
Choosing the Optimum Modifier to Increase the Durability of Parts
Made of 110g13l Steel
Shukhrat Chorshanbiev
a
, Nodir Turakhodjaev
b
, Ibrokhim Nasirkhujaev
c
and Asrorkhan Saidakhmatov
d
Tashkent State Technical University, 100095, University str. 2, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Modifier, Steel, Durability Optimization
Abstract: In this article, the production of high-quality, abrasion-resistant, high-strength grinding cones and other
similar details and heavy industrial products for machine-building production enterprises that meet world
standards sets an important task for experts and scientists in this field to improve the existing equipment and
technology. It is important to improve the existing technology and technologies in this field. In turn, the
increase in the level of improvement of equipment in machine-building production enterprises also requires
paying great attention to the quality of metals. It is shown that steel plants, as a rule, do not have special
equipment for processing steel. Under these conditions, the only and very effective way to practically improve
the quality of steel is to process the liquid metal in the steel casting department with special complex modifier
alloys. Modification of metals and alloys (its variety) is a deep process of their presence, which actively affects
the state of metal solutions during crystallization by introducing small additions of substances (modifiers) that
lead to changes in the morphology of mirror inclusions.
1 INTRODUCTION
In production enterprises of the Republic of
Uzbekistan, measures are being taken to obtain high-
quality cast products during the period of liquefaction
of steels with the help of electric arc and induction
furnaces. In production enterprises of the Republic of
Uzbekistan, measures are being taken to obtain high-
quality cast products during the period of liquefaction
of steels with the help of electric arc and induction
furnaces. In this regard, it is important to increase the
priority of research on the improvement of
technologies that provide resource and energy
efficiency in the liquefaction of steels widely used in
industry.
Mechanical engineering consists of a number of
technological processes in production enterprises that
form a unique technological chain. This chain is
closely related to the work unit of each unit and the
work quality of the preceding machines. Considering
this issue, it can be concluded that the influence of
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-7690-7089
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-4970-5785
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6126-4028
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-2864-9699
technological chain equipment on the quality
indicators of machine-building enterprises and heavy
industrial products is great. Therefore, the more
efficient operation of machine-building enterprises
and heavy industry technological equipment without
damage depends to a large extent on the strength of
their details. This mainly requires studying the
working process of the parts that rub against each
other (Dubinin, 1961, Nasser, 2002).
Many scientific practitioners and experts know
that metals used in technology are mainly divided into
two groups - ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Ferrous
metals include iron and its compounds (cast iron,
steel, ferrocolates). The rest of the metals and their
alloys make up the group of non-ferrous metals.
Until now, iron and its alloys, considered the main
material of machine building, are of special
importance among metals. 90% of metals produced
worldwide are iron and its alloys. This is explained
by the fact that ferrous metals have important
physical and mechanical properties, as well as the fact
264
Chorshanbiev, S., Turakhodjaev, N., Nasirkhujaev, I. and Saidakhmatov, A.
Choosing the Optimum Modifier to Increase the Durability of Parts Made of 110g13l Steel.
DOI: 10.5220/0014261200004738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies (I-CRAFT 2024), pages 264-268
ISBN: 978-989-758-773-3; ISSN: 3051-7710
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

that iron ores are widely distributed in nature, and the
production of cast iron and steel is cheap and
uncomplicated.
The fact that metals have the ability to dissolve
various elements allows the atoms of the substance
surrounding the metal to diffuse into the metal at high
temperature, as a result of which the chemical
composition of the metal surface layer changes.
Diffusion of atoms into a metal is a chemical process,
but temperature plays a major role during this
process, so the diffusion process cannot be considered
a pure chemical process. Such treatment, which
changes the chemical composition of the surface layer
of the alloy, is called chemical-thermal treatment.
