
The Role of Simulation in Creating Project: A Literature Review
Widia
1 a
, Ida Kaniawati
2 b
and Lilik Hasanah
2 c
1
Student of the Department of Science Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Indonesia
2
Department of Science Education, STKIP Harapan Bima, Indonesia
Keywords: Simulation, Creating, Projects, Literature Review.
Abstract: The implementation of simulation in projects facilitates the examination, strategizing, and experimentation of
solutions while circumventing the need for costly and specialized technical expertise. The purpose of this
study is to examine the results of thinking and research on the use of simulation and its benefits in creating
projects that have been published by Scopus over the past 10 years. This research is a literature review, with
procedures consisting of four steps: namely, research design, filter methodology, online database search,
inclusion & exclusion criteria, and data analysis. The findings from 15 scholarly articles indicate that
simulation is employed in the domain of science education at a prevalence of 74%. Within the realm of
education in engineering, the utilization rate of the aforementioned concept stands at 27%. In contrast, the
utilization rate of said concept in education pertaining to health and management is 13% each. The
incorporation of simulation into project-based learning has been found to be a highly efficacious approach for
enhancing educational outcomes and fostering skill acquisition. Additional investigation is required to delve
deeper into the results of the literature review. The limitations and shortcomings identified in the literature
review are acknowledged by the researchers.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the realm of education, institutions of higher
learning hold a pivotal position in facilitating
progress and ought to actively participate in the
attainment of educational objectives. The dynamic
nature of technology necessitates that education must
adjust to meet the evolving demands of learners
(Abulrub et al., 2011). Furthermore, it is imperative
to maintain regular updates of technology and
educational support devices (He et al., 2019). The
methodology utilized during instruction, along with
the instructor's intentions, constitutes a multifaceted
amalgamation that characterizes the approach to
teaching and learning (Cao et al., 2019). Providing
learners with exposure to authentic real-world
problems and involving them in a thorough
investigative process can facilitate the cultivation of
proficient communication skills and interdisciplinary
learning through the application of prior knowledge
(Toledano-O’Farrill, 2019; Pan et al., 2019). To
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-9053-2015
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2787-7892
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7281-2556
clarify, the aforementioned approach furnishes
learners with prospects for practical learning and the
acquisition of proficiencies such as collaborative
work, analytical thinking, and numerical
computation, which are deemed indispensable for
optimal organizational performance (Sindre et al.,
2018). As per the constructivism theory, learners have
a tendency to establish links between newly acquired
information and their pre-existing knowledge (Zadok,
2020).
Simulations are highly beneficial for learners as
they offer tasks or projects that present challenges or
problems that require resolution (Lee & Tsai, 2017).
The process of incorporating simulation
environments, scenarios, or models into project-
based learning experiences is aimed at augmenting
the learning process. Simulations are employed as
instruments for the purpose of examining,
strategizing, and evaluating remedies (De Oña &
Lova, 2019). The approach being referred to in this
statement fosters the acquisition of a range of
competencies by students, including but not limited
700
Widia, , Kaniawati, I. and Hasanah, L.
The Role of Simulation in Creating Project: A Literature Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0013422600004654
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science (ICHELS 2024), pages 700-707
ISBN: 978-989-758-752-8
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

to problem-solving, collaboration, communication,
critical thinking, and creativity. The incorporation of
simulations in projects enables the exploration of
various possibilities without incurring substantial
expenses or necessitating intricate technical
proficiency (Eskrootchi & Oskrochi, 2010).
Several scholarly articles elucidate the utilization
of simulations as a means to facilitate the
achievement of project success, as per the
aforementioned depiction. Hence, it is imperative to
conduct a more comprehensive analysis of the
publication patterns concerning simulations carried
out by researchers across diverse projects. The
objective of the author is to conduct an analysis of the
ideas and research findings pertaining to simulations
over the last decade, spanning multiple nations and
academic disciplines, as documented in global
scholarly publications. Considering the
aforementioned, the writer presents a number of
inquiries:
• Which disciplines have extensively explored the
topic of simulations?
