
Emotion Recognition in Human-Robot Interaction: Multimodal
Fusion, Deep Learning, and Ethical Considerations
Yuan Gao
College of Arts and Sciences, University of Washington, 4801 24th Ave NE APT 6130, Seattle, U.S.A.
Keywords: Emotion Recognition, Human-Robot Interaction, EEG-Based Emotion Detection, Multimodal Fusion,
Empathy in Robotics, Ethical AI.
Abstract: This paper explores recent advancements in emotion recognition techniques within Human-Robot Interaction
(HRI), focusing on the evolution of perception-based, electroencephalogram (EEG)-based, and multimodal
fusion approaches. Emotion recognition has become essential for enhancing the emotional intelligence of
robots, which can now better detect and respond to human emotions, particularly within service and healthcare
applications. Key contributions of this study include the integration of deep learning models, such as
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformer-based architectures, which have shown significant
improvements in real-time emotion recognition accuracy. Additionally, the paper discusses the integration of
hardware innovations that optimize responsiveness, enabling robots to provide a more empathetic and
supportive experience. This research also examines the role of empathy within social robotics and its ethical
implications, covering data privacy, user consent, and the need for fair, unbiased artificial intelligence (AI).
By emphasizing the importance of regulatory frameworks, this study outlines the future of emotion-aware AI
in safe, ethical, and effective human-robot collaboration.
1 INTRODUCTION
As robots become an increasingly common presence
in our daily lives, the need for them to understand and
respond to human emotions has never been more
crucial. Imagine a healthcare robot comforting a
patient not just with physical assistance, but also with
emotional support, or a customer service robot that
can detect frustration and adjust its responses to calm
the situation. These scenarios, once considered
science fiction, are rapidly becoming reality due to
advancements in emotion recognition technology.
Homburg’s research in robotic psychology, over the
past two decades, has laid the foundation for these
developments by emphasizing the importance of
emotional interaction in enhancing human-robot
collaboration (Stock-Homburg, 2022). The question
is: What kind of an emotion recognition system could
we employ to boost Human-Robot Interaction (HRI)?
Accurately detecting and interpreting human
emotions is fundamental to enhancing robot
efficiency in interacting with humans. Emotion
recognition enables robots to adjust their behavior in
real-time, improving the perceived naturalness of
interactions and creating a more personalized
experience. This ability is especially crucial in HRI
scenarios that demand immediate emotional
responses, such as when assisting patients or
managing customer inquiries. However, according to
Marcos-Pablos and García-Peñalvo (2022), real-time
emotion detection remains a challenging task due to
the complexity of human emotions and the need to
integrate multimodal data such as facial expressions,
speech, and physiological signals (Marcos-Pablos &
García-Peñalvo, 2022). Techniques like multitask
learning have shown promise in addressing these
challenges by improving emotion detection accuracy
across various data modalities (Li, Kazemeini, Mehta
& Cambria, 2022).
The purpose of this review is to provide an
overview of the development and the latest
advancements in emotion recognition technologies,
particularly focusing on their application in HRI. This
paper will first examine traditional methods of
emotion detection, such as facial expression and
speech recognition. Next, it will explore cutting-edge
innovations like transformer-based models that offer
improved real-time performance and multimodal
systems that enhance detection accuracy across
diverse contexts (Heredia, Lopes-Silva, Cardinale,
Gao and Y.
Emotion Recognition in Human-Robot Interaction: Multimodal Fusion, Deep Learning, and Ethical Considerations.
DOI: 10.5220/0013526100004619
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning (DAML 2024), pages 459-465
ISBN: 978-989-758-754-2
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
459

Diaz-Amado, Dongo & Graterol, 2022). The review
concludes with a discussion of the ethical
considerations and future trends that will shape the
development of emotionally intelligent robots (Stark
& Hoey, 2021).
