
Analysis of Building Energy Consumption Based on Geographical
Location: Taking a Dormitory Building in a University in Wuhan as
an Example
Yipeng Wang
Birmingham Institute of Fashion and Creative Art, Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan, 430073, China
Keywords: University Buildings, Building Energy Consumption, Energy Consumption Analysis.
Abstract: In the context of increasing concerns about global environmental sustainability, the impact of building energy
consumption on the environment and resources has attracted attention. In order to cope with global climate
change, university dormitories are densely populated places, and their energy consumption is directly related
to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. Taking the impact of dormitory building energy
consumption in a university in Wuhan as an example, this article uses Revit software to model and conduct
data analysis to explore the impact of different geographical locations on dormitory building energy
consumption. By comparing the three cities of Harbin, Hong Kong and Singapore, this paper concludes that
building energy consumption in different geographical locations has a significant impact. Climate conditions
and geographical environment cause differences in energy consumption in different regions. Based on the
actual situation, this article puts forward relevant suggestions, such as using renewable energy, improving
energy conversion efficiency, optimizing building design, etc. The research in this article can provide a
relevant scientific basis, promote the rational utilization and conservation of energy in university dormitory
buildings, and positively contribute to promoting the development of green buildings and achieving the goal
of carbon peak carbon neutrality.
1 INTRODUCTION
The "dual carbon" strategy is a significant
development strategy proposed by the country to
respond to global climate change and promote
sustainable development. "Carbon peaking" and
"carbon neutrality" are currently environmental
protection projects that have received widespread
attention worldwide. In the process of development,
green buildings take environmental friendliness and
pollution reduction as their main goals, and are one of
the important means for the country to implement the
"double carbon" strategy (Ge, 2024). Energy
consumption mainly comes from the construction
industry and other fields. In terms of building energy
conservation, the country started late, which resulted
in high building energy consumption and low
utilization rates. According to statistics, in 2022, the
total energy consumption in the entire building
process will be 2.27 billion tce (ton of standard coal
equivalent), accounting for approximately 45.5% of
China's total energy consumption (Xu et al., 2021).
To reach the carbon dioxide emissions peak before
2030 and achieve the strategic goal of carbon
neutrality before 2060, buildings need to reduce
energy consumption through green and
environmentally friendly processing methods. As an
important building type, university dormitories bear
the living needs of many students (Yang, 2023). As
one of the important buildings that account for the
largest proportion of construction area among
university buildings and are used by students for the
longest time, dormitory buildings have disadvantages
such as high energy consumption, poor living
environment, high density, and single form. They not
only cause a large amount of waste of money and
energy in universities but also directly Affect
students' quality of life (Wu, 2020). In addition,
geographical location will affect the design and
construction of buildings, and building energy
consumption is particularly affected by geographical
location. Therefore, studying the impact of
geographical location on building energy
consumption will help formulate targeted energy-
10
Wang, Y.
Analysis of Building Energy Consumption Based on Geographical Location: Taking a Dormitory Building in a University in Wuhan as an Example.
DOI: 10.5220/0013843300004914
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Renewable Energy and Ecosystem (ICREE 2024), pages 10-16
ISBN: 978-989-758-776-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
saving and emission reduction measures and provide
a more effective path for realizing the "dual carbon"
strategy.
Compared with foreign countries, the
development of building energy conservation in the
country was late and started slowly. For example,
there are certain disadvantages in dormitory buildings
in Chinese universities, including unreasonable early
design, aging equipment, and inadequate energy
consumption management. In the energy-saving
design of university dormitory buildings based on
BIM technology, Wu Shuang discovered that the
energy-saving problems of university dormitory
buildings in Xi'an are mainly caused by factors such
as university planning, building orientation, building
lighting, building shape design, and door and window
materials. Consumption increased significantly. In
addition, Qiu Yanyan's research on energy-saving
strategies for existing buildings in some universities
in Guangzhou found that existing buildings in
universities in Guangzhou mainly have problems
such as poor thermal performance of envelope
structures, poor shading effects, unreasonable use of
air-conditioning equipment, and backward lighting
equipment (Qiu, 2021).
