
Biological Characteristics of the Causative Agent of Cotton
Gommosis Xanthomonas Campestris Var Malvacearum
Sh. Gulmurodova
a
and R. Sattarova
b
Tashkent State Agrarian University, 100140, University str. 2, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Cotton Gommosis, Xanthomonas Campestris, Pathogenic Features.
Abstract: The following article is devoted to the study of morphological-cultural and pathogenic features of six strains
of the causative agent of cotton gommosis - Xanthomonas campestris var malvacearum, isolated by us from
cotton varieties Sultan and S–6524. The study of the fermentation of carbohydrates and alcohols of six strains
of Xanthomonas campestris var malvacearum showed that all the strains we studied ferment carbohydrates
and alcohols to form acid, have the ability to break down protein and peptone to form hydrogen sulfide, and
cause diseases of cotton gommoses. The study of the morphology of Xanthomonas campestris var
malvacearum showed that the causative agent of cotton gommosis has flagella, capsule, shell and nucleoids,
and polymorphism of both the individuals and their nuclear apparatus is characteristic of diurnal cultures
.
1 INTRODUCTION
As known that diseases of cotton significantly reduce
its yield both in quantity and quality, worsen the
textile properties of the fiber and the quality of the
seeds sown. The threat to the harvest of raw cotton
from numerous diseases constantly exists. Gommosis
causes significant damage to cotton production.
Nowadays, cotton gommosis is registered in
almost every country where cotton is grown. This
disease is considered as a serious threat to cotton in
India, Pakistan, China, the countries of the former
Soviet Union, South America, and Australia.
Gommosis was first described by G.F. Atkinson
in 1891. The first report on the appearance of cotton
gommosis in Central Asia was made by R.R.
Schreder in 1903.
Gommosis affects the aboveground organs of
cotton cotyledons and real leaves, stipules, stems,
bracts, flowers, boxes. The signs of the disease in all
parts of the plant are basically the same. In the first
stage of the disease, the affected parts are covered
with oily round, angular or elongated spots, which
then dry out, darken, become covered with dried
mucus and die off.
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-4792-8451
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-2161-5867
In 1901, Erwin Smith established the bacterial
origin of cotton gommosis and isolated it into a pure
culture.
The author gave the first scientific name to the
causative agent of cotton gommosis Bacterium
malvacearum. Bergey (1936) et al called Phytomonas
malvacearum. In 1949, M.A.Krasilnikov restored its
former name Pseudomonas malvacearum, noting as a
characteristic indicator of the genus Pseudomonas the
polarly located flagella of non–spore-bearing rods,
the presence of fluorescent pigment and some other
properties, not considering it advisable to isolate
phytopathogenic forms into a special genus -
Phytomonas.
V.P.Israilskiy (1960) includes the causative agent
of gommosis in the genus Xanthomonas isolated by
Stoughton, which is characterized by abundant mucus
formation, yellow color of colonies and monotrichial
flagellation.
Many scientists have studied the biological
properties of cotton gommosis (Askarova, 1960;
Babayan, 1963; Wickens, 1961; Yogan, 1960; Jones,
1983; Grigoryants et al. 2009; Bobonazarov, 2012).
X. malvacearum according to W.H. Burkholder
(1932) does not form acids on dextrose, sucrose and
lactose.
338
Gulmurodova, S. and Sattarova, R.
Biological Characteristics of the Causative Agent of Cotton Gommosis Xanthomonas Campestris Var Malvacearum.
DOI: 10.5220/0014268800004738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies (I-CRAFT 2024), pages 338-344
ISBN: 978-989-758-773-3; ISSN: 3051-7710
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

According to Nizametdinova (1968), the
causative agent of cotton gommosis belongs to a
weak acid-forming agent.
X. malvacearum as an acid-forming agent was
described by N.A. Krasilnikov, Bergey, Israilskiy,
Nizamitdinova.
Other researchers like, Smith, Yevis, Yachevskiy,
Gorlenko think that, the causative agent of gommosis
does not form acids on environment with sugars.
Data on the morphological-cultural properties of
the causative agent of cotton gommosis is limited and
contradictory.
Therefore, the literature data indicate that many
researches have been devoted to the study of the
morphological-cultural properties of the causative
agent of cotton gommosis (Verderevsky, 1960;
Babayan, 1963; Marupova, 1968; Sattarova, 1973;
Shukri Mohamed El Gremi, 1990; Rashidov, 2003;
Fallhzaden, Ahmadzaden, 2010; Gulmurodova,
2023).
