
Brine Shrimp Lethality Assay of Ethyl Cinnamate Derivatives
Synthesized by Microwave Irradiation of Cinnamic Acids with
Ethyl Acetate
Rose Malina Annuur
1a
, Nisa Urribah
2
, Lia Meilawati
1
, Faris Hermawan
1b
,
Salahuddin Salahuddin
1c
, Megawati Megawati
1d
and Zetryana Puteri Tachrim
1e*
1
Research Center for Pharmaceutical Ingredient and Traditional Medicine, National Research and Innovation Agency,
Kawasan Sains Teknologi (KST) BJ Habibie, South Tangerang, Banten, 15314, Indonesia
2
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Negeri Semarang,
Semarang, Central Java, 50229, Indonesia
Keywords: Microwave Irradiation, Ethyl Cinnamates, Brine Shrimp Lethality, Cinnamic Acids.
Abstract: The simple and low-cost bioassay of brine shrimp lethality assay can be used to examine the toxicity effect
of potential drugs. Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate is a major compound that can be isolated from the rhizome of
Kaempferia galanga which was suggested that its ethyl ester is the most important functional group
contributing to its bioactivity. In general, the synthesis of this typical ethyl ester of cinnamic acids is derived
from the reaction of ethanol and cinnamic acid under reflux with the contribution of acid as a catalyst. In this
study, cinnamic acid and selected para-substituted cinnamic acid derivatives are subjected to microwave
irradiation-guided ethyl esterification by using ethyl acetate and sulfuric acid. This alternative method for
ethyl esterification yielded 19–39% products of ethyl cinnamate derivatives and ethyl p-chloro cinnamate
showed the highest toxicity level among the tested ethyl cinnamate derivatives with LC
50
of 1.29 µg/mL.
1 INTRODUCTION
The simple and low-cost bioassay of brine shrimp
lethality assay can be used to examine the toxicity
effect of potential drugs (Michael, et al., 1956; Dash,
et al., 2014). Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate is a major
compound derived from Kaempferia galanga which
is a main constituent as an anti-inflammatory agent
(Elshamy, et al., 2019; Umar, et al. 2014). It is
suggested by the study on the structure-activity
relationship that the ethyl ester form of this cinnamic
acid derivative is the most important functional group
contributing to the anti-inflammatory activity
(Komala, et al., 2018). In general, the synthesis of this
typical ethyl ester of cinnamic acids is derived from
the reaction of ethanol and cinnamic acid under reflux
with the contribution of sulfuric acid (Anthony, et al.,
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-7107-507X
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-6923-4050
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0580-0579
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6698-0668
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6637-541X
2022). Ethyl acetate under sulfuric acid can be
hydrolyzed (Jaques, 1971; Vinnik and Librovich,
1975) for presenting ethanol and can be donated as an
ethyl ester group candidate for direct
transesterification with cinnamic acid. Microwave
irradiation is believed to increase the efficiency
during organic synthesis by offering rapid
temperature increments (Hoz, et al., 2005). To the
best knowledge, no reported study has synthesized
ethyl cinnamate by microwave irradiation of ethyl
acetate and sulfuric acid. Since several cinnamic acid
derivatives are relatively less soluble in the ethanol,
thus by taking advantage of ethyl acetate hydrolysis
under a high concentration of sulfuric acid this study
then directly conducts the ethyl esterification of
selected cinnamic acids with sulfuric acid as a
catalyst under microwave irradiation. The
representative ethyl ester of cinnamic acid derivatives
Annur, R. M., Urribah, N., Meilawati, L., Hermawan, F., Salahuddin, S., Megawati, M. and Tachrim, Z. P.
Brine Shrimp Lethality Assay of Ethyl Cinnamate Derivatives Synthesized by Microwave Irradiation of Cinnamic Acids with Ethyl Acetate.
