
Intelli-Fusion: An Integrated Multi-Lingual Assistive Platform with
Advanced Features for Community and Hemi Plegic People
S. Suresh Kumar
a
, Kotha Suyash
b
, Kotha Sri Charan
c
, P. Keerthi Sharin
d
and V. Harsha
e
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education,
Virudhnagar, Tamilnadu, India
Keywords: UI and UX, Dashboard Integration, Speech Recognition, Text to Speech Conversion, Language Translation,
Gesture Control, Fraud Detection, Seeds Prosperity, Mental Health Support, Sports Analytics, Human
Computer Interaction, Scalability, Multi Tool Integration, NLP, Cybersecurity, AI driven Support.
Abstract: This paper aims to develop a comprehensive user interface that integrates multiple helpful functionalities,
enhancing accessibility and usability for a diverse user base. The interface features a central dashboard
providing an overview and quick access to individual modules, each representing a distinct helpful tool. A
modular design facilitates easy management and updates, while an intuitive and user-friendly interface
ensures smooth navigation with clear labels, tooltips, and help sections.
1 INTRODUCTION
The goal of this paper is to create a complete, machine
learning-powered user interface that unifies many
features on a single platform. To protect user data, the
interface opens with a secure login page. After
logging in, users are presented with a dashboard that
explains the project's objectives and gives a system
overview. Advanced machine learning algorithms
were used in the design of each module to ensure
strong and flexible performance. The project's goal is
to develop a modular, user-friendly interface that
improves usability and accessibility for a wide variety
of users. The main goal of this paper is to create an
intuitive interface driven by machine learning that
combines a number of cutting-edge tools into a single,
well-functioning platform. The interface guarantees
that user data is protected while offering a
personalized experience, beginning with a secure 1
login page. Users are taken to a dashboard that
describes the project's goals and acts as a main center
for navigation after logging in.
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-0301-9572
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-3328-1422
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-2768-3431
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-8169-0637
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6254-4706
The interface guarantees that user data is
protected while offering a personalized experience,
beginning with a secure login page. Users are taken
to a dashboard that describes the project's goals and
acts as a main center for navigation after logging.
2 DATASET
A publicly accessible dataset called which integrates
functionalities of all the modules they are:
LibriSpeech is a sizable collection of read English
speech that can be used to train speech recognition
software.
Mozilla Common Voice: A speech dataset gathered
from the public that features a range of languages and
dialects.
TED-LIUM Dataset: Speech-to-text applications can
benefit from transcriptions of TED presentations.
IEEE-CIS Fraud Detection Dataset: A comprehensive
dataset that includes transactional data, used for
identifying fraudulent transactions.
Suresh Kumar, S., Suyash, K., Sri Charan, K., Keerthi Sharin, P. and Harsha, V.
Intelli-Fusion: An Integrated Multi-Lingual Assistive Platform with Advanced Features for Community and Hemi Plegic People.
DOI: 10.5220/0013653000004639
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems (ISPES 2024), pages 191-197
ISBN: 978-989-758-756-6
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
191

Credit Card Fraud Detection (Kaggle): A popular
dataset with anonymized credit card transactions
labeled as fraudulent or non-fraudulent.
Synthetic Financial Dataset For Fraud Detection
(SFD-FD): A synthetic dataset for exploring financial
fraud detection.
Reddit Mental Health Dataset: A collection of mental
health-related posts from Reddit, useful for sentiment
analysis and mental health prediction.
DAIC-WOZ (Distress Analysis Interview Corpus): A
dataset containing clinical interviews for mental
health research, including audio, video, and
transcripts.
eRisk Dataset: A dataset used for early detection of
mental health issues from social media posts.
Soccer/Football Player Statistics (Kaggle): A dataset
with detailed statistics on football/soccer players and
matches, useful for performance analysis.
NBA Player Statistics Dataset: Provides
comprehensive stats on NBA players and games for
basketball analytics.
Tracking Data (Stats Bomb, FIFA World Cup): For
more detailed analytics, you can use tracking data
from football matches.
LibriVox Audiobooks: Public domain audiobooks
that can be used for text-to-speech models or
audiobook generation.
