
Mitigating the Vector76 Attack: Enhancing Security in the Bitcoin
Network
Haoyun Tang
a
School of Software, South China Normal University, Guangdong, China
Keywords: Vector76 Attack, Selfish Mining, Blockchain Transactions.
Abstract: This research paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the Vector76 attack within the Bitcoin network, a
notable double-spending threat that undermines the integrity of blockchain transactions. Similar to the Finney
attack, the Vector76 attack exploits Bitcoin's pre-mining function, enabling miners to secretly mine and
strategically broadcast blocks, thus deceiving the network into accepting fraudulent transactions. The study
investigates the operational principles of the Vector76 attack, its generalized versions, and the influence of
selfish mining in facilitating these attacks. Furthermore, this research outlines a series of countermeasures,
including security strategies designed to thwart double-spending attacks and monitoring technologies such as
Enhanced Observer (ENHOBS), which are employed to review transactions and detect anomalies.
Additionally, the study examines detection and punitive mechanisms aimed at combating selfish mining
attacks, thus safeguarding the blockchain from malicious mining behaviors. In conclusion, a thorough review
of the findings highlights the critical need for robust defense mechanisms to protect the Bitcoin ecosystem
against complex threats. The implications of this research extend to the wider cryptocurrency community,
underscoring the necessity for ongoing innovation in security strategies to address emerging vulnerabilities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system
that records transactions across multiple computers
without the need for a central authority. The
information in blockchain is extremely difficult to
tamper with, ensuring the integrity and security of
data. Due to this prominent feature, it can underpin
many cryptocurrencies, as well as various
applications in fields such as finance, supply chain
management, and more. Bitcoin is a revolutionary
digital currency based on this technology. It operates
on a decentralized network that facilitates peer-to-
peer transactions. However, the double-spending
problem is a potential vulnerability where an attacker
could attempt to spend the same bitcoins twice.
Therefore, many researchers have conducted
research on this issue. Finney describes a double-
spending attack on Bitcoin which is now known as
the Finney attack (Aggarwal and Kumar, 2021). This
is an attack that utilizes pre-mining attacks and allows
attackers to choose specific moments to launch
attacks to achieve the goal of reusing cryptocurrency.
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-3868-283X
The attacker mined a block in advance, which
contained a transfer between two addresses of the
attacker. When an attacker pays a vendor using one
of the addresses, the pre-mined block can be
broadcasted simultaneously, rendering the vendor's
transaction invalid. Vector76 attack is another double
spending attack similar to the Finney attack
(Sompolinsky and Zohar, 2016). Even if the
transaction is confirmed once, the attacker can still
complete a double-spending attack. However, many
researchers have proposed different countermeasures
for these diverse forms of double-spending attacks.
Nicolas et al. studied various defense strategies
against double-spending attacks and selfish mining
attacks (Nicolas et.al, 2020). These strategies are
divided into six categories and evaluated for their
strengths and weaknesses. Karame et al. studied the
effectiveness of Bitcoin in combating double-
spending attacks in fast payment scenarios, and the
results showed that these attacks have a high
likelihood of success (Karame et.al, 2012). At the
same time, Karame et al. studied the countermeasures
against double-spending attacks proposed by Bitcoin
500
Tang and H.
Mitigating the Vector76 Attack: Enhancing Security in the Bitcoin Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0013527100004619
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning (DAML 2024), pages 500-505
ISBN: 978-989-758-754-2
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
developers and found that these countermeasures are
not always effective. Therefore, Karame et al. made
necessary modifications to the implementation of
Bitcoin to improve the possibility of detecting
double-spending attacks. Podolanko et al. studied
past countermeasures against double-spending
attacks and found that these countermeasures can still
be bypassed through certain means (Podolanko et.al,
2017). Therefore, Podolanko et al. proposed
enhanced observers (ENHOBS) and proved that this
countermeasure can deal with double-spending
attacks at a reasonable cost.
This study investigates the Vector76 attack, a
sophisticated threat within the Bitcoin ecosystem, and
examines countermeasures to mitigate its effects. It
begins by outlining the foundational concepts behind
Bitcoin's double spending attack, followed by a
detailed explanation of the Vector76 attack and its
generalized version. This research also incorporates
an analysis of the selfish mining attack, which plays
a crucial role in the mechanics of the Vector76 attack.
Subsequently, the study presents various
countermeasures designed to address the technical
vulnerabilities associated with the Vector76 attack,
assessing their effectiveness and potential limitations.
