
The Technical Application of Blockchain in the Field of Cold
Chain Logistics
Yicheng Wang
Information Security, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
Keywords: Blockchain, Cold Chain Logistics, Information Traceability.
Abstract: While cold chain logistics is not a brand-new technology, it does have certain drawbacks, such as insufficient
product security, limited digitalization in related processes, and high costs. However, the utilization of
blockchain technology in cold chain logistics is a comparatively recent development that offers numerous
benefits. Three fields of applications have been identified based on pertinent research literature: fresh food,
medicine, and food. The precise application methods of merging blockchain with other technologies were
introduced separately. If an emergency blood trading plan is offered, the information monitoring, disclosure,
and traceability functions of fresh items, and the efficient resource allocation plan for food trading are
proposed to obtain maximum benefits. Research has shown that the use of blockchain in conjunction with
other technologies makes information on the chain publicly available, allowing for effective information
querying and monitoring across a range of processes and emphasizing the benefits of lower logistics costs.
Additionally, weaknesses and opportunities were mentioned at the same time.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a special supply chain system, cold chain plays an
important part in many areas like food safety, medical
product preservation and economic trade. A special
kind of logistics is called cold chain logistics, which
is defined as "a systematic project in which
refrigerated and frozen foods are kept in a specified
low-temperature environment at all stages of
production, storage, transportation, sales, and
consumption to ensure food quality and reduce food
loss (Dong et al. 2021)." By keeping an environment
at a low temperature, it tries to preserve the safety and
quality of perishable foods and short-term
medications. Cold Chain Logistics (CCL) has a
number of traits, including high implementation
costs, demanding technical support and challenging
monitoring in transportation process. As a result,
perfecting the cold chain presents a significant
difficulty. However, if substantial progress is made,
the advancement of cold chain logistics will have a
profound positive impact on economic trade and the
quality of life in modern society. In terms of the
traditional cold chain logistics, there are some
limitations. For example, because CCL is at an
inadequate level of digitalization, so real-time access
to a wealth of information is impeded, and product
quality and safety are tightly under control (Han et al.
2021). At the same time, in the absence of digital cold
chain logistics, temperature monitoring and
adjustment are delayed, posing a risk to logistics and
subsequently compromising business performance
(Ali et al. 2018).
Blockchain was first proposed by Satoshi
Nakamoto in 2008, since then it has progressively
grown to become a widely recognized technology that
now is being continuously developed, studied and
used in a variety of industries (Sarmah 2018). These
days, cold chain logistics and blockchain are
combined in a lot of technologies. Combining cold
chain logistics with blockchain technology has many
benefits. For example, it can lower transaction costs
by reducing the number of middlemen involved in the
transaction process and streamlining operations
(Mendonça et al. 2021). This not only makes
decentralized and quick public transactions possible,
but it also minimizes costs, saves time on products
transit, and keeps the environment at the proper
temperature while guaranteeing the quality of the
items. Blockchain increases the transparency and
public availability of supply chain data, which
encourages medical facilities to share blood supplies
and optimizes resource use (Kim et al. 2020).
Wang, Y.
The Technical Application of Blockchain in the Field of Cold Chain Logistics.
DOI: 10.5220/0013338000004558
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Modern Logistics and Supply Chain Management (MLSCM 2024), pages 461-466
ISBN: 978-989-758-738-2
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
461

Utilizing blockchain technology can also lead to on-
chain data traceability and monitoring, which makes
it be able to efficiently construct an effective cold
chain logistics and satisfy the needs of several parties
in terms of services (Tian 2017), it can also
minimizing transaction errors and the spread of fake
goods (Agarwal et al. 2022). It is evident that the use
of blockchain technology is crucial for cold chain
logistics, and cold chain logistics can be greatly
improved.
However, these innovations are still in the early
stages of development, and before they can be used,
more must be proposed, tested, and refined.
Therefore, it is necessary to provide a comprehensive
review on how blockchain has been applied in cold
chain logistics. The rest sections of this paper will
make a detailed analysis on how blockchain
technology is being used in cold chain logistics and
offer pertinent potential problems and future
development opportunities.
