
Scientific Mapping in Scopus with Biblioshiny: A Bibliometric
Analysis of Disaster Literacy
Hayatul Khairul Rahmat
1,2 a
, Nurhasan Syah
1 b
, Eri Barlian
1 c
and Joshua Banjarnahor
3 d
1
Doctoral Program of Environmental Science, Graduate School, Universitas Negeri Padang, Padang, Indonesia
2
Department of Disaster Management, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Budi Luhur, Jakarta, Indonesia
3
National Search and Rescue Agency, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Bibliometric, Disaster, Literacy, Scopus.
Abstract: The goal of this research is to examine the scientific mapping in disaster literacy research with bibliometric
analysis. The method of this research is a bibliometric analysis. Based on the analysis carried out on the theme
of disaster literacy from 2014 to 2024, there are 50 documents with the country with the largest number of
publications is Indonesia. The author who published the most on disaster literacy is D. Zhang Meanwhile, the
most dominant keywords are disasters, followed by disaster literacy, earthquake, and literacy. For prediction
in the future, research should be carried out related to disaster literacy for students.
1 INTRODUCTION
Natural disasters are a global phenomenon that
impacts various aspects of human life, including
health, the economy, and social stability (Akbar et al.,
2024; Aprilyanto et al., 2023; Pratama et al., 2024;
Rahmat, Ramadhani, et al., 2020; Rahmat, Sari, et al.,
2020). Over the past decades, the frequency and
intensity of natural disasters such as earthquakes,
tsunamis, floods, wildfires, and storms have been
increasing due to climate change and uncontrolled
urbanization. These impacts underscore the
importance of enhancing disaster literacy as part of a
global strategy to build more resilient and prepared
societies. Disaster literacy has become a key focus in
international research, both in academic and practical
contexts (Ashgaf et al., 2024; Asshiddiqi et al., 2023;
Khairunnisa et al., 2021; Rahmat & Pernanda, 2021).
Disaster literacy involves individuals’ and
communities’ understanding of disaster risks, their
ability to mitigate impacts, and their readiness to
respond to emergencies (Asshiddiqi et al., 2023;
Maghfirah & Mutia, 2023). Worldwide, the level of
disaster literacy varies significantly depending on
a
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0001-5962-8407
b
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0003-0264-5884
c
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0002-3166-1288
d
https://orcid.org/ 0009-0005-8489-4658
social, economic, educational, and governmental
factors. Countries with higher levels of disaster
literacy tend to be more successful in reducing the
impacts of disasters compared to those without
adequate disaster literacy strategies (Ahmed et al.,
2023; Shalahuddin et al., 2022; Utama et al., 2020).
Globally, research on disaster literacy
encompasses various topics, such as the role of formal
education in raising risk awareness, the effectiveness
of public awareness campaigns, the use of digital
technologies for disaster mitigation, and community-
based approaches to preparedness (Asshiddiqi et al.,
2023). This research often involves interdisciplinary
collaboration across social sciences, engineering,
education, and public policy. However, systematic
mapping of global research trends in disaster literacy
remains limited.
A bibliometric approach offers an effective method
for analyzing and mapping research trends in the field
of disaster literacy worldwide. Using data from
scientific databases such as Scopus or Web of Science,
bibliometric analysis can identify key topics,
publication trends, researcher collaborations, and the
contributions of specific institutions or countries to the
296
Rahmat, H. K., Syah, N., Barlian, E. and Banjarnahor, J.
Scientific Mapping in Scopus with Biblioshiny: A Bibliometric Analysis of Disaster Literacy.
DOI: 10.5220/0013422400004654
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science (ICHELS 2024), pages 296-300
ISBN: 978-989-758-752-8
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
body of disaster literacy literature (Ellegaard & Wallin,
2015; Fiandini et al., 2024). Furthermore, this method
can help identify research gaps and opportunities for
cross-national or regional collaborations.
