
Designing a Sumatran Tiger Motif as an Effort to Increase Public
Awareness in Protecting the Crisis of Protected Animal’s Populations
in Indonesia
Jovany Margareth Depthios, Niken Savitri Anggraeni, Andra Rizky Yuwono and Rahmat Zulfikar
Desain Komunikasi Visual (Kampus Kota Makassar), Universitas Ciputra Surabaya,
Kawasan CitraLand City CPI, Jalan Sunset Boulevard, Makassar, Indonesia
Keywords: Communication, Motifs, Sumatran Tiger, Sustainability, Population, Protected Animals.
Abstract: The Sumatran Tiger is one of faunae which is threatened with extinction due to illegal logging and hunting.
In efforts to protect the Sumatran Tiger, management and conservation, habitat monitoring, trade law
enforcement, confiscation and rehabilitation of suspected violators are carried out. However, public awareness
still needs to be increased regarding the population condition of this species. Communication in various forms
is needed to convey messages to the public. One of them that can be used is visual communication, which is
a creative process that conveys ideas from art and technology guides. The aim of this research is to raise
public awareness of the conservation of the endangered Sumatran tiger through developing motifs on fabric.
For this reason, a design is needed that is able to communicate the message so that it is easily understood by
the public. The method used is to first design a motif based on observations and interviews with the target
audience, then distribute a questionnaire to the target audience regarding their perceptions and impressions of
the motif.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sumatra is one of the islands that has large mining
wealth in Indonesia such as gold, silver, nickel, etc.,
so it has a positive impact on national development.
Apart from that, Sumatra also has varied flora and
fauna. One of the famous faunae is the Sumatran
Tiger which is threatened with extinction. In 1996 the
Sumatran Tiger was in the Critical Endangered level
according to IUCN (International Union for
Conservation of Nature) data. It is estimated that in
1992, the remaining animal population was 400 in
five national parks. Sumatran Tigers have spread
from Aceh to Lampung numbering 600 heads but fell
to 400 heads in 2004. Although in 2012 there were
618 heads however the animal’s population dropped
drastically to 371 heads in 2016. (Khoirunnisa and
Mahendra, 2021).
The decline in animal population is caused by
logging and illegal hunting. Illegal logging in
Sembilang National Park in the SPTN III area which
has been carried out by the society has caused the loss
of natural animal habitat. Hunting for wild animals
was carried out by luring, snares and shooting,
thereby threatening the sustainability of the Sumatran
Tiger. Lastly, there is a lack of public awareness
regarding the threat of extinction of the Sumatran
Tiger (Paiman et al., 2018). Based on POLDA
(Mirwazi Regional Police) data, there were 15 cases
of wildlife trafficking, such as the trade of Sumatran
Tiger furs in Aceh in 2014. In 2015 there were 10
cases until 2016, the Aceh POLDA succeeded in
handling these cases in Bireun Regency (Lestari and
Efendi, 2017).
In implementing the protection of Sumatran
Tigers, training and consultations, habitat monitoring,
trade law enforcement, confiscation and
rehabilitation of suspects who violate are carried out.
Apart from that, the government is improving the
quality of human resources in supervision and law
enforcement, outreach and knowledge to increase
public understanding of the importance of Sumatran
Tiger conservation, as well as collaborating with law
enforcers and the citizens to improve animal
protection and preservation (Lestari and Efendi,
2017).
Depthios, J. M., Anggraeni, N. S., Yuwono, A. R. and Zulfikar, R.
Designing a Sumatran Tiger Motif as an Effort to Increase Public Awareness in Protecting the Crisis of Protected Animal’s Populations in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0013330600004557
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Creative Multimedia (ICCM 2024), pages 29-37
ISBN: 978-989-758-733-7; ISSN: 3051-6412
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
29

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Motifs are often used in the field of arts with various
inspirations from surrounding objects or events with
their own styles and variations to provide a message
or visual to the public. Motifs are works that function
in product efficiency as messages or visual
expressions, so they include visual communication.