2 METHODS
2.1 Introduction of Blockchain
Technology
Blockchain creates a distributed database by using
encryption methods to connect a number of
chronologically ordered data blocks. Users start
transactions on the blockchain, broadcast transaction
information publicly, and the network verifies it. This
is the fundamental way the blockchain operates.
Through consensus processes, nodes validate
transactions and matching blocks; if the verification
is successful, the transactions and accompanying
blocks are appended to the blockchain (Puthal et al.
2018). The information is kept open and united thanks
to blockchain's decentralization, consensus process,
and transparency. By joining the transaction data
contained in the block together with their hash values,
it creates a chain that makes it simple to follow any
step in the transaction chain. The data is encrypted for
security and to prevent tampering. This essentially
stops fraudulent transactions because all nodes must
come to a consensus before making any modifications
to the data. However, there are still a lot of
blockchain-related areas that need to be developed
and improved, like how to scale up, improve
information anonymity, efficiently minimize energy
consumption, and further safeguard data security
(Yli-Huumo et al. 2016).
2.2 Blockchain in Medical Cold Chain
Logistics
The application of blockchain in medical cold chain
logistics is an important direction. Kim et al.
proposed a system based on the Hyperledger Fabric
private blockchain technology in the study. It
involves the design and development of a novel blood
cold chain system that facilitates emergency blood
transactions between hospitals and records blood
information via a distributed ledger. The transaction
contains nodes in the blockchain made of participants
and validators, who validate each link of the
transaction, record consensus information on the state
of blood and transaction content, and update blood
inventory information in various hospitals (Kim et al.
2020).
The use of pharmaceutical cold chain
management is the second application. Using
blockchain technology and the Internet of Things to
control the pharmaceutical cold chain is one way to
find a solution. The cloud storage module stores the
pertinent data signatures for registering medications.
The generated drug information will be added to the
blockchain and the registration request will be
verified by the next blockchain platform. Based on
the medicine information in the blockchain, the cold
chain warehouse simultaneously asks the IoT
monitoring module for a data storage address. The
blockchain platform will also authenticate the drug
related information provided by the cold chain
warehouse and write it into the blockchain. Another
strategy is to figure out the ideal level of cold chain
inventory and manage it based on drug storage data
stored in blockchain (Zhang et al. 2021).
2.3 Blockchain in Fresh Agricultural
Cold Chain Logistics
One application addresses the issues of data storage
and transaction permissions in cold chain logistics by
putting forth a multi-mode agricultural cold chain
logistics model based on blockchain data model. In
order to save the file index hash value, Si proposed a
method that first creates a dual structure consisting of
a private chain and an alliance chain. Alliance chains
are used to search and share information, while
private chains are used to collect and store
information. Smart contracts were later created
independently for each of the two chains. Upon
completion of the transaction, the endorsing node on
the smart contract executes the transaction request
that was started by the client and returns the
transaction outcome. After that, the transaction data
MLSCM 2024 - International Conference on Modern Logistics and Supply Chain Management
462

package is distributed to every node for validation
and is updated in the blockchain copy (Si 2022).
Blockchain is also employed in the traceability
system of cold chain logistics for agricultural
products. Tracing the information flow inside the
system is the most essential step. All information
pertaining to the planting, processing, storing,
shipping, and selling procedures is included in this
information flow, including standard product data,
temperature of the surrounding environment, product
quality, intervals of time, and other pertinent
information. The QR code on the box will store these
streams of information. A dual chain structure is also
used by the traceability system. This structure
consists of operation layer, data acquisition layer,
data layer, consensus and network layer, presentation
layer, and user layer. Key blockchain technologies,
like peer-to-peer networks, propagation and
authentication procedures, PoW and PoS consensus
techniques, etc., are included in the consensus and
network layers. It uses two different methods of data
storage: full data is kept in a relational database and
data summaries are kept on the blockchain network
(Zhang et al. 2022).
2.4 Blockchain in Food Cold Chain
Logistics
Zhang et al. suggested a blockchain-based distributed
cold chain logistics system and allocated resources
using the Stackelberg game model. A decentralized
cold chain logistics alliance is formed, bringing
together all the institutions and users involved in
transactions, based on the Hyperledger Fabric idea.
