
Nutritional Regime, Trace Element Composition and Microbiological
Nutritional Value of Soils Under Various Crops Under the Influence
of Electrical Treatment
Ashiraf
Mukhammadiev
1a
, Kenzhemirza Baymakhanov
2b
, Bekzod Choriev
3c
,
Zilola Hakimova
3d
and Zafar Radjapov
4e
1
Institute of Energy Problems of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan, 100076 Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2
Auezov South Kazakhstan State University, Shymkent,160018, Kazakhstan
3
Tashkent State Agrarian University, Tashkent, 100140, Uzbekistan
4
Urgench State University, Urgench, 220100, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Electrical Treatment, Soil Microbiology, Crop Productivity.
Abstract: This article presents the results of scientific research conducted in the Aral Sea region to study the aftereffect
of electrical treatment of a complex biological system consisting of «seed, soil, plant» using the example of
cultivation of cotton, sunflower, millet, corn, and sesame. The electrical effect on the "seed, soil, plant" system
has a positive effect on the content of digestible forms of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and trace elements
in the soil, had a positive effect on the microflora of the rhizosphere of cotton, increasing the content of useful
and reducing quantitative microorganisms in the soil, which improves the phytosanitary condition of the soil
by reducing microscopic mold fungi and increasing the number of actinomycetes. It has been experimentally
proven that differentiated irrigation regimes in combination with electrical technologies increase the yield of
agricultural crops and save irrigation water.
1 INTRODUCTION
The problem of increasing the productive capacity of
irrigated lands and crop productivity has always been
in the focus of scientists' attention. Currently, this
problem is of particular relevance due to the fact that
in the 21st century, soil degradation, deterioration of
their useful properties, intensive decomposition of
natural humus reserves and, in general, a decrease in
soil fertility is noted on the irrigated lands of Central
Asia.
The search for new environmentally friendly,
economical and effective plant growth stimulants is
one of the important problems of crop production,
including cotton growing, etc. Most of the plant
growth stimulants widely used in the world are
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-6036-3468
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-9379-9487
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-4806-1982
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-0182-5261
e
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-2773-2167
chemicals that ultimately harm the environment and
humans.
In addition, the well-known agrotechnical
methods of cultivating crops have also exhausted
their capabilities to a certain extent and their further
improvement over the years does not, in fact, give any
tangible results.
The improvement of technical means, intensive
use of chemicals, increased doses of mineral
fertilizers, etc. become not only economically
unjustified, but also harmful, taking into account the
environmental situation.
The deteriorating environmental situation due to
environmental pollution, moisture deficiency,
salinization of the soil environment and other adverse
environmental factors, along with a decrease in soil
366
Mukhammadiev, A., Baymakhanov, K., Choriev, B., Hakimova, Z. and Radjapov, Z.
Nutritional Regime, Trace Element Composition and Microbiological Nutritional Value of Soils Under Various Crops Under the Influence of Electrical Treatment.
DOI: 10.5220/0014269700004738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies (I-CRAFT 2024), pages 366-371
ISBN: 978-989-758-773-3; ISSN: 3051-7710
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

fertility, lead to significant crop losses and
deterioration in the quality of agricultural products.
Meanwhile, the intensification of crop production
and the need to increase the productivity and quality
of agricultural products remain an urgent problem of
the day.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
A solution to this problem based on the improvement
of well-known agricultural technologies is not
expected in the future.
Therefore, it is vital to create a fundamentally new
alternative highly efficient, environmentally friendly,
industrial technology for cultivating crops.
In Uzbekistan, the Head Design Bureau for
Cotton-growing Machines has been conducting
scientific research since 1995 on the creation of a new
environmentally friendly agricultural technology for
growing crops, which consists in the integrated use of
electricity in the technological process of cultivated
crops (Mukhammadiev, 1992, Khuyae et al., 2000).
Moreover, depending on the operation of the
technological process of cultivation, the type and
variety of seeds, as well as on the degree of their
infestation with pathogenic fungi, bacteria and pests.