2 EMOTION DETECTION
TECHNIQUES IN HUMAN-
ROBOT INTERACTION
With the rapid development of human-robot
interaction in various fields, emotion recognition has
become a critical component in enhancing natural
interactions between humans and robots. Emotion
recognition not only enables robots to better
understand human emotions but also allows them to
adjust their behaviour based on the user’s emotional
state, which is particularly important in applications
such as healthcare, customer service, and
collaborative robots. Currently, emotion recognition
techniques in HRI primarily focus on three
categories: traditional perception-based detection
methods, electroencephalogram (EEG)-based
physiological emotion recognition, and multimodal
emotion detection techniques.
2.1 Traditional Emotion Recognition
Techniques
Traditional emotion recognition methods primarily
rely on observable external features such as facial
expressions, voice signals, and body language. Facial
expression recognition, which analyzes specific facial
muscle movements to infer emotional states, has been
widely used in emotion detection for HRI. Based on
Ekman’s facial expression theory, this method
identifies basic emotions like anger, joy, and sadness,
providing robots with intuitive emotional cues. For
example, Cavallo et al. (2018) have shown that facial
expressions can assist service robots in recognizing
customers' emotional responses, thereby improving
the quality of service (Cavallo et al., 2018).
However, facial expression recognition
techniques face limitations in complex or occluded
environments. Chuah and Yu (2021) shared that
facial expressions do not always accurately reflect an
individual’s true emotional state (Chuah & Yu, 2021).
Due to social norms or environmental pressures, users
may conceal their true emotional expressions.
Consequently, researchers have shifted toward
speech recognition techniques, analyzing tone,
speech rate, and volume to complement emotion
recognition accuracy. Emotional information
embedded in voice signals can significantly enhance
HRI, especially in scenarios where visual cues are
unavailable or unreliable (Rawal & Stock-Homburg,
2022).
While traditional facial expression and voice
recognition methods play a significant role in emotion
detection, their reliance on a single modality limits
their effectiveness in complex interaction scenarios,
motivating the exploration of more sophisticated
emotion recognition methods.
2.2 EEG-Based Emotion Recognition
To improve the accuracy and reliability of emotion
recognition, physiological signals have gained
attention in the field, particularly EEG-based emotion
recognition techniques. Emotion influences brain
activity at the neurological level, and EEG signals can
capture these changes in real time, making them a
powerful tool for emotion recognition (Cui et al.,
2020). EEG-based emotion recognition in HRI
benefits from its ability to detect subtle emotional
states, especially when facial expressions or voice
signals are not clearly exhibited.
In recent years, deep learning models for EEG-
based emotion recognition have shown significant
progress. For instance, Li, Meng, Wang and Hou
(2023) have proposed the Source-guided Multi-
Target Learning model, which processes the regional
differences in EEG signals to achieve high-accuracy
emotion recognition (Li, Meng, Wang & Hou, 2023).
Compared to traditional methods, this model captures
more complex emotional patterns and is suitable for
real-time applications in HRI where responsiveness is
critical. Furthermore, by combining EEG with
recurrent neural networks (RNN), Shen et al. (2020)
enhances the model’s ability to process temporal
sequences of data, improving both the speed and
accuracy of emotion detection (Shen et al., 2020).
Although EEG-based emotion recognition
surpasses traditional facial and voice recognition
methods in terms of accuracy, it still faces challenges.
Firstly, the wearable nature of EEG devices can affect
user comfort and natural interaction experiences.
Secondly, individual variability in brain signals
demands that emotion recognition models be highly
personalized and adaptive to achieve consistent
results.
DAML 2024 - International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning
460

2.3 Multimodal Emotion Detection
Techniques
Multimodal emotion detection techniques integrate
various sensory inputs such as facial expressions,
voice, and EEG signals to enhance the accuracy and
robustness of emotion recognition (Xie, Sidulova &
Park, 2021). By combining information from
different modalities, multimodal approaches
overcome the limitations of single-modality methods.
For example, when visual signals are unstable or
speech is ambiguous, EEG signals can provide
supplementary information, ensuring continuous
emotion detection.