However, the analysis of the literature materials
indicates the need to continue research on the
morphological-cultural characteristics of the
pathogen causing cotton gommosisn world practice,
it has been proven that in pneumatic diluents it is most
acceptable to use landing discs rotating along a
vertically longitudinal surface, and most companies
producing pneumatic diluents produce diluents
equipped with just such discs. The research paper
considers the main parameters of the landing disc,
which rotates on a vertically longitudinal surface, that
is, on a horizontal axis located transversely to the
direction of movement of the seal (Fattah, 1976;
Babanazarov et al., 1993; Babayan, 1963;
Verderevsky, 1960; Grigoryats et al., 2009;
Beltyukova, 1968).
It is known that in order to obtain higher crop
yields, it is necessary to evenly distribute seeds
throughout the field, that is, plant them evenly to the
desired depth, ensuring a given range and distance to
the node. In world practice, when using seeds
prepared with high quality, seed sowing is used in a
clear norm, one seed per slot.
In addition to the general requirements, specific
planting requirements are developed according to the
climate and soil of each area. In particular, the soil
and climatic conditions of Uzbekistan are such that in
the spring sowing period, after precipitation, in most
cases tar appears in the soil, and seeds planted in one
grain risk getting stuck under it, failing to split the
resin.For this reason, when planting rotten seeds or
other seed materials, it is advisable to sow them in a
slot way, that is, laying 2-3 seeds in each slot
(Gulmurodova & Sattarova, 2023; Gorlenko, 1966;
Marupova, Sattarova, 1973; Rashidov et al., 2003;
Gremi, 1990).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The objects of the research were samples of diseased
cotton plants of S-6524 and Sultan variety affected by
gommosis, as well as isolates of isolated by us from
diseased cotton plants.
Isolation of the causative agent of cotton
gommosis was carried out from cotyledon leaves
affected by gommosis according to the method of K.I.
Beltyukova (1968).
A section of cotton leaf tissue affected by
gommosis was placed for 2-3 minutes in 96% alcohol,
which was then thoroughly washed with sterile water
and placed in Petri dishes with potato–glucose agar.
Pure cultures of phytopathogens were obtained by
three-times re-sowing of individual colonies on solid
nutrient environment. The appearance and size of
colonies were determined on various nutrient
environment.
Cell morphology and size, Gram staining, were
studied using light microscopy.
The cultural-morphological biochemical and
physiological properties of microorganisms were
studied according to generally accepted methods and
tests described in the relevant manuals (Yegorov,
1976; Bergey S of terminative bacteriology1974).
The morphology of colonies and cells was studied
on potato agar, meat– peptone broth and Ashby
nitrogen-free medium. The shape and size of colonies
and cells were determined. The colony structure was
studied under a magnifying glass and a microscope.
The cultural properties were determined by the
nature of growth on oblique potato agar, meat peptone
broth, gelatin, potato slices.
In order to study the biochemical properties of the
studied strains, X.malvacearum was sown on a color
row containing glucose, sucrose, lactose, maltose,
levulose, xylose, arabinose, mannitol, glycerin,
dulcite, sorbitol, sallicin in an amount of 0.5%. The
results were taken into account on days 3,5,7.
Gelatin was used to identify proteolytic
properties. Sowing on gelatin was performed by
injection of a loop. The culture tubes were left at room
temperature and scanned 2-3 times a week.
The formation of ammonia was established by
reaction with the Griss reagent. Indole was
determined by the method of Morelli and Beltyukov
(1968) using strips of filter paper impregnated with a
saturated solution of oxalic acid. In the presence of
indole, the indicator paper is colored red.
Biological Characteristics of the Causative Agent of Cotton Gommosis Xanthomonas Campestris Var Malvacearum
339

Nitrate reduction was determined by the reaction
of the studied culture sown in a meat-peptone broth
containing 0.1% potassium nitrate with Griss reagent.
To identify the ability of bacteria to hydrolyze
starch, they were sown with strokes on meat –
peptone agar containing soluble flagella was detected
by staining a suspension of Xanthomonas
malvacearum with silver nitrate according to the
Nefedov method (Peshkov, 1855). The capsule was
stained using the Anthony method (Peshkov, 1955).
