoencoder
and a Hausdorff loss function, geometric embed-
dings are generated for unlabelled trajectories that
capture fine-grained attributes rather than aver-
age metrics such as mean squared error (MSE).
Cluster analysis within this embedding space is
achieved by Hierarchical Density-Based Spatial
Clustering of Applications with Noise (HDB-
SCAN) to reveal attribute patterns.
• Integrated Embedding of Scene Elements and
Interactions: The joint geometric embedding en-
compasses infrastructure, general scene context,
manoeuvres, and object interactions, reflecting
multi-object scenarios.
• Behavioural Scenario Description and Search-
ability: By describing and comparing trajec-
tory clusters in the geometric embedding through
prompting an LLM for natural language descrip-
tions (Wei et al., 2022), the method improves in-
terpretability and enables behaviour-based search-
ability across clusters, allowing natural language
queries to be mapped to trajectory data.
• Indexing Through the GraphRAG Pipeline:
Embeddings are indexed within a Graph
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline
(Edge et al., 2024), enabling natural language re-
trieval and open vocabulary manoeuvre mapping,
along with combinatorial behaviour scenario
search.
• Demonstrated Retrieval Performance: Evalua-
tion results indicate an average retrieval precision
of 80.2% with promising results in scenarios re-
trieval involving infrastructure and object interac-
tions, as well as in the combinatorial manoeuvre
space.
2 RELATED WORK
Current behavioural scenario extraction methods can
be classified into learning-based embeddings, trajec-
tory clustering and rule-based manoeuvre extraction.
Learning-based trajectory embedding approaches
use deep learning techniques to generate embeddings
of driving scenarios.
Sonntag et al. introduced a method to minimise
the test space by identifying edge cases using deep
learning based outlier detection (Sonntag. et al.,
2024). Their approach used autoencoders to gener-
ate trajectory embeddings and calculated MSE recon-
struction errors to identify unusual scenarios. How-
ever, this method has limitations as it focuses primar-
ily on spatio-temporal features and relies on an overall
scenario embedding, which limits its applicability for
detailed scenario analysis, particularly when address-
ing SOTIF. The use of MSE often fails to preserve
the finer geometric properties of the trajectories, re-
sulting in a more generalised representation that may
miss critical behavioural nuances such as local lateral
driving behaviour. In addition, the interpretability and
searchability of the embedding is challenging as the
properties of the clusters are not described.
Hoseini et al. present a non-parametric trajectory
clustering framework using Generative Adversarial
Networks (GANs) to generate realistic synthetic data
(Hoseini et al., 2021). Their approach incorporates
geometric relations through Dynamic Time Warping
(DTW) and models transitive relations within an em-
bedding space. However, its applicability to be-
havioural scenario search is limited due to the limited
interpretability of the embedding space. Furthermore,
it only considers lateral and longitudinal positioning,
omitting key parameters essential for dynamic sce-
nario characterisation, and focuses on only three spe-
cific scenarios: cut-in and left or right pass-by ma-
noeuvres.
Clustering-based methods have also been ex-
plored to group similar driving scenarios, often focus-
ing on the temporal and dynamic aspects of trajecto-
ries.
Ries et al. introduced a method for trajectory-
based clustering using DTW, which identifies similar
driving scenarios by comparing the temporal align-
ment of dynamic object trajectories (Ries et al., 2021).
While this method is effective for querying similar
trajectories, it does not capture the full complexity of
driving scenarios, particularly in terms of abstraction
layers that involve multiple interacting entities and re-
lated infrastructure.
Similarly, Watanabe et al. proposed a sce-
nario clustering method based on predefined features
(Watanabe et al., 2019). Although this approach al-
lows for the organisation of scenario data, it lacks the
ability to adaptively discover relevant features from
the trajectory data itself, limiting its applicability to
Large Language Model-Informed Geometric Trajectory Embedding for Driving Scenario Retrieval
67

behavioural scenario search.
Rule-based manoeuvre extraction approaches for
driving scenario retrieval are based on pre-defined
rules and patterns.
Montanari et al. introduced a pattern cluster-
ing method that identifies recurring scenario patterns
from time series data (Montanari et al., 2020). While
this method is useful for recognising common scenar-
ios and corner cases, it does not explicitly consider
the geometric properties of the trajectories in relation
to the infrastructure and lacks interpretability due to
missing pattern descriptions.
Elspas et al. introduced a more sophisticated
rule-based system using regular expressions to extract
driving scenarios (Elspas et al., 2020). Their method
focuses on detecting specific manoeuvres, such as
cut-ins and lane changes, by applying pre-defined
rules to time series data. While this allows for a
functional interpretation of scenario patterns, the rule-
based nature of the system requires significant manual
effort to define appropriate patterns, which limits its
scalability and adaptability to new scenarios, and may
also lead to missing specifications of certain edge and
corner cases.
Later, Elspas et al. used fully Convolutional Neu-
ral Networks (CNNs) to extract scenarios from time
series data (Elspas et al., 2021). However, their ap-
proach relies on labelled datasets with ground truth
annotations, which presents challenges in terms of
complexity and scalability, as manually annotating
large and diverse datasets is labour intensive and
may not cover all relevant aspects of real-world be-
havioural driving scenarios.
Sohn et al. investigated natural language sce-
nario retrieval, assessing the ability of different LLMs
to capture scenario information (Sohn et al., 2024).
