
Employment and Income in the Tourism Sector in Uzbekistan,
Factors that Develop the Flow of Tourists
Adilova Zulfiya, Mansurov Jakhongir and Iskandarova Dilafruz
Tashkent State University of Economics, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Tourism, Employment, Tourist Flow, Tourism Development, Economic Factors, Social Factors, Cultural
Factors.
Abstract: This article describes the relationship between the employment of personnel in the tourism sector, the income
from this sector and the flow of tourists in Uzbekistan, herewith, the factors of tourism development, the state
policy and measures for the development of tourism in the country, as well as the current state of the country
in the world ranking in the field of tourism. Based on the information of the Statistical Agency under the
President of the Republic of Uzbekistan and the official website of the UNWTO, the current state of
development of tourism in Uzbekistan is shown. In addition, with the help of econometric analysis, the factors
shaping the flow of tourists in Uzbekistan were studied, and it was determined which influencing factor is the
most important today. Key determinants affecting the influx of incoming tourists – including business
travelers, educational visitors, medical service users, the consumer price index, transport service volume,
hotel availability, and the number of sanatoriums and spas – were systematically selected.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tourism is a type of service industry that generates
income for a country by creating various jobs and
allowing foreigners to enter the country for various
reasons. As an intangible asset, human resources can
contribute to achieving competitive advantage for
organizations. Human resources skills and
competencies may be unique and difficult for
competitors to imitate. Organizations that want to win
in the face of fierce competition must focus on human
resource development. It is included in the human
resources of tourism. Improving the quality of
personnel is a strategic step in increasing the
efficiency of the tourism sector.
According to a report by the (WTTC) World
Travel and Tourism Council, tourism is a powerful
driver of the global economy, accounting for nearly
10 percent of the world's gross domestic product and
employing millions of people (Kitsios, Mitsopoulou,
Moustaka, & Kamariotou, 2022). Because, tourism is
the basis of the development of socio-economic life
and a catalyst for achieving the Sustainable
Development Goals (Boluk, Cavaliere, & Higgins-
Desbiolles, 2019; Sharpley, 2022). Various factors
can cause a large flow of tourists entering a country:
such as demographic and social changes, economic
development, political and legal regulation,
technological changes, educational opportunities,
trade development, transport infrastructure, and
travel safety (Anaba, Ching, & Masud, 2023). Many
developing economies, including Uzbekistan, are
now heavily dependent on the tourism industry for
their income. According to the decree of the President
of the Republic of Uzbekistan dated 05.01.2019 No.
PF-5611 "On additional measures for the rapid
development of tourism in the Republic of
Uzbekistan", diversification of tourism in the national
economy, rapid development of regions, new
comprehensive measures to develop as one of the
strategic sectors that provide jobs, increase the
income and living standards of the population, and
increase the investment attractiveness of the country
are being implemented step by step.
The liberalization of the visa regime, the
simplification of the procedure for registration of
foreign citizens, the granting of privileges and
preferences for the development of the tourism
network made it possible to effectively promote the
potential of national tourism in domestic and foreign
markets.
Currently, visa-free entry for citizens of 93 foreign
countries, electronic entry visa for 56 countries, five-
122
Zulfiya, A., Jakhongir, M. and Dilafruz, I.
Employment and Income in the Tourism Sector in Uzbekistan, Factors that Develop the Flow of Tourists.
DOI: 10.5220/0013491400004654
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science (ICHELS 2024), pages 122-128
ISBN: 978-989-758-752-8
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

day transit visa-free entry for 47 countries, as well as
a simplified procedure for issuing tourist visas for 76
countries have been established.
In 2023, 6.6 million foreign citizens came to
Uzbekistan for tourist purposes. This indicator has
increased by 1.4 million or 26.6% compared to 2022.
Their stay in the country has increased to four days
on average, which is 1.3 times more than in 2022.