One of the commonly used tools for bibliometric
analysis is Biblioshiny, a web-based application from
the R Bibliometrix package. With Biblioshiny,
bibliometric data can be visualized as network
graphs, keyword analyses, or geographic distribution
maps of publications. This enables researchers to
understand the development of disaster literacy from
various perspectives, both academic and practical,
intuitively and interactively.
This study aims to conduct a bibliometric analysis
of the global disaster literacy literature. The research
focuses on identifying the most widely discussed
topics, the countries or institutions that are most
active, and the authors and journals that are influential
in this field. By doing so, this study seeks to provide
a comprehensive overview of how disaster literacy
has evolved as an essential area of study to address
global challenges.
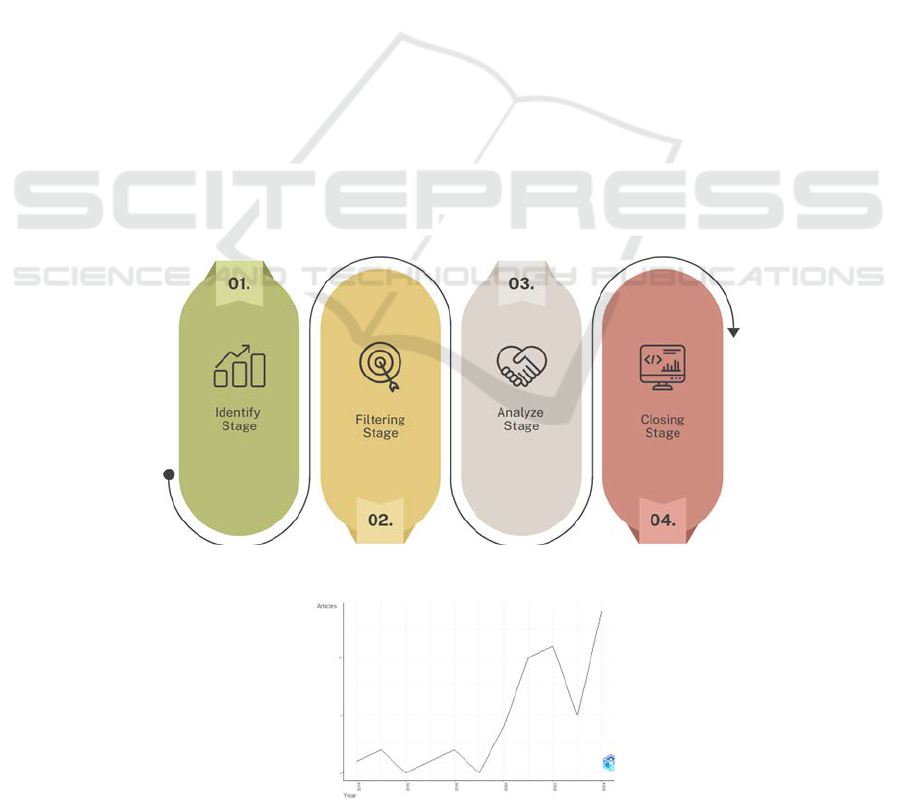
2 METHOD
This research used a bibliometric approach.
Bibliometric analysis is a quantitative method for
analyzing bibliographic data contained in scientific
publications, such as scientific journals, scientific
proceedings, or scientific periodicals. (Araújo-Vila et
al., 2023; Fiandini et al., 2024; Harahap et al., 2021;
Hasan & Moorthy, 2016; Hudha et al., 2020; Rahmat
et al., 2021, 2023). This research uses bibliometric
analysis using the Scopus database. On November 1
st
,
2024, research conducted keywords related to
education for sustainable development. Figure 1
illustrates the flow of this research. Initially, we
identified the topic for this research as education for
sustainable development. Next, we filter the results
by restricting the publication period from 2014 to
2024. In the third stage, the Biblioshiny application is
used to analyze creating a visualization of publication
data. In the last stage, the result derived from the third
stage discusses the findings.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Publication Output and Source
Document
Figure 2 shows the trend of publication on disaster
literacy from 2014 to 2024. During this period, the
number of publications experienced an annual
decreased but overall increased.
