
Analysis and Research on Building Foundation Selection in Soft Soil
Area of Heqing, Yunnan Province
Fengfeng Ding
1a
and Jinyong Jiao
2,* b
1
College of Resources and Environment, Yunnan Vocational College of Land and Resources,
Yunnan, Kunming, 652501, China
2
China Power Construction Group Kunming Survey Design and Research Institute Co., LTD,
Yunnan Kunming, 650000, China
*
Keywords: Engineering Geological Conditions, The Soft Soil Foundation, Foundation Selection.
Abstract: This paper analyzes the engineering geological conditions of a building site in Heqing, Yunnan Province,
evaluates the seismic effect of the site and the uniformity of the foundation soil, and finally analyzes the
foundation selection of the soft soil foundation site.
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-9483-487X
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-0300-129X
1 INTRODUCTION
With its unique geographical environment and
geological conditions, Heqing area of Yunnan
Province brings many challenges to the foundation
selection of construction projects. Among them, the
selection of building foundation in soft land area is
particularly critical, which is directly related to the
safety, stability and economy of buildings. The
purpose of this study is to analyze the geological and
hydrological conditions of the soft soil area of
Heqing, Yunnan Province, and to discuss the
selection scheme of building foundation suitable for
this area by combining the practical engineering
experience and the existing research results.
2 PROJECT OVERVIEW
The proposed site is located in Yunhe Town, Heqing
County. Heqing County is located in the northwest
of Yunnan Province, at the southern end of
Hengduan Mountain Range in western Yunnan, east
of Yunling Mountain Range and north end of Dali
Bai Autonomous Prefecture. Its geographical
coordinates are 100°01 '-100°29' east longitude and
25°57'-26°42' north latitude. Yunhe Town is located
in the center of Heqing County, the terrain is high in
the west and low in the east. It is 129 kilometers to
the south from Dali and 42 kilometers to the north
from Lijiang. The proposed site is close to Yunxin
Road and North Ring Road, and the traffic is very
convenient. The location of the proposed site is
shown in Figure 1.
The proposed project consists of 11 buildings
with 7 floors above ground and one underground
floor. The basement is distributed in the whole site,
and the basement storey is 4.7m.
Figure 1: Location of the proposed site.
Ding, F., Jiao and J.
Analysis and Research on Building Foundation Selection in Soft Soil Area of Heqing, Yunnan Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0013573200004671
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Environmental Science and Civil Engineering (ICESCE 2024), pages 45-53
ISBN: 978-989-758-764-1; ISSN: 3051-701X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
45

3 REGIONAL GEOLOGICAL
CONDITIONS
3.1 Topography
The proposed site is located in Yunhe Town, Heqing
County, lake accumulation of highland mountain
intermittent basin west, east of Yunxin Road, south
of the North ring road, south of Huashu Village. The
site was originally cultivated land with flat and open
terrain. The site is a quaternary lacustrine
sedimentary landform.
3.2 Regional Structure and Neotectonic
Movement
Regionally, the site is located in the sag area of
Lijiang platform margin in Yanyuan Basin of
Yangtze platform, southwest of Lijiang fold belt.
Heqinging-xinmincun fault and Heqinging-Junying
fault are the main active faults of the site and its
adjacent areas. It can be seen that the structure of the
site is complex, faults are developed and neotectonic
activities are frequent. Heqing is an intermittent
depression basin in the plateau mountains.
3.3 Neotectonic Movement and
Earthquake
The neotectonic movement in the area where the
proposed site is located mainly shows that the
Diancang Mountain has risen strongly and the
mountain has risen strongly since the Tertiary period;
Along the main fault, there are more than ten
Cenozoic faulted basins at different heights. Folds
and fractures can be seen in the Pleistocene deposits.
The region is affected by the intermittent and
different movement of the modern crust, which
makes the ground stress complex, faults developed
and earthquakes relatively frequent.
4 SITE ENGINEERING
GEOLOGICAL CONDITIONS
4.1 Formation Lithology
The foundation soil of the site is composed of silty
clay, silt and clay of quaternary lacustrine
sedimentary origin, except the surface of the site is
filled and cultivated soil, which is divided from top
to bottom as follows:
① Layer, cultivated soil: brown gray, slightly wet -
wet, plastic state, underconsolidation, high
compressibility, mainly composed of silty clay
with a few gravel particles and a large number
of plant roots. The buried depth is 0.00-1.50m,
the layer thickness is 0.40-0.60m, and the top
elevation is between 2199.03-2201.68m.