According to the analysis, in 2023, 810 new
tour operators and travel agencies will be launched in
Uzbekistan. 70,000 new jobs were created in tourism
and related industries. 183 hotels, 215 hostels, 356
family guesthouses have been opened. Placement
tools reached 5,477, and the number of places reached
142,720 (Statistics agency under the President of the
Republic of Uzbekistan, n.d.).
During 2023, the most visits were from Tajikistan (2
million 155.2 thousand), Kyrgyzstan (1 million 757.1
thousand) and Kazakhstan (1 million 333.3 thousand
people). 714,300 people came from Russia as tourists,
while Turkey's figure was 106,500.
Despite the fact that Uzbekistan has a place in
the world tourism market, the level of creating
comfortable conditions for tourists, improving
service, increasing the attractiveness of tourist
attractions and strengthening advertising is very low.
Therefore, thinking about a significant increase in this
regard depends on these factors.
However, understandings of changes in social
structures resulting from tourism and related
economic development in Uzbekistan often remain
unclear, and this often requires attention to
understanding local impacts of tourism development.
In particular, the relationship between tourism and
infrastructure, the country's economic, social and
cultural situation.
Be advised that papers in a technically unsuitable
form will be returned for retyping. After returned the
manuscript must be appropriately modified.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Tourism is the world's largest and most diverse
service sector, and many countries rely on it as a
source of income, employment, private sector growth
and investment. The ranking of competitive countries
in tourism includes the 140 most attractive tourist
destinations in the world (in terms of cultural
resources, cheap infrastructure, price of tourist
products, level of security, international
transparency), and Uzbekistan is not included in this
ranking.
Governments play an important role in promoting
tourism by offering stable policies and a strong
framework (Anaba, Masud, & Ching, 2020). Any
government cannot ignore the importance of tourism,
as tourism not only benefits the industry but also
generates positive economic results at the national
and local levels. Government involvement in tourism
development is vital and has produced remarkable
results, such as in Malaysia, Indonesia, Bahamas,
Jamaica, Kenya, South Africa, Morocco, Dubai,
Tunisia and other countries (Akama, 2002). They
stimulate tourism, which increases the country's gross
domestic product (GDP) and the standard of living of
its citizens. The growth of the tourism sector is
closely related to the availability of necessary
infrastructure, such as transport and tourist
attractions, in addition to investment (Anaba, Masud,
& Ching, 2020).
Therefore, today, both the state and the private
sector are directing large resources to the tourism
industry. According to Keum, due to globalization
and market liberalization worldwide, the trend of
tourist flow in tourist destinations is constantly
increasing (Keum, 2010).
Also, a number of researchers have stated that the
theories of international tourist flow are mainly
related to globalization, international trade, bilateral
agreements, tourism demand and tourism supply
(Keum, 2010; Mansfeld, 1990; Var, Mohammad, &
Icoz, 1990; Morley, 1992; Witt & Witt, 1995; Zhang
& Jensen, 2005; Song & Li, 2008; Claveria & Torra,
2014; Adeola, Boso, & Evans, 2018).
According to Boniface (Boniface, Cooper, &
Cooper, 2016), the flow of tourists is not just a
movement of people, but an important economic
value for the tourism system, that is, international
tourism represents a flow of money that earns money
in one place and spends it in another.
Also, various factors affecting the development of
tourism have been studied by many scientists in their
research and they have listed many factors that are
similar and close to each other. They include: income,
transportation costs, relative tourism prices,
promotion expenditure of tourism destination, and
availability of special events, availability of money
and leisure time, GDP per capita and bi-lateral trade
volume between countries, price, personal financial
capacity to travel and budget, destination image and
destination competitiveness and etc (Lim, 1999; Song
& Witt, 2000; Seyidov & Adomaitienė, 2016;
Narayan, 2004; Eryiǧit, Kotil, & Eryiǧit, 2010;
Prideaux, 2005).
