
Synthesizers: A Meta-Framework for Generating and Evaluating
High-Fidelity Tabular Synthetic Data
Peter Schneider-Kamp
a
, Anton D. Lautrup
b
and Tobias Hyrup
c
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Southern Denmark, Campusvej 55, Odense, Denmark
Keywords:
Synthetic Data, Generative AI, Evaluation Metrics, Privacy, Utility, Pipelines, Method Chaining.
Abstract:
Synthetic data is by many expected to have a significant impact on data science by enhancing data privacy,
reducing biases in datasets, and enabling the scaling of datasets beyond their original size. However, the
current landscape of tabular synthetic data generation is fragmented, with numerous frameworks available,
only some of which have integrated evaluation modules. Synthesizers is a meta-framework that simplifies the
process of generating and evaluating tabular synthetic data. It provides a unified platform that allows users
to select generative models and evaluation tools from open-source implementations in the research field and
apply them to datasets of any format. The aim of Synthesizers is to consolidate the diverse efforts in tabular
synthetic data research, making it more accessible to researchers from different sub-domains, including those
with less technical expertise such as health researchers. This could foster collaboration and increase the use of
synthetic data tools, ultimately leading to more effective research outcomes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Synthetic data is by many expected to have a signif-
icant impact on data science by enhancing data pri-
vacy (Zhang et al., 2022; Hernandez et al., 2022), re-
ducing biases in datasets (van Breugel et al., 2021),
and enabling the scaling of datasets beyond their orig-
inal size (Strelcenia and Prakoonwit, 2023). In appli-
cations working with sensitive personal data such as
tabular health records (Yale et al., 2020; Hernandez
et al., 2022), synthetic data generation often presents
the only feasible way of making data publicly accessi-
ble for research without obfuscating the data beyond
usability. Numerous frameworks are available for tab-
ular synthetic data generation (Nowok et al., 2016;
Ping et al., 2017; Qian et al., 2023), potentially en-
abling researchers and businesses alike to generate
and utilize synthetic data. However, there are three
major caveats.
First, evaluating the utility and privacy properties
of synthetic data is an important part of the synthetic
data generation pipeline, but very few synthetic data
generation frameworks come with integrated evalu-
ation modules, e.g. (Qian et al., 2023; Ping et al.,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4000-5570
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9228-2417
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4783-9893
2017). There are dedicated frameworks for evaluat-
ing synthetic data, e.g. (Lautrup et al., 2024), but these
are not trivially integrated with the workflow of using
different generation frameworks.
Second, there are a plethora of data formats used
by different generation and evaluation frameworks as
well as used to represent the original data and the
generated synthetic data. Navigating between formats
ranging from comma-separated values (CSV) and Ex-
cel files (XLSX) to Hugging Face DataSets, Pandas
DataFrames, and Numpy N-dimensional arrays re-
quires significant effort.
Third, potential users with limited software devel-
opment experience are challenged in using existing
frameworks that typically require an understanding of
at least the data formats and API calling conventions.
The situation is exacerbated when users attempt to
combine two or more frameworks in their generation
workflow and especially when multi-processing is re-
quired for parallelized hyperparameter tuning, which
is often necessary to generate synthetic data satisfying
high utility and privacy demands.
In this paper, we present a novel meta-framework
aptly named Synthesizers (available on GitHub
1
) that
makes the often intricate tools for generating and
evaluating synthetic data readily available to all users,
1
https://github.com/schneiderkamplab/synthesizers
Schneider-Kamp, P., Lautrup, A. and Hyrup, T.
Synthesizers: A Meta-Framework for Generating and Evaluating High-Fidelity Tabular Synthetic Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0012856000003753
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Software Technologies (ICSOFT 2024), pages 177-184
ISBN: 978-989-758-706-1; ISSN: 2184-2833
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
177

be they novices without extensive software develop-
ment expertise or researchers in generative AI meth-
ods. The framework has been designed to abstract
synthetic data generation and evaluation tasks on a
high level, as well as to abstract from the underlying
data formats.