Recent studies have demonstrated that
multimodal approaches can significantly improve
emotion recognition accuracy. Xie, Sidulova and
Park’s (2021) study combined voice, text, and facial
expressions to develop a cross-modal emotion
detection model, greatly enhancing the accuracy of
emotion recognition in conversational settings (Park
et al., 2021). Last but not the least, the Multimodal
Fusion Network (MMFN), which integrates touch
gestures and facial expression data, introduced a
novel framework that substantially improved emotion
detection accuracy in complex interaction scenarios
(Li et al., 2023).
The Interactive Emotional Dyadic Motion
Capture (IEMOCAP) dataset is widely used for
evaluating multimodal emotion detection systems,
making it a benchmark for comparing methods like
speech, facial expression, text, and multimodal fusion
techniques. Table 1 illustrates the accuracy and
applicability of these emotion recognition methods
based on IEMOCAP results.
Table 1: Comparison of Emotion Detection Techniques on
IEMOCAP Dataset (Tripathi, Tripathi & Beigi, 2019)
Method Data
Type
Accurac
y (%)
Applicability
Facial
Emotion
Recognition
Motion
Capture
(Face,
Head,
Hand
)
48.99% Suitable for
clear facial
cues in well-
lit
environments.
Speech
Expression
Recognition
Audio
Signal
55.65% Effective for
remote
interactions or
limited visual
data.
Text
Emotion
Detection
Text
(Transcr
ipts)
64.78% Useful in
conversations
or textual
dialo
g
ues.
Multimodal
Fusion
Audio,
Text,
Motion
Signals
71.04% Optimal in
dynamic and
complex
interaction
environments.
Among different models, EEG stands out for its
high accuracy in detecting subtle emotional states that
are often missed by speech or facial cues, making it
invaluable for nuanced emotional analysis.
Multimodal approaches, which integrate signals from
various sources, consistently outperform single-
modality techniques. By leveraging speech, visual,
and physiological data, these systems offer improved
accuracy and adaptability, enabling more natural and
responsive human-robot interactions in dynamic
environments.
3 INNOVATIONS IN EMOTION
REGOGNITION
In recent years, the field of emotion recognition in
human-robot interaction has seen substantial growth
due to advancements in both algorithmic methods and
hardware developments. This chapter explores these
innovations, focusing on improvements in traditional
emotion recognition techniques, the application of
deep learning in multimodal systems, and the role of
hardware in enhancing real-time emotion detection.
3.1 Deep Learning in Multimodal
Emotion Recognition
The application of deep learning has greatly advanced
the field of emotion recognition, especially in systems
that combine multiple data modalities such as visual,
auditory, and physiological signals. Convolutional
neural networks (CNNs) and Long Short-Term
Memory (LSTM) networks have been pivotal in
extracting features from large, complex datasets,
improving the accuracy and adaptability of emotion
detection systems (Cui et al., 2020).
One significant innovation in this area is the use
of Transformer-based models, which outperform
traditional methods by capturing long-range
dependencies between different modalities. These
models have been applied to fuse data from speech,
text, and visual sources, thereby enhancing the
accuracy of emotion recognition in conversation-
based interactions (Park et al., 2021). According to
Park et al., the use of Transformers enabled real-time
integration of multiple data streams, allowing for
Emotion Recognition in Human-Robot Interaction: Multimodal Fusion, Deep Learning, and Ethical Considerations
461
more nuanced emotion detection in human-robot
interaction.
Multitask learning is another deep learning
technique that has been effectively utilized in emotion
recognition systems. It allows a single model to
simultaneously predict multiple emotional states or
personality traits, leading to better generalization
across tasks and more efficient use of data (Li et al.,
2022). These advancements are particularly relevant
in dynamic, real-time applications in HRI, where
systems must continuously adapt to varying
emotional cues from users.