According to X. Luo (Luo, 2019), the willingness
to serve other people creates the added value
Employment and Income in the Tourism Sector in Uzbekistan, Factors that Develop the Flow of Tourists
123
necessary for HR in the tourism industry. Hence, HR
has a potential mediating function in enterprises in the
tourism sector (Fig 1).
A.A. Eshtaev (Eshtayev, 2023), M.T. Alieva,
A.N. Norchaev and Z.D. Adilova (Alieva, Norchaev,
& Adilova, 2010; Adilova, 2024) and others from
local scientists have covered tourism, personnel
management in tourism and its development factors
in Uzbekistan in their research works.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In the research work, econometric-statistical analysis,
correlation-regression methods were used in order to
study the current state of the tourism industry in
Uzbekistan, development factors, the main goals of
tourists entering the country, and which sector can be
developed to increase the number of incoming
tourists. Also, in order to carry out this analysis, the
data of the official website of the Statistical Agency
under the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan and
the data of the official website of UNWTO were used
(UNWTO, 2024).
4 ANALYSIS AND RESULTS
In this research, we have analyzed the main factors of
tourism development in Uzbekistan, and we have
determined the purpose of tourists visiting
Uzbekistan. The number of tourists entering the
country is increasing, and we need to analyze the
reasons for the arrival of these tourists and study
which sectors attract more foreigners to the country
and in which sectors we need to improve the
infrastructure.
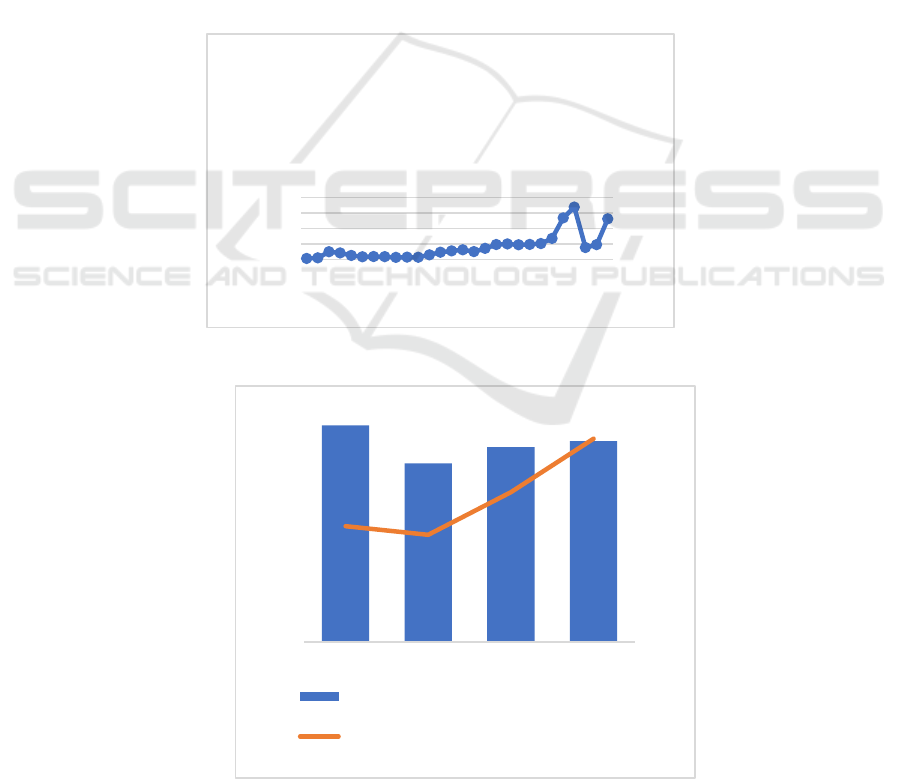
Figure 1: Employment and created gross added value in tourism sectors of Uzbekistan (Irmatova, Iskandarova, Pirnazarova,
Mansurov, & Xakimova, 2024)
Figure 2: Total arrivals to Uzbekistan (Statistics Agency, n.d.)
