
Intelligent Living Space Control Using AI and Wireless Sensors
Priyanka R
a
, Logesh K
b
Sugumar R
c
and Suresh M
d
Department of Electrical Electronic Engineering S A Engineering College, Anna University, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Intelligent Living Space, Artificial Intelligence, Wireless Sensor Networks, Smart Homes, Energy Efficiency,
Home Automation, IoT, Sustainability, Security.
Abstract: This project presents an AI-based smart home automation system and Bluetooth technology. The system
integrates sensors, devices, and an Android app for remote operation. Machine learning algorithms optimize
energy consumption. The system enhances comfort, user satisfaction, and promotes sustainable living. The
concept of an intelligent living space integrates artificial intelligence (AI) and wireless sensor networks
(WSNs) to create smart, adaptive environments that enhance comfort, energy efficiency, and security. This
system employs AI-driven algorithms to interpret data from wireless sensors, enabling dynamic control of
various household systems such as lighting, temperature, humidity, and security. The wireless sensors collect
real-time data, including motion, environmental conditions, and user preferences, which is processed by a
central AI module. The AI utilizes machine learning to analyse patterns, predict user behaviour, and optimize
system responses Energy efficiency is a significant focus, with the system minimizing wastage by deactivating
unused appliances and employing adaptive power management strategies. Key features include intelligent
appliance control, remote monitoring, energy efficiency, and personalized experience.
1 INTRODUCTION
The evolution of technology has led to significant
advancements in various sectors, including home
automation. As the demand for smart living
environments continues to grow, integrating
innovative technologies into residential spaces has
become a focal point for enhancing comfort, security,
and energy efficiency. This project introduces an AI-
based smart home automation system that utilizes
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) and Bluetooth
technology to provide an intelligent and user-friendly
solution for home management. The system aims to
streamline the control of household appliances,
offering enhanced convenience and optimizing
energy consumption.
The concept of smart homes is predicated on the
integration of various electronic devices that
communicate with each other, allowing homeowners
to manage their living spaces more effectively.
Traditional home automation systems often lack the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9203-7393
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0007-0812-0559
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0007-3444-9032
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-6479-5440
adaptability and intelligence required to cater to the
dynamic nature of user needs. This project addresses
this gap by incorporating machine learning
algorithms that analyze sensor data, enabling the
system to learn user preferences and adjust appliance
operation accordingly.
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) serve as the
backbone of the proposed smart home automation
system. By deploying a network of interconnected
sensors, the system can monitor various
environmental parameters, such as temperature,
humidity, and occupancy. This real-time data
collection facilitates a deeper understanding of the
home environment, enabling the system to make
informed decisions about appliance control. For
instance, if the temperature exceeds a certain
threshold, the system can automatically adjust the fan
speed or turn on air conditioning, ensuring a
comfortable living space for the occupants.
Bluetooth technology plays a critical role in
enhancing the connectivity of the smart home system.
It enables seamless communication between the
130
R, P., K, L., R, S. and M, S.
Intelligent Living Space Control Using AI and Wireless Sensors.
DOI: 10.5220/0013636200004639
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems (ISPES 2024), pages 130-134
ISBN: 978-989-758-756-6
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

Android application and the various connected
devices, providing users with a straightforward
interface for controlling their home environment.
This wireless communication ensures that users can
operate their appliances remotely, allowing them to
monitor and manage their home even when they are
away. Such capabilities are particularly valuable for
individuals with busy lifestyles, as they can easily
adjust settings or receive notifications about their
home status through their mobile devices. The
system's design prioritizes energy efficiency, an
increasingly crucial factor in modern households. By
utilizing machine learning algorithms to analyze
usage patterns, the smart home automation system
can optimize the operation of connected devices,
minimizing energy consumption. For example, the
system may identify periods of inactivity and
automatically switch off lights or appliances that are
not in use. This proactive approach not only reduces
energy bills but also contributes to environmental
sustainability by decreasing overall power usage.
2 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system for Intelligent Living Space
Control integrates artificial intelligence (AI) with
wireless sensor networks (WSNs) to create an
adaptive and efficient home automation framework.