The capsule was colored using the Anthony
method. The smears are dried in air and stained
without fixing in the cold with a 1% solution of
crystal violet, the paint is washed off with a 2%
solution of copper sulfate, dried and washed with
water.
The coloring on nuclear elements was carried out
as follows: the smears were dried in air, fixed with
Carnois liquid for 15 minutes, placed in a wet
chamber, a ribonuclease solution was poured on top
of the smears at a concentration of 2 mg/ml and
placed in a thermostat for 1 hour at t 37
0
C. They were
washed off under running tap water and painted
according to Gimsa for 1 hour at 37
0
С.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We have isolated six strains of Xanthomonas
campestris var malvacearum from cotton leaves of
Sultan and S-6524 cotton varieties affected by
gommosis.
The structure of X.malvacearum cells was studied
by light microscopy. The method of prints from the
surface of the agar was used for the work.
X.malvacearum has mobility, there was used the
method to clarify the nature of flagellation. As a result
of the staining of X.malvacearum to identify flagella,
it was found that Xanthomonas malvacearum has
monotrichial flagella.
There was also conducted research on staining for
nuclear elements with pretreatment with RNA – aza.
Smears prints were prepared through 2, 6, 10, 12, 14,
and 24 hours after sowing on the surface of potato
agar.
To make completely sure that the well–colored
granules and strands located in the center of
X.malvacearum cells are nucleoids and have a DNA
nature, the preparations were treated before staining
(azur – eosin) first with RNA aza and then with DNA
aza. As a result of such treatment, preparations
consisting of cells devoid of any colored structures
were obtained.
In four-hour cultures, the length of individuals
increases. In most individuals, the nucleotides are in
the stage of division. There are cells with three
nucleotides.
Starting from six-hour cultures, the
polymorphism characteristic of X. malvacearum
manifests itself, reaching its greatest development in
24 hour-cultures. Giant individuals (4-9 mmc) with
strands of nuclear matter appear in the smears from
the seals.
In the studied isolates, the cells of Xanthomonas
campestris var malvacearum are small in shape,
slightly tapering towards the end, movable rods 1.5
mk long, 0.5 mk wide, with rounded ends, nonporous,
gram-negative, forming a capsule. Some strains have
cells 9 microns long in 18-hour or daily cultures.. The
presence of long chains of cells indicates a significant
polymorphism of the microorganism.
The optimal temperature for growing X.
malvacearum culture in laboratory conditions is 20-
30
0
С. The morphology of young cells (6-10 hour)
cultures varies when growing on different nutrient
media.
On potato agar, the culture of Xanthomonas
campestris var malvacearum has the appearance of
slender sticks. On meat–peptone agar, the cell
contours are vague, indistinct, the cells are irregularly
shaped, short and strongly thickened. On Ashby's
nitrogen-free environment, the sticks are large and
slender. The measurement of bacteria grown on
various media gave the following results: on meat–
peptone agar -1,9-2,5/0, 8-1,0, 8-1,0 mk, on potato
1,25 – 1,5 /0,5 – 0,8 mk, on pepton – 1,3 -1,5/0,9 –
1,0 mk, on Ashby – 1,8 /0.3 – 1 mk.
On sterile potato slices with a small amount of
water, the growth of X.malvacearum is moistly
convex, shiny, pale yellow, waxy yellow with growth,
a brown plaque forms, the potatoes darken.
The growth on oblique potato agar is good,
strong, spreading, convex, the growth surface is
smooth, moist, the edges are even, the pigment is
yellow.
The development of X.malvacearum cultures on
meat-peptone broth causes uniform turbidity of the
medium. At the bottom of a small slimy sediment,
turbidity rises when shaken. A loose, granular film
forms on the surface of the meat-peptone broth.
The morphology of colonies of X.malvacearum
was also studied on various media. On potato agar in
Petri dishes, X.malvacearum bacteria form round,
flat, soft, pale yellow colonies with smooth edges,
which darken on 5-7 days. The diameter of adult
colonies is 1-10 mm. In transmitted light, colonies
have a homogeneous structure, sometimes
I-CRAFT 2024 - 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies
340

concentric, radial, and spindle-shaped. On days 7-10,
a seal forms in the center of the colonies. On meat-
peptone agar, colonies are rounded, pale yellow,
darken with age. On the Ashby mineral medium, the
colonies are small, transparent, shiny, the edges of the
colonies are smooth in the transmitted light and have
a granular structure.
