
Implementation of Bigdata Techniques in Supply Chain
Management: Evidence from Predictive Analytics
Fanrong Liu
Eurasia Internation School, Henan University, Kaifeng, China
Keywords: Bigdata Analysis, Supply Chain Management, Risk Management.
Abstract: Supply chain management (SCM) is changing as a result of several technologies that are propelling significant
digital trends. Numerous supply chain situations, such as demand forecasting, supplier management, risk
management, transportation management, and sales and marketing analysis, make use of big data analytics.
Supply chains are changing as a result of big data analytics breakthroughs that enable these connections. This
study summarizes the progress with an emphasis on the supply chain's two modules of risk management and
prediction analysis. In addition to analysing the tenets and outcomes of big data analysis technology in these
two connections, this article highlights the significance of predictive analysis and risk management modules
in supply chains. This research delves into the difficulties that predictive analytics and risk management
encounter while utilizing big data analytics, as well as the future prospects. Overall, these results offer a
synopsis of the constraints and potential applications of big data analysis in the two fields.
1 INTRODUCTION
Oliver and Webber made their original proposal for
supply chain management (SCM) in 1982. Supply
chain challenges are getting more and more
complicated in today's globalized world, where there
is an increasing need for innovation, diversity in
products, and offshore manufacturing. International
material and financial flows, foreign policy,
responsibility for society, economic dangers, and
other intricate processes are among these complicated
frameworks. In this case, SCM continues to be an area
that requires substantial scholarly attention (Yalcin,
Shi & Rahman, 2020). Over the past ten years, the
supply chain has seen a significant transformation,
evolving from a merely operational function to an
autonomous supply chain management function. The
supply chain management role now prioritizes
sophisticated planning techniques including
analytical demand planning; ensure sure that supplier
and customer operations are connected. Furthermore,
partner cooperation and trust are highly valued in
supply chain management (Attaran, 2020).
Businesses have been driving the development of Big
Data Analytics (also known as BDA) for supply
chains (SC) over the past few years because of the
increasing demand in big data. The goal of SC is to
obtain valuable information that will improve their
ability to estimate, anticipate, and identify hidden
patterns—all of which will increase their
competitiveness. This most recent development
offers companies fresh chances to develop new trade
patterns and improve current operations, which will
help the market but also present unforeseen
difficulties (Chehbi-Gamoura et al., 2020).
SCM unifies supply and demand management
both within and between businesses. The supply
chain management process begins with the purchase
of raw materials. The product manufacturer's supplier
obtains the raw ingredients. The manufacturer
provides the finished product after refining the raw
material. The product's distribution is beneath the
distributor's control. Customers usually purchase
things from merchants, while retailers get these
products from wholesalers (Taj et al., 2023). Superior
supply chain performance has strategic importance
since it can result in quick financial gains, increased
earnings and productivity, and advancements in
important worldwide competitive advantages. The
impact of the digital economy on supply chains is
significant. The digital economy, which conducts
commercial activity both online and on mobile
devices, is built on electronic computing technologies.
In this economy, connections between individuals,
devices, channels, and organizations, all made
Liu, F.
Implementation of Bigdata Techniques in Supply Chain Management: Evidence from Predictive Analytics.
DOI: 10.5220/0013208100004568
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on E-commerce and Artificial Intelligence (ECAI 2024), pages 143-147
ISBN: 978-989-758-726-9
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
143
possible by technology, create value. Customers
explore and purchase products using digital channels
like social media, mobile networks, and e-commerce.
Customers can purchase whenever and wherever they
choose, tailor their requirements to their
specifications, and anticipate delivery in a few days.
Businesses are able to get real-time data about the
locations, products, and methods of consumers'
purchases, and customized product delivery is
starting to spread over the world. The transformation
of traditional supply networks is imperative in the
digital age. Important components of supply chain
operations are currently digitizing more quickly.
Innovation and technology are two major aspects
influencing how the supply chain is evolving. With
the use of contemporary technologies like big data,
the cloud, IoT, and sophisticated computing driven by
algorithms that utilize machine learning, intelligent
digital models of supply chains are being produced.
These technologies are starting to replace traditional
supply chain structures. Shorter response times,
increased collaboration, improved visibility, and
better insight are all made possible by this new digital
supply chain (Attaran, 2020).
