
Development of Rechargeable Batteries, Focusing on Sustainability
and Comparison
Lingyu Meng
Darlington School, Rome Georgia, 30161, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Rechargeable Batteries, Sustainability, Advantage, Disadvantage.
Abstract: Rechargeable batteries (RBs) have become integral to modern energy storage solutions, with their
development accelerating significantly over recent decades. Beginning with Gaston Planté's invention of the
first rechargeable battery in 1859, the field saw notable advancements, particularly with the introduction and
commercialization. This paper explores various types of RBs, comparing their advantages, disadvantages, and
sustainability aspects. Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market but pose environmental challenges due to
material extraction and disposal issues. The paper also delves into future development trends, highlighting
emerging technologies which promise enhanced performance and safety. Sustainability is still a major issue,
highlighting the necessity of efficient recycling and the usage of eco-friendly products. The integration of
RBs in renewable energy systems and their role in reducing dependence on fossil fuels underscore their
importance. Continued research, global collaboration, and investment are essential to advance rechargeable
batteries (RB) technology, ensuring it meets growing demand and supports a sustainable energy future.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of rechargeable RBs is growing
rapidly. People discovered that rechargeable batteries
could play an important role. A French physicist
brought up the first rechargeable battery; however,
rechargeable lithium-ion batteries were not invented
until the 1970s (Motoma). The first prototype of a
lithium-ion battery was not created until
1985(Motoma). Still, due to its great performance and
outstanding feasibility, it made huge developments in
the recent decade. The demand of the market also
fostered the development of lithium-ion batteries.
Different progress in rechargeable batteries is being
made at different periods. Harris looks at how soluble
lithium is in different types of non-aqueous
electrolytes in 1958. This leads to the discovery of a
passivation layer that can stop direct chemical
reactions between lithium and the electrolyte, which
piques interest in studies on this field (Souchay &
Désilets, 2020). In the late 1960s market availability
of non-aqueous batteries begins (Souchay & Désilets,
2020). Research into rechargeable (secondary)
lithium-ion batteries was the main progress made in
the 1970s (Souchay & Désilets, 2020). In 1972,
Transition metal chalcogenides were evaluated as
electrode materials (Souchay & Désilets, 2020).
Later, from the late 1970s to the 1980s, Li//MoS2
cells (MOLICELTM) were manufactured (Souchay
& Désilets, 2020). And NbSe3 emerged as a cathode
element (Souchay & Désilets, 2020). The
commercialization of lithium-ion batteries in the
1990s was made possible by other advancements in
cathode materials, such as V2O5, which were
developed in the late 1980s (Souchay & Désilets,
2020).
The process of charging general rechargeable
batteries is primarily based on chemistry, as they store
electrical energy in the form of chemical energy.
These batteries have two electrodes including cathode
and anode and what between them are electrolyte (IQ
Direct). During discharge, the battery releases
electricity through a chemical reaction at the
electrodes, converting chemical energy into electrical
energy (Matsusada Precision). The positive electrode
will absorb the electron released from the negative
electrode (Matsusada Precision). When the battery is
recharged, it stores the electricity for future usage, the
whole process will now reverse. The positive
electrode will release the electron the negative
electrode will absorb the electron released
(Matsusada Precision). The aim of this paper is to
compare the advantage and disadvantage of
214
Meng, L.
Development of Rechargeable Batteries, Focusing on Sustainability and Comparison.
DOI: 10.5220/0013877400004914
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Renewable Energy and Ecosystem (ICREE 2024), pages 214-217
ISBN: 978-989-758-776-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

rechargeable batteries and analyse the further
development trends.