When we study the literature of our country and
foreign scientists, the types of chemical-thermal work
are described in detail. In recent years, the method of
changing the structure of alloys simultaneously with
working under pressure is being used more and more
widely. Such processing of alloys is called
thermomechanical processing. When the alloy is
deformed, not only its appearance changes, but also a
coating is formed in it, this coated alloy is heat
treated. Therefore, thermomechanical indicators
should also be included in the literature review
process, which is characteristic of our
various
scientific researches on thermal indicators
(Mirboboev et al., 2004).
2 METHODS
It is important to improve the modern machine-
building industry in the world, to create new
improved technologies, machines and mechanisms
that meet global requirements for various branches of
production, to replace competitive and imported
industries, to conduct deep fundamental research, and
to solve current scientific and technical issues. Also,
the production of high-quality, high-strength and
high-capacity heavy industrial products that meet
world standards has set an important task for experts
and scientists in this field.
In this regard, special attention is paid to the
development of scientific centers of developed
countries, including Russia, Germany, USA,
England, Japan, China and other countries, in order to
create competitive techniques and technologies in
production. In particular, with the help of modifiers
of various composition, they carry out a number of
scientific and research works on obtaining high-
quality castings from parts with high strength
properties of steel and increasing the service life of
mechanical engineering parts made from them.
Scientists from all over the world have conducted
extensive research on the possibilities of heating and
cooling the alloy, making changes to its internal
structure, chemical, physical and mechanical
properties, changing the structure of steel by heating
and cooling, and achieved results.
Modern engineering is the main consumer of
metals produced in our country. A large number of
machine parts and accessories are made of metals in
the machine tool industry, in the automotive and
aviation industries, in electronics and radio
engineering.
Metals used in technology are mainly divided into
two groups - ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Ferrous
metals include iron and its compounds (cast iron,
steel, ferrocolates). The rest of the metals and their
alloys make up the group of non-ferrous metals.
Until now, iron and its alloys, considered the main
material of machine building, are of special
importance among metals. 90% of metals produced
worldwide are iron and its alloys. This is explained
by the fact that ferrous metals have important
physical and mechanical properties, as well as the fact
that iron ores are widely distributed in nature, and the
production of cast iron and steel is cheap and
uncomplicated (Nurmurodov et al., 2016,
Torakho'jaev et al., 2018).
To stay competitive in the steel industry,
steelmakers use a variety of production methods to
reduce production costs without compromising
product quality. In steel production, the production
process plays an important role in its purity. Recently,
the increase in the requirements for the level of purity
requires the optimization of the production process to
meet this demand. Often, the types and distribution of
non-metallic inclusions in steel determine the purity
of the steel. For optimization, it is necessary to fully
evaluate the production process, non-metallic
inclusions in steel, and extensive work is being
carried out by world researchers to implement many
measures to control and clean up non-metallic
inclusions in steel.
Grinding cones are widely used in metallurgical
enterprises of the Republic of Uzbekistan, including
ore crushing units at the enterprise "Almaliq KMK".
As a result of the rapid consumption of used grinding
cones and many similar parts, their service life is not
up to the required level. The average service life of
one grinding cone is 3 months. Therefore, in the
process of their preparation, a number of measures are
being taken to increase the strength of surfaces prone
to cracking, and new developed technologies are
being put into practice. One of such technologies
consists in selecting and adding optimal modifiers
Choosing the Optimum Modifier to Increase the Durability of Parts Made of 110g13l Steel
265

during the melting process to increase the mechanical
properties of the obtained cast products, as well as
increasing its dispersion, durability and hardness as a
result of thermal treatment.
110G13L steels are melted in electric arc furnaces
DS-5MT, DSP-3 in the foundry of TsRMZ JSC
"Almalik KMK" (Ikramov, 2003; Pakhadnya
&Turkevich, 2013).
