
Integration of Digital Citizenship Values on Pancasila Education’s
Curriculum at Junior High School Level in Surabaya City
Harmanto
1 a
, Beti Indah Sari
1b
, Siti Maizul Habibah
1c
, Muhammad Abdul Ghofur
1d
,
Puspita Sari Sekardani
1
, Binar Kurnia Prahanani
1*
, Oksiana Jatiningsih
1e
, Noortje Anita Kumaat
1
,
Budi Santosa
1
, Rianda Usmi
1
, Wahyudi
1
and Dila Lintang Harmanto Putri
2
1
Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia
2
Universitas Diponegoro, Central Java, Indonesia
Keywords: Integration of values, Digital Citizenship, Pancasila Education Curriculum, Junior High School Level.
Abstract: In recent years, digital citizenship has become a very interesting topic to study, especially those who pursue
the field of Citizenship Education. The rapid development of digital learning encourages everyone, including
students and other human resources, to be ready to face change and be ready to change. Technological devices
that are balanced with social media such as WhatsApp, TikTok, Facebook, Twitter, and others bring very
fundamental changes in communication, including increased competence in digital citizenship. The purpose
of this study is to provide an overview of PPKn teachers regarding the integration of digital citizenship values
in Pancasila Education learning materials at the junior high school level. Therefore, the research method used
in this study is quantitative descriptive with PPKn teacher respondents at the junior high school level who are
selected porposively, namely the management of the Pancasila Education MGMP in Surabaya. The data
collection process is carried out using a survey, namely through the distribution of questionnaires to
respondents. The collected data was then analyzed descriptively using the IBM SPSS version 29 application.
The results of the study show that the majority of PPKn teachers stated that they strongly agree with the
integration of the values of (1) digital ethics, (2) digital law, and (3) digital rights and responsibilities
contained in digital citizenship as a basis for students to use information technology, and the internet in various
daily activities of students.
1 INTRODUCTION
Along with the rapid development of information and
communication technology, the lives of global people
have undergone transformations in various fields,
including education, economy, social, and culture.
Digital technology not only facilitates access to
information but also creates new spaces for social
interaction and political participation, thus impacting
the way individuals interact, access information, and
participate in social and political life (Scholl, 2009).
Furthermore, the impact of technological
developments is also the cause of the emergence of
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-6149-3942
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0259-0230
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7454-417X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2422-8144
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5973-1903
f
https://orcid.org/ 0009-0006-1902-9673
g
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-9432-7840
digital citizenship as a necessity for people to be able
to understand their rights and responsibilities in the
digital space, especially for the young generation who
grow up in the midst of technological advances (S.
Ribble & D. Bailey, 2004) Therefore, education plays
an important role in preparing the younger generation
to be able to adapt and act responsibly in the digital
world. This is reinforced by the opinion of Ribble,
(2015) which explains that digital citizenship is
closely related to values such as ethics, security,
responsibility, and the critical ability to use digital
technology for the common good. Thus, the concept
of digital citizenship emphasizes more on awareness,
Harmanto, , Sari, B. I., Habibah, S. M., Ghofur, M. A., Sekardani, P. S., Prahanani, B. K., Jatiningsih, O., Kumaat, N. A., Santosa, B., Usmi, R., Wahyudi, and Putri, D. L. H.
Integration of Digital Citizenship Values on Pancasila Education’s Curriculum at Junior High School Level in Surabaya City.
DOI: 10.5220/0013411100004654
In Proceedings of the 4th Inter national Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science (ICHELS 2024), pages 607-613
ISBN: 978-989-758-752-8
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
607

understanding, and mastery of digital skills that
enable individuals to participate positively, safely,
and ethically in the digital environment. This concept
has become very relevant for education in Indonesia,
especially in Civic Education which plays a role in
shaping the character of the younger generation as
active and responsible citizens (Mossberger &
Tolbert, 2021). In this case, the emergence of digital
citizenship is in line with the development of digital
learning which is increasingly adopted in the modern
education system. Digital-based learning has become
part of students' daily lives, both in academic
activities and in social activities. Through platforms
such as WhatsApp, TikTok, Facebook, and Twitter,
students have unlimited access to communicate and
obtain information. However, this convenience also
presents new challenges, such as privacy issues,
communication ethics, and the dissemination of
inaccurate information. Therefore, it is important for
students to understand the aspect of digital citizenship
as a foundation for participating in the digital space
responsibly (Howard, 2015).