2 COMPARISON BETWEEN
DIFFERENT KINDS OF
RECHARGEABLE BATTERIES
Scientists continue to try many different elements to
see which can store the most energy and which works
best. From 1958 when the Lead-acid battery was first
invented to the Aluminum-ion battery which was
brought up in the 2010s, scientists have been
searching for better and better solutions. Different
kinds of batteries have different chemical
characteristics. Lead-acid batteries use lead plates and
sulfuric acid to make the electrolyte. Nickel
hydroxide serves as the cathode in nickel-cadmium
batteries, while cadmium serves as the anode and
potassium hydroxide serves as the electrolyte. In
terms of nickel-metal hydride batteries, potassium
hydroxide serves as the electrolyte, nickel hydroxide
serves as the cathode, and an alloy anode that absorbs
hydrogen is used. In lithium-ion batteries, graphite is
the stuff in the anode, while the cathode is made of
lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, or other
lithium-based materials. The electrolyte is just some
lithium salt. Unlike conventional Li-ion batteries,
which employ liquid-polymer, lithium-polymer
batteries use a solid or gel-like polymer substance.
Rechargeable batteries (RBs) are essential for
advancing versatile and efficient energy storage
technologies, facilitating the global transition from
traditional fossil fuels to renewable energy sources
(Weiss et al, 2021). Rechargeable batteries (RBs) are
widely employed in several sectors and have been
shown to improve human well-being by providing us
with a multitude of desirable and necessary products
(Kim et al, 2019). Since RBs are a kind of renewable
energy, they are better for the environment and don't
release carbon dioxide when used in place of fossil
fuels like extracting oil from the ground. Batteries
perform a wide range of tasks, including powering
power systems, electric automobiles, wearable
technology, space exploration, medical equipment,
and smartphone apps (Chao et al, 2020).
Rechargeable batteries are most employed in two
applications: electric cars and large power systems
that use renewable energy sources such as solar,
wind, waves, and internal earth heat (Abdul et al,
2020). Since they are lighter than other varieties,
lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) are currently among the
most often used batteries for electric vehicles (Duan
et al, 2023). Recently, the use of electric vehicles has
increased due to their ability to emit no emissions
(Caneon et al, 2019). Although lithium batteries are
seen to be the greatest option for electric vehicles,
there may not be enough of them if everyone wants
one (Caneon et al, 2019).
Rechargeable batteries have unique advantages
and drawbacks. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are
particularly popular, suitable for portable electronics
and electric vehicles (Dala et al, 2010). However,
they are sensitive to high temperatures and can pose
a fire risk if damaged or improperly handled. NiCd
batteries, although largely obsolete, are robust and
perform well in extreme temperatures, but their use
has significantly declined due to toxic metals and the
memory effect. Lead-acid batteries have various uses
but they are heavy and present significant
environmental disposal challenges because of their
toxic lead content (Zhang et al, 2022). Each type of
rechargeable battery has its specific use cases,
determined by its unique properties and limitations.
3 ANALYSIS OF
SUSTAINABILITY
The performance of rechargeable batteries is
relatively the most significant factor for people to
look at. There are many characteristics of
rechargeable batteries that count as their
performance, gravimetric energy density, volumetric
energy density, battery voltage, cycle life, self-
discharge per month, charging time, toxicity,
overcharge tolerance, and operating temperature
range (Liang et al, 2019). Figure 1 shows the