College buildings are an important part of school
buildings and bear the important responsibility of
providing students with learning and living places
(Dai, 2024). This paper takes a dormitory building in
a university in Wuhan as the research object to
explore the impact of the outdoor environment
affected by climate change due to different
geographical locations on building energy
consumption. By using Revit software to model the
dormitory building, the data is unified, and the model
selects the calculation and analysis of energy
consumption data from different geographical
locations to explore the specific impact of
geographical location on energy consumption, such
as climate conditions, light, rain, etc. The degree of
influence of factors on dormitory energy
consumption. Through in-depth analysis, this article
will propose more feasible building energy-saving
methods and measures to promote the construction
industry's development in a more energy-saving and
environmentally friendly direction. This article is of
great significance to the energy consumption of a
dormitory building in a university in Wuhan but also
helps to comprehensively understand the universal
impact of geographical location on building energy
consumption, providing reference for sustainable
development.
2 DATA AND METHODS
2.1 Research Objects
Wuhan City is located in central China, in the eastern
part of Hubei Province. As can be seen from Figure
1, the geographical coordinates are between 113°41’
and 115°05’ east longitude and between 29°58’
and 31 ° 22’ north latitude. It is located in the
subtropical monsoon climate zone, with a humid
climate, abundant annual rainfall, and moderate
temperatures. It has the characteristics of rain and
heat in the same season, light and heat in the same
season, cold winters and hot summers, and four
distinct seasons. The average annual temperature in
Wuhan is between 15.8℃ and 17.5℃, and the annual
precipitation is between 1150 mm and 1450 mm. The
central rainfall is concentrated from June to August
every year, accounting for about 40% of the annual
rainfall.
Figure 1: Geographical location of Wuhan City (Picture
credit: Original)
2.2 Method
Building information modeling (BIM) has five major
characteristics: visualization, coordination,
simulation, optimization, and graphability. It can also
conduct a more accurate and comprehensive energy
consumption analysis of buildings (Bao et al., 2024).
BIM technology can convert traditional two-
dimensional engineering drawings into three-
dimensional visual models, and is widely used in
many fields such as passive building engineering,
building construction engineering, building
protection engineering, and municipal drainage
construction engineering (Wang, Zhao and Liu,
2023). Revit is a professional building information
modeling (BIM) software launched by Autodesk,
Analysis of Building Energy Consumption Based on Geographical Location: Taking a Dormitory Building in a University in Wuhan as an
Example
11
which is used for modeling and design of architecture,
structure, electromechanical and other majors. It
includes functions such as parametric modeling,
automatic updates, intelligent object libraries, and
model collaboration, which can improve modeling
efficiency and team collaboration efficiency. Revit
software is not only a powerful architectural design
tool, but it can also be used to analyze building energy
consumption. With the help of Revit's energy
consumption analysis function, architects and
engineers can evaluate and optimize the energy
consumption of buildings during the design stage and
can also simulate and calculate the energy
consumption of existing buildings to achieve energy
conservation and emission reduction goals.
2.3 Modelling Process
The model is based on the actual architectural
structure of a dormitory building in a university in
Wuhan, as can be seen in Figure 2. Revit software is
used to build a simplified model and perform data
analysis.
Figure 2: A three-dimensional view of a dormitory building
in a university (Picture credit: Original)
Table 1: Basic information of building model.
Paramete
r
Value
Geographical
location
Latitude 30.4843, Longitude
114.4009
Climate
North subtropical monsoon
(
humid
)
climate
Building Type Dormitor
y
Building
orientation
north
Construction area
The total area is 2756.28 square
meters
Floor numbe
r
Level 6
As shown in the basic information of the building
model in Table 1, the building type in this study is a
dormitory, with coordinates of 30.4843 north latitude
and 114.4009 east longitude. The main climate type
is tropical monsoon climate. The building has six
floors and a building area of 2756.28 square meters.
Table 2: Parameter settings of the building model.
Paramete
r
Value
Project Dormitor
y
Building
Schedule
Default
Building
Equipment
VAV-Single Duct
HVAC System
Central VAV, HW Heating, Chilled
Water Unit COP: 5.96, Boiler
Efficienc
y
: 84.5
Fresh Air
Information
Fresh air per person: 8.00 L/s
As shown in the building model parameter
settings in Table 2, the building equipment of the
dormitory building uses VAV-single air duct, the
building air penetration level is medium, the HVAC
system uses central VAV, HW heating, chiller unit
COP is 5.96, and boiler efficiency is 84.5, the fresh
air volume per person is 8 liters/second.