Figure 1: Stages of the Bibliometric Analysis Methods.
Figure 2: Yearly distribution of documents in disaster literacy research.
Scientific Mapping in Scopus with Biblioshiny: A Bibliometric Analysis of Disaster Literacy
297
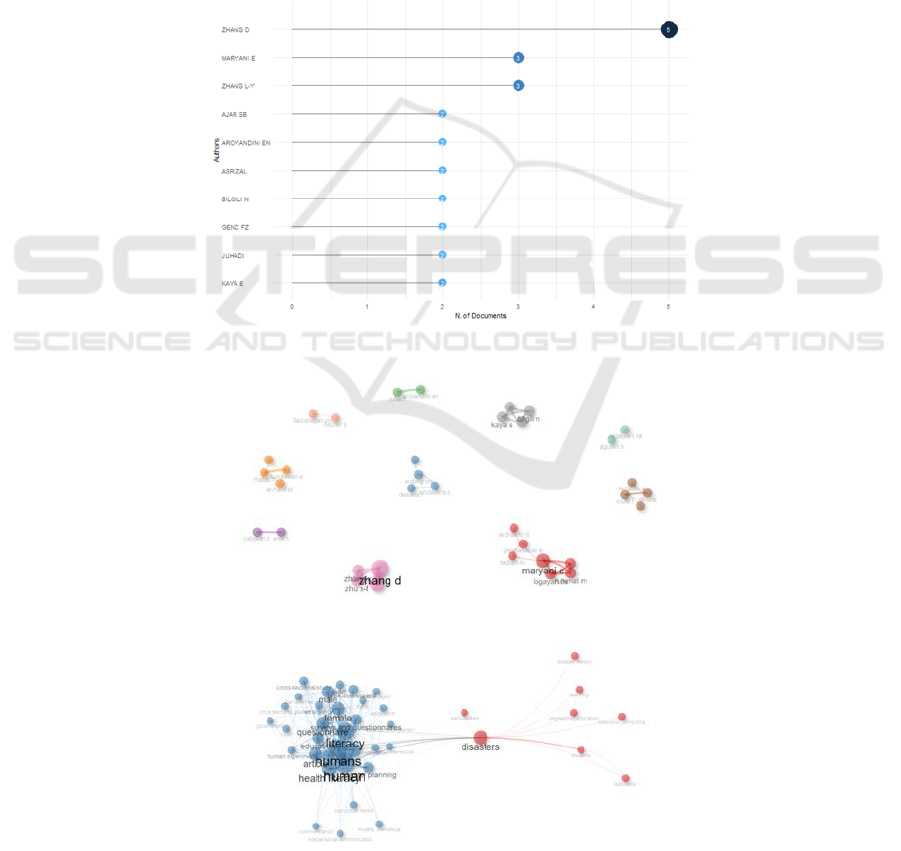
3.2 Key Author of Disaster Literacy
From 2014 until 2024, the authors who published the
most on disaster literacy are D. Zhang, with 5
documents, followed by E. Maryani and L. Y. Zhang,
with 3 documents. This can be seen in Figure 3 and
the network collaboration in Figure 4.
3.3 Thematic Area-Related Disaster
Literacy Using Biblioshiny
Bibliometric studies are carried out the present results
based on frequently occurring terms (Alvarez et al.,
2022; Araújo-Vila et al., 2023). In this research, it
starts from 2014 until 2024. The term that appears can
be seen in the visualization can be seen in Figure 5.
3.4 Future Research for Disaster
Literacy
Figure 6 illustrates the keywords’ density. According
to the figure, the most dominant keywords are
disasters, followed by disaster literacy, earthquake,
and literacy.
Figure 7 represents the focus of the previous main
research. The thematic maps of this research can be
seen in Figure 7.