② 1 layer, mixed fill: brown gray, brown, slightly
wet, loose state, mainly composed of silty clay
mixed gravel particles, underconsolidation,
buried depth 0.00m, layer thickness 0.50 ~
1.90m, the top elevation between 2200.53 ~
2201.98m. The side of the distribution site near
the North Ring Road is backfilled during th
e
construction of the North Ring road. The
backfilling period is greater than 3 years, and
the backfill is not rolled by
layers.
③ Layer, silty clay: brown, brown yellow, wet,
plastic state mainly, local hard plastic state,
medium compressibility, section rough or
slightly shiny, no shaking reaction, medium dry
strength, medium toughness, local even gravel
.
The
buried depth is 0.40-2.10m, the laye
r
thickness is 0.70-3.00 m, and the top elevation is
between 2198.53-2201.08m. It's distributed
throughout the field.
④ Layer, silt: gray, brown gray, wet, soft plastic -
fluid plastic state, high compressibility. The
section surface is slightly shiny, no shaking
reaction, medium dry strength, poor toughne
ss,
a little organic matter and a small amount of
shell residue inside. The buried depth is
1.20-4.90m, the layer thickness is 2.70-7.50m,
and the top elevation is b
etween
2196.18-2199.88m. It's distributed throughout
the site.
⑤ Layer, clay: gray, brown gray, wet, soft plastic
state, high compressibility. The section
surface
is slightly shiny, no shaking reaction, medium
dry strength, medium toughness, and partia
l
shell residue. The buried depth is 6.30-9.00m,
and the top elevation is between
21
91.00-2194.52m, which is distributed in th
e
whole site.
⑥ Layer, clay: gray, blue-gray, wet, soft plastic
state, local plastic state, high compressibility.
Section is slightly shiny, medium dry strength,
medium toughness, no shaking reaction. The
buried depth is 19.90-21.20m, and the top
elevation is between 2178.23-2180.78m.
Based on the comprehensive analysis of the
indoor geotechnical test and in-situ test, and
combined with the calculation of relevant norms, the
physical and mechanical index parameters of each
soil layer are obtained comprehensively (see Table 1
for details).
ICESCE 2024 - The International Conference on Environmental Science and Civil Engineering
46

Table 1: Physical and mechanical parameters of each soil layer.
Floor
numbe
r
Geotechnical
designation
natural
densityρ
(g/cm
3
)
Quick
shear
Set fast
Triaxial
(CU)
Compressio
n test mean
Double bridge
static test
standard value
Precast pile
Bearing
capacity
characteristi
c value
Cq
(kPa
)
Φq
(度
)
Ccq
(kPa
)
Φc
q
(度
)
Ccu
(kPa
)
Φc
u
(度
)
Es
1-2
(MPa
)
Es
2-3
(MPa
)
q
c
(Mpa)
Fs
(Kpa)
Standard value
of limit side
resistanceQ
sik
(kP
a)
Standard
value of
ultimate
end
resistanc
e
Q
pk
(kPa)
f
ak
(kPa)
①
Cultivated
soil
1.75* 15* 4* 3.0* 0.5 22.9
①
1
Miscellaneo
us
fill
1.70* 14* 5* 3.5*
②
Silty clay 1.78 35.0 7.4 38.5 8.9 5.43 6.84 0.77 32.7 65 130
③
muck 1.51 16.6 4.6 16.3 4.8 1.78 2.35 0.51 13.6 15 40
④
clay 1.56 17.9 4.7 32.0 6.7 2.80 3.35 0.74 15.6 25 1000 85
⑤
clay 1.55 16.8 4.7 26.8 6.6 2.94 3.67 0.84 17.9 27 1100 95
Note: Values marked with * are experience values
4.2 Bad Geological Effects and Special
Soil
(1) Bad geological effects
The proposed site is located on the west side of
Heqing Basin with open and flat terrain. According
to the on-site engineering geological survey, no
adverse geological effects and geological disasters
such as karst, collapse, debris flow and landslide
have been found in and around the proposed site.