Big data analytics techniques can be used to
analyse the data gathered by numerous businesses in
order to create business growth plans, forecast market
instructions and simulate the manufacturing process,
optimize delivery, manage inventory, reduce risk, and
carry out numerous additional supply chain tasks like
marketing and sales procedures. In the framework of
big data technology, this article examines the
pertinent uses of risk management and predictive
analytics in the supply chain and offers opinions on
their drawbacks and future directions. The application
scenarios of SCM and big data technology are
introduced in the second section. The theory and
findings of the supply chain prediction analysis are
presented in the third section. An introduction to risk
management application is provided in the fourth
section. Lastly, an analysis is conducted regarding
these two application scenarios' future development
and constraints. This work began the literature review
by searching electronic databases, such as
ScienceDirect and Google Scholar, among others.
Using different keyword combinations such as "risk
management," "supply chain management,"
"predicting analytics," "applications," and "positive
effects" ensures a comprehensive search of academic
journals, conference proceedings, and related
publications.
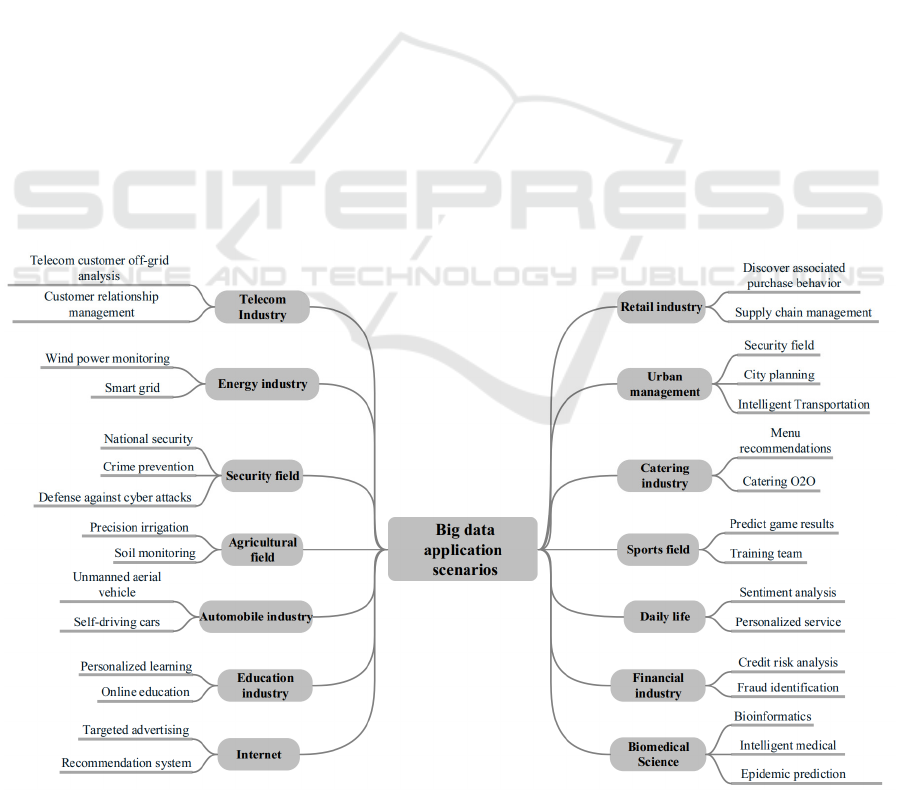
Figure 1: Big data application scenarios (Wang et al., 2020).
ECAI 2024 - International Conference on E-commerce and Artificial Intelligence
144

2 DESCRIPTIONS OF BIGDATA
The advent of big data, one of the key themes of this
century, is a result of recent information technology
advancements. Big data, describes the practice of
businesses gathering vast volumes of data from
various sources. This data is analyzed by
sophisticated computer systems to provide business
insights that can boost the organization's
productivity(Albqowr et al., 2024).
Big data technologies can advance scientific
research and increase production efficiency.
Innovative algorithms are needed to tackle certain
difficult and complex jobs that are outside the scope
of conventional methods. Big data technology has
permeated every area of people's life and been used
in a wide range of sectors (including energy, sports,
entertainment, banking, Internet, catering, and
healthcare). Fig. 1 illustrates how big data is used in
a variety of sectors. (Wang et al., 2020) The ideas and
outcomes of pertinent application scenarios of risk
management and predictive analysis in the context of
big data in the supply chain will be the main topics of
this presentation.
