
BlockIoTintelligence: Integrating Blockchain and AI for Enhanced
Performance in IoT and Healthcare
Yuxuan Chen
a
School of Advanced Technology, Xi'an Jiaotong Liverpool University, Xi'an, China
Keywords: Blockchain; Artificial Intelligence; Internet of Things (IoT); Healthcare.
Abstract: With the advancement of technology, the integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged
as a prominent research topic. This paper aims to explore the core technologies involved and analyze the
performance of their combination. The approach utilizes blockchain to provide secure, transparent, and
immutable data storage, while AI offers advanced data analysis and predictive insights. The discussion of the
study focuses specifically on two sectors, Internet of Things (IoT) and healthcare. The methodology involves
developing AI algorithms to analyze data from IoT devices and healthcare systems and integrating these
algorithms with a blockchain ledger to improve the performance while making sure data integrity and
preventing unauthorized access. The proposed framework, termed BlockIoTintelligence architecture, is
evaluated for its effectiveness. Results reveal significant improvements in data security, operational efficiency,
and accuracy in both fields. The paper also points out the limitations and challenges associated with this
integration. It concludes by summarizing the value of combining AI and blockchain technology, providing
valuable insights for practitioners in IoT and healthcare, and highlighting its implications for social and
business management.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence (AI), as two
most advanced technology, each play an important
role in their own field. Blockchain is an innovative
technology that makes it possible to create
dependable applications without requiring peer trust
(Mattos et.al, 2020). Blockchain is implemented
through a decentralized distributed network and
encryption technology, while AI technology achieves
automated decision-making intelligent functions
through data analysis and machine-learning. With
various AI technologies, blockchain implementation
can be aided or augmented. It is believed that the
combination of AI and blockchain can create
countless possibilities in the future (Marwala and
Xing, 2018). This combination not only improves
data security and promotes the development of smart
contracts, but also promotes the realization of
decentralised decision-making, which has significant
impact in many fields such as social governance and
enterprise management.
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-4612-9137
The combination of blockchain and AI has
already been widely used and led to many innovative
applications and create synergies in a variety of fields.
In healthcare, the accuracy of early sickness detection
might be significantly improved by potent AI and
computer technologies. However, security is still a
concern because of the centralized nature of the
existing system. Therefore, safety can be offered via
blockchains, a relatively new and developing
technology (Kumar et.al, 2019; Thomason et.al, 2018;
Clauson et.al, 2018; Sylim et.al, 2018). In this case,
A decentralized access control strategy built on
blockchain technology and artificial intelligence is
suggested (Rana et.al, 2022). Furthermore, utilizing
the most recent cutting-edge techniques and
applications, a blockchain-enabled Intelligent
Internet of Things (IoT) Architecture with AI was
present, which offers an efficient way to combine
blockchain technology with AI in the area of IoT
(Singh et.al, 2020). In data management, blockchain
can provide secure, transparent and traceable data
storage for AI systems, addressing issues such as data
privacy and data ownership. For instance, to make
374
Chen and Y.
BlockIoTintelligence: Integrating Blockchain and AI for Enhanced Performance in IoT and Healthcare.
DOI: 10.5220/0013524300004619
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning (DAML 2024), pages 374-378
ISBN: 978-989-758-754-2
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

documentation about the cargo to be carried easier,
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM)
and Maersk collaborated to build TradeLens, a
blockchain- powered supply chain management
platform (Junior et.al, 2024). Blockchain technology
is also used to protect supply chain data and offer a
trustworthy source of data for AI algorithms. At the
same time, Blockchain can also supply reliable data
for AI model training, enhancing the models'
functionality and readability.
The primary purpose of this paper is to investigate
the relationship between blockchain and AI, offering
an in-depth analysis of their complementarity and
integration possibilities. The research seeks to
provide new perspectives and directions for future
scientific and technological advancements in these
fields. The paper is structured as follows: The first
section provides a summary of the relevant concepts
and background information on the intersection of AI
and blockchain, outlining the potential synergies
between these technologies. Section II offers a
detailed analysis and discussion of the core
technologies used. In Section III, the performance of
key technologies is demonstrated and evaluated,
highlighting their practical applications and
effectiveness. Lastly, Section IV assesses the
strengths and weaknesses of these integrated
technologies, summarizes the key findings, and
presents the overall conclusions of the study.
2 METHODOLOGIES
2.1 Specific Structure
The study then progresses to an analysis of the core
technologies underpinning blockchain and AI. The
specific structure of this study is illustrated in Figure
1. This section introduces blockchain's data
structures, consensus mechanisms, and smart
contracts, followed by a discussion of AI algorithms,
models, and data processing capabilities.
