
Chain Accident Prevention by Applying Automatic Braking via
Vehicle to Vehicle Communication
Sowmya P.
a
, Prajjwal Kumar
b
, Kumar Pratyush
c
, Sachin Chaudhary
d
and Sachin Srivastava
e
Department of Electronics and Communication, Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering, Bengaluru, India
Keywords: Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks (VANETs), Collision Detection, Zigbee Communication, Arduino UNO,
ESP32, UV Sensors, ADXL345 Accelerometer, Light Dependent Resistor (LDR), Telegram-Based
Notifications, Internet of Things (IoT), Smart Transportation, Emergency Response Systems, Road Safety
Systems, Real- Time Data Exchange, Centralized Communication Hub, Low-Latency Communication,
Automated Braking.
Abstract: Chain collisions are significant causes of traffic-related accidents and casualties as well as property damage,
resulting largely from delayed driver reaction time and inadequate communication between various vehicles.
This research shall design an IoT-based system equipped with V2V communication capability and automatic
braking to preclude such accidents. Implementing the system by taking advantage of cost-effective materials
such as Arduino UNO microcontrollers, Zigbee communication modules, and UV sensors ensures real-time
danger detection and response. A centralized hub powered byESP32 facilitates emergency notifications via
the Telegram platform, hence enhancing coordination with stakeholders. Other features include glare
reduction using LDR sensors and real-time environmental monitoring to enhance night-time visibility and
driving safety. Combining these technologies, the system reduces chain collisions, shortens response times in
emergencies, and improves overall traffic safety. This research points out the enormous potential of
integrating IoT and V2V technologies to shape smarter, safer transportation networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
Chain collisions on roads and highways are a
significant cause of site visitors’ accidents
internationally, often resulting in excessive injuries,
fatalities, and full-size property harm. These injuries
typically occur due to behind schedule driver
reactions, bad visibility, and the absence of effective
communication be- tween vehicles. As the need for
safer and smarter transportation systems grows,
modern answers that leverage emerging technologies
are vital to addressing those challenges. This study
introduces an IoT-based machine that makes use of
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) conversation and
automatic braking mechanisms to save.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0211-6130
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-9188-1842
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-7281-6586
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-3860-3159
e
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-5004-0475
Additionally, it contains a centralized
communication hub that transmits critical indicators,
consisting of accident notifications warnings, to
nearby automobiles and emergency responders
through Telegram. By combining hardware and
software components, the system ensures seamless
communication and reliable responses to
emergencies
.
At the core of the system are UV sensors for
obstacle detection and ADXL345 accelerometers for
impact sensing, which monitor the vehicle’s
environment continuously. Zigbee communication
modules enable low-latency data exchange be- tween
vehicles, facilitating rapid hazard detection and
response. Arduino UNO microcontrollers process
P., S., Kumar, P., Pratyush, K., Chaudhary, S. and Srivastava, S.
Chain Accident Prevention by Applying Automatic Braking via Vehicle to Vehicle Communication.
DOI: 10.5220/0013652500004639
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems (ISPES 2024), pages 157-163
ISBN: 978-989-758-756-6
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
157

sensor data to make decisions in real time, while LDR
sensors dynamically adjust headlight intensity to
reduce glare during nighttime driving. The
centralized hub, equipped with WiFi connectivity,
relays alerts to a Telegram based notification system,
ensuring timely communication with drivers and
authorities. The system aims to reduce the likelihood
of rear-end and chain collisions by enabling real-time
hazard detection and intervention. It additionally
enhances driving safety with the aid of enhancing
midnight visibility and providing reliable emergency
communication. By addressing those important gaps
in current road protection measures, the proposed
system gives a complete technique to mitigate
accidents, enhance response times. Early checks of
the system dis- play its potential to noticeably
improve road protection, marking a leap forward in
the development of intelligent transportation
networks.
This research paper details the design,
implementation, and testing of the proposed system,
high- lighting its contribution to advancing IoT-based
road safety solutions. Through this integration of
sensors, communication modules, and centralized
control, the project lays the foundation for smarter,
safer roads in the future.