However, as this work focused on the description and
retrieval of perceptual data within the 6-Layer Model
(6LM) framework (Scholtes et al., 2021), behavioural
scenario retrieval was not a primary focus.
The methods reviewed address different aspects of
trajectory embedding and scenario retrieval, but tend
to either over-generalise or focus narrowly on specific
aspects of driving behaviour. Learning-based meth-
ods tend to oversimplify trajectory embeddings by re-
lying on MSE and overall scenario representations,
which may obscure critical geometric and relational
properties. Clustering methods focus primarily on
temporal alignment and pre-defined features, but fail
to capture the full complexity of multi-agent interac-
tions. Rule-based methods, while useful for detecting
specific manoeuvres, require significant manual effort
and may struggle to adapt to new or complex scenar-
ios. All presented methods lack searchability and in-
terpretability of the derived clusters, leaving out the
mapping of user queries or behavioural scenario de-
scriptions to the trajectory space.
3 METHOD
To overcome these limitations, a novel method is
proposed that aims to enhance the retrieval of driv-
ing scenarios by combining geometry-aware trajec-
tory embeddings with word embeddings from LLMs,
enabling behavioural-level searchability through nat-
ural language queries (Fig. 1). This approach is in-
tended to support V&V processes for ADS, ensuring
that behavioural patterns in unlabelled driving data
can be effectively analysed and retrieved through nat-
ural language or behavioural scenario descriptions.
3.1 Fine-Grained Trajectory
Embedding Using Geometric Loss
To generate a trajectory embedding that models the
fine-grained geometric aspects of behavioural scenar-
ios, a Variational Recurrent Autoencoder (VRAE) is
employed using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
cells with self-attention to capture sequential pat-
terns. The model is trained using the Hausdorff Dis-
tance (HD) as the loss function. Unlike the MSE,
which tends to generalise trajectory features, the HD
is able to preserve spatial properties by quantifying
the largest deviation between trajectory points. This
property is necessary to preserve the geometric at-
tributes required for fine-grained analysis of driving
behaviour, particularly in scenarios involving multi-
ple agents and dynamic interactions such as cut-ins,
overtaking manoeuvres or multiple lane changes.
The HD (d
H
) between two trajectories A =
{a
1
, a
2
, . . . , a
m
} and B = {b
1
, b
2
, . . . , b
n
} in a metric
space with the Manhattan (L1) distance d
M
(a, b) =
∑
d
i=1
|a
i
− b
i
| is defined as follows:
d
H
(A, B) = max
sup
a∈A
inf
b∈B
d
M
(a, b), sup
b∈B
inf
a∈A
d
M
(a, b)
This metric ensures that each point in A is close to
at least one point in B and vice versa, capturing tra-
jectory similarity based on maximum deviation. Us-
ing HD as a loss function within the VRAE allows for
a more accurate representation of trajectory structure,
which is required for behavioural scenario analysis.
VEHITS 2025 - 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
68

3.2 Clustering of Trajectory
Embeddings with HDBSCAN
Following embedding generation, trajectories are
clustered using Hierarchical Density-Based Spatial
Clustering of Applications with Noise (HDBSCAN)
(McInnes et al., 2017). It is well suited to dealing
with the distinctive features of unlabelled, naturalis-
tic trajectory data by identifying clusters of different
densities based on spatial and behavioural character-
istics from coarse to fine-grained properties. HDB-
SCAN helps to isolate clusters that reflect different
driving behaviours, allowing further analysis at a sce-
nario level. By explicitly accounting for noise in the
data, it also helps to identify unique patterns that rep-
resent outliers. This clustering step thus organises
the trajectory embeddings according to fine-grained
attributes, preserving the distinctions between the dif-
ferent driving behaviours observed.
3.3 Semantic Interpretation of
Scenarios Using LLMs
To make the generated embedding interpretable, each
trajectory cluster and individual scenarios within the
clusters are described using an LLM, in this approach
GPT-4o (OpenAI, 2024). This is achieved using a
prompt pipeline consisting of three main steps for
each sample in the dataset:
1. A single scenario is given as context with the task
to analyse overall properties such as traffic density
and each of the object trajectories in relation to
the infrastructure (road properties such as lanes)
as well as the interaction with other objects.
2. The corresponding cluster in the embedding space
is used to sample the five nearest neighbours of the
sample within its cluster to describe the intrinsic
attributes of the cluster by comparing the samples
to each other.
3. Each of the other clusters is considered by sam-
pling randomly five samples and describing them
as well as comparing them with the previously de-
scribed cluster.
Each description is referenced to the correspond-
ing data samples and associated clusters. This en-
sures interpretability at sample level, within clusters
and between clusters of behavioural scenarios, and
allows user queries to search from coarse to fine-
grained behavioural similarities and differences. This
step facilitates the translation of raw geometric data
into semantically meaningful interpretable represen-
tations, bridging the gap between abstract trajectory
data and functional driving behaviour. The integration
of LLMs improves searchability by linking trajectory
embeddings to a descriptive language.
3.4 Natural Language Scenario
Retrieval via GraphRAG Pipeline
The generated descriptions, combined with the corre-
sponding references in the dataset and the clustered
embedding, are indexed using a GraphRAG pipeline.
The idea of RAG is to provide a queryable external
context source for LLMs to answer targeted questions
about specific data not previously used to train the
LLM. GraphRAG implements this idea by modelling
the data into a knowledge graph, addressing relation-
ships between entities as well as general concepts by
clustering the knowledge graph (Edge et al., 2024).