In motifs, objects that can be used as visual assets are
flora, fauna, geometric, abstract, and others that are
combined into one repetitive visual. Each motif can
be used to produce a work that has meaningful beauty
(Mutiarani, 2021).
According to Untoro (2019) motifs are the
characteristics and patterns in the embodiment of the
concepts and themes that have been explained. Motifs
are sometimes repeated to obtain appropriate patterns
and manifestations. According to Sunaryo (2009), a
motif is an ornament which is generally formed from
nature (leaves, mountains, sun, animals, etc.). Finally,
according to Suhersono (2004), in the process of
creating motifs, sequence, combining basic shapes
and various lines is needed to produce new authentic
and beautiful motifs (Siana et al., 2022).
The motif requires wastra that is a piece of cloth
as a placement material. According to Ahmad Karoni
(2021), lit is a unity that has a complete decorative
variety inside. Wastra is determined through motifs
and is seen as values, impressions, messages, symbols
and information that were included.
Motifs are for communicating messages to the
target audience, because visual perception is built on
appearance, shape and space as in perceiving a
product (Alizamar & Couto, 2016). This is no
exception, as motifs can form perceptions that can be
captured by the target audience visually. In the
Gestalt theory of perception, humans have the ability
to simplify and group elements that can be seen and
felt into one unified form (Alizamar & Couto, 2016).
In line with the basic principles of unification, the
principles apply, namely:
- Figure & ground: The stimulus received will be
connected to the context or circumstances
surrounding the object. In the organization of human
perception, the main pattern (figure) that describes
the elements in a field of perception will be the most
important. The elements that are less important are
called basic patterns (ground). The phenomena of
main patterns (figure) and basic patterns (ground) are
the most basic forms of perceptual organization (Van
Eymeren, 2014)
The application of Gestalt theory can influence
human perception. Perception begins with a sensing
process where the stimulus is received by the five
senses, then the individual has attention and is
transmitted to the brain. After that, the individual is
aware of and can understand the surrounding
environment and what is within the individual.
Perception can be interpreted as a process of
receiving stimulation from the five senses, preceded
by attention so that the individual is able to perceive,
know and appreciate the good things that are
observed both outside and within the individual
(Sunaryo, 2002)
A visual object such as a motif can function as
brand awareness to increase public attention. In
principle, brand awareness refers to the strength with
which a brand can be present in consumers' minds.
(Pappu, Quester, and Cooksey, 2005), this can happen
if there is a relationship between the brand and the
type of product, where potential consumers recognize
or associate it with a particular product. With that,
awareness can only be from brand recognition to
brand memory or simply memory of the product
becoming dominant, if it is the only brand that
consumers remember. (Hakala, Svensson & Vincze,
2012). In terms of designing motifs and efforts to
instill them in the minds of consumers, it is important
to give uniqueness to a motif so that it can be
remembered by the target audience. Motifs also
function to show identity related to creative works as
personal, corporate or regional identity (Sartika, et al,
2017). Therefore, motifs can be used as a medium to
convey messages to the target audience through their
uniqueness.
3 METHOD
The methods that are used in this research are
exploring the life and image of tigers and the habitat
of Sumatran tigers. The exploration method is a
method that see, observe, understand and feel to
produce something. The exploration method is
applied in artistic activities because it is closely
related to creativity (Faida, et.al, 2020).
First, identify the conflict faced by the Sumatran
Tigers. Second, reset the shape and color of the
Sumatran Tiger to be used as a moodboard. Third,
carry out the design process that will be used as a
motif. Finally, carry out a literature study to
understand all of the datas that has been collected,
problems, solutions and other explanations about
animals. This method improves the process of
creating motifs for order, meaning and significance of
art, as well as motif quality.
Then, use a documentation method to personify the
meaning of the motif. Lastly, collect all the sketches
ICCM 2024 - The International Conference on Creative Multimedia
30

that have been assisted without any plagiarism then
carry out digital documentation of the motif during
the practicum class from design to repetition.