• Which types of simulation are frequently
employed in project development?
• What are the benefits of simulations in the
project creation of process?
2 METHODS
2.1 Research Design
The objective of this investigation is to conduct a
comprehensive analysis of diverse literature sources
pertaining to the function of simulations in the
context of project advancement. The process of
scrutinizing extant literature through the application
of specific criteria is deemed a pivotal undertaking.
The filter methodology has been employed in the
design as it is considered the most effective approach
for discerning research inquiries.
2.2 Data Search
A systematic search was performed to retrieve
scholarly literature on simulations from various
databases, including Scopus, Web of Science, Publish
or Perish, ERIC, Wiley Online Library, and Google
Scholar. The present study examined articles that
were published in the past decade, specifically
between 2013 and 2022, by utilizing the keywords
"simulation" and "project." The search for data was
executed in the month of May in the year 2023.
2.3 Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The research employs specific inclusion criteria,
namely: (a) the articles utilized were published in
2014 or later, (b) the articles utilized are indexed in
international journals, and (c) the articles utilized
pertain to the topic of simulation-based teaching and
learning. The criteria for exclusion are outlined as
follows: The guidelines for article selection in this
study are as follows: (a) articles written in languages
other than English are prohibited; (b) articles utilized
must be composed in globally recognized languages;
and (c) articles utilized must remain within the scope
of the field of education.
2.4 Data Analysis
The present study undertook a three-phase analysis of
articles. The initial phase entailed scrutinizing 50
articles based on their titles and abstracts, which
yielded a final selection of 30 articles. During the
subsequent phase, the analysis was centered on the
research objectives, methodologies, and findings,
culminating in the production of 15 articles (as
depicted in Figure 1).
Figure 1: The process of analysis and selection of literature review articles.
The Role of Simulation in Creating Project: A Literature Review
701
After analyzing and identifying relevant articles
based on predetermined criteria, the descriptive
analysis was conducted with a focus on various
aspects including authors, publication year,
objectives, methods, and research findings. The
objective of this descriptive analysis is to furnish a
comprehensive outline of the prevalence of integrated
simulation in project-based learning. The process
entails engaging in reading activities with the aim of
acquiring a broad comprehension of the subject
matter. The authors conducted an analysis of research
findings in specific sections of the selected articles.
3 RESULTS
In this study, the literature review comprised a
selection of 15 articles that were deemed relevant to
the research questions posed at the outset. Table 1
provides a comprehensive overview and comparative
analysis of the chosen articles, encompassing the
distribution of said articles with respect to authors,
year of publication, research objectives,
methodologies employed, and resultant findings.
Table 1: Descriptive data of the analyzed studies (N = 15).
Author (year)
Objective
Method
Effect
Bajow et al,
(2022)
Analyze the success of a
simulation-
based strategy
for chemical exposure
prevention.
Mixmethods
n = 41
The utilization of advanced simulations has
the potential to augment the cognitive and
practical proficiencies of individuals in
effectively addressing incidents of mass
chemical exposure (Bajow et al., 2022).
Chang et
al.,
(2017).
Examine the process of
resolving physics problems
through the utilization of
simulations, both
individually and
collaboratively.
Qualitative
Squencial
n = 30
Simulations that are based on collaboration
have the potential to transform discussions into
problem-
solving endeavors. In contrast,
simulations based on individual units exhibit a
lower magnitude
(Chang et al., 2017).
Jin &
Durlofsky
(2020)
Employing
computational fluid
dynamics (CFD) simulation
to mitigate data loss and
minimize errors.
Ekperiment
n = 200
In general, the E2C ROM demonstrated a
high degree of dependability in its
prognostications, surpassing the current POD
methodology in terms of disturbance
management (Jin et al., 2020).
Yang et al.
