
Designing a Meta-Model for the Eclipse Qrisp eDSL for High-Level
Quantum Programming
Sebastian Bock
1 a
, Raphael Seidel
1 b
, Matic Petri
ˇ
c
1 c
, Nikolay Tcholtchev
2,1 d
,
Andreas Hoffmann
1
and Niklas Porges
1
1
Fraunhofer Institute for Open Communication Systems (FOKUS), Berlin, Germany
2
RheinMain University of Applied Sciences, Wiesbaden, Germany
fi
Keywords:
Quantum Computing, Meta-Model, High-Level Quantum Programming Language, Quantum Programming
Language Modelling.
Abstract:
Eclipse Qrisp is a high-level programming language designed to simplify quantum programming and make it
accessible to a wider range of developers and end users. Initially developed at Fraunhofer FOKUS and now
part of the Eclipse Foundation, Eclipse Qrisp abstracts complex quantum operations into user-friendly con-
structs, enhancing code readability structure. Currently, Eclipse Qrisp is realized as an extension of the Python
programming language, in the form of an embedded Domain Specific Language (eDSL), allowing to develop
hybrid quantum algorithms, while at the same time utilizing the potential of the overall Python ecosystem in
terms of libraries and available developer resources. We firmly believe that the eDSL approach to high-level
quantum programming will prevail over the idea of defining specific languages - with their own grammar and
ecosystem - due to its ease of integration within available ICT products and services. However, in order to
reach higher levels of scalability and market penetration, the Eclipse Qrisp eDSL should be available for vari-
ous platforms and programming languages beyond Python, e.g. C/C++, Java or Rust. In order to provide the
means for implementing Eclipse Qrisp in other programming languages, this paper specifies a meta-model,
thereby outlining the pursued design philosophy, architecture, and key features, including compatibility with
existing frameworks. The purpose of such a Qrisp meta-model is two-fold: On one hand it formalizes and
standardizes the Eclipse Qrisp programming model. On the other hand, such a meta-model can be used to
formally extend other programming languages and platforms by the capabilities and concepts specified and
implemented within Eclipse Qrisp.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid progress in quantum computing more
complicated algorithms are required and being devel-
oped. With increasing complexity it is important to
have access to an easy and comprehensible program-
ming language for quantum computing. A high-level
programming language helps with the readability and
structure of the code. This would make getting started
easier for developers especially for those without a
physics background.
In the past years, the Eclipse Qrisp program-
ming framework/language (Seidel et al., 2024) (Sei-
del et al., 2023) (Seidel et al., 2022b) (Seidel et al.,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8362-8458
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3560-9556
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-4482-5270
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6821-4417
2022a) for quantum computing was developed in vari-
ous national (Bock et al., 2022) and European projects
(Chochliouros et al., 2023) (Cid et al., 2024). In the
course of the development activities, Qrisp has been
contributed and integrated into the Open Source de-
velopment processes of the Eclipse Foundation (Ecl,
2024a) and opened up for a larger community of
developers (Ecl, 2024b) under the EPL 2.0 license
(Eclipse Foundation, 2017). The full name of the
framework is thus Eclipse Qrisp. For simplicity rea-
sons we will mostly use Qrisp throughout the docu-
ment and by that refer to Eclipse Qrisp.
Qrisp is intrinsically designed as an extension of
the Python programming language (Python Software
Foundation, 2024). By utilizing certain properties of
Python, Qrisp introduces new environments and arti-
facts that enable the high-level definition of quantum
programming flows thereby providing a new high-
Bock, S., Seidel, R., Petri
ˇ
c, M., Tcholtchev, N., Hoffmann, A. and Porges, N.
Designing a Meta-Model for the Eclipse Qrisp eDSL for High-Level Quantum Programming.
DOI: 10.5220/0013121000003896
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering (MODELSWARD 2025), pages 27-39
ISBN: 978-989-758-729-0; ISSN: 2184-4348
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
27

level programming paradigm for quantum comput-
ers. In this context, it is important to remark that
Qrisp removes the low-level assembler-like program-
ming of quantum processing units (QPU) by introduc-
ing layers of abstractions that enable coding through
functions, modules, environments and special arti-
facts rather than based on primitive qubit handling
and gate-based programming.
The above considerations clearly position Qrisp
as an eDSL (embedded Domain Specific Language)
(Dinkelaker et al., 2010) within the Python program-
ming language and its ecosystem of libraries and plat-
forms. We firmly believe that this approach bears
more chances of success and industrial penetration
than the approach of defining and developing specific
languages such as Silq (Bichsel et al., 2020), Classiq
(Cla, 2024) or QCL (
¨
Omer, 2005) to mention a few.
These languages come with their own formal gram-
mar, their own lexer, tokenizer, parser and compiler
and face the challenge of building their own ecosys-
tem of modules, libraries and tools. Hence, in order
to reach industrial relevance and exploitation, we ar-
gue that is needed to build on existing platforms and
ecosystems, which are widely adopted in relevant in-
dustrial domains.
The above considerations imply that the Qrisp
concepts must be transferable to other programming
languages and platforms, such as C/C++, Java, PHP
or Rust, to mention a few. In order to achieve this,
there must be a clear and formal definition of the
Qrisp concepts and programming models, which can
be implemented and transferred to other program-
ming languages and platforms. A possible formaliza-
tion with excellent acceptance in industry is the con-
cept of a meta-model as introduced by MOF (Meta-
Object Facility) (Weisem
¨
oller and Sch
¨
urr, 2008).
Hence, in the current paper we aim at defining a meta-
model for the Qrisp eDSL for high-level program-
ming of quantum computers. We present the struc-
tures and artifacts of the meta-model based on the
UML-notation and give examples for their implemen-
tation and utilization in the Python based Qrisp ver-
sion. We argue that the presented meta-model lays
down a foundation for Qrisp based quantum high-
level programming in the scope of other languages,
such as Java, C/C++, PHP or Rust.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows: Sec-
tion II presents an overview of state-of-the-art re-
garding quantum programming. Section III gives a
brief introduction of the Qrisp eDSL for high-level
programming. In Section IV, we present the key
artifacts of the meta-model and give corresponding
code examples in Python. Section V summarizes the
sub-results to an overall Eclipse Qrisp meta-model.
Lastly, Section VI discusses the presented interrela-
tions and concludes the paper.
2 STATE OF THE ART
In this section, we look at the current state of the art
of existing quantum software frameworks, program-
ming languages and interfaces. For this purpose, we
focus on common solutions and frameworks, as this is
sufficient to get a good overview of the general state
of the art in this area.
Probably the most widely used software frame-
work for writing quantum programs is Qiskit, mainly
developed by IBM (Javadi-Abhari et al., 2024). It
provides support for IBM backends as well as for
some other service providers such as AQT (Qis,
2024). The programming style is strongly based on
the assembler-like circuit model mentioned above. To
overcome this problem, IBM is working on an exten-
sive library with modules for machine learning, simu-
lation of quantum systems or optimisation problems.
However, the underlying style of the quantum pro-
grams still resembles the circuit model. The same
applies to other common software frameworks such
as Cirq developed Google (Cirq Developers, 2024)
(Heim et al., 2020), Quipper (Green et al., 2013), Pen-
nylane from Xanadu (Bergholm et al., 2022) or TKET
by Quantinuum (Sivarajah et al., 2020). The latter in-
cludes a highly competitive compiler based on the ZX
calculus (Coecke and Duncan, 2007). In addition, the
Scaffold programming language (Abhari et al., 2012)
comes with some high-level structures like conditions
and loops, however still requiring to operate on qubit
and gate-level. Moreover, Scaffold is not embedded
in another platform and will suffer the difficulty of
integrating into existing products and platforms with
their respective ecosystems.