The evaluation of these countermeasures is critical, as
it sheds light on the practicality of implementing them
within existing systems. By identifying weaknesses
in current security measures and proposing targeted
solutions, this study contributes to the ongoing efforts
to enhance the resilience of Bitcoin against evolving
threats. The insights gained from this research not
only inform future developments in blockchain
security but also highlight the importance of
continuously evolving countermeasures in response
to new attack vectors.
2 METHODOLOGIES
The study begins by providing the necessary
background on Bitcoin's double spending attack and
the Vector76 attack. This foundational knowledge
sets the stage for understanding the complexities of
the vulnerabilities inherent in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Next, the operational principles of the Vector76
attack will be detailed. This section will outline the
specific steps involved in executing the Vector76
attack, culminating in a generalized version capable
of achieving a double spending attack after k
confirmations of a transaction. Additionally, the
concept of selfish mining, which underpins the attack
execution, will be thoroughly explained. Beyond the
methods of attack, this study will also present
countermeasures designed to thwart these attacks.
The discussion will focus on two main aspects:
strategies to combat double-spending attacks and
those aimed at counteracting selfish mining attacks.
Following this, an analysis of existing literature on
these attack vectors will highlight the advantages and
disadvantages of the proposed countermeasures. This
critical examination aims to identify gaps and areas
for improvement in current defense mechanisms.
Finally, a comprehensive summary will synthesize
the key findings of the research and provide an
outlook on future developments in this field. The
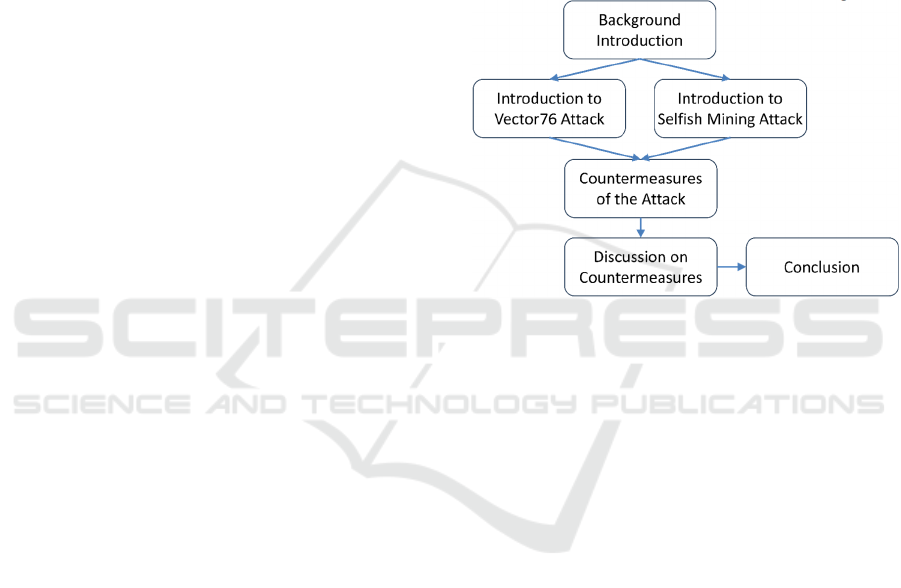
overall research framework is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The pipeline of the study (Picture credit:
Original).
2.1 Blockchain and Bitcoin
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that
allows data to be stored across a network of
computers in a secure and tamper-proof manner. Each
block in the chain contains a list of transactions, and
each subsequent block is linked to the previous one
through cryptographic hashes, creating an unbroken
chain of records. This technology is the backbone of
cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, enabling direct, peer-
to-peer transactions without the need for a central
authority.
Bitcoin, introduced in 2009, is the first and most
widely recognized cryptocurrency. It operates on a
global, decentralized network where transactions are
confirmed by miners who solve complex
mathematical problems. These miners are rewarded
with Bitcoins for their efforts, a process known as
mining. The Bitcoin protocol caps the total number of
coins that can ever be mined at 21 million, making it
a deflationary currency. The decentralized nature of
Bitcoin offers increased security, lower transaction
fees, and financial opportunities for those
traditionally underserved by banks. However, it also
presents challenges such as scalability issues and high
Mitigating the Vector76 Attack: Enhancing Security in the Bitcoin Network
501
energy consumption for mining. Despite these,
Bitcoin's introduction of blockchain technology has
been transformative, paving the way for innovative
financial systems and applications.