By embedding the knowledge graph in the same em-
bedding as the LLM queries, natural language search
can be performed by referencing the previously gener-
ated descriptions as well as their associated data sam-
ples and trajectory embedding clusters.
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Dataset
In this paper, a naturalistic vehicle trajectory dataset is
used to support trajectory embedding generation and
retrieval tasks.
The HighD dataset consists of more than 110,500
vehicles covering approximately 44,500 kilometres of
driving over 147 hours. The data, focusing on high-
way scenarios, was collected with a drone at six dif-
ferent German highway locations, overcoming com-
mon limitations of traditional traffic data collection
such as occlusion. The trajectory of each vehicle, in-
cluding manoeuvres and dimensions, was extracted
with a positioning error of less than ten centimetres
(Krajewski et al., 2018). For analysis, within the
frame of this research, the dataset is segmented into
15-second sequences to allow for the analysis of ve-
hicle interactions and manoeuvres at a higher granu-
larity.
4.2 Embedding Generation and Cluster
Analysis of Driving Scenarios
To analyse the embedding, both MSE and HD are
used as loss functions to generate the trajectory em-
bedding with VRAE. The differences identified are
compared by analysing the HDBSCAN clusters on
Large Language Model-Informed Geometric Trajectory Embedding for Driving Scenario Retrieval
69

a t-distributed Stochastic Neighbour Embedding (t-
SNE) projection and mapping general properties such
as number of lanes, lane change, speed, acceleration,
and traffic density to the embedding.
These metrics not only provide insight into the
specific behavioural characteristics of each cluster,
but also help validate the plausibility of behavioural
scenario representations, as clusters are expected to
reflect infrastructure characteristics, ego-object dy-
namics, as well as manoeuvres and interaction pat-
terns.
Both the description and the retrieval performance
of the proposed approach are validated using a set of
33 different user queries related to behavioural sce-
nario analysis (Table 1). Specifically, these queries
are categorised as follows:
• General Scene: Retrieval of scenarios based on
general properties such as traffic density or base
infrastructure such as amount of lanes.
• Infrastructure Manoeuvres: Focused retrieval
based on manoeuvre interactions with infrastruc-
ture elements such as lane markings (e.g. a lane
change).
• Ego Manoeuvres: Retrieval based on trajectory
characteristics and behaviour of the trajectory it-
self, which can be broken down into motion prim-
itives such as speed and acceleration.
• Object Interaction: Retrieval focused on inter-
actions between road users, capturing multi-agent
dynamics.
• Combinatorial Scenarios: Retrieval based on
combinations of general, infrastructure, ego ma-
noeuvres and interactions, such as simultaneous
high density traffic and lane change manoeuvres.
Scenario retrieval performance is assessed using
the Precision@k (prec@k) metric, measured across
different retrieval categories (General, Infrastructure,
Ego, Interaction and Combinatorics). Specifically, the
prec@k metric is used to determine the relevance of
the top five retrieved samples for each query. The av-
erage prec@k value for all queries belonging to the
same category is used for the analysis.
5 RESULTS
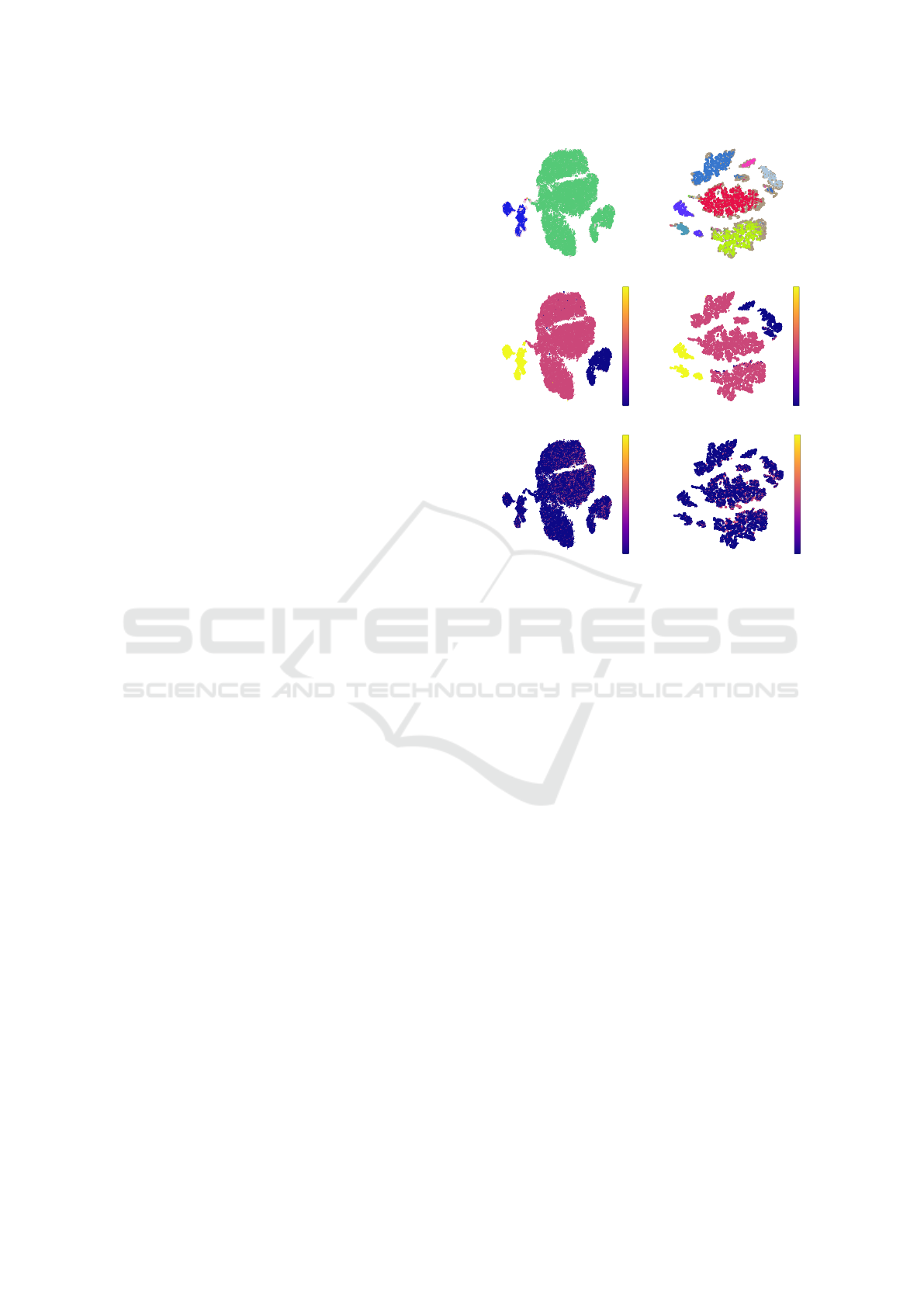
5.1 Analysis of Geometric Embedding
In order to evaluate the properties and feasibility of
geometric embedding using HD, a comparison with
an MSE-based embedding is performed.
(a)
(b)