DOI: 10.5220/0013471800004612
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of BRIN’s 2nd International Conference for Health Research (ICHR 2024), pages 5-8
ISBN: 978-989-758-755-9
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
5

then aims to understand its toxicity by utilizing a
brine shrimp lethality assay.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Generals
Hexane and ethyl acetate were distillate before use,
the distilled ethyl acetate was further dried with
MgSO
4
before reaction, conc. H
2
SO
4
(96%, Merck),
and reverse osmosis (RO) water were produced on-
site. Non-modified domestic microwave oven 900-
Watt (Moderna MG 2516) was utilized for the
synthesis and the reaction mixture was covered with
heat resistance glass before irradiation. Seawater was
taken from Anyer, Banten, Indonesia, stored at room
temperature, and filtered before use. NMR spectra
(
1
H and
13
C) were collected using AVANCE NEO
700MHz NMR (BRIN, Serpong, Indonesia). GC-MS
data were collected using GC-MS Agilent 7890B GC
and 5977A MSD (BRIN, Serpong, Indonesia).
2.2 Synthesis of Ethyl Cinnamate
Derivatives via Microwave
Irradiation of Cinnamic Acids with
Ethyl Acetate
Cinnamic acid derivatives (1–3, 100 mg, 0.51–0.69
mmol) are dissolved in 20 mL ethyl acetate. 1 mL
conc. H
2
SO
4
is added to the cinnamic acid derivatives
solution in the ice bath. This solution was then
microwaves irradiated for 60 seconds x 12 times and
intervals with cooling for 3 minutes. After the
reaction, the mixture was cooled to room temperature
and added 20 mL of ethyl acetate. Then, RO water
was added, and the pH was adjusted to 9–10 with 5%
NaOH
(aq)
. Separation of ethyl acetate fraction and
water fraction was conducted. The ethyl acetate
fraction was washed with brine, dried with MgSO
4
,
and evaporated to result in ethyl cinnamate
derivatives (5–7).
Ethyl cinnamate (5). Colourless liquid.
1
H NMR
(700 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.68 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H),
7.51 (dd, J = 6.7, 3.1 Hz, 2H), 7.39 – 7.35 (m, 3H),
6.43 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.26 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H),
1.33 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H) ppm.
13
C NMR (176 MHz,
CDCl
3
) δ 167.0, 144.6, 134.4, 130.2, 128.9, 128.0,
118.3, 60.5, 14.3 ppm. C
9
H
7
O
+
calculated m/z 131.05
and found m/z 131.10 (100%).
Ethyl 4-chlorocinnamate (6). Colourless liquid.
1
H NMR (700 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.62 (d, J =
16.0 Hz, 1H), 7.44 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (d, J =
8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.40 (d, J = 16.1 Hz, 1H), 4.26 (q, J =
7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.33 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H) ppm.
13
C NMR
(176 MHz, CDCl
3
) δ 166.8, 143.2, 136.2, 133.1,
129.3, 129.3, 119.0, 60.7, 14.4 ppm. C
9
H
6
ClO
+
calculated m/z 165.10 and found m/z 165.00 (100%).
Ethyl 4-nitrocinnamate (7). Colourless crystal.
1
H
NMR (700 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.25 (d, J = 8.8 Hz,
1H), 7.71 (d, J = 16.2 Hz, 2H), 7.68 (d, J = 8.7 Hz,
2H), 6.56 (d, J = 16.1 Hz, 1H), 4.30 (q, J = 7.0 Hz,
2H), 1.36 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H) ppm.
13
C NMR (176
MHz, CDCl
3
) δ 166.2, 148.6, 141.7, 140.7, 128.7,
124.3, 122.7, 61.1, 14.4 ppm. C
9
H
6
NO
3
+
calculated
m/z 176.03 and found m/z 176.10 (100%).
2.3 Isolation of
Ethyl 4-Metoxycinnamate (9)
Isolation of ethyl 4-metoxycinnamate (9) was
conducted according to literature (Tachrim, et al.,
2022).