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
1995
1997
1999
2001
2003
2005
2007
2009
2011
2013
2015
2017
2019
2021
Total arrivals
231.4
190.8
208.1
214.6
24742.7
22903.6
31988.2
43426.6
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
30000
35000
40000
45000
50000
0.0
50.0
100.0
150.0
200.0
250.0
2019 2020 2021 2022
Employment in tourism, thousand people
Gross added value created in tourism
industries, billion soums
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
124
In the tourism sector, employment and gross value
added are interrelated (GVA), and a higher level of
employment leads to an increase in GVA. At the same
time, the development of tourism creates new jobs
and contributes to the growth of the country's GDP.
Employment in tourism is formed depending
on the flow of tourists. Many jobs are created in
places that attract a lot of tourists (Fig 2).
Since the measurement units of the variables are
different and to better explain the interpretation of the
multifactor econometric model, we can conduct
descriptive statistics on the factors before creating a
multifactor econometric model. The obtained results
are reflected in Table 1. The average value, median,
mode, maximum and minimum values for the
dynamics of each factor can be seen from the table
data. It is also possible to see the standard deviation,
variance, excess and asymmetry of each factor. A
correlational analysis is necessary to select factors for
a multifactor econometric model. First, starting with
the correlation analysis, we will determine the
correlation density of each factor. For this, we use the
pair correlation coefficient.
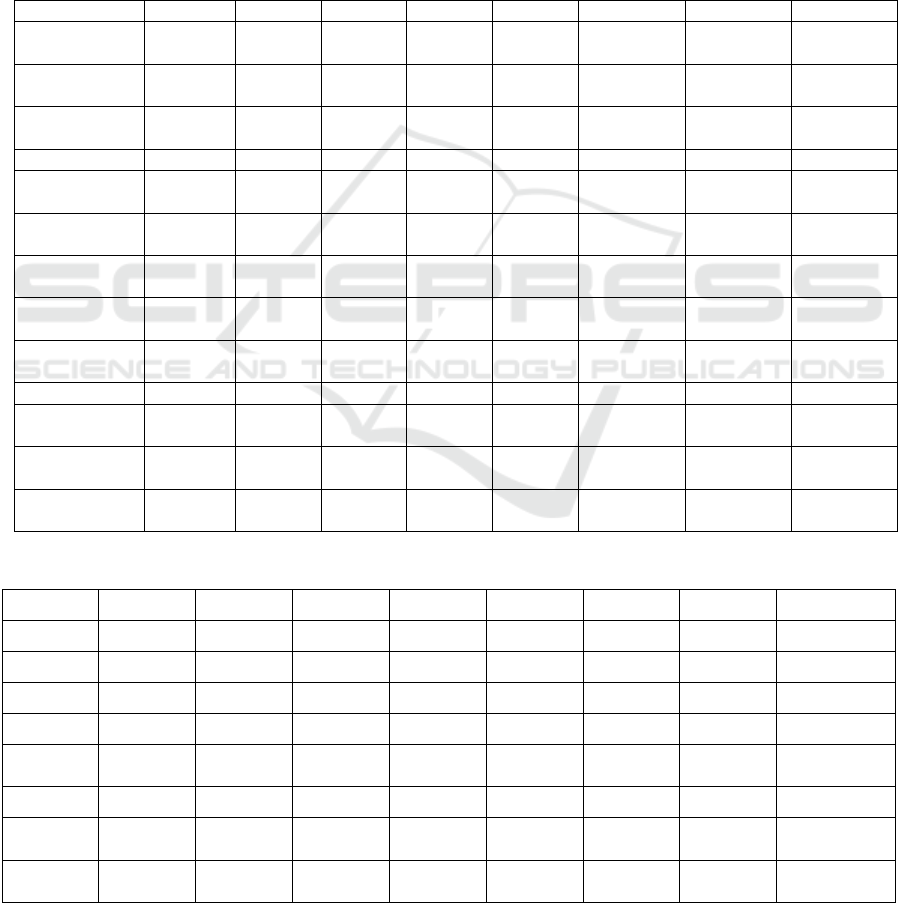
Table 1: Descriptive statistics on selected factors
Variables Y X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7
Mean 3774,889
30,7444
4
10,6777
8
44,2444
4
110,822
2
56136,
31
998,77
78
455,22
22
Standard
Erro
r
726,3986
7,16021
2
1,89683
8 6,24878
1,20528
7 8864,064 77,29269 25,50533
Median 2690 18,5 8,8 52,5
111,
1
53662,
9 1051 460
Mode - - ---- - -
Standard
Deviation 2179,196
21,4806
4
5,69051
4
18,7463