(2019)
This study involves a
comparative analysis of
flood simulations derived
from five distinct global
hydrological models (GHM)
in conjunction with the Inter-
Sectoral Impact Model
Intercomparison Project 2a
(ISIMIP2a).
Eksperiment
The global hydrological models (GHM)
method yields favorable outcomes in regards to
peak amplitude. The statement posits that the
integration of traditional flood simulation
methods with machine learning techniques could
potentially enhance the reliability of flood risk
evaluation (Yang et al., 2019).
Correia, et
al.
(2019)
Examine the utilization
of simulation-based learning
systems, specifically the
PhET platform, in
conjunction with the
cognitive processing of
chemical concepts.
case study
n = 114
The simulation laboratory facilitates the
visualization of gas behavior for students, while
the system's design promotes comprehension of
gas behavior at the submicroscopic level
(Correia et al., 2019).
Dong et al.
(2021)
This study aims to
examine the level of
uncertainty associated with
the cost of generating wind
energy by utilizing
contemporary wind turbine
simulations.
Meta
analysis
The utilization of simulation techniques has
the potential to decrease the expenses associated
with the production of wind power. The
sensitivity analysis indicated that the combined
impact of the scale parameter, shape parameter,
and air density on the total effect coefficient was
positive (Dong et al., 2021).
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
702
Chung et al.
(2013)
Conduct an examination
of sites that pose a risk to
human health or the
environment through the
utilization of specialized
simulation software,
specifically the Interactive
Site Investigation Software
(ISIS).
Qualitative
n = 23
The Interactive Site Investigation Software
(ISIS) is a computer program designed for
interactive site investigation purposes. The
aforementioned approach has a significant
positive impact on students and is efficacious in
enhancing their ability to manage intricate
projects, bridging the gap between theoretical
concepts and practical scenarios, and
augmenting their proficiency in resolving
complex problems (Chung et al., 2013).
Zwikael &
Chih
(2015)
The present study aims
to evaluate the efficacy of
simulation-
based training
(SBT) in the context of
project management
education.
Eksperimen
n = 25
The utilization of Simulation-Based
Training (SBT) has been shown to enhance the
participants' declarative knowledge within the
simulation and bolster their overall learning
process. There exist multiple scenarios in which
SBT proves to be a more efficacious approach
for educating students in project management
(Zwikael et al., 2015).
Crespo &
Quiroz
(2015)
This study aims to
evaluate the effects and
potential advantages of
implementing virtual reality
technology in the operation
of the Mitsubishi
Movemaster RV-M1 robot.
Eksperiment
n = 10
The use of simulation technology enables
the user to program individual joints of the robot
and showcase various features of the robot in a
virtual setting. These features may include
animations, images, and textual information,
which are a direct outcome
of the developed
features. The present software has the capability
to perform a comparison between input
sequences provided by the user and sequences
generated by the computer, utilizing specific
algorithms (Crespo et al., 2015).
Akkoyun
(2017)
We are pleased to
present a recently developed
simulation software that has
the capability to simulate
natural stone mills,
specifically designed for
engineering students.
Qualitative
The favorable response received from
students regarding the novel simulation software
serves as a motivating factor for researchers to
undertake additional projects. It also attests to
the efficacy of the software in accomplishing its
pedagogical objectives (Akkoyun, 2017).
Chakrabort
y & Elzark
(2019)
Perform simulations of
diverse machine concepts to
facilitate the development of
energy models that are more
precise and effective.
Comparativ
e Analysis
The XGBoost algorithm has demonstrated a
high degree of precision in generating energy
models. Furthermore, the inclusion of
intermediate steps is deemed crucial in the
development of both XGBoost and artificial
neural network (ANN) models (Chakraborty &
Elzarka, 2019).
Chaplin, et
al.
(2020)
Simulation plays a
crucial role in the healthcare
system, as it has the potential
to
enhance the quality of
medical education by
providing various
applications.
