
Research on Green Finance in the Context of Dual-Carbon Strategy
Mohan Wu
a
School of Applied Mathematics, Shanxi University of Finance and Economics, Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province 030000
China
Keywords: Green Finance, Dual-carbon Strategy, Green Financial Instruments, Carbon Dioxide Emissions.
Abstract: As the global climate change problem gets more serious, carbon neutrality has become an important issue.
And green finance is a bridge between economy and environment. Green finance to support carbon neutrality
is the focus of current research. Therefore, this study summarizes the present application of green financial
tools from domestic research on green finance. This article shows that green financial tools primarily involve
green credit, bonds as well as taxes, which can help the dual-carbon strategy. In addition, different tools and
their combinations can help the dual-carbon strategy to a different extent and to various regions. At the
regional level, Green finance helps to reduce carbon emissions by updating and streamlining the industrial
structure., promoting energy transformation and enhancing resource utilization. At the same time, at the
enterprise level, it helps the dual-carbon strategy by raising enterprises' awareness of environmental protection,
easing financing constraints and improving productivity. However, Research on green financing to achieve
carbon neutrality and reduce emissions lags behind leading countries, unevenly distributed, and thin in
connotation, which will help future scholars' research.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the increase in carbon dioxide emissions in
recent years, extreme weather events such as extreme
heat and extreme precipitation are occurring more
frequently, which greatly impacts people's daily lives.
China has proposed a dual-carbon strategy to mitigate
extreme weather problems. It is estimated that more
than 10 billion dollars are needed to realize this policy,
90% of which needs to be provided by the capital
market centered on commercial banks (Qiao, 2024).
However, the traditional financial model, based on
the business law of unlimited environmental capacity,
is not able to sustain the supply of appropriate capital.
Traditional financial industry enterprises pollute the
environment, waste of resources, sloppy business
model, cannot achieve sustainable development, and
in the allocation of funds are often oriented to
economic efficiency. Green finance is becoming a
financial innovation in the financial sector.
Traditional financing's shortcomings can be
overcome and the capital needs of the environmental
protection industry can be met.
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-8592-4457
Green finance and dual-carbon strategies research
has been highly regarded by many scholars in recent
years. And a series of excellent research results in
various aspects have emerged, covering the
realization path of green finance to help carbon
emission reduction in the context of dual-carbon. The
concept of green finance has been reviewed by some
scholars due to the high attention given to it, its
comparison with traditional finance and its
constraints, etc., and summarized the relevant results
regarding the connotation, role, policy and
development status of green finance, etc. In this thesis,
the author will summarize the appropriate results
from the perspective of green finance.
Based on this, this paper will focus on
summarizing the influence of financial instruments
related to green finance on the dual-carbon strategy
and the ways of green finance to help carbon emission
reduction from the relevant domestic research on
green finance and systematically sorting out the
relevant research results of green finance to help
carbon emission reduction. However, Green finance
research to support carbon neutrality and carbon
emission still has some shortcomings reduction, and
102
Wu, M.
Research on Green Finance in the Context of Dual-Carbon Strategy.
DOI: 10.5220/0013207300004568
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on E-commerce and Artificial Intelligence (ECAI 2024), pages 102-108
ISBN: 978-989-758-726-9
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
further deepening research, perfecting research and
innovative research are needed.
2 THE RESEARCH LINEAGE OF
GREEN FINANCE
Green finance is crucial in promoting economic
transformation to green and low-carbon development
and realizing sustainable development by directing
the flow of funds towards protecting the environment
and sustainable development. During the period
between the end of the 20th century and the start of
the 21st century, China has not yet started the
research and practice of green finance. Relevant
research is only in the embryonic stage; some
scholars have put forward the operation mechanism
and implementation program of green management in
China's financial industry, and some have introduced
foreign research results in order to carry out academic
research and industry practice. Financial institutions
have not yet practiced green management, and there
is a lack of mechanisms for identifying, preventing
and managing environmental risks in their operations.