3 PREDICTIVE ANALYTICS
The application of statistical algorithms, machine
learning, and data mining approaches to historical
data analysis and future event or trend prediction has
been referred to as predictive analytics. Predictive
analytics offers a proactive solution to supply chain
management (SCM) problems such inventory control,
supply chain interruptions, and fluctuating demand
(Oyewole et al., 2024). Early supply chain
management (SCM) predictive analytics research
concentrated on simple forecasting techniques that
relied on historical data and employed
straightforward statistical models for computations.
More advanced predictive analytics methods have
been developed as a result of improvements in
processing power and data storage. Understanding the
fundamental terms and concepts is crucial to
comprehending the predictive analytics environment
in supply chain management. Machine learning, data
mining, and predictive modeling are essential
elements. The predictive analytics environment
inside SCM is depicted in the Fig. 2.
Figure 2: Predictive analysis environment.
The application of predictive analytics in the
supply chain visibility, inventory management, and
demand forecasting domains of supply chain
management (SCM) has been the subject of numerous
research that have looked at its practical ramifications.
These domains range from more conventional
statistical methods to more sophisticated artificial
intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms.
These studies offer insightful information about
applications that are successful, difficulties
encountered, and the overall effect on supply chain
performance. Utilizing past data, current market
conditions, and outside variables, predictive analytics
creates complex models that increase the precision of
demand projections. These models can optimize
inventory levels, predict changes in client demand,
and streamline production procedures. Accurate data
integration and information exchange improve supply
chain performance by lowering inventory and
squeeze, improving demand visibility, and reducing
inventory. One of the most important components of
an efficient supply chain is inventory management
optimization. Analytics that predict Determine the
ideal inventory levels by looking at lead times, past
sales information, and outside variables that impact
demand. Organizations can use sophisticated
algorithms to find patterns and connections that help
them decide on order quantities, safety stock levels,
and stock replenishment. A primary advantage of
implementing predictive analytics is enhanced
visibility across the whole supply chain. Predictive
analytics provides firms with information on supplier
performance, the efficiency of their transportation,
and general logistics management, enabling real-time
tracking of critical supply chain indicators.
Simultaneously, the elasticity of the supply chain
and overall efficiency are enhanced by the control of
potential hazards. Estimating future demand, optimal
utilization of inventory, and supply chain
transparency are just a few real-world examples of
how predictive analytics can revolutionize supply
chain management processes. These applications,
which demonstrate the significant advantages of
predictive analytics in SCM processes, are not merely
Implementation of Bigdata Techniques in Supply Chain Management: Evidence from Predictive Analytics
145

theoretical ideas; rather, they are supported by actual
data and real-world instances.
4 RISK MANAGEMENT
Any supply chain that has to make decisions while
dealing with uncertainty does so in part by using a risk
management strategy. Information ignorance is the
source of risk, and many risk factors (e.g., COVID-
19), are uncontrollable by humans, but big data
analytics may help us create a robust supply chain
system that can strengthen the information system
and reduce risk (Araz et al., 2020). Big data analytics
can generally be used to protect against hazards
associated with shipping, default between merchants
and suppliers, dangerous chemicals during the
connection between recyclers and remanufacturers,
and environmental harm (Ghalehkhondabi et al.,
2020).
Risks in supply chain management (SCM) include
globalization, shorter product life cycles, demand
forecasts, cost pressures, outsourcing, and offshore.
The business environment is become more uncertain
as a result of the increasing complexity of SCM and
networks. These are supply chain risk events that
have an impact on the network as a whole. An
indication of a potential disruption to the supply chain
is a risk event. Global supply chains are more
vulnerable to risk and confront several obstacles.
Increased openness and information exchange
amongst supply chain actors are necessary for this.
Globalization and nations' economic interactions with
partner nations have altered global production
methods. Each of these raises the supply chain's risk
and complexity. Distribution centers are another
name for distribution centers in contemporary global
supply networks. The needs of buyers are fulfilled at
the operations center. Because their effectiveness
influences the overall SCM value, these centers must
be efficient. Pay close attention to how the disaster
affects the supply chain and make sure it has an effect
on operational performance as well. In the current
global marketplace, supply chain interruptions and
the related risks to operations and finances are among
the most urgent problems affecting rival businesses.