2 BACKGROUND AND
RELATED WORK
2.1 Background
Chain collisions are among the most hazardous types
of traffic accidents, often resulting in multiple
fatalities and extensive property damage. These
accidents typically occur due to a cascade of delayed
reactions among drivers, particularly in high-speed or
congested traffic scenarios. Factors such as poor
visibility, insufficient warning systems, and the lack
of Real Time communication be- tween vehicles
exacerbate these events. As mod- ern transportation
systems evolve, there may be a pressing need for
technological advancements that no longer only
beautify motive force protection but also cope with
those systemic challenges comprehensively. Vehicle-
to-Vehicle (V2V) verbal exchange has emerged as a
promising solution for enhancing avenue protection.
By permitting cars to percent- age real-time records
about their environment and riding situations, V2V
communication structures can offer timely signals to
drivers or even trigger computerized responses,
consisting of braking or lane adjustments. The
integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in
addition enhances the ability of such systems, bearing
in mind seam- less communication, advanced threat
detection, and centralized manipulation of safety
mechanisms.
Despite significant advancements, current
implementations face limitations. Most existing
solutions rely heavily on expensive hardware, such as
LIDAR or radar systems, which are not eco-
nomically feasible for widespread adoption.
Additionally, issues such as connectivity disruptions,
latency in data transmission, and environmental
sensitivity of sensors remain significant hurdles.
Addressing these challenges requires a cost effective,
robust, and scalable solution that integrates affordable
hardware with reliable communication protocols.
2.2 Related Work
Several research efforts have focused on improving
road safety through V2V communication and
automated systems. Studies on Adaptive Cruise
Control (ACC) and Lane Departure Warning Systems
(LDWS) have demonstrated the benefits of
automated systems in reducing accidents. ACC
systems help maintain safe distances between
vehicles, while LDWS systems alert drivers to un-
intended lane departures. However, these systems are
often standalone and lack the ability to communicate
with other vehicles in real-time, limiting their
effectiveness in preventing chain collisions.
Recent research has explored the use of Zig- bee
communication modules for V2V interaction. Zigbee
offers low-latency and energy- efficient data
exchange, making it suitable for real-time
communication in vehicular networks. Researchers
have also investigated the use of UV sensors for
obstacle detection and accelerometers for impact
sensing, which provide critical data for hazard
identification. However, these systems often lack
integration with centralized hubs for emergency
communication, reducing their scope of applicability.
IoT-enabled systems have further expanded the
possibilities for road safety. Projects utilizing WiFi
and mobile networks to transmit accident
notifications to authorities have shown promise in
improving emergency response times. The use of
messaging platforms, such as Telegram, for real- time
alerts adds another layer of efficiency and
convenience. Despite these advancements, the
challenge of creating a cohesive system that combines
hazard detection, automated response and emergency
communication remains largely unaddressed.
The system proposed in this research builds upon
ISPES 2024 - International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems
158

these advancements by integrating affordable and
reliable hardware, such as Arduino UNO
microcontrollers, UV sensors, and Zigbee modules,
with a centralized communication hub. Un- like
standalone systems, this approach ensures seamless
coordination between vehicles, enabling rapid
response to hazards and reducing the likelihood of
chain collisions. By addressing the limitations of
existing solutions, this project con- tributes to the
development of safer and smarter transportation
networks.
3 SYSTEM DESIGN
The proposed system integrates Arduino UNO as the
primary microcontroller for vehicles and ESP32 for
the centralized communication hub. This design
ensures cost-effective and efficient vehicle-level
operations while leveraging the ESP32’s advanced
connectivity capabilities for emergency
communication. The architecture is divided into three
primary components: vehicle hardware, vehicle-to-
vehicle (V2V) communication, and the centralized
communication hub.
Vehicle Hardware: Each vehicle is equipped with
Arduino UNO to control essential sensors, actuators,
and communication modules. The hardware
components include:
UV Sensors: Positioned at the front and rear of the
vehicle to measure distances from nearby obstacles or
vehicles. These sensors enable real-time hazard
ADXL345 Accelerometers: Detect sudden
acceleration changes along three axes (X, Y, Z) to
identify potential collisions or abrupt movements.
LDR Sensors: Monitor ambient light levels to
dynamically adjust the vehicle’s headlight in- tensity,
reducing glare during nighttime driving.
Arduino UNO: Functions as the vehicle’s primary
processing unit, handling sensor data acquisition,
processing, and triggering actions like braking or
V2V communication.