Qualitative
Survey
Research that utilizes emergency
simulations can effectively identify factors that
promote or hinder progress and establish
agreement on key research topics. The initial
phase involves formulating a research plan
centered on simulation-
based approaches
tailored to the context of emergency medicine in
Canada (Chaplin et al., 2020).
Allaire
(2015)
Assess the impact of
virtual patient simulation on
the development of critical
thinking skills among
students.
Mixed
Methods
n= 31
The findings did not demonstrate a
statistically significant rise in the average score.
However, the students expressed that the
utilization of virtual patients was a productive
pedagogical approach in fostering critical
thinking, problem-solving, and self-assurance in
the clinical milieu (Allaire, 2015).
The Role of Simulation in Creating Project: A Literature Review
703
Li & Yang
(2021).
The present study aims
to evaluate the efficacy of
the Base Station (BS)
approach in comparison to
the
Deep Neural Network
(DNN) method for problem-
solving purposes. To achieve
this objective, simulation
techniques were employed.
Eksperiment
n = 22
The findings of the simulation indicate that
the employment of the simulation-assisted Deep
Neural Network (DNN) approach offers benefits
over the Base Station (BS) technique in
addressing problems. This presents the proposed
approach for addressing the is
sue of model
mismatch between the training and testing
datasets (Li et al., 2021).
Scholtz et
al (2017)
The practical
application of an enterprise
resource planning (ERP)
system has the potential to
mitigate the cost and
complexity associated with
such tools.
Qualitative:
Survey
n = 50
Simulation-based learning and mobile
learning (m-learning) are integral components of
a broader and more extensive research endeavor
that seeks to augment the acquisition of
knowledge and skills related to Enterprise
Resource Planning (ERP) systems in the context
of higher education (Scholtz et al., 2017).
Information:
- E2C = Embed-to-control - POD = Proper-orthogonal-decomposition
- ROM = Reduced-order modelling - n = Number of research samples
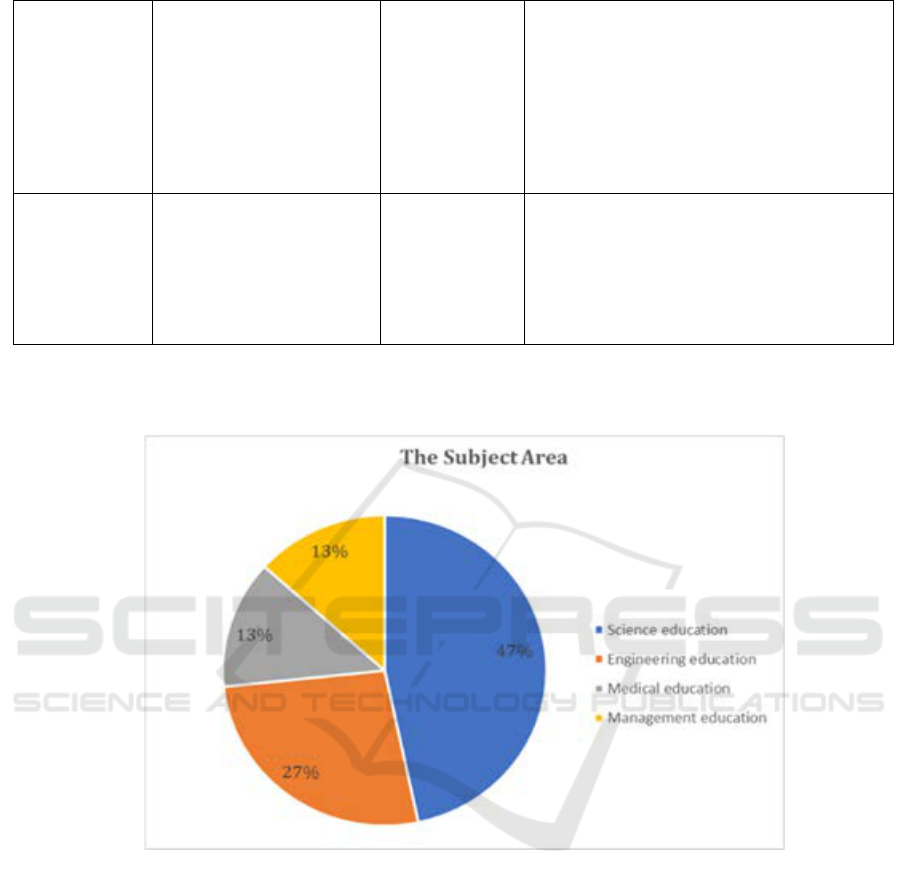
Figure 2: Distribution of articles by subject area in education.