3.2 Hardware Innovations for Emotion
Recognition
In addition to breakthroughs in algorithms,
advancements in hardware have played a crucial role
in improving the practicality of emotion recognition
systems. Wearable sensors, particularly those used
for capturing electroencephalography signals, have
become more lightweight and portable, making it
easier to integrate physiological data into emotion
recognition frameworks (Cui et al., 2020). These
sensors provide real-time data on brain activity,
which, when combined with deep learning
algorithms, allows for more accurate inference of
emotional states in naturalistic settings.
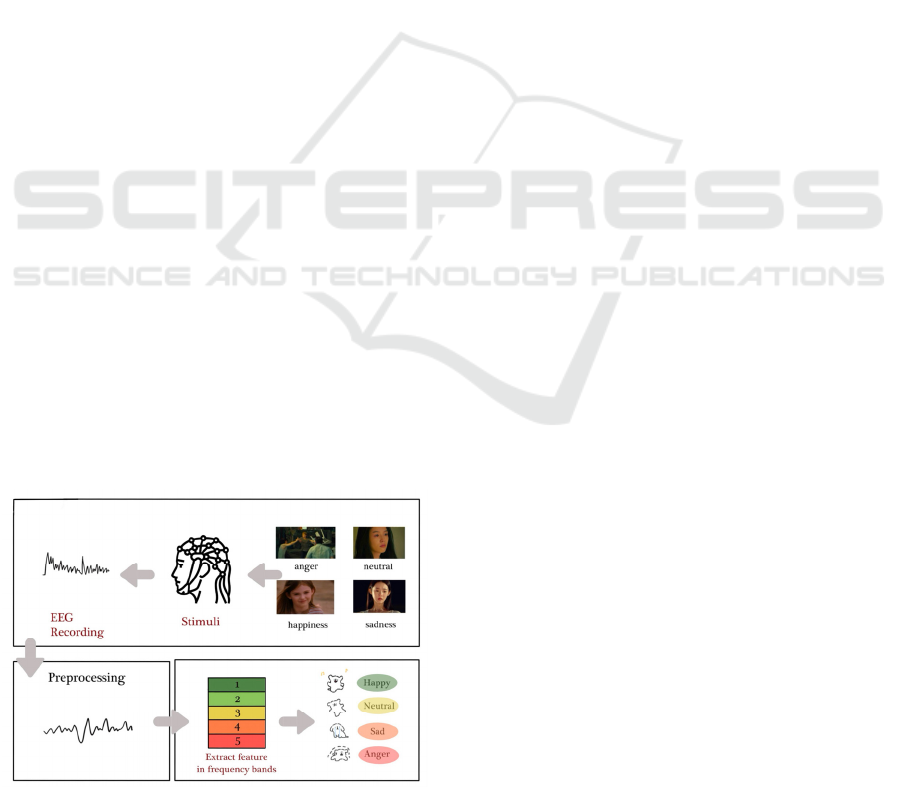
Figure 1 illustrates the process of EEG-based
emotion recognition, where brain activity is recorded
in response to emotional stimuli. The raw EEG data
is then preprocessed to remove artifacts, followed by
feature extraction of key brainwave frequencies.
These features are input into an emotion recognition
model, which classifies the emotional state of the user
(e.g., happy, neutral, sad). This integration of EEG
sensors and emotion recognition models enables real-
time, accurate detection of emotions, further
enhancing the effectiveness of human-robot
interaction in naturalistic environments.
Figure 1: Process of EEG-based
emotion recognition
Moreover, memristive circuits have emerged as a
powerful tool for enhancing hardware-based emotion
recognition. Memristive circuits simulate brain-like
learning processes, enabling more energy-efficient
processing of emotional data (Wang, Wang & Zeng,
2023). This innovation allows for the deployment of
emotion recognition systems on low-power devices,
such as robots, while maintaining high processing
speed. The development of brain-computer interfaces
(BCIs) has also improved the potential for seamless
human-robot interaction. By allowing robots to
access real-time emotional feedback from users via
direct neural signals, BCIs facilitate more intuitive
and empathetic interactions (Wang, Wang & Zeng,
2023).