Electricity is used in various forms (pulsed,
electrothermal, radiation, etc.) and also in
combination, which makes it possible to completely
abandon the use of pesticides in the cultivation of
crops.
The essence of environmentally friendly
agroelectrotechnology consists in the combined and
stage-by-stage electrical effects on the «seed, soil,
plant» system.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Environmentally friendly electrotechnological
techniques have been developed to prepare
agricultural seeds for sowing, to stimulate and protect
them from diseases and pests. A number of technical
means for the implementation of
agroelectrotechnological techniques in agricultural
production have been manufactured and tested in
production conditions in almost all the republics of
Central Asia, the People's Republic of China and the
Arab Republic of Egypt (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Agroelectrotechnological methods of agricultural
production
In the conducted studies on the mechanisms of
electrical stimulation of seeds and plants during the
growing season, it was found that electrical
stimulation of seeds and plants (for example, cotton,
potatoes, tomatoes, cereals) enhances nucleic and
protein metabolism, the intensity of photosynthesis,
the activity of enzymes, proteins at the cell level, etc.
(Mukhammadiev et al., 2002, Sodikova and Turapov,
2004). Electrical action does not disrupt pollen
formation, does not reduce its viability and
fertilization process, has a positive effect on the
microflora of the rhizosphere, increasing the content
of beneficial and reducing the number of harmful
microorganisms in the soil, improving the
phytosanitary condition of the soil by reducing
microscopic mold fungi and increasing the number of
actenomycetes (Mukhammadiev, 2003).
It has been experimentally proven that
electrostimulation of soil, seeds and plants using
ultraviolet rays (hereinafter referred to as
electrotreatment) contributes to a significant
(Mukhammadiev et al., 2001).
In this article, we will highlight the results of these
studies in more detail.
The effect of electrical treatment on the nutrient
regime of the studied soils has shown that under
Nutritional Regime, Trace Element Composition and Microbiological Nutritional Value of Soils Under Various Crops Under the Influence of
Electrical Treatment
367

various crops and under the influence of electrical
treatment, noticeable changes occur both in the soil
and in plant nutrition (Khusanov et al., 2002).
A slight increase in the assimilable potassium in
the arable horizon was found under the influence of
electrical treatment. A slight decrease in the content
of digestible phosphorus under the influence of
electrical treatment was also recorded under millet
culture.
The data obtained show that the content of N-NO3
under the rhizosphere of cotton, regardless of the time
of year, is always higher in the variants with electrical
treatment compared with the control. For example, at
the beginning of the growing season, the content of
mobile nitrogen in the control variant ranges from
71.4 to 95.2 mg/kg and in the electrotreated variant
from 108.0 to 148.0 mg/kg. The P2O3 content under
the same crop and under the influence of electrical
treatment always increases in control variants – from
40.0 to 60.0 mg/kg of soil, and in variants with
electrical treatment from 50.0 to 70.0 mg/kg of soil.
As for the content of mobile potassium, it can be said
that the impact of electrical technology on the soil and
on the seeds of cotton crops has shown the best
results.
The content of mobile potassium in the humus
horizon ranged from 219.0 to 398.8 mg/kg, in low
horizons – from 94.0 to 350.8 mg/kg of soil. Under
sunflower culture, regardless of the season, there is an
increase in the content of N-NO3 and K2O under the
influence of electrical treatment compared with the
control. The amount of mobile nitrogen under the
influence of electrical treatment ranged from 119.0 to
166.0 mg/kg, and without electrical treatment from
38.1 to 123.8 mg/kg of soil. The exception is
phosphorus (P2O5). Its content in the version with
electrical treatment is from 20.0 to 70.0 mg/kg, and in
the version without electrical treatment – from 20.0 to
180.0 mg/kg of soil.
During the study, it was found that even in bad
weather, more favorable conditions are created under
the influence of electrical treatment in various
cultures. Compared with the control variant, the
processed variants improve the nutrition of various
crops. In order to definitively clarify the reasons for
the decrease or increase in the NPK content, it is
necessary to conduct a more detailed comprehensive
study of the processes occurring in the "seed-soil-
plant" system under the influence of electrical
treatment.