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
(c)
2
3
4
(d)
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
(e)
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
(f)
Figure 2: Trajectory embeddings using MSE (a) and HD
(HD) (b), along with their corresponding embeddings of
scenario features such as the number of lanes (c, d) and lane
changes (e, f).
5.1.1 General Structure of the Embedding
Space and Resulting HDBSCAN Clusters
The MSE and HD embeddings, along with their re-
spective clustering results, show differences in cluster
granularity, as seen in the clustering results produced
by the HDBSCAN algorithm (Fig. 2a, 2b). The iden-
tified clusters show differences in coarseness between
the embedding methods, with a notable difference in
the number of clusters observed in each embedding
type, which is 8 for MSE and 49 for HD.
5.1.2 Mapping of Behavioural Scenario Features
to the Embedding Space
To illustrate the separability of features within clus-
ters, two features are mapped: one general (number
of lanes) and one trajectory-specific (lane change). In
both embeddings, clusters representing different lane
numbers are visually distinct (Fig. 2c, 2d). The map-
ping of lane changes shows different distributions,
with the MSE embedding showing a randomly dis-
tributed pattern of samples, whereas the HD embed-
ding shows these changes along the edges of visu-
ally separated clusters, as seen in the grey HDBSCAN
cluster (Fig. 2e, 2f).
VEHITS 2025 - 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
70

5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
(a)
10
20
30
40
50
(b)
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
(c)
−10
−5
0
5
10
15
(d)
Figure 3: HD embeddings of driving scenario features, including mean velocity in [m/s] (a), number of road users (b), lateral
velocity change in [m/s²] (c) and longitudinal velocity change in [m/s²] (d).
Given these observations, while the MSE embed-
dings can be used to identify general attributes, the
ability to identify fine-grained details of the trajecto-
ries is significantly compromised. Consequently, only
the HD embedding is considered for the subsequent
analysis.
5.2 Driving Scenario Features
To analyse the interpretability and searchability of
the HD embedding, additional previously extracted
features such as mean velocity, number of objects,
lateral velocity change and acceleration are mapped
onto the embedding visualisation. These features are
also cross-referenced with the descriptions generated
by the LLM for the corresponding clusters.
The mean velocity evaluation shows a clear gradi-
ent across the clusters, with low speed scenarios con-
centrated on the left and high speed conditions on the
right (Fig. 3a).
The number of road users within a scenario fur-
ther supports this division, as a higher density of road
users appears on the left side of the visualisation (Fig.
3b). In particular, a dense cluster at the leftmost tip
of the embedding, characterised by a high number of
road users and low speed, suggests traffic congestion.
This observation is consistent with the LLM descrip-
tions, which highlight congestion and disrupted flow
in this area. Conversely, the right side of the visual-
isation, characterised by fewer road users, correlates
with high speed scenarios and continuous traffic flow.
Changes in lateral velocity are more pronounced
at the periphery of the clusters (Fig. 3c), consis-
tent with the HD embedding’s identification of lane
changes, particularly at the edges (Fig. 2f). The LLM
descriptions support this by noting lane changes and
multi-lane adjustments within the edges of the respec-
tive main clusters.