Another initiative worth mentioning is the higher-
level language Silq (Bichsel et al., 2020) introduced
by ETH Zurich. Silq includes some of the afore-
mentioned features of a high-level programming lan-
guage, but does not provide a compiler. Furthermore,
Silq does not offer a software stack that enables pro-
grams to be executed on physical backends after com-
pilation.
Furthermore, the Q# programming language of
Microsoft should be mentioned (Svore et al., 2018).
Q# is a domain specific language, which is aligned
to C# from Microsoft and is integrated in the cor-
responding tools and tool-chains like Visual Studio
Code. Q# provides a type system, which mostly fo-
cuses on classical data types, e.g., int, bool, string
and only three quantum related types: Qubit, Result,
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
28

Pauli. This indicates that Q#, like the other frame-
works mentioned above, also focuses more on qubit
and gate based operations. Q# is declared to be an
Open Source software distribution and, similarly to
Qrisp, comes with a powerful simulator that is easily
accessible to execute and test quantum programs. A
big difference to Qrisp, additional to the different typ-
ing approach, is that Q# is not intrinsically embedded
in a host languages, but needs additional setups, in or-
der to operate inside Python for the purpose of hybrid
quantum computing (Hyb, 2024). With the current
paper, we want to go a step beyond and enable a seam-
less integration of Qrisp concepts in various program-
ming languages and platforms. To summarize: There
is a lot of developments in the domain of quantum
programming languages and frameworks. However,
many of them either still require the manual low-level
handling of qubits and gates (Svore et al., 2018), (Ab-
hari et al., 2012), (Green et al., 2013), or are of a the-
oretical nature (Bichsel et al., 2020), (Voichick et al.,
2023), (Wright et al., 2024), as they provide no means
of compiling/connecting a program to actual quantum
hardware as of now. Currently, there are only pro-
prietary approaches for interfaces and intermediate
representations for connecting to real quantum hard-
ware/backends, i.e. there are no standardised solu-
tions available between the relevant components, e.g.
between compiler and backend. This harbours the
risk of vendor lock-in, and a program written in IBM
Qiskit, for example, is only optimal (after compila-
tion and transpilation) for a QC instance provided by
IBM. Initiatives such as the QIR Alliance (QIR, 2024)
and formats like OpenQASM (Cross et al., 2017a) are
making efforts in this direction, but do not yet offer
standardised interfaces and appear to be difficult to
extend in the context of a completely open business
ecosystem with various stakeholders (e.g. SMEs, in-
dustry and science). We therefore see the need to use
clearly defined interfaces, which should be discussed
within the framework of relevant standardisation bod-
ies such as DIN or CEN/CENELEC.
3 ECLIPSE QRISP: BRIEF
INTRODUCTION
Qrisp was designed with a few key concepts and goals
in mind as depicted in Figure 1. Its goal is to make
developing code for quantum computers easier and
more accessible for a broad spectrum of developers.
After formulating a problem, Qrisp can be used to cre-
ate a circuit to solve this task on a quantum computer
or a simulation on a classical one.
Figure 1: Eclipse Qrisp (Qri, 2024) and its main features
positioning it as a framework/eDSL for high-level quantum
programming.
3.1 High-Level Programming
Quantum computing is an active field of research
and requires more and more complicated algorithms.
Qrisp is designed to be a high-level programming lan-
guage, in order to make the development of increas-
ingly complex algorithms easier. Its algorithms con-
stitute of variables and functions instead of qubits and
circuits, which helps with the structure of the code
and reduce the technical debt. Qrisp implemented
so called QuantumVariables, which are the quantum
counterpart to classical variables. Therefore, the de-
veloper does not need to work with single qubits and
can use high-level functionality, such as a smoothly
integrated system of floating-point arithmetic, arrays
and strings. Qrisp handles the qubit resource manage-
ment and uncomputation (i.e. garbage collection) of
quantum variables in the background. A simple syn-
tax is achieved by combining the concept of Quan-
tum Variables and the simplicity and flexibility that
comes with the Python language. The goal in this pa-
per is to bring the Qrisp programming concepts on a
more abstract level and to enable the implementation
of Qrisp as an embedded DSL in other host languages
(e.g. Java or C/C++).
3.2 Abstraction Levels
Qrisp was developed with different abstraction lev-
els in mind. The lowest level is the quantum cir-
cuit level, where use can create their quantum cir-
cuits by directly assigning gate operations to qubits.
This makes it possible to program close to hardware
specifications. On the other hand, development with
QuantumVariables and the arithmetic and logic that
Designing a Meta-Model for the Eclipse Qrisp eDSL for High-Level Quantum Programming
29

comes with them, enables to focus more on the al-
gorithm itself instead of taking care of small details,
e.g., qubit connectivity. Lastly, with the use of a sig-
nificant number of algorithms implemented in Qrisp
(e.g. Grover’s Algorithm, QFT, Shor, QAOA etc.) it
is possible to program on an even higher abstraction
level.
3.3 Compatibility
Qrisp comes with a simulator, that enables direct ex-
ecution and testing of the code. The resulting com-
piled circuits can be run on integrated backends as
well. Furthermore, the compiled circuit objects can be
imported and exported to other common libraries and
formats such as OpenQASM (Cross et al., 2017b).
The compilation of the circuits can be adapted to ac-
count for different hardware architectures by varying
the native gate set the compiler compiles to.
3.4 Visualization
Qrisp has an inbuilt functionality for visualizing
quantum circuits and the state of the simulation,
which is run for a compiled circuit. The circuit vi-
sualization is based on ASCII characters. During the
simulation, the probability distribution can be plotted,
in addition to the possibility to view and print the cur-
rent state vector within the simulation.
3.5 Simulator
The circuits generated can be run on the efficient
Qrisp internal simulator that makes use of sparse ma-
trices. These are used to store and process quantum
states. This makes it possible to run some circuits
that involve more than 100 qubits. Before executing
the simulation, the circuit is further optimized to re-
duce the complexity.
3.6 Modularity and Extensibility
Qrisp users/developers have access to the vast ecosys-
tem of Python libraries. These can assist in the devel-
opment of complicated algorithms. Automated qubit
allocation and handling allows to independently de-
velop and reuse algorithmic modules.
4 DESIGNING THE ECLIPSE
QRISP META-MODEL
In this section, we will guide the reader through the
elements of the high-level Qrisp eDSL, thereby de-
scribing the underlying meta-model and giving code
examples where appropriate.
4.1 Basic Infrastructure
We begin by outlining the basic infrastructure for han-
dling and describing the processes on the QPU. This
infrastructure provides the means to enable the high-
level constructs and abstractions (e.g. QuantumVari-
ables) described in the following sections.