When all strains of X.malvacearum were sieved
on potato agar to obtain individual colonies, 4 types
of colonies were found: 1. Smooth, round, shiny,
convex colonies, yellowish–green, with smooth
edges, in the transmitted light there is a seal in the
center; 2. Slightly convex, shiny, slimy, greenish–
yellow, the edges are smooth, transparent, concentric
circles are visible in the transmitted light; 3. Large,
flat, shiny grayish-yellow, the edges are transparent,
structures in the form of grains are visible in passing
light, which are located radically along the edge and
acquire a fusiform shape; 4. Convex, round, slimy,
bright yellow, smooth edges, homogeneous in
passing light.
Type I and II colonies are most characteristic of
the causative agent of cotton gommosis Xanthomonas
campestris var malvacearum and contains 80%.
At this point, the morphological properties of the
colonies were preserved, and no further dissociation
was observed. According to the literature,
Xanthomonas malvacearum forms acid on sugars,
peptonizes and coagulates milk, and hydrolyzes
starch (Gorlenko, 1961; Babayan, 1963).
The study of the fermentation of some
carbohydrates and alcohols showed that the studied
strains of Xanthomonas malvacearum slightly differ
in their ability to ferment individual carbohydrates
from the control strain. As a control strain, we used
the data given in the determinant by N.A.Krasilnikov,
Bergey.
The control strain forms acid without gas on
glucose, sucrose, lactose, galactose, xylose, raffinose,
glycerin, does not ferment arabinose, rhamnose,
dulcite and mannitol, coagulates and peptonizes milk,
hydrolyzes starch, indole and hydrogen sulfide does
not form.
The studied strains of Xanthomonas
malvacearum, with the exception of strains 2 and 5,
do not form acid on xylose. Only strains 1 and 3 form
acid on maltose, which brings them closer to the
control one. Strain 3 does not ferment sucrose (Table
1).
As a result of studying the proteolytic activity, it
was found that the studied strains of Xanthomonas
malvacearum have the ability to cleave protein and
peptone with the release of hydrogen sulfide (Table
2), and some strains (1, 2, 3) intensively secrete
hydrogen sulfide, others (5, 6) have a weak reaction
to the formation of indole in all strains of
Xanthomonas campestris var malvacearum is
negative.
Due to N.A. Krasilnikov, M.V. Gorlenko, V.P.
Israelsky, the causative agent of cotton gommosis
does not emit hydrogen sulfide and indole.
Xanthomonas malvacearum cultures slowly
dilute the gelatin, which remains transparent. Strains
1, 2, 3 dilute gelatins more strongly than strains 5 and
6 (tab 2).
All researched strains of Xanthomonas
malvacearum have proteolytic activity and
saccharolytic properties. Xanthomonas malvacearum
strain peptonizes and coagulates milk with the
exception of the fifth strain, which only peptonizes
milk. The rate and intensity of hydrolysis in all strains
of Xanthomonas malvacearum is different; strains (1,
2, 3) hydrolyzed starch already on the 3rd day, and (5
and 6) – on the 7th day.
In order to identify reducing properties, a litmus
serum was used, on which cultures develop in
different ways. Some strains (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5) alkalize
the medium, others (2 and 6) do not change it (tab 2).
Microorganisms are able to restore nitrates.
However, according to N.A.Krasilnikov (1949),
Xanthomonas malvacearum does not restore nitrates.
According to the data, only strains 2 and 4 are capable
of reducing nitrates to nitrites.
In Clark’s medium, no strain of Xanthomonas
malvacearum secretes acetyl–methyl–carbinol.
On the Klodnisky–Peshkov medium, all strains
grew throughout the entire thickness of the medium.
Consequently, Xanthomonas malvacearum is a
facultative anaerobe.
The studied strains of Xanthomonas
malvacearum do not hydrolyze fats, i.e. they are not
capable of forming lipase.
Cultures obtained from different types of colonies
differ in cultural and physiological properties.
Strains differing in colony morphology differ
from the main strains in some cultural-physiological
features (Table 3).
In cultures isolated from colonies of types II and
IV (strains 3/II, 3 IV), proteolytic activity is more
pronounced than in the main strain 3.
