
The Methodology for Determining and Evaluating the Effectiveness
of Innovations in Human Resource Management
G. K. Abdurakhmonova
1
, M. Sh. Khaydarova
1
, T. Rakhmonova
2
and Sh. J. Kabilova
2
1
Tashkent State University of Economics, Uzbekistan
2
Karshi State University, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Environment, Economic, Renewal, Innovation.
Abstract: The In today's economic environment, renewal, continuous improvement, and innovation are essential not
only for development but also for the survival of economic systems. Despite this, the primary focus tends to
be on product and technological innovations, while the implementation of management innovations, such as
those in HR management (HRMI), significantly lags behind. This disparity in the adoption rates of production
and management innovations is known as organizational lag in innovation management. Nonetheless, the
importance of HRMI for the successful implementation of product and technological innovations is equally
critical, even though predicting their impact and efficiencies is more complex. This article aims to describe
and categorize contemporary approaches to implementing innovations in HR Management (HRMI) and
evaluate their efficiencies. The practical value of the article lies in its detailed examination of HRMI, which
can be utilized to enhance and develop economic systems and create algorithms for assessing process
efficiency. The findings of this article are beneficial for managers and organizational leaders in making
decisions about adopting HRMI, selecting alternative organizational development strategies, developing
performance measurement systems for HR management, and modifying HR management systems.
Additionally, the article advances the scientific field by systematizing and evaluating organizational
innovations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Any innovation implemented within an organization
represents a complex process that affects many
internal subsystems and has an indeterminate
measure of implementation effectiveness. Currently,
neither economic literature nor the legislative and
regulatory framework provide universally accepted
terminology in the field of innovation activities.
Similarly, there are no universal indicators that allow
for the evaluation of the effectiveness of any
implemented or ongoing innovation. The definition of
innovation, as stipulated by the International
Standards in the Statistics of Science, Technology,
and Innovation, is as follows: "Innovation is the
outcome of innovative activity, embodied in the form
of a new or improved product/technological process,
introduced to the market, applied in production, or in
a new approach to the provision of social services."
The concept of intra-organizational innovation,
therefore, essentially encompasses all products,
processes, or approaches to social services that are
new to a particular organization, regardless of
whether they have been applied in other
organizations. The goal of implementing any
innovation is to improve the overall performance of
the organization. As a result, the functioning of
individual subsystems within the organization
undergoes significant changes, while the activities of
other subsystems are either partially affected or
remain unchanged. HRMI are classified as
managerial innovations with specific properties that
influence the methods and possibilities for calculating
their effectiveness. A managerial innovation is
defined as any organized solution, system, procedure,
or management method that significantly differs from
the established practices within the organization and
is being used by it for the first time.
The foundation for this article is contemporary
domestic and international scientific literature,
represented by the works of P. Drucker, N.P. Zavlin,
E.A. Utkina, M. Armstrong, R. Dornbusch, S.
Fischer, K.X. Abdurakhmanov,
100
Abdurakhmonova, G. K., Khaydarova, M. S., Rakhmonova, T. and Kabilova, S. J.
The Methodology for Determining and Evaluating the Effectiveness of Innovations In Human Resource Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0013424800004654
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science (ICHELS 2024), pages 100-106
ISBN: 978-989-758-752-8
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

specific
aspects of
application for
innovations
technical
and
economic
organizatio
nal and
economic
legal
socio -
psychologic
al
G.K.Abdurakhmanova, A.B. Khaitov, I.Bakirova,
A.B.Irmatova, S.B. Gaibnazarov and others.
The main reason for the need to distinguish
management innovations as a separate category of
innovations is the sociality of innovations of this type,
which determines the presence of a set of aspects
(Figure 1) specific to this type of innovation, which
must be taken into account simultaneously when
implementing and evaluating such an innovation.
Such aspects include:
- technical and economic;
- organizational and economic;
- legal;
- socio-psychological.
The technical and economic effect in the
sphere of management is achieved by reducing the
labor intensity of performing procedures related to the
direct implementation of management functions,
including possible benefits from choosing the most
cost-effective management methods. The economic
effect in production arises as a result of the
improvement in productivity and quality of labor
associated with the implementation of a management
innovation and being its indirect consequence.