(2) Special soil
①
Filling
Th
e filling soil in the site is formed by backfilling
during the construction of the North Ring Road and
has a large distribution range. The filling soil is only
distributed near the North Ring Road in the whole
site. The composition of the filling soil is mainly
composed of silty clay mixed gravel, partial mixed
gravel and block stone, and the backfilling period is
more than 3 years. The thickness of the layer is 0.50
~ 1.90m, which is not suitable for use as the
foundation bearing layer, and it is recommended to
remove it when the foundation pit is excavated.
②
cu
ltivated so
il
It
is mainly composed of clay soil mixed plant roots
and a few gravel particles, which is in a plastic state
and underconsolidated. This part of cultivated soil
has been soaked by farmland irrigation water all the
year round, and its property is poor. The layer
thickness is 0.40-0.60m. It is recommended to
remove all cultivated soil during foundation pit
excavation.
③
soft soil layer
I
n the site, the ③ layer of silt, ④ layer of clay and
⑤ layer of clay are in the soft-plastic and
fluid-plastic state, with high compressibility, low
bearing capacity, poor physical and mechanical
properties, and large layer thickness. It should not be
used as natural foundation. It is suggested that the
foundation should be strengthened or the building
structure should be strengthened in the project
construction, and the influence of soft soil subsidence
should be considered in the design.
4.3 Site Hydrogeological Conditions
The stable water level in the inland of the site ranges
from 0.37 to 1.93m, the water level elevation ranges
from 2198.10 to 2201.20m, and the height difference
is 3.10m. According to the characteristics of
foundation soil, ① cultivated soil and ①1 layer of
mixed fill have certain permeability, and the other
viscous soil layers are weak permeability.
Groundwater mainly exists in the silty clay (②
layer), silt (③ layer), clay (④ layer) and clay (⑤
layer) with the change of climate, but the amplitude
is small. Groundwater is fed by atmospheric
precipitation, surface water and Caohai seepage, and
discharged by atmospheric evaporation and
infiltration into Bonan River, and then deposited in
Caohai. The exploration and construction period is
in the rainy season, and the water level is greatly
affected by the season. According to the
hydrogeological data collected by our institute in
Analysis and Research on Building Foundation Selection in Soft Soil Area of Heqing, Yunnan Province
47
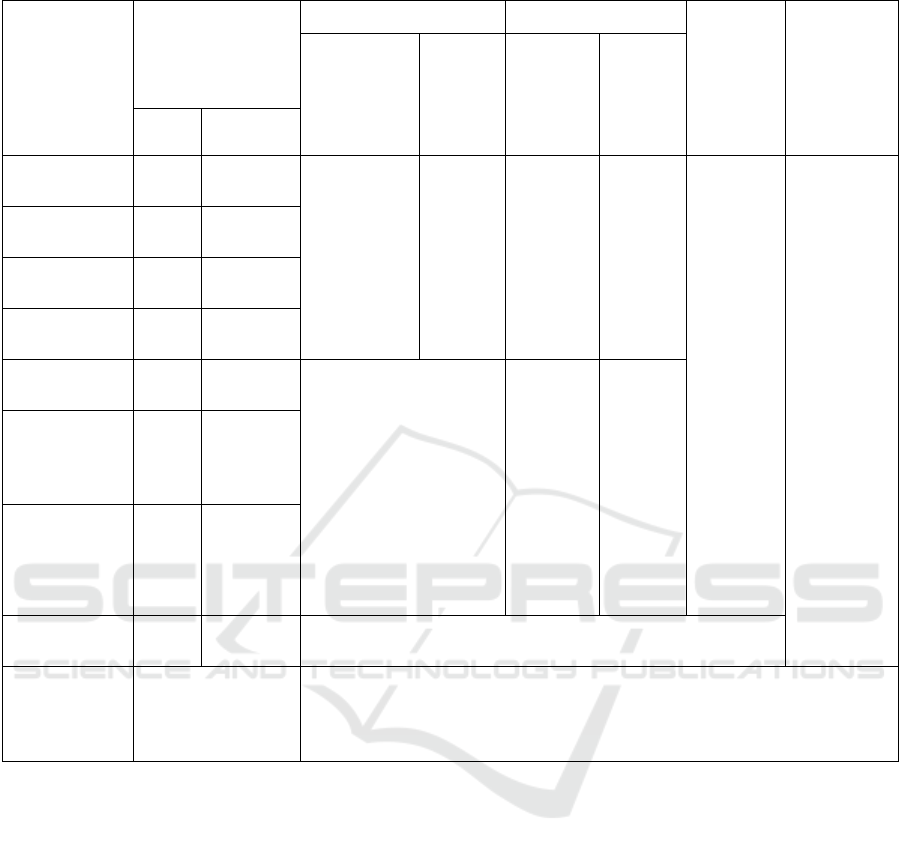
Table 2: Groundwater corrosivity evaluation table.