The effect of electrical treatment on the trace
element composition of the studied soils.
Trace elements are an integral part of living matter
and are necessary for the normal functioning of
plants, animals and humans.
It has been established that the distribution of
trace elements in the soil, their migration, and
mobility depend on a number of factors: soil pH,
gross humus content, mechanical composition,
humidity, content of 〖 CO 〗 2 carbonates,
composition of absorbed bases, and degree of salinity
(Khusanov et al., 2002).
Copper. The main sources of copper in
biogeocenoses are bedrock. In the studied soils, the
available copper content mainly ranges in low
numbers – from 0.30 to 0.50 mg/kg, but sometimes
ranges from 0.70 to 1.27 mg/kg (Table 2).
Zinc. The availability of zinc to plants is mainly
determined by the pH of the soil solution. The results
of determining the content of available forms of zinc
indicate a suspended content in the upper humus
horizons and a gradual decrease in the depth of the
profile. However, it should be noted that when
studying the composition of trace elements, we
studied only the arable and sub-arable horizons of the
soil profile. In the studied soils, the content of
available zinc in all variants of the experiment ranges
from 3.30 to 5.30 mg/kg.
Manganese. It is known that manganese
promotes the synthesis of carbohydrates, affects the
colloidal chemical properties of plasma, the content
of bound water, increases the intensity of
photosynthesis, is a catalyst for the activity of
enzymes, vitamins, and plays an important role in the
processes of protein synthesis in the body. The
content of available manganese in the studied soils is
insufficient. In the upper horizons, in all variants
under different crops, in the first phase -29.0 to 31.0
mg/kg, and in the second phase (budding) ranges
between 24.4 and 31.3 mg/kg.
In connection with the above, the use of
manganese micro fertilizers on the studied soils is
promising. Thus, the soils formed on alluvial deposits
differ somewhat in the content of mobile Zn, Mn, Cu
from meadow soils of a gray-earth oasis, depending
on the climate of humus content and degree of
cultivation. The microelement composition, the
nature of their distribution along the soil profile under
the influence of electrical treatment changes
markedly.
The work of microorganisms is able to
continuously raise the potential fertility of the soil.
Human activity can transform the potential wealth of
the soil into actual fertility and realize it in the form
of a high yield. The biochemical processes occurring
in the soil are crucial in creating soil fertility. These
I-CRAFT 2024 - 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies
368
processes are carried out under the influence of a
variety of numerous enzymes produced by soil
microorganisms, microfauna and higher plants. The
result of their pathological activity is both the
transformation of complex organic substances into a
mineral form accessible to plants, and the synthesis of
new high-molecular compounds, also necessary for
normal plant growth and development.
Data on the total number of microorganisms are
presented in Table 3, for the main physiological
groups of microorganisms in tables 4, 5. We studied
the dynamics of the development of soil microflora
under the influence of electrical treatment and
without electrical treatment under various crops.
Electrotreatment has different effects on the
microbiological activity of soils under different crops.
Thus, electrical treatment had a positive effect and
increased the total number of microorganisms in the
rhizosphere of cotton at all stages of the growing
season.