Table 3: Thermal property parameters of building materials.
Element Construction
Exterior Walls
Lightweight construction -
typical mild climate insulation
Interior Walls
Lightweight construction – no
insulation
Exterior wall-
under
g
roun
d
Heavy construction – classic
mild climate insulation
Roof
Typical Insulation - Light
Colored Roofin
g
Floors
Lightweight construction – no
insulation
Slabs
Heavy construction – no
insulation
Glass
Coloring
Double layer clear –
uncoated
Basic sunshade
As shown in Table 3, the thermal property
parameters of building materials, in the material
thermal properties, the exterior wall uses a
lightweight structure and a typical mild climate
insulation layer, the interior wall uses a lightweight
structure and no insulation layer, and the roof uses a
typical insulation layer and light-colored roofs, while
using uninsulated floors and slabs.
3 RESULTS
Energy consumption analysis was conducted through
the Revit building model, and the energy monitoring
ICREE 2024 - International Conference on Renewable Energy and Ecosystem
12
time was 24 hours. As shown in Table 4, the
following data was obtained. The total source energy
is 6078.63GJ, and the total site energy is 3078.57GJ.
The total source energy is nearly twice the total site
energy. The energy consumption of the site energy
per unit total building area and energy consumption
per air-conditioned building area is 1116.93 MJ/m2,
and the source energy is 2205.37 MJ/m2. In building
energy consumption, source energy usually refers to
the energy consumed by the building, that is, the form
of energy supplied to the building. Energy
consumption during operation mainly comes from the
building's ventilation, heating, refrigeration, lighting,
and electrical equipment (Gao et al., 2024). If the use
of source energy is too high, the energy efficiency of
the building is likely low or there is energy waste.
Table 4: Site and source energy of the modeling building.
Total
Energy
[GJ]
Energy Per
Total
Building
Area
[MJ/m2]
Energy Per
Conditioned
Building
Area
[MJ/m2]
Total/Net
Site
Energ
y
3078.57 1116.93 1116.93
Total/Net
Source
ener
gy
6078.63
2205.37 2205.37
As shown in Table 5, the cooling energy
consumption in Wuhan is much higher than the
heating energy consumption. The heating energy
consumption is 309.48GJ, and the cooling energy
consumption is 1804.23GJ, which is close to six
times. This is because Wuhan's geographical location,
climatic conditions and other factors result in high
refrigeration energy consumption.
Table 5: End use of the modeling building.
District Cooling
[GJ]
District Heating
[GJ]
Heatin
g
0.00 309.48
Cooling 1804.23
0.00
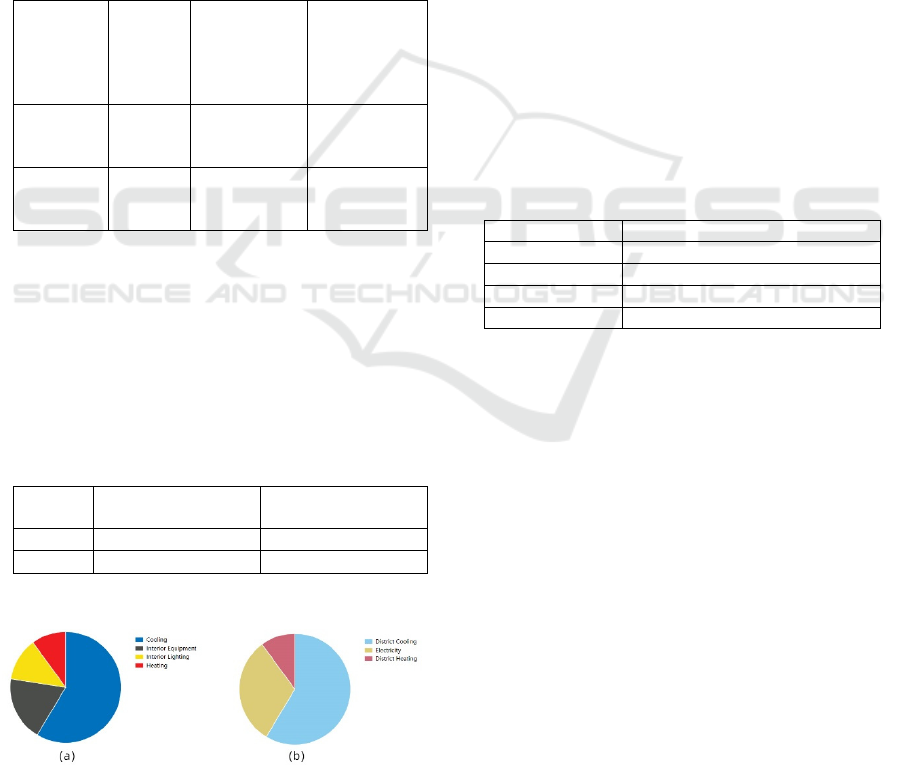
Figure 3: Pie chart of energy consumption and specific
uses: (a)Terminal energy consumption diagram; (b)
Regional energy usage map (Photo/Picture credit: Original)
As shown in Figure 3, cooling accounts for more
than three-fifths of the total energy consumption,
internal lighting and equipment account for two-fifths
of the total energy consumption, and the remaining
one-fifth is used for heating. This also illustrates the
significant demand for refrigeration due to climatic
conditions. As shown in Figure 3, in the area of
heating energy consumption, its proportion is smaller
than the electricity energy consumption and much
lower than the cooling energy consumption,
indicating that the demand for heating is small and the
building is less affected by the outdoor temperature.