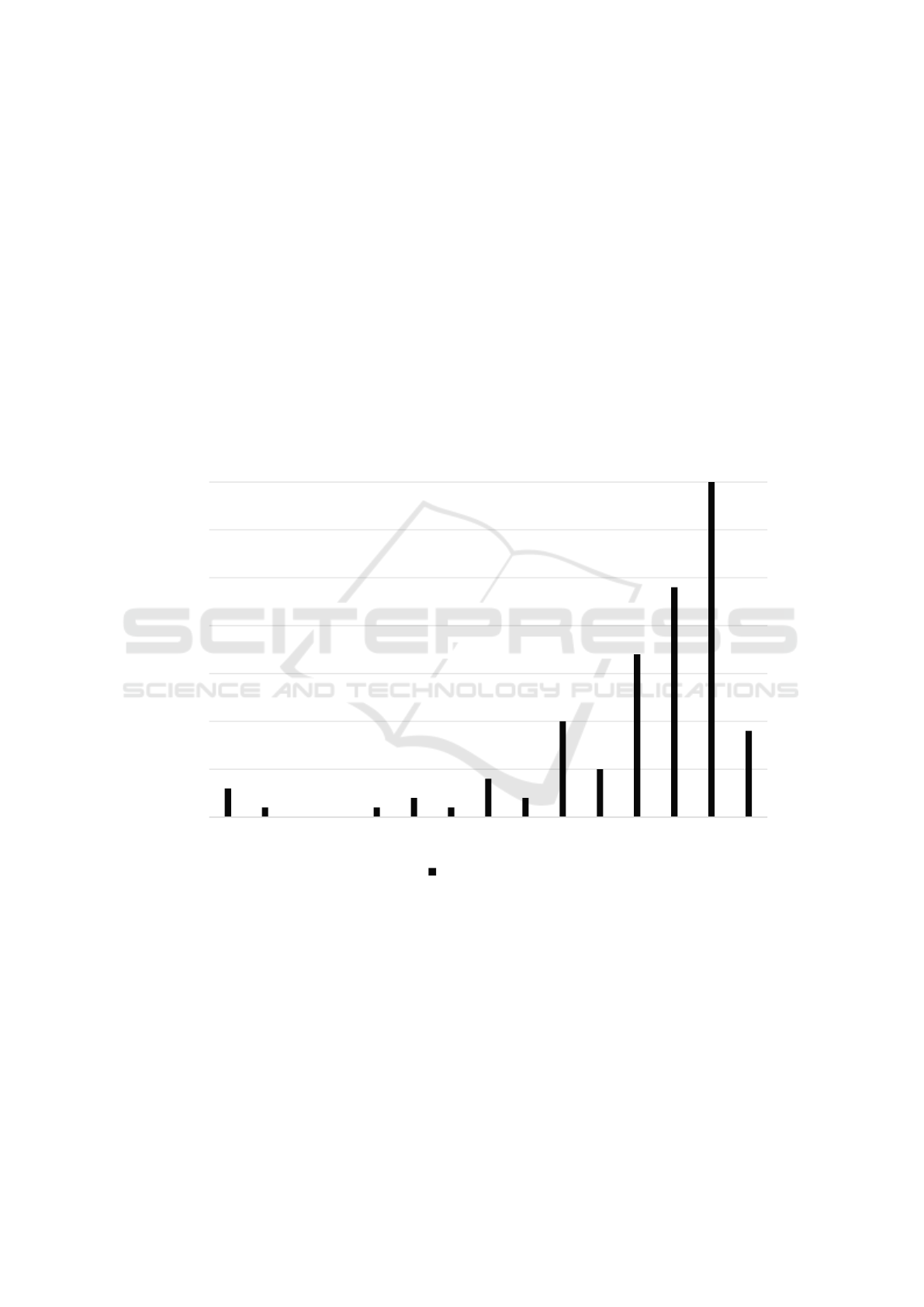
As illustrated in Figure 1, research on the topic of
green finance has gradually increased since 2013,
with scholars analyzing data and reviewing
investigation into the progress of green finance
development at that time (Qiao, 2024). Moreover,
other research fields have emphasized the importance
of green finance as a measure to govern the
environmental economy, which shows that the
importance attached to green finance in various
research fields has been further strengthened.
Figure 1: Histogram of 114 publications in Web of Science database under the topic of green finance, sorted by the number
of publication years (Qiao, 2024).