The evaluation of the effectiveness of managerial
innovations, therefore, requires consideration of both
types of economic effects that arise. This poses
certain difficulties due to the large number of non-
production and production factors that these effects
can influence, as well as the complexity of converting
all components of economic effects into a unified
measurement system to calculate the overall effect.
When assessing any managerial innovation, it is
necessary to account for the synergistic effect.
Managerial innovation primarily impacts the
intangible aspects of a company's activities and is
weakly linked to the financial outcomes of the
organization's operations.
The analysis of scientific literature, including the
aforementioned sources, shows that the majority of
works primarily focus on narrowly specialized issues
directly related to personnel management processes
and lack results with practical value for evaluating
effectiveness. Studies addressing the evaluation of
personnel management effectiveness and the
effectiveness of innovations in personnel
management predominantly do not differentiate
between these categories. Moreover, it is important to
note the actual absence of works that primarily aim to
address the evaluation of the effectiveness of
innovations in personnel management.
Overall, theoretical approaches to defining
the effectiveness of innovations in human resource
management can be classified according to two
criteria.
Criterion 1: According to the Type of Calculated
Effectiveness
- Economic effectiveness
- Social effectiveness
Economic effectiveness of innovations in human
resource management is assessed as the resultant
change in the company's financial indicators (profit,
cost, etc.) expected or actualized after the
implementation of the innovation in human resource
management. This type of effectiveness is relatively
under-researched in the theoretical literature. The
primary obstacles to calculating this type of
effectiveness are considered to be:
- The impossibility of translating changes in
qualitative indicators into a monetary equivalent
- The difficulty of accounting for all
consequences of the innovation implementation when
determining the overall impact on financial results.
Analyzing scientific concepts, two approaches to
evaluating the economic effectiveness of human
resource management can be identified.
Figure 1
:
Specific aspects of application for innovations
The Methodology for Determining and Evaluating the Effectiveness of Innovations In Human Resource Management
101

The first approach suggests considering the entire
organization's workforce as a single "aggregate"
worker. The second approach involves differentiating
labor by products and types of work. Social
effectiveness of innovations in human resource
management is viewed from the perspective of
assessing the potential to achieve positive and
eliminate negative (socially) changes within the
organization, as well as attaining any goals not aimed
at changing financial indicators.
Thus, positive changes associated with the
implementation of innovations and measurable
through the calculation of social effectiveness may
include:
1. Providing personnel with a proper level and
quality of life (favorable working conditions, decent
wages, necessary social services, etc.);
2. Offering employees conditions that allow them
to realize and develop their individual abilities;
3. Granting a degree of autonomy (decision-
making opportunities, determining task
methodologies, establishing work schedules and
intensity, etc.);
4. Developing a positive socio-psychological
climate (communication opportunities, information
access, increasing the degree of conflict-free
relationships with management and colleagues, etc.).
Social effectiveness of innovations in human
resource management also considers the prevention
of negative changes, including:
1. Damage caused by unfavorable working
conditions (occupational diseases, workplace
accidents, etc.);
2. Harm to individuals (due to intellectual and
physical overloads and underloads, stressful
situations, etc.).
Several authors, including G.K.
Abdurakhmanova, note the positive social outcomes
formed outside the organization as a component of
the social effectiveness of implementing innovations
in human resource management.
Such social outcomes may include:
1. Improvement of the organization's image;
2. Creation of new jobs;
3. Establishment of stable regional employment
levels;
4. Enhancement of the safety of production results
for consumers and reduction of negative
environmental impacts.
