
Application of Various Smart Technologies in the Field of Agriculture
Dildora Alimova
a
, Dildora Sabirova
b
and Kamola Samatova
c
Tashkent State Technical University, 100095, University str. 2, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Precision Farming, Smart Agriculture, Blockchain Technologies.
Abstract: The agricultural sector is undergoing a significant transformation driven by the integration of smart
technologies. This paper explores the application of various smart technologies in agriculture, highlighting
their potential to create a more sustainable, efficient, and data-driven food system. The paper discusses five
key areas: precision agriculture powered by data analytics and AI, automation and robotics for enhanced
efficiency, block chain for increased transparency and traceability, vertical farming and controlled
environments for optimized resource utilization, and education and workforce development to equip farmers
with the skills needed for this new agricultural landscape. While these technologies offer significant benefits,
including increased yields, reduced resource consumption, and enhanced food security, challenges exist in
terms of implementation costs, digital literacy, and regulatory frameworks.
1 INTRODUCTION
The world's agricultural landscape is undergoing a
profound transformation, driven by a wave of
innovative technologies that are reshaping how we
cultivate, manage, and produce food. This revolution,
driven by the rapid advancements in fields like
artificial intelligence, robotics, and data analytics, is
collectively known as “smart agriculture” or
“precision agriculture”. These technologies are not
merely enhancing efficiency; they are fundamentally
changing the very fabric of farming, offering a
glimpse into a future of increased productivity,
resource sustainability, and enhanced resilience
(Жумаев, 2016; Ahmatovich, 2018; Sulaymonov,
2020; Kimsanbaev et al., 2021).
This exploration delves into the application of
various smart technologies in the field of agriculture,
highlighting their potential to address pressing
challenges like resource depletion, climate change,
and food security. From precision farming and
robotics to vertical farming and block chain
technology, we'll examine the innovative solutions
emerging at the intersection of technology and
agriculture, paving the way for a more sustainable and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6413-4233
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9661-8160
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-2470-8015
equitable future for food production (Кимсанбаев,
2016; Jumaev, 2023).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This paper emphasizes the need for collaboration,
research, and strategic policy development to fully
realize the potential of smart technologies in
achieving a more sustainable and resilient agricultural
sector. This paper explores how the integration of
smart technologies is revolutionizing agriculture and
paving the way for a more sustainable food system
(Сулаймонов, 2018). It highlights five key areas:
precision agriculture driven by data analytics and AI,
automation and robotics for enhanced efficiency,
block chain for increased transparency and
traceability, vertical farming and controlled
environments for optimized resource utilization, and
education and workforce development to empower
farmers with the skills needed for this new
agricultural landscape (Jumaev & Rakhimova, 2020).
By leveraging these technologies, the agricultural
sector can achieve significant gains in resource
efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and enhance
food security while adapting to a changing climate
18
Alimova, D., Sabirova, D. and Samatova, K.
Application of Various Smart Technologies in the Field of Agriculture.
DOI: 10.5220/0014041400004738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies (I-CRAFT 2024), pages 18-22
ISBN: 978-989-758-773-3; ISSN: 3051-7710
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

(Axmatovich, 2016). The paper emphasizes the need
for collaboration between technology developers,
farmers, policymakers, and researchers to overcome
implementation challenges and realize the full
potential of smart technologies for a sustainable food
future (Jumaev, 2017).
Evaluating the impact and effectiveness of smart
technologies in agriculture requires a comprehensive
approach, encompassing multiple dimensions of
analysis. The following materials and methods
provide a framework for assessing the adoption,
performance, and sustainability of these technologies:
1. Data Collection and Analysis:
• Field Experiments: Conduct controlled trials
comparing the performance of smart
technology-enabled practices (e.g.,
precision irrigation, robotic harvesting) with
traditional methods, analyzing yield
differences, resource consumption, and
operational efficiency.