In cultures isolated from colonies of types I and
III (strains 2 I and 2 III), proteolytic activity turned
out to be weaker than that of the main strain 2. In
addition to this, strains 2 (I) and 2 (III), unlike the
main one, do not dilute gelatin and do not form acid
on xylose.
Biological Characteristics of the Causative Agent of Cotton Gommosis Xanthomonas Campestris Var Malvacearum
341
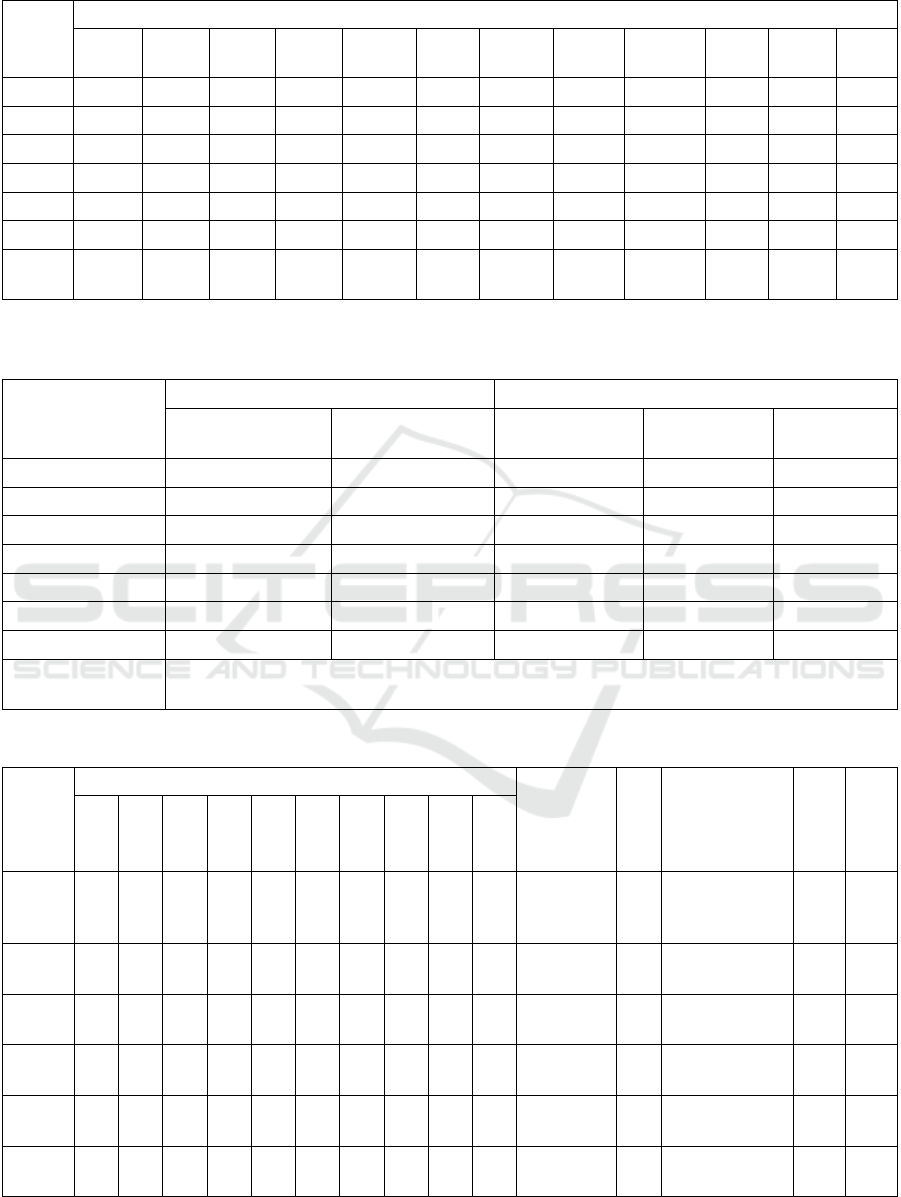
Table 1: Fermentation of carbon sources by various strains of Xanthomonas campestris var malvacearum.