Corrosive
medium
The content in water
(mg/l)
Climate influencing facto
r
Osmotic facto
r
Corrosion
grade of
concrete
structure by
water
Corrosion
grade of steel
bar in
concrete
structure by
water
Environmental
category
Corrosion
grade
Penetration
category
Corrosion
grade
ZK1 Zk25
Ca
2+
44.89 38.48
Ⅱ weak
weak
weak
Mg
2+
11.67 36.95
K
+
+Na
+
151.91 149.37
SO
4
2-
40.38 28.13
PH 7.00 7.01
A weak
侵蚀性 CO
2
4.40 8.80
HCO
3
-
(mol/l) 6.80 7.00
Cl
-
14.18 21.27
Comprehensive
evaluation of
corrosiveness
level
weak
Groundwater has slight corrosiveness to concrete structures in Class II site
environments and steel structures in reinforced concrete structures
this
area, 0.0-0.37m below the surface is the highest
water level in this area in recent years, and the
variation range of the highest groundwater level is
within 1m. According to the site topography,
hydrogeological conditions and the final leveling of
the elevation, it is suggested that the anti-floating
design water level should be 2201.50m, and
anti-floating treatment measures should be carried
out in accordance with relevant norms.
4.4 Analysis of Soil and Water
Corrosion
According to the relevant provisions of the Code for
Geotechnical Engineering Investigation (8th edition
of 2009) (GB50021-2001, 2009), groundwater is
slightly corrosive to concrete structures. It is slightly
corrosive to reinforcement in concrete structure.
Specific evaluation is shown in the table below in
Table 2.
According to the corrosion analysis of soil
samples taken from drilling, the PH values are 7.01
and 7.04 respectively, belonging to weakly alkaline
soil, and the site environment type is Class II.
According to the Code for Geotechnical Engineering
Investigation (GB50021-2001) (2009 edition), it is
comprehensively determined that the foundation soil
of the site is slightly corrosive to the concrete in
Class II site environment and the reinforced concrete
and steel structure in the concrete (see Table 3 for
details).
ICESCE 2024 - The International Conference on Environmental Science and Civil Engineering
48
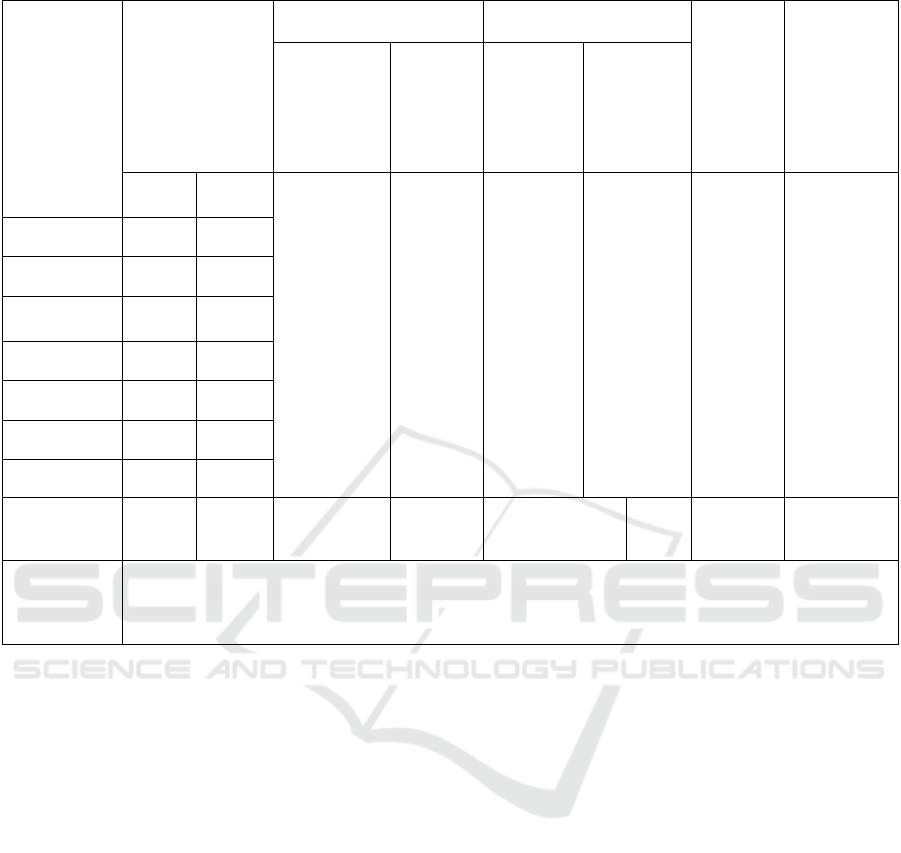
Table 3: Soil corrosivity evaluation table.