• Surveys and Interviews: Gather data from
farmers, researchers, industry experts, and
consumers through surveys, interviews, and
focus groups to understand adoption rates,
perceptions, challenges, and potential
benefits of implementing these
technologies.
• Economic and Environmental Impact
Assessments: Analyze the financial cost-
benefit analysis of different technologies,
considering upfront investments, operating
expenses, and potential return on
investment, along with their environmental
footprint in terms of resource consumption,
greenhouse gas emissions, and land use.
• Case Studies: Identify and study successful
implementations of smart technologies in
various agricultural contexts to understand
best practices, scalability, and real-world
applications (Жумаев, 2016).
2. Technology Evaluation:
• Performance Metrics: Establish clear
metrics to evaluate the performance of
different technologies based on factors like
yield increase, resource efficiency, labor
reduction, overall productivity, and food
safety enhancements.
• Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a thorough
financial analysis of implementing different
technologies, considering upfront
investments, operational expenses, potential
return on investment, and potential long-
term financial benefits.
• Sustainability Assessment: Assess the
environmental, social, and economic
sustainability of the technology, considering
its impact on resource consumption,
biodiversity, social equity, and community
development (Saidova et al., 2024).
3. Stakeholder Engagement:
• Farmer Feedback: Regularly engage with
farmers to understand their experiences,
challenges, and requirements for effective
technology integration.
• Industry Collaboration: Collaborate with
agricultural research institutions, technology
companies, and government agencies to
promote knowledge sharing, technology
development, and policy development.
• Consumer Awareness: Engage with
consumers to raise awareness about the
benefits of smart technologies and promote
responsible consumption patterns (Saidova
et al., 2024).
4. Ethical Considerations:
• Data Privacy & Security: Develop robust
data management practices and security
protocols to protect sensitive information
collected through smart technologies and
ensure responsible data use.
• Social Equity: Ensure equitable access to
technology and resources for all
stakeholders, particularly smallholder
farmers and marginalized communities, to
prevent further marginalization and promote
inclusive development.
•
Environmental Responsibility: Evaluate the
potential environmental impacts of
technologies and prioritize solutions that
minimize negative consequences and
promote responsible environmental
stewardship (Alimova et al., 2024).
5. Monitoring & Evaluation:
• Regular Data Collection and Analysis:
Establish a system for ongoing monitoring
and evaluation of the impact of smart
technologies on agricultural outcomes,
sustainability goals, and economic
performance (Axmatovich, 2022).
• Performance Tracking: Regularly assess the
performance of implemented technologies,
identify areas for improvement, and
optimize their effectiveness.
• Adaptive Management: Continuously adapt
and refine strategies based on new data,
emerging trends in technology and
agricultural practices, and evolving
Application of Various Smart Technologies in the Field of Agriculture
19
environmental challenges (Rakhimov and
Tairova, 2021).
By employing this comprehensive framework, we
can gain a deeper understanding of the impact of
smart technologies in agriculture, ensuring their
responsible implementation, addressing potential
challenges, and maximizing their potential for
building a more sustainable and equitable future for
food production (Karimov et al., 2020).