Motor Drivers and Relays: Enable control over the
vehicle’s movement and safety mechanisms, such as
braking and headlight adjustments.
Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication: Zigbee modules
connected to the Arduino UNO facilitate real-time
communication between vehicles. This V2V
communication ensures prompt data sharing for
critical scenarios, such as Obstacle detection alerts to
nearby vehicles. Notifications of sudden deceleration
or impact. Warnings about low fuel levels to prevent
breakdowns. The Arduino UNO collects and
processes sensor data and transmits these alerts via
Zigbee modules to nearby vehicles, ensuring a rapid
and coordinated response.
Centralized Communication Hub: The central
communication hub, using ESP32, plays an important
role in managing the emergency notification and
more widespread communication. Equipped with
WiFi connectivity, the ESP32 connects to the internet
for sending messages to the cloud-based services or
the stakeholders. It integrates with a Telegram bot for
forwarding the critical alerts such as accident reports
and low-fuel warnings to the preconfigured contacts
including the authorities and owners of the vehicles.
It processes incoming Zigbee messages that it
translates into actionable alerts for efficient
dissemination.
The hybrid system workflow starts with hazard
detection by Arduino UNO-based vehicles using UV
sensors and accelerometers, which sends safety
signals such as auto-braking and alerting other
vehicles in the neighborhood through Zigbee. These
alerts are received by ESP32 hub and broadcast to
concerned parties in real-time, which makes this
hybrid design an economical option of Arduino
UNO-based design with ESP32-based connectivity
for hazard detection, which can be scaled in the
future. It addresses gaps in transportation safety,
paving the way for smarter, safer roads.
4 METHODOLOGY
Sensor Integration: UV sensors are used for front
object detection and blind spot monitoring. ADXL
accelerometer sensor detects sudden changes in
vehicle movement, identifying accidents. The LDR
sensor detects high beams from on- coming vehicles
for automatic headlight adjustment message
transmission.
Data Processing: The Arduino UNO microcontroller
collects and procedures information from all of the
sensors in actual- time.
Collision Detection: When a potential collision or
accident is detected, the system immediately
identifies the hazard using UV and accelerometer
data.
Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication: Zigbee
communication is utilized to send alerts to nearby
vehicles, warning them of potential danger.
Automatic Braking: Upon receiving the collision
Chain Accident Prevention by Applying Automatic Braking via Vehicle to Vehicle Communication
159

alert, nearby vehicles automatically apply their brakes
to prevent a chain accident.
Headlight Adjustment: If an LDR sensor detects a
high beam from oncoming traffic, the vehicle will
receive a message to switch to a low beam to improve
visibility.
Emergency Communication: A central hub collects
accident data and sends emergency alerts to pre-
configured contacts via Telegram for quick
assistance.
Real-Time Monitoring: The “Chain Accident
Prevention by Applying Automatic Brake via
Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication” project utilizes
IoT-based technology to improve road safety and
prevent chain collisions. Here, the system uses UV
sensors for real-time object detection along with blind
spot monitoring wherein the system triggers
immediate responses if obstacles are detected to be
within critical range. An ADXL accelerometer finds
sudden deceleration or im- pacts, prompting accident
alerts. Zigbee modules enable low- latency vehicle-
to-vehicle communication, allowing surrounding
vehicles to activate automatic braking mechanisms,
reducing re- action times and mitigating collisions.
To address night-time driving hazards, LDR sensors
detect and with the help of Zigbee send messages to
adjust headlights from high to low beams, reducing
glare and enhancing visibility. The system also
includes a centralized hub that relays emergency
notifications with location details via Telegram,
ensuring swift response from emergency services.
Each car carries an LCD which will be displaying
real-time sensor data, alerts, and system statuses. This
means there will be a greater improvement in safety,
with reduced accidents and a more efficient driving
environment.
Below are the core components and
functionalities of the proposed system:
Front Object Detection and Blind Spot Monitoring:
The system utilizes UV sensors to monitor the
distance between the vehicle and obstacles in front or
within blind spots. This ensures continuous tracking
of close by items, alerting the machine if an
impediment is within a predefined safe range.
Accident Detection System: ADXL accelerometer is
used to come across unexpected changes in
acceleration, including those as a result of a collision
or difficult braking. If the gadget detects values
exceeding the protection threshold, it acknowledges
the occasion as a potential accident and triggers alerts.
Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication (V2V): Zig- bee
modules facilitate verbal exchange between vehicles
within a defined range. When a car detects a coming
near collision or a coincidence, it sends an alert to
close by motors. These cars routinely have interaction
with their braking structures upon receiving the alert,
preventing a chain reaction.
Automatic Braking Mechanism: Upon receiving a
collision alert, the machine automatically activates
the vehicle’s braking gadget. This function removes
human response delays, imparting a faster reaction to
keep away from or mitigate collisions.
High Beam Detection: The system incorporates an
LDR sensor to detect high beam headlights from
oncoming vehicles. When detected, the system
automatically informs the other vehicle to switch to a
low beam, enhancing visibility and reducing glare for
all drivers on the road.
Centralized Hub and Emergency Communication:
The proposed system includes a centralized hub
connected to all vehicles via the Zigbee network. In
the event of an accident, the hub receives alerts and
sends emergency notifications to pre- configured
contacts through the Telegram plat- form. This
ensures timely assistance and quick response from
emergency services.
Real Time Monitoring and Display: LCD is in- stalled
in the vehicle to provide real-time feed- back to the
driver. The display shows critical information,
including the distance to obstacles, system alerts, and
the status of vehicle-to-vehicle communication. This
helps drivers stay aware of their surroundings and the
system’s actions.
System Workflow is discussed below
Continuous Monitoring: UV sensors and the ADXL
accelerometer continuously monitor the vehicle’s
environment and movement.
Hazard Detection: If an obstacle or sudden decel-
eration is detected, the system evaluates the risk of a
collision.
Alert Transmission: The vehicle sends alerts to
nearby vehicles via Zigbee.
Automatic Braking: On receiving an alert, the nearby
vehicles automatically apply brakes to pre- vent a
chain collision.
High Beam Adjustment: LDR sensors detect on-
coming high beams and communicate to switch
headlights to low beam to the other vehicle.
Emergency Alerts: In case of an accident, the system
communicates with the hub, which sends
notifications through Telegram for emergency
response.
ISPES 2024 - International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems
160
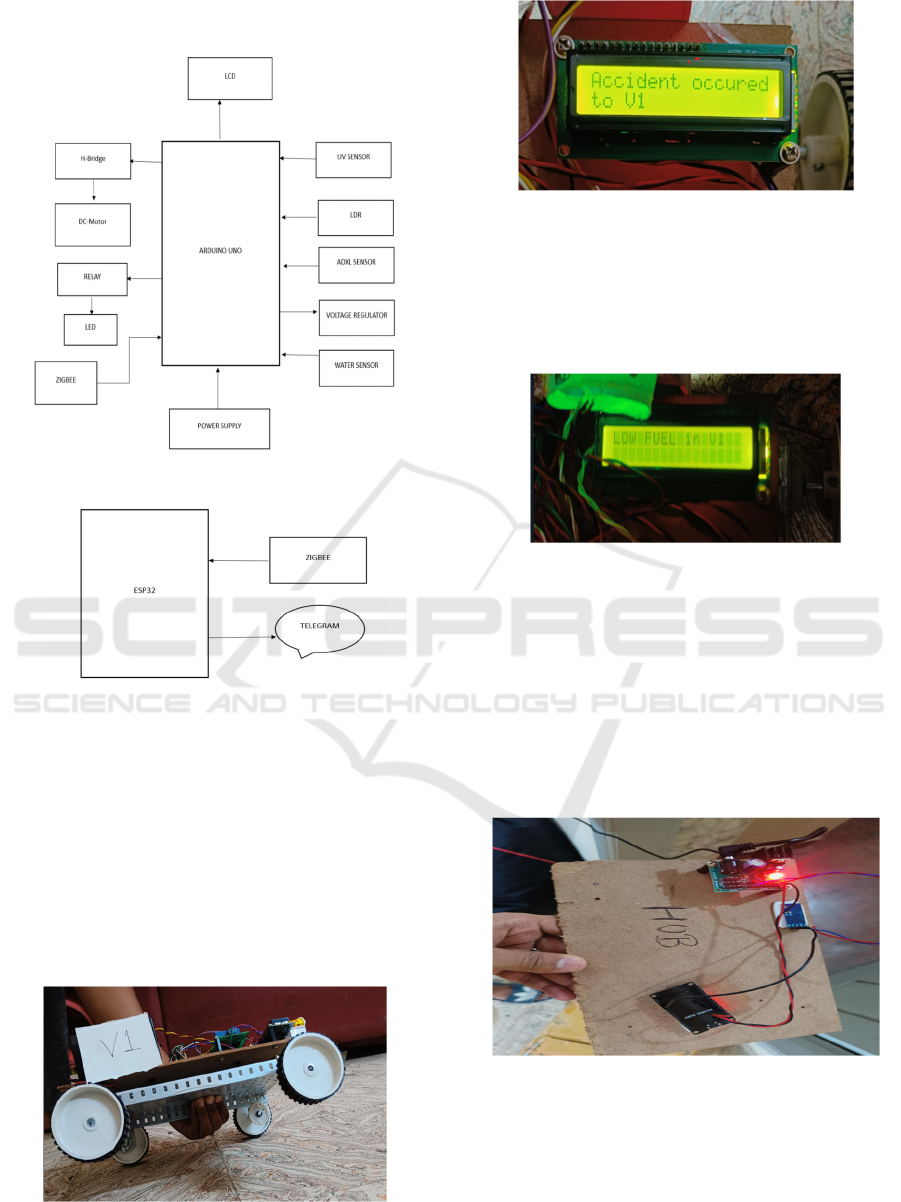
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Figure 5.1: Block diagram of the proposed System.
Figure 5.2: ESP32 interface.
6 RESULTS OF THE RESEARCH
Reliable Hazard Detection: The system was found to
be working well in detecting obstacles and hazards
through UV sensors while monitoring the
surroundings of a vehicle in Real Time.
Accelerometers (ADXL345) successfully detected
jerks or collisions, thus enabling alerts and safety
mechanisms accordingly.
Figure 6.1: Prototype of the system.
Figure 6.2: Result 1.
Improved Communication: Communication modules
based on Zigbee ensured low-latency trans- mission
of data between vehicles efficiently, thus allowing for
swift transmission of alerts about potential hazards,
accidents, or sudden braking
.
Figure 6.3: Result 2.
Automatic Braking Implementation: Vehicles with
the system deployed automatically applied brakes in