Green finance research has become more
comprehensive in recent years and is mainly divided
into studies that examine how green finance and its
related products affect regions and companies. These
studies are summarized in the following section.
3 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF
THE EMISSION REDUCTION
EFFECT OF GREEN
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Green financial tools primarily include green credit,
bonds, taxes, etc. These tools can provide the
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024
Publications
Publications
Research on Green Finance in the Context of Dual-Carbon Strategy
103

necessary financial support for green projects,
accelerate renewable energy development, promote
ecological protection, and other fields, promote
enterprises to strengthen environmental risk
management, and guide the optimal allocation of
social resources.
3.1 Green credit
Green credit refers to the government's environmental
economic policy to realize the goal of environmental
protection through financial regulation (Zeng, 2024).
This policy provides preferential credit support for
technological innovation, industrial structure
optimization, new energy development and other
related industries or projects based on national
policies (Wang, 2008). The following section will
organize and summarize the research results from the
perspective of fitting the above definition.
On the impact of green innovation, green credit
restricts the green innovation performance of the
industry to be more active, but the green innovation's
quality is not obvious, and the intensity of its role has
regional differences, with the strengthening of the
enforcement of regional environmental laws and the
protection of intellectual property rights. In terms of
technological innovation, green credit mainly through
R & D investment to promote the regional green
technological innovation’s level. Besides, green
utility model patents are promoted significantly by
green invention patents, but the role of green utility
model patents to promote the existence of not
significant.
At the corporate level, the green credit policy is
reflected in the impact of heavy pollution enterprises.
The implementation of this policy results in a
significant financial penalty and an inhibition of
investment, through optimizing energy structure,
promoting technological transformation, and
increasing the intensity of innovation investment to
inhibit the carbon emissions’ volume of the “two high”
enterprises. Green credit policies hinder the green
innovation of heavily polluting enterprises compared
to non-heavily polluting enterprises, and to a certain
extent promotes the transformation of enterprises that
are heavily polluting, and performs the function of
'elimination of the fittest', which is mainly reflected
in the state-owned enterprises, highly socially
responsible enterprises and enterprises with high
transparency of information, and in the non-state
enterprises, low social responsibility enterprises and
enterprises with low information transparency. It is
mainly found in state-owned enterprises, high social
responsibility enterprises and high information
transparency enterprises, but not in enterprises not
owned by the state, low social responsibility firms
and low information transparency firms.
3.2 Green Bonds
Green bond is the government, financial institutions,
industrial and commercial enterprises and other
issuers to investors issued by the creditor's debt
certificates, with legal effect, and the ultimate
investment of the funds raised for the green project in
line with the specified conditions, which is also
different from the ordinary bonds of its nature (Chai,
2023).
Compared with ordinary bonds, green attributes
can significantly reduce the credit spreads of bonds,
lower the financing costs of bond issuers, and thus
increase the level of environmental protection
investment. This effect varies significantly among
different types of green bonds, different issuers and
different regulatory authorities. Green bonds also
have higher capital gains, better liquidity and a
“reputational spillover” effect. By increasing
profitability and risk tolerance, stock liquidity is also
improved.. Its issuance can also significantly increase
enterprise value and have dynamic continuity. The
impact of an increase in enterprise value varies
depending on the geography and nature of enterprises.
The issuance of green bonds not only enables
enterprises to obtain more benefits, but also
substantially lowers the intensity of urban carbon
emissions, and the role of emission reduction is more
prominent in areas that have a higher level of
financial marketization and weaker environmental
regulations, and also improves urban green total
factor productivity.
3.3 Green taxation
Environmental taxation, or green taxation, aims to
raise funds for environmental protection through tax
policy, and strengthen the environmental protection
behavior of enterprises and individuals (Jia, 2002).