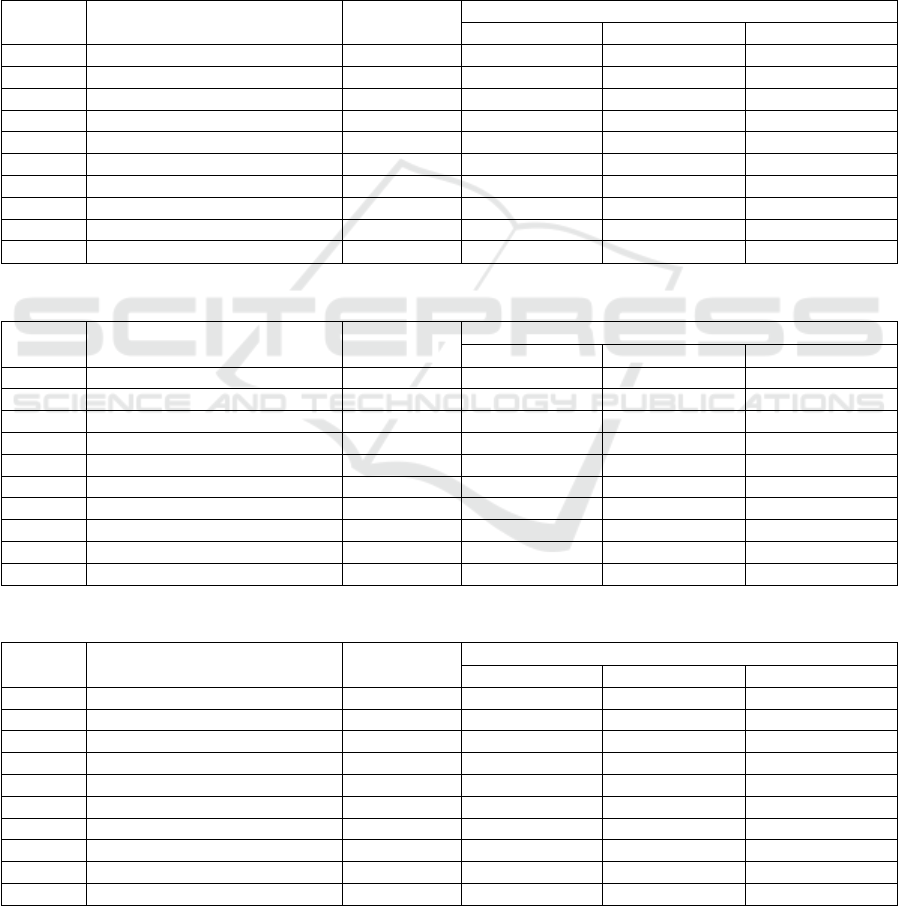
Table 1: The effect of electrical treatment on the total number of soil microorganisms 1000/1g of soil.
№ Experience options Depth, cm
The phase of the growing season
June July Аugus
t
1 Cotton-control 0-30 53475 40290 43425
2 With electrical processing 0-30 114925 80143 73515
3 Sunflower control 0-30 64065 60990 27225
4 With electrical processing 0-30 40320 40743 79890
5 Sesame control 0-30 33675 72885 33039
6 With electrical processing 0-30 71055 34101 26685
7 Millet control 0-30 72735 35145 44910
8 With electrical processing 0-30 36795 94713 49950
9 Corn control 0-30 12825 15750 24210
10 With electrical processing 0-30 19185 105060 35355
Table 2: The effect of electrical treatment on the amount of soil ammonifying bacteria 1000/1g of soil.
№ Experience options Depth, cm
The phase of the growing season
June July Аugus
t
1 Cotton-control 0-30 51000 39000 42000
2 With electrical processing 0-30 112500 79500 72000
3 Sunflower control 0-30 63000 60000 25500
4 With electrical processing 0-30 39000 39000 78000
5 Sesame control 0-30 31500 72000 31500
6 With electrical processing 0-30 69000 33000 24000
7 Millet control 0-30 72000 34500 43500
8 With electrical processing 0-30 33000 93000 48000
9 Corn control 0-30 12000 15000 22500
10 With electrical processing 0-30 18000 99000 33000
Table 3: The effect of electrical treatment on the number of soil oligonitrophils 1000/1g of soil.
Experience options Depth, cm
The phase of the growing season
June July Аugus
t
1 Cotton-control 0-30 2460 1185 1275
2 With electrical processing 0-30 2895 1200 1350
3 Sunflower control 0-30 1050 900 1650
4 With electrical processing 0-30 1290 1680 1740
5 Sesame control 0-30 2160 810 1470
6 With electrical processing 0-30 2025 1080 2550
7 Millet control 0-30 720 600 1320
8 With electrical processing 0-30 3780 1695 1800
9 Corn control 0-30 810 675 1530
10 With electrical processing 0-30 1155 6000 2145
Nutritional Regime, Trace Element Composition and Microbiological Nutritional Value of Soils Under Various Crops Under the Influence of
Electrical Treatment
369
Electrical treatment did not have a significant
effect on the total number of microorganisms at the
beginning of the growing season for sunflower and
millet. And in the middle of the growing season,
under sesame culture, electrical treatment did not
affect the total number of microorganisms, the best
options were corn with and without electrical
treatment. From the data obtained, it was revealed
that electrical technology had a beneficial effect on
the dynamics of microorganisms.