case of collision alerts, preventing chain reaction
accidents.
Centralized Emergency Response: The ESP32-based
centralized hub relayed emergency notifications to
preconfigured contacts via Telegram, thus ensuring
timely responses from authorities and other
stakeholders.
Figure 6.4: HUB.
Scalability and Cost Efficiency of the System: The
use of low-cost hardware, such as Arduino UNO and
Zigbee modules, made the system cost- effective
enough for mass adoption without affecting
reliability. The system would allow easy integration
of additional sensors or technologies in the future
Chain Accident Prevention by Applying Automatic Braking via Vehicle to Vehicle Communication
161

because of its modular structure.
Real-time monitoring and feedback: The inclusion of
an LCD in the vehicle allowed the drivers to
continuously monitor distance to obstacles, status of
the system, and alerts, thereby enhancing situational
awareness and decision-making.
Figure 6.5: Result 3.
Overall Safety Enhancement: In the initial tests, a
significant reduction in the likelihood of rear end and
chain collisions was observed, whereas response in
emergency situations was faster thus indicating the
scope of saving lives on the roads is vast.
7 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, it’s the project “Vehicle-to-Vehicle
Communication” an ambitious development aimed
toward improving road safety through reducing a
common danger found in present-day traffic, namely
the chain collision. Advanced technologies of IoT in
the system allow real-time communication from one
vehicle to another which enables immediate
automated response. UV sensors perceive obstacles
or blind spots; the accelerometer ADXL picks up
rapid deceleration and impacts hence, prompt
detection of accidents is ensured. Zigbee
communication ensures smooth data transfer,
automated braking to minimize human factors, and
prevention of multi-car collisions. The LDR sensor
enhances night safety from glare by informing the
driver about adjusting headlights. It is a centralized
hub that ensures proper emergency response through
alerts on Telegram, making sure timely help reaches
the affected area. An LCD keeps the driver updated
about the status of the system and the environment,
ensuring an informed decision. This will be an all-
inclusive approach by combining automation,
communication, and safety technologies for safer
roads. Scalable and adaptable, it can be used in smart
city infrastructures and future
development like
machine learning.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We express our sincere gratitude to Dayananda
Sagar College of Engineering for providing the
necessary resources and infrastructure to carry out
this research. We are deeply thankful to the
Department of Electronics and Communication
Engineering for their unwavering support and
guidance throughout the project. Our heartfelt thanks
extend to our project guide, Prof. Sowmya P., whose
expertise, encouragement, and constructive feedback
were instrumental in shaping this project and
overcoming challenges. We also acknowledge the
assistance provided by the college in testing and
validating the system’s components. Finally, we are
grateful to our peers and collaborators, whose
valuable insights and encouragement inspired us to
achieve the objectives of this research.