Next, a questionnaire was created to determine
consumers' perceptions of the designed motifs. The
questionnaire was created on a Likert scale and then
tested on 40 respondents to test its validity and
reliability. Then 11 questions were obtained to be
distributed again and then 102 respondents were
obtained and then processed using Factor Analysis.
The results of the Factor Analysis were then verified
by conducting a Focus Group Discussion with 10
respondents to find out their perceptions and
impressions of the Sumatran tiger motif that had been
designed.
4 RESULT & DISCUSSION
4.1 Result
4.1.1 Exploration Process
Before carrying out the exploration process, the
designer chose Sumatran Tiger’s fur to determine the
color of the motif and from the face to neck for the
shape. In addition, the designer's goal is to provide a
visual protection for animals. Then, because Daun
Sang/Sang Leaves is an endemic plant in the Sumatra
region and gives the impression of nature surrounding
it, the designer included Daun Sang/Sang Leaves as a
form of asset. Lastly, Mount Sibayak to depict life in
nature and prosperity.
The Sumatran Tiger is the smallest species
currently, almost the same size as leopards and
jaguars. Sumatran Tigers have dark orange fur and
wide black stripes. In addition, Sumatran Tigers have
short manes with longer fur on the sides of their faces
(possibly as protection against forest vegetation)
(Moretti, 2021).
Sang leaves are one of the widespread plants in
Sumatra, so they were previously used as roofs for
local people's houses. According to the IUCN, Sang
Leaf is included in the Red Data Book as a plant that
is threatened with extinction due to its use by
residents in forest areas as roofing material for
houses, wall materials and huts or cottages as well as
land clearing activities, forest fires and deforestation
(Sihombing et al., 2014).
According to Karo people's beliefs, Mount
Sibayak is associated with prosperity and wealth (the
word 'bayak' means 'rich'). According to Karo, the
concept of wealth is not only material but also
spiritual and cultural. The meaning of the name
Mount Sibayak teaches about inherent cultural
interpretations (Rizal, 2023).
In the exploration process, a mood board is
created based on the concept that was included. Mood
board is defined as a board media to provide ideas and
help designers in the design process. Mood board can
raise a designer's enthusiasm for learning in achieving
competency in learning fashion design so that there is
visual knowledge and understanding. Apart from that,
mood board can be a guide in creating themed
creative works so that the creative process is in
suitable with the specified theme and the purpose of
creating the work (Bestari and Ishartiwi, 2016).
Figure 1: MoodBoard.
In the mood board, there were various photos of
Sumatran Tigers and Sang Leaves with different
perspectives and poses so that the designer could
understand the anatomy of the tiger and leaf in
geometric shapes as well as two photos of Mount
Sibayak as a reference. In the color palette, the
designer used complementary colors which are
opposite colors, two colors that contrast and stand
out, such as red and green. Apart from that, accent
colors are used in clothing which are the addition of
different colors to not destroy the color unity, such as
cream and orange as well as light and dark green
(Meilani, 2013). The cream color was taken from
tiger fur and symbolizes hope and purity (Novelisari,
et.al, 2020). The red color was taken from autumn
leaves gives the impression of courage, enthusiasm
and spirit. Then, the orange color was taken from tiger
fur gives the impression of caring, motivation,
enthusiasm. The light green color was taken from the
leaves gives the impression of growth, fertility and
even health. Lastly, the dark green color gave the
impression of prosperity.
After the mood board, sketches were made to
combine various geometric shapes in the form of
triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, rectangles and
crystals. The sketches were drawn onto A4 paper in a
Designing a Sumatran Tiger Motif as an Effort to Increase Public Awareness in Protecting the Crisis of Protected Animal’s Populations in
Indonesia
31

13 x 13 cm square box and dialed. The sketching
process was carried out in various types to determine
the arrangement, combination of shapes and
composition that were interesting and according to
the concept.
Figure 2: Alternative Design.
The designer also explored the shapes of the
Sumatran Tiger, Sang Leaves and Mount Sibayak to
match the geometric shapes in the motif. The
exploration process was carried out according to the
student's theme and goal of conveying something
through design and students. The longest process was
sketching because it requires a lot of exploration and
strong imagination to create an attractive and
proportional design for a motif and avoid plagiarism.