Corrosive
medium
The content in
the soil(mg/kg)
Climate influencing
facto
r
Osmotic factor
Corrosio
n grade
of soil to
concrete
structure
Corrosion
grade of soil
to
reinforceme
nt in
concrete
structure
Environment
al category
Corrosio
n grade
Penetratio
n category
Corrosion
grade
Zk2-6 Zk37-2
Ⅱ weak A weak weak weak
Ca
2+
19.24 17.64
Mg
2+
4.86 17.50
Soluble salt
(%)
0.0216 0.0283
SO
4
2-
29.15 26.80
PH 7.01 7.04
HCO
3
-
170.86 219.67
Cl
-
21.27 28.36
Electrical
resistivity
(
Ω.m
)
60.00 60.00
Comprehensi
ve evaluation
of corrosion
grade
The soil is slightly corrosive to the concrete structure and the reinforcement in the reinforced concrete
structure.
5 ENGINEERING GEOLOGICAL
EVALUATION
5.1 Evaluation of Seismic Effect
1.seismic fortification standards
According to the 2016 edition of the national
seismic fortification intensity Code for Seismic
Design of Buildings (GB50011-2010), the seismic
fortification intensity of Heqing County is 8 degrees,
the design basic earthquake acceleration is 0.30g,
and the design earthquake is divided into the third
group. The characteristic period of the site is 0.65s.
The seismic facilities shall meet the requirements of
the local seismic fortification intensity.
2.
Venue category
The proposed site is located in Yunhe Town,
Heqing County. The site is generally Huxiang
sedimentary landform of the whole quaternary
system. The seismic fortification category of this
project is standard fortification category (Class C).
According to the wave velocity report of drilling
holes ZK17 and ZK27 under the surface of the site
at a depth of 0-20m, the equivalent shear wave
velocity is 158m/s and 159m/s respectively, and the
thickness of the covering layer of the site is greater
than 50m. According to articles 4.1.3 and 4.1.6 of
the Code for Seismic Design of Buildings
(GB50011-2010) (2016 edition), the site soil type is
determined to be medium soft soil and the
construction site category is Class III.
soft soil earthquake subsidence and sand
liquefaction
There is no distribution of saturated sand and silt
with a thickness of more than 0.5m in the depth of
20.0m in the proposed site, and there is no problem
of liquefaction of saturated sand.
According to Article 6.3.4 of the Code for
Geotechnical Engineering Investigation in Soft Soil
Areas (JGJ83-2011) (J1186-2011), the seismic
fortification intensity of the proposed site is 8
degrees, there is silt in the site, the equivalent shear
wave velocity is less than 140m/s, and the bearing
capacity is less than 100Kpa. The earthquake
Analysis and Research on Building Foundation Selection in Soft Soil Area of Heqing, Yunnan Province
49

subsidence value of the building is estimated at
150mm.
4.
Seismic section division of building site
The topography of the site is large, the maximum
height difference of the site is greater than 5.0m, the
terrain is relatively open, there is no bad geological
phenomena such as collapse, landslide, debris flow
in the drilling range, but there is soft soil in the
foundation soil, according to the Code for Seismic
Design of Buildings (GB50011-2010) (2016 edition)
4.1.1 division standard, the site is divided into
adverse seismic areas.