Still, there's a distinction between danger and
disruption. An indication of supply chain risk is
disruption. However, the risk is still remained
unaffected (Gurtu & Johny, 2021).
5 LIMITATIONS AND
PROSPECTS
Supply chain management is now much more
efficient thanks to big data analysis. Although supply
chain management can benefit greatly from
predictive analytics, there are certain drawbacks to its
application. First, historical records provide the data.
Inadequate historical data can have an impact on how
well predictive analysis works. The second issue is a
compatibility issue brought on by predictive analysis
tool upgrades. It will be possible to thoroughly
examine how the forecasting tool improvement
affects the forecasted results in the future.
There are also restrictions on this paper's use of
risk management. This document only chooses a
small number of key phrases; an article may go
unresearched if it does not have the word "risk" in its
title, keyword, or abstract. Further research on
particular under- or undiscovered areas can be
conducted using the summary results of this paper. It
is anticipated that this study of the literature will help
scholars investigate supply chain risk management
(SCRM) more thoroughly. The way supply chains
function across industries will continue to change as
a result of these applications. Supply chains will
depend more and more on big data analytics as
technology continues to change the world around us.
This will increase the reliance of these networks on
ubiquitous digital information at every link. Big data
analytics will play a significant role in the ongoing
development and improvement of the supply chain. It
may also provide solutions to the various issues that
various sectors are facing as a result of market trends.
The foundation of the world economy, supply chains
promote trade, consumption, and growth in the
economy.
6 CONCLUSIONS
To sum up, the foundation of the world economy,
supply chains promote trade, consumption, and
growth in the economy. The rapid advancement of
modern information technology has made data an
essential basis for the development of manufacturing
supplies and techniques. In this study, the architecture
of big data services, some existing big data
application scenarios, and predictive analytics based
on big data and risk management services are
analysed. This study first provides an overview of the
history, state of development, and future prospects of
SCM. The big data analysis technology and its
ECAI 2024 - International Conference on E-commerce and Artificial Intelligence
146

application scenarios are then briefly introduced.
Next, this study presents the use of big data in two
supply chain components: risk management and
predictive analytics. This study concludes by
summarizing the drawbacks and potential
applications of big data analysis to these two areas.
REFERENCES
Albqowr, A., Alsharairi, M., Alsoussi, A., 2024. Big data
analytics in supply chain management: a systematic
literature review. VINE Journal of Information and
Knowledge Management Systems, 543, 657.
Araz, O. M., Choi, T. M., Olson, D. L., Salman, F. S., 2020.
Data analytics for operational risk management. Decis.
Sci., 516, 1316.
Attaran, M., 2020. Digital technology enablers and their
implications for supply chain management. Supply
Chain Forum: An International Journal, 21(3) 9258-172.
Chehbi-Gamoura, S., Derrouiche, R., Damand, D., Barth,
M., 2020. Insights from big Data Analytics in supply
chain management: an all-inclusive literature review
using the SCOR model. Production Planning Control,
315, 375.
Ghalehkhondabi, I., Ahmadi, E., Maihami, R., 2020. An
overview of big data analytics application in supply
chain management published in 2010-2019. Production,
30, e20190140.
Gurtu, A., Johny, J., 2021. Supply chain risk management:
Literature review. Risks, 91, 16.
Oyewole, A. T., Okoye, C. C., Ofodile, O. C., Ejairu, E.,
2024. Reviewing predictive analytics in supply chain
management: Applications and benefits. World Journal
of Advanced Research and Reviews, 213, 568-574.
Taj, S., Imran, A. S., Kastrati, Z., Daudpota, S. M., Memon,
R. A., Ahmed, J., 2023. IoT-based supply chain
management: A systematic literature review. Internet of
Things, 24, 100982.
Wang, J., Yang, Y., Wang, T., Sherratt, R. S., Zhang, J.,
2020. Big data service architecture: a survey. Journal
of Internet Technology, 212, 399.
Yalcin, H., Shi, W., Rahman, Z., 2020. A review and
scientometric analysis of supply chain management
SCM. Operations and Supply Chain Management: An
International Journal, 132, 123.
Implementation of Bigdata Techniques in Supply Chain Management: Evidence from Predictive Analytics
147