4.1.1 Meta-Model
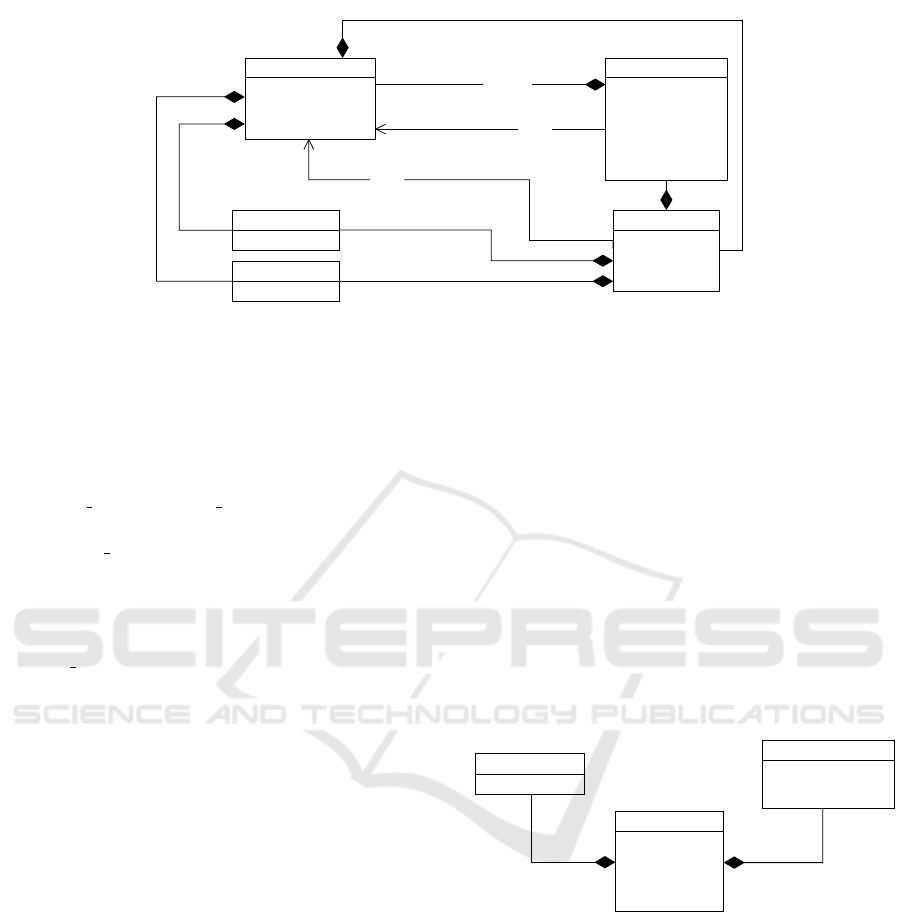
The meta-model for the basic infrastructure is pre-
sented in Figure 2. Thereby, it is possible to observe
a number of classes that interact with each other,
in order to enable the structured representation of a
quantum program/circuit:
Qubit. This class is used to describe qubits.
Qubits are distinguished by an identifier string.
Clbit. The Clbit classe describes classical bits
and can be distinguished by the identifier string.
Operation. This class represents an operation
that can be executed either on a quantum computer or
on a classical computer. An operation can be either
a single gate, such as the X-Gate, a classical logic
gate or a set of gates specified in the definition
field of the class. The operation class can also be
used to describe measurements. It is given a name,
which is used to identify the operation. The class
keeps track of the parameters that further specify the
operation. The number of qubits that are required
for the operation is stored in the num qubits field
and the number of classical bits in num clbits. This
class does not specify which Clbit or Qubit it acts
on. This is done in the Instruction class. The
unitary matrix which represents the operation can be
obtained with the get unitary method. An inverted
instance can be created with the inverse method and
a controlled version with the control function.
Instruction. The Instruction class combines an
operation op with a list of qubits qubits and another
list of classical bits clbits, which it operates on.
This class acts as the link between qubits, classical
bits for measurements and the operations. Instruc-
tions can be inverted using the inverse method
and be merged with another instance to form a new
instruction with the merge function.
QuantumCircuit. This class describes a quantum
circuit. The data attribute stores all the instructions,
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
30
QuantumCircuit
data: list<Instruction>
qubits: list<Qubit>
clbits: list<Clbit>
Operation
name: string
num_qubits: int
num_clbits: int
params: list<float>
definition: QuantumCircuit
Instruction
op: Operation
qubits: list<Qubit>
clbits: list<ClBit>
Qubit
identifier: string
Clbit
identifier: string
toOperation()
append()
append()
Figure 2: The Meta-Model for the Eclipse Qrisp Basic Infrastructure for Quantum Processing.
which the circuit consists of. It also keeps track of all
qubits and classical bits in the qubits and clbits
attributes. The circuit can be extended by operations
and instructions via the append method or by another
QuantumCircuit object with the extend function.
A QuantumCircuit can be turned into an operation
via the to gate or the to op function. The unitary
matrix which represents the circuit can be obtained
with the get unitary function. An inverted instance
can be generated using the inverse method. A
QuantumCircuit object is used as the definition for
operations. The class implements several methods
to evaluate the size and depth of the Circuit such
as cnot count and depth. The run method runs
the quantum circuit on a given backend. Quantum
circuits can be imported and exported to and from
other APIs and formats, such as Qiskit, OpenQASM
and Pennylane.
4.1.2 Example Code
The following listing shows a short piece of Qrisp
code that allows to create a quantum circuit based on
low-level assembler-like repetitive coding approach.
Thereby, a quantum circuit object is created at the
beginning, followed by the appending of different
gates with corresponding parameters to the quantum
circuit. Even though such type of programming is
not the general idea behind Qrisp it is important to
support it, such that the higher abstraction layers can
be compiled to the circuit level, which is described
in the coming sections. Additionally, in some
special cases, e.g., when specific new gates shall be
implemented or other hardware constraints should be
considered, it is also important to be able to write
programs on a circuit level.
from qrisp import QuantumCircuit, XGate,
CXGate, PGate
qc = QuantumCircuit(2)
qc.append(XGate(), 0)
qc.append(CXGate(), [0,1])
qc.append(PGate(0.5), 1)
synthed_op = qc.to_op()
qc.append(synthed_op, qc.qubits)
4.2 Quantum Variables
After having shed light on the basic infrastructure for
quantum circuit building, the next step is to move to
a higher abstraction level within the Qrisp program-
ming model. The basic ingredient within the higher-
level programming of Qrisp is the QuantumVariable,
which is presented in the following subsections.
QuantumSession
qv: list<QuantumVariable>
env_stack:
list<QuantumEnvironment>
Qubit
identifier: string
QuantumVariable
name: string
size: int
reg: list<Qubit>
qs: QuantumSession
Figure 3: The Eclipse Qrisp Meta-Model for
QuantumVariables - the key structure for qubit Manage-
ment.
4.2.1 QuantumVariable Meta-Model
Figure 3 depicts the meta-model around the Qrisp
QuantumVariable, which is the basic abstraction
for managing qubits. This part of the overall Qrisp
meta-model consists of the following classes:
Qubit. Qubit is the basic class for managing
qubits, within the Qrisp meta-model and constitutes
a key part of the basic infrastructure presented
above. Instances of this class are an integral part of a
QuantumVariable as depicted in Figure 3.
Designing a Meta-Model for the Eclipse Qrisp eDSL for High-Level Quantum Programming
31

QuantumVariable. This is the QuantumVariable
class and the quantum equivalent of a classical
variable. When initializing a QuantumVariable the
number of Qubits it can use has to be specified but
the specific management of the qubits, e.g., which
qubit gets assigned to which QuantumVariable or
QuantumSession respectively is done automatically
and hidden from the user. QuantumVariables are
decoded to and encoded from human readable repre-
sentations with the encoder and decoder method.
After its creation the size of the QuantumVariable
can be modified with the extend and the reduce
method. The outcome of a measurement on a variable
is returned by the get measurement method and the
most likely measurement outcome by most likely.
The measurement outcome can be visualized with the
plot histogram function.
QuantumSession. The class QuantumSession
is the wrapper that manages multiple quantum vari-
ables in one session while steering the execution and
the exchange of data within one run on a quantum
processing unit (in a backend) or in a simulator.
More details on quantum sessions within Qrisp are
provided in the following sections.
4.2.2 QuantumVariable Example Code
The following small code example illustrates the
initialization and utilization of QuantumVariables.
This shows the core concept of Qrisp, which is using
QuantumVariables instead of qubit objects, and in-
terpret the in- and outputs in a human readable format.