2.2 Bitcoin Double Spending Attack
2.2.1 Vector76 Attack
The Vector76 attack, named after a user on the
Bitcoin Talk forums who initially proposed it, is a
sophisticated form of double spending assault within
the Bitcoin network. This is accomplished by sending
a self-built block for the network to give the victim a
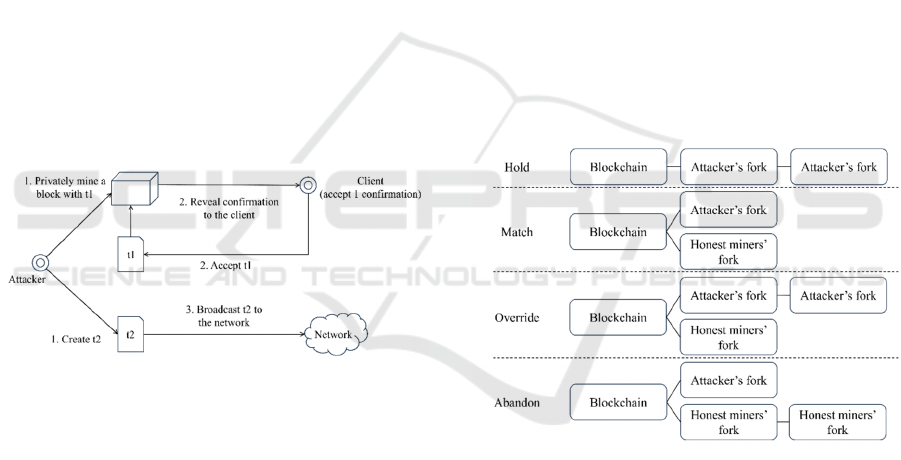
confirmation thinking the block is valid. Figure 2
shows the unfolding steps of the Vector76 attack.
First, the miner privately mines a block and creates
two transactions called t1 and t2, embedding t1 in the
block. Second, then the attacker reveals the
transaction confirmation to a lightweight client which
accepts the confirmation as valid. Third, lastly, the
attacker then broadcasts a conflicting transaction t2 to
the network. Since the network is unaware of the
attacker's secret block, it incorporates t2 into the
blockchain, thereby facilitating the double spend.
Figure 2: The steps of Vector76 attack (Picture credit:
Original).
The generalized version of the Vector76 attack is
similar. If the victim receives a k-confirmed
transaction, the attacker will mine a chain of length k
with t1 at the top of the chain. The network is unaware
of this chain, leaving enough time for t2 to become
longer. The Vector76 attack underscores the
vulnerability of lightweight clients, which do not
propagate blocks, making them more susceptible to
such attacks compared to full nodes.
2.2.2 Selfish Mining Attack
Eyal et al. were the first to propose selfish mining
(Eyal and Sirer, 2018). The basic idea of a selfish
mining attack is that the attacker creates a fork in the
blockchain and chooses the timing to release the
blocks in the forked chain. Four actions can be used
to describe the attack state, which are hold, match,
override, and abandon. Figure 3 provides
explanations for these different states. Hold indicates
that the attacker holds the fork without publishing it.
In the match state, the fork lengths of honest miners
and the attacker are equal, and the attacker issues the
fork to compete. In the override state, the attacker's
fork length is longer than that of honest miners, and
the fork published by the attacker will become the
main chain. In the abandon state, honest miners have
a longer fork and the attacker’s fork may be
abandoned. In the Vector76 attack, the fork obtained
from selfish mining was abandoned. Selfish mining
attack has multiple different strategies. Sapirshtein et
al. used Markov decision-making to optimize selfish
mining strategies (Sapirshtein et.al, 2017), while
Nayak et al. combined the selfish mining attack with
the eclipse attack, and proposed stubborn mining
attacks (Nayak et.al, 2016).
Although the selfish mining attack is a waste of
computing power, the introduction of different
strategies makes this attack more effective, and it is
commonly used in double-spending attacks, which
means that its ways of profiting are very diverse.
Figure 3: States of selfish mining attack (Picture credit:
Original).
2.3 Countermeasures
2.3.1 Countermeasures of Double Spending
Attack
Different countermeasures are used to counter the
double spending attack on Bitcoin. Among them,
adopting security strategies is a common approach.
Security strategies refer to a series of security rules
that merchants follow when accepting transactions.