At the macro level, the increase in green tax
revenue is conducive to the growth of gross domestic
product and fixed asset investment, and can
effectively reduce the urban unemployment rate and
generate employment dividends, as well as a short-
lived role in suppressing the rise of CPI. Some
scholars divide green tax policy into “narrow” and
“broad” green tax policy. Narrow green tax policy
concerns those taxes levied for the intention of
protecting the environment and have the strongest
environmental protection function. In contrast, broad
ECAI 2024 - International Conference on E-commerce and Artificial Intelligence
104

green tax policy refers to those taxes that have
environmental protection function but are not levied
to protect the environment. It is also pointed out that
in the context of China's slowly rising carbon
emissions, both narrow and broad eco-friendly tax
policies have significantly suppressed China's carbon
emissions, and there is an obvious path-dependent
influence on carbon emissions. When the energy
conservation and emission reduction policy is
incorporated into the evaluation system for local
governments, the inhibitory effect of the narrow-
minded green tax scheme on carbon emissions is
further strengthened, and the inhibitory effect of the
broad-minded green tax scheme on carbon emissions
begins to appear (Fu, 2008).
At the micro level, green tax policy is mainly
manifested as green tax incentives. Although the
benefits of green transformation of enterprises are
much higher than the costs, due to the long cycle,
enterprises face higher transformation costs,
including the purchase of new environmental
protection equipment, the creation of green processes,
as well as adjusting the production structure, staff
training and other aspects of the necessary
expenditures. At the same time, the return brought by
the transformation to enterprises is uncertain within a
short period of time, and the full benefits of green
transformation activities cannot be obtained, thus
hindering the normal development of enterprises. As
a result, China has introduced a variety of green tax
incentives to promote environmental protection in
recent years, giving green tax incentives to
environmentally friendly industries and green
behaviors of enterprises investing in environmental
protection projects, and the intensity of the incentives
has been increasing. And some scholars pointed out
that green tax incentives by reducing the adjustment
costs faced in the transition of the sustainable changes
in companies to play an incentive role, and the
incentive effect with The essence of ownership rights
and the regional marketization process of different
differences (Bi, 2019).
3.4 Comparative analysis of emission
reduction effect
Some scholars combine and compare different kinds
of green financial products.
For example, Jiang Hongli et al (Jiang, 2020) pointed
out that green credit and green venture capital alone
can inhibit emissions of carbon When both are
included in the same model, Green credit and green
venture capital have the same effect on carbon
emission reduction in both high and low carbon
emission groups, but there is a significant difference
in the carbon emission reduction effect of green credit
and green venture capital in the high and low green
credit group.
In the empirical investigation of You Zhiting et al
(You, 2022), overall each green financial business has
a significant impact on reducing emissions, but the
combination of green credit and green bonds shows a
negative moderating effect, and the rest of the
combination is a complementary effect. In the
regional analysis, green industrial investment in the
western region has a stronger impact on reducing
emissions, but green credit is less effective. In the
central region, green bonds do not significantly affect
regional carbon emissions, and the complementary
effect exists only between green credit and green
industrial investment. In the eastern region, the single
or interactive terms are significantly negatively
correlated with regional emissions of carbon, and the
impact of reducing emissions is optimal.
Wang et al (Leiling, 2024) analyzed different
combinations of green financial instruments and
concluded that The emission reduction effects of
green credit and green investment were significantly
higher than those of green securities and green
insurance, and the main ways of emission reduction
differed in various regions. Among them, emission
reduction in the eastern region is significantly aided
by green credit and investment, and green credit and
green insurance are the main ways of the decrease in
emissions in the central and western regions.
Li Boyang et al (Li, 2024) showed that renewable
energy development can be significantly influenced
by green credit and venture capital. Although the
upgrading of the industrial structure can be aided by
green credit and venture capital and incentivize green
technological innovation through two channels in the
development of renewable energy, but green credit on
industrial structure upgrading to promote the stronger
effect, while green venture capital has the ability to
effectively motivate green technological innovation
to improve both quality and quantity.And the
development of renewable energy can be aided by the
role of developed financial regions in the
development of green credit and green venture capital,
which are geographically different, and a high degree
of marketization in the region more significant.
Research on Green Finance in the Context of Dual-Carbon Strategy
105

4 PATHWAYS AND IMPACTS OF
GREEN FINANCE FOR DUAL
CARBON STRATEGY
4.1 Region and industry
At the regional level, Wang Jie and Wang Jun (Wang,
2024) highlighted that the development of green
finance enhances the efficiency of local energy use,
but at the same time, it will result in a decrease in the
efficiency of energy utilization in neighboring
regions, which is not in accordance with the concept
of sustainable development. Thus, some scholars
conducted further research and found that a 46.72%
reduction in carbon emission intensity was achieved
through the establishment of pilot zones for green
financial reform and innovation at the municipal and
prefectural levels. The policy can successfully
achieve carbon emission reduction effect through the
promotion of green technological innovation and
industrial structure optimization, and green financial
reform and innovation pilot zone policy has a positive
impact on reducing carbon emissions, which is still
significantly positive under the moderating effect of
environmental regulation.