4 3,61586 26592,19 231,8781 76,51598
Sample
Variance 4748895
461,417
8
32,3819
4
351,425
3
13,0744
4 7,07E+08 53767,44 5854,694
Excess
-
1,9944
-
0,5732
-
0,21508
-
1,40819
-
1,23143 0,37979
-
0,66135 0,396131
Asymmetr
y
0,387231
1,06860
7
0,94723
2
-
0,24224
-
0,37608 0,954889 0,094528 0,105057
Interval
5244
,4 56,8 16,7 55 9,6 81272,9 726 263
Minimu
m
1504,1 13,6 4,7 15 105,6 26817,3 661 328
Maximu
m
6748
,5 70,4 21,4 70
115,
2
108090
,2 1387 591
Sum
3397
4
276,
7 96,1
398,
2
997,
4
505226
,8 8989 4097
Observati
ons 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
Table 2: Correlation matrix
ln Y ln X1 ln X2 ln X3 ln X4 ln X5 ln X6 ln X7
ln Y 1,000
ln X1 0,828 1,000
ln X2 0,823 0,880 1,000
ln X3 0,527 0,510 0,715 1,000
ln X4 0,561 0,339 0,268
-
0,108 1,000
ln X5 0,590 0,365 0,228 0,022 0,414 1,000
ln X6 0,526 0,350 0,159
-
0,166 0,488 0,970 1,000
ln X7 0,585 0,731 0,476
-
0,059 0,352 0,357 0,455 1,000
Employment and Income in the Tourism Sector in Uzbekistan, Factors that Develop the Flow of Tourists
125
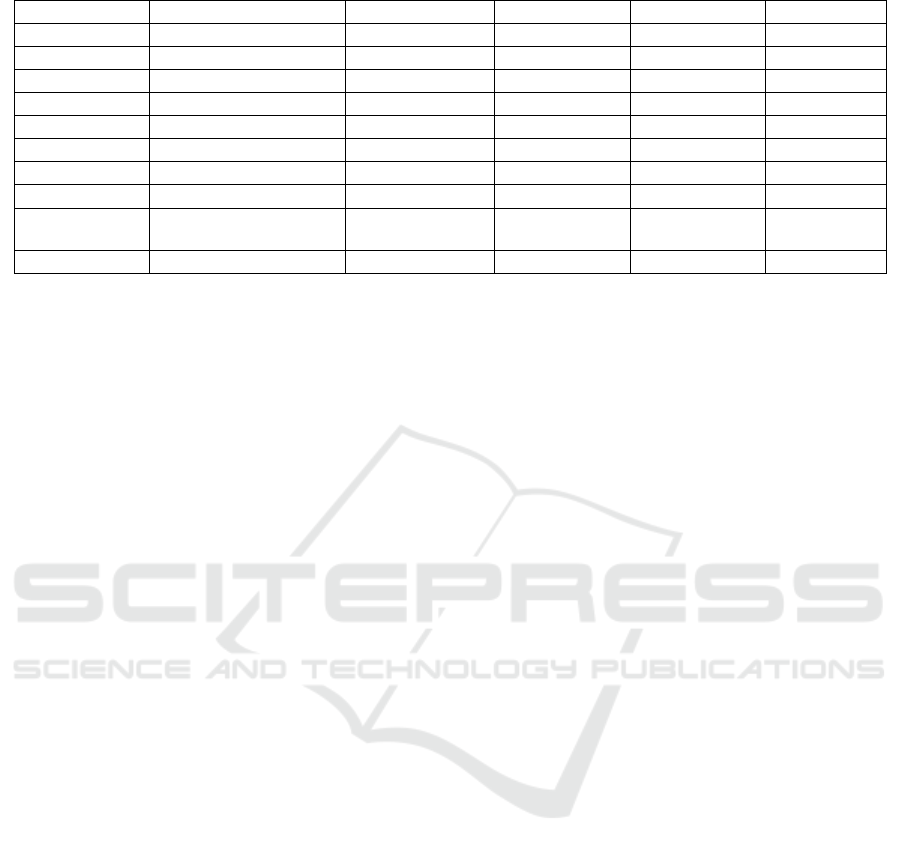
Table 3: Estimated parameters of the multifactor econometric model
Variables Coefficients Standard erro
r
t-statistic
p
-value
С
-30,3169 18,46392
-1,64196 0,242301
lnх1
-0,03374 0,553308
-0,06098 0,95692
lnх2
0,527567 0,577619
0,913347 0,457474
lnх3
0,036277 0,58211
0,062319 0,955976
lnх4
6,445349 3,674672
1,753993 0,221523
lnх5
1,902719 1,7946
1,060247 0,40015
lnх6
-3,10896 3,60776
-0,86174 0,479649
lnх7
1,244211 1,254464
0,991827 0,425808
Observations Normalized, R
2
R-squared F-statistics Probability
(
F-statistic
)
10 0.77 0.95
5,3 0.17
Since the measurement units of the variables are
different and to better explain the interpretation of the
multifactor econometric model, we create a
correlation matrix by logarithmizing the values of all
factors in natural form (Table 2).
It can be seen from Table 2 that private correlation
coefficients indicate the density of connections
between the resulting factor (ln y) and the factors
affecting it. That is, the values of private correlation
coefficients are greater than 0.5 and they can be