Depending on the goals of the innovation
implementation, social outcomes of improving the
system and technology of human resource
management are considered separately for each
component of the human resource management
system:
i. Subsystem of Personnel Planning and Personnel
Marketing (improving the utilization of the
organization's employee potential, achieving
alignment between employees' individual
abilities and interests and their job content,
reducing negative consequences of employee
layoffs, ensuring personnel stability, and
enhancing the organization's favorable image);
ii. Subsystem of Recruitment and Personnel
Accounting (hiring personnel who quickly adapt
to the organization, justifying personnel
decisions regarding staff movements);
iii. Subsystem of Working Conditions (compliance
with psychophysiological, ergonomic, and
aesthetic requirements, implementation of
occupational safety and health standards, level
of work humanization, reduction of negative
environmental impact);
iv. Subsystem of Labor Relations (timely
identification of problems in team relationships,
raising ethical standards in relationships,
positive influence on organizational culture,
improvements in interaction mechanisms for
resolving issues in social and labor relations);
v. Subsystem of Personnel Development
(organizing employee adaptation, enhancing job
content, improving professionalism and
competitiveness of personnel, achieving
alignment between employees' and managers'
goals in career management);
vi. Subsystem of Motivation and Incentives
(creating a link between work efficiency and
remuneration, personal development of
employees, creating conditions for managing
business careers, professional advancement of
personnel, improvements in the personnel
motivation system);
vii.
Subsystem of Social Development (increasing
the level of satisfaction of personnel needs,
fostering a favorable socio-psychological
climate, positively impacting feedback with
employees, providing opportunities for
employees to socialize outside of work and
participate in public life, positive changes in
employees' living conditions);
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
102

viii. Subsystem of Organizational Structure
Development (improving the ability to
restructure organizational structures in response
to environmental changes, clear articulation of
goals and objectives to support decision-
making, ensuring clear definition of employees'
rights and responsibilities);
ix. Subsystem of Legal Support (personnel
decisions compliant with labor legislation,
justification of personnel decisions, legal
protection of employees);
x. Subsystem of Information Support (providing
management with information necessary for
managing the HR system, successful
management of information quality, timeliness,
and justification, equipping employees with
technical tools).
Criterion 2: By Approach to Evaluating the
Effectiveness of Innovations in Human Resource
Management
Based on the analysis of scientific literature, two
approaches to evaluating the effectiveness of
innovations in human resource management can be
identified:
Approach 1: The effectiveness of innovations in
human resource management can be measured as the
increase in the effectiveness of the entire HR
management system or its individual subsystems. In
this case, the effectiveness of an HR innovation is
calculated as the difference between specific
indicators used to evaluate the effectiveness of the
HR system at reporting dates before and after the
implementation of a particular innovation. The
number of methods for calculating the effectiveness
of HR innovations is quite large, as it is derived from
the numerous methods for assessing the HR
management system and its individual subsystems.
The effectiveness of HR innovations is determined
through the construction of econometric models that
relate the company's final financial result (profit) to
changes in specific HR management system
indicators.
The most relevant work on this topic is the
dissertation by M.A. Mitrofanova
1
, where the author
proposes the following methodology for evaluating
1
Alberg, V.F. (1993). *Formation of a Personnel
Management System at an Enterprise Using Functional
the effectiveness of innovations in human resource
management:
1. Conduct regular quantitative and qualitative
assessments of HR management subsystems. The
assessment method includes calculations (for
quantitative indicators) and surveys (for obtaining
qualitative indicators);
2. Convert the obtained qualitative results using a
developed expert scoring system;
3. Develop an econometric model, where the
endogenous variables represent changes in the
obtained indicators, and the exogenous variable
represents changes in the company's financial results;
4. Identify the quantitative relationship between
changes in profit and changes in indicators reflecting
the results of implementing innovations in human
resource management.
Approach 2: The effectiveness of an innovation
is determined by its impact on specific,
predetermined indicators of the organization's
success. In this case, the effectiveness of the
innovation refers to the organization's achievement of
its strategic and tactical goals—both at the
organizational level and at the departmental level.
This approach is developed in the scientific works
listed in Table 1.
The concept of evaluating the effectiveness of
human resource management, as found in the works
of both foreign and domestic authors, shares common
features: it is proposed to determine the effectiveness
of human resource management by comparing the
costs and benefits of applying specific working
methods in the HR management system.
The components of economic effectiveness in
human resource management, according to L.
Vodachek and O. Vodachkova, include:
1. Ratio (economic result/costs) as the central
component of HR management, viewed as the
determination of the degree of the organization's
strategic goals.
2. Degree of achievement of long-term
components of economic effectiveness in the HR
management system, reflecting the contribution of
employees to the company's activities and
development in the long term, including:
System Analysis: Organizational and Economic
Aspect* (Ph.D. dissertation, Moscow).