Chen Yan and Li Hao (Chen, 2024) based on
empirical analysis, concluded that green finance can
help reduce carbon emissions by utilizing advanced
industrial structures and rationalizing industrial
structures, in which the indirect carbon reduction
effect produced by green finance through the
advanced industrial structure is comparable to the
direct effect, but the indirect carbon reduction effect
produced by green finance through the rationalization
of industrial structure is comparable to the direct
effect.Green finance's indirect carbon reduction effect
can be compared to the direct effect of industrial
structure rationalization, but the indirect carbon
reduction effect of green finance through industrial
structure rationalization is much weaker than the
direct effect.
Su Xiaorong and Liu Yan (Su, 2024) discovered
that the dual-carbon strategy can be aided by the use
of green finance to reduce carbon emissions,
promoting energy transformation and enhancing
resource utilization. In terms of reducing carbon
emissions, The flow of funds can be directed towards
low-carbon industries and clean energy industries can
be promoted through green finance. Secondly, green
finance can promote the transformation and
modernizing traditional industries that produce a lot
of carbon dioxide, give financial assistance to the
application of low-carbon technologies and energy-
saving equipment, and encourage enterprises to
change their production methods, reduce the use of
resources and the emission of pollutants. In
promoting energy transformation, the rational use of
green finance can promote progress in clean energy
technology and industrial development, as well as
China's energy transformation. When it comes to
improving the utilization rate of resources, the
traditional financial system has problems such as
imprecise flow of funds and unclear investment
direction, while green finance establishes special
green funds, green credit and other mechanisms,
which makes the allocation of funds more reasonable
and focuses on resources to promote ecological
protection work.
4.2 Enterprises
The reduction of corporate carbon emissions can be
achieved through green finance by enhancing
corporate environmental awareness, as found by Xu
Yan (Xu, 2024) and others, easing financing
constraints to increase green investment and other
channels to accomplish a decrease in carbon
emissions. Meanwhile, green finance development
improves enterprises' ESG performance and
economic performance, realizing the 'win-win'
between economic growth and protecting the
environment. At the same time, the ESG scoring
system has different degrees of positive impacts on
listed companies in different industries, and the
carbon emission intensity of various types of
enterprises is affected differently by green finance.
Non-state-owned enterprises have an effect on carbon
emission intensity that is inhibited, non-heavily
polluted enterprises and high-tech enterprises is more
significant, and enterprises in first-tier cities, non-
resource cities and regions with stronger basic system
regulations can reduce carbon emission intensity
more effectively.
Wang Yulin and Zhou Yahong (Wang, 2023)
found that green financial development also has a
significant role in promoting enterprise innovation,
green financial development of state-owned
enterprises, enterprises that are in areas with better
intellectual property protection and less heavy
pollution are more significant in promoting
innovation, and green invention patent innovation can
significantly improve the financial performance and
environmental performance of enterprises.
ECAI 2024 - International Conference on E-commerce and Artificial Intelligence
106

5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper reviews the domestic research on green
finance, specifically on the effect that green financial
instruments have on the dual-carbon strategy and
green finance to help the dual-carbon strategy in two
ways to summarize.
This paper finds that carbon emissions can be
effectively reduced through the use of green financial
tools. The integration of various tools has different
effects on carbon emission reduction, and the effects
of emission reduction vary depending on the regions
and enterprises involved. At the same time, it is found
that the main way to reduce carbon emissions is by
promoting the structural upgrading of high-carbon
industries and directing capital towards industries that
reduce carbon emissions. at the regional level. At the
enterprise level, the dual-carbon strategy is practiced
mainly through promoting enterprise innovation and
alleviating financing constraints.
The future financial development will be led by
green finance, a major innovation and change in the
financial field. At present,the field of green finance
research is still in its infancy and exploration stages,
and there are still some issues that need to be resolved.