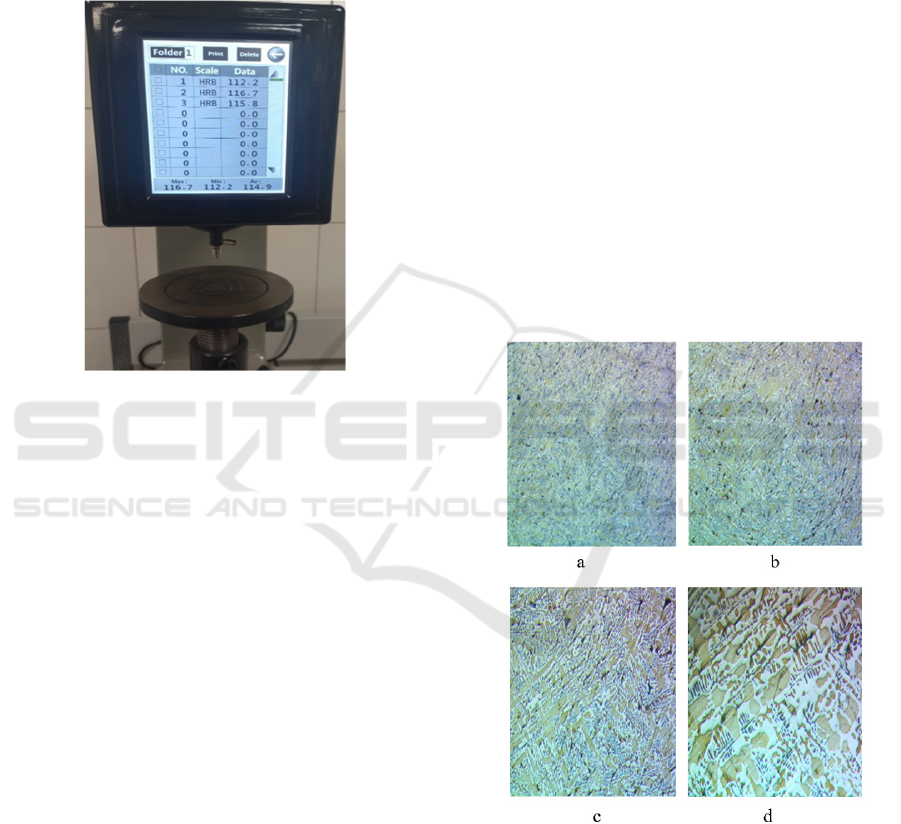
Figure 1: “ТР-5018 PAC Tochline” hardness measurement
machine.
In accordance with the requi- rements of GOST
977-88, in the casting workshop of the Central Repair
Mechanics Plant, a mixture of various chemical
elements was melted into 110G13L steel in an electric
arc furnace DS-5MT, and we took ingot samples
taken as samples. In order to test the hardness of this
solution and in the induction melting furnace
(Induction Melting Machine), several researches
were carried out. We took ferrochrome as an
example, which gave the best results from these
studies. We added 0.5% to 3% of ferrochrome to the
melting solution as a modifier. When added to steel,
ferrochromium provides several of the following
advantages, i.e. increases hardness and strength
improves anti-corrosion properties, increases fluidity,
and increases oxidation resistance at high
temperatures.
On January 26, 2024, cutting and turning of
castings 60x40x20 mm in the laboratory of Tashkent
State Technical University, Department of "Casting
Technologies" was carried out for 2 hours and 45
minutes in the mechanical shop of the Central Repair
Mechanical Plant of "Almaliq KMK" JSC on the
S11MV universal lathe. increased and prepared in
order to determine the hardness, chemical properties
and structures of these metals.
The hardness of cast layers prepared by the most
modern metal-102 stationary Rockwell hardness
tester was checked at the branch of the federal state
autonomous higher educational institution "Misis
National Technological Research University" in
Olmaliq, Republic of Uzbekistan. According to Gost,
designated as NV-186-229.
In this device, the hardness of the metal made of
three parts was measured, it was found to be 116.7
when measured from the middle, and 112.2 and 115.8
when measured from the two ends. When we take the
average of all sizes, 114.9 HRB and NV-321.