In Section 2, we present the design goals and high-
level design of the Synthesizers meta-framework with
respect to related work. Section 3 introduces and ex-
plains the implementation of the basic building blocks
for splitting data, training generative models, gener-
ating synthetic data, and evaluating utility and pri-
vacy of the generated data, as well as how to com-
bine these basic building blocks into powerful syn-
thetic data generation pipelines.
In Section 4 we demonstrate the power of the Syn-
thesizers meta-framework through three use cases of
increasing complexity and sophistication before con-
cluding in Section 5 on future work and community
involvement.
2 DESIGN GOALS
The primary objective of Synthesizers is to simplify
applying, combining, and switching between the nu-
merous existing frameworks for generating and eval-
uating synthetic tabular data. Instead of developing
and implementing new methods, Synthesizers aims to
create a unified platform where existing implementa-
tions can be used concurrently, making synthetic data
approachable to a wider audience. The framework
draws on the design and implementation ideas of re-
lated work, such as the unified Hugging Face plat-
form for sharing and loading data and models (Wolf
et al., 2020) and the concept of multiple abstraction
levels from TensorFlow (Abadi et al., 2015), PyTorch
(Paszke et al., 2019), and Lightning AI (Lightning AI,
2024).
2.1 Loading Data
Data can be represented using a wide variety of data
formats. Consequently, it can be a cumbersome task
to ensure that the data conforms to various libraries’
specifications. Therefore, an important task in mak-
ing synthetic data generation available to a broad au-
dience is automating the data loading and processing
operations for multiple data formats. Synthesizers au-
tomatically detects the data format and manages the
necessary pre-processing required to interface with
the selected generative framework. Table 1 presents
the data formats supported by Synthesizers separated
into four categories:
Local Files: Data are often found as files in a local
directory and should be immediately accessible to
the user.
Python Objects: For cases where manual pre-
processing is required, the file format is not sup-
ported, or the user prefers manually reading data,
Synthesizers should accept common Python ob-
jects such as a Pandas DataFrame, a NumPy
ndarray, and a Python list.
Hugging Face: Access to publicly available datasets
through the Hugging Face datasets module can
prove advantageous to researchers and developers
to facilitate reproducible testing and benchmark-
ing.
synthesizers State: Beneath the surface, Syn-
thesizers produces and outputs data through a se-
ries of sub-processes with intermdiate data and
states contained in a StateDict object. The
StateDict object enables three important pro-
cesses: 1) stop and resume at any time, 2) reuse
trained models, and 3) share model instances and
data.
Table 1: All the data formats Synthesizers accepts for the
Load module.
Category Formats
Local files .csv .tsv .xlsx
.json .jsonl .pickle
Python objects Pandas DataFrame
NumPy ndarray
Python list
Hugging Face All datasets available via
the datasets package
synthesizers state Save and load the current
state of synthesizers
2.2 Saving Data
The Synthesizers framework generates several out-
puts, including the trained model, the evaluation re-
sults, and the synthetic data, all of which should be
available to the user in a variety of formats. Specifi-
cally, the output formats should match the input for-
mats. Accordingly, the data formats presented in Ta-
ble 1 are also available as output formats, including
local Hugging Face DataSets but excluding upload to
the Hugging Face hub. Intermediate states should be
accessible for output, allowing reloading, as detailed
in Section 2.1.