In addition, Pancasila education not only focuses
on instilling the values of nationalism and patriotism
but also aims to develop critical thinking skills and
the ability to respect differences (Padilah & Dewi,
2021). However, in today's digital era, these values
need to be interpreted in a broader context, namely
through the digital context, to be relevant to the lives
of today's young generation. Thus, the integration of
digital citizenship in Pancasila Education can enrich
the curriculum and make it more relevant and
responsive to changing times (Prasadana et al., 2024;
Triyanto, 2020). This is in line with the goal of
implementing Pancasila Education in Indonesia,
which aims to form students with character and have
a strong national identity. Therefore, the subject of
Pancasila Education is one of the compulsory subjects
in schools because, in Indonesia, the subject of
Pancasila Education at the Junior High School (SMP)
level has an important role in shaping the character
and national identity of students. The values
contained in Pancasila can be the foundation for
integrating the concept of digital citizenship, which is
relevant to preparing students to face challenges in
the global era (Padilah & Dewi, 2021). In the city of
Surabaya, which is one of the cities with rapid
technological development, the need to integrate
digital citizenship values in the Pancasila Education
curriculum is becoming increasingly urgent. This is
driven by the fact that students in the digital era need
skills to actively and responsibly participate in the
digital world without forgetting national values
(Triyanto, 2020).
Although the integration of digital citizenship
values is increasingly recognized as important, its
practical implementation in school curricula still
faces various challenges. The Pancasila Education
curriculum in Indonesia still focuses on traditional
citizenship aspects, such as nationalism and
patriotism, and does not fully cover the digital
dimension that must be understood by the current
generation (Prasadana et al., 2024). In addition,
several studies show that teachers still face obstacles
in implementing digital citizenship due to the lack of
guidance and resources to support this learning
process (Mulyani et al., 2024; Prasadana et al., 2024).
Therefore, this study aims to explore how digital
citizenship values can be integrated into the Pancasila
Education curriculum at the junior high school level
in the city of Surabaya. This research is expected to
contribute to the development of a curriculum that is
responsive to the times and relevant to the needs of
the current digital generation. By integrating digital
citizenship in education, it is hoped that students will
not only have a deeper understanding of Pancasila but
also be able to apply these values in the digital
environment critically and responsibly.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 The Concept of Digital Citizenship
In recent decades, the concept of digital citizenship
has become a major topic in education and
community discussion. Digital citizenship is a
concept that develops along with the wider
penetration of technology in daily life, so digital
citizenship refers more to responsible, ethical, and
ethical behavior in the digital space, including how a
person uses information and communication
technology to interact and participate in society
positively (Ribble, 2012). This includes an
understanding of the rights, responsibilities, and rules
that govern cyberspace, as well as ways to actively
and positively participate in it. Furthermore, Ribble
(2015) has also identified nine basic elements of
digital citizenship consisting of digital access, digital
trade, digital communication, digital literacy, digital
ethics, digital law, digital rights and obligations,
digital health, and digital security. These elements are
designed to provide guidance for individuals to access
and use technology wisely and responsibly, which are
as follows:
• Digital Access: It relates to the right of
individuals to have access to digital technology.
This includes the availability of technological
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
608

devices, internet infrastructure, and the ability to
use those devices. In Indonesia, digital access is
a big challenge, especially in remote areas that do
not have adequate infrastructure (Choi, 2016)
• Digital Communication: Involves the ability to
communicate and collaborate through digital
platforms. With the advent of social media such
as WhatsApp, Instagram, and Twitter, digital
communication has become the primary means
for students to interact. However, digital
communication also poses new challenges such
as cyberbullying and the spread of hoaxes, which
require an understanding of digital ethics.(Jones
& Mitchell, 2016)
• Etika Digital: Refers to the moral rules that
govern interactions in cyberspace. Digital ethics
teach users to respect the privacy of others, avoid
harmful actions such as cyberbullying, and
understand the boundaries of acceptable
behavior in the digital space. Digital ethics are
very important for students to understand the
importance of positive and respectful behavior in
social media.(Gleason et al., 2018)
• Digital Law: This includes rules and regulations
governing the digital world, including laws
related to copyright, privacy, and intellectual
property rights. Digital law violations such as
content piracy and copyright infringement are
often a problem among students who do not
understand the rules of the law in
cyberspace.(Ribble, 2012)
• Digital Security: Involves measures to protect
personal data and privacy. In a digital world full
of risks such as hacking and online fraud,
students need to understand how to protect their
personal information and practice good digital
security (Ribble, 2015).