The traceability function can be attained by this
model, and in the end, game theory can be used to
identify the best resource price and quantity that
maximizes gains for all stakeholders (Zhang et al.
2023).
Another application is suggested that it is a
blockchain-based cold chain supply chain system.
There are four layers in this structure: the application
layer, platform layer, data layer, and physical layer.
In addition to the B/S structure and web front-end
interface utilized in the application layer, all food-
related data connected to all operations will be stored
in the chain for simple one-click viewing. This will
give users access to data interfaces that facilitate
information exchange and traceability (Fu & Dong
2023).
3 DISCUSSION
3.1 Advantages of Blockchain
Technology in Different Scenarios
The benefits of blockchain technology in various
industries can be summed up by looking at the study
mentioned above. First, information disclosure can be
achieved by directly storing the status information of
traded products in linked fields in the chain, which is
made possible by the structure and features of
blockchain technology. Consensus methods are
employed by blockchain technology to ensure data
consistency and prevent malicious attacks that alter
data. Data can be swiftly synchronized to the
blockchain, decreasing the likelihood of fraud, when
multiple technologies, such as GPS positioning
systems, are combined to locate the transportation
process and real-time information monitoring is
accomplished through various technologies in the
Internet of Things (IoT). By simply scanning the
relevant QR code, customers can quickly grasp the
details of each product link and subsequently
purchase the item with confidence, all while having
faith in the product's transaction process based on
publicly accessible information. It can increase cold
chain logistics efficiency in addition to stimulating
economic growth and consumption. This is a
thorough examination of the technology.
In terms of the medical field, Kim et al.’s
proposed blockchain-based emergency blood supply
cold chain system design efficiently reduces the time
required for verification and transportation across
several links in accordance with the overall state of
the blood supply, freeing up critical time for patient
rescue (Kim et al. 2020). For patients, blood type
matching and status information are crucial.
Physicians can use donated blood from other
hospitals with confidence thanks to real-time
information sharing and disclosure enabled by IoT
and Hyperledger Fabric technology. Additionally, it
raises the pace at which blood is utilized.
Store drug lifecycle data on the blockchain so that
consumers can utilize timestamps to trace back
depending on certain time points. It is much less
expensive and takes up less room to store hash values
simultaneously rather than the entire original piece of
data.
In terms of the agricultural field, when real-time
data from IOT is coupled with agricultural or
transportation processes, items can be checked
promptly based on quality standards. This allows for
the early use of resources to cultivate the next batch
of products, saving time and money on unqualified
The Technical Application of Blockchain in the Field of Cold Chain Logistics
463
products. Users' purchases of products will rise as a
result, significantly raising the qualification rate of
products exchanged in the market. Consumption is
encouraged by this.
The dual chain structure of blockchain is used in
the process of implementing data traceability.
Enterprises use the private chain for private purposes,
which can achieve information concealment, while
the consortium chain stores hash values for viewing
shared information for simple traceability. The
enterprise's anonymity is further safeguarded by the
difficulty of deciphering the hash value, even in cases
where the information is publicly accessible.
Additionally, the two chains operate separately, have
no effect on one another, and inspire confidence in the
system's security in users.
In terms of the food field, the blockchain's public
data disclosure leverages pre-existing decision
models for thorough analysis, shortens the time spent
by both parties negotiating their objectives ,
effectively maximizing revenues and minimizing
disputes between participants. Additionally, due to
the disclosure of information, it can stop one party
from committing transaction fraud. In addition, it can
guarantee food safety and lower the possibility of
mishaps for both sides.