ICSOFT 2024 - 19th International Conference on Software Technologies
178
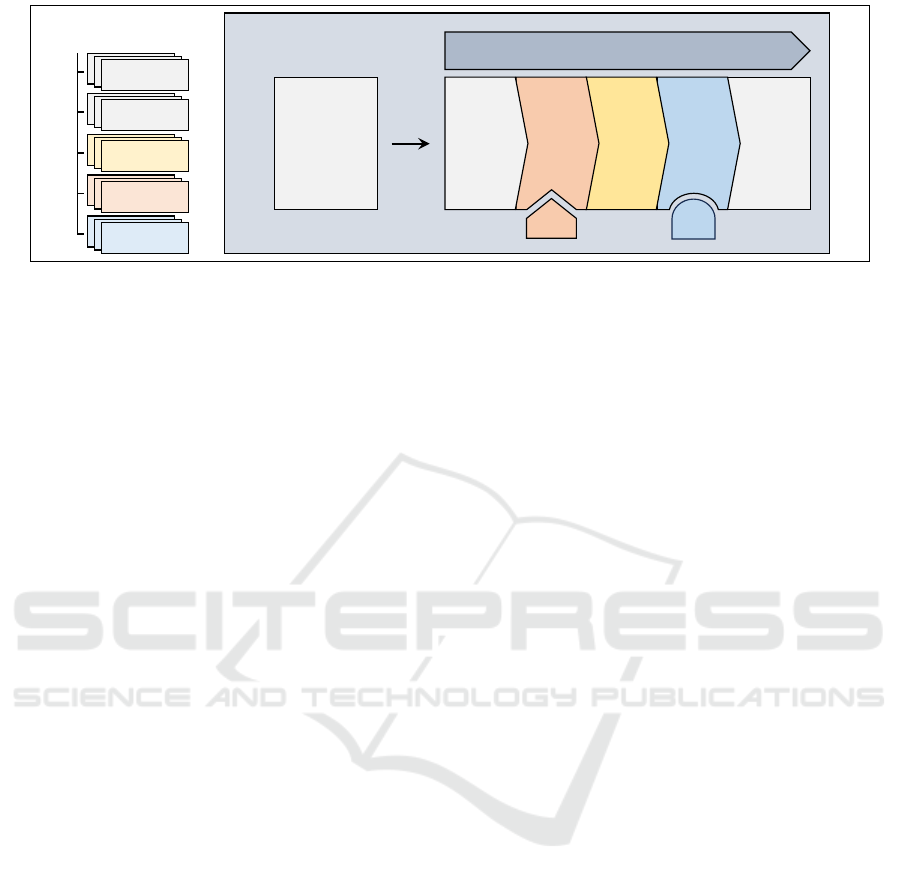
StateDict
Save
Evaluate
Generate
Train
Split
Pipeline structure
Load
EA
TA
Synthesize
“train”
“test”
“synth”
“model”
“eval”
“train”
“test”
“synth”
“model”
“eval”
“train”
“test”
“synth”
“model”
“eval”
Figure 1: Overview of the Synthesizers framework. The StateDict object is at the heart of Synthesizers and manages input
to and output from the other functionalities. StateDicts can hold train, test, and synthetic data, together with a model and
an evaluation report. To create and manipulate StateDict objects, the user applies the pipeline or the individual functional
abstractions. Passing an iterable to the pipeline results in a list of StateDicts. Most common data formats are accepted,
even loading straight from a Hugging Face dataset identifier. Splitting, generating, and saving results are generic functions
in Synthesizers, but training and evaluating methods can use multiple backends as illustrated by the train adapter (TA) and
evaluation adapter (EA). The Synthesize method chains the components with a single method.
2.3 Integrating Frameworks
One major barrier comes with the aim of Synthe-
sizers to integrate existing frameworks into a single
unified library: the frameworks do not directly work
with each other. Synthesizers addresses this issue by
accepting adapters for training and evaluation, aptly
named train adapter and evaluation adapter. Any
train adapter works seamlessly with any evaluation
adapter, and vice versa, creating a highly modular
workflow. Furthermore, the adoption of adapters en-
ables easy extension of Synthesizers’ capabilities by
including additional frameworks.
2.4 Pipeline Design
Considering the wide application range of synthetic
tabular data, it is likely that users of a frame-
work such as Synthesizers have varying levels of
programming proficiency or simply different needs.