These strategies can effectively reduce the risk of
merchants facing double-spending attacks. For the
Vector76 attack, there are the following security
DAML 2024 - International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning
502

strategies (Sompolinsky and Zohar, 2016): One of the
strategies is applied to independently generated
transactions that attackers cannot control their time,
and transactions require a certain amount of
confirmation before being accepted. The strategy
aimed at long-term fraction of transactions ensures a
small portion of payments will be double spent, but
the proportion of double spending transactions in the
long term is relatively small. There is also a strategy
that expects to protect all transactions. The strategy
ensures that all transactions have sufficient
confirmation, making double-spending attacks
almost impossible to complete. For lightweight
clients, there is also an appropriate security strategy.
The strategy is aimed at lightweight clients that do not
maintain a complete copy of the blockchain, and it
requires a logarithmic relationship between the
number of confirmations and the length of the
blockchain.
In addition to adopting appropriate security
strategies, different monitoring techniques have been
proposed for more common double-spending attacks
(Karame et.al, 2012; Podolanko et.al, 2017): The
simplest way is adopting a listening period. Vendors
check all transactions within a few seconds of the
listening period to ensure there are no conflicting
transactions. Inserting observers into the Bitcoin
network is also effective. The observer, a node
controlled by the vendor, will forward all transactions
it receives to the vendor. Figure 4 illustrates this
process. It improves the possibility of discovering
double-spending transactions. There is a method
called forwarding double-spending attempts. Figure 5
illustrates it. This method utilizes peers, a type of
node used to maintain blockchain ledgers, to forward
conflicting transactions in the network to their
neighbors, making double-spending transactions
easier to be detected by vendors and observers.
ENHOBS is a hybrid of observer and peer alert
system. ENHOBS will conduct a more in-depth
examination of all received transactions and compare
the outputs and inputs.
Figure 4: Using observers to counter double spending attack
(Picture credit: Original).
Figure 5: Using peers to forward double spending attempts
(Picture credit: Original).
2.3.2 Countermeasures of Selfish Mining
Attack
Since the Vector76 attack requires the use of a selfish
mining attack, countermeasures of selfish mining
attacks can also effectively counter the Vector76
attack. One method of detecting selfish mining
attacks is called truth state. The truth state is a concept
used to detect selfish mining behavior (Saad et.al,
2019). The core idea is to evaluate whether a block
may have been generated by selfish miners by
analyzing the expected confirmation height of
transactions in the block. The expected confirmation
height is the expected location where a transaction is
packaged into a block, calculated based on factors
such as transaction size, transaction fees, and
transaction backlog in the memory pool. The
algorithm designed using the concept of truth state
can effectively identify and reject selfish miners'
chains during blockchain forks, thereby protecting the
blockchain network from the impact of selfish mining
attacks.
There is also a countermeasure that can not only
detect selfish mining attacks but also reduce such
attacks by punishing attackers. Lee et al. proposed a
method to deal with block withholding attack (BWH),
which consists of two stages, infiltration detection
and infiltration punishment (Lee and Kim, 2019). The
infiltration detection stage deploys "sensor" miners
(i.e. honest miners) in other mining pools to detect
whether the mining pool has been attacked by BWH.
These miners are working normally in the attacker's
mining pools. After detecting an attack, the
subsequent stage is called infiltration punishment. A
penalty parameter in this stage is used to reduce the
contribution value of the attacker miners, thereby
reducing their profits.
Mitigating the Vector76 Attack: Enhancing Security in the Bitcoin Network
503

3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This article reveals potential double-spending
vulnerabilities in the Bitcoin system by analyzing the
Vector76 attack and its key technology, selfish
mining. The Vector76 attack exploits the pre-mining
feature of the Bitcoin network, where attackers
secretly mine and broadcast blocks at appropriate
times to achieve double spending for the same
Bitcoin. The countermeasures summarized in the
research include security strategies and monitoring
techniques for double-spending attacks, as well as
detection and punishment mechanisms for selfish
mining attacks. These strategies theoretically provide
effective means of defending against Vector76 attack.
However, it may encounter some challenges in
practical applications.
Firstly, the effectiveness of security strategies
depends on users' correct understanding and
application of transaction confirmation numbers.
Users need to carefully choose the appropriate
number of confirmations to ensure both the security
and efficiency of transactions. This is a challenge for
some users. Secondly, although monitoring
technologies can increase the likelihood of detecting
double-spending attacks, they may increase the
communication burden on the network, especially
during high transaction volumes. In addition, the
effectiveness of monitoring technologies is also
limited by the degree of cooperation among network
nodes and the quality of implementation of
monitoring systems.