included in the multifactor model. However,
according to the results of the calculation - the book,
some of the values of the mutual pair correlation
coefficients (rx,y) of the influencing factors described
above are higher than 0.5. It appears that there is a
problem of multicollinearity among the selected
factors.
To perform the analysis, we construct a
multivariate regression equation, in which we assume
that the relationship between y and x is linear
(lny=a0+a1lnx1+a2lnx2+a3lnx3+a4lnx4+a5lnx5+a6
lnx6+a7lnx7+ɛi) and determine the parameters a0, a1,
a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7 (Table 3).
Thus, the linear regression equation of the
correlational link takes the following form:
Y=-30.3-0.03x1+0.53x2+0.04x3+6.45x4+1.9x5-
3.11x6+1.24x7
Here, the regression coefficients α1, α2, α3, α4, α5,
α6, α7 determine the relationship between the
outcome variable (Y) and the influencing factor
variable (x). This answers the question of how many
units the resultant sign increases when the factor sign
increases by one unit.
5 DISCUSSION
According to the results of the above econometric
model, the number of foreign tourists entering
Uzbekistan is equal to the number of tourists entering
for study and treatment, the number of sanatoriums
and spas, the increase in the amount of transport
services, and the consumer price index. has a
connection. An increase in the number of people
entering the country for study and treatment by one
thousand people will increase the number of foreign
tourists entering the country by 530 and 40 people,
respectively. Also, an increase in the number of
sanatoriums and spas, transport services and the
consumer price index by one unit increases the
number of tourists by 1.24, respectively; 1.9 and 6.45
leads to an increase in units. Significantly, there is an
inverse relationship between the increase in the
number of commercial visitors and the number of
hotels and the number of inbound tourists, with a one-
unit increase in these two factors leading to a decrease
in tourist arrivals by 0.03 and 3.11 units, respectively.