Table 4 presents data on the effect of electrical
treatment on the amount of ammonifying bacteria in
the soil under the rhizosphere of different crops. From
the presented data, it can be seen that cotton and corn
turned out to be the best options in terms of the
number of bacteria: at the beginning of the growing
season under the rhizosphere of cotton-51000
thousand /1 g of soil in the control variant, 114925
thousand/1 g of soil with electrical treatment.
However, it should be noted that at the beginning of
the growing season, in the phase of 3-4 real leaves and
in the budding phase, electrical treatment had a
somewhat weak effect on the number of ammonifiers
in the direction of their decrease in the rhizosphere of
sunflower, millet and sesame. For example, 64065
thousand / 1 g of sunflower soil in the control version
40320 thousand / 1 g of soil in the version with
electrical treatment.
The content of micromycetes increases in
experimental variants under all studied crops
throughout the vegetation of plants. Electrical
processing had a significant positive effect on
increasing the number of fungi in the rhizosphere of
cotton, sunflower, millet and corn. For example,
under the rhizosphere of cotton in the control variant,
75 thousand / 1 g of soil, and in the variant with
electrical treatment-80 thousand/ 1 g of soil, under
sunflower-45 thousand/ 1 g of soil –control, 60
thousand/1 g of soil – with treatment, 30 thousand/1
g of soil in the millet variant – in control, 45 thousand
/1g of soil with treatment. In the control variant and
with electrical treatment, the number of them is equal
under the corn crop – 30 thousand / 1g of soil.
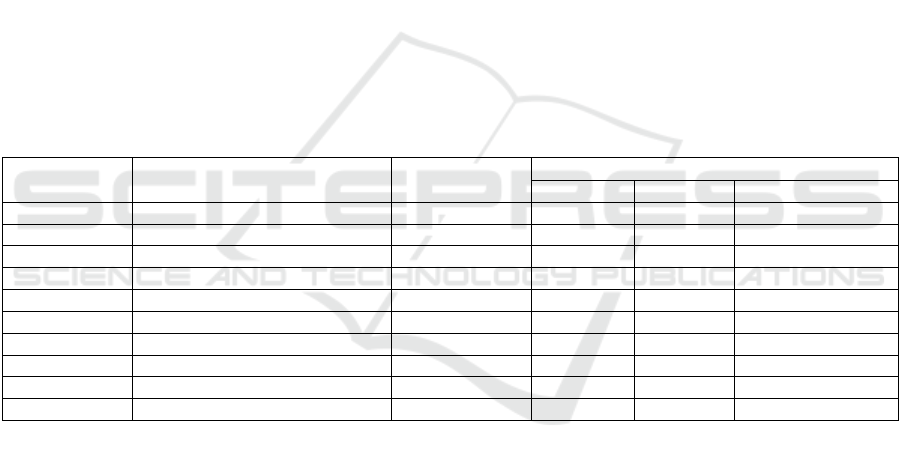
Table 4: The effect of electrical treatment on the number of micromycetes (fungi) of soils of the RCC Research Institute,
2005, 1000/1g of soil
№ Experience options Depth, cm
The phase of the growing season
June July Аugus
t
1 Cotton-control 0-30 15 75 120
2 With electrical processing 0-30 45 80 135
3 Sunflower control 0-30 15 45 45
4 With electrical processing 0-30 30 60 105
5 Sesame control 0-30 15 15 60
6 With electrical processing 0-30 30 6 75
7 Millet control 0-30 15 30 75
8 With electrical processing 0-30 15 45 120
9 Corn control 0-30 15 30 135
10 With electrical processing 0-30 30 30 150
Electrical treatment had a different effect on the
development of alligonitrophils. In the rhizosphere of
cotton, sunflower, millet and corn during their
growing season. The number of olligonitrophils
increased under the influence of electrical treatment
in the sesame rhizosphere, a decrease in the number
of olligonitrophils was observed at the beginning of
the growing season and an increase in the middle and
end of the growing season (Table 4).