(Tursunbaev et al., 2023, Tursunbaev et al., 2024).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Together with the professor scientists of Tashkent
State Technical University, steel constructions of
brand 110G13L and elements added to this steel as a
ferrochrome modifier were examined under a special
microscope and the desired results were obtained.
Figure 2: The appearance of the modified 110G13L brand
steel structure in different sizes. a- 110G13L-view of the
branded steel structure with a size of 5 µm
;
b- 110G13L-
the appearance of the branded steel structure with a size of
10 µm; c- 110G13L-the appearance of the branded steel
structure with a size of 20 µm; d- 110G13L-view of the
branded steel structure with a size of 50 µm.
As the amount of manganese in carbon steels
increases, austenite in the structure begins to stabilize
I-CRAFT 2024 - 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies
266
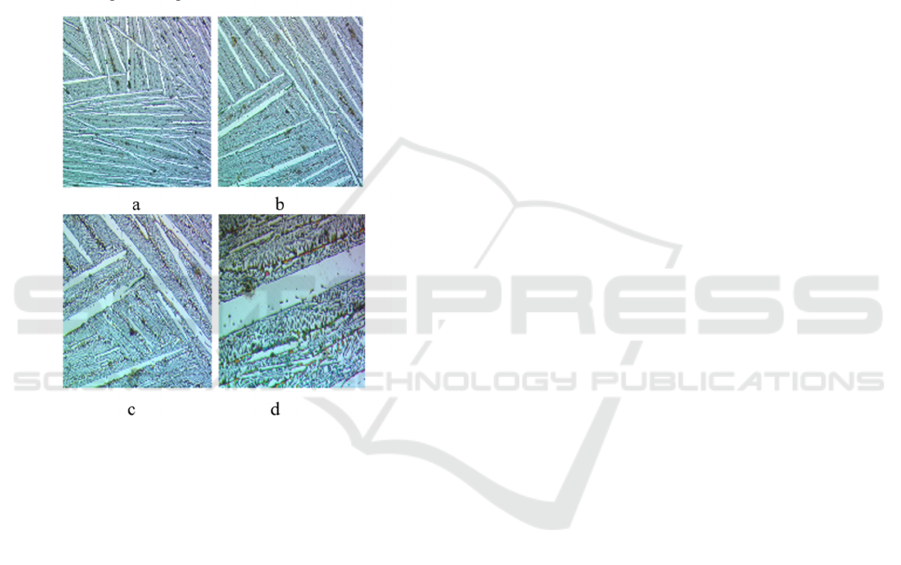
gradually, as a result of which the as-cast state or the
structure after normalization of the alloy changes
from pearlite to sorbite, trostite, martensite, and
finally to austenite (Rasulov and Grachev, 2004,
Kozlov et al., 2003).
Manganese austenite is characterized by its
durability and is prone to scurvy. This type of steel is
mainly used to increase the corrosion resistance under
shock load conditions, where shock occurs on the
surface layer of the metal, and the surface layer of the
material made of such steel is not contaminated under
abrasive cutting conditions, so the use of 110G13L
steel in such conditions does not have an advantage
over other engineering steels.
Figure 3: The appearance of structures detected when 1%
ferrochrome is added to steel of the 110g13l brand. a- The
appearance of the 110g3l brand steel with the addition of
1% ferrochrome as a modifier is 5 µm in size; b- The
appearance of 110g3l branded steel 10 µm in size with the
addition of 1% ferrochrome as a modifier; c- The
appearance of 110g3l branded Steel 20 µm in size with the
addition of 1% ferrochrome as a modifier; d- The
appearance of 110g3l branded Steel 50 µm in size with the
addition of 1% ferrochrome as a modifier.
It is known that the amount of carbon in steel has
a strong influence on its corrosion resistance, so in
some cases, increasing the amount of carbon in steel
to 1.5% leads to a number of complications.