The longitudinal speed changes show the dynam-
ics of acceleration and deceleration across the sce-
narios (Fig. 3d). Acceleration values are concen-
trated on the left side of the embedding, where lower
General Scene
Infrastructure Manoeuvre
Ego Manoeuvre
Object Interaction
Combination
1 1 1 1
0.9
1
0.94
0.8
0.67 0.6
0.6
0.72 0.73
0.6
0.47
L1
L2
L3
Figure 4: Retrieval performance of the LLM for behavioural
queries and their combinatorics with three levels of detail
(average prec@5 over several queries).
speeds dominate, allowing greater acceleration poten-
tial. Conversely, deceleration values are concentrated
in the right-hand clusters, corresponding to the high-
speed conditions. This inversion, where lower speeds
allow greater acceleration and higher speeds involve
greater deceleration, is consistent with typical driving
behaviour, as confirmed by the LLM scenario descrip-
tions, which capture this contrasting pattern between
the low-speed, acceleration-rich areas and the high-
speed, deceleration-dominant clusters.
5.3 Retrieval Analysis
For retrieval analysis, the LLM is queried at three lev-
els of detail: L1, L2 and L3. Example queries are
listed in Table 1. The query results are shown in Fig-
ure 4, where darker tiles indicate better model per-
formance, with 0% being the lowest score and 100%
being the best possible score. As the prec@k is calcu-
lated based on the top five retrieved samples, values
up to 100% are possible for the average prec@k value
of several queries.
The performance of the model varies with the
complexity of the queries. At the lowest level of de-
tail (L1), simple queries, such as keeping the speed of
the ego trajectory constant, give an average prec@k of
98%. At the medium complexity level (L2), queries
such as ” pass-by from left” result in an average
Large Language Model-Informed Geometric Trajectory Embedding for Driving Scenario Retrieval
71
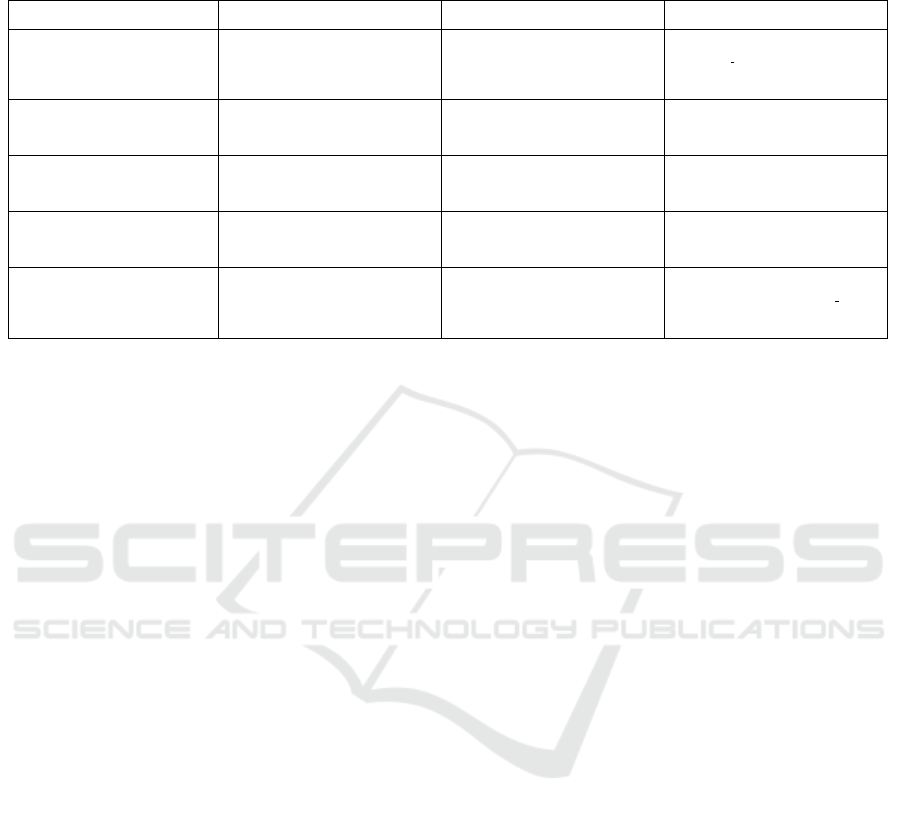
Table 1: Overview of query types for trajectory retrieval: Categorisation of General Scene, Infrastructure Manoeuvre, Ego
Manoeuvre, Object Interaction and Combination queries by level of complexity (L1, L2, L3). Text in italic denotes place-
holders for specific values (e.g., direction = left, speed value = 20 km/h)
Description Objective L1 Queries L2 Queries L3 Queries
General Scene
Retrieve trajectories of vehicles on a two-
lane highway; three-lane highway sce-
nario
Retrieve trajectories in moderate traffic
density; congested traffic conditions
Retrieve trajectories with high traffic den-
sity in lane number; heavy traffic in mid-
dle and left lanes with free traffic flow in
right lane
Infrastructure Manoeuvre
Retrieve trajectories of vehicles maintain-
ing lane number
Retrieve trajectories involving lane
changes at speeds above speed value;
performing aggressive lane changes
Retrieve trajectories showing lane change
to the direction; multi-lane changes of
different road users at the same time
Ego Manoeuvre
Retrieve trajectories of vehicles travelling
at a constant speed of speed value
Retrieve trajectories with acceleration;
deceleration; lateral movement without
lane change
Retrieve stop-and-go trajectories; acceler-
ation up to speed value; braking to below
speed value
Object Interaction
Retrieve trajectories following an object
at speed value; approaching an object at
speed value
Retrieve trajectories with pass-by ma-
noeuvre from the direction; cut-in at
speeds above speed value
Retrieve trajectories with evasive ma-
noeuvre; overtaking; merging into high-
way traffic in high density
Combination
Retrieve trajectories following a lane on a
two-lane highway with high acceleration
Retrieve trajectories showing lane change
after pass-by in moderate traffic
Retrieve trajectories with evasive ma-
noeuvre to the right to lane lane number
at high speeds; multi-lane changes of one
road user in heavy traffic
prec@k of 80.2%, indicating the ability to cover fine
granularities in the description of behavioural sce-
narios. At the highest level of complexity (L3),
queries such as ”evasive manoeuvre to the right at
high speed” are challenging and result in an average
prec@k of 62.4%.