In the code example two QuantumVariables, each
consisting of 3 qubits, are created and given unique
identifiers. Subsequently, a CX-gate is applied on
the qubits of both variables. Hence, the developer
no longer needs to deal with single qubits but rather
with the human readable representation of the quan-
tum variables.
from qrisp import QuantumSession,
QuantumVariable
example_qv_1 = QuantumVariable(3,
name = "alice")
example_qv_2 = QuantumVariable(3,
name = "bob")
cx(example_qv_1, example_qv_2)
4.3 Quantum Sessions
The QuantumSessions are one of the main ingredi-
ents for effectively managing the execution of quan-
tum code on a backend or a QPU simulator. Assuming
that the quantum related code is executed in a hybrid
setting, where an overall program runs on a CPU and
is having subroutines executed on various computing
architectures (e.g. GPUs, SNNs, HPC-clusters ...), the
quantum sessions are the artifacts encapsulating the
communication and seamless integration of quantum
backend executions within a hybrid program.
Figure 4: The Role of Quantum Sessions in Interacting with
Quantum Processing Units and Backends.
The role of quantum sessions within Qrisp is vi-
sually depicted in Figure 4. On the left side, one
can observe the various quantum variables and data
types, including data structures (more to come in
the following sections) of the Qrisp eDSL, such as
quantum arrays. These variables and data structures
within a program are compiled to a quantum circuit
(see section 4.1), which together with different exe-
cution environments all reside in a quantum session.
The QuantumSession is the main object encapsulat-
ing the various aspects and requests of the quantum
part of a hybrid program and managing the interac-
tions with the quantum backend - e.g. QPU or a (lo-
cal) quantum simulator. The communication proto-
cols between client side and host/ backend side are
not focus of the current publication
1
. However, it
is important to establish that the QuantumSession is
the one managing the state of the computation within
the interactions with backends, similarly as session
management is conducted in legacy web-technologies
(Wedman et al., 2013).
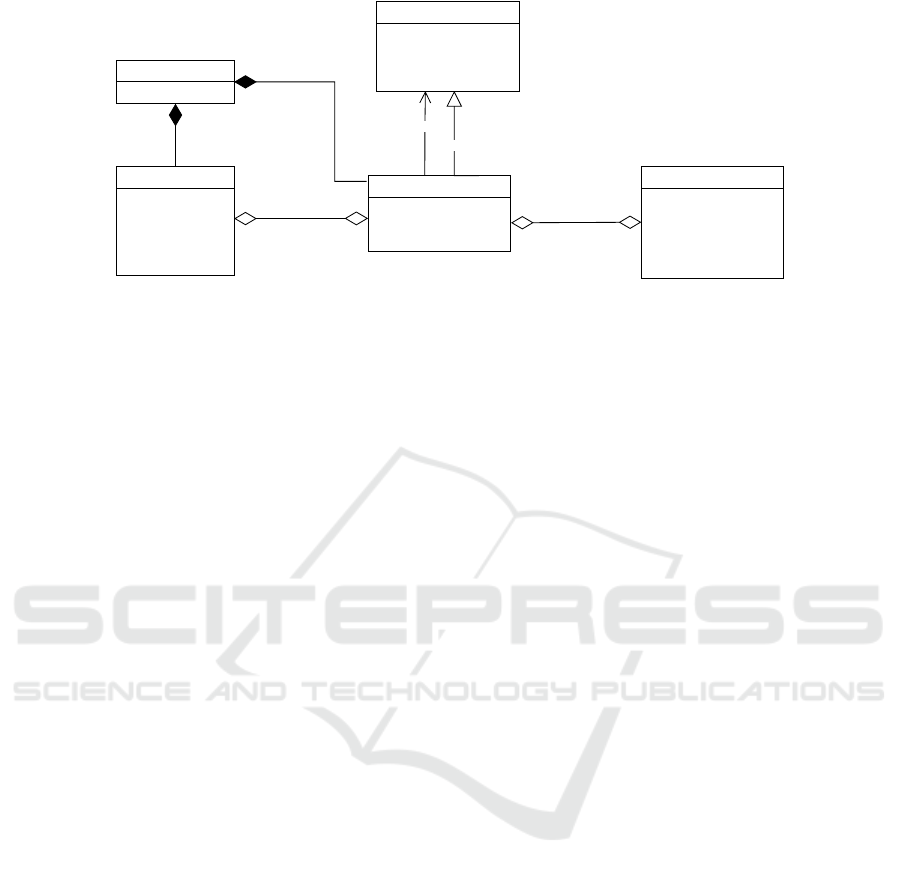
4.3.1 QuantumSession Meta-Model
The overall meta-model for the Qrisp
QuantumSessions is depicted in Figure 5 and
consists of the following classes:
QuantumSession. This QuantumSession class
extends the QuantumCircuit class. It manages
the life cycle of QuantumVariables by keeping
track of them in a list called qv. If an operation
acts on qubits from different sessions, they are
automatically merged into one. Sessions can also be
merged manually via a special merge function. An
1
For more details on the communication protocols and
architecture we refer the reader to (Seidel et al., 2022a)
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
32
QuantumVariable
name: string
size: int
reg: list<Qubit>
qs: QuantumSession
QuantumSession
qv: list<QuantumVariable>
env_stack:
list<QuantumEnvironment>
QuantumArray
qtype: QuantumVariable
QuantumCircuit
data: list<Instruction>
qubits: list<Qubit>
clbits: list<Clbit>
Extends
QuantumEnvironment
env_qs: QuantumSession
env_data: list<Operation>
original_data: list<Operation>
parent: QuantumEnvironment
compile()
Figure 5: The Meta-Model for the Quantum Sessions towards a Quantum Backend.
Operation or Instruction can be appended to a
QuantumSession with a dedicated append method.
A Quantum Session enables the use of additional
features such as QuantumEnvironments and uncom-
putation, which corresponds to garbage collection in
legacy programming languages (Seidel et al., 2023).
Through a method called compile, a Quantum-
Session can be synthesized to a QuantumCircuit
from the basic infrastructure. The class has methods
to evaluate the size of the quantum session, such
as the amount of CNOT gates used or the num-
ber of quantum variables. The representation of
the state vector (e.g. from a simulator) for a quan-
tum session is returned by the statevector function.
QuantumEnvironment. This class denotes special
environments for executing different types of code
within a hybrid programm flow. It is described in
more details in the coming sections.
QuantumArray. The QuantumArray is a class
that consists of many QuantumVariables of a certain
type, much like a classical array consists of classical
variables. It is described in more detail in section 4.5.
4.3.2 QuantumSession Example Code
Following the above description of the meta-model,
the following illustrates a simple example of the ex-
plicit usage of QuantumSessions within Qrisp. The
code snipet demonstrates the initiation of a quantum
session and the creation of a quantum variable as-
signed to this session. At the end, two of the qubits
within the quantum variable are connected over a CX-
gate. This simple example demonstrates how straight
forward it is, to create and operate sessions for quan-
tum program execution within Qrisp.
from qrisp import QuantumSession,
QuantumVariable
qs = QuantumSession()
qv = QuantumVariable(3, qs = qs)
qv.qs.cx(qv[0], qv[1])
4.4 Data Types
Similarly to classical high-level programming lan-
guages, Qrisp provides the possibility to use specific
(native) data types (such as floats, integers, characters
...), which can be used to steer the program flow and
ensure quality and soundness of the quantum com-
putations. The meta-model for this typing system is
presented in the following subsection.