3.1 Distribution of Simulated in the
Subject Area
The literature review comprises 15 articles published
within the last decade (2013-2022), as depicted in
Figure 2. These articles cover diverse subject areas
and educational disciplines. The preponderance of
articles pertained to the domain of science education,
comprising 7 articles, trailed by engineering
education with 4 articles, medical education with 2
articles, and management education with 2 articles.
3.2 Distributed Simulation in Terms of
Publication Year
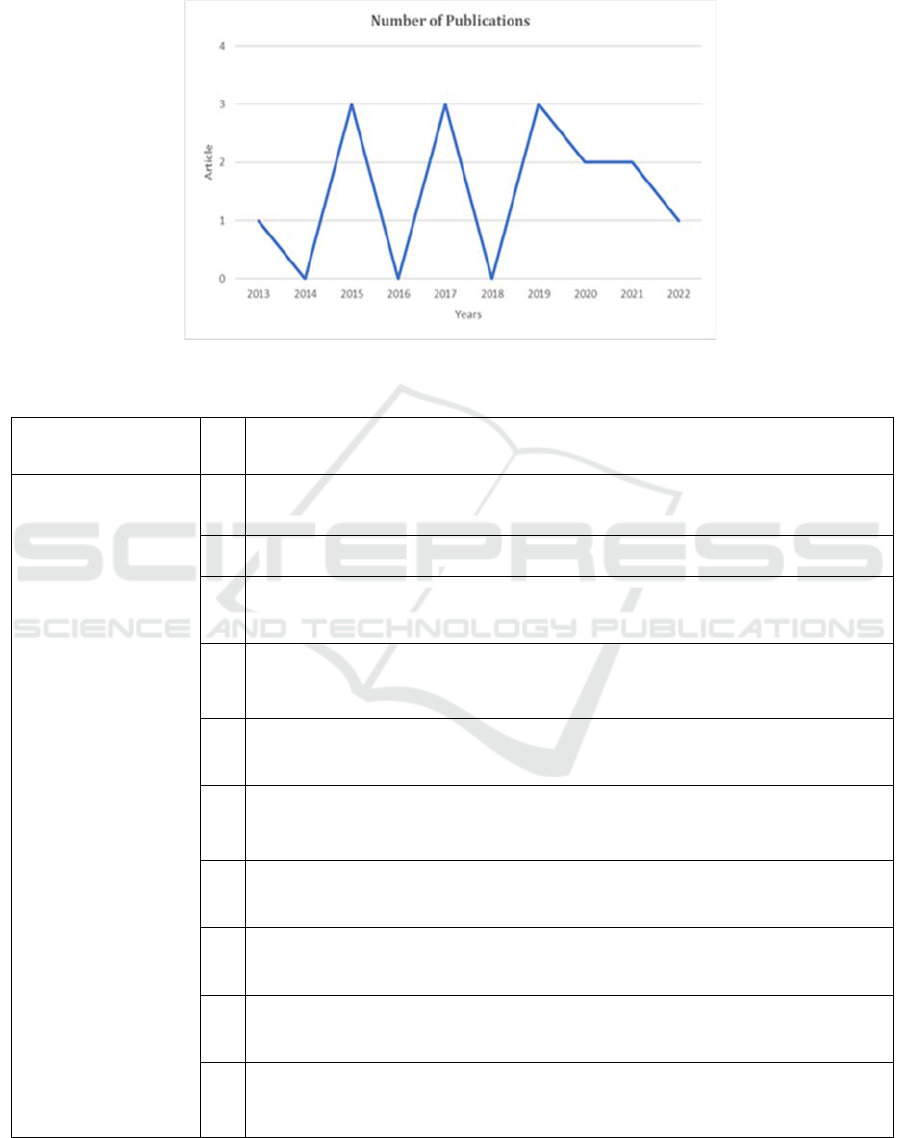
Regarding the temporal distribution of simulation-
related articles analyzed in the literature review
spanning the period of the last decade (2013-2022),
as illustrated in Figure 3, it was observed that three
articles were published in 2015, 2017, and 2019, two
articles were published in 2020 and 2021, one article
each in 2013 and 2022, and no articles were published
in 2014, 2016, and 2018. The current research
suggests that there is a relatively low volume of
publications within the last ten years. This implies
that the incorporation of simulation in educational
and pedagogical pursuits is not a prominent topic.