Gutenberg Text Collection: A vast collection of free
eBooks that can be converted to audio using text-to-
speech models.
Project Gutenberg Audiobooks: Text and
corresponding audio pairs from public domain books
for training models.
3 RELATED WORK
3.1 Integrated AI Systems
Microsoft AI Platform: Microsoft’s AI platform
integrates various machine learning models and
functionalities, including natural language processing
(NLP), fraud detection, and text-to-speech (TTS)
capabilities. This platform demonstrates how diverse
AI tools can be unified under a single interface,
offering solutions for multiple domains
.
3.2 AI-Powered Assistants
IBM Watson offers a suite of AI services that include
speech- to-text, natural language understanding, and
predictive analytics. Watson has been applied in
healthcare for mental health assistance and in finance
for fraud detection, showing the potential of
combining different AI functionalities within one
system.
3.3 Comprehensive Health Platforms
Mind strong integrates mental health monitoring
through mobile data with AI-driven analysis to detect
and predict mental health issues. This is coupled with
speech recognition and natural language processing
to enhance user interaction and provide personalized
mental health support.
3.4 Smart Sports Analytics Platforms
Zebra integrates machine learning for sports
analytics, combining tracking data with predictive
models to analyze player performance. It also
incorporates voice-based interfaces and other AI
tools, showing how sports analytics can be part of a
larger AI system.
3.5 Financial AI Systems
Ayasdi: This platform integrates various AI tools,
including fraud detection, natural language
processing, and predictive analytics, into a single
system used by financial institutions. Which may help
people from illegal networking. Ayasdi's approach
showcases how AI-driven platforms can address
multiple challenges within one framework.
4 OVERVIEW/APPROACH
Creating a secure login page where users submit their
credentials, like a username and password, is the first
step in the project. By cross-referencing user
credentials with a backend database or authentication
service, the login system is intended to authenticate
users. Users are automatically led to the main
dashboard after completing the login procedure
successfully, guaranteeing a seamless transition from
the login process to the platform's primary features.
In order to safeguard user information and tailor the
experience according to the user's profile, this step is
essential.
Upon logging in, users are presented with an
extensive dashboard that functions as the centre of the
site. The dashboard's introduction part delineates the
goal and salient characteristics of the platform, and it
serves as a comprehensive summary of the project.
Users can learn more about the platform's features
and potential benefits from this introduction. Users
ISPES 2024 - International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems
192

can quickly manage the system because of the user-
friendly dashboard structure, which makes all
required information and functionality readily
available.
A sidebar is incorporated on the left side of the
interface to enable effortless navigation. The sidebar
features a list of several modules that are grouped
according to the particular requirements of various
user groups, including government officials,
employees, professors, students, and elders. Modules
in each category are created to specifically cater to the
needs of the target audience. For instance, the
government section might have administrative
resources, but the student section might have
instructional tools. Users may easily locate and utilize
the tools that are most pertinent to their roles thanks
to this categorisation
Every module is developed with careful thought
for the people who will use it. Modules are designed
to be relevant to the needs of the particular user group
they serve, functional, and easy to use. These modules
are incorporated into the dashboard following the
development stage, guaranteeing that they function as
a unit and are conveniently accessible from the
sidebar. Then, extensive testing is done to confirm
that every module functions as planned and offers
users the desired benefit. In order to maintain the
platform's effectiveness and user-centric design, user
feedback is gathered and used for enhancements.
The platform's scalability and adaptability enable
the development of additional modules and features
as user demands change, in addition to its core
functionality. This project's flexibility is crucial since
it guarantees that it will be able to adapt to new
developments in technology and user input in the
future. The platform's modular architecture allows
developers to add or update specific components with
ease without interfering with the operation of the enti
system. This design strategy not only extends the
platform's life but also guarantees that it will
continue to be valuable and relevant to users in a
variety of
industries.
Furthermore, the platform's design places a high
priority on user experience, or UX. The end user is
the primary focus of each module and feature, with an
emphasis on usability, accessibility, and
effectiveness. Throughout the UI, tooltips, help
sections, and unambiguous labelling are used to assist
users—particularly non-techies. Additionally, the
platform offers customization choices, enabling
customers to modify dashboard and module settings
to suit their unique requirements and work processes.