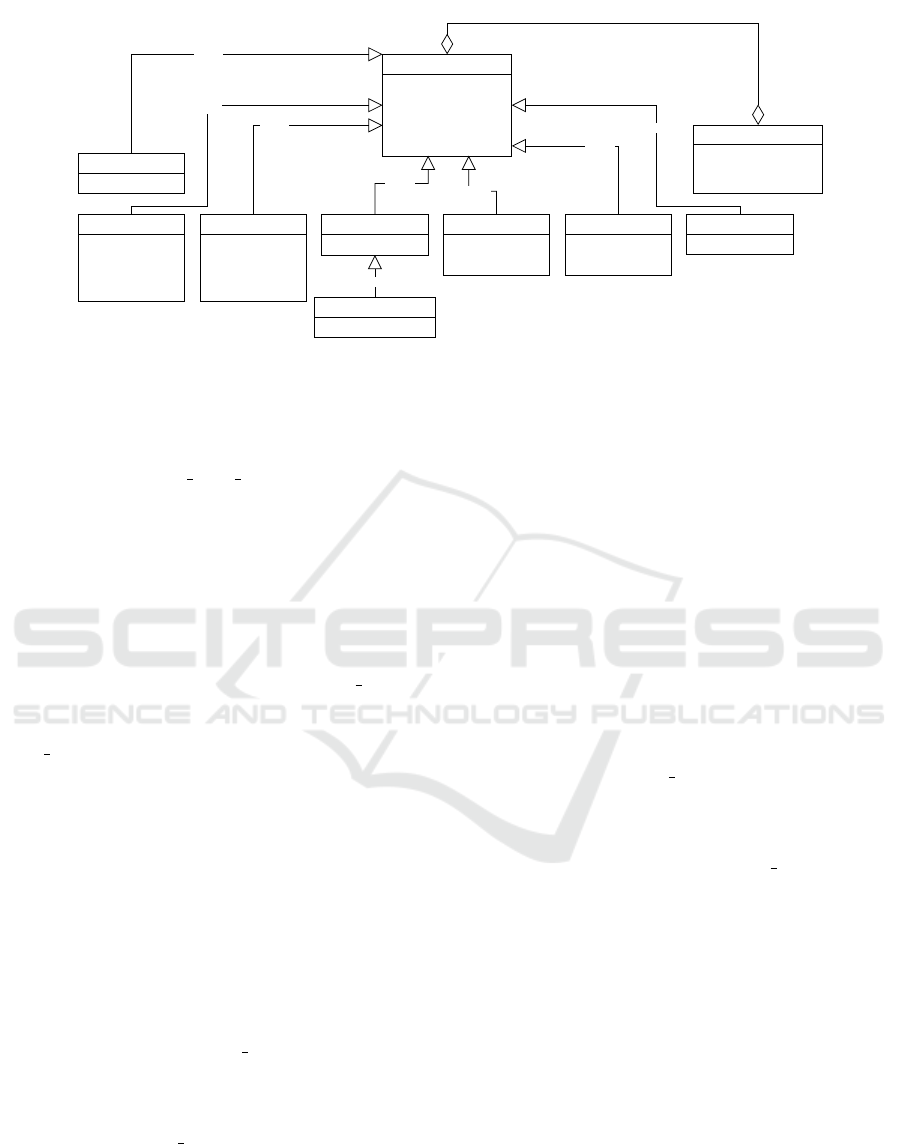
4.4.1 Data Types Meta-Model
The meta-model for the Qrisp data types is depicted
in Figure 6 and consists of the following classes:
QuantumFloat. This class extends the
QuantumVariable class and represents the quantum
equivalent of a classical floating point number with a
predetermined exponent and mantissa size. However,
there are some differences compared to classical
floating point numbers. Due to the restricted size
of current quantum computers, a QuantumFloat
variable can’t just use 64 qubits as in a classical
setting. For this reason Qrisp is designed in a way
that users have to set the size of the QuantumFloat
and the exponent when initializing them. The
QuantumFloat class supports operations such as
addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and
comparisons. The class adds bit-wise operations and
functionality to change the size and exponent of the
floating-point number.
QuantumModulus. This class extends
QuantumFloat and is used to model and pro-
cess modular arithmetic which is important for Shor’s
algorithm. It supports the same operations as the
QuantumFloat class.
Designing a Meta-Model for the Eclipse Qrisp eDSL for High-Level Quantum Programming
33
QuantumVariable
name: string
size: int
reg: list<Qubit>
qs: QuantumSession
QuantumSession
qv: list<QuantumVariable>
env_stack:
list<QuantumEnvironment>
QuantumArray
qtype: QuantumVariable
QuantumDictionary
return_type: QuantumVariable
QuantumFloat QuantumBool QuantumChar
QuantumString
Extends
Extends
Extends
Extends
Extends
QuantumModulus
modulus: int
Figure 6: The Meta-Model for Quantum Types and Data Structures in Eclipse Qrisp.
QuantumBool. This class inherits from the
QuantumVariable class and is used to represent the
quantum equivalent of a boolean truth value. They
can either be created manually or automatically when
comparing a QuantumVariable with a concrete
value or with another QuantumVariable derivative.
QuantumChar. This class extends
QuantumVariable and represents a single character.
To represent multiple characters the QuantumString
class is used.
QuantumString. This class inherits from
QuantumArray - elaborated on in the section
4.5 - and represents a string of characters. The
class adds functionality for concatenation and string
operations in general. The QuantumString objects
created this way share the same qubits.
4.4.2 Data Types Example Code
The following example shows how two floating point
numbers in a superposition are added. Firstly, two
instances of QuantumFloat are initialized and subse-
quently a Hadamard gate is applied on the least sig-
nificant qubit of the first float. In the last step the ad-
dition of the two variables is performed and the result
is stored in a new QuantumFloat variable. The gen-
erated circuit is then executed on the integrated Qrisp
simulator and the result is printed to the console.
# Import Qrisp classes/functions
from qrisp import QuantumFloat
from qrisp.core import h
# Initialize QuantumFloats with 3 Qubits
n = 3
a = QuantumFloat(n, exponent=0, signed=False)
b = QuantumFloat(n, exponent=0, signed=False)
# Set the values of both variables
a[:] = 2
b[:] = 4
# Apply a Hadamard gate on
# the least significant qubit
h(a[0])
# Add both QuantumFloats
res = a+b
# Print the result to the console
print(res)
# returns: {6: 0.5, 7: 0.5}
To elaborate more on the example code: The two
quantum floats - a and b - are initialized with three
qubits each and assigned with the values of 2 and 4
respectively. Single qubits within a quantum float can
be accessed using square brackets. This is used to ap-
ply the Hadamard gate only on the least significant
qubit of a. Therefore, the variable a is in an equal
superposition between the values 2 and 3. Mathemat-
ical operations can be used on quantum floats just as if
they were classical floats, since they are converted to
the quantum equivalent in the background. The result
of the added floats is stored in a new variable called
res and is also of type QuantumFloat, automatically
created by Qrisp. By print(res) the result is printed
to the console. To do so, Qrisp actually performs a full
simulation of the quantum program with a measure-
ment in the end. This is also why the result is shown
as a dictionary (i.e. a hash map) with all the possi-
ble outcomes of a measurement with their respective
probability. In this case the possible outcomes are 6
and 7, which are both equally likely.
4.5 Data Structures
Data structures come on top of the data types and al-
low for handling more complex constellations and re-
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
34

lations between data entities within the quantum part
of a Qrisp program.
4.5.1 Data Structures Meta-Model
The meta-model for Qrisp data structures is depicted
together with the data types in figure 6 and consists
of the following classes:
QuantumArray. This is a class, which inherits
from ndarray of the popular NumPy python library
(Harris et al., 2020). It can be used to manage mul-
tiple QuantumVariable objects. QuantumArrays
support many convenient array manipulation meth-
ods such as slicing and reshaping. Using the array
for matrix multiplication is possible as long as
the array consists of QuantumFloat objects. It
can be multiplied by another such array or a clas-
sical ndarray which consists of numbers. The
most likely measurement outcome is obtained by in-
voking a special method called most likely method.
QuantumDictionary. This class extends the
python class dict and is the quantum equivalent of a
classical dictionary. This class makes inputing data
into the quantum computer easier. The value of a
dictionary can be loaded into a QuantumVariable
using the load method.