Additionally, it will examine the technical
architectures of both technologies and their
interactions through illustrative case studies.
Following the technological analysis, the study will
demonstrate and analyze the performance of key
technologies. By selecting representative application
cases, this part evaluates how AI performs within
blockchain environments. The scientific research and
data analysis carried out here are intended to
emphasize the useful advantages and possible
applications of merging blockchain with AI. Finally,
the study's conclusion part evaluates the benefits and
problems related to the integration of blockchain and
AI. It synthesizes the findings from the previous
sections, provides recommendations for future
research, and discusses the technical barriers, ethical
considerations, and policy implications that may arise
during implementation.
Figure 1: The structure of the study (Picture credit:
Original).
2.2 Core Technologies
2.2.1 Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a decentralized technology that
maintains a shared database through multiple network
nodes to ensure data transparency, security, and
immutability. blocks, chains, Cryptographic
algorithms, distributed ledgers, and consensus
techniques, are core constituent parts. These blocks
are sets of data that are connected chronologically to
form a chain, that is where the blockchain name
comes from. Every block is unique in its hash value,
a fixed-length value calculated from the input data via
a hash function. Every new block contains the hash of
the preceding block, which ensures data integrity and
tamper resistance. With distributed ledgers, single
points of failure are eliminated and greater reliability
and security are achieved by ensuring that every node
has the same copy of the ledger, updated
concurrently. Transaction validation criteria are
established using consensus techniques like Proof of
Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), which
guarantee node agreement on the legitimacy of
transactions. Public-key cryptography securely
verifies transactions, while cryptographic algorithms
such as Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA)-256 offer data
security and anonymity. These tenets allow
blockchain to provide trusted transaction records and
decentralized data management, which are highly
valued in supply chain management, smart contracts,
and finance.
2.2.2 AI Technology
AI is probably better known than blockchain. As a
branch of computer science, it aims to mimic human
thinking by creating complex algorithms that perform
difficult tasks that previously required human
intelligence to complete (Bekbolatova et.al, 2024).
For example, AI can perform tasks like learning,
reasoning, and understanding natural language. Key
concepts in AI include machine learning, neural
BlockIoTintelligence: Integrating Blockchain and AI for Enhanced Performance in IoT and Healthcare
375
networks, natural language processing (NLP), and
computer vision. Through machine learning,
computers may learn from data without the need for
explicit programming, finding patterns that help them
anticipate future events. Typical techniques include
reinforcement learning, which maximizes decision-
making through trial and error, supervised learning,
which makes use of labeled data, and unsupervised
learning, which uncovers structure in unlabeled data.
Deep learning applies neural networks similar to the
structure of the human brain to process more complex
data, including speech and images. Neural networks
are made up of interconnected nodes, or neurons. By
utilizing statistical techniques and machine learning,
NLP gives AI the power to understand, process and
react nearly as well as humans. This is helpful for
sentiment analysis, machine translation, and
detection of speech. Machines can now understand
pictures and videos thanks to computer vision, which
has applications in everything from autonomous
driving to facial recognition. In summary, AI models
human intelligence across various domains,
transforming industries and unlocking new potential
as technology advances.