2.4 Brine Shrimp Lethality Assay
The procedure for BSLT followed the literature
(Primahana, et al, 2015). Brine shrimps were hatched
using brine shrimp eggs (Artemia salina) in a conical-
shaped vessel, filled with filtered seawater. The
number of dead and surviving nauplii in each tube
was counted and recorded. LD
50
values were
determined from the best-fit line plotted
concentration versus percentage lethality.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
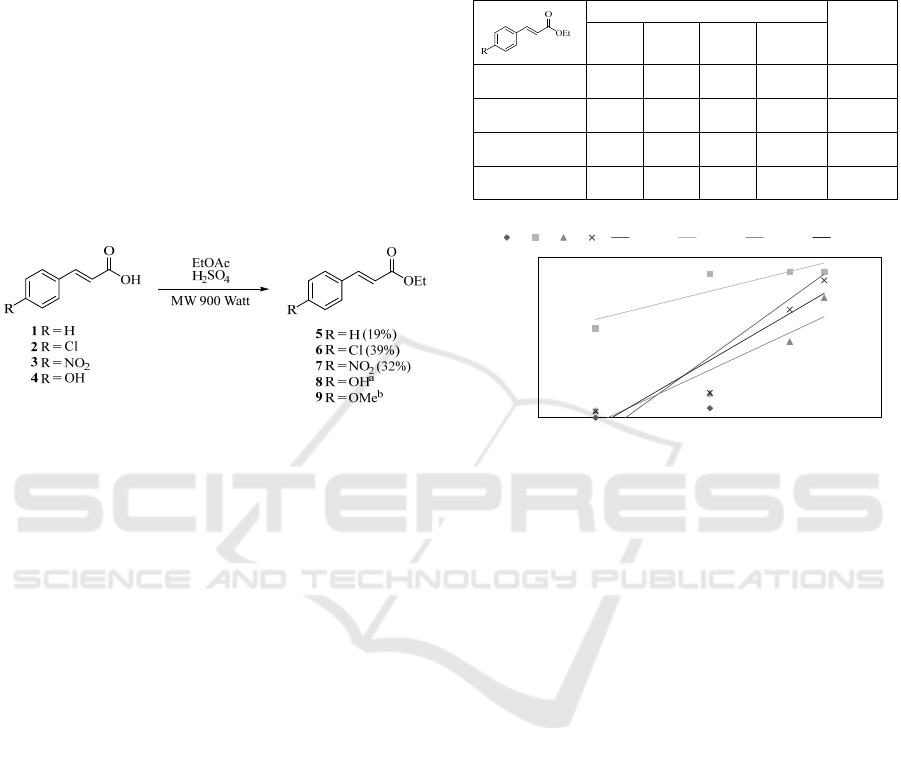
The reaction of cinnamic acid derivatives (1–4) with
ethyl acetate and H
2
SO
4
via microwave irradiation
can be conducted without a reflux system within 60
seconds of irradiation time with 3 minutes cooling
process. This interval is utilized for the prevention of
further ethyl acetate evaporation due to the rapid
high-temperature condition offered by microwave
irradiation. The resulted ethyl cinnamate derivatives
(5–7) resulted in moderate yield from the
correspondent cinnamic acid (1), p-chloro (2), and p-
nitro (3), respectively (Scheme 1). As for p-hydroxy
(4, Scheme 1), after quenching the reaction mixture,
no ethyl 4-hydroxycinnamate (8, Scheme 1) is
isolated. Compound 4 might need a longer reaction
time to conduct with the ethyl acetate system, since
this compound has low solubility towards ethyl
acetate and found up until 10 minutes of irradiation it
cannot be dissolved completely.