2.2 The Relevance of Digital
Citizenship in Education
According to Gleason et al., (2018) Digital
citizenship education not only aims to teach technical
skills, but also to help students develop the critical
thinking and social awareness necessary to interact
responsibly in the digital world. By being taught
digital citizenship, students are expected to have a
deeper understanding of positive behaviors and social
norms that apply in cyberspace. Therefore, digital
citizenship also emphasizes a critical understanding
of technology, including the ability to identify
trustworthy content, respect copyright, and protect
the privacy of oneself and others. In other words,
digital citizenship is a social skill that helps
individuals to participate positively and safely in the
digital world (Gleason et al., 2018). The importance
of this skill is increasingly felt considering the
increasing use of the internet and social media,
especially among the younger generation. Thus,
digital citizenship education has become relevant and
essential for students to prepare them as responsible
and adaptive citizens in an increasingly digital world.
However, the process of integrating digital
citizenship in the Pancasila Education curriculum in
Indonesia is not easy, especially due to various
obstacles, such as infrastructure, teacher knowledge,
and differences in the level of digital understanding
between students. This has an impact on the digital
divide between teachers in Indonesia. This is a major
challenge in terms of the digital divide, especially
between urban and rural areas, as there are still many
schools in remote areas that do not have adequate
internet access, which causes students in those areas
to have fewer opportunities to learn digital
citizenship. This has an impact on the inequality of
digital education, where students in cities have a
greater advantage in accessing technology compared
to students in remote areas (Triyanto, 2018). In
addition to the digital divide, obstacles and challenges
in the implementation of digital citizenship in
education and curriculum are also caused by the
limited knowledge of teachers as the main
implementers of the curriculum. This is closely
related to the role of teachers in providing digital
citizenship education to students. However, there are
still many Citizenship Education teachers in
Indonesia who are not familiar with the concept of
digital citizenship. The lack of adequate training and
resources makes it difficult for teachers to teach
digital skills to students. According to Prasadana et
al., (2024), intensive training for teachers on the
concept and implementation of digital citizenship is
essential to ensure that they can teach this material
effectively.
In addition, obstacles and challenges are also
caused by socio-cultural differences, which are
caused by the fact that Indonesia has a very wide
cultural diversity, and this affects students' views on
technology and digital interaction. Some regions have
norms that may be at odds with the use of modern
technology, leading to a rejection of digital
citizenship education. In addition, in certain
environments, there is a stigma towards the use of
social media and digital technology as negative or
unnecessary (Choi & Cristol, 2021). Digital
citizenship education must adapt to the local cultural
context so that it can be accepted by the community.
In addition, one of the main obstacles and challenges
Integration of Digital Citizenship Values on Pancasila Education’s Curriculum at Junior High School Level in Surabaya City
609

in integrating digital citizenship in Pancasila
educational materials and curriculum is also seen in
the burden of the curriculum that is already quite
dense, so that many teachers feel burdened with the
demand to deliver various materials in a limited time,
so they do not have enough time to teach digital
citizenship skills. To overcome this challenge, an
integrative approach that combines digital citizenship
with other Civic Education materials can be a solution
(Mulyani et al., 2024). In addition to these various
obstacles and challenges, the application of digital
citizenship in the Pancasila curriculum and
educational materials is also able to bring positive
opportunities such as being able to increase social
awareness through social media. This is closely
related to the great potential of social media that can
be used as a means of digital citizenship education.
For example, through the utilization/use of platforms
such as Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp can be
used to build learning communities and discuss issues
related to digital citizenship. For example, students
can be invited to discuss digital ethics through online
discussion groups, or share information on how to
protect privacy on social media (Gleason et al., 2018).