2.2.3 Combined Application
The combination of AI and blockchain technology
offers significant potential across various domains,
including the IoT, healthcare, and financial data
management. In the area of IoT, Blockchain provides
data integrity and security through unique device
identifiers and tamper-proof records, while AI
improves device operation and maintenance by
analyzing massive amounts of data. In the medical
field, this collaboration produces safe digital health
records that protect patient confidentiality and
identity while permitting safe data exchange. For
individualized diagnosis and treatment suggestions,
AI evaluates vast amounts of health data, and
blockchain prevents unwanted access. Moreover,
Blockchain strengthens the reliability of data by
offering transparent, unchangeable transaction
records for data management. AI improves prediction
accuracy by using this data for market trend research
and real-time risk assessment. Furthermore, the smart
contracts of blockchains automate the execution of
transactions, enhancing security and efficiency. In
conclusion, the combination of AI and blockchain is
revolutionizing various domains by improving data
security, effective management, and intelligent
applications.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Analysis
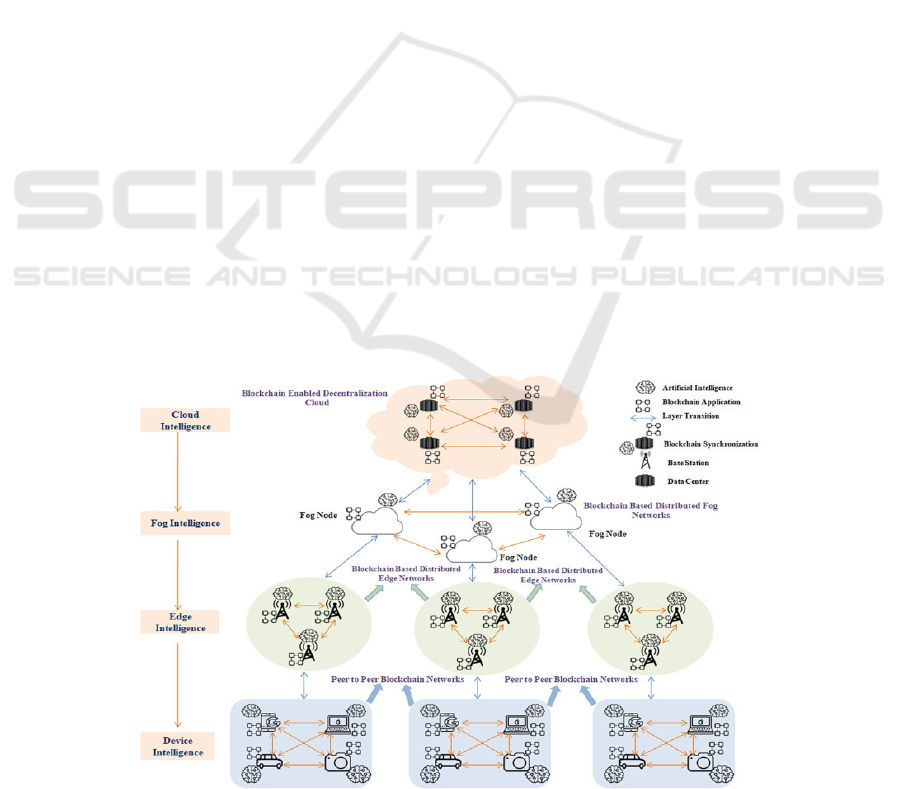
SK Singh, S Rathore and JH Park present the
BlockIoTintelligence architecture illustrated in
Figure 2, which combines blockchain and AI. Device
intelligence, edge intelligence, cloud intelligence, and
fog intelligence are the four intelligence layers that
make up this architecture. It demonstrates how to
enhance large data processing, security, and
centralization in Internet of Things applications, like
smart cities, smart transportation, and smart
healthcare, by merging blockchain technology with
artificial intelligence.
Figure 2: Overview of the proposed BlockIoTIntelligence Architecture (Singh et.al, 2020).
DAML 2024 - International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning
376

According to their experimental quantitative
evaluation, when utilized for safe and decentralized
large data analysis tasks in IoT applications, the
BlockIoTintelligence structure offers excellent
efficiency in the areas of accuracy, centralization,
safety, confidentiality, and latency (Singh et.al,
2020). For every stakeholder involved, distributed
ledger technology in healthcare has several benefits,
as shown in Figure 3. It makes it easier to develop
"smart" healthcare professionals who can create
individualized treatment programs. Because the
technology offers more secure and comprehensive
health records, interoperability is improved. Smart
contracts prevent fraudulent insurance claims,
automatically manage rights, and enhance data
coordination. By using distinct addresses and
cryptographic security, it guarantees correctness in
provider directories. Furthermore, blockchain makes
it easier to obtain thorough medical records, which
results in a less intrusive and more user-friendly
procedure. Overall, it facilitates a dynamic
relationship between clients and insurers by
effectively handling smart contract interactions (Rana
et.al, 2022).
Figure 3: Benefits of using blockchain technology in
healthcare sector (Rana et.al, 2022).
3.2 Discussion
The integration of AI and Blockchain shows great
potential, especially in the IoT and healthcare area.
This combination can enhance data security and
analytics while addressing some of the limitations
present in traditional systems. As the analysis above,
blockchain offers a decentralized, safe method of data
storage, while AI can process and analyze data
gathered from multiple devices in real time. IoT
devices can share and validate data more effectively,
which improves decision-making, by fusing
blockchain technology with AI algorithms. For
instance, blockchain technology enables smart home
devices to protect user privacy and data security
against unauthorized access by leveraging AI to
analyze user behavior. This combination also leads to
improved patient health data management in the
healthcare industry. Blockchain protects the
confidentiality and transparency of this sensitive data,
while AI analyses a patient's medical history to give
personalized treatment options. Smart contracts can
automate patient-provider interactions, eliminating
the need for middlemen and boosting productivity.