ICHR 2024 - BRIN’s International Conference for Health Research (ICHR)
6
The conventional method of refluxing cinnamic
acid derivatives with ethanol for the synthesis of ethyl
ester derivatives (5–7) was also tested and showed a
higher yield (60–80%) with 5 hour reaction time. In
comparing these results with the current method,
microwave irradiation is relatively more efficient due
to its faster reaction time. Herein, the ethyl acetate
utilization in sulfuric acid can offer esterification of
semi-polar compounds of cinnamic acid derivatives
(1–3) into its ethyl ester derivatives (5–7). This
method can be used as an alternative to direct ethanol
utilization (Fisher esterification) in which ethanol can
be formed from the hydrolysis of ethyl acetate
(Jaques, 1971; Vinnik and Librovich, 1975) under
high temperature by microwave irradiation.
Scheme 1: Synthesis of ethyl cinnamate derivatives via
microwave irradiation of cinnamic acids with ethyl acetate.
The bracket showed an isolated yield.
a
No ethyl 4-
hydroxycinnamate is isolated.
b
Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate
is isolated from rhizomes of K. galanga according to
literature (Tachrim, et al., 2022).
The result of brine shrimp assay lethality assay of
synthesized ethyl cinnamate derivatives 5–7 and ethyl
4-methoxycinnamate 9 isolated from the rhizome of
K. galanga are shown in Table 1 and Fig. 1. Based on
these results, the toxicity level of all tested compound
is 6 > 9 > 5 > 7. The synthesized ethyl cinnamate 5
and p-nitro 7 showed moderate toxicity compared
with the ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate 9 isolated from
the rhizome of K. galanga. p-Chloro 6 showed high
toxicity among all tested compounds with LC
50
of
1.29 µg/mL and has highest % mortality on 10 ppm.
For comparison, the reported brine shrimp lethality
assay on crude CH
2
Cl
2
extract of K. galanga with the
major compound of ethyl cinnamate and ethyl 4-
methoxycinnamate showed almost 100% mortality
can be achieved at a concentration of 10 ppm
(Othman, et al., 2006). The previous brine shrimp
lethality assay of methyl cinnamate also showed a
moderate LC
50
of ~120 µg/mL (Primahana, et al.,
2015). Despite further study is needed to understand
the structure correlation with the toxicity, the high
toxicity of p-chloro 6 is due to the introduction of
chloro as a substituent on the aromatic moiety.
Moreover, this compound has the potential to be used
for the study of its bioactivity in the future.
Table 1: Brine shrimp lethality assay of synthesized ethyl
cinnamate derivatives.
Mortalit
y
(%)
LC
50
(ppm)
10
ppm
100
ppm
500
ppm
1000
ppm
5 (R = H) 0 6 100 100 234.42
6 (R = Cl) 61 98 100 100 1.29
7 (R = NO
2
) 4 17 74 93 301.99
9 (R = OMe) 5 17 52 82 173.78
Figure 1: Effect of synthesized ethyl cinnamate derivatives
5–7 and 9 on brine shrimp nauplii.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The reaction of cinnamic acid derivatives (1–3) with
ethyl acetate and H
2
SO
4
via microwave irradiation
can be used as an alternate method for the synthesis
of their representative ethyl esters (5–7). Among the
synthesized ethyl cinnamate derivatives 5–7 and ethyl
4-methoxycinnamate 9 isolated from the rhizome of
K. galanga, ethyl p-chloro cinnamate 6 showed the
highest toxicity level with LC
50
of 1.29 µg/mL. The
brine shrimp lethality assay tested in this study can
provide the toxicity data comparison of several ethyl
esters of cinnamic acid derivatives before in vivo
study and contribute to the preliminary study of drug
development.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
RMA was supported by the Postdoctoral Fellowship
National Research and Innovation Agency,
Indonesia. NU thanks to Research Assistant
Fellowship National Research and Innovation
Agency, Indonesia.
0
20
40
60
80
100
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5
Percent of
mortality (%)
Log conc.