This emphasis on user experience (UX) makes sure
that the platform is not just strong and useful but also
approachable and easy to use, appealing to a wide
range of users with different degrees of experience.
When the platform is finally launched, users can
access it. The platform's functioning and performance
are tracked continuously to make sure that any
problems are promptly fixed. Updates are given on a
regular basis to maintain overall performance,
strengthen security, and improve functionality. In
order to guarantee that the platform continues to be a
useful and trustworthy resource for all users, user
assistance is also accessible to help with any queries
or problems. This methodical strategy guarantees that
the project not only achieves its initial objectives but
also keeps improving and changing over time.
5 METHODS AND
TECHNOLOGIES USED
5.1 HTML
The primary language used to create online pages and
web apps is called HTML (HyperText Markup
Language). With the use of different elements
including headings, paragraphs, links, photos, and
forms, it offers the organisation and content of a web
page. HTML is necessary for setting up the
fundamental components of a webpage since it
defines how content is arranged and displayed in a
browser using a system of tags and attributes.
5.2 CSS
The display and layout of HTML components can be
managed using the stylesheet language CSS
(Cascading Style Sheets). It enables designers to
create aesthetically pleasing and responsive designs
by applying styles to HTML text, including colours,
fonts, spacing, and positioning. By keeping design
and content separate and enabling the management of
numerous pages' appearances from a single
stylesheet, CSS can improve a web page's aesthetics
and user experience.
5.3 Java Script
JavaScript is a flexible programming language that
makes dynamic and interactive web page features
possible. Without requiring a page reload, it enables
developers to incorporate client-side features like
animations, form validation, and real- time updates.
By enabling responsive and interactive web apps,
JavaScript enhances user experience by interacting
Intelli-Fusion: An Integrated Multi-Lingual Assistive Platform with Advanced Features for Community and Hemi Plegic People
193

with HTML and CSS to modify web page content and
behaviour
5.4 IBM Watson
An effective tool for turning spoken words into
printed text is IBM Watson. It is capable of processing
data in batches as well as in real time and supports a
large number of languages. Applications requiring the
transcription of audio content, like customer support
conversations or meeting transcription, will find this
service very helpful. Additionally, users can
customise the IBM Watson Speech to Text model to
increase accuracy for certain accents or industry
terms. Because the service is available via REST APIs
and SDKs for a number of programming languages,
it can be easily integrated into a wide range of
applications. It also has sophisticated features like
keyword spotting, which allows you to locate specific
terms in the speech, and speaker diarization, which
allows you to distinguish between distinct speakers in
an audio file.
5.5 Tacotron
Tacotron 2, a cutting-edge text-to-speech (TTS)
model that produces natural-sounding, high-quality
voice from text. It works by first employing a
sequence-to-sequence model with attention
mechanisms to transform the input text into a mel
spectrogram. A WaveNet vocoder is then used to
synthesise this spectrogram into raw audio, ensuring
that the output is clear and expressive speech.
Tacotron 2 can generate high- fidelity, lifelike
speech through end-to-end training, which makes it
appropriate for use in audiobooks, virtual assistants,
and other TTS services. It is a popular model in both
commercial and research contexts because of its
versatility in fine-tuning and support for multiple
languages and voices.
5.6 Random Forest Classifier
Random Forest can handle complicated, high-
dimensional data and recognize patterns suggestive of
fraudulent activity, it is a popular algorithm for fraud
detection. By utilising its ensemble learning
methodology to construct many decision trees that
enhance prediction accuracy and robustness
collectively, Random Forest succeeds in the fraud
detection space. In order to capture a variety of data
properties and minimise overfitting, each tree is
trained on a distinct subset of the data then split using
a random subset of features.
5.7 Neural Machine Translation (NMT)
For language translation, neural machine translation
(NMT) models—specifically, the Transformer
architecture—are extensively employed. Vaswani et
al. introduced the Transformer model, which
efficiently captures complex dependencies and
interactions between words by processing input
sequences in parallel using self-attention
mechanisms. This method allows the model to
comprehend context across extended sequences,
resulting in accurate and fluid translations. Many
sophisticated translation systems, such as Google's
BERT and OpenAI's GPT models, which further
improve translation capabilities through deep
learning methods and extensive pretraining, are built
on top of transformers.