After the sketching process, the color selection
process was carried out to be assigned to each motif
element according to the concept. The placement of
colors provides an expressive atmosphere and attracts
attention. The designer emphasized that the colors
should be in harmony with each other to suit the
process of repeating the shape. After sketching, the
designer used Adobe Illustrator software to create
vectors and color.
4.1.2 Design Process
In this process, the sketch is digitized in Adobe
Illustrator software with CMYK color mode. The
purpose of using Adobe Illustrator software is to
correct colors and repetitions to form patterns and
motifs. The designer could refine and change
elements in the design to provide the right
composition. Starting from the sketch, it was traced
using the pen tool in the tool bar to form precise and
neat elements for printing. In the design design
process, a mature concept was determined according
to the theme and meaning. The following were all of
the sketches that had been digitized:
Figure 3: Motifs 1.
In this first pattern, it gives the impression that the
Sumatran tiger population is decreasing and is
threatened with extinction. The circle at the end
comes from the shape of Mount Sibayak which is
simplified into a plane because Mount Sibayak is not
completely triangular and curved and gives the
impression of a life cycle (changes experienced by
species) after repetition. The Sumatran tiger in the
center is given a green color to represent health and
prosperity. The circles and small crystals found on the
Sumatran Tiger's body are part of the tiger's body and
the tiger stripes are formed from Sang Leaves. The
large and small crystals come from the shape of the
inner Sang Leaves which is covering the tiger and is
placed for protection.
Figure 4: Motifs 2.
In the second pattern, it gives the impression of a
Sumatran Tiger opening its mouth to growl and roar
for help. The crystal at the end of the motif and other
elements in the mount and the tiger come from the
Sang Leaf. At the top of the tiger, there is a triangular
shape as Mount Sibayak to protect and provide
prosperity so that the tiger and mountain elements are
combined. The two triangles on the right and left of
the tiger give the impression of a threat to the tiger.
At the end, a crystal element for the Sang Leaf is
placed so that after it is repeated, it forms a 'bloom'
from extinction.
ICCM 2024 - The International Conference on Creative Multimedia
32

Figure 5: Motifs 3.
In the third pattern, it gives the impression of a
warning sign for the Sumatran Tiger, which is why
there is a red circle on the back of the tiger in the
middle of the image to give attention. The circle at the
end of the motif comes from the shape of Mount
Sibayak which is simplified to give the impression of
a life cycle (changes experienced by species) after
repetition. The small crystals together with the
triangles in the shape of a bow and arrow give the
impression of a threat because initially, the extinction
of tigers started from illegal hunting. The large crystal
gives the impression that the tiger is being protected.
In all these patterns, the designer placed the tiger
in the center to draw attention. For coloring, harmony
and meaning. After forming a pattern from all the
elements that have been combined, a pattern
technique is used in the object bar where the process
of repeating motifs was carried out horizontally and
vertically. The following is a motif from a pattern that
has been repeated using the pattern technique:
Figure 6: Motifs 1.
Figure 7: Motifs 2.
Figure 8: Motifs 3.
Then, the motifs that had been created digitally are
made in the form of fabric products. The designer has
reasons for selecting the type of fabric that will be
applied. The following are the results of the mock up
motif:
Figure 9: Material Cotton Cloth.
Designing a Sumatran Tiger Motif as an Effort to Increase Public Awareness in Protecting the Crisis of Protected Animal’s Populations in
Indonesia
33

Figure 10: Tapestries.
Figure 11: Flannel.
The purpose of choosing the fabric materials listed is
to be able to print via digital printing and maintain the
condition of the furniture and provide comfort with
good softness. In the digital printing process, a
process of "transferring" the design via sublimation
or digital transfer will be carried out on the printer
machine. Even though the sublimation method uses
synthetic materials, there are also natural materials.