The concept of the truth state provides a method
for detecting and resisting attackers' secret mining
behavior as a countermeasure against selfish mining
attacks. However, this method requires an in-depth
analysis of each block in the blockchain, which may
increase the complexity and computational burden of
the system. The infiltration detection and punishment
mechanism punishes attackers by adjusting the profit
distribution of miners, but it still has shortcomings.
Firstly, this method assumes that all mining pools are
public, which may not apply to closed mining pools
that do not allow external miners to join. Secondly, if
attackers adopt anonymization strategies to hide the
identity of their infiltrating miners, the difficulty of
detecting the attack will increase. In addition, the
effectiveness of this method also depends on the
timely identification and response of mining pool
managers to attack behaviors. In addition to the above
issues, evaluating the security of Bitcoin protocol
variants such as Bitcoin- Next Generation (NG) and
Ethereum in the face of similar attacks is also an
important direction. Considering that different
cryptocurrencies may have different mining
mechanisms and characteristics; future work can
evaluate and adjust this method to make it applicable
to a wider range of cryptocurrency ecosystems. It is
also important to quantify the security of the above
measures, as this facilitates users and merchants to
more accurately evaluate the security of transactions.
In addition, the forms of the double-spending attack
and the selfish mining attack have become more
complex and diverse with the development of
blockchain technology. Therefore, this study also
suggests conducting more in-depth research on the
security model of Bitcoin, especially when
considering network latency and the diversity of
attacker strategies.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study offers a comprehensive examination of the
Vector76 attack, a significant double spending threat
within the Bitcoin network, alongside its underlying
technology, selfish mining. The findings indicate that,
despite the formidable challenges posed by this
attack, strategic countermeasures can be effectively
employed to mitigate its impact. To counter double
spending attacks, implementing robust security
strategies is essential. This includes establishing
requirements for the number of transaction
confirmations and developing customized methods
tailored for lightweight clients. Furthermore,
integrating monitoring technologies, such as
ENHOBS, enhances the system's vigilance against
suspicious transactions, thereby providing users with
an additional layer of protection. The selfish mining
attack serves as a critical enabler of the Vector76
attack. In addressing these threats, the detection
methods and punitive measures outlined in this study
present proactive approaches for identifying selfish
mining activities and ensuring a fair distribution of
mining rewards. In conclusion, this research
underscores the necessity of continuously evaluating
and enhancing security measures within the Bitcoin
ecosystem. Future efforts should prioritize the
practical implementation of these strategies,
optimization across various blockchain platforms,
and the development of innovative solutions to
address the evolving landscape of cryptocurrency
security.
DAML 2024 - International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning
504

REFERENCES
Aggarwal, S., Kumar, N., 2021. Attacks on blockchain.
Advances in computers. Elsevier, 121, 399-410.
Eyal, I., Sirer, E.G., 2018. Majority is not enough: Bitcoin
mining is vulnerable. Communications of the ACM,
61(7), 95-102.
Karame, G.O., Androulaki, E., Capkun, S., 2012. Double-
spending fast payments in bitcoin. Proceedings of the
ACM conference on Computer and communications
security. 2012, 906-917.
Lee, S., Kim, S., 2019. Countering block withholding attack
efficiently. IEEE INFOCOM IEEE Conference on
Computer Communications Workshops, 330-335.
Nayak, K., Kumar, S., Miller, A., et al. 2016. Stubborn
mining: Generalizing selfish mining and combining
with an eclipse attack. IEEE European Symposium on
Security and Privacy, 305-320.
Nicolas, K., Wang, Y., Giakos, G.C., et al. 2020.
Blockchain system defensive overview for double-
spend and selfish mining attacks: A systematic
approach. IEEE Access, 9, 3838-3857.
Podolanko, J.P., Ming, J., Wright, M., 2017. Countering
double-spend attacks on bitcoin fast-pay transactions.
Proc. Workshop Technol. Consum. Protection. 2017, 1-
3.
Saad, M., Njilla, L., Kamhoua, C., et al. 2019. Countering
selfish mining in blockchains. International Conference
on Computing, Networking and Communications, 360-
364.
Sapirshtein, A., Sompolinsky, Y., Zohar, A., 2017. Optimal
selfish mining strategies in bitcoin. Financial
Cryptography and Data Security: International
Conference, 515-532.
Sompolinsky, Y., Zohar, A., 2016. Bitcoin's security model
revisited. arXiv preprint :1605.09193.
Mitigating the Vector76 Attack: Enhancing Security in the Bitcoin Network
505