As shown in Table 6, the conversion coefficient
of heating energy consumption is 3.613, accounting
for the largest proportion, indicating that in energy
consumption, the energy conversion efficiency
required for heating is low, and relatively more raw
energy needs to be consumed to meet the heating
demand. Secondly, the conversion coefficient of
electric energy is 3.167. Although it is not as high as
the heating energy consumption, it still accounts for a
large proportion. This shows that buildings have a
large demand for electrical energy consumption,
which is used for power supply, lighting, air
conditioning, etc., resulting in a high conversion
coefficient of electrical energy.
Table 6: Site to Source Energy Conversion Factors.
Ener
gy
t
yp
es Site=>Source Conversion Facto
r
Electricit
y
3.167
Natural Gas 1.084
District Cooling 1.056
District Heatin
g
3.613
4 DISCUSSION
The climate type of a geographical location greatly
impacts building energy consumption. For example,
building heating energy consumption in northern
regions is relatively large. Due to the cold climate in
the north, the building insulation performance of
homogeneous buildings is relatively poor, resulting in
a large amount of energy being required to maintain
indoor temperatures in winter. Therefore, the location
of the research project was compared with three cities
with different climates: Harbin, Hong Kong and
Singapore; the energy consumption of the dormitory
building model was analyzed and the differences and
effects of geographical location on energy
consumption were compared.
Harbin is located in the northeastern region of
China and belongs to the southwest of Heilongjiang
Province. It is located between 125°42′~130°10′ east
longitude and 44°04′~46°40′ north latitude. It has a
mid-temperate continental monsoon climate, with
Analysis of Building Energy Consumption Based on Geographical Location: Taking a Dormitory Building in a University in Wuhan as an
Example
13

long and cold winters, short and cool summers, and
four distinct seasons. The annual average temperature
is about 5.6℃, and the annual precipitation is about
423 mm.
Hong Kong is located in southern China, across
the sea from Macau and adjacent to Shenzhen. It has
an oceanic subtropical monsoon climate, abundant
rainfall, and four distinct seasons. The annual average
temperature is about 23.3°C, which may drop below
10°C in winter and exceed 31°C in summer.
Singapore is located at the southern tip of the
Malay Peninsula, adjacent to Malaysia across the
Strait of Johor to the north and facing Indonesia
across the Singapore Strait to the south. It has a
tropical rainforest climate with abundant rainfall,
small annual and daily temperature differences, and
an average annual temperature between 23-35°C.
As shown in Table 7, the energy consumption of
source energy and site energy in the four locations is
compared. In Harbin, the site energy is relatively
close to Wuhan and Hong Kong, but the source
energy is much higher than the three cities, indicating
that the total amount of raw materials and fuel
consumed in the operation process is relatively
higher. Harbin has long and cold winters, so buildings
require a lot of energy for heating. Buildings may also
use traditional heating methods, such as coal-fired
and gas-fired boilers, which have relatively low
energy efficiency. Secondly, some college dormitory
buildings may have old structures and poor thermal
insulation performance, requiring more energy to
maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. In
Singapore, the site energy is much higher than that of
the other three cities. This may be because Singapore
has a tropical rainforest climate with high temperature
and humidity. Dormitory buildings require a lot of
energy to cope with indoor cooling and ventilation
needs, so the site energy consumption is relatively
high. big. The data shows that the building energy
consumption in Harbin is the highest, mainly due to
the cold and long winter in Harbin. The temperature
is low, the heating demand is large, and the energy
utilization rate is low. This also shows that the more
direct influencing factor is the huge difference in
energy consumption due to different climate types
and temperature changes caused by geographical
location.