The chemical properties of the "Almalik KMK"
JSC MTM(SRMZ) plant were studied in laboratory
conditions and the following results were obtained
(Novikov, 1996; Tursunbayev et al., 2023).
Manganese increases the stability of austenite and
is usually in the range of Mn:C˃10 for most
standards. If we take into account that the amount of
manganese in steel is 9.5 - 10%, then this has little
effect on the resistance to bending of steel in abrasive
conditions. Therefore, the amount of manganese in it
can be reduced to 9%.
Silicon if its content in steel is 0.8-1%, it almost
does not affect the strength and plasticity of steel, but
it allows to increase the bending resistance of silicon
steel only in abrasive bending conditions without
forging.
Sulfur if it is present in small amounts in
manganese steel, it forms manganese sulfide and does
not significantly affect the properties of the
(Mukushev et al., 2010; Torakho'jaev et al., 2018;
Torakho'jaev et al., 2020).
Phosphorus it begins to have a negative effect on
strength properties when its amount increases from
0.06 to 0.08% in 110G13L steels.
Chrome it is used in alloying manganese steels,
especially 110G13L steels, in such cases the pre-
deformation of the steel is reduced. As a result of
alloying steel with chromium in the amount of 5-20%,
the plasticity and impact viscosity of the material is
significantly reduced, but the hardness of steel
increases, for example, as a result of alloying steel
with 3% chromium, its hardness increases to NV 255.
The advantages of adding ferrochrome to steel are;
reduces graininess, increases hardness and strength,
and increases oxidation resistance at high
temperatures.
Nickel practically does not affect the strength
properties of manganese steels. 0.1 - 0.15% of
titanium included in the composition of steel allows
to increase its resistance to bending, similarly, 0.1 -
0.2% of zirconium affects the strength properties of
manganese steels. Chromium microalloying has a
good effect on the mechanical properties and bending
resistance of steels (Chorshanbiev, 2020, Yu and
Schulte, 1983, Parasyuk, 2014).
A large number of various (different types of
crushers, parts, teeth of excavator pits, etc.) parts
made of 110G13L steel are used in the enterprise of
"Almalik KMK" OJSC. The surfaces of such details
are made without cracks as a result of exposure to
abrasive or abrasive wear under various operating
conditions. As a result, a large amount of manganese
steel scrap is collected. It is recommended that such
steels be microalloyed and modified during remelting
to obtain a structure that allows for increased
corrosion resistance.
When we measured the hardness of selected
modifiers, it was reflected that the hardness of
ferrochrome and molybdenum is high.
Choosing the Optimum Modifier to Increase the Durability of Parts Made of 110g13l Steel
267

In addition, copper and ferrosilium were also
found to have superior performance compared to
other modifiers.
Based on the process of studying the structure of
the above-mentioned modifiers, the following
conclusions were drawn (Korshunov, 1973; Tsurkan,
2012a; Tsurkan et al., 2012b).
4 CONCLUSIONS
1. The following recommendations were developed
as a result of theoretical and practical research on
the topic of choosing the optimal modifier to
increase the durability of steel parts.
2. Optimum modifiers were selected to increase the
strength of steel parts.
3. Properties and structures of several types of
modifiers were studied to increase the durability
of steels.
REFERENCES
Chorshanbiev, Sh., 2020. Collection of scientific works
"Talented youth of New Uzbekistan", first book.
"Development of the technology to increase the
flexibility of shaft-gear teeth". Educational Publishing
House, Tashkent. Bit 8, 212-220.
Dubinin, N.P., 1961. Casting steel, manual, edited by.
Moscow, 887.
Ikramov, U. 2003. Tribanika. Tashkent, Uzbekistan. 77, 84,
126.
Korshunov, V.V., 1973. Issledovanie vliyaniya
modifitsirovaniya na kinetiku protsessa usadki i
deformatsionnuyu sposobnost’ stali 110G13L [veya
110G1ZL] (Avtoreferat dissertatsii kandidata
tekhnicheskikh nauk). Chelyabinsk.