The Methodology for Determining and Evaluating the Effectiveness of Innovations In Human Resource Management
103
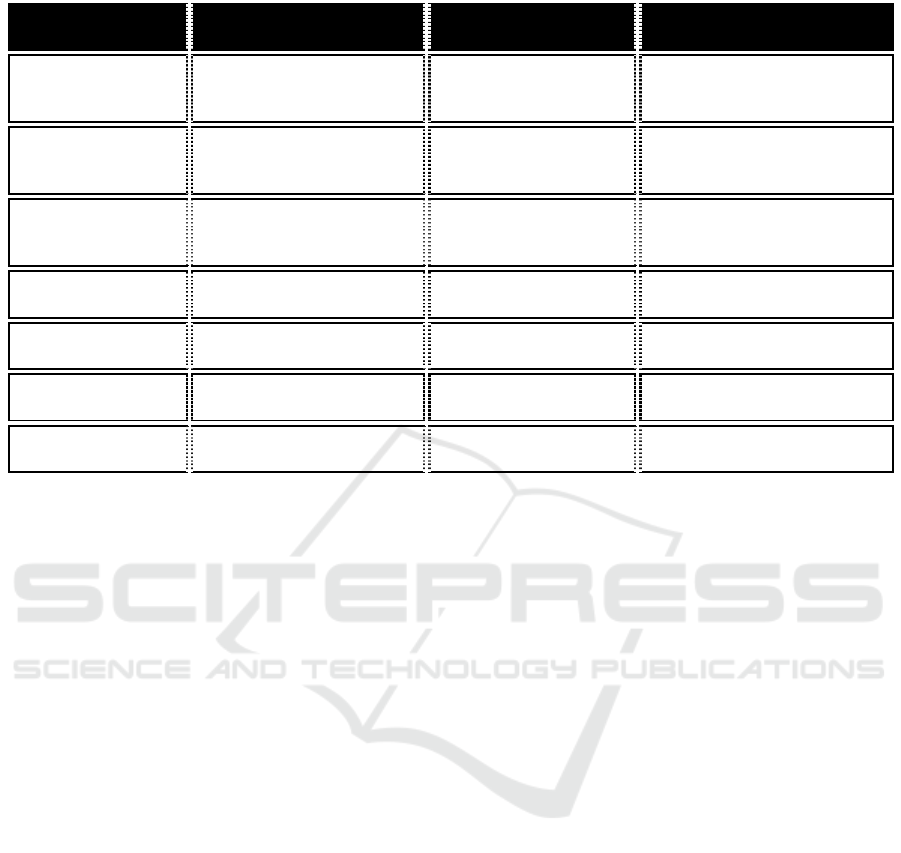
Table 1: The methods for assessing the effectiveness of innovations through organization performance indicators
Assessment
Method
Description Advantages Disadvantages
ROI (Return on
Investment)
Calculating the return on
funds invested in innovation
Clear financial metric,
easily understood
Only considers financial
aspects, doesn't show long-term
impact
KPI (Key
Performance
Indicators)
Measuring key
performance indicators
Flexible, applicable to
various fields
Can be difficult to select the
right indicators
Balanced
Scorecard
Balanced assessment o
f
financial and non-financial
indicators
Comprehensive, linked
to strategic goals
Complex, time-consuming
Patent Analysis
Studying the number and
q
ualit
y
of
p
atents
Clearly shows
innovative activit
y
Not all innovations are
p
atente
d
Customer
Satisfaction
Studying customer
opinions and satisfaction levels
Shows market
relevance
Can be subjective
Employee
Productivit
y
Measuring employee
efficienc
y
Shows internal impact
of innovation
Difficult to isolate from other
factors
Market Share
Chan
g
e
Tracking changes in the
com
p
an
y
's market
p
osition
Indicates
com
p
etitiveness
Can be heavily influenced by
external factors
- Stability, ensured by smoothly running
personnel-related processes (succession planning,
reliability in task performance without tension and
conflicts within the team);
- Flexibility, indicating employees' ability to
adapt their work to new conditions in response to
changes (e.g., the ability to develop new solutions to
emerging problems and implement them, actively
participate in organizational changes, and be prepared
for conflicts when necessary to implement innovative
concepts).