Table 7: Site and Source energy of the buildings in different sites.
Areas Energy Type
Total Energy
[GJ]
Energy Per Total Building
Area [MJ/m2]
Energy Per Conditioned
Building Area [MJ/m2]
Wuhan
Total/Net Site Energy 3078.57 1116.93 1116.93
Total/Net Source Energ
y
6078.63 2205.37 2205.37
Hong Kong
Total/Net Site Ener
gy
3724.90 1351.42 1351.42
Total/Net Source Ener
gy
6023.76 2185.47 2185.47
Singapore
Total/Net Site Ener
gy
5205.29 1888.52 1888.52
Total/Net Source Energ
y
7532.19 2732.74 2732.74
Harbin
Total/Net Site Energy 3294.24 1195.18 1195.18
Total/Net Source Energ
y
9528.84 3457.14 3457.14
As shown in Table 8, the four cities' regional
heating and cooling energy consumption is very
different. Due to the different geographical locations
of the four cities, Singapore is located near the
equator and has a tropical rainforest climate with high
temperature and humidity. Frequent use of air-
conditioning equipment is required inside the
dormitory building to cool down to maintain indoor
comfort. On the contrary, in winter, the temperature
is comfortable, the heating demand is extremely low,
and the heating energy consumption is zero. Harbin's
geographical location has the highest latitude among
the four cities. It has a mid-temperate continental
monsoon climate. Winters are long and cold, while
summers are short and cool. The building structure
has insufficient thermal insulation and poor thermal
insulation, and the climate is cold and heating. The
high demand has led to high heating energy
consumption, which is almost three times that of
Wuhan.
Table 8: End use of the buildings in different sites.
Areas
District Cooling
[GJ]
District Heating
[GJ]
Wuhan
1804.23 309.48
Hongkong
2738.78 21.26
Singapore 4240.43 0.00
Harbin 759.96 1569.43
Regarding the energy consumption of cooling and
heating, the city's climate zone and seasonal
temperature directly impact energy consumption. In
Wuhan, Hong Kong, and Singapore, summers are
relatively hot, and cooling demand and energy
consumption increase as they get closer to the
equator, showing an increasing trend. On the
ICREE 2024 - International Conference on Renewable Energy and Ecosystem
14

contrary, heating energy consumption shows an
increasing trend as the latitude increases.
5 SOLUTIONS
The above research shows that building energy
consumption will be affected by changes in
geographical location, thus exacerbating carbon
emissions. Based on the climate conditions and
geographical environment of different geographical
locations, we need to take a series of targeted
response measures to improve energy efficiency,
thereby reducing energy consumption and achieving
sustainable development goals. Therefore,
formulating and implementing effective
countermeasures is the key to solving the impact of
geographical location on the energy consumption of
university dormitory buildings.
On the one hand, renewable energy can reduce
energy consumption. Renewable energy has the
characteristics of low energy consumption and cost.
In a sense, energy is the foundation for the
development of modern social civilization and the
key to maintaining social operations, people's
production and life, and industrial development and
other social activities. However, most of the energy is
non-renewable. In order to solve the increasingly
severe energy dilemma and better maintain the
operation of society, people have discovered
renewable energy based on this, mainly including
solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, hydro
energy and other non-renewable energy sources.
Fossil renewable energy. The advantages of this
energy are strong energy saving effect, high
environmental protection and high economic
benefits. In this study, the energy-consuming
equipment is air conditioning, fresh air, heating, etc.
The purpose of these equipment is to maintain the
comfortable temperature of the human body as the
main goal. Wind energy is a kind of usable energy
provided to humans due to the work done by air flow.
In the early design of the building, measures such as
the layout, proportion, and orientation of windows
and walls were optimized to achieve natural
ventilation, increase indoor air flow rate, reduce
reliance on traditional energy, and reduce carbon
emissions.