In addition, the integration of digital citizenship
values in the educational curriculum at the junior high
school level can also be used to open up opportunities
and opportunities to collaborate with technology
companies such as Google, Microsoft, and social
media platforms can help develop relevant learning
resources and materials for digital citizenship
education.
Many technology companies provide digital
literacy and online safety programs that can be used
by schools in Indonesia. This collaboration not only
provides access to additional resources, but also helps
reduce the burden on teachers in preparing learning
materials (Jones & Mitchell, 2016). In line with this,
through the integration of digital citizenship values, it
can also be carried out and implemented through the
learning process, namely through the use of a project-
based learning approach that can be applied to teach
digital citizenship to students. In this approach,
students can be given the task of creating a project
involving digital technology, such as creating an
online campaign on digital ethics or developing a
guide on how to use social media wisely. This
approach allows students to learn directly and
actively, as well as apply their knowledge in relevant
contexts (Gleason et al., 2018)
3 RESEARCH METHODS
3.1 Research Design
This study uses a descriptive quantitative design to
provide a general overview of teachers' responses
related to the integration of digital ethical values,
digital laws, and digital rights and responsibilities
contained in digital citizenship into Pancasila
education materials through the integration of these
values in the Pancasila Education curriculum in
accordance with the relevant phases in the Pancasila
Education curriculum.
3.2 Respondent
The context in this study is the level of digital
citizenship competence owned by teachers related to
Pancasila education materials that are relevant to
digital citizenship competencies included in the
management of MGMP Pancasila Education at the
junior high school level in the city of Surabaya. The
research sample was taken from several schools in the
city of Surabaya which were selected by probability
sampling because it was possible to choose based on
a random sample that was convenient to use in the
study (Mertens, 2015). A total of 63 Pancasila
education teachers who are included in the MGMP
management were successfully collected and
involved as participants in the process of filling out
an online questionnaire developed by the researcher
in accordance with the objectives of this study.
3.3 Instrument Development
The development of the instrument in this study was
compiled and developed by researchers related to the
integration of materials in Pancasila education that
are relevant and related to digital citizenship
competencies in teachers as a parameter for
measuring skills related to knowledge and
understanding of digital citizenship that is relevant
and related to Pancasila Education materials at the
junior high school level based on the concept of nine
elements of digital citizenship from (Ribble, 2015),
which in this article only focuses on three elements of
teachers' digital citizenship competencies which
include digital ethics, digital law, and digital rights
and obligations that are relevant to the characteristics
of Pancasila Education subjects, namely Stage D
which is measured using measurement parameters
using a 4-point likert measurement scale with an
interval of 4 = strongly agree with 1 = strongly
disagree with a total of 37 items.
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
610
4 RESULTS AND DISSCUSSION
4.1 Profil Respondent
Of the 63 respondents, the majority of respondents
were female teachers, namely 43 teachers (68.3%)
dominated by teachers with an age range of more than
40 years, as many as 24 teachers (38.1%) followed by
teachers with an age range between 31-35 years and
26-30 years, namely 13 teachers (17.6%) and 12
teachers (16.2%), respectively. Meanwhile, in the
aspect of teaching for a long time, there are 16
teachers (25.4%) who have taught for 6-10 years, and
there are 13 teachers (20.6%) who have taught for 11-
15 years and more than 21 years, respectively.
Meanwhile, the least number of teachers was found in
the teaching period of 3-5 years, which was as many
as 5 teachers (7.9%). The full description can be seen
in Table 1.
Table 1: Respondent Demographics.