However, because the fabric is made from natural
materials, color absorption is carried out. In order to
make the colors match or are the same as the digital
design, the printed design colors are given a higher
saturation. Then, use the screen printing or screen-
printing method which is a fast method of combining
digital or traditional printing techniques on the
screen. The materials used are colored pigment and
adhesive glue for foiling. Then, the fabric is washed
and a machine border technique is used so that the
details of the motif can be seen (Arihta and
Saftyaningsih, 2013).
Apart from that, it can be applied to furniture such
as tables made from ecobrick materials. Ecobricks are
a creative effort to manage plastic waste into usable
objects with the aim of reducing pollution and toxins
caused by plastic waste. Then, it can prevent tree
logging for materials that are used as furniture and
protect the habitat of tigers and other species
(Suminto, 2017).
The designer can learn how designs are
communicated in visual forms to provide meanings
and messages through geometric motifs during basic
design learning. In applying the motifs, the products
were designed in the form of fabric as one of the
materials mostly used by the citizens with the aim of
increasing public awareness of the importance of
protecting animals and the environment.
The results of this design were then tested on
respondents to determine their perception of
aesthetics and the communication message conveyed.
The results obtained through factor analysis are as
follows:
Figure 12: The results of the KMO and Bartlett's Test.
From the results of the KMO and Bartlett's Test
above, it showed that the result of 0.855 stated that
the results of distributing the questionnaire had good
value so that the results of the questionnaire could be
interpreted.
Table 1: Questionnaire Results.
Question Motif 1 Motif 2 Motif 3
This motif design caught
my attention
.567 .779 .784
I'm interested in using
this motif as a
clothing/accessories
motif
.608 .747 .803
This motif made me
want to know more about
the issue regarding the
condition of Sumatran
tigers
.662 .563 .944
I feel that the motif on
this cloth depicts the
protection of the
Sumatran tiger and
provides support for the
conservation of
endangered animals
.732 .794 .816
I feel that the motif on
this cloth depicts the
protection of the
Sumatran tiger which is
threatened with
extinction due to
p
oachin
g
/ille
g
al lo
gg
in
g
.771 .798 .805
ICCM 2024 - The International Conference on Creative Multimedia
34
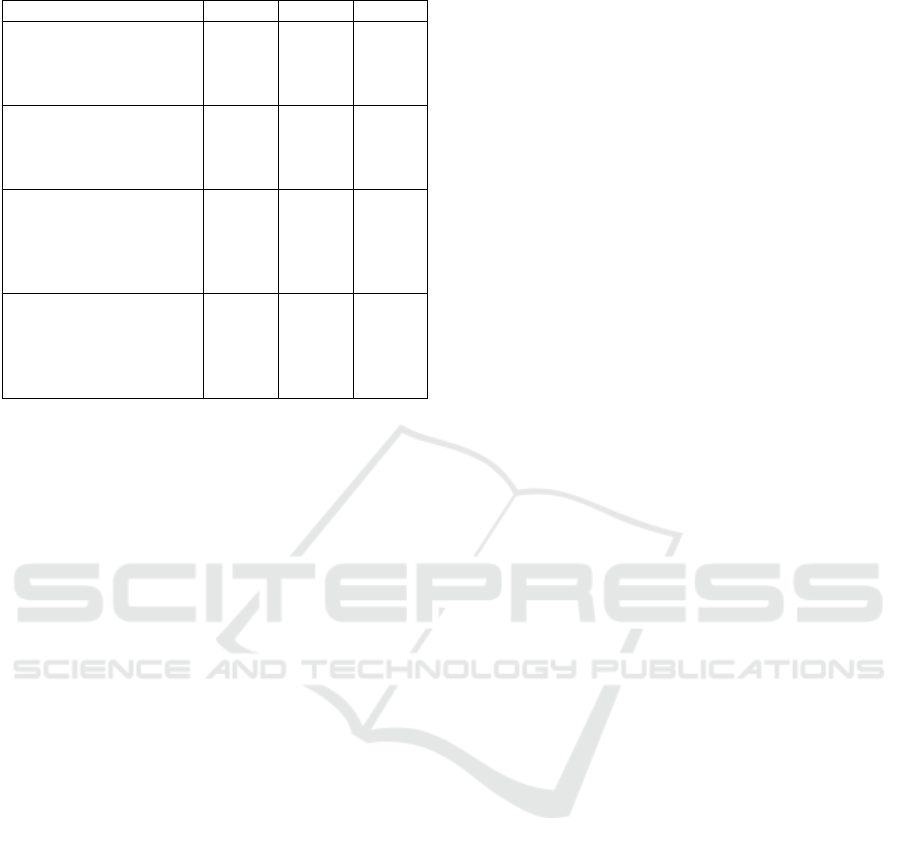
Table 1: Questionnaire Results (cont.).