4 INNOVATIONS IN EMOTION
REGOGNITION
4.1 Emotional Intelligence Through
Multimodal Integration
In modern human-robot interaction, robots are
required not only to recognize human emotions but
also to respond to them through integrated
multimodal feedback mechanisms. Emotionally
intelligent robots collect data from various sources
such as voice, facial expressions, and behaviors,
dynamically adjusting their responses to create a
more natural and emotionally sensitive interaction
experience. These systems enhance the user
experience by tailoring robot behavior based on real-
time emotional cues.
Hong et al. (2021) emphasizes the significance of
bidirectional emotional interaction between robots
and humans. Through the integration of multiple data
sources, robots can more accurately gauge users'
emotions and provide immediate, contextually
appropriate feedback (Hong et al., 2021). This real-
time emotional processing allows robots to adjust
their interaction strategies and align their behavior
with the emotional state of the user, improving both
engagement and user satisfaction. Additionally, Yan,
Iliyasu and Hirota (2021) highlights how robots can
utilize structured emotional representations to fine-
tune their responses, contributing to a more fluid
emotional exchange (Yan, Iliyasu & Hirota, 2021).
Artificial Emotional Intelligence (AEI) ought to seek
to simulate and amplify natural emotions—
particularly human emotions—to equip robots with
the ability to recognize and express emotions during
HRI.
DAML 2024 - International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning
462

4.2 The Role of Empathy and Emotional
Feedback in Social Robots
As social robots evolve, empathy has become a
crucial component in improving the quality of
human-robot interactions. Robots that can understand
and respond empathetically to human emotions are
more likely to be accepted and integrated into fields
such as healthcare, education, and customer service.
Park and Whang (2022) present a framework for
developing empathetic systems in social robots. This
framework focuses on how robots can enhance
emotional connections with users through effective
emotion recognition and feedback (Park & Whang,
2022). Additionally, Chiang, Trimi and Lo (2022)
discusses how emotional feedback in service robots
improves the overall user experience, demonstrating
that empathetic robots can significantly enhance the
perceived quality of interactions (Chiang, Trimi &
Lo, 2022). By responding to users' emotions, these
robots can foster deeper emotional bonds and
improve satisfaction across a variety of applications.
5 APPLICATIONS AND FUTURE
TRENDS
5.1 Service Robots
Emotional Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a crucial
role in the advancement of service robots, particularly
in customer service and personalized interaction.
Emotional intelligence in robots allows them to
recognize and adapt to users’ emotional states,
thereby enhancing user satisfaction and making
interactions more meaningful. This capability is
essential in environments such as retail, hospitality,
and healthcare, where personalized service is critical
to improving user experiences.
Chuah and Yu (2021) emphasize that emotion-
aware robots significantly improve the quality of
service by responding to customers’ emotional needs
and tailoring interactions accordingly. A robot
capable of detecting customer frustration can adjust
its behavior to offer more supportive responses.
Similarly, by employing edge clouds on smart
clothing, Yang et al. (2020) highlights how emotional
intelligence in robots contributes to a deeper
engagement, enabling them to build rapport with
users by offering more human-like interaction (Yang
et al., 2020). These advancements make service
robots more effective at handling complex customer
needs, fostering trust, and ensuring long-term user
satisfaction.
5.2 Collaborative Robots and Safety
Emotion recognition can also enhance the safety and
efficiency of collaborative robots, especially in
industrial and workplace settings. By understanding
and responding to human emotional cues,
collaborative robots can adjust their actions to prevent
accidents or discomfort, contributing to a safer
working environment. Emotional AI allows these
robots to anticipate and react to potentially dangerous
situations, such as stress or frustration in human
coworkers, which may otherwise lead to mistakes or
unsafe behavior.