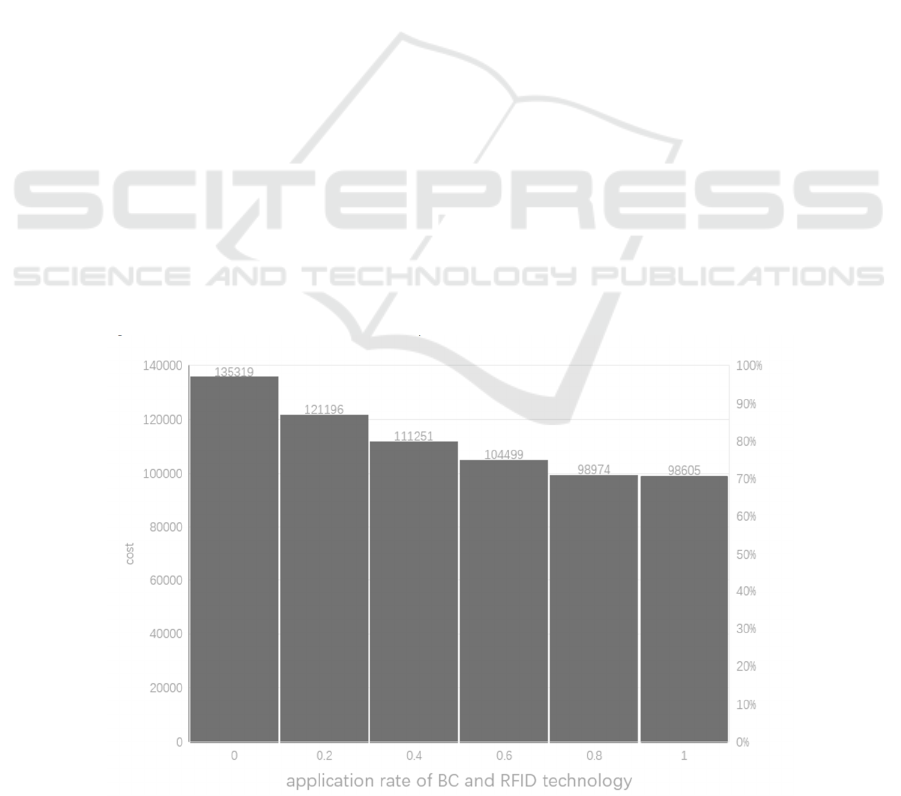
Analyzing a research model that can be applied to
assess the cost analysis of BC technology at various
application levels in the food cold chain is the
following part. It is a study conducted by Zixuan L et
al. regarding the impact of blockchain and Radio
Frequency Identification (RFID) technologies on
cold chain logistics costs (Liu et al. 2022). They
developed a cost calculation model, and the Fig. 1
displays the final results derived from the data.
It can be concluded that the use of blockchain
technology may successfully cut the cost of cold
chain logistics because the table makes it evident that
the more the percentage of blockchain and RFID
technology applications, the cheaper the cost
compared to not applying them.
3.2 Challenges and Future Work
But as of right now, there are still certain challenges
and restrictions with this technology. For example,
there might be a greater need for computer processing
power. Each link needs computer power sufficient to
meet the requirements for chain data in order to obtain
complete information about the chain. As the number
of links in various cold chain domains increases, so
does the number of verification nodes. As a result,
there is a greater need for processing power to update
and store data nodes.
Secondly, it is found from the entire procedure
that the cold chain needs to store a massive amount of
data. A significant quantity of storage space is
undoubtedly needed if different product kinds and
transaction chain data are saved on the blockchain.
Additional development is necessary to expand the
storage space.
There must be chances and directions for future
development because the current state of affairs
presents obstacles and restrictions. For instance,
conquering current obstacles, overcoming
constraints, and taking on challenges head-on.
Figure 1: Costs in different situation (Liu et al. 2022).
MLSCM 2024 - International Conference on Modern Logistics and Supply Chain Management
464

There are now no defined regulations in this area
due to the ongoing development of blockchain
applications in big cold chain systems; therefore,
industry guidelines and pertinent regulatory
constraints must be harmonized. For instance,to place
restrictions on integrity, utilizing information
transparency to support hierarchical management is a
good method .
At the same time new technological integrations
to automate specific workflows can be added. To
automatically verify the quality of products in terms
of cold and fresh food after monitoring data and
uploading it, CCL based on BC can also utilize
machines or internal programs. If it is practical, the
next future work is to find ways to enhance the
utilization rate of cold chain resources for products by
promptly providing feedback to product responsible
personnel. Or, when paired with AI, robots can take
the place of people in order to do tasks. By doing this,
tasks can be done more accurately and efficiently
while reducing human mistake.
In conclusion, the use of blockchain technology in
cold chain logistics remains relatively new, hence
potentially expanding the technology's potential
applications. For example, expanding application
mode in financial sector.