4.5.2 Data Structures Example Code
The following code examples illustrate the us-
age of QuantumDictionaries and QuantumArrays.
The first code snippet demonstrates the usage of
QuantumDictionaries. We see the creation of
the QuantumDictionary, followed by storing a nu-
merical value with a numerical key in the dictio-
nary. Afterwards, a tupel (3,4) is stored in the
dictionary with the key of 42. Finally, we store
two words with corresponding string keys in the
QuantumDictionary.
from qrisp import QuantumDictionary,
QuantumVariable
qd = QuantumDictionary()
qd[1] = 2
qd[42] = (3,4)
qd["hello"] = "hallo"
qd["world"] = "welt"
The second code example illustrates the usage
of QuantumArrays. It starts with the creation of a
special QuantumFloat based type, which is subse-
quently used for the creation of theQuantumArray.
The second parameter (shape) determines the size
of the array thereby creating a 3-dimensional array.
The subsequent 2 lines are used to create a superpo-
sition between various array configurations in the 3-
dimensional space, yielding the final outcome shown
as comments at the end of the code example.
import numpy as np
from qrisp import QuantumArray,
QuantumFloat, h
qtype = QuantumFloat(5, -2)
q_array = QuantumArray(qtype = qtype,
shape = (2, 2, 2))
qv = q_array[0,0,1]
h(qv[0])
print(q_array)
# returns:
# {OutcomeArray([[[0., 0.],
# [0., 0.]],
# [[0., 0.],
# [0., 0.]]]): 0.5,
# OutcomeArray([[[0. , 0.25],
# [0. , 0. ]],
# [[0. , 0. ],
# [0. , 0. ]]]): 0.5}
4.6 Quantum Environments
The quantum environments are another key element
of the Qrisp meta-model allowing for the execution of
different flows depending on the specific environment
surrounding the belonging code snippet.
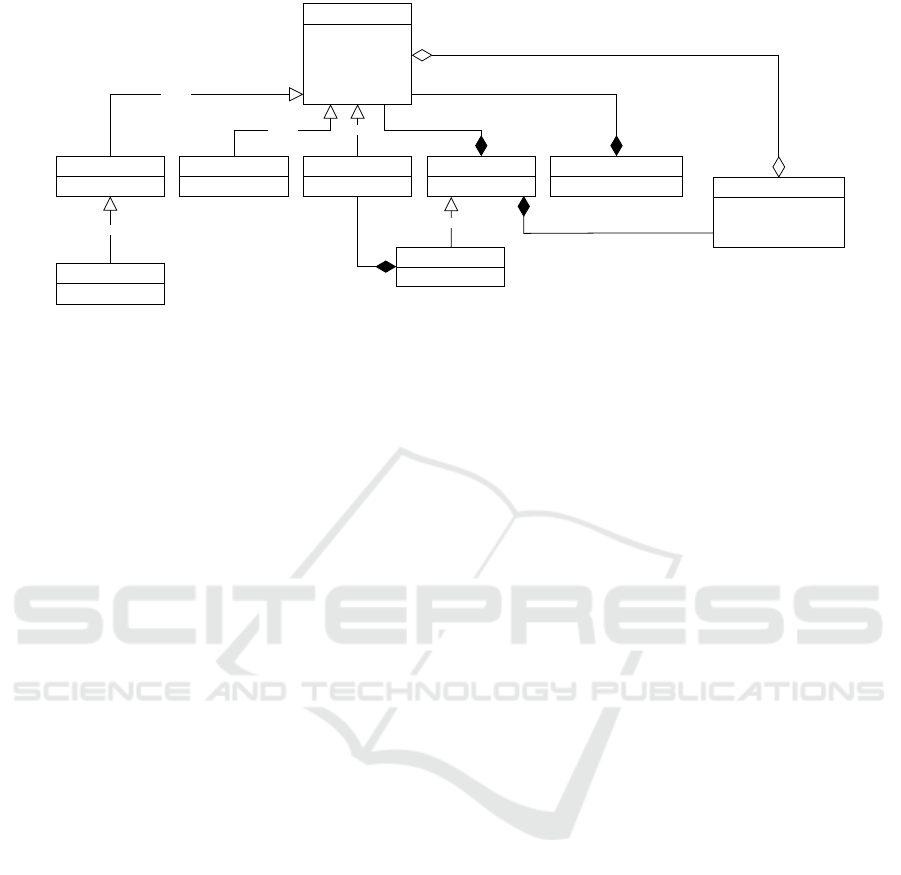
4.6.1 Quantum Environments Meta-Model
The meta-model for realizing quantum environments
is presented in Figure 7 and consists of the following
classes:
QuantumEnvironment. The main environment
class represents a block of code, which undergoes
a specific compilation process. After entering an
environment, the resulting circuit data is compiled
into the env data, while keeping the unchanged
part in the original data attribute. The compiling
process is specified in the compile method. An
environment has references to the QuantumSession
where all the active QuantumVariable objects are
located together at the parent environment.
Designing a Meta-Model for the Eclipse Qrisp eDSL for High-Level Quantum Programming
35
QuantumSession
qv: list<QuantumVariable>
env_stack:
list<QuantumEnvironment>
ConditionEnvironment
cond_eval_function:
function
args: list
kwargs: dict
ControlEnvironment
ctrl_qubits: list<Qubit>
ctrl_state: string
InversionEnvironmentConjugationEnvironment
conjugation_function:
function
args: iterable
kwargs: dict
GateWrapEnvironment
name: string
IterationEnvironment
qs: QuantumSession
iteration_amount: int
GMSEnvironment
QuantumEnvironment
env_qs: QuantumSession
env_data: list<Operation>
original_data: list<Operation>
parent: QuantumEnvironment
Extends
Extends
Extends
Extends
Extends
Extends
CustomControlEnvironment
control_qb: Qubit
Extends
Extends
Figure 7: The Meta-Model for the various Environments in Eclipse Qrisp.
ConditionEnvironment. This class inherits from
QuantumEnvironment and enables if-conditionals
similar to classical programming. The environment
takes a function cond eval function which eval-
uates the truth value as an input. The arguments
and keyword arguments are given by the args and
kwargs attributes. The program part inside of the
environment is activated if the condition function
returns true.
ControlEnvironment. This class extends
QuantumEnvironment and its logic is controlled
on a supplied list of Qubits stored in ctrl qubits.
The environment is activated, if the control Qubits
match the computational basis state given in the
ctrl state argument. A ControlEnvironment can
be activated using the control function.
GateWrapEnvironment.. This class extends
QuantumEnvironment and allows to hide complexity
in the QuantumCircuit visualization. This is done
by bundling the content in a single Instruction
object, which is given the name determined by the
name argument.
CustomControlEnvironment. This class in-
herits from GateWrapEnvironment and allows to
specify the controlled version of a decorated function.
This is done with the custom control decorator. If
the function is called within a ControlEnvironment,
the controlled version is called instead of the regular
one. The controlled version is controlled by a Qubit
stored in the control qb attribute.
IterationEnvironment. This class extends
QuantumEnvironment and can be used to re-
peatedly execute the same quantum circuit, which
can reduce the compilation time. The environment
takes the QuantumSession, in which the repeated
operations should be performed and the iteration
amount as arguments. The logic of the environment
is executed the specified amount of times, basically
creating a loop type of behaviour.
ConjugationEnvironment. This class extends
QuantumEnvironment and can be used to perform
conjugated operations. An arbitrary unitary matrix
(i.e. quantum operation) can be conjugated by
another unitary quantum operation. This structure
appears in many quantum algorithms such as Grover,
quantum backtracking or Fourier arithmetic. Using
the ConjugationEnvironment not only helps
to structure the code, but can also grant perfor-
mance advantages. The ConjugationEnvironment
takes the conjugation function as an argument.