Figure 3: Most of the authors in disaster literacy research.
Figure 4: Network collaboration research in disaster literacy.
Figure 5: Visualization of co-keywords network in disaster literacy.
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
298
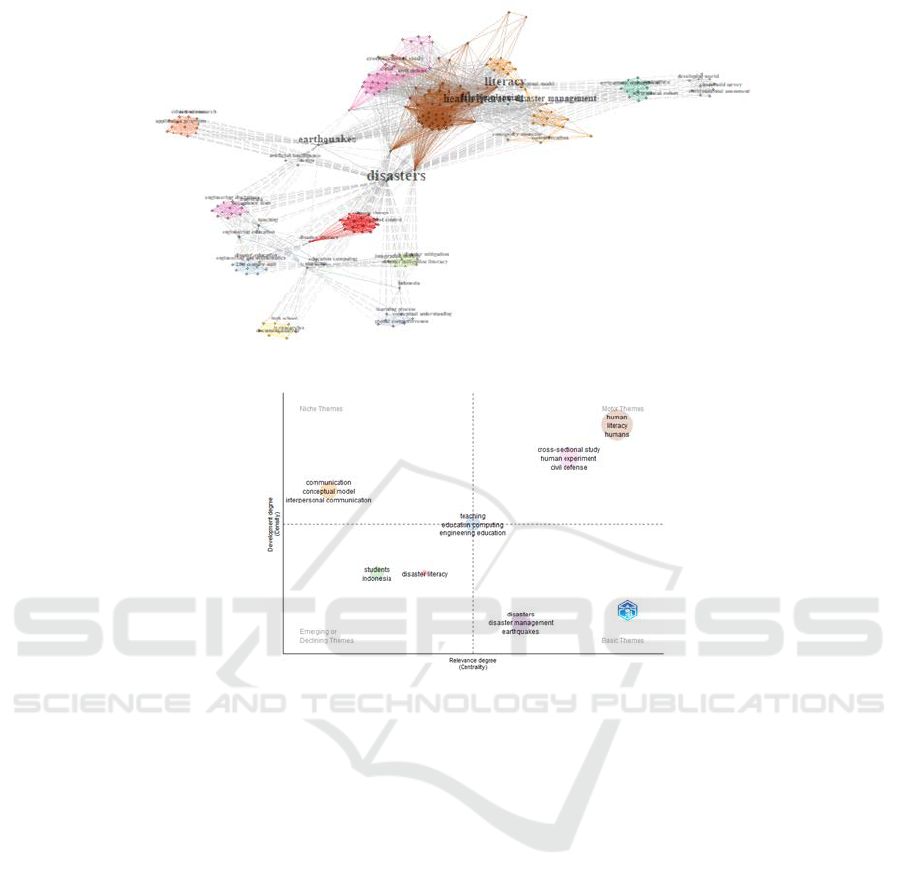
Figure 6: Keywords Cooccurare in disaster literacy research.
Figure 7: Thematic maps in disaster literacy research.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the analysis carried out on the theme of
disaster literacy from 2014 to 2024, there are 50
documents with the country with the largest number
of publications is Indonesia. The author who
published the most on disaster literacy is D. Zhang
Meanwhile, the most dominant keywords are
disasters, followed by disaster literacy, earthquake,
and literacy. For prediction in the future, research
should be carried out related to disaster literacy for
student.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, I., Garfias Royo, M., Opabola, E., Nurdin, S.,
Meilianda, E., Idris, Y., Rusydy, I., Joffe, H., & Parikh,
P. (2023). Assessment of WASH infrastructure in
schools in Central Sulawesi, Indonesia using structured
observations and principal interviews. Journal of Water
Sanitation and Hygiene for Development, 13(6), 375–
390. https://doi.org/10.2166/washdev.2023.147
Akbar, A. A., Dwiningtias, H., & Rahmat, H. K. (2024).