5.8 YOLOV7
The cutting-edge object detection model YOLO (You
Only Look Once) is made for real-time processing.
YOLO, created by Joseph Redmon and associates,
stands out from the conventional method of
employing several steps by approaching object
identification as a single regression problem. It splits
an image into a grid and forecasts bounding boxes and
class probabilities for every grid cell at the same time.
YOLO's unified methodology enables it to achieve
high-speed processing and real-time performance,
which makes it perfect for applications like real-time
image analysis, autonomous driving, and video
surveillance that require fast object detection.
YOLO's position as a top object identification model
has been cemented by the introduction of
advancements in accuracy and efficiency in its many
versions.
5.9 TensorFlow
The open-source TensorFlow machine learning
framework, which makes it easier to create and
implement machine learning models. It offers an all-
inclusive ecosystem for developing, honing, and
implementing models for a range of applications,
such as computer vision, natural language processing,
and deep learning. With its adaptable and scalable
architecture, TensorFlow facilitates both low-level
APIs for precise control over model construction and
optimisation and high-level APIs for quick model
prototyping. TensorFlow is widely utilised in both
research and production environments to construct
powerful artificial intelligence (AI) applications and
ISPES 2024 - International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems
194
systems because of its broad support for neural
network operations.
5.10 MediaPipe
MediaPipe is an open-source framework developed
by Google for building cross-platform, real-time
machine learning pipelines. For a variety of computer
vision and machine learning tasks, including position
estimation, hand tracking, and face detection, it offers
a set of pre-built models and components. Developers
may effectively design complicated solutions by
integrating and customising these components thanks
to MediaPipe's modular architecture. Because of its
enhanced efficiency and compatibility with various
platforms, such as the web and mobile ones, it is a
well-liked option for creating real-time apps that
demand superior audio and visual processing.
5.11 Optical Flow
Video data is analysed and player motions are
interpreted using Optical Flow Models. With the use
of optical flow models, movement patterns, speed,
and spatial relationships on the field may be
thoroughly analysed. These models track the mobility
of players and objects across frames. This model
measures how players move and interact during a
match, offering important insights on player
performance, strategy efficacy, and game dynamics
5.12 BERT (Bidirectional Encoder
Representations from
Transformers)