The arguments and keyword arguments for the
conjugation function are given by the args and
kwargs attributes. The content of the environment
is conjugated by the conjugation function. A
ConjugationEnvironment can be called by using
the conjugate function.
InversionEnvironment. This class inherits from
QuantumEnvironment and can be used to invert a
block of operations or more precisely the content of
the environment. An InversionEnvironment can
be called using the invert function.
GMSEnvironment. This class inherits from
QuantumEnvironment and can be used to conve-
niently construct circuits using GMS-Gates, which
are the native entangling gates of trapped ion quantum
computers. The environment allows only phase-only
Gates and compiles them to GMS-Gates.
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
36

4.6.2 Quantum Environments Example Code
The following code example demonstrates the us-
age of the ConditionEnvironment. Thereby, it
can be observed how a quantum character is de-
fined, followed by putting the first qubit of the char-
acter in a superposition. Subsequently, the with-
clause activates the ConditionEnvironment and ex-
ecutes an if-statement on the previously created quan-
tum character. Based on the if-condition evalu-
ation, different values are assigned to a previous
declared QuantumFloat. Finally, we measure the
QuantumChar and the QuantumFloat and obtain the
probabilities for all possible states, which are consti-
tuted by different values of both variables depending
on the superposition and the with-clause.
from qrisp import QuantumChar, QuantumFloat,
h, multi_measurement
q_ch = QuantumChar()
qf = QuantumFloat(3, signed = True)
h(q_ch[0])
with q_ch == "a":
qf += 2
print(multi_measurement([q_ch,qf]))
# returns: {('a', 2): 0.5, ('b', 0): 0.5
4.7 Quantum Loops
The final programming concept we introduce is the
quantum loop construct in Qrisp. Analogous to
for/while and iterator loops in traditional program-
ming languages, quantum loops are implemented
within the previously discussed quantum environ-
ments.
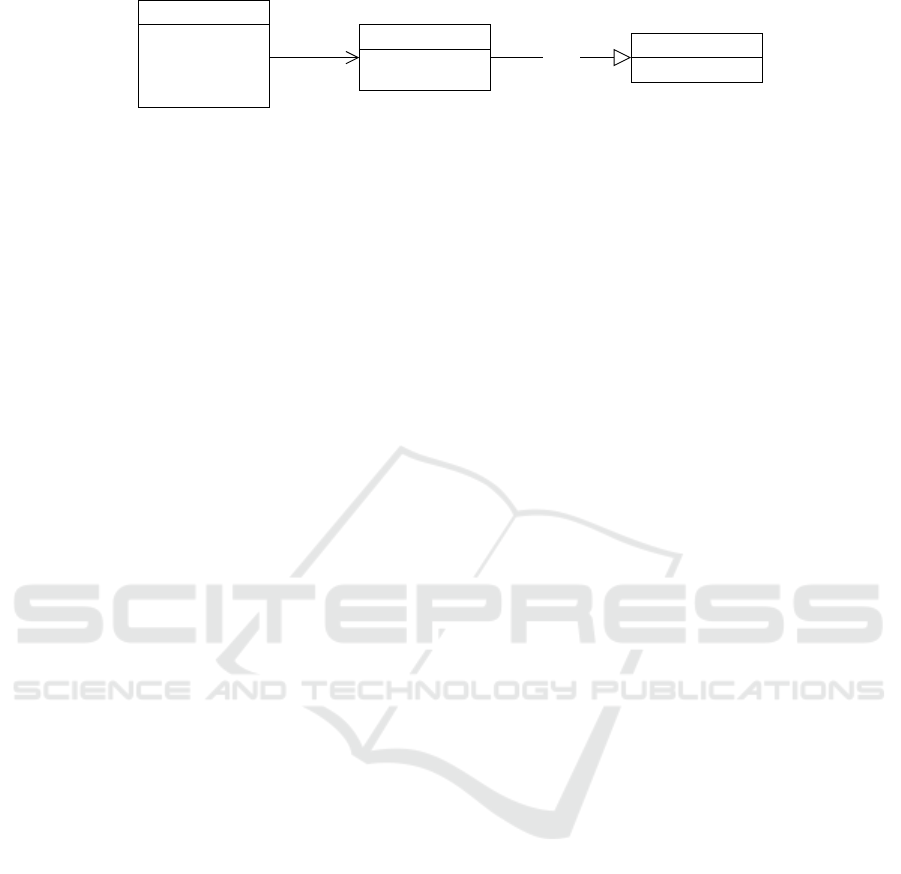
4.7.1 Quantum Loops Meta-Model
The meta-model for quantum loops in Qrisp is illus-
trated in figure 8. The new component is constituted
by the qRange class, which is the core class to mimic
a loop from classical computing. The end of the loop
is determined by a QuantumFloat stored in the at-
tribute max index qf. The qRange concept embodies
a quantum ControlEnvironment, with its belong-
ing functions to determine the end of a programming
loop.
4.7.2 Quantum Loop Example Code
The following example code demonstrates the usage
of quantum loops. At the beginning, corresponding
float variables are defined that are used to demonstrate
the effects of the iterations. Next, the n variable is set
to 4, which is meant to be the upper boundary for the
number of iterations in the loop. Afterwards, the first
qubit of n is put in a superposition leading to it being
10 and 15 with a probability of 0.5 for each value.
Having prepared all relevant variables, a qRange
based loop is executed, in which an incremented value
of index variable i is iteratively added to the over-
all sum. Finally, the resulted sum is measured and
printed showing two different values depending on
the loop upper limit, which was put into superposition
in advance. These overall sum values emerge with a
probability of 0.5 each, as expected based on the su-
perposition of the upper boundary.
from qrisp import QuantumFloat, qRange, h
n = QuantumFloat(3, signed = True, name = "n")
qf = QuantumFloat(5, name = "qf")
n[:] = 4
h(n[0])
for i in qRange(n):
qf += i
print(qf)
# returns: {10: 0.5, 15: 0.5}
5 CASE STUDY: GROVER IN
ECLIPSE QRISP
This example shows the level of abstraction - based
on Qrisp - which can be achieved for the implemen-
tation of the Grover search algorithm. The developer
does not need to deal with qubits or gates, but rather
relies on predefined functions and programming con-
structs according to the above described meta-model.
One can observe the definition of the corresponding
Grover oracle for solving a simple quadratic equation
x
2
= 0.25. Based on standard Eclipse Qrisp functions,
we can implement a Grover quantum search for the
suitable solutions of the equation.
from qrisp.grover import diffuser
from qrisp import auto_uncompute, z,
h, QuantumFloat
@auto_uncompute
def sqrt_oracle(qf):
temp_qbool = (qf*qf == 0.25)
z(temp_qbool)
qf = QuantumFloat(3, -1, signed = True)
n = qf.size
iterations = int((2**n/2)**0.5)
h(qf)
Designing a Meta-Model for the Eclipse Qrisp eDSL for High-Level Quantum Programming
37
QuantumFloat
ConditionEnvironment
cond_eval_function:
function
args: list
kwargs: dict
qRange
max_index_qf:
QuantumFloat
Extends
Figure 8: The Qrisp Meta-Model for Quantum Loops.
for i in range(iterations):
sqrt_oracle(qf)
diffuser(qf)
6 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the development of Qrisp marks a sig-
nificant advancement in making quantum computing
more accessible to a broad spectrum of developers,
including those without a background in physics.
By providing a high-level programming language
specifically designed for quantum computing, Qrisp
simplifies the creation and management of com-
plex quantum algorithms. The language’s design
philosophy emphasizes ease of use, abstraction,
compatibility, visualization, and extendibility, which
collectively enhance the development experience
and lower the entry barriers for new users. Qrisp’s
modular architecture, which integrates seamlessly
with Python’s extensive ecosystem, further facili-
tates the development of complex hybrid quantum
applications. This modularity also ensures that
code written by domain experts can interoperate
efficiently, leveraging automated qubit management
and optimized resource allocation.