This system aims to enhance comfort, optimize
energy consumption, and ensure security by utilizing
real-time data and intelligent decision-making
algorithms. It is designed to be scalable, user-
friendly, and sustainable, catering to the diverse needs
of modern households.
2.1 Wireless Sensor Network (WSN):
▪ A network of wireless sensors deployed across
the living space collects data on parameters such as
temperature, humidity, light intensity, motion, and air
quality.
▪ The sensors communicate wirelessly with a
central control unit, eliminating the need for
extensive wiring and making the system suitable for
both new and retrofitted homes.
2.2 Central AI Control Unit
The AI module processes sensor data, learns user
preferences, and makes intelligent decisions. It uses
machine learning algorithms to identify patterns,
predict behavior, and provide personalized responses.
AI also ensures seamless integration with IoT devices
and external data sources, such as weather forecasts,
to improve system accuracy and adaptability.
2.3 Actuators and Smart Devices
The system controls actuators and smart devices,
including lighting, HVAC systems, appliances, and
security cameras. Commands are executed based on
AI-driven decisions, ensuring optimal performance
and energy efficiency.
2.4 User Interface
A mobile application and voice-activated assistant
provide a user-friendly interface for monitoring and
controlling the system. Users can remotely adjust
settings, view real-time data, and receive alerts for
security or maintenance issues.
3 MERITS
Merits of the AI-Based Smart Home Automation
System the AI-based smart home automation system
offers numerous advantages that enhance the overall
living experience for homeowners.
3.1 Convenience and Comfort:
One of the primary merits of this system is its ability
to provide users with seamless control over their
household appliances. The intuitive Android
application allows for remote operation and
monitoring, enabling users to manage their home
environment from anywhere at any time. This
flexibility enhances user comfort, as individuals can
adjust settings without being physically present.
3.2 Energy Efficiency
The integration of machine learning algorithms
enables the system to analyze usage patterns and
optimize energy consumption effectively. By
automatically adjusting appliance operation based on
real-time data, such as occupancy and environmental
conditions, the system reduces unnecessary energy
expenditure. This proactive energy management
contributes to lower utility bills and promotes
sustainable living practices.
Intelligent Living Space Control Using AI and Wireless Sensors
131
3.3 Personalization
The system's ability to learn user preferences and
adapt to individual habits further enhances the smart
home experience. By understanding the unique
patterns of its users, the system can automate routine
tasks, such as adjusting lighting or temperature,
ensuring a comfortable living environment tailored to
specific needs.
3.4 Enhanced Security
The smart home automation system can integrate
security features, such as surveillance cameras and
motion sensors, providing real-time monitoring and
alerts. This added layer of security ensures
homeowners feel safe and secure in their living
spaces.
3.5 Scalability
The modular design of the system allows for easy
expansion and integration of additional devices and
features. As technology evolves, users can upgrade
their systems without significant changes to the
existing infrastructure, ensuring long-term viability
and adaptability.
4 LITERATURE REVIEW
1. Smart Home Devices for Supporting Adults:
A Systematic Review-Authors:
M. Ghafurian, K. Wang, I. Dhode, M. Kapoor, P.
P. Morita, K. Dautenhahn-Published In: IEEE
Access, 2023.
2. Smart Home Security: An Efficient Multi-
Factor Authentication Protocol Authors:
G. Sarbishaei, A. Masoud Aminian Modarres, F.
Jowshan, F. Zahra Khakzad, H. Mokhtari
Published In: IEEE Access, 2024.
3. An Automation Script Generation
Technique for the Smart Home Authors:
J. Kuang, G. Xue, Z. Yan, J. Liu
Published In: Journal of Web Engineering, 2023.
4. EmoSecure: Enhancing Smart Home
Security with FisherFace Emotion Recognition
and Biometric Access Control Authors:
P. Ghadekar, M. Ranjan Pradhan, D. Swain, B.
Acharya Published In: IEEE Access, 2024.
5. Ontology-Based Classification and
Detection of the Smart Home Automation Rules
Conflicts Authors:
A. M. Ansari, M. Nazir, K. Mustafa
Published In: IEEE Access, 2024.