REFERENCES
Liu, Y., & Wu, J. (2019). Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks:
Protocols, Applications, and Challenges. Wiley.
Chen, C., & Huang, C. (n.d.). Review of vehicle-to-vehicle
communication technology for road safety. Journal of
Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 7(2).
Kato, N., & Nishio, S. (2020). Vehicle-to-vehicle
communication: An overview. IEEE Wireless
Communications, 27(5), 38–45.
Wu, Y., & Zhang, J. (2021). A survey on the safety
applications of vehicle-to-vehicle communication. In
Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International
Conference on Communications (ICC) (pp. 1–6).
Alshahrani, A., & Alotaibi, F. (2022). Integration of
vehicle-to-vehicle communication and sensor
technologies for road safety. In Proceedings of the 2022
International Conference on Smart Cities (ICSC) (pp.
121–126).
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
(NHTSA). (2020). Vehicle-to-vehicle communication:
A guide for policy makers. NHTSA Report. Retrieved
from NHTSA Report.
European Commission. (2018). C-ITS deployment: A
European perspective. C-ITS Deployment Report.
Retrieved from C-ITS Deployment Report.
Muslam, M. M. A. (2024). Enhancing security in vehicle-
to-vehicle communication: A comprehensive review of
protocols and techniques. Vehicles, 6(1), 450–467.
MDPI.
Cormos, A. C., Stan, V. A., Stancel, I. N., & Stoica, V.
(2024). Integrating connected vehicles into IoT
ecosystems: A comparative study of low-power, long-
ISPES 2024 - International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems
162

range communication technologies. Sensors, 24(23),
7607. MDPI.
Xu, R., Xiang, H., Tu, Z., Xia, X., Yang, M.-H., & Ma, J.
(2022). V2X-ViT: Vehicle-to-everything cooperative
perception with vision transformer. In Proceedings of
the IEEE European Conference on Computer Vision
(ECCV) (pp. 110–120).
Li, J., Xu, R., Liu, X., Ma, J., Chi, Z., Ma, J., & Yu, H.
(2023). Learning for vehicle-to-vehicle cooperative
perception under lossy communication. IEEE
Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 8(1), 78–91.
Ezenwa, L. C. (2022). Wireless V2V communication with
DSRC technology in comparison to CV2X. ATZ
Worldwide, 124(3), 50–58.
Pethakar, S. S., Sagar, A. K., & Student, P. G. (2022).
Communication in autonomous vehicles through 5G
onboard units. In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Energy Systems and
Applications (ICESA) (pp. 88–94).
Zhang, Y., Li, C., Luan, T. H., Yuen, C., & Fu, Y. (2022).
Collaborative driving: Learning-aided joint topology
formulation and beamforming. In Proceedings of the
IEEE International Conference on Communications
(ICC) (pp. 55–62).
Yoshizawa, T., Singelée, D., Muehlberg, J. T., Delbruel, S.,
Taherkordi, A., Hughes, D., & Preneel, B. (2022). A
survey of security and privacy issues in V2X
communication systems. IEEE Communications
Surveys & Tutorials, 24(2), 243–268.
Smirnov, N., Tschernuth, S., Morales-Alvarez, W., &
Olaverri-Monreal, C. (2022). Interaction of
autonomous and manually-controlled vehicles:
Implementation of a road user communication service.
In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles
Symposium (IV) (pp. 301–307)
Chain Accident Prevention by Applying Automatic Braking via Vehicle to Vehicle Communication
163