It is impossible to achieve complete stability and
flexibility simultaneously, so the task of HR
management is to find a balance between them,
considering the dynamic conditions.
Thus, methods of evaluating the effectiveness of
HR innovations based on calculating changes in
individual performance indicators of the HR
management system as a whole carry the same
drawbacks as the methods of evaluating the HR
management system from which they are derived. It
is also important to note that evaluating the
effectiveness of the HR management system is
typically a process based on assessing a significant
number of factors through expert evaluations.
Calculating innovation effectiveness by comparing
expert evaluations from different time periods can
lead to substantial distortion in the resulting
assessment due to differences in the subjective views
of the experts conducting the evaluation at different
times.
In European countries, so-called "assessment
centers" are common. These centers utilize experts
and a specialized set of indicators to identify the
potential abilities of management employees. When
using such services, a company implementing an
innovation conducts preliminary consultations with
the assessment center experts. This allows for a
qualitative preliminary measurement of the
indicators, which are later compared with similar
indicators calculated after the innovation has been
implemented.
The national practice of evaluating the
effectiveness of innovations in human resource
management is still in its early stages, as evidenced
by the limited amount of information available in
open sources. This information deficit is partly due to
the relatively small number of implemented
innovations in human resource management in our
country.
Conducting applied research on HR management
processes based on the comprehensive use of
statistical methods has recently become challenging
in Uzbekistan. This requires the availability of long-
term time series with simultaneous comparability
across individual time periods/dates. However, most
Uzbek companies have relatively short operational
histories and are not inclined to disclose data
regarding their HR management systems.
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
104

In analyzing innovations in HR management, it's
crucial to employ econometric modeling to determine
their effectiveness and impact. This section will
conduct an econometric analysis to measure the
efficiency of applying innovative approaches in HR
management. We offer using statistical methods to
identify the factors influencing the success of these
HR innovations.
Variables: Include economic indicators such as
employee productivity (production metrics),
employee satisfaction (based on surveys and
interviews), employee turnover, and financial
outcomes.
Data Sources: The article's sources, surveys,
interviews, company reports, and statistical data used
to measure HRMI variables.
Descriptive Analysis: Describing the innovations
being applied in HR management.
Regression Analysis: Using multiple regression
models to identify key variables that influence the
effectiveness of innovations.
Performance Indicators: Utilizing various metrics
to evaluate the efficiency of innovative approaches.
A general form of regression model can be
studied as follows:
E = HRMI + EE + Tr + Mc + ε (1)
Where
E- Employee productivity indicator;
HRMI- Indicator of innovations applied in HR
management;
EE- Employee training;
Tr- Employee training courses and sessions;\
Mc- Model coefficients;
Ɛ- Error term.
By analyzing data with this regression model we
can identify which innovations are effective in HR
management. Using the above mentioned
methodology and econometric analysis, we can more
precisely evaluate the efficiency of innovations in HR
management and their positive impact on the
organization’s overall performance. This aids in
further refining HR strategies and accurately
pinpointing the implementation of innovations.
Thus, this article examined modern approaches to
defining, classifying, and evaluating the effectiveness
of innovations in human resource management.
1. Innovations in human resource management are a
type of managerial innovation, which implies their
close connection with the social environment and the
necessity of considering the synergistic effect when
evaluating the results of implementing such
innovations.
2. The scientific literature notes the existence of two
main concepts underlying the evaluation of the
effectiveness of human resource management, which
are found in publications in this field:
The effectiveness of human resource
management is assessed from the perspective of
the unity of management and production
processes; according to survey participants, the
direct contribution of human resource
management to production efficiency cannot be
measured and is not measured;
The effectiveness of human resource
management is assessed as the determination of
the contribution of human resource management
to the overall effectiveness of the organization’s
activities.
Quantitative evaluation of such a contribution is
challenging because reporting indicators that would
allow for regular measurement have not been
developed.
Thus, most methodologies for evaluating the
effectiveness of human resource management are
based on the first concept, i.e., they assess not so
much the contribution of the HR management system
to production efficiency, but rather its qualitative
impact on such efficiency.