On the other hand, it can improve energy usage
efficiency and reduce energy conversion coefficient.
Improving energy efficiency is inseparable from the
use of energy-saving equipment and the supervision
and management of equipment. Such as air
conditioners, fans, washing machines, lighting
facilities, etc. The energy consumption generated by
the operation of these equipment is high, and more
energy-saving technologies need to be adopted to
improve energy efficiency and reduce energy
conversion coefficients. The factors that affect the
cooling load of air conditioners mainly include
building layout, thermal performance of the building
envelope, and heat dissipation of lighting equipment.
Therefore, reducing the cooling load of air
conditioners requires improving the building layout,
improving the thermal performance of the envelope
structure, and reducing the heat dissipation of lighting
equipment personnel (Qiu, 2021). The increase in
metreing devices is helpful for determining the
energy consumption in each building area in a timely
manner, discovering weak links in energy use,
effectively preventing the unreasonable utilization of
energy, and enhancing people's energy-efficiency
awareness to some extent (Liu and Ren, 2020).
Realize the control of equipment when it is not in use,
to reduce unnecessary losses, thereby more
effectively improving usage efficiency.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This article selects a dormitory building in a
university in Wuhan for analysis, and conducts
energy consumption analysis and explores the impact
of different climates on the cooling and heating loads
of dormitory buildings through three cities in
different climate zones. Conduct simulation analysis
through Revit software to intuitively obtain detailed
results of building energy consumption. This article
found that geographically, the building energy
consumption of cities closer to the equator is higher
than that of areas farther from the equator, and the
source energy of areas with lower latitudes is higher
than that of areas with higher latitudes. In terms of
cooling energy consumption, areas with lower
latitudes face greater energy consumption pressure,
while heating energy consumption is lower. In terms
of heating energy consumption, areas with higher
latitudes have greater heating needs and consume
more energy. This shows that geographical location
significantly impacts the energy consumption of
university dormitory buildings. With the continuous
development of social economy and the increasingly
prominent energy issues, we can respond to the
challenges posed by geographical location and
different climate types through more refined energy
management and intelligent building design. At the
same time, increase the research and utilization of
renewable energy, actively promote energy-saving
and emission reduction technologies, promote the
sustainable use of building energy in universities,
jointly respond to challenges such as global climate
change and energy security, and promote the
Analysis of Building Energy Consumption Based on Geographical Location: Taking a Dormitory Building in a University in Wuhan as an
Example
15

sustainable development of building energy
consumption.
REFERENCES
Ge Boxuan. Innovative thinking on the development of
green buildings based on "carbon peaking and carbon
neutrality" Housing and Real Estate, 02, pp.109-111
(2024).
Xu W, Ni J, Sun D, Huang S, Dong J. My country's building
carbon peak and carbon neutrality target decomposition
and path analysis, Architectural Science, 10, p.1-8+23
(2021).
Yang T. Research on optimization of energy-saving
potential of university teaching buildings in Beijing
area (Master's thesis, North China University of
Technology, 2023).
Wu S. Research on energy-saving design of university
dormitory buildings based on BIM technology
(Master's thesis, Chang'an University, 2020).
Qiu Y. Research on energy-saving strategies for existing
buildings in some universities in Guangzhou area
(Master's thesis, South China University of
Technology, 2021).
Dai L. Research on energy-saving design of teaching
buildings in colleges and universities in Jinan area
based on energy consumption analysis (Master's thesis,
Shandong Jianzhu University, 2024).
Bao S, Chen C, Lou X, Qin X, Dong F. Building energy
consumption analysis based on BIM, Science and
Technology Bulletin, 01, pp.49-54 (2024).
Wang S, Zhao F, Liu Y. Application of BIM technology in
green construction energy consumption control of
construction projects, Juye, 07, pp.43-45 (2023).
Gao Z, Li J, Chen N, Kong W, Xie H. Design optimization
of teaching buildings in Xinjiang universities based on
energy consumption and cost targets, Journal of Shihezi
University (Natural Science Edition, 2024).
Liu Q and Ren J. Research on the building energy efficiency
design strategy of Chinese universities based on green
performance analysis, Energy and Buildings, 224, p.
110242 Available at:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2020.110242 (2020).
ICREE 2024 - International Conference on Renewable Energy and Ecosystem
16