However, this combination also faces many
challenges. First, data privacy and security remain a
major concern. Although blockchain provides
security, how to achieve effective data sharing while
ensuring data privacy still needs to be explored.
Second, the complexity of the technology may lead to
high implementation costs, limiting its popularity.
Overall, The outlook for the future is still optimistic.
As technology advances, BlockIoTintelligence is
expected to play an increasingly important role in
improving efficiency, reducing expense and
enhancing user experience. Solutions to these
challenges include developing smarter algorithms,
optimising blockchain technology to increase its
processing speed, and establishing industry standards
to facilitate interoperability between different
systems.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study explores the integration applications of
two hot technologies, blockchain and AI, focusing on
the achievability and great potential for improved
performance, particularly in the IoT and healthcare
sectors. The research introduces the
BlockIoTintelligence architecture, a combined
framework designed to capitalize on the strengths of
both technologies. This framework utilizes AI for
advanced data analysis and predictive insights, while
blockchain ensures secure, transparent, and
immutable data storage. The methodology involved
developing AI algorithms to process and analyze data
from IoT devices and healthcare systems, integrating
these algorithms with a blockchain ledger to uphold
data integrity and prevent unauthorized access. The
results showed substantial improvements in data
security, operational efficiency, and accuracy within
both domains. In conclusion, this emerging
integration of AI and blockchain opens new avenues
for advancements in IoT, healthcare, and beyond.
Despite the promising outcomes, challenges such as
technical implementation and data privacy remain.
Continuous innovation and refinement of this
integration are crucial for unlocking its full potential.
BlockIoTintelligence: Integrating Blockchain and AI for Enhanced Performance in IoT and Healthcare
377

Future research will focus on enhancing AI
algorithms, with the goal of improving the scalability
and adaptability of combined models. This effort
aims to optimize their effectiveness and broaden their
applicability across various IoT and healthcare
environments.
REFERENCES
Bekbolatova, M., Mayer, J., Ong, C.W., & Toma, M., 2024.
Transformative potential of AI in Healthcare:
definitions, applications, and navigating the ethical
Landscape and Public perspectives. In Healthcare,
12(2), 125.
Clauson, K.A., Breeden, E.A., Davidson, C., & Mackey,
T.K., 2018. Leveraging Blockchain Technology to
Enhance Supply Chain Management in Healthcare: An
exploration of challenges and opportunities in the
health supply chain. Blockchain in healthcare today.
Junior, P.C.T., & de Almeida, N.N., 2024. Industry 4.0:
blockchain and its Application Possibilities in Maritime
trade. International Journal of Scientific Management
and Tourism, 10(2), e849-e849.
Kumar, G., Saha, R., Rai, M.K., Thomas, R., & Kim, T. H.,
2019. Proof-of-work consensus approach in blockchain
technology for cloud and fog computing using
maximization-factorization statistics. IEEE Internet of
Things Journal, 6(4), 6835-6842.
Marwala, T., & Xing, B. 2018. Blockchain and artificial
intelligence. arxiv preprint: 1802.04451.
Mattos, D.M.F., Krief, F., & Rueda, S.J., 2020. Blockchain
and artificial intelligence for network security. Annals
of Telecommunications, 75, 101-102.
Rana, S.K., Rana, S.K., Nisar, K., Ag Ibrahim, A.A., Rana,
A. K., Goyal, N., & Chawla, P., 2022. Blockchain
technology and artificial intelligence based
decentralized access control model to enable secure
interoperability for healthcare. Sustainability, 14(15),
9471.
Singh, S.K., Rathore, S., & Park, J.H., 2020.
Blockiotintelligence: A blockchain-enabled intelligent
IoT architecture with artificial intelligence. Future
Generation Computer Systems, 110, 721-743.
Sylim, P., Liu, F., Marcelo, A., & Fontelo, P. 2018.
Blockchain technology for detecting falsified and
substandard drugs in distribution: pharmaceutical
supply chain intervention. JMIR research protocols,
7(9), e10163.
Thomason, J., Ahmad, M., Bronder, P., Hoyt, E., Pocock,
S., Bouteloupe, J., & Shrier, D., 2018. Blockchain—
powering and empowering the poor in developing
countries. In Transforming climate finance and green
investment with blockchains, 137-152.
DAML 2024 - International Conference on Data Analysis and Machine Learning
378