Overall, the Infrastructure Manoeuvre category
achieves the highest performance across all levels,
with an average prec@k of 88.7%. Conversely, the
Combination category shows the lowest performance,
with an average prec@k of 65.7%.
An extract of the detailed output from the LLM in
response to a natural language query is shown in Table
2, which includes the exact query, the corresponding
retrieved trajectory, and a condensed response from
the LLM, shortened for total length.
Qualitative analysis of these responses reveals the
model’s deep overall understanding of the objects in-
volved and their relationships by querying the knowl-
edge graph. The LLM provides detailed references
within the knowledge graph, specifying information
such as concrete object IDs and precise speed and ac-
celeration values relevant to the queries. In partic-
ular, the model demonstrates high accuracy by pro-
viding the vehicle ID and specific time frames for
each queried manoeuvre. In addition, the LLM out-
put includes direct indices to data sources relevant to
the query context, supporting traceability across data
layers. Responses to complex queries remain clear
and comprehensive, providing descriptions that cap-
ture both the sample retrieved and its contextual pa-
rameters.
6 EVALUATION
The embedding analysis results indicate that the HD
embedding is highly effective for trajectory data.
Compared to the MSE embedding, the HD embed-
ding shows better performance in modelling and clus-
tering trajectories, allowing for fine-grained differen-
tiation of attributes such as lane change behaviour and
specific ego manoeuvres. In contrast, MSE embed-
ding primarily captures broader scenario characteris-
tics and lacks the resolution to distinguish between
detailed manoeuvres. Beyond the more distinct clus-
ters, the applicability of the HD embedding is re-
inforced by consistent performance across different
visualisations, such as the clear correlation between
high-speed scenarios and low object counts, and vice
versa. This geometric embedding approach facili-
tates the targeted search for behavioural scenarios and
supports nuanced trajectory analysis. The generated
LLM descriptions include the previously extracted
features in their descriptions at the same locations in
the same clusters as visualised in the embedding. This
further demonstrates the feasibility of the three-stage
cluster description by prompting an LLM for the pur-
poses of interpretability and searchability.
Evaluating the retrieval performance, with an av-
erage prec@k of 80.2%, the presented approach
shows that even higher levels of detail of the general
scene, infrastructure, ego manoeuvres as well as ob-
ject interactions can be described and retrieved. On
the other hand, the high degree of combinatorics in
the queries can be a challenge, with performance de-
grading towards higher levels of detail, affecting the
overall performance.
VEHITS 2025 - 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
72

Table 2: Detailed overview of trajectory retrieval queries: Examples of query types, corresponding top retrieved trajectories
and shortened responses from the LLM, highlighting different driving manoeuvres and traffic conditions in real-world highway
scenarios.
Query Top Retrieved Trajectory Shortened Answer of LLM
Retrieve trajectories in
dense traffic on the right
lane with low speed.
(General Scene, L3)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
xVelocity
In several highway scenarios, Lane 0, which is the rightmost lane, ex-
hibits dense traffic with vehicles maintaining low speeds. Vehicles
in Lane 0 generally show consistent following behavior, maintaining
steady speeds and positions without significant lane changes or aggres-
sive maneuvers. For instance, Vehicle ID 300 travels at below 9.3 m/s,
maintaining a consistent lane-following behavior without significant
speed variation [Data: Entities (981)]. Similarly, Vehicle 369 travels
slower at around 15.3 m/s, slightly decelerating over time and main-
taining its position in Lane 0, indicating moderate traffic density [Data:
Entities (963)]. Additionally, Vehicle 678 follows a steady path with
incremental velocities, further indicating a following behavior in Lane
0 [Data: Entities (193)]. These observations highlight the dense and
low-speed traffic conditions in Lane 0, contributing to the overall traffic
flow on the highway [Data: Reports (226); Entities (1480, 198, 347);
Relationships (697, 743, 741, 1839, 2039)].
Retrieve trajectories of a
lane change to the left.
(Infrastructure Maneuver, L2)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
xVelocity
Several vehicles in the dataset exhibit lane changes to the left, indicat-
ing maneuvers from a higher-numbered lane to a lower-numbered lane.
Notable examples include: Vehicle ID 273: Changes from Lane 1 to
Lane 2 at frame 2990, showing a leftward shift in trajectory [Data: Re-
ports (147); Entities (1956); Relationships (663, 1583, 3782)]. Vehicle
ID 2286: Moves from Lane 2 to Lane 1 at frame 27404, indicating a
smooth, controlled transition [Data: Reports (147); Entities (304, 309);
Relationships (2672, 128)]. Vehicle ID 2295: Lane change from Lane
1 to Lane 2 at frame 27488, demonstrating a smooth high-speed ma-
neuver [Data: Reports (147); Entities (307, 310); Relationships (2674,
129)]. Vehicle ID 1383: Leftward shift from Lane 1 to Lane 2 around
frame 16407[Data: Entities (630); Relationships (240)]. Vehicle ID
1176: Changes from Lane 1 to Lane 2 at frame 14070, possibly indicat-
ing an overtaking maneuver or adaptive lane positioning [Data: Entities
(90); Relationships (1099)].