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
704
3.3 The Benefits of Simulation in the
Project
Figure 3: Distribution of articles in terms of publication year.
Table 2: Simulation utilization data in project creation.
Benefits of
Simulation
Descriptions
Simulation in creation
of project
1.
These simulate real-world chemical exposure incidents where participants practice
sorting and treating patients.
2.
The computer simulations for facilitating collaborative problem-solving learning.
3.
The simulation offers a powerful combination of speed, accuracy, and adaptability,
especially in scenarios where real-time or large-scale optimization is required.
4.
These simulations offer a comprehensive and improved approach to global flood
risk assessment, enabling better preparedness for climate-induced changes in flooding
patterns.
5
The ability to manipulate variables in the simulation, observe changes dynamically,
and promote active experimentation and deeper learning through trial and error.
6.
By simulating hazardous waste site investigations, students practiced applying
engineering principles in realistic, controlled environments, improving their
preparedness for real-world projects.
7.
The simulation to improve training efficiency, accessibility, interactivity, and
accuracy in robotic programming,
8.
The simulation offers an interactive and effective way to teach complex industrial
processes, leading to improved understanding and positive student experiences.
9.
That virtual patient simulations are a promising tool for enhancing critical thinking,
problem-solving, and confidence in clinical practice.
10.
The using simulation-based learning includes accessibility, ease of use, experiential
learning, improved content presentation, and flexibility, which collectively enhance the
effectiveness of learning in higher education.
The Role of Simulation in Creating Project: A Literature Review
705

4 DISCUSSION
In response to the initial research inquiry concerning
the domains in which simulation is implemented in
projects, the examination of 15 articles through a
literature review reveals that simulation is utilized
74% in the realm of science education, 27% in
engineering education, and 13% in both medical
education and management education. Simulation is
employed in each of these fields to address the
problems or challenges specific to each. Simulation is
a widely used technique in the scientific field.
Simulation is a key technology of Industry 4.0 to
support the development of planning and exploration
models to optimize decision-making, design, and
operation of complex systems (Scholtz et al., 2017).
Its primary purpose is to minimize losses and data
errors that may arise during implementation (Jin et
al., 2020). The utilization of a particular project
model can potentially improve its efficacy (Yang et
al., 2019). Similar principles are applicable to other
domains of education, including but not limited to
medicine, engineering, and management.
In response to the second research inquiry
pertaining to the prevalent simulation techniques
employed in project development, the examination of
15 scholarly articles reveals that simulation is
employed in diverse modes of instruction,
encompassing virtual reality, models, software, and
virtual patients (Chung et al., 2013; Allaire, 2015; Li
et al., 2021). Simulation is utilized as a means to
replicate real-world scenarios or settings that are
challenging or costly to replicate in the tangible realm
(Crespo et al., 2015). Simulation, within the realm of
education, encompasses various forms such as
computer simulation, virtual simulation, physical
simulation, and game-based simulation. Simulations
offer a secure and regulated setting for students to
engage in experimentation, decision-making, and
skill-building (Crespo et al., 2015).