Thus, the study of the quantitative distribution of
microorganisms in the studied soils showed the
dependence of the number of different physiological
groups within the same soil type on the content of
organic matter (humus), the degree of salinity and
vegetation. Changes in soil conditions significantly
affect the ordinary composition of microorganisms,
but do not affect the presence of a particular
physiological group.
In this regard, the dynamics of soil microflora
with different degrees of water availability under
various agricultural crops (cotton, sunflower, millet,
corn and sesame) has been studied.
Table 2,3,4 shows the results characterizing the
microbiological activity of soils under different crops
with different degrees of water availability.
During the research, the influence of the
anthropogenic factor of electrical treatment and
various degrees of water availability on stimulation,
suppression or indifference to soil and plant
microorganisms was studied.
I-CRAFT 2024 - 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies
370

Electrotreatment has different effects on the
microbiological activity of soils under different crops
with different degrees of water availability.
The conducted research allows us to conclude
that, in general, electrotreatment of soil, seeds and
vegetative organs of agricultural crops grown in
saline soils with varying degrees of water availability
has a positive effect on microbiological activity, on
the rhizosphere of various crops, even with moisture
deficiency (Khusanov et al., n.d).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The use of differentiated irrigation regimes in
combination with electrical technology contributed to
an increase in crop yields by 1.5-2.0 kg/ha and saving
irrigation water by 10-15%.
It was found that the effect of electrical
treatment of seeds and vegetative organs of plants
provided an increase in the yield of the tested crops.
For example, under the influence of electrical
treatment, the yield of cotton increased by 3-12%;
sunflower by 4-14%; corn by 6-15%; sesame by 10%,
millet by 3-12%. The optimal result for all
agricultural crops was obtained with a 50-60% degree
of water availability.
It was revealed that the electrical effect on the
"seed, soil, plant" system has a positive effect on the
content of assimilable forms of nitrogen, phosphorus,
potassium and trace elements in the soil, which
contributes to the creation of a favorable plant
nutrition regime.
The electrical effect had a positive effect on the
microflora of the rhizosphere of cotton, increasing the
content of beneficial and reducing the number of
harmful microorganisms in the soil, improved the
phytosanitary condition of the soil by reducing
microscopic mold fungi and increasing the number of
actinomycetes.
REFERENCES
Mukhammadiev A. Electrical processing of cotton.
Diss. doctor. Tech. sciences. Tashkent Nau, 1992
500 p.
Khuyaev J.H. Mukhammadiev A. Holliev A.E.,
Ataeva G.S. Hydroelectric power plant
hydroelectric power plant hydroelectric power
plant electronegativity. // Analytical kime and
ecology of muammolari. Samarkand, 2000
Mukhammadiev A. Turapov I., Sadikova G.
Tuprakka ishlow berishning tuprok a
microorganism, an active effect. // Uzbekistan
agrarian fan newsletter. 2002, №6
Sodikova G. Turapov I. Influence of electrical
treatment on the content of nutrients in the post
office. Tashkent 2004
Mukhammadiev A. (Head of work) and others.
Scientific and technical report on the project.
GNTP 11.1.7. Migration of chemical elements in
the "soil, water, plant" system under the
influence of electrical treatment. Tashkent, 2003,
49c
Mukhammadiev A., Kadyrova D.N., Umarova G.,
Staparova B.Y. Study of the physico-biological
mechanism of electrical action on cotton.
Bulletin of Agrarian Science. Uzbekistan 2001.
Khusanov R., Kosymov M., Mambetnazarov B.,
Turopov I., Mukhammadiev A., Saidova M.
Problems of stabilization of agricultural
development in arid zones and lower reaches of
the Amu Darya in conditions of low water
Nutritional Regime, Trace Element Composition and Microbiological Nutritional Value of Soils Under Various Crops Under the Influence of
Electrical Treatment
371