Retrieve trajectories of a
multi lane change to the
left.
(Infrastructure Maneuver, L3)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
xVelocity
Vehicle 210 initiates in Lane 2 and shifts to Lane 0 around frame 2321,
with slight speed changes before and after the lane change, indicating
a maneuver to overtake or evade slower traffic [Data: Entities (4); Re-
lationships (15, 17, 663, 1583, 3782)]. Vehicle 2186 starts in lane 0
with a velocity around
˜
31.9 m/s initially and changes to lane 2 around
frame 2165, demonstrating a lane change maneuver without any signif-
icant speed variation [Data: Entities (1414); Relationships (478, 2763,
3955, 3962, 3969)]. Vehicle 273 changes lanes from Lane 2 to Lane 0
around frame 2990, indicated by a laneId change and a minor deviation
in y-velocity [Data: Entities (1956); Relationships (663, 1583, 3782)].
Vehicle 1994 starts in lane 0 and transitions to lane 1 with a higher xVe-
locity around 33.58 and noticeable x-Velocity, indicating a lane change
from 0 to 2, possibly for evasive maneuver [Data: Entities (1946); Re-
lationships (4371, 2107, 2109)].
Retrieve trajectories of a
aggressive lane change
over multiple lanes to the
right.
(Infrastructure Maneuver, L3)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
xVelocity
In the provided data, Vehicle 214 exhibits aggressive lane-changing be-
havior over multiple lanes to the right. Vehicle 214 maintains a high
speed ranging from 35.65 to 37.17 m/s and shifts between Lanes 0,
1, and 2 over various frames, indicating multiple lane changes. These
maneuvers suggest attempts to overtake other vehicles or adjust to vary-
ing traffic densities, reflecting a responsive and adaptive driving pattern
[Data: Reports (261); Entities (6); Relationships (21, 20, 22, 24, 19,
+more)].
Retrieve trajectories of an
evasive maneuver to the
right with a speed over
70 km/h.
(Combination, L3)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
xVelocity
The data provided indicates the presence of evasive maneuvers to the
right by vehicles with speeds over 20 m/s. Within the highway scene,
several vehicles exhibit high-speed driving with specific instances of
abrupt lane changes or swerving actions that qualify as evasive maneu-
vers. For instance: Vehicle 214, and Vehicle 221 are noted for high-
speed driving and dynamic lane-changing behaviors, which include
evasive actions intended to avoid potential collisions. These maneu-
vers go beyond strategic overtaking or adaptive driving, as they involve
rapid adjustments in trajectory to evade other vehicles. Additionally,
the entity labeled ”EVADE” confirms instances of evading within the
dataset, specifically highlighting scenarios where evasive actions were
observed. This entity references particular relationships and data points
(Entities 32 and 867; Relationships 1810) that document recorded eva-
sive maneuvers to the right by vehicles traveling over 20 m/s.
At the lowest levels of detail (L1 and L2), the
LLM retrieves scenarios with high accuracy, and the
descriptions it generates closely match the queried
behaviours. This high accuracy indicates that the
LLM effectively understands simple and moderately
detailed scenarios, capturing key trajectory features
and behavioural cues with little difficulty.
However, performance drops for the most com-
plex queries (L3). This drop is most noticeable
for queries that capture combined manoeuvres over
Large Language Model-Informed Geometric Trajectory Embedding for Driving Scenario Retrieval
73

longer periods of time, such as stop-and-go scenarios
or long overtaking manoeuvres. One reason for this
performance drop could be the segmentation of the
data into 15 second sequences. As a result, these sce-
narios cannot be adequately queried as they are not
properly embedded within this short time window. In
these cases, the LLM reports that there are few or no
such instances in the dataset, again demonstrating a
good understanding but limiting its retrieval perfor-
mance score for these queries. Choosing variable time
windows to capture both short and long term manoeu-
vre development could help to capture these manoeu-
vres with the presented method. Additional perfor-
mance challenges are particularly notable within the
Combination category, which captures combinatorial
queries of multiple behavioural elements. In many
cases, the response contains specific subsets of the
combinatorics, but often struggles to capture all re-
lated aspects for highly combinatorial queries at L2
and L3.
Qualitative analysis of the model responses shows
a comprehensive understanding of the LLM in terms
of the data samples and the associated clusters in the
geometric embedding space. By providing both data
and knowledge graph references, coupled with a full
text answer and detailed reasoning about the retrieved
scenarios, interpretability is facilitated.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presents a comprehensive approach for re-
trieving behavioural scenarios on unlabelled trajecto-
ries from real driving data. The geometric embed-
ding based on HD is able to capture detailed scenario
attributes such as infrastructure, specific features of
object trajectories as well as their interactions. The
guided description of the trajectory space by GPT-4o
combined with the indexing by a GraphRAG pipeline
allows users to query and analyse the generated repre-
sentation with natural language and behavioural sce-
nario descriptions without prior annotation and addi-
tional information extraction. The open context na-
ture of the LLM, by providing an open vocabulary,
allows queries that do not necessarily need to be con-
sidered prior to data extraction.