Toichoa, Mohammed and Martinez (2021)
demonstrate how emotion recognition helps
collaborative robots better understand human intent
and adjust their operational behavior to enhance
safety and collaboration (Toichoa, Mohammed &
Martinez, 2021). Additionally, Zacharaki, Kostavelis,
Gasteratos and Dokas (2020) explore how integrating
emotional awareness into robots’ control systems can
help set safety parameters that minimize risk while
maximizing operational efficiency (Zacharaki,
Kostavelis, Gasteratos & Dokas, 2020). By
incorporating emotional cues, collaborative robots
become more aware of their human coworkers’
needs, making teamwork more fluid and secure.
5.3 Ethical Considerations
As emotional AI becomes more prevalent, ethical
concerns surrounding privacy, emotional
manipulation, and data security have become critical
issues. Emotionally intelligent robots process
sensitive emotional data, which raises concerns about
how this information is collected, stored, and used.
The potential for emotional manipulation—where
robots could influence users' emotions in unethical
ways—also poses a significant ethical challenge,
particularly in vulnerable populations such as
children, the elderly, or individuals with cognitive
impairments.
Stark and Hoey (2021) addresses these concerns
by highlighting the need for strict regulatory
frameworks to ensure emotional AI systems respect
user privacy and autonomy. There are also concerns
about emotional manipulation, especially when
robots are used with vulnerable populations such as
children, the elderly, or individuals with cognitive
impairments. The ethical design of emotion-aware
systems must prioritize the well-being of users,
ensuring that emotional feedback is used responsibly
Emotion Recognition in Human-Robot Interaction: Multimodal Fusion, Deep Learning, and Ethical Considerations
463

and without crossing personal boundaries. Ensuring
transparency and user consent will be vital as
emotional AI becomes more integrated into daily life.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Emotion recognition has become a critical aspect of
human-robot interaction, with profound implications
for how robots understand and respond to human
needs. This review has examined the key
advancements in emotion detection technologies,
highlighting the significance of both traditional
methods and more innovative approaches such as
multimodal integration and deep learning techniques.
The use of multimodal data, including facial
expressions, speech, and physiological signals, has
substantially improved the accuracy and reliability of
emotion recognition systems, enabling robots to
adapt in real time and enhance the naturalness of
human-robot interactions.
Despite the progress made, there are still
significant challenges that need to be addressed. Real-
time processing of complex, multimodal emotional
data remains a technical hurdle, particularly in
environments where quick adaptation is required.
Additionally, understanding and responding to
emotions in a way that is culturally sensitive and
contextually appropriate poses ongoing difficulties.
Addressing these challenges will require not only
advances in algorithms and hardware but also a
deeper exploration of the psychological and social
dimensions of emotion in human-robot interaction.
Looking forward, the future of emotional
intelligent robots lies in further refining these
technologies to create more seamless, empathetic
interactions. This includes the development of more
adaptive and personalized emotion recognition
models that can operate across diverse environments
and user groups. Moreover, ethical considerations
must be an integral part of future research, ensuring
that the deployment of emotion-aware robots
promotes positive human experiences without
infringing on privacy or autonomy.
REFERENCES
Cavallo, F., Semeraro, F., Fiorini, L., Magyar, G., Sinčák,
P., & Dario, P. (2018). Emotion modelling for Social
Robotics Applications: A Review. Journal of Bionic
Engineering, 15(2), 185–203.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-018-0015-y
Chiang, A.-H., Trimi, S., & Lo, Y.-J. (2022). Emotion and
service quality of anthropomorphic robots.
Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 177,
121550.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121550
Chuah, S. H.-W., & Yu, J. (2021). The future of service:
The power of emotion in human-robot interaction.
Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 61,
102551.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2021.102551
Cui, H., Liu, A., Zhang, X., Chen, X., Wang, K., & Chen,
X. (2020). EEG-based emotion recognition using an
end-to-end regional-asymmetric convolutional neural
network. Knowledge-Based Systems, 205, 106243.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106243
Heredia, J., Lopes-Silva, E., Cardinale, Y., Diaz-Amado, J.,
Dongo, I., Graterol, W., & Aguilera, A. (2022).