Kozlov, L., Kolokoltsev, V.M., Vdovin, K.N., Ten, E.B.,
Dolgopolova, L.B., Filippenkov, A.A., 2003.
Production of steel ingots, textbook L. Yes. Kozlov.,
Moscow, Mrs. 357.
Mirboboev, V.A., 2004. Structural Materials Technology.
Tashkent, Uzbekistan. 148, 157, 162
Mukushev, D.A., Tsurkan, A.N., Samsonov, Yu.P.,
Makushev, V., Kanya, A., 2010. Increasing the wear
resistance of the lower parts of bulldozers. Bulletin of
the Siberian Branch of the Academy of Military
Sciences, A. Appendix to VN Bulletin.
Nasser, I., 2002. Materials Science. Tashkent "Uzbekistan"
173-179.
Novikov, I.I., 1996. Theory of Heat Treatment of Metals. -
M: Metallurgy, 123-178.
Nurmurodov, S., Rasulov, A., Torakho'jaev, N.,
Bakhodirov, K., Yakubov, L., Abdurakhmanov, Kh.,
Tursunov, T., 2016. Development of new structural
materials with improved mechanical properties and
high quality of structures using new methods. Journal
of Materials Science Research, Canada. Canadian
Center for Science and Education, 5(3), 52-58.
Pakhadnya, V., Turkevich, Z., 2013. Fizika-technicheskie
problem sovremennogo materialovedeniya. Kyiv-
Akademperiodika 39, 55, 77.
Parasyuk, P.F., 2014. The main component is steel
110G13L, and the mode of heat treatment and
durability is sought. Technology, organization and
mechanization of liteynogo proizvodstva, Jorn.
SNIITEITEJMASh 9,18,79.
Rasulov, S.A., Grachev, V.A., 2004. Anthrax metallurgy.
Tashkent "Teacher", 87, 89, 95, 142.
Torakho'jaev N., Chorshanbiev Sh., Sadikova N.,
Chorshanbiev Q., 2020. Journal of Critical Appraisal.
"Methods for increasing the strength of shaftgear teeth
operating in highly abrasive grinding environments".
Journal of Critical Review, 103(4), Roosevelt Rd, Da'an
District, Taipei City, Taiwan.
Torakho'jaev, N.D., Yakubov, L.E., Tursunov, 2018.
Mathematical Model of Heat Treatment to Improve TX
Mechanical Properties. Composite materials. -
Tashkent, 3, 56-60.
Tsurkan D. A., 2012a. Increasing the structural strength of
110g1zl steel and cast parts used in special machines by
modification by Mo, Ni alloy and Polzunovskaya
vestnik N 1/1.
Tsurkan, D.A., Leontiev, A. N.,. Ishkov, A. V., 2012b.
Improving the durability and operational reliability of
caterpillar engine parts of agricultural machinery and
special machines. Altai State University newsletter.
Tursunbaev, S., Turakhodjaev, N., Mardonakulov, S., &
Toshmatova, S., 2024. Effect of germanium oxide on
the properties of aluminum casting details in
agricultural machinery. BIO Web of Conferences, 85.
https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/20248501024.
Tursunbaev, S., Turakhodjaev, N., Odilov, F.,
Mardanokulov, S., & Zokirov, R., 2023. Change in
wear resistance of alloy when alloying aluminium alloy
with germanium oxide. E3S Web of Conferences, 401.
https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202340105001.
Tursunbayev, S., Turakhodjayev, N., Mardanokulov, S.,
Zokirov, R., & Odilov, F., 2023. The effect of lithium
on the mechanical properties of alloys in the Al-Li
system. E3S Web of Conferences
, 390.
https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202339005046
Yu, A., Schulte, 1983. Praizvodstva atlivak iz stali., Kiev-
Donetsk. izd Vitsha scale. 183.
I-CRAFT 2024 - 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies
268