Teacher
Characteristics
F (n=63)
Persentase
(%)
Jenis kelamin
Male 20 31,7
Female 43 68,3
A
g
e
≤ 25 years ol
d
8 12,7
26-30 years ol
d
9 14,3
31-35
y
ears ol
d
14 22,2
36-40
y
ears ol
d
8 12,7
≥ 41
y
ears ol
d
24 38,1
Teaching Duration
1-2 yea
r
10 15,9
3-5 yea
r
5 7,9
6-10
y
ea
r
16 25,4
11-15 t
y
ea
r
13 20,6
16-20
y
ea
r
6 9,5
≥ 21 yea
r
13 20,6
Furthermore, in this study, it was also found that
the results of the description/general description of
the opinions of junior high school teachers regarding
the integration of digital citizenship values in the
Pancasila Education curriculum in the city of
Surabaya were also found. The distribution of
respondents' responses has been presented in full in
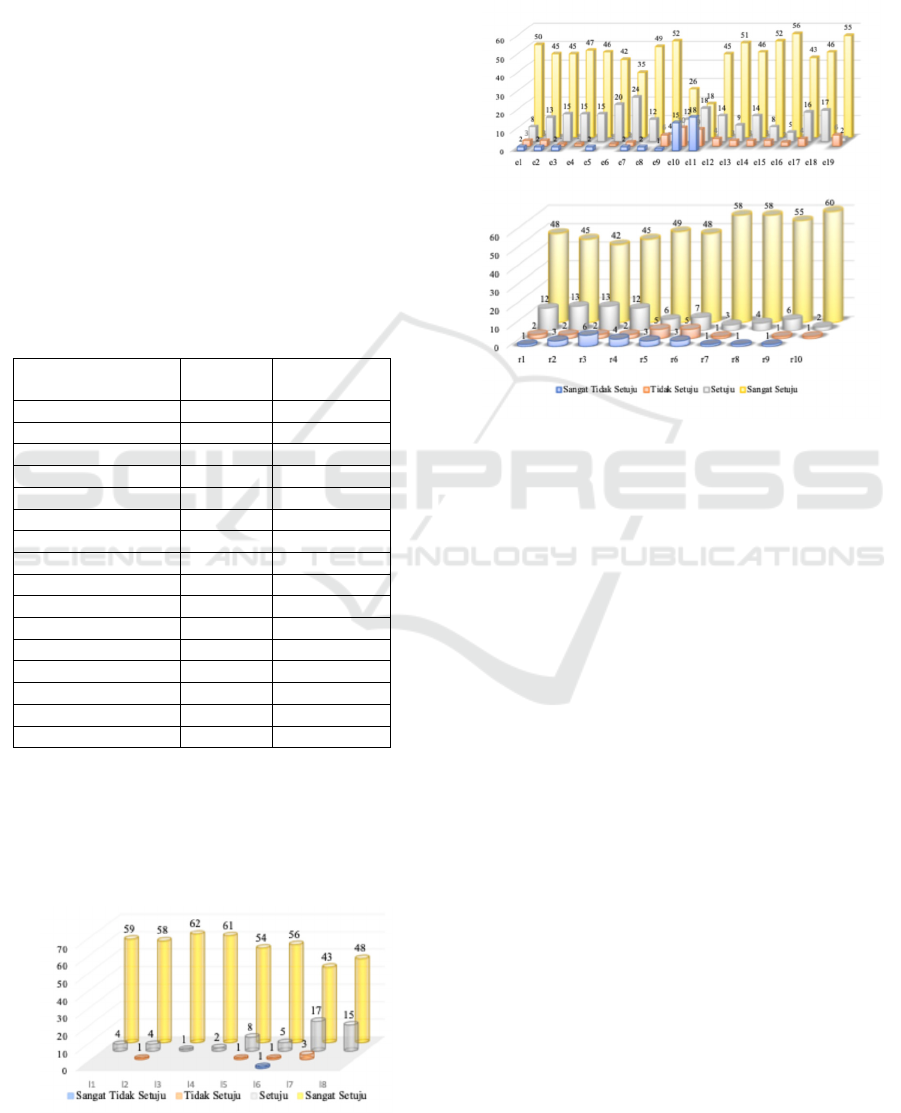
figures 1, 2 and 3.
Figure 1: Distribution of Respondents' Responses
Regarding Digital Ethics
Figure 2: Distribution of Respondents' Responses on
Digital Law
Figure 3: Distribution of Respondents' Responses on
Digital Citizenship Rights and Responsibility
Figures 1, 2 and 3 present the distribution of
respondents' response frequencies related to the
integration of digital citizenship values in the
Pancasila education curriculum. From the three
diagrams, it shows that both in terms of digital ethical
values, digital laws and rights and obligations in
digital citizenship, the majority of respondents stated
that they strongly agree with the integration of digital
citizenship values into the Pancasila education
curriculum. In line with this, the integration of digital
ethics values, digital law and digital ethics in learning
through the use of digital platforms that are able to
provide valuable new insights and knowledge into the
application to its users.