Urgensi Koordinasi dalam Organisasi Tanggap
Darurat Bencana di Indonesia : Sebuah Tinjauan
Pustaka. 1(1), 15–20.
Alvarez, V., Austin, M. C., Rodriguez, Z., Mora, D., & De
Leon, L. L. (2022). Sustainability Actions towards
Neutral Carbon Footprint Higher Education
Institutions: A Systematic Review. Proceedings - 2022
8th International Engineering, Sciences and
Technology Conference, IESTEC 2022, 608–615.
https://doi.org/10.1109/IESTEC54539.2022.00101
Aprilyanto, A., Widana, I. D. K. K., Subiyanto, A., &
Rahmat, H. K. (2023). Pemulihan Pascabencana
Tsunami 2018 Guna Mendukung Program
Pembangunan Daerah Kabupaten Pandeglang.
Jagratara: Journal of Disaster Research, 1(1), 25–32.
https://doi.org/10.36080/jjdr.v1i1.109
Araújo-Vila, N., Otegui-Carles, A., & Fraiz-Brea, J. A.
(2023). Bibliometric Analysis of Academic Research in
Education for Sustainable Development in the Field of
Tourism. International Journal of Social Ecology and
Sustainable Development, 14(1).
https://doi.org/10.4018/IJSESD.326280
Scientific Mapping in Scopus with Biblioshiny: A Bibliometric Analysis of Disaster Literacy
299

Ashgaf, I. M., Utomo, D. A. B., & Kusdiwanggo, S. (2024).
The Linkage between Economic Growth and Ecology
of Urban Area Development in Indonesia: A Systematic
Review. In M. D. & F. of E. Bina Nusantara University
Civil Engineering Department, Jl. KH Syahdan No 9,
Jakarta (Eds.), IOP Conference Series: Earth and
Environmental Science (Vol. 1324, Issue 1). Institute of
Physics. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-
1315/1324/1/012086
Asshiddiqi, M. R., Vitasari, M., Biru, L. T., Zhang, D.,
Zhang, L. Y., Zhang, K., Zhang, H. F. H., Zhang, H. F.
H., Zhao, K., Logayah, D. S., Maryani, E., Ruhimat, M.,
Wiyanarti, E., Hale Manek, A., Khairunnisa, K.,
Abubakar, Y., Sugianto, D., Nur Aziz, S., Maryani, E.,
& Yani, A. (2023). Literasi Bencana Dalam
Pembelajaran Geografi Pada Kurikulum Merdeka
Belajar. Jurnal Samudra Geografi, 23(2), 139–144.
https://doi.org/10.33059/jsg.v6i2.7706
Ellegaard, O., & Wallin, J. A. (2015). The bibliometric
analysis of scholarly production: How great is the
impact? Scientometrics, 105(3), 1809–1831.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-015-1645-z
Fiandini, M., Nandiyanto, A. B. D., & Muktiarni, M.
(2024). EXPERIMENTAL DEMONSTRATION FOR
TEACHING THE CONCEPT OF STEAM ENGINE
POWER PLANT TO VOCATIONAL STUDENTS TO
SUPPORT THE SUSTAINABILITY
DEVELOPMENT GOALS (SDGS) AND ITS
COMPARISON TO INDONESIAN MERDEKA
CURRICULUM. Journal of Engineering Science and
Technology, 19(5), 1878–1905.
Harahap, J., Gunawan, T., Suprayogi, S., & Widyastuti, M.
(2021). A review: Domestic wastewater management
system in Indonesia. In A. L., R. null, R. A., Y. H., &
M. A. (Eds.), IOP Conference Series: Earth and
Environmental Science (Vol. 739, Issue 1). IOP
Publishing Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-
1315/739/1/012031
Hasan, M. S., & Moorthy, R. (2016). Bantuan Kemanusiaan
dan Pertolongan Bencana (HADR) Sebagai Alat
Diplomasi Amerika Syarikat di Asia Tenggara.