Effectiveness at the company level as an integral
indicator can be transformed into many others at
lower levels, reflecting the performance of specific
HR management systems/subsystems.
In practice, organizations encounter difficulties
when evaluating the effectiveness of innovations in
human resource management. Existing methods are
perceived as ineffective in establishing causal
relationships between the innovation and its final
result. There is a need for indicators that clearly
reflect the impact of the implemented innovation in
HR management on the company's performance
indicators or that clearly demonstrate the extent to
which the organization has achieved its goals as a
result of implementing such an innovation.
REFERENCES
Abdurakhmanova, G. (2020). Human resources
management (Textbook), T.
Abdurakhmanova, G. (2023). Human resources
management (Textbook), T.
Abdurakhmanova, G. K. (2020). Science and practice, 3,
77.
Abdurakmanova, G., Shayusupova, N., Irmatova, A., &
Rustamov, D. (2020). Архив научных исследований,
25.
The Methodology for Determining and Evaluating the Effectiveness of Innovations In Human Resource Management
105

Abdurrahman, K., & M. Sh. (2020). International Journal
of Artificial Intelligence, 4(04), 13-26.
Alberg, V. F. (1993). (Ph.D. dissertation, Moscow).
Competence Centre International Innovation and CME
Research. (2014). The Quarterly Journal of Economics.
Available at: The Quarterly Journal of Economics.
Frechette, H., & Wertheim, E. (1985). New York:
Amacom, 1550 p.
Gomez-Mejia, L. R., & Welbourne, T. M. (1988). Southern
Management Association Proceedings, 58-60.
Grimm, M., Harttgen, K., Klasen, S., et al. (2010). Social
Indicators Research, 97(2), 191-211. DOI:
10.1007/s11205-009-9497-7.
Jørgensen, F., Becker, K. L., & Matthews, J. H. (2009).
Proceedings of the 10th International CINet
Conference, Brisbane, 451-463.
Khafizova, U. R., Kurbanova, Z. K., Rakhmonova, D. B.,
& Kadirkhodjaeva, F. B. (2020). J. Xi'an Univ. Arch.
Technol., XII, 2789–2796.
Khaitov, A. B. (2019). Human resources management
(Textbook), T.
Khaydarova, M. (2024). Journal of Academic Research and
Trends in Educational Sciences, 3(2), 367-374.
Khaydarova, M. Sh. (2024). Economy and Society, 3-
2(118), 851-864.
Kh. K. (2023). FGBOU VO «REU im. G.V. Plekhanova".
356 pages.
Lobanova, T. N. (2004). M.: Gorodets, 400 p.
Nikolaev, A. A. (2001). Problems and theories and
practices of management, 5, 44-51.
OECD. (2002). 6th ed., 256 p. DOI:
10.1787/9789264199040-en.
Ovchinnikova, T. (2003). Personnel management, 7, 34-39.
Prigogine, A. I. (2003). Personnel management, 1, 78-94.
Rakhmonova, B. (2020). Electron. J. Actual Probl. Mod.
Sci., Educ. Train., VII, 23-31.
Rakhmonova, B. (2020). ECLSS Econ. Soc. Sci.,
Proceeding Book, Istanbul, Turkey, 59-67.
Rakhmonova, B. (2020). Innovations in Economics, 10,
173-181. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.26739/2181-9491-
2020-10-23.
Rakhmonova, B. (2022). Electron. J. Actual Probl. Mod.
Sci., Educ. Train., 7, 24-29.
Rakhmonova, B. (2023). Tashkent Irrigation and
Agricultural Mechanization Engineers Institute
National Research University.
Shermatov, O., Nosirov, B., Imomov, R., & Qobulova, M.
(2020). South Asian J. Mark. Manag. Res., 10(4).
Sparrow, P. R. (1988). Journal of Organizational Behavior,
9(3), 289-291.
Suhrcke, M., Rocco, L., & McKee, M. (2007). Trowbridge:
Cromwell Press, 280 p.
Thurow, L. C. (1970). Belmont: Wadsworth Publishing,
170 p.
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
106