5 6 7 9 Linear (5) Linear (6) Linear (7) Linear (9)
Brine Shrimp Lethality Assay of Ethyl Cinnamate Derivatives Synthesized by Microwave Irradiation of Cinnamic Acids with Ethyl Acetate
7

REFERENCES
Anthony, P. C., Eseyin, O. A., Attih, E., Johnson, E.,
Ebong, A., Effiong, A. E., 2022. Synthesis of Some
Esters of Cinnamic Acid and Evaluation of Their in
Vitro Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Properties. 2022.
Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 21 (1), 131–136.
Dash, P. R., Nasrin, M., Ali, M. S., 2014. In Vivo Cytotoxic
and In Vitro Antibacterial Activities of Kaempferia
galanga. J. Pharmacogn and Phytochem. 3 (1), 172–
177.
Elshamy, A. I., Mohamed, T. A., Essa, A. F., Abd-
ElGawad, A. M., Alqahtani, A. S., Shahat, A. A.,
Yoneyama, T., Farrag, A. R. H., Noji, M., El-Seedi, H.
R., Umeyama, A., Paré, P. W., Hegazy, M. F., 2019.
Recent Advances in Kaempferia Phytochemistry and
Biological Activity: A Comprehensive Review.
Nutrients 11 (10), 2396.
Hoz, A. D., Diaz-Ortiz, A., Moreno, A., 2005. Selectivity
in Organic Synthesis under Microwave Irradiation.
Curr. Org. Chem. 8 (10), 903–918.
Jaques, D., 1971. Hydrolysis of Ethyl Acetate in
Concentrated Sulfuric Acid. A Group Experiment for
Advanced Students. J. Chem. Educ. 48 (9), 623.
Komala, I., Supandi, Nurhasni, Betha, O. S., Putri, E.,
Mufidah, S., Awaludin, M. F., Fahmi, M., Reza, M.,
Indriyani, N. P., 2018. Structure-Activity Relationship
Study on the Ethyl p-Methoxycinnamate as an Anti-
Inflammatory Agent. Indones. J. Chem. 18 (1), 60–65.
Michael, A. S., Thompson, C. G., Abramovitz, M., 1956.
Artemia Salina as a Test Organism for Bioassay.
Science 123 (3194), 464–464.
Primahana, G., Ernawati, T., Dewi, N. L. P., Dwiyatmi, I.
D., Darmawan, A., Hanafi, M., 2015. Synthesis of 2-
Allylphenyl Cinnamate and Brine Shrimp Lethality
Test Activity Evaluation. Procedia Chem. 16, 694–699.
Othman, R., Ibrahim, H., Mohd, M. A., Mustafa, M. R.,
Awang, K., 2006. Bioassay-Guided Isolation of a
Vasorelaxant Active Compound from Kaempferia
galanga L. Phytomedicine 13 (1–2), 61–66.
Tachrim, Z. P., Kurniawan, K., Andreani, A. S., Sundowo,
A., Ernawati, T., Darmawan, A., Dewi, R. T., 2022.
Insight Study of Trans-Ethyl 4-Methoxycinnamate
Isolation and Hydrolysis. AIP Conf. Proc. 2493,
070014–15.
Umar, M. I., Asmawi, M. Z., Sadikun, A., Majid, A. M. S.
A., Al-Suede, F. S. R., Hassan, L. E. A., Altaf, R.,
Ahamed, M. B. K., 2014. Ethyl-p-Methoxycinnamate
Isolated from Kaempferia galanga Inhibits
Inflammation by Suppressing Interleukin- 1, Tumor
Necrosis Factor-α, and Angiogenesis by Blocking
Endothelial Functions. Clinics 69 (2), 134–144.
Vinnik, M. I., Librovich, N. B., 1975. Mechanism of the
Hydrolysis of Ethyl Acetate in Aqueous Solutions of
Strong Acids. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR Div. Chem. Sci. 24
(10), 2097–2102.
ICHR 2024 - BRIN’s International Conference for Health Research (ICHR)
8