Drawing on well-established machine learning frame-
works such as TensorFlow (Abadi et al., 2015), Py-
Torch (Paszke et al., 2019), and Lightning (Lightning
AI, 2024), Synthesizers offers two distinct approaches
to application development. Similar to TensorFlow,
which differentiates between sequential models and
the functional API, and much like Lightning, which
serves as a lightweight wrapper for PyTorch, Synthe-
sizers features a pipeline for comprehensive con-
trol of sub-processes, while a functional abstraction
simplifies the entire process down to one-liners. The
functional abstraction, while simple, still enables full
control of train and evaluation adapters as well as in-
termediate states.
3 GENERATION PIPELINES
The Synthesizers meta-framework achieves its design
goals through the StateDict and pipeline objects
that hide algorithmic complexity. The workflow is in-
spired by how the Hugging Face transformers li-
brary (Wolf et al., 2020) abstracts machine learning
backends such as TensorFlow (Abadi et al., 2015) and
PyTorch (Paszke et al., 2019). Figure 1 provides a
simple illustration of abstraction levels.
The StateDict Object. provides a unified struc-
ture to contain data in various formats, and a con-
tainer for the trained models and the evaluation re-
sult (illustrated in Figure 1). For each trained model,
a StateDict object is created containing the data
splits, the trained model, the evaluation results and
the synthetic data.
The pipeline Object. manages processing of
the relevant tasks, using the selected train and eval-
uation adapters. The pipeline passes the relevant
information from one sub-process to the next and en-
sures that the right adapters are used appropriately.
The pipeline can be used as is, or through a func-
tional abstraction which presents the combination of
pipelines in a more expressive format. The methods
Split, Train, Generate, Evaluate, and Save can
be run sequentially by method chaining. In the back-
ground, the appropriate pipeline objects are created
to suit the individual methods. Thus, the functional
abstraction enables a high-level interface that removes
some boilerplate, while the pipeline offers an experi-
ence with more granular control.
Synthesizers: A Meta-Framework for Generating and Evaluating High-Fidelity Tabular Synthetic Data
179

The Load Method. accepts all the formats pre-
sented in Table 1 and loads the data into the uni-
fied structure, the StateDict object, under the “train”
key, ensuring a consistent base when integrating third-
party backends. The module automatically detects the
data format, that the user has entered. Specifically, the
data format is detected as follows:
Local Files. If a string is entered with a file exten-
sion, the Load method attempts to read a local file
if it has a known file extension.
Python Object. If anything other than a string is en-
tered, the Load module checks whether it is an in-
stance of a Pandas DataFrame, NumPy ndarray,
Hugging Face DataSet, or a 2-d Python list and
loads accordingly, if recognized.
StateDict. If a string with no extension is entered,
and it corresponds to a local directory, the Load
module recognizes it as a saved StateDict and at-
tempts to load accordingly.
Hugging Face. If the input is a string without a file
extension and it is not recognized as a valid local
directory, the Load method assumes that the string
corresponds to a dataset from the Hugging Face
Hub and attempts to load it accordingly.
An iterable of any combination of data formats can be
passed as an argument, and the subsequent pipeline
will create a synthesis instance for each dataset, re-
sulting in a list of StateDicts, one for each dataset.
The Split Method. separates the data into a train
and a test split, updating the “train” value in the
StateDict object and creating a data element under
the “test” key. The test data is withheld from model
training and can, therefore, be used in the evaluation
process of the synthetic data, to validate data general-
izability by checking overfitting behaviour as well as
other data integrity modes. Depending on the evalua-
tion backend and its settings, the “test” element may
remain unused, but accessible to the user.
The Train Method. is the first module where
different backend adapters are available. Currently,
SynthCity (Qian et al., 2023) is the default train
adapter, with others available. The Train method
sends the training data to the chosen train adapter,
which automatically applies the syntax specified by
the underlying generative framework. The trained
model is saved in the StateDict under the “model”
key. All keyword arguments are passed to the train
adapter, allowing the user to specify all parameters
as if using the adapter framework directly.