Adaptive Multimodal Emotion Detection Architecture
for Social Robots. IEEE Access, 10, 20727–20744.
https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3149214
Hong, A., Lunscher, N., Hu, T., Tsuboi, Y., Zhang, X.,
Franco dos Reis Alves, S., Nejat, G., & Benhabib, B.
(2021). A multimodal emotional human–robot
interaction architecture for social robots engaged in
bidirectional communication. IEEE Transactions on
Cybernetics, 51(12), 5954–5968.
https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2020.2974688
Li, Y., Kazemeini, A., Mehta, Y., & Cambria, E. (2022).
Multitask learning for emotion and personality traits
detection. Neurocomputing, 493, 340–350.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.04.049
Li, Y.-K., Meng, Q.-H., Wang, Y.-X., & Hou, H.-R. (2023).
MMFN: Emotion recognition by fusing touch gesture
and facial expression information. Expert Systems with
Applications, 228, 120469.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120469
Marcos-Pablos, S., & García-Peñalvo, F. J. (2021).
Emotional intelligence in robotics: A scoping review.
Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 66–75.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87687-6_7
Park, S., & Whang, M. (2022). Empathy in human–robot
interaction: Designing for social robots. International
Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,
19(3), 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031889
Rawal, N., & Stock-Homburg, R. M. (2022). Facial
emotion expressions in human–robot interaction: A
survey. International Journal of Social Robotics, 14(7),
1583–1604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12369-022-
00867-0
Shen, F., Dai, G., Lin, G., Zhang, J., Kong, W., & Zeng, H.
(2020). EEG-based emotion recognition using 4D
convolutional recurrent neural network. Cognitive
Neurodynamics, 14(6), 815–828.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09634-1
Stark, L., & Hoey, J. (2021). The ethics of Emotion in
Artificial Intelligence Systems. Proceedings of the
2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability,
and Transparency.
https://doi.org/10.1145/3442188.3445939
DAML 2024 - International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning
464

Stock-Homburg, R. (2021). Survey of emotions in human–
robot interactions: Perspectives from robotic
psychology on 20 years of research. International
Journal of Social Robotics, 14(2), 389–411.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12369-021-00778-6
Toichoa Eyam, A., Mohammed, W. M., & Martinez Lastra,
J. L. (2021). Emotion-driven analysis and control of
human-robot interactions in collaborative applications.
Sensors, 21(14), 4626.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s21144626
Tripathi, S., Tripathi, S., & Beigi, H. (2019a, November 6).
Multi-modal emotion recognition on IEMOCAP dataset
using Deep Learning. arXiv.org.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.05788
Wang, Z., Wang, X., & Zeng, Z. (2023). Memristive circuit
design of brain-like emotional learning and generation.
IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 53(1), 222–235.
https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2021.3090811
Xie, B., Sidulova, M., & Park, C. H. (2021). Robust
multimodal emotion recognition from conversation
with Transformer-based crossmodality fusion. Sensors,
21(14), 4913. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21144913
Yan, F., Iliyasu, A. M., & Hirota, K. (2021). Emotion space
modelling for social robots. Engineering Applications
of Artificial Intelligence, 100, 104178.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104178
Yang, J., Wang, R., Guan, X., Hassan, M. M., Almogren,
A., & Alsanad, A. (2020). Ai-enabled emotion-aware
robot: The fusion of Smart Clothing, edge clouds and
robotics. Future Generation Computer Systems, 102,
701–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.09.029
Zacharaki, A., Kostavelis, I., Gasteratos, A., & Dokas, I.
(2020). Safety Bounds in human robot interaction: A
survey. Safety Science, 127, 104667.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104667
Emotion Recognition in Human-Robot Interaction: Multimodal Fusion, Deep Learning, and Ethical Considerations
465