5.2 Site Stability and Suitability
Evaluation
The overall terrain of the site is basically flat, and
the terrain and geomorphology are complete. There
are no undesirable geological effects such as
Holocene active faults, slippage and debris flow
within the drilling range. There is weak soil layer in
the site, which can be used as the construction land
of the project after the reinforcement treatment of
the foundation or strengthening of the building
structure.
5.3 Evaluation of Foundation Soil
The foundation soil of the site is composed of silty
clay, silt and clay of Quaternary Huxiang
sedimentary origin, except the surface of the site is
filled and cultivated soil, which is divided from top
to bottom as follows:
① Layer, cultivated soil: brown gray, sligh
tly wet -
wet,
plastic state, underconsolidation, h
igh
co
mpressibility, mainly composed of silty c
lay
with
a few gravel particles and a large number
of plant roots. The physical and mechan
ical
p
roperties of this layer are poor, so it
is
recommen
ded to remove all the soil
during
co
nstruction.
② 1 layer, mixed fill soil: brown gray,
brown,
sl
ightly wet, loose state, mainly composed of
silty clay mixed gravel p
articles,
un
derconsolidated, distributed in the site near
the North ring road side, for the construction of
the North ring road backfill, backfill more tha
n
3
years, backfill has not been rolled by laye
rs.
The
soil of this layer is only produced in a lo
cal
sect
ion, the uniformity is poor, and it is
recommended to remove all the so
il.
③ Lay
er, silty clay: brown, brown yellow, wet
,
p
lastic state, local hard plastic, medium
compressibility, section rough or slightly shiny,
no shaking reaction, medium dry strength,
medium toughness, local even gravel, the whole
field are distributed. The soil of this layer has
good physical and mechanical properties, but
the layer thickness is uneven, and some parts
have been cleared after the excavation of
foundation pit, so it is not suitable for use as the
foundation supporting layer of the proposed
building.
④ Layer, silt: gray, brown gray, wet, soft plastic -
fluid plastic state, high compressibility. Th
e
sect
ion surface is slightly shiny, no shaking
reaction, medium dry strength, poor tough
ness,
a
little organic matter and a small amount of
shell residue inside. The physical a
nd
mecha
nical properties of this layer of soil are
poor, and it is strictly prohibited to use as
a
n
atural foundation.
⑤ Layer, clay: gray, brown gray, wet, soft p
lastic
state,
high compressibility. The section
surface
is
slightly shiny, no shaking reaction, mediu
m
dr
y strength, medium toughness, and partial
shell residue. The physical and mechanical
properties of this layer are better than that
of
th
e third layer, and it can be used as th
e
su
pporting layer of the pile end of the propo
sed
co
nstruction.
⑥ Layer, clay: gray, blue-gray, wet, soft pl
astic
state,
local plastic state, high compressibility
.
Sectio
n is slightly shiny, medium dry strength,
medium toughness, no shaking reaction. It
can
be
used as the supporting layer of pile end or
the underlying layer of the proposed
construction.
5.4 Evaluation of Foundation
Uniformity
There is little difference in the composition,
thickness, spatial distribution and physical and
mechanical properties of each soil layer of the
foundation, but the foundation soil of the site is
medium-high compressibility foundation, the
complexity of the site foundation is second class,
and the ratio of the maximum and minimum
compressive modulus of the layer silt is greater than
1.3. According to the current "Geotechnical
Investigation Standard for High-rise Building
Concrete" (JGJ/T72-2017 Article 8.2), it is
determined that the site is an uneven foundation.
ICESCE 2024 - The International Conference on Environmental Science and Civil Engineering
50
6 TYPE SELECTION DESIGN OF
FOUNDATION
According to the characteristics of the proposed
building and the engineering geological conditions
of the site, it is not appropriate to use natural
foundation in this project, and it is recommended to
use pile foundation or composite foundation + raft
foundation. The bearing layer of pile foundation and
composite foundation should choose ④ layers of
clay and ⑤ layers of clay. The basic form is
suggested as follows:
(1) Composite foundation + raft: The solution of
cored stirred pile composite foundation + raft
foundation can be adopted for the foundation
form of Building 1-11, Building 1 and pure
basement. The effective pile length is about
15.00m, pile diameter is 0.50m, and ④ layer
clay is used as the pile end bearing layer. The
bearing capacity characteristic value of single
pile is estimated to be 280KN, the pile spacing
is 1.5m, the rectangular pile layout is m=0.087.