Question Motif 1 Motif 2 Motif 3
This motif design makes
me want to further
support Sumatran tiger
conservation efforts
.746 .682 .845
I feel this motive
encourages me to
participate in preserving
the Sumatran ti
g
e
r
.782 .786 .837
I feel that this motif is a
creative and effective
way to convey
conservation messages
to the target audience
.610 .630 .865
I feel that this motif can
be an effective tool in
campaigns on social
media for Sumatran tiger
conservation
.566 .635 .755
From the results above, it could be seen that Figure A
did not attract the attention of the target audience as
indicated by the poor correlation value. It also showed
that this motif did not attract the attention of various
ages of the target audience. However, the target
audience still felt that this motif could raise their
awareness to preserve endangered animals, especially
the Sumatran tiger. Figure B was enough to attract the
attention of the target audience, but did attract their
curiosity about the condition of the Sumatran tiger.
Figure C had attractive visuals and was able to attract
the attention of the target audience in preserving the
Sumatran tiger. Of the three images, Figure B was
considered the most visually interesting, indicated by
the highest correlation value among the three.
However, after being applied to the design object,
Figure C looked more attractive among the three.
Although visually interesting, Figure B did encourage
the target audience to want to know more about
Sumatran tigers. After being confirmed through FGD
with the target audience, Figure B was more visually
attractive but was not yet able to convey a message
through shapes related to the tiger image. In terms of
efforts to convey conservation messages for
Sumatran tigers, Figure C was better to convey these
messages than the other two images so that Figure C
was considered more effective in building public
awareness related to tiger conservation.
Based on the results of the Focus Group
Discussion conducted with 10 respondents, it was
concluded that Figure C had the best response among
the three as a media campaign for the protection of
Sumatran tigers. From the results of the FGD, they
got the impression that the shape was similar to a
tiger's head in terms of visual perception.
4.2 Discussions
The Sumatran tiger is one of the animals experiencing
a population crisis in Indonesia due to illegal logging
which causes loss of animal habitat as well as illegal
hunting due to lack of public awareness. The
government has held activities and outreach on
Sumatran Tiger protection to increase public
awareness. In designing there are several important
elements such as dimension points, lines, planes,
texture, space and color. During the exploration and
design process, the designer summarizes his
inspiration in the form of a moodboard to determine
the shape approach and color palette of the design
pattern which will be repeated into a geometric motif.
In the color palette, complementary colors such as
cream, red, orange, light green and dark green are
used to give a natural impression of protection and
peace and train the designer's sensitivity in color
combinations in a design. After the sketch process is
digitized and the design application of the image is
determined after it is printed on natural fabric. After
designing the pattern, the designer creates a pattern
that is repeated into a motif. The first motif gives the
impression that the Sumatran tiger population is
decreasing because it is threatened with extinction, so
it needs to be protected and preserve the life cycle of
this species. In the second motif, the Sumatran tiger
under the mountain opens its mouth to growl and roar
for help because its need for natural life is
disappearing. Finally, the third motif, as a warning
sign for the Sumatran Tiger which needs to get public
attention. The motif that has been designed will be
printed on fabric in the form of cotton, tapestry and
flannel. Then it is applied to plastic ecobrick furniture
to become objects that can be used to prevent
excessive felling of trees and protect animal habitats.