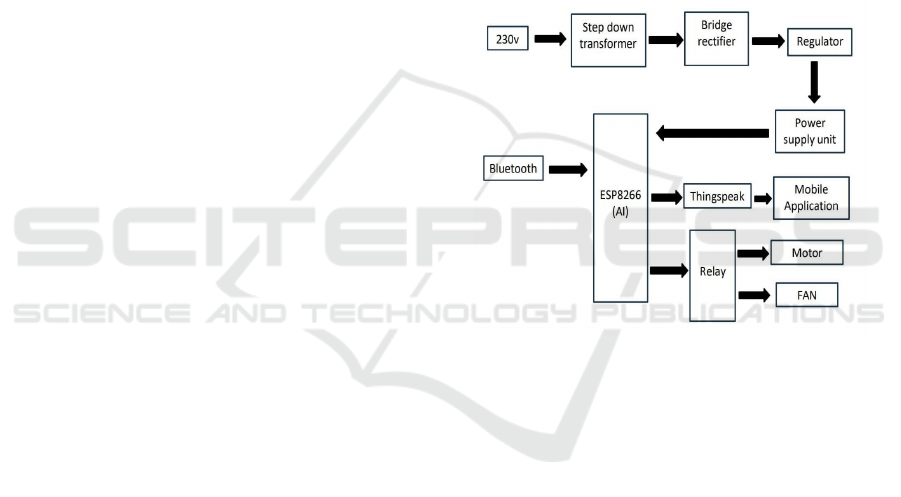
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
5.1 NodeMCU
Definition: Open-source IoT platform based on
ESP8266 Wi-Fi Soc.
Firmware
: Uses Lua scripting, built on eLua
project and Es press if non-OS SDK.
Figure 1: Block Diagram.
Features:
- ESP-12E Wi-Fi module with additional
GPIOs.
-Micro USB for power, programming, and
debugging.
- Includes GPIO, SPI, UART, ADC, and power
pins.
- Low-cost (< $2) for prototyping IoT
applications.
- Power Requirements: Operates at 3.3V; not 5V
tolerant.
5.2 Bluetooth Technology
Definition: Short-range wireless technology for
device interconnection.
Key Characteristics:
- Operates in 2.45 GHz frequency band.
- Max range: 10 meters; data rates up to 2 Mbps.
ISPES 2024 - International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems
132

- Uses Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum
(FHSS) for interference avoidance.
Piconet: Network of Bluetooth devices, typically
with one master and up to seven slaves.
Security Tips:
- Activate only when needed.
- Verify sending devices.
- Use antivirus software.
5.3 L293D Motor Driver
Function: Controls two DC motors in both directions
using an H-bridge configuration.
Pin Configuratio:
- 16 pins; requires high signals on enable pins (1
and 9) to operate.
- Four input pins control motor direction
(clockwise/anticlockwise).
Applications: Common in robotics for
controlling DC motors.
5.4 Power Supply Components
Transformer: Converts AC mains to a suitable
amplitude; ensures sufficient current capacity.
Rectifier: Converts AC to DC, typically using a
bridge rectifier for full-wave rectification.
Filter:
- Reservoir Capacitor: Smooths DC output by
storing charge.
- Low Pass Filter: Further removes AC ripples.
Voltage Regulator: Maintains a stable DC
output, available in positive and negative
configurations (e.g., LM78XX series).
6 SOFTWARE USED
6.1 ESP8266 Software (IDE)
The ESP8266 Integrated Development Environment
or ESP8266 Software (IDE) contains a text editor for
writing code, a message area, a text console, a toolbar
with buttons for common functions and a series of
menus. It connects to the ESP8266 and Genuino
hardware to upload programs and communicate with
them.
Sketches:
1. Programs are called sketches, saved with the. ino
extension.
2. Written in a text editor with features like
cut/paste and search/replace.
3. Feedback and error messages are displayed in
the message area and console.
● Basic Functions:
1. Verify: Checks code for compilation errors.
2. Upload: Compiles and uploads code to the
configured board.