Sarjana, 31(2), 44–61.
Hudha, M. N., Hamidah, I., Permanasari, A., Abdullah, A.
G., Rachman, I., & Matsumoto, T. (2020). Low Carbon
Education: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis.
European Journal of Educational Research, 9(1), 319–
329. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.9.1.319
Khairunnisa, K., Abubakar, Y., & Sugianto, D. (2021). Do
Disaster Literacy and Mitigation Policy Affect
Residents Resettling in Tsunami Prone Areas? Study
from the City of Banda Aceh, Indonesia. Forum
Geografi, 35(1), 38–48.
https://doi.org/10.23917/forgeo.v35i1.11510
Maghfirah, L., & Mutia, F. (2023). Dampak Literasi
Bencana Terhadap Kesiapsiagaan Pustakawan
Perguruan Tinggi Negeri di Surabaya. BACA: Jurnal
Dokumentasi Dan Informasi, 44(2), 97–111.
https://doi.org/10.55981/baca.2023.927
Pratama, J. P., Dewo, L. P., & Rahmat, H. K. (2024). Model
Sinergitas Pentahelix dalam Rangka Pengurangan
Risiko Bencana di Indonesia : Sebuah Tinjauan
Pustaka. 1(1), 1–6.
Rahmat, H. K., Hasrian, H., & Bimantara, M. A. (2023).
Membangun Kesiapsiagaan Bencana pada Siswa
Melalui BLU-DISCARE sebagai Inovasi Pendidikan
Kebencanaan di Sekolah Guna Mewujudkan Generasi
Tangguh Bencana. Jagratara: Journal of Disaster
Research, 1(2), 49–58.
https://doi.org/10.35719/ijdr.v1i2.120
Rahmat, H. K., & Pernanda, S. (2021). The Importance Of
Disaster Risk Reduction Through The Participation Of
Person With Disabilities In Indonesia. Proceeding of
Batusangkar International Conference V, 137–148.
Rahmat, H. K., Ramadhani, R. M., Ma’rufah, N.,
Gustaman, F. A. I., Sumantri, S. H., & Adriyanto, A.
(2020). Bantuan China Berupa Alat Uji Cepat Covid-
19 Kepada Filipina: Perspektif Diplomacy and
International Lobbying Theory. Jurnal Pendidikan
Ilmu Sosial, 30(1), 19–27.
https://doi.org/10.23917/jpis.v30i1.10623
Rahmat, H. K., Sari, F. P., Hasanah, M., Pratiwi, S., Ikhsan,
A. M., Rahmanisa, R., Pernanda, S., & Fadil, A. M.
(2020). Upaya pengurangan risiko bencana melalui
pelibatan penyandang disabilitas di Indonesia: Sebuah
tinjauan kepustakaan. Jurnal Manajemen Bencana
(JMB), 6(2), 70–75.
https://doi.org/10.33172/jmb.v6i2.623
Rahmat, H. K., Widana, I. D. K. K., Basri, A. S. H., &
Musyrifin, Z. (2021). Analysis of Potential Disaster in
The New Capital of Indonesia and its Mitigation
Efforts: A Qualitative Approach. Disaster Advances,
14(3), 40–43.
Shalahuddin, I., Maulana, I., Pebrianti, S., & Eriyani, T.
(2022). Efektifitas pendidikan kebencanaan terkait
kesiapsiagaan penduduk di daerah rawan gempa: Studi
literatur. Holistik Jurnal Kesehatan, 16(2), 128–141.
https://doi.org/10.33024/hjk.v16i2.2079
Utama, D. B., Prewito, H. B., Pratikno, H., Kurniadi, Y. U.,
& Rahmat, H. K. (2020). Kapasitas pemerintah Desa
Dermaji Kabupaten Banyumas dalam pengurangan
risiko bencana. Nusantara: Jurnal Ilmu Pengetahuan
Sosial, 7(3), 591–606.
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
300