These platforms include social media, learning
management systems, and online forums, as well as
significant opportunities to foster the value of digital
ethics, digital law and digital ethics through guided
use, content regulation, and digital literacy programs.
In addition, the integration of digital citizenship
education values in this study is expected to be able
to explore potential strategies for educators and
policymakers, such as implementing ethical online
behavior guidelines, as well as promoting awareness
of digital law to students. This is reinforced by the
results of several research related to digital ethics,
digital law and digital responsiveness that have been
Integration of Digital Citizenship Values on Pancasila Education’s Curriculum at Junior High School Level in Surabaya City
611

carried out previously, finding that digital platforms
can support and be used in increasing the value of
digital ethics, digital law and digital responsiveness
in students.
Hollandsworth et al., (2011) argue that the
integration of digital platforms in learning, such as the
use of LMS such as google classroom or moodle as a
means to provide a forum for students to discuss, has
indirectly educated students to behave politely and
respect the opinions of other students by paying
attention to every word conveyed in online
discussions. Meanwhile, the use of other digital
platforms, such as youtube and instagram, can also be
used to strengthen student digital laws, namely
related to copyright infringement or data protection
that has been regulated in laws such as the ITE Law
in Indonesia (Livingstone & Third, 2017). In line with
the above explanation, Ribble, 2015) also explained
that online discussion forums such as Google can
provide a space for students to practice freedom of
expression in accordance with clear guidelines on
responsible content.
However, the use of digital platforms such as
social media in learning can also have a negative
impact on students if teachers are not able to make the
best use of the platform. In addition, access to the use
of the internet by students is also one of the aspects
that must be considered, in addition to students'
ability to use and utilize the internet in their various
activities. This is one of the obstacles that teachers
must pay attention to. Thus, to be able to overcome
this, various preparations are needed from teachers,
so that learning in the classroom can run optimally by
utilizing various existing digital platforms.
5 RESEARCH CONCLUSIONS
This study aims to provide an overview of the
responses of Pancasila Education teachers regarding
the integration of digital citizenship values in
Pancasila Education materials. In this study, it is
known that of the 63 PPKn teachers at the State Junior
High School (SMPN) level in the city of Surabaya,
the majority stated that they strongly agreed with the
integration of digital citizenship values into the
Pancasila Education curriculum as an effort to
prepare students to face various challenges and
obstacles that students will face in the current era of
disruption.
The integration of digital citizenship values into
the Pancasila curriculum and educational materials
also aims to be the basis for students to take advantage
of the use of technology in carrying out digital
activities. Thus, students can avoid various negative
activities that can harm themselves and others and can
be used as a provision for students in facing various
obstacles and challenges that may be faced by
students in the future. In addition, by integrating these
values in Pancasila Education materials, it is hoped
that students can be more aware and more responsible
for all actions they take in the online sphere that can
harm themselves and others.
6 COPYRIGHT FORM
For the mutual benefit and protection of Authors and
Publishers, it is necessary that Authors provide
formal written Consent to Publish and Transfer of
Copyright before publication of the Book. The signed
Consent ensures that the publisher has the Author’s
authorization to publish the Contribution.
The copyright form is located on the authors’
reserved area.
The form should be completed and signed by one
author on behalf of all the other authors.
7 CONCLUSIONS
We hope you find the information in this template
useful in the preparation of your submission.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the
postgraduate program of the State University of
Surabaya for providing important funding support for
the completion of this research.
REFERENCES
Choi, M. (2016). A Concept Analysis of Digital Citizenship
for Democratic Citizenship Education in the Internet
Age. 44(4), 565–607.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00933104.2016.1210549
Choi, M., & Cristol, D. (2021). Digital citizenship with
intersectionality lens: Towards participatory
democracy driven digital citizenship education. Theory
Into Practice, 60(4), 361–370.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00405841.2021.1987094
Gleason, B., Gillern, S. von, & von Gillern, S. (2018).