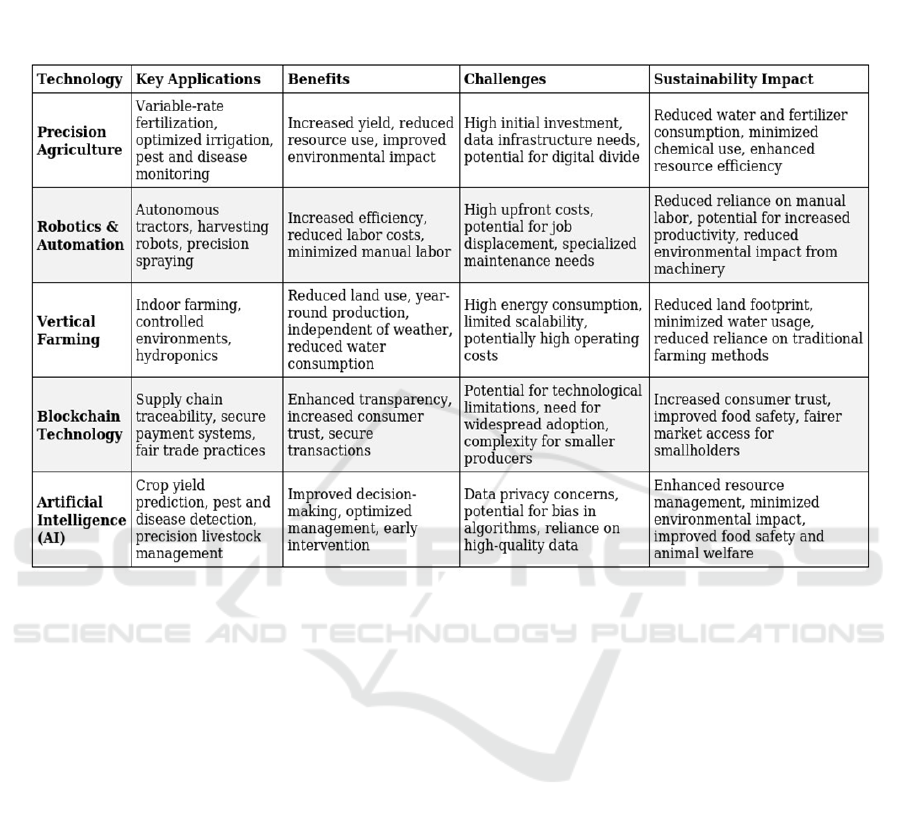
Figure 1: Smart Technologies in Agriculture: A Comparative Overview.
This table provides a general overview. Specific
benefits, challenges, and sustainability impacts can
vary depending on the technology, context, and
implementation.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The adoption of smart technologies in agriculture is
yielding promising results, though challenges and
opportunities remain. Here's a summary of key
findings and areas for further exploration:
1. Enhanced Productivity and Resource
Efficiency:
• Increased Yields: Precision agriculture
techniques have demonstrated significant
increases in crop yields, often surpassing
traditional methods by 10-20%. Data-driven
irrigation and targeted fertilization optimize
resource use, leading to more efficient
production.
• Reduced Resource Consumption: Smart
technologies enable farmers to use water,
fertilizers, and pesticides more efficiently,
minimizing environmental impact and
reducing production costs. Studies indicate
water usage reductions of up to 50% and
fertilizer use reductions of 20-30% through
precision application.
• Labor Optimization: Robotics and
automation are reducing reliance on manual
labor, freeing up farmers for more
specialized tasks and increasing overall
efficiency. This can lead to increased
productivity and lower labor costs.
2. Improved Food Safety and Quality:
• Enhanced Traceability: Blockchain
technology revolutionizes supply chains,
allowing for real-time tracking of food
products from farm to table, ensuring greater
transparency and enhancing consumer
confidence. This can help reduce food fraud
and improve trust in the food system.
• Precision Pest Control: AI-powered pest
detection systems and targeted pesticide
applications minimize chemical usage,
promoting food safety and reducing
I-CRAFT 2024 - 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies
20

environmental damage. This can lead to
safer and healthier food production, while
reducing the reliance on harmful chemicals.
3. Challenges and Opportunities:
• Adoption Barriers: Cost, lack of access to
technology, and digital literacy gaps pose
significant barriers to widespread adoption
of smart technologies, particularly among
smallholder farmers. Supporting farmers
through training, access to financing, and
technology adoption programs is crucial.
• Data Privacy Concerns: The collection and
use of agricultural data raise concerns about
privacy and security, requiring robust data
management protocols and ethical
considerations. Transparency and user
control over data are essential for building
trust and responsible data practices.