comparison of different batteries. As shown in the
figure, although the whole performance of Li-ion
batteries is good and ideal, the mining of lithium,
cobalt, and other rare metals participated, which can
cause significant environmental degradation and
ethical concerns regarding labor practices (Endalkac,
2023). This is why we always say that recycling
batteries is very important. In this way, people can
reuse the rear metal and recover valuable materials in
the battery without re-extracting them, and it saves
the environment significantly. Effective end-of-life
management of rechargeable batteries is crucial for
sustainability (Endalkac, 2023). If improperly
disposed of, these batteries can cause environmental
hazards, including fires and the release of toxic
substances (Endalkac, 2023). Nickel-metal hydride
batteries are more environmentally friendly than
lithium-ion and nickel-cadmium batteries, as they
Development of Rechargeable Batteries, Focusing on Sustainability and Comparison
215
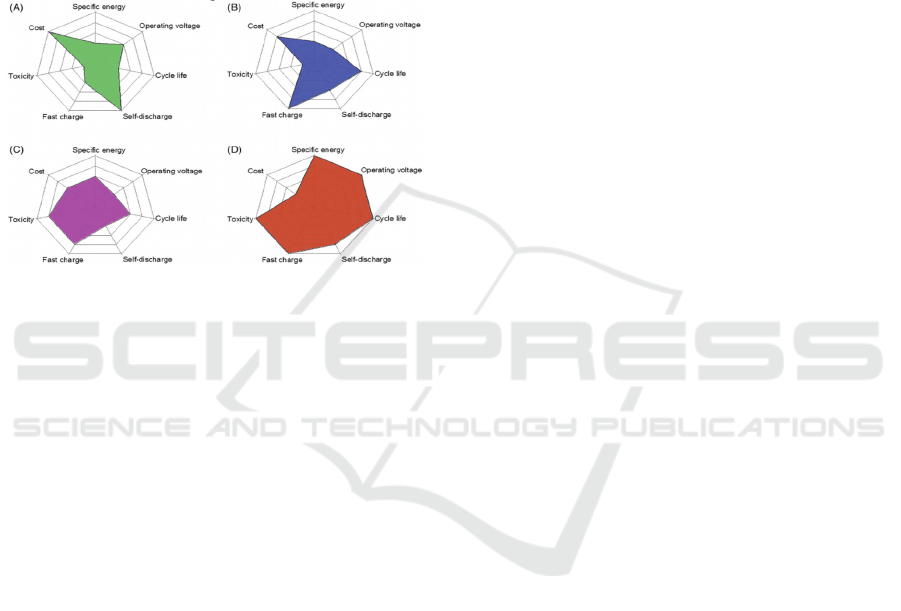
avoid the use of toxic cadmium and rely on more
abundant materials (Müller & Friedrich, 2006).
Improvements in battery technology and recycling
methods are crucial for enhancing the sustainability
of rechargeable batteries, reducing their
environmental footprint, and ensuring a steady supply
of essential materials. In summary, while
rechargeable batteries are more sustainable than
disposable ones, their overall environmental impact
depends on advancements in recycling technologies
and regulatory frameworks that ensure their safe and
efficient end-of-life management (Endalkac, 2023).
Figure 1. Performance comparison of four kinds of batteries
(Müller & Friedrich, 2006)
4 FUTURE DEVELOPMENT OF
RECHARGEABLE BATTERIES
Examining new technologies and advancements in
rechargeable materials should be our first step in
creating better rechargeable batteries. Modern
lithium-ion batteries are inferior to solid-state-
batteries in terms of safety, energy density, and
charging speed. They might completely alter portable
electronics and electric vehicles (Endalkac, 2023).
Research into lithium-sulfur and lithium-air batteries
is also gaining traction, offering the potential for even
greater energy storage capacities, which could
dramatically extend the range of EVs and the lifespan
of portable devices (Endalkac, 2023). Additionally,
advancements in nanotechnology and the use of
advanced materials like graphene are being explored
to improve battery performance, including higher
energy densities and longer lifespans (U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency). The shift towards
sustainable materials is another critical development,
with efforts to create cobalt-free and nickel-free
batteries aimed at reducing the environmental impact
and ethical concerns associated with battery
production (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency).
Global collaboration and significant investments in
research and development by governments,
universities, and private companies are vital to
accelerate the development of next-generation battery
technologies (U.S. Environmental Protection
Agency). Efforts to improve battery recycling
processes and promote a circular economy are also
crucial, ensuring that valuable materials are recovered
and reused, thus enhancing the sustainability of future
battery technologies (Endalkac, 2023).
5 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the rapid advancement of rechargeable
batteries has significantly transformed energy storage
technology. RB technology has advanced
significantly, starting with the lead-acid battery's
introduction and continuing with the creation and
marketing of lithium-ion batteries. These days,
lithium-ion batteries are the best option for portable
electronics and electric cars due to their high energy
density, extended lifespan, and excellent efficiency.