Digital Citizenship With Social Media: Participatory
Practices of Teaching and Learning in Secondary
ICHELS 2024 - The International Conference on Humanities Education, Law, and Social Science
612

Education. Educational Technology & Society, 21(1),
200–212. www.commonsense.org
Hollandsworth, R., Dowdy, L., & Donovan, J. (2011).
Digital Citizenship in K-12: It Takes a Village.
TechTrends, 55(4), 37–47.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-011-0510-z
Howard, P. (2015). Digital Citizenship in the Afterschool
Space: Implications for Education for Sustainable
Development. Journal of Teacher Education for
Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1515/jtes-2015-0002
Jones, L. M., & Mitchell, K. J. (2016). Defining and
measuring youth digital citizenship. New Media &
Society, 18(9), 2063–2079.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444815577797
Livingstone, S., & Third, A. (2017). Children and young
people’s rights in the digital age: An emerging agenda.
New Media & Society, 19(5), 657–670.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444816686318
Mertens, D. M. (2015). Research and Evaluation in
Education and Psychology: Integrating Diversity with
Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed Methods /. In
SAGE Publications (Vol. 4, Issue 1).
https://revistas.ufrj.br/index.php/rce/article/download/
1659/1508%0Ahttp://hipatiapress.com/hpjournals/inde
x.php/qre/article/view/1348%5Cnhttp://www.tandfonli
ne.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09500799708666915%5Cnhtt
ps://mckinseyonsociety.com/downloads/reports/Educa
Mossberger, K., & Tolbert, C. J. (2021). Digital Citizenship
and Digital Communities: How Technology Matters for
Individuals and Communities. International Journal of
E-Planning Research, 10(3), 19–34.
https://doi.org/10.4018/IJEPR.20210701.OA2
Mulyani, H., Komalasari, K., Permatasari, M., Bribin, M.
L., & Suriaman, S. (2024). Transformasi Pendidikan
Kewarganegaraan Global di Era Abad 21: Analisis
Implementasi dan Tantangan. Jurnal
Kewarganegaraan, 21(1), 88.
https://doi.org/10.24114/jk.v21i1.55115
Padilah, A. N., & Dewi, D. A. (2021). Nilai moral Pancasila
untuk membangun bangsa di era globalisasi. Jurnal
Citizenship: Media Publikasi Pendidikan Pancasila
Dan Kewarganegaraan, 4(2), 82.
https://doi.org/10.12928/citizenship.v4i2.20536
Prasadana, M. A. F., Akbar, F., & Zahwa, St. (2024).
Peluang dan Tantangan Implementasi Nilai-Nilai
Pancasila melalui Pemanfaatan Microsoft Copilot
dalam Pembelajaran di Era Digital. Prosiding Seminar
Nasional Ilmu Pendidikan, 1(1), 167–174.
https://doi.org/10.62951/prosemnasipi.v1i1.19
Ribble. (2015). Understanding Digital Citizenship. Iste, 9–
22.
Ribble, M. (2012). Digital Citizenship for Educational
Change. Kappa Delta Pi Record, 48(4), 148–151.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00228958.2012.734015
S. Ribble, M., & D. Bailey, G. (2004). Digital Citizenship
Focus Questions For Implementation. In
Learning &
Leading with Technology (Vol. 32).
http://www.iste.org/
Scholl, R. M. (2009). Media and Political Engagement:
Citizens, Communication, and Democracy, by Peter
Dahlgren. Political Communication, 26(4), 477–479.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10584600903297430
Triyanto, T. (2018). Enhancing Student Scientific Attitudes
Towards Civic Education Lesson Through Inquiry-
Based Learning. Journal of Education and Learning
(Edulearn).
https://doi.org/10.11591/edulearn.v12i2.8489
Triyanto, T. (2020). Peluang dan tantangan pendidikan
karakter di era digital. Jurnal Civics: Media Kajian
Kewarganegaraan, 17(2), 175–184.
https://doi.org/10.21831/jc.v17i2.35476
Integration of Digital Citizenship Values on Pancasila Education’s Curriculum at Junior High School Level in Surabaya City
613