In order to capture, the Qrisp programming model
and to enable the transfer of the Qrisp embedded DSL
to other programming languages and platforms, the
current paper presented a meta-model for the Qrisp
eDSL. By following this meta-model, it becomes fea-
sible to develop new iterations of Qrisp for languages
such as Java, C/C++, Rust, and others. The adaptation
of Qrisp to these languages will be explored in future
research endeavors. Furthermore, this meta-model
holds potential for standardization, which could sig-
nificantly enhance large-scale industrial collaboration
in high-level quantum programming.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by the Federal Ministry
for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (German:
Bundesministerium f
¨
ur Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz)
under the projects Qompiler (01MQ22005A) and
EniQma (01MQ22007A). The authors are responsi-
ble for the content of this publication.
REFERENCES
(2024). AQT Qiskit Provider. https://qiskit-community.
github.io/qiskit-aqt-provider/. Accessed: 14.08.2024.
(2024). Classiq. https://www.classiq.io.
(2024a). Eclipse Foundation. https://www.eclipse.org/org/
foundation/. Accessed: 14.08.2024.
(2024b). Eclipse Qrisp GitHub Repository. https://github.
com/eclipse-qrisp/Qrisp. Accessed: 14.08.2024.
(2024). Hybrid Computing with Q#. https:
//learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/quantum/
hybrid-computing-integrated. Accessed: 14.08.2024.
(2024). QIR Alliance. https://www.qir-alliance.org. Ac-
cessed: 14.08.2024.
(2024). Qrisp documentation page. www.qrisp.eu. Ac-
cessed: 26.04.2024.
Abhari, A., Faruque, A., and Dousti, M. J. e. a. (2012).
Scaffold: Quantum programming language.
Bergholm, V. et al. (2022). PennyLane: Automatic differ-
entiation of hybrid quantum-classical computations.
arXiv:1811.04968 [physics, physics:quant-ph].
Bichsel, B., Baader, M., and Gehr, T. e. a. (2020). Silq: A
high-level quantum language with safe uncomputation
and intuitive semantics. In Proceedings of the 41st
ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Programming Lan-
guage Design and Implementation, PLDI 2020, page
286–300, New York, NY, USA. Association for Com-
puting Machinery.
Bock, S., Seidel, R., and Becker, C. K. (2022). Towards a
standardised quantum software stack. ERCIM News,
2022(128).
Chochliouros, I. P. et al. (2023). OASEES: an innovative
scope for a dao-based programmable swarm solution,
for decentralizing AI applications close to data gener-
ation locations. In Maglogiannis, I. et al., editors, AIAI
2023 IFIP WG 12.5 International Workshops, volume
677 of IFIP Advances in Information and Communi-
cation Technology, pages 91–105. Springer.
Cid, M. I. G. et al. (2024). PQ-REACT: Post Quantum
Cryptography Framework for Energy Aware Contexts.
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference
on Availability, Reliability and Security, ARES 2024,
Vienna, Austria, 30 July 2024 - 2 August 2024, pages
65:1–65:7. ACM.
Cirq Developers (2024). Cirq. https://doi.org/10.5281/
zenodo.11398048.
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
38

Coecke, B. and Duncan, R. (2007). A graphical calculus for
quantum observables. Preprint.
Cross, A. W., Bishop, L. S., Smolin, J. A., and Gambetta,
J. M. (2017a). Open Quantum Assembly Language.
arXiv:1707.03429 [quant-ph].
Cross, A. W., Bishop, L. S., Smolin, J. A., and Gambetta,
J. M. (2017b). Open quantum assembly language.
Dinkelaker, T., Eichberg, M., and Mezini, M. (2010). An ar-
chitecture for composing embedded domain-specific
languages. AOSD ’10, page 49–60, New York, NY,
USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Eclipse Foundation (2017). Eclipse Public License 2.0
(EPL) | The Eclipse Foundation. https://www.eclipse.
org/legal/epl-2.0/. Accessed: 2024-10-02.
Green, A. S., Lumsdaine, P. L., and Ross, N. J. e. a. (2013).
Quipper: A scalable quantum programming language.
SIGPLAN Not., 48(6):333–342.
Harris, C. R. et al. (2020). Array programming with
NumPy. Nature, 585(7825):357–362.
Heim, B. et al. (2020). Quantum programming languages.
Nature Reviews Physics, 2(12):709–722.
Javadi-Abhari et al. (2024). Quantum computing with
Qiskit. arXiv:2405.08810 [quant-ph].
Python Software Foundation (2024). Python Language Ref-
erence. https://www.python.org/.
Seidel, R., Bock, S., Tcholtchev, N., and Hauswirth, M.
(2022a). Qrisp: A framework for compilable high-
level programming of gate-based quantum computers.
In PlanQC - Programming Languages for Quantum
Computing.
Seidel, R., Bock, S., Zander, R., Petri
ˇ
c, M., Stein-
mann, N., Tcholtchev, N., and Hauswirth, M. (2024).
Qrisp: A Framework for Compilable High-Level
Programming of Gate-Based Quantum Computers.
arXiv:2406.14792 [quant-ph].
Seidel, R., Tcholtchev, N., Bock, S., Becker, C. K.,
and Hauswirth, M. (2022b). Efficient floating point
arithmetic for quantum computers. IEEE Access,
10:72400–72415.
Seidel, R., Tcholtchev, N., Bock, S., and Hauswirth, M.
(2023). Uncomputation in the Qrisp High-Level
Quantum Programming Framework. In Kutrib, M.
and Meyer, U., editors, Reversible Computation - 15th
International Conference, RC 2023, Giessen, Ger-
many, July 18-19, 2023, Proceedings, volume 13960
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 150–
165. Springer.
Sivarajah, S., Dilkes, S., and al., A. C. (2020). tket: a retar-
getable compiler for NISQ devices. Quantum Science
and Technology, 6(1):014003.
Svore, K., Roetteler, M., Geller, A., and al., M. T. (2018).
Q#. In Proceedings of the Real World Domain Specific
Languages Workshop 2018 on - RWDSL2018. ACM
Press.
Voichick, F., Li, L., Rand, R., and Hicks, M. (2023).
Qunity: A Unified Language for Quantum and Clas-
sical Computing. Qunity: A Unified Language for
Quantum and Classical Computing (Type Checker),
7(POPL):32:921–32:951.
Wedman, S., Tetmeyer, A., and Saiedian, H. (2013). An
Analytical Study of Web Application Session Man-
agement Mechanisms and HTTP Session Hijacking
Attacks. Information Security Journal: A Global Per-
spective, 22(2):55–67.
Weisem
¨
oller, I. and Sch
¨
urr, A. (2008). Formal definition
of mof 2.0 metamodel components and composition.
In Czarnecki, K., Ober, I., Bruel, J.-M., Uhl, A., and
V
¨
olter, M., editors, Model Driven Engineering Lan-
guages and Systems, pages 386–400, Berlin, Heidel-
berg. Springer.
Wright, C. J., Luj
´
an, M., Petoumenos, P., and Goodacre, J.
(2024). Quff: A dynamically typed hybrid quantum-
classical programming language. In Proceedings of
the 21st ACM SIGPLAN International Conference
on Managed Programming Languages and Runtimes,
MPLR 2024, page 65–81, New York, NY, USA. As-
sociation for Computing Machinery.
¨
Omer, B. (2005). Classical Concepts in Quantum Program-
ming. International Journal of Theoretical Physics,
44(7):943–955.
Designing a Meta-Model for the Eclipse Qrisp eDSL for High-Level Quantum Programming
39