3. New/Open/Save: Manage sketches (create,
open, save).
● Menus:
1. File Menu: Access sketches, examples, and
preferences.
2. Edit Menu: Basic editing functions (cut, copy,
paste, find).
3. Sketch Menu: Includes verification, upload
options, and library management.
4. Tools Menu: Formatting, archiving, and
bootloader options.
5. Help Menu: Access to documentation and
references.
● Sketchbook:
1. A standard location for storing sketches,
automatically created on first run.
2. Allows easy access to all stored programs.
● Compilation and Uploading:
1. Select appropriate board and port from Tools
menu.
2. Use the bootloader for uploading sketches
without additional hardware.
● Libraries:
1. Libraries enhance functionality (hardware
access, data manipulation).
2. Imported via Sketch > Import Library.
Intelligent Living Space Control Using AI and Wireless Sensors
133
● Serial Monitor:
1. Displays data exchange with connected boards.
2. Allows sending commands and receiving data in
real time.
● Language Support:
1. Available in 30+ languages; set according to the
operating system or manually via preferences.
Board Selection:
Essential for compiling and uploading; varies
by board type (e.g., ESP8266 Uno, Mega, etc.).
● Additional Features:
Support for third-party hardware.
Multiple tabs for managing sketches with various
file types.
Figure 2: Simulation Output.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, the AI-based smart home automation
system utilizing Wireless Sensor Networks and
Bluetooth technology represents a significant
advancement in home management. By integrating
various components such as sensors, micro
controllers, and machine learning algorithms, the
system enhances user convenience, energy
efficiency, and overall comfort. The intuitive Android
application allows for seamless remote control of
appliances, while the use of machine learning enables
the system to adapt to individual preferences and
optimize energy consumption.
The implementation of this smart home solution
not only simplifies daily tasks but also promotes
sustainable living practices by reducing unnecessary
energy use. With features like real-time monitoring
and automated control, homeowners can enjoy a
personalized living experience tailored to their needs.
Furthermore, the scalability of the system ensures that
it can evolve with technological advancements and
user demands. As the world increasingly shifts
towards smart technologies, this project serves as a
foundation for future developments in intelligent
home management, ultimately contributing to a more
efficient, comfortable, and sustainable lifestyle. By
embracing such innovations, homeowners can
enhance their quality of life while playing a part in
promoting environmental responsibility.
REFERENCES
A. M. Ansari, M. Nazir, and K. Mustafa, "Ontology-Based
Classification and Detection of the Smart Home
Automation Rules Conflicts," IEEE Access, (2023) vol.
12, pp. 6558-6571, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3415632.
A. Arora, A. Jain, D. Yadav, V. Hassija, V. Chamola, and
B. Sikdar, "Next Generation of Multi-Agent Driven
Smart City Applications and Research Paradigms,"
IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society,
(2023) vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 423-440, doi:
10.1109/OJCOMS.2023.3310528.
J. Kuang, G. Xue, Z. Yan, and J. Liu, "An Automation
Script Generation Technique for the Smart Home,"
Journal of Web Engineering, (2023) vol. 23, no. 1, pp.
102-118, doi: 10.13052/jwe1540-9589.2222.
P. Ghadekar, M. R. Pradhan, D. Swain, and B. Acharya,
"EmoSecure: Enhancing Smart Home Security With
FisherFace Emotion Recognition and Biometric Access
Control,"(2024) IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 4589-4605
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3423783.
G. Sarbishaei, A. M. Aminian Modarres, F. Jowshan, F. Z.
Khakzad, and H. Mokhtari, "Smart Home Security: An
Efficient Multi-Factor Authentication Protocol," (2023)
IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 4995-5010, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3437294.
M. Ghafurian, K. Wang, I. Dhode, M. Kapoor, P. P. Morita,
and K. Dautenhahn, "Smart Home Devices for
Supporting Older Adults: A Systematic
Review,"(2023) IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 37285-
37298, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3266647.
ISPES 2024 - International Conference on Intelligent and Sustainable Power and Energy Systems
134