In relation to the third research inquiry, assert that
the utilization of simulation has the potential to
facilitate the successful completion of projects by
users (Crespo et al., 2015). The implementation of
simulation techniques has been shown to effectively
mitigate expenses, optimize resource allocation, and
minimize potential hazards, including accidents and
safety-related issues (Bajow et al., 2022: Dong et al.,
2021). Simulation allows experimentation with
different approaches to completing a project without
having to be on site, which can result in a better
understanding of the process, lower costs, shorter
durations, and quality (Scholtz et al., 2017). This
framework aims to help teams design holistically to
create a quality project overall (Scholtz et al., 2017).
Project-based simulations facilitate the process of
acquiring new knowledge through self-directed
learning and collaborative problem-solving (Chang et
al., 2017). The utilization of simulations is based on a
problem-centered learning methodology and aims to
cultivate a range of proficiencies such as critical
analysis, resolution of complex issues, self-assurance,
and efficient strategizing (Chung et al., 2013; Allaire,
2015; Li et al., 2021). Additionally, extant research
has demonstrated that simulation projects elicit
contentment among students with regards to their
involvement and acquisition of knowledge.
Simulations can improve students' skills and
confidence and prepare them for real situations
(Chang et al., 2017).
The utilization of simulation in project-based
learning has been deemed essential for showcasing
enhancements in educational outcomes, as per the
results of the literature review encompassing 15
international articles (Chaplin et al., 2020). Hence,
the integration of simulation with project-based
learning is recommended. The process entails the
incorporation of simulation environments, scenarios,
or models into project-based learning endeavors with
the aim of augmenting the learning process. The
incorporation of simulation in project-based learning
can provide students with the opportunity to confront
authentic challenges, comprehend the consequences
of their choices, and enhance their comprehension of
the subject matter being instructed. The selection of
simulation modality ought to be congruent with the
academic level, contextual setting, and content
domain.
5 CONCLUSION
Optimizing learning through projects involving
simulation requires careful consideration of the
suitable simulation type that aligns with the subject
matter, environment, and level of instruction. The
present study presents the outcomes of the literature
review on the application of simulation in project-
based learning. (a) The application of simulation is
widespread in diverse educational domains,
encompassing science, engineering, medicine,
management, and other sectors. (b) Project
development commonly employs simulation
techniques such as virtual reality, models, modeling,
software, and virtual patients. (c) The utilization of
simulation in projects yields several favorable
outcomes, such as cost and resource reduction, and
risk mitigation, including accidents. (d) The
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
706

integration of simulation is also a crucial aspect to
consider.
The limitations of this pepper is the present
literature review's delineation of inclusion and
exclusion criteria may not comprehensively explicate
the function of simulation in the process of designing
and executing projects. Furthermore, there exist
certain variables that have not been extensively
deliberated upon in the literature scrutinized during
the course of this review. Given this constraint, the
researcher recognizes the imperative of undertaking a
comprehensive investigation into this issue.
6 AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization, W. and I.K.; methodology, W.
and I.K.; formal analysis, W.; data curation, I.K. and
L.H; writing—review and editing, W., I.K. and L.H.;
Submid and Correspondent, W. and I.K., All authors
have read and agreed to the published version of the
manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author would like to thank the promoter and co-
promoter who have guided the author in completing
this pepper.The author also wants to say thank you to
Puslapdik Kemdikbudristek, LPDP who have fully
financed the doctor's program with a financing
scheme Beasiswa Pendidikan Indonesia (BPI) for the
grant with a contract number:
01523/J5.2.3/BPI.06/9/2022.
REFERENCES
Abulrub, A. H. G., Attridge, A. N., & Williams, M. A.