4 CONCLUSION
The implementation of blockchain-related
technologies in cold chain logistics for
pharmaceuticals, fresh agricultural items, and food is
detailed in this paper, which also introduces
blockchain technology and cold chain logistics. It is
clear from the study of technology applications that
cold chain logistics has benefited greatly from the use
of blockchain technology. Improving the quality of
real life is the ultimate goal, starting with streamlining
and regulating the logistics process, cutting costs, and
effectively meeting the fundamental needs of cold
chain logistics throughout the entire process, like
environmental temperature. All information is then
integrated into the blockchain to achieve information
disclosure and security maintenance. Furthermore,
blockchain still has a lot of issues. Being a relatively
new technology, there are evident problems that need
to be resolved, like the lack of pertinent laws and
industry regulations. If there are weaknesses, there
are certain areas that require improvement. Based on
current research and market analysis, cold chain
logistics supported by blockchain offers high
development potential because the technology is still
in its early stages of research and development and
has not yet reached a large enough user base.
REFERENCES
D. Puthal, N. Malik, S. P. Mohanty, et al. 2018.
Everything you wanted to know about the blockchain:
Its promise, components, processes, and problems.
IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 7(4): 6-14.
F. Tian. 2017. A supply chain traceability system for food
safety based on HACCP, blockchain & Internet of
things. In: International conference on service systems
and service management. IEEE, 1-6.
I. Ali, S. Nagalingam, B. Gurd. 2018. A resilience model
for cold chain logistics of perishable products. The
International Journal of Logistics Management, 29(3):
922-941.
J. W. Han, M. Zuo, W. Y. Zhu, et al. 2021. A
comprehensive review of cold chain logistics for fresh
agricultural products: Current status, challenges, and
future trends. Trends in Food Science & Technology,
109: 536-551.
J. Yli-Huumo, D. Ko, S. Choi, et al. 2016. Where is current
research on blockchain technology? A systematic
review. PLoS One, 11(10): e0163477.
L. B. Fu, C. Y. Dong. 2023. Research on the Construction
of Food Cold Chain Supply Chain System Based on
Blockchain. Chinese Market, (10): 20-23.
P. Zhang, X. Liu, W. Li, et al. 2021. Pharmaceutical cold
chain management based on blockchain and deep
learning. Journal of Internet Technology, 22(7): 1531-
1542.
R. D. Mendonça, O. S. Gomes, L. F. M. Vieira, et al. 2021.
Blockcoldchain: Vaccine cold chain blockchain. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2104.14357.
S. Kim, J. Kim, D. Kim. 2020. Implementation of a blood
cold chain system using blockchain technology.
Applied Sciences, 10(9): 3330.
S. S. Sarmah. 2018. Understanding blockchain technology.
Computer Science and Engineering, 8(2): 23-29.
U. Agarwal, V. Rishiwal, S. Tanwar, et al. 2022.
Blockchain technology for secure supply chain
management: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access,
10: 85493-85517.
X. Zhang, Y. Sun, Y. Sun. 2022. Research on cold chain
logistics traceability system of fresh agricultural
products based on blockchain. Computational
Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2022(1): 1957957.
Y. Dong, M. Xu, S. A. Miller. 2021. Overview of cold chain
development in China and methods of studying its
environmental impacts. Environmental Research
Communications, 2(12): 122002.
Y. Si. 2022. Agricultural Cold Chain Logistics Mode Based
on Multi‐Mode Blockchain Data Model. Computa-tional
Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2022(1): 8060765.
Y. Zhang, C. Li, X. Xin. 2023. Stackelberg game-based
resource allocation with blockchain for cold-chain
The Technical Application of Blockchain in the Field of Cold Chain Logistics
465

logistics system. Computers, Materials & Continua,
75(2): 2429-2442.
Z. X. Liu, J. X. Li, L. W. Song. 2022. Cost Analysis of Cold
Chain Logistics Based on Blockchain and RFID
Technology. Journal of Wuhan University of
Technology (Information and Management
Engineering Edition), 44(1): 75-83.
MLSCM 2024 - International Conference on Modern Logistics and Supply Chain Management
466