The bearing capacity characteristic value of
composite foundation is estimated to be
140-160KPa. The foundation soil of the
proposed site is mainly silty clay, silt and clay
with normal consolidation, and its natural water
content is higher than 30%. Silt and clay
plasticity index is greater than 25, according to
local engineering experience, the site can be
used as a core mixing pile foundation treatment.
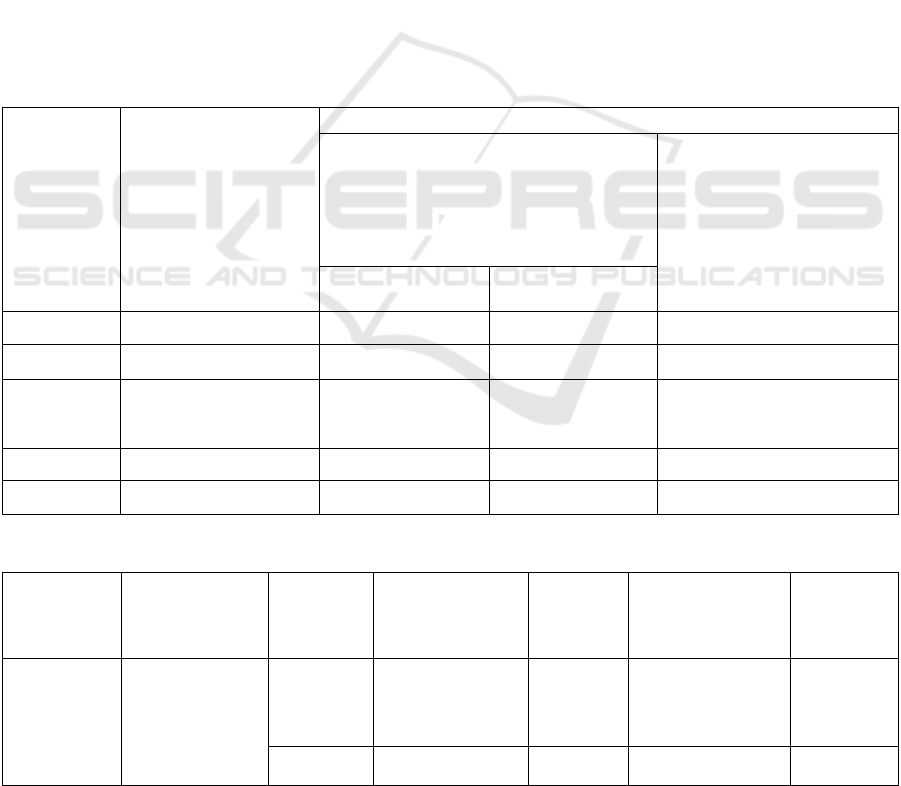
(2) Pile foundation: For this project, static pressure
prefabricated pipe pile and prestressed concrete
pipe pile (PC) can be used. The effective pile
length is about 20.00m, outer diameter is 0.50m,
wall thickness is 0.10m, concrete strength is
C60, and ⑤ layer clay is used as the pile end
bearing layer. The estimated bearing capacity
limit value of a single pile is about 1000KN in
Table 4 and Table 5.
Table 4: calculation results of ultimate bearing capacity of single core-mixed pile.
Soil layer
numbering
Soil layer name
Deep mixing pile
Characteristic value of soil side resistance
q
s
(kpa)
Characteristic value of bearing
capacity of pile end soil
q
p
(kpa)
Core pile segment Coreless pile section
③
muck
8 8
④
clay
13 13
85
Estimated
hole number
Pile end bearing layer
Pile dimension
d×L(m)
Core length
Standard value of vertical
ultimate bearing capacity of
single pile Q
uk
(kN)
ZK2
④clay
0.5×15.0 15 283.90
ZK25
④clay
0.5×15.0 15 284.75
Table 5: Estimation results of standard value of vertical ultimate bearing capacity (Quk) of single pile.
unit Pile shape
Hole
number
Pile
diameter(mm)
Pile
length(m)
Ultimate bearing
capacity of single
pile(kN)
Supporting
course
Building
1-11 and the
next one
Hydrostatic
prefabricated
pipe pile
Zk2 Φ500 20 1060.40 ⑤
Zk25 Φ500 20 1060.00 ⑤
Note: 1. The bearing capacity of single pile is estimated according to the table above, and the test pile shall prevail
according to the code requirements;
Analysis and Research on Building Foundation Selection in Soft Soil Area of Heqing, Yunnan Province
51

7 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
7.1 Conclusion
(1) The proposed site is located in Yunhe Town,
Heqing County, with silty clay and clay layer of
Quaternary Holocene lacustrine sedimentary
origin in addition to the soil filling and tillage
on the surface.