Strains Omelyanskiy medium
Glucos
e
Sucros
e
Lactos
e
Maltos
e
Levulos
e
Xylos
e
Mannit
ol
Glyceri
n
Arabinos
e
Dulcit
e
Sorbit
ol
Salici
n
1 + + + + + - - + - - - -
2 + + + - + + - + - - - -
3 + - + + + - - + - - - -
4 + + + - + - - + - - - -
5 + + + - + + - + - - - -
6 + + + - + + - + - - - -
Contr
ol
+ + + + + + - + + - - -
Note: + existence of acid, - absence of acid
Table 2: Reducing and proteolytic properties of Xanthomonas campestris var malvacearum.n
Strains
Reducing properties Proteolytic properties
Nitrate recovery
Reduction of
litmus serum
Release of
hydrogen sulfide
Dilution of
gelatin
Starch
hydrolysis
1 + AF ++++ +++ +++
2 - AF ++++ +++ +++
3 - AF ++++ +++ +++
4 + AF +++ ++ ++
5 - AF ++ + +
6 - AF ++ ++ ++
Control N/A N/A - ++ ++
Note
AF - change of the medium towards alkali formation
+ - intensity of proteolytic properties, starch hydrolysis
Table 3: Cultural-biochemical properties of colonies differing in morphology Xanthomonas malvacearum.
Strains Omelyanskiy medium
Meat
p
eptone
b
roth
Litmus
serum
Mil
k
Gelatin
Hydrogen
sulfide
Glucose
Sucrose
Lactose
Maltose
Mannitol
Dulcite
Sorbitol
Mannose
Xylose
Glycerin
3
+ - + + - - - + - -
Wall film
mud
sludge
AF Peptonizes ++ +
3 (II)
+ - + - - - - + - -
Small film
of mud
AF Peptonizes +++ ++
3 (IV)
+ - + - - - - + - -
Small film
of mud
AF
Peptonizes and
coagulates
+++ +++
2
+ + + - - - - + - -
Small film
of mud
- Peptonizes ++ +++
2 (I)
+ + + - - - - + - -
Muddy
film
-
Coagulates,
peptonizes
- +
2 (III)
+ + + + - - - + - -
Mud is a
small film
-
Peptonizes and
coagulates
- +
Note: AF - alkali formation + - presence of hydrogen sulfide acid, reduction of nitrates, dilution of gelatin.
I-CRAFT 2024 - 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies
342

The main criterion for the belonging of unknown
crops to the species Xanthomonas campestris var
malvacearum is their pathogenicity to cotton.
Regarding to this, we studied the ability of
Xanthomonas malvacearum strains isolated by us to
cause the incidence of cotton gommosis. For this
purpose, artificial contamination of Sultan and S-
6524 cotton seeds was carried out.
The results of artificial infection of cotton seeds
with the studied strains of X. malvacearum showed
that all strains cause cotton disease with gommosis,
but not to the same extent (Peshkov, 1955; Vinay,
2013; Fallahzadeh & Ahmadzaden, 2010; Eholvel &
Kurundkar, 2007; Yogan, 1960; Hillocks, 1992;
Jnnes, 1992; Wickens, 1961; Saidova et. al., 2023).
The disease occurred after seven days, from the
beginning of the experiment. The clearest results
were observed in 15-day-old seedlings.
Strains 1, 2, 3 strongly affected Sultan cotton. The
cotyledon leaves were completely covered with large
oily spots.
Strains 5 and 6 were weakly affected. 2-3 small
oily spots appeared on cotyledon leaves.
The difference in the degree of pathogenicity was
also manifested in varieties S-6524.
Strains 1, 2, 3 affected the studied varieties more
strongly, more intensively, and 5, 6 weaker.
Consequently, all the studied strains isolated from
cotton leaves belong to the species X. malvacearum,
because with artificial infection of seeds, symptoms
of cotton gommosis appeared on cotyledon leaves.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the experiments of the conducted studies, it
can be concluded that all cultures isolated from cotton
leaves affected by gommosis are representatives of
the species Xanthomonas campestris var.
malvacearum, since they are similar to the species in
terms of the main cultural morphological,
physiological and pathogenic signs. Xanthomonas
malvacearum described in the determinants of
Bergey and N.A. Krasilnikov. While studying the
cytology of Xanthomonas malvacearum, we found at
the level of light microscopy that Xanthomonas
malvacearum has flagella, capsule and isolated
nucleoids.
X. malvacearum cells aged 18-24 hours are
characterized by the presence of polymorphism, both
of the individuals themselves and their nucleoids.