Through this design process, designers can identify
certain visuals that can provide meaning and
messages through motifs and understand the
dangerous situations faced by protected animals
during this time.
From the results of the discussion above, there is
something interesting and a finding that a motif can
remind target consumers of a message, in this case to
raise awareness of the target audience regarding the
conservation of Sumatran tigers. Motif C reminds the
target audience of the shape of the Sumatran tiger's
head. In Gestalt theory there is the principle of the law
of equivalence. In observation, objects that have
similarities (similarity) to each other will be
organized into one perception. In other words, things
that are similar to each other will be perceived as a
group or a totality. (Hidayati, 2011). The use of green
Designing a Sumatran Tiger Motif as an Effort to Increase Public Awareness in Protecting the Crisis of Protected Animal’s Populations in
Indonesia
35

and brown colors reminds the target audience of the
forest as a habitat for Sumatran tigers. Meanwhile, at
first glance, the object in the middle resembles the
shape of a tiger's mouth and nose. However, after
being repeated into a unified motif, at first glance it
will look like a tiger's head.
Figure 13: Shape of the Sumatran tiger's head from Motif
3.
From this it can be concluded that the application of
Gestalt principles in building public awareness is very
important. Gestalt principles can help designers in
formulating and creating object forms or images that
can improve an individual's perception of an object.
The presence of several design elements related to the
image and habitat of tigers can be unique and capable
of raising awareness among the target audience.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From the explanation above, it can be concluded that
the motif can be used to build public awareness about
the conservation of the endangered Sumatran tiger.
However, several efforts are needed so that the
communication message can reach the target
audience. One way is to apply several elements
related to the tiger's image, for example body shape,
body parts, use of relevant colors, and the tiger's
habitat. In the case above, image C, which has several
elements that are similar to the shape of a tiger's body
parts, is complemented by the use of colors that are
relevant to the image of the forest. It is important to
apply the principles of Gestalt theory to strengthen
the impression of closeness (similarity) to the shape
of the original object so that it will make it easier for
the target audience to recognize the shape and in turn
will help make them aware of the existence of the
endangered Sumatran tiger.
5.1 Recommendation
For those who wish to initiate further research, it is
highly recommended to find out the effectiveness of
the motifs created when implemented in social media
campaigns, such as Protection of Endangered
Animals. This research focuses on rare animals such
as the Sumatran tiger. This motif can also be applied
to various types of media or explored into new
designs based on research to increase awareness of
the Sumatran Tiger.
REFERENCES
Arihta, T., & Saftyaningsih, K. A. (2013). Eksplorasi
Visual Kain Tradisional Uis Gara pada Produk Busana
Siap Pakai Wanita (Doctoral dissertation, Bandung
Institute of Technology).
https://www.neliti.com/publications/242335/eksplorasi
-visual-kain-tradisional-uis-gara-pada-produk-busana-
siap-pakai-wanita
Alizamar, N., & Couto, N. (2016). Psikologi Persepsi dan
Desain Informasi: Sebuah Kajian Psikologi Persepsi
dan Prinsip Kognitif untuk Kependidikan dan Desain
Komunikasi Visual. Yogyakarta. Media akademi.
Bestari, A. G., & Ishartiwi, I. (2016). Pengaruh Penggunaan
Media Mood Board Terhadap Pengetahuan Desain
Busana pada Mahasiswa Pendidikan Teknik Busana.
Jurnal Inovasi Teknologi Pendidikan, 3(2), 121-137.
Faida, P. E., Udin, T., & Latifah, L. (2020). Pengaruh
metode eksplorasi seni menggambar terhadap
kreativitas siswa kelas V Madrasah Ibtidaiyah.
UNIEDU: Universal Journal of Educational Research,
1(2), 116-131.
Hakala, U., Svensson, J. & Vincze, Z., 2012. Consumer-
based brand equity and top-of-mind awareness: a cross-
country analysis. Journal of Product & Brand
Management, 21(6), pp.439- 451.