• Social Equity: It's crucial to ensure that the
benefits of smart technologies are shared
equitably across all stakeholders, preventing
further marginalization and promoting
inclusive development. Addressing digital
divides and ensuring access to technology
for all farmers is vital for a just transition.
4. Future Directions:
• Focus on Smallholder Farmers: Developing
tailored solutions and providing targeted
support to smallholder farmers is crucial to
democratizing access to smart technologies.
This requires addressing their specific needs
and challenges.
• Data Sharing and Collaboration: Promoting
open-source data sharing and fostering
collaboration between researchers, industry,
and farmers will accelerate innovation and
knowledge dissemination. Sharing data and
expertise can accelerate the development
and adoption of new solutions.
• Sustainable Development Goals: Integrating
smart technologies into broader
sustainability initiatives, such as climate
change adaptation and food security
programs, is critical for achieving long-term
impact. These technologies can play a
significant role in addressing global
challenges and achieving sustainable
development.
The integration of smart technologies into
agriculture presents a transformative opportunity to
reshape food production for the better. We've seen
how these innovations can enhance productivity,
improve resource efficiency, and bolster food safety
and quality. However, realizing this potential requires
a multifaceted approach that addresses challenges,
fosters collaboration, and prioritizes ethical
considerations.
Here are key takeaways:
• Innovation is Essential: Continued research
and development of smart technologies,
alongside their adaptation to diverse
agricultural contexts, are vital for achieving
greater impact.
• Equity and Inclusivity: Ensuring equitable
access to technology, resources, and training
is crucial for empowering all farmers,
particularly smallholders, to participate in
this transformation.
• Sustainability is Paramount: Smart
technologies should be implemented with a
focus on environmental sustainability,
minimizing negative impacts and promoting
responsible resource management.
• Collaboration is Key: Fostering partnerships
between researchers, industry leaders,
policymakers, and farmers is crucial for
accelerating innovation, overcoming
barriers, and sharing knowledge.
From precision farming and robotics to vertical
agriculture and blockchain, a wave of technological
advancements is sweeping through the agricultural
landscape, fundamentally altering the way we
cultivate, manage, and distribute food. This
revolution promises a future of increased efficiency,
environmental sustainability, and food security, but it
also presents unique challenges and opportunities.
In the pages ahead, we'll explore the burgeoning
field of smart agriculture, examining the applications
of these technologies, their potential benefits, and the
crucial considerations for ensuring a responsible and
equitable transition towards a smarter and more
sustainable future for food production.
The future of agriculture lies in harnessing the
power of smart technologies to create a more resilient,
efficient, and sustainable food system. By embracing
innovation, prioritizing inclusivity, and working
collaboratively, we can build a future where
agriculture thrives, ensuring food security for
generations to come while safeguarding our planet.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The evidence is clear: smart technologies have the
power to transform agriculture, creating a food
system that is more efficient, resilient, and
sustainable. However, realizing this potential requires
a collective effort, a shared commitment from all
Application of Various Smart Technologies in the Field of Agriculture
21

stakeholders to embrace a new paradigm of food
production.
1. Governments: To invest in research and
development, create policies that incentivize the
adoption of smart technologies, and ensure equitable
access to resources and technology for all farmers.
2. Industry Leaders: To develop affordable and
accessible technologies, prioritize sustainability in
product design, and work closely with farmers to
ensure successful implementation.
3. Researchers: To continue pushing the
boundaries of innovation, develop solutions tailored
to diverse agricultural contexts, and ensure ethical
considerations are at the forefront of research.
4. Farmers: To embrace new technologies as tools
for empowerment, share best practices, and advocate
for policies that support their adoption.
5. Consumers: To demand sustainable and
traceable food products, support farmers who are
utilizing smart technologies, and actively engage in
shaping a future where food systems prioritize both
environmental and social well-being.
REFERENCES
Ahmatovich R. A. et al. In biocenosis the degree of
appearing entomophagous types of vermins which suck
tomatoey sowings //Austrian Journal of Technical and
Natural Sciences. – 2018. – №. 9-10. – С. 3-5.