It is surprising that the increase in the number of
hotels does not serve to increase the number of
incoming tourists. So, this shows that it is necessary
to pay serious attention not only to the increase in the
number of hotels, but also to the quality of their
service. The inverse relationship between business
visitors and general visitors emphasizes the need for
a more in-depth study of the facilities created for
foreigners to do business in the country.
a0≈ -30.3 represents the average effect of other
factors taken as constant values in our analysis on the
resulting sign, that is, in the conditions where the
factor signs are x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7→0, at the
expense of other factors taken as constant the
resulting sign represents Y=-30.3 equal to unity.
6 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, traveling outside one's own country or
region for various reasons, such as education,
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
126

medicine, leisure, or business, falls under the
category of social and economic activity known as
tourism. In general, foreign visitors for educational,
medical and commercial purposes have a positive
effect on the tourism sector. For example, through
medical tourism, patients and their attendants can use
local services and increase tourism income. Also,
these visitors tend to stay longer and use
accommodation, meals, transportation and other
services. This increases economic activity and brings
additional income to the local economy. In addition,
necessary infrastructure - hotels, clinics, educational
centers, restaurants and entertainment places - will be
developed in order to create comfort for visitors.
However, it should be noted that various factors
can affect the increase or decrease in the number of
visitors to each country, including geographic
location, attractiveness of historical and cultural
heritage, business opportunities (tax policy),
education and the level of development or
affordability of medicine, population welfare,
ecology and other such factors. Each of these factors
has developed differently across countries. In this
study, we analyzed the factors that shape the flow of
tourists to the country on the example of Uzbekistan.
It should be noted that regression and correlation
indicators (parameters of the regression equation,
determination and correlation coefficients) may be
distorted by random errors due to the fact that they are
based on quantitatively limited set of data. The effect
of random errors on regression and correlation
indicators should not be too large, otherwise such
indicators will become meaningless.
REFERENCES
A.A. Eshtayev. O’zbekistonning turizm salohiyati va uni
rivojlantirish istiqbollari. (Monografiya) – Samarqand:
“Ipak yo’li” turizm xalqaro universiteti nashriyoti,
2023, 288 bet.
A.Irmatova, D.Iskandarova, G.Pirnazarova, J.Mansurov,
M.Xakimova. “Green jobs in a sustainable labor
market: remote work, skills and training”, E3S Web
Conf., Volume 574, 2024, 1st International Scientific
Conference “Green Taxonomy for Sustainable
Development: From Green Technologies to Green
Economy” (CONGREENTAX-2024),
https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202457407002
Adeola O, Boso N, Evans O (2018). Drivers of international
tourism demand in Africa. Business Economics
53(1):25-36.
Akama, J. S. (2002). The role of government in the
development of tourism in Kenya. International Journal
of Tourism Research, 4(1), 1-14.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.318
Alieva, M.T., Norchaev, A.N., & Adilova, Z.D. (2010).
Turizm menejmenti: O’quv qo’llanma. T.: TDIU, 116
b.
Anaba, M. I., Masud, M. M., & Ching, G. H. (2020).
Predominant factors affecting community’s willingness
to invest in tourism industry. Sarjana, 35(2), 52-67.
Anaba, M. I., Ching, G. H., & Masud, M. M. (2023).
Factors influence residents’ investment decision for
tourism industry development, International Journal of
Applied Economics, Finance and Accounting. ISSN
2577-767X, Vol. 16, No. 1, pp. 66-76. DOI:
10.33094/ijaefa.v16i1.890
Adilova, Z.D. (2024). Development and assessment factors
of HR branding: foreign practice. Monography.