First of all, in terms of research on green financial
products, the gap between China and foreign leaders
is still obvious. Relevant research is unevenly
distributed, mostly focusing on green bonds and
green credit, with lacking knowledge about other
green finance products, such as green securities and
green insurance. Connotation of green finance
Secondly, more research needs to be conducted on the
concept of green finance.The proposal of carbon
neutral targets and the end of domestic environmental
pollution control have made carbon finance the core
of green finance. Therefore, the center of gravity of
the connotation of green finance in the future needs
to shift to carbon finance. Finally, green finance's
realization path and product research to support
carbon neutrality need to be further innovated. In
regards to the implementation of green finance to
achieve carbon neutrality, new innovative paths can
be explored based on China's national conditions. For
example, it is necessary to explore the innovation of
financial products that are focused on reducing
carbon emissions (including carbon credit, carbon
bonds, carbon equity and carbon funds, etc.) and how
green finance can be combined with financial
technology and digital finance.
REFERENCES
Bi X., Li H. Can Green Tax Preferences Promote Green
Transformation of Enterprises. Journal of Guizhou
University of Finance and Economics, 2019, (04): 89-
99.
Chen Y., Li H. Research on the Path of Green Finance to
Help Carbon Emission Reduction under the
Background of Dual Carbon. China Business Journal,
2024, (01): 114-117.
Chai H., Zhao R., Fang Y. Research on green bond issuance
and “green” incentive effect under the background of
“double carbon”. Statistics and Information Forum,
2023, 38(09): 80-94.
Fu S., Wang J. Has Green Tax Policy Reduced Carbon
Emissions in China? – An empirical study based on the
extended STIRPAT model. Modern Economic
Discussion, 2008, (02): 72-78.
Jia A. The Concept of Introducing Green Tax System in
Environmental Management. Environmental Protection,
2002, (10): 12-14.
Jiang H., Wang W., Wang L., et al. Research on the carbon
emission reduction effect of China’s green financial
development-- Taking green credit and green venture
capital as an example. Financial Forum, 2020, 25(11):
39-48+80.
Leiling W., Xiaoyun Y., Qihua C. Influence mechanism of
green finance on regional emission reduction. Heliyon,
Volume 10, Issue 1, 2024. e23861, ISSN 2405-8440.
Li B., Li T., Shen Y. Can green finance promote renewable
energy development: an example of green credit and
green venture capital. Ecological Economy, 2024,
40(05): 63-70.
Qiao D., Xu F., Li B., et al. Current Research Status and
Pathway Prospects of Green Finance to Promote the
Realization of Carbon Neutrality. Journal of Xi’an
Jiaotong University (Social Science Edition), 2024,
44(03): 87-101.
Su X., Liu Y. Study on the Path of Green Finance to Help
Carbon Emission Reduction under the Background of
“Double Carbon”. Low Carbon World, 2024, 14(06):
169-171. Wang A. Supporting Green Economy and
Developing Green Credit. Daqing Social Science, 2008,
(05): 104-106.
Wang J., Wang J. Green finance development and energy
utilization efficiency improvement: theory and Chinese
experience. Financial Forum, 2024, 29(05): 70-80.
Wang Y., Zhou Y. Green financial development and
enterprise innovation. Financial Research, 2023, 49(01):
49-62.
Xu Y., Song Y., Shao S. Impact of low-carbon transition
policy on environment-social responsibility-corporate
governance of listed companies and the mechanism of
action[J/OL]. China Population-Resources and
Environment, 2024, (04): 60-75 [2024-07-18].
Zeng H., Zhao X. Research Progress and Hot Spots of
Green Credit in China-- Based on CiteSpace
Visualization and Analysis. Times Economy and Trade,
2024, 21(03): 49-52.
Research on Green Finance in the Context of Dual-Carbon Strategy
107

You Z., Peng Z., Lai P. Research on the Impact of Green
Financial Development on Regional Carbon Emission-
- Taking Green Credit, Green Industry Investment and
Green Bond as Examples. Financial Theory and
Practice, 2022, (02): 69-77.
ECAI 2024 - International Conference on E-commerce and Artificial Intelligence
108