Жумаев Р.А. Биолабораторияда трихограммани in vitro
усулида ўстириш технологияси. Трихограммани
сунъий озиқада ўстириш курси (1)(Hymenoptera:
Trichogrammatidae). – 2016.
Sulaymonov B.A. et al. Effectiveness of Application of
Parasitic Entomophages against Plant Bits in Vegetable
Agrobiotensenosis //Solid State Technology. – 2020. –
Т. 63. – №. 4. – С. 355-363.
Kimsanbaev X. X., Jumaev R. A., Abduvosiqova L. A.
Determination Of Effective Parasite-Entomofag
Species In The Management Of The Number Of Family
Representatives In Pieridae //The American Journal of
Agriculture and Biomedical Engineering. – 2021. – Т.
3. – №. 06. – С. 135-143.
Jumaev R. Invitro rearing of parasitoids //E3S Web of
Conferences. – EDP Sciences, 2023. – Т. 371.
Кимсанбаев Х. Х. и др. Биоценозда ўсимлик
зараркунандалари паразит энтомофагларини
ривожланиши.« //O’zbekiston» НМИУ,–Тошкент. –
2016.
Сулаймонов Б. А. и др. Ўрмон биоценозида фитофаг
турлари ва улар миқдорини бошқариш
//O’zbekiston» НМИУ,–Тошкент. – 2018.
Jumaev R., Rakhimova A. Analysis of scientific research on
reproduction of species of Trichograms in
Biolaboratory //The American Journal of Agriculture
and Biomedical Engineering. – 2020. – Т. 2. – №. 08. –
С. 148-152.
Axmatovich J. R. In vitro rearing of trichogramma
(Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) //European
science review. – 2016. – №. 9-10. – С. 11-13.
Jumaev R. A. et al. The technology of rearing Braconidae
in vitro in biolaboratory //European Science Review. –
2017. – №. 3-4. – С. 3-5.
Жумаев Р.А. Массовое размножение трихограммы на
яйцах хлопковой совки в условиях биолаборатории
и ее применение в агробиоценозах //Халқаро
илмий-амалий конфренция “Ўзбекистон мева-
сабзавот маҳсулотларининг устунлиги” мақолалар
тўплами. Тошкент. – 2016. – С. 193-196.
Saidova, M., Tursunbaev, S., Boltaeva, M., & Isakulova, N.
(2024). Comparison of pneumatic sowing machines by
the number of seeds in the slots of the discs and the
distance between the slots. BIO Web of Conferences,
105. https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/202410501004
Saidova, M., Tursunbaev, S., Boltaeva, M., Ismoilov, T., &
Gilijova, A. (2024). Analysis of a pneumatic seeder
equipped with an improved planting disc. BIO Web of
Conferences, 105.
https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/202410501024
Alimova, F., Saidova, M., Primqulov, B., & Erdem, T.
(2024). Optimization of the parameters of the
pneumatic feed mechanism for precise clustered
sowing. BIO Web of Conferences, 85.
https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/20248501026
Axmatovich J. R. In Vitro Rearing of Parasitoids
(Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae and Braconidae)
//Texas Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences.
– 2022. – Т. 4. – С. 33-37.
Rakhimov A.M., Tairova N.S., New innovative
technologies in the teaching of the Subjects drawing
geometry and engineering graphics// Russian
Federation Journal of Economy and society. – 2021. –
T. 11. – C. 487-493.
Karimov, R., Bobojanov, M., Tairova, N., Xolbutayeva, X.,
Egamov, A., & Shamsiyeva, N. (2020, July). Non-
contact controlled voltage stabilizer for power supply
of household consumers. In IOP Conference Series:
Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 883, No. 1, p.
012120). IOP Publishing.
I-CRAFT 2024 - 4th International Conference on Research of Agricultural and Food Technologies
22