Bert is a well-known paradigm for sentiment and
emotion analysis in mental health studies. BERT can
reliably discern attitudes and emotions from text data
because of its deep learning architecture, which
analyses and comprehends the context of words in a
phrase. This feature aids in the identification of
mental health problems by examining written
correspondence, social media posts, and treatment
notes to spot indications of ailments like anxiety or
depression.
6 RESULT
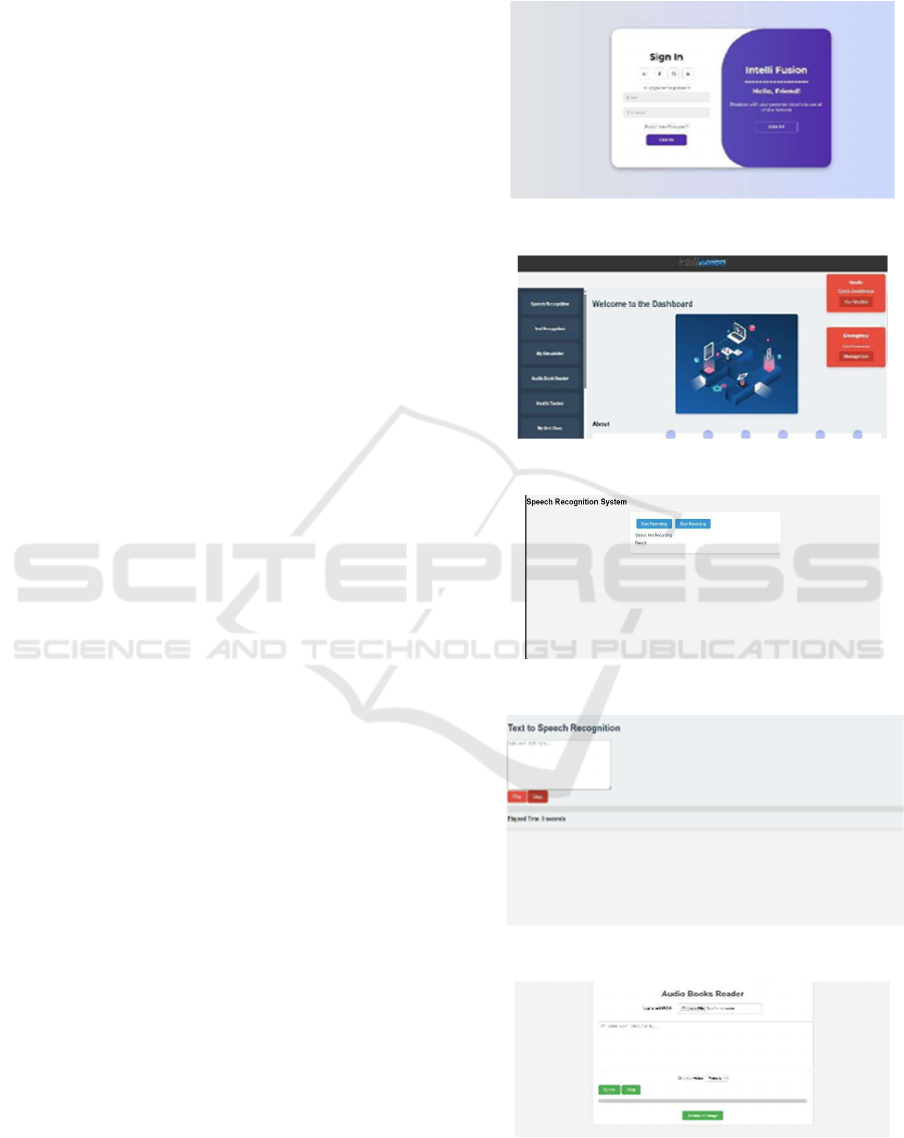
Figure 1: Login Page.
Figure 2: Dashboard.
Figure 3: Real time Speech recognition system.
Figure 4: Real time test to speech conversion.
Figure 5: Audio Book Reader.
Intelli-Fusion: An Integrated Multi-Lingual Assistive Platform with Advanced Features for Community and Hemi Plegic People
195

7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
SCOPE
This work effectively illustrates the creation of an all-
encompassing, machine learning-driven user
interface that combines several cutting-edge tools
into a unified platform. Not only the given modules
present from the fig (iv) to fig(xiv) there are so many
other real time applications that can be helpful for
students, employees, and also for government that
starts with a secure login page, it places a high priority
on data protection. A well-organised dashboard
provides a personalised, user-friendly experience.
Robust and adaptable performance is guaranteed
throughout the modules thanks to the application of
advanced machine learning algorithms. The
interface's seamless and simple user experience is
intended to improve accessibility and usability for a
wide range of users. In the future, turning the website
into a mobile application is part of the project's scope.
With this change, accessibility will be increased and
users will be able to interact with the platform while
on the road and take advantage of device- specific
features like push notifications and offline access.
The mobile application that will expand upon the
well-received online interface, enhancing its usability
and adjusting to changing user demands and technical
development
REFERENCES
Agarwal, S., & Yadav, S. P. S. (2014). A survey on machine
learning algorithms and applications. International
Journal of Computer Applications.
Allen, T. (2000). A day in the life of a Medicaid fraud
statistician. Stats.
Arik, S., Chrzanowski, C., Coates, A., Diamos, G.,
Gibiansky, A., Kang, Y., & Li, X., et al. (2005). Deep
voice: Real-time neural text-to-speech. In Proceedings
of the ICML.
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., & Bengio, Y. (2014). Neural
machine translation by jointly learning to align and
translate. CoRR.
Bastien, F., Lamblin, P., Pascanu, R., Bergstra, J.,
Goodfellow, I. J., Bergeron, A., Bouchard, N., Warde-
Farley, D., & Bengio, Y. (2012). Theano: New features
and speed improvements. CoRR.