Tashkent, 164 p.
Boluk, K., Cavaliere, Ch.T., & Higgins-Desbiolles, F.
(2019). A critical framework for interrogating the
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals 2030
Agenda in tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism,
27(3):1-18, May 2019. DOI:
10.1080/09669582.2019.1619748
Boniface, B., Cooper, R., & Cooper, C. (2016). Worldwide
Destinations: The Geography of Travel and Tourism
(7th ed.). London: Routledge.
Claveria, O., & Torra, S. (2014). Forecasting tourism
demand to Catalonia: Neural networks vs. time series
models. Economic Modelling, 36, 220-228.
Eryiǧit, M., Kotil, E., & Eryiǧit, R. (2010). Factors
affecting international tourism flows to Turkey: A
gravity model approach. Tourism Economics, 16(3),
585-595.
Eshtayev, A.A. (2023). O’zbekistonning turizm salohiyati
va uni rivojlantirish istiqbollari. Samarqand: “Ipak
yo’li” turizm xalqaro universiteti nashriyoti, 288 bet.
Keum, K. (2010). Tourism flows and trade theory: A panel
data analysis with the gravity model. Annals of
Regional Science, 44(3), 541-557.
Kitsios, F., Mitsopoulou, E., Moustaka, E., & Kamariotou,
M. (2022). User-generated content behavior and digital
tourism services: a SEM-neural network model for
information trust in social networking sites. Int. J. Inf.
Manag. Data Insights, 2(1), 100056-100056. DOI:
10.1016/j.jjimei.2021.100056
Lim, C. (1999). A meta-analytical of international tourism
demand. Journal of Travel Research, 37(3), 273-284.
Luo, X. (2019). Self-Empowerment and Its Discontents-
Shanghai Private Art Museums in Contemporary
China.
Mansfeld, Y. (1990). Spatial patterns of international tourist
flows: towards a theoretical framework. Progress in
Human Geography, 14(3), 372-390.
Morley, C.L. (1992). A microeconomic theory of
international tourism demand. Annals of Tourism
Research, 19(2), 250-267.
Narayan, P.K. (2004). Fiji’s tourism demand: The ARDL
approach to cointegration. Tourism Economics, 10(2),
193-206.
Prideaux, B. (2005). Factors affecting bilateral tourism
flows. Annals of Tourism Research, 32(3), 780-801.
Employment and Income in the Tourism Sector in Uzbekistan, Factors that Develop the Flow of Tourists
127

Sharpley, D. (2022). Criminal Litigation: 2022/2023: Legal
Practice Course Guides (LPC). Paperback.
Seyidov, J., & Adomaitienė, R. (2016). Factors influencing
local tourists’ decision-making on choosing a
destination: A case of Azerbaijan. Ekonomika, 95(3),
112-127.
Song, H., & Li, G. (2008). Tourism demand modelling and
forecasting: A review of recent research. Tourism
Management, 29(2), 203-220.
Song, H., & Witt, S.F. (2000). Tourism Demand Modelling
and Forecasting: Modern Econometric Approaches.
Pergamon, Oxford.
Statistics agency under the President of the Republic of
Uzbekistan. www.stat.uz
UNWTO. (2024). Tourism Statistics Database. The latest
update took place in 31 January 2024.
Var, T., Mohammad, G., & Icoz, O. (1990). Research notes
and reports. Annals of Tourism Research, 17, 606-638.
Witt, S.F., & Witt, C.A. (1995). Forecasting tourism
demand: A review of empirical research. International
Journal of Forecasting, 11(3), 447-475.
Zhang, J., & Jensen, C. (2005). Comparative advantage in
tourism: A supply-side analysis of tourism flows, 5th
Congress of the European Regional Science
Association: Land Use and Water Management in a
Sustainable Network Society, pp. 23-27, Amsterdam,
The Netherlands.
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
128