(2) The proposed site has complete topography,
open and flat terrain, small elevation difference,
no Holocene active faults, slippage, debris flow
and other adverse geological effects in the site,
there is soft soil in the site, divided into adverse
seismic areas, there is soft soil in the site, and it
can be used as the construction land of the
project after the foundation reinforcement
treatment or strengthening of building structure
measures.
(3) The seismic fortification intensity of the site is
8 degrees, the design basic seismic acceleration
is 0.30g, and the design earthquake group is the
third group. The site soil type is medium soft
soil, the construction site category is Class III,
and the site is an unfavorable seismic area.
(4) The seismogenic fault zones F166, F167 and
F168 pass through about 4.50Km, 3.00Km and
2.30Km away from the proposed site.
(5) There is little difference in the composition,
thickness, spatial distribution and physical and
mechanical properties of each soil layer of the
foundation, but the foundation soil of the site is
medium-high compressibility foundation, and
the complexity of the site foundation is second
class. According to the uniformity evaluation
standard of the current Geotechnical
Investigation Standard for High-rise Building
Concrete (JGJ/T72-2017), the foundation of the
site is an uneven foundation.
(6) According to the soil analysis results, it is
determined that the foundation soil of the site is
slightly corrosive to the concrete in the Class II
site environment, the reinforced concrete
structure in the concrete and the steel structure.
7.2 Suggestions
(1) The upper part of the ground water in the site is
pore diving, and the main aquifer is silty clay
and clay layer. According to the water quality
analysis results of the two groups of water
samples taken in the site, the ground water is
slightly corrosive to the concrete and the
reinforced concrete structure in the concrete
environment of the class II site. It is suggested
that the design water level of anti-floating
should be 2201.50m, and anti-floating measures
should be carried out according to relevant
specifications.
(2) The foundation type is suggested to adopt the
foundation form of pile foundation or
core-mixed pile composite foundation + raft.
The construction of core-mixed pile or pile
foundation should pay attention to the
protection of the soil at the bottom of the pit
before and after excavation to avoid disturbance
as far as possible.
(3) The foundation pit support can be carried out in
the form of moderate slope slope + steel sheet
pile or double drainage soil mixing pile
according to the actual situation. When the
foundation pit is excavated, the water inflow of
the foundation pit is large, and there should be
better water separation and precipitation
measures.
(4) The foundation pit of the proposed project is
mostly located in the soft soil layer, and near
the building, the foundation pit project is a
dangerous project, the construction unit, the
design unit, the construction unit, the
supervision unit should strictly implement the
relevant provisions of the "Safety Management
Regulations of dangerous sub-projects" ( 2011,
Ministry of Housing and Construction Order
No. 37) during the design and construction
process of the foundation pit.
(5) Because there is a thick layer of soft soil in the
site, it is suggested that the uniformity and
integrity of the building structure should be
strengthened in the design to avoid uneven
settlement.
(6) In the foundation construction process, the
foundation soil should be avoided as far as
possible by water immersion or exposure, and
the construction should ensure the drying of the
foundation pit, which is conducive to the
construction. If abnormal phenomenon is found,
please inform the design and investigation
personnel to conduct on-site inspection of the
tank, and study and solve the possible
problems.
(7) After the foundation construction is completed,
settlement observation points should be buried
in time for settlement observation.
ICESCE 2024 - The International Conference on Environmental Science and Civil Engineering
52

REFERENCES
GB50021-2001, 2009. Code for Geotechnical
Investigation, 8
th
edition.
GB50011-2010, Code for Seismic Design of Buildings,
2016 edition.
JGJ83-2011, Code for Geotechnical Investigation in Soft
Soil Areas.
Regulations on the Safety Management of Hazardous
Sub-Projects (Order No. 37 of the Ministry of Housing
and Urban-Rural Development).
Analysis and Research on Building Foundation Selection in Soft Soil Area of Heqing, Yunnan Province
53