Khoirunnisa, K., & Mahendra, A. (2021). Strategi WWF
Terhadap Perlindungan Harimau Sumatera Dari
Perburuan Liar Di Indonesia (Tahun 2016-2018).
Jurnal Polinter: Kajian Politik Dan Hubungan
Internasional, 6(2), 123-151.
Lestari, Y., & Efendi, E. (2017). Perlindungan Harimau
Sumatera Di Kabupaten Aceh Tenggara. Jurnal Ilmiah
Mahasiswa Bidang Hukum Kenegaraan, 1(1), 1-12.
Meilani, M. (2013). Teori warna: penerapan lingkaran
warna dalam berbusana. Humaniora, 4(1), 326-338.
Moretti, J. (2021, August 17). Full Sumatran Tiger
Information | Project Endangered Tigers.
Retrieved from https://endangeredtigers.org/tiger-
species/sumatran-tiger/
Mutiarani, R. A. (2021). Perancangan Buku Decoupage
berdasarkan Desain Komunikasi Visual. Ars: Jurnal
Seni Rupa dan Desain, 24(1), 15-20.
Novelisari, I., Fitriana, R., & Susanti, H. (2020). Analisis
Makna Motif Bunga Pada Kimono. IDEA: Jurnal Studi
Jepang, 2(1), 1-13.
Rizal, H. (2023). Makna Mendalam di Balik Nama Gunung
Sibayak: 'Si Kaya' dari Warisan Orang Karo -
Timenews. Makna Mendalam Di Balik Nama Gunung
Sibayak: “Si Kaya” Dari Warisan Orang Karo -
Timenews.
ICCM 2024 - The International Conference on Creative Multimedia
36

https://www.timenews.co.id/hiburan/9959925714/makna-
mendalam-di-balik-nama-gunung-sibayak-si-kaya-
dari-warisan-orang-karo
Sartika, D., Eskak, E., & Sunarya, I. K. (2017). Uma
Lengge dalam Kreasi Batik Bima. Dinamika Kerajinan
Dan Batik, 34(2), 73–82
Siana, R., Darmawanto, E., & Alfian, T. (2022). Kajian
Motif Wastra Cakra Manggilingan Omah Petrok Troso
Dalam Desain Komunikasi Visual. SULUH: Jurnal
Seni Desain Budaya, 5(1), 1-10.
Sihombing, A. F., Anna, N., & Hartini, K. S. (2014).
Analisis Asosiasi Daun Sang (Johannesteijsmannia
Altifrons) Dengan Jenis-jenis Palem Di Resort Sei
Betung, Taman Nasional Gunung Leuser, Kabupaten
Langkat, Sumatera Utara. Peronema Forestry Science
Journal, 4(2), 218-223
Suminto, S. (2017). Ecobrick: solusi cerdas dan kreatif
untuk mengatasi sampah plastik. Productum: Jurnal
Desain Produk (Pengetahuan dan Perancangan
Produk), 3(1), 26-34.
Sunaryo, S. (2002). Psikologi untuk Keperawatan. Jakarta:
Penerbit Buku Kedokteran EGC
Paiman, A., Anggraini, R., & Maijunita, M. (2018). Faktor
Kerusakan Habitat dan Sumber Air Terhadap Populasi
Harimau Sumatera (Panthera tigris sumatrae Pocock,
1929) di Seksi Pengelolaan Taman Nasional (SPTN)
Wilayah III Taman Nasional Sembilang. Jurnal Silva
Tropika, 2(2), 22-28.
Pappu, R., Quester, P. G., & Cooksey, R. W. (2005).
Consumer-based brand equity: improving the
measurement–empirical evidence. Journal of Product &
Brand Management, 14(3), 143-154.
Van Eymeren, M. M. (2014). Memahami Persepsi Visual:
Sumbangan Psikologi Kognitif Dalam Seni Dan
Desain. Ultimart: Jurnal Komunikasi Visual, 7(2), 47-
63.
Designing a Sumatran Tiger Motif as an Effort to Increase Public Awareness in Protecting the Crisis of Protected Animal’s Populations in
Indonesia
37