(2011). 2011 IEEE Global Engineering Education
Conference (EDUCON), 751.
https://doi.org/10.1109/EDUCON.2011.5773223
Akkoyun, O. (2017). Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ., 25, 404.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cae.21807
Allaire, J. L. (2015). J. Dent. Educ., 79, 1082.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.0022-
0337.2015.79.9.tb06002.x
Bajow, N., Alkhalil, S., Maghraby, N., Alesa, S., Najjar, A.
A., & Aloraifi, S. (2022). BMC Med. Educ., 22, 350.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-022-03427-2
Cao, Y., Postareff, L., Lindblom-Ylänne, S., & Toom, A.
(2019). Teach. Teach. Educ., 85, 125.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2019.06.013
Chakraborty, D., & Elzarka, H. (2019). J. Build. Perform.
Simul., 12, 193.
https://doi.org/10.1080/19401493.2018.1498538
Chang, C. J., Chang, M. H., Liu, C. C., Chiu, B. C., Fan
Chiang, S. H., Wen, C. T., & Chai, C. S. (2017). J.
Comput. Assist. Learn., 33, 649.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12208
Chaplin, T., Thoma, B., Petrosoniak, A., Caners, K.,
McColl, T., Forristal, C., & Hall, A. K. (2020). Can. J.
Emerg. Med., 22, 103.
https://doi.org/10.1017/cem.2019.416
Chung, G. K., Harmon, T. C., & Baker, E. L. (2013). IEEE
Trans. Educ., 44, 390.
https://doi.org/10.1109/13.965789
Correia, A. P., Koehler, N., Thompson, A., & Phye, G.
(2019). Res. Sci. Technol. Educ., 37, 193.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02635143.2018.1487834
Crespo, R., García, R., & Quiroz, S. (2015). Procedia
Comput. Sci., 75, 107.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.12.226
De Oña, J., & Lova, A. (2019). Computers Ind. Eng., 134,
221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.07.009
Dong, M., Li, Y., Song, D., Yang, J., Su, M., Deng, X., &
Joo, Y. H. (2021). Energy Convers. Manag., 229,
113781.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113781
Eskrootchi, R., & Oskrochi, G. R. (2010).
J. Educ. Technol.
Soc., 13, 236.
https://www.jstor.org/stable/jeductechsoci.13.1.236
He, Z., Sui, X., Jin, G., & Cao, L. (2019). Appl. Opt., 58,
A74. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.58.000A74
Jin, Z. L., Liu, Y., & Durlofsky, L. J. (2020). J. Pet. Sci.
Eng., 192, 107273.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107273
Lee, K., & Tsai, C. (2017). Computers Educ., 113, 228.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.05.014
Li, Y., Han, S., & Yang, C. (2021). IEEE Trans. Wirel.
Commun., 20, 7813.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2021.3088224
Pan, G., Seow, P. S., & Koh, G. (2019). J. Int. Educ. Bus.,
12, 167. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIEB-06-2018-0022
Scholtz, B. M., Kapeso, M., & De Villiers, M. R. (2017).
South Afr. Comput. J., 29, 87.
http://dx.doi.org/10.18489/sacj.v29i2.475
Sindre, S., Giannakos, M., Krogstie, B. R., Munkvold, R.,
& Aalberg, T. (2018). Uniped, 41, 147.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.10.001
Toledano-O’Farrill, R. (2019). Higher Educ., Skills Work-
Based Learn., 9, 305.
https://doi.org/10.1108/HESWBL-07-2018-2078
Yang, T., Sun, F., Gentine, P., Liu, W., Wang, H., Yin, J.,
& Liu, C. (2019). Environ. Res. Lett., 14, 114.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab4d5e
Zadok, Y. (2020). J. Eng. Des. Technol., 18, 941.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JEDT-01-2019-0023
Zwikael, O., Shtub, A., & Chih, Y. Y. (2015). J. Manag.
Eng., 31, 04014035.
https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)ME.1943-
5479.0000238
The Role of Simulation in Creating Project: A Literature Review
707