Strains differing in morphology of the colony differ
from the main strains in some cultural-morphological
features. It’s worthy to note that some of the
differences we have established between X.
malvacearum strains may be strain-specific features
rather than species-specific. To identify the causative
agent of cotton gommosis, we need to conduct
additional studies at the molecular level. Research in
this direction will continue
.
REFERENCES
Abdel Fattah, A.A., 1976. The study of the cytopathological
process of immunity and the role of peptic enzymes in
the disease of cotton gommosis. Abstract of the
dissertation of the Candidate of biological sciences.
Tashkent, 20-24.
Babanazarov A., Autonomov, V.A., Khasanov, O.,
Allakumiev, B., Musaeva, K., 1993. The effect of germ
in the resistance of cotton sprouts to root rot diseases
selection of cotton genetics, a set of germ and alfalfa.
Tashkent, p. 139-142.
Babayan, A.A., 1963. Gommosis of cotton. Yerevan.
Verderevsky, D.D., Prinu, Ya.I., 1960. Diseases and pests
of cotton in Moldova and measures to combat them.
Chisinau, 155-158.
Grigoryats, E., 2009. Gommoz – a dangerous disease of
cotton seeds. Journal of Plant Protection and
Quarantine, 2, 10-11.
Beltyukova, K.I., 1968. Bacterial diseases of plants and
methods of combating them. Kiev, ed. Naukova
Dumka.
Gulmurodova, Sh.D., Sattarova, R.K., 2023. The effect of
inter-row processing of acorns against root rot disease.
Journal of Agro Chemistry and Plant Quarantine, 2,
82-83.
Gorlenko, M.V., 1966. Bacterial diseases of plants.
Moscow, Higher School, 29.
Marupova, M.A., 1988. Gommosis of cotton and the
development of measures to combat. Dissertation of the
candidate of biol. sciences, Leningrad, 10-23.
Sattarova, R.K., 1973. Cytophysiological features of the
causative agent of cotton gommosis – Xanthomonas
malvacearum. Dissertation of the candidate of biol.
sciences. Tashkent, 10-26.
Rashidov, M., Khakimov, A., Khujaev, Sh., Mukhamedov,
A., 2003. Protection of cotton from disease and pests.
Journal of Agriculture of Uzbekistan, 6, 12-13.
Ali Gremi, S. M., 1990. The effect of some soil antagonists
on phytopathogenic bacteria and cotton productivity.
Dissertation of the Candidate of Biological Sciences
Tashkent, 10-24.
Peshkov, M.V., 1955. Cytology of bacteria//Moscow, ed.
USSR Academy of Sciences.
Vinay, B., Raghavendra, Siddalingaiah, Y., Sugunachar,
N.K., Nayak, C., Ramachandrappa, N.S., 2013.
Jnduction of systemie resistance by biocontrol agents
against bacterial blight of cjtton caused by
Xanthomonas campestris pv malvacearum. Plant/
Patholigi, 2, 59-69.
Biological Characteristics of the Causative Agent of Cotton Gommosis Xanthomonas Campestris Var Malvacearum
343

Fallahzadeh, V., Ahmadzaden, M., 2010. Induction of
systeme xesistance to fluorescent pseudomonads of
cotton rhizophore. Journal of Agricultural Technology,
6 (2), 341-348.
Eholvel, V.M., Kurundkar, B.P., 2007. Transmission of
Xanthomonas axanopodis pv. malvacearum through
infected seed. Agricsci Digest, 27(1), 41-43.
Yogan, C., 1960. Anestimate of the effect of seed treatment
in reducing cotton crop losses caused by Xanthomonas
malvacearum (E.F.Smith) Dow in Uganda. Empire
Cotton Grousing Review, 37, 241-255.
Hillocks, R.J., 1992. Cjtton Diseases. Walli u gford, UK,
CAB Juternational, 415.
Jnnes, N.L., 1983. Bacterial blight of cotton. Biological
Reviens, 58, 157-176.
Wickens, G.M., 1961. Bacterial blight of cotton: its
iffluence on yield. Empire Cotton Growing Review, 38,
241-257.
Saidova, M., Alimova, F., Tursunbaev, S., Kulmuradov, D.,
& Boltaeva, M., 2023. Influence of the shape of the disc
slots of the seeder on the suction force of the vacuum
for precise sowing of seeds. IOP Conference Series:
Earth and Environmental Science, 1284(1), 012014.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1284/1/012014.
I-CRAFT 2024 - 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies
344