Beyond Moneyball: The future of sports analytics. (2019).
Analytics Magazine (March). Retrieved online.
Bishop, C. M. (2024). Pattern recognition and machine
learning. New York, NY: Springer..
Building provincial mental health capacity in primary care:
An evaluation of a Project ECHO Mental Health
Program. (2011). Academic Psychiatry. Retrieved from
Springer.
Embedding mental health support in schools: Learning
from the Targeted Mental Health in Schools (TaMHS)
national evaluation. (2011). Emotional and
Behavioural Difficulties.
Furui, S. (2005). 50 years of progress in speech and speaker
recognition research. ECTI Transactions on Computer
and Information Technology, 1(2), November.
Gerrard, B. (2021). Moneyball and the role of sports
analytics: A decision-theoretic perspective. In
Proceedings of the North American Society for Sport
Management Conference.
Greenhalgh, T., Robert, G., MacFarlane, F., Bate, P., &
Kyriakidou, O. (2004). Diffusion of innovations in
service organizations: Systematic review and
recommendations. Milbank Quarterly.
Kleppmann, M. (2022). Designing data-intensive
applications: The big ideas behind reliable, scalable,
and maintainable systems. Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly
Media.
M. F. S., et al. (2023). Securing user interfaces against
attacks: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Dependable
and Secure Computing.
Neumann, K., Schwindt, C., & Zimmermann, J. (2003).
Project scheduling with time windows and scarce
resources. Berlin, Germany: Springer.
Ng, A. (2021). Machine learning yearning. San Francisco,
CA: Self-published.
Nielsen, J. (2018). Designing for user experience: How to
improve usability through user interface design.
Journal of Usability Studies.
Prasad Babu, M. S., & Srinivasa Rao. Leaves recognition
using back-propagation neural network: Advice for pest
and disease control on crops. Technical report,
Department of Computer Science & Systems
Engineering, Andhra University, India.
Preece, J., & Rogers, Y. (2024). Human-computer
interaction. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Rosenheck, R. A. (2005). Organizational process: A
missing link between research and practice.
Psychiatric
Services.
Russell, T., & van Beek, P. (2009). Determining the number
of games needed to guarantee an NHL playoff spot. In
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on
Integration AI OR Techniques Constraint Programming
Combinatorial Optimization Problems.
Schoenwald, S. K., & Hoagwood, K. (2001). Effectiveness,
transportability, and dissemination of interventions:
What matters when? Psychiatric Services.
Sennrich, R., Schwenk, H., & Aransa, W. (2013). A multi-
domain translation model framework for statistical
machine translation. In Proceedings of the ACL.
Stolfo, S., Fan, W., Lee, W., Prodromidis, A. L., & Chan, P.
(1999). Cost-based modeling for fraud and intrusion
detection: Results from the JAM project. In
Proceedings of the DARPA Information Survivability
Conference and Exposition. IEEE Computer Press.
Stone, D., & Jarrett, C. (2022). User interface design and
evaluation. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Morgan
Kaufmann Publishers.
ISPES 2024 - International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems
196

Taheri, A., & Tarihi, M. R., et al. (2005). Fuzzy hidden
Markov models for speech recognition on based FEM
algorithm. Transactions on Engineering, Computing,
and Technology, 4(February), ISSN 1305-5313.
Taigman, Y., Wolf, L., Polyak, A., & Nachmani, E. (2017).
Voice synthesis for in-the-wild speakers via a
phonological loop. arXiv preprint.
Torrey, W. C., Drake, R. E., Dixon, L., Burns, B. J., Flynn,
L., Rush, A. J., Clark, R. E., & Klatzker, D. (2001).
Implementing evidence-based practices for persons
with severe mental illnesses. Psychiatric Services.
Vincent, C. B., & Eastman, B. (2009). Defining the style of
play in the NHL: An application of cluster analysis.
Journal of Quantitative Analysis in Sports
Intelli-Fusion: An Integrated Multi-Lingual Assistive Platform with Advanced Features for Community and Hemi Plegic People
197