Future research could focus on improving the pro-
posed approach in several ways. First, the introduc-
tion of different segment lengths can be considered
to accommodate different granularities in manoeuvre
combinations, which would address potential perfor-
mance issues, such as the observed challenges in stop-
and-go scenarios as longer length takeovers. Subse-
quently, the use of alternative models to VRAE, such
as Transformers, may also prove beneficial for ex-
tended context representation. This can be coupled
with the inclusion of additional scenario parameters
based on the 6LM for enhanced context representa-
tion and search. The database should be extended
beyond the highway scenarios in the highD dataset,
such as intersections, urban scenarios and other real-
world use cases. To evaluate the scenario retrieval
performance, ground truth datasets should be created
that allow for additional performance metrics such as
Recall@k. This can be combined with the evalua-
tion of different alternative prompting and RAG ap-
proaches to improve retrieval specifically for combi-
natorial queries. Besides the HD which introduces a
spatial distance, additional metrics should be evalu-
ated with respect to the resulting embedding space for
driving scenarios, specifically including temporal and
spatial distances. Finally, the method should be eval-
uated and improved on the basis of user studies with
the involvement of V&V engineers, investigating the
most important types of queries as well as drawing the
relation to the application related to the SOTIF stan-
dard.
REFERENCES
Edge, D., Trinh, H., Cheng, N., Bradley, J., Chao, A., Mody,
A., Truitt, S., and Larson, J. (2024). From local to
global: A graph rag approach to query-focused sum-
marization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.16130.
Elspas, P., Klose, Y., Isele, S. T., Bach, J., and Sax, E.
(2021). Time series segmentation for driving scenario
detection with fully convolutional networks. In VE-
HITS, pages 56–64.
Elspas, P., Langner, J., Aydinbas, M., Bach, J., and Sax,
E. (2020). Leveraging regular expressions for flexible
scenario detection in recorded driving data. In 2020
IEEE International Symposium on Systems Engineer-
ing (ISSE), pages 1–8. IEEE.
Hoseini, F., Rahrovani, S., and Chehreghani, M. H. (2021).
Vehicle motion trajectories clustering via embedding
transitive relations. In 2021 IEEE International In-
telligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC),
pages 1314–1321.
International Organization for Standardization (2022).
Road vehicles - safety of the inteded fuctionality. ISO
21448:2022(E). ICS: 43.040.10.
Krajewski, R., Bock, J., Kloeker, L., and Eckstein, L.
(2018). The highd dataset: A drone dataset of natural-
istic vehicle trajectories on german highways for val-
idation of highly automated driving systems. In 2018
21st International Conference on Intelligent Trans-
portation Systems (ITSC), pages 2118–2125.
McInnes, L., Healy, J., and Astels, S. (2017). hdbscan: Hi-
VEHITS 2025 - 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
74

erarchical density based clustering. Journal of open
source software, 2(11):205.
Montanari, F., German, R., and Djanatliev, A. (2020). Pat-
tern recognition for driving scenario detection in real
driving data. In 2020 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Sym-
posium (IV), pages 590–597. IEEE.
OpenAI, I. (2024). Hello gpt-4o. https://openai.com/index/
hello-gpt-4o/. Accessed: 2024-08-29.
Ries, L., Rigoll, P., Braun, T., Schulik, T., Daube, J., and
Sax, E. (2021). Trajectory-based clustering of real-
world urban driving sequences with multiple traffic
objects. In 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Trans-
portation Systems Conference (ITSC), pages 1251–
1258.
Scholtes, M., Westhofen, L., Turner, L. R., Lotto, K.,
Schuldes, M., Weber, H., Wagener, N., Neurohr, C.,
Bollmann, M. H., K
¨
ortke, F., et al. (2021). 6-layer
model for a structured description and categoriza-
tion of urban traffic and environment. IEEE Access,
9:59131–59147.
Sohn, T. S., Dillitzer, M., Ewecker, L., Br
¨
uhl, T., Schwa-
ger, R., Dalke, L., Elspas, P., Oechsle, F., and Sax, E.
(2024). Towards scenario retrieval of real driving data
with large vision-language models. In 10th Interna-
tional Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelli-
gent Transport Systems (VEHITS 2024), pages 496–
505.
Sonntag., M., Vater., L., Vuskov., R., and Eckstein., L.
(2024). Detecting edge cases from trajectory datasets
using deep learning based outlier detection. In Pro-
ceedings of the 10th International Conference on Ve-
hicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems -
VEHITS, pages 31–39. INSTICC, SciTePress.
Watanabe, H., Tobisch, L., Rost, J., Wallner, J., and Prokop,
G. (2019). Scenario mining for development of
predictive safety functions. In 2019 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Vehicular Electronics and Safety
(ICVES), pages 1–7. IEEE.
Wei, J., Wang, X., Schuurmans, D., Bosma, M., ichter,
b., Xia, F., Chi, E., Le, Q. V., and Zhou, D. (2022).
Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large
language models. In Koyejo, S., Mohamed, S., Agar-
wal, A., Belgrave, D., Cho, K., and Oh, A., editors,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
volume 35, pages 24824–24837. Curran Associates,
Inc.
Large Language Model-Informed Geometric Trajectory Embedding for Driving Scenario Retrieval
75