These advancements are accompanied by challenges,
notably the environmental and ethical concerns
associated with the extraction and disposal of
materials like lithium and cobalt. The sustainability
of RBs hinges on effective recycling and the
development of materials which have no negative
effect on environment. Advancements in battery
chemistry, such as the creation of cobalt-free and
nickel-free batteries, aim to reduce the environmental
impact and address resource scarcity issues.
Moreover, innovations like solid-state, lithium-
sulfur, and lithium-air batteries promise to further
enhance energy storage capabilities, safety, and
environmental sustainability. Solid-state-batteries,
for instance, offer more energy per mass unit and
faster charging times, potentially revolutionizing the
electric vehicle market. Future developments in RB
technology are crucial for supporting the global
energy transition. Enhanced recycling processes and
the promotion of a circular economy will be vital in
mitigating environmental hazards and ensuring a
sustainable supply of essential materials. Continued
research, global collaboration, and substantial
investment are necessary to drive these innovations
forward, ensuring that RBs can meet the growing
demand and contribute to a sustainable and energy-
efficient future.
ICREE 2024 - International Conference on Renewable Energy and Ecosystem
216

REFERENCES
Motoma. History and evolution of rechargeable batteries.
Retrieved on June 12, retrieved from
https://www.motoma.com/industry/history-and-
evolution-of-rechargeable-batteries.html
Souchay, D., & Désilets, S. 2020 History of the
development of lithium batteries Chimia (Aarau) 74
280-287
IQ Direct. Exploring the Chemistry Behind Rechargeable
Batteries. Retrieved on June 12, retrieved from
https://iq.direct/blog/419-exploring-the-chemistry-
behind-rechargeable-batteries.html
Matsusada Precision. What happens inside the rechargeable
battery during charging and discharging? Retrieved on
June 12, retrieved from
https://www.matsusada.com/column/battery_chaege-
dischaege.html
Weiss M, et al 2021 Fast charging of lithium-ion batteries:
a review of materials aspects Adv Energy Mater 11
2101126
Kim T, et al. 2019 Lithium-ion batteries: outlook on
present, future, and hybridized technologies J Mater
Chem 7 2942-2964
Chao D, et al. 2020 Roadmap for advanced aqueous
batteries: from design of materials to applications. Sci
Adv 6 eaba4098
Abdul Ghani O, et al. 2020 Rechargeable batteries:
Technological advancement, challenges, current and
emerging applications Energy 266 126408
Duan J, et al. 2023 Building safe lithium-ion batteries for
electric vehicles: a review Electrochem Energy Rev 3 1-
42
Caneon K, et al. 2019 Impact of Electric Vehicles on
Indirect Carbon Emissions and the Role of Engine
Posttreatment Emission Control Strategies 16 234-244
M Dala, et al. 2010 Lithium-ion battery life prognostic
health management system using particle filtering
framework Proceedings of the Institution of
Mechanical Engineers, Part O: Journal of Risk and
Reliability 225 81-90
Yong Zhang et al. 2022 Advances and challenges in
improvement of the electrochemical performance for
lead-acid batteries: A comprehensive review Journal of
Power Sources 520 230800
Yeru Liang, et al. 2019 A review of rechargeable batteries
for portable electronic devices InfoMat 1 6-32
Sahle-Demessie Endalkac. 2023 End-of-Life Management
of Lithium-Ion Batteries. U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, U.S.
Müller, T., & Friedrich, B. 2006 Development of a
recycling process for nickel-metal hydride batteries
Journal of Power Sources 158 1498-1509
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Frequent
Questions on Lithium-Ion Batteries. Retrieved on June
12, retrieved from
https://www.epa.gov/recycle/frequent-questions-
lithium-ion-batteries
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Used Lithium-Ion
Batteries. Retrieved on June 12, retrieved from
https://www.epa.gov/recycle/used-lithium-ion-
batteries
Development of Rechargeable Batteries, Focusing on Sustainability and Comparison
217