The Generate Method. prompts the trained
model object to generate a synthetic dataset using the
train adapter’s generation method. The generated
data are processed through the output formatter, to en-
sure consistent output, and stored in the StateDict
object under the “synth” key. Generate can be called
multiple times on the same trained model, creating
multiple instances of generated data, and as a conse-
quence, multiple StateDict objects.
The Evaluate Method. uses the selected eval-
uation adapter to evaluate the synthetic data. Cur-
rently, SynthEval (Lautrup et al., 2024) is the default
evaluation adapter. The evaluator takes training data
and compares it to the generated synthetic data. De-
pending on the adapter and the selected options, the
evaluation process may also involve optional test data
and/or a designated target column for predictive as-
sessment tasks. Once completed, the result object is
stored in the StateDict object under the “eval” key.
The Save Method. can be used, at any point dur-
ing the workflow to save files or serializations in
Python’s pickle format of the various elements of
the StateDict object. Multiple objects in the same
StateDict list can be saved as unique or combined
files and loaded again using the Load method. Pick-
ling the entire StateDict object via the Save method
allows for interrupting and resuming complex training
processes involving multiple datasets and generation
methods. Particularly, it also allows saving trained
models in order to generate synthetic data at a later
point in time, enabling possible sharing of pre-trained
models.
The Synthesize Method. can be used on a
StateDict object to perform all (or some) of the
previously mentioned actions in the intended order,
see Figure 1. For keyword arguments to be properly
passed, the framework makes use of keyword pre-
fixes to ensure that keywords with prefixes “split ”,
“train ”, “gen ”, “eval ”, and “save ” are passed
to the appropriate workflow with the prefixes re-
moved.
4 USE CASES
To illustrate the versatility of the Synthesizers frame-
work, a series of use cases are presented in this section
with increasing complexities. We apply Synthesizers
to a range of datasets presented in Table 2 which in-
cludes various combinations of data types. The im-
ICSOFT 2024 - 19th International Conference on Software Technologies
180

plementations of the use cases are all available on
GitHub.
2
The installation of synthesizers is available
through pip with the command:
pip install synthesizers
The framework is designed for ease of use. Thus, the
code shown in this section includes everything needed
to operate Synthesizers completely. There is no need
for extra pre- or post-processing, and it includes all
necessary imports.
Table 2: Datasets used throughout the use cases with corre-
sponding aliases.
idx Data name #rows #atts
D1 mstz/titanic 891 10
D2 mstz/breast 683 10
D3 mstz/heart failure 299 13
D4 mstz/mammography 831 5
D5 mstz/haberman 306 4
D6 mstz/pima 768 9
4.1 Use Case 1: Synthesize from Local
File
Having a dataset as a local file is a common scenario,
in general, and when generating synthetic versions of
sensitive data, in particular (Yale et al., 2020). There-
fore, Synthesizers has the ability to load data from
multiple sources, including local directories, vari-
ous file types and formats, as well as Hugging Face
datasets.
Methods. With a dataset as a local file, the simple
workflow illustrated in Figure 2 can be followed to
load, synthesize, and save data corresponding to the
full code in Figure 3. The main consideration required
by the user is to ensure that the file format is sup-
ported (cf. Section 2 for a list of supported formats).
Everything else, from pre-processing and training to
generation and evaluation is automatically performed
by the Synthesizers framework.
The code in Figure 3 makes use of the
Synthesize method, which encompasses the sub-
methods Split, Train, Generate, Evaluate, and
Save, each of which has a series of parameters to
set. The Synthesize method handles these keywords
using corresponding prefixes such as split for the
Split parameters and is further detailed in Section 3.
2
https://github.com/schneiderkamplab/synthesizers/
tree/main/examples
Input
Load
Synthesize
Save
Output
Figure 2: Use case 1: Synthesize from local file. The
workflow is simple: 1) load from one of the available input
formats, 2) call Synthesize method, 3) and output to a file.
Results After model training and data generation,
evaluation is performed using an evaluation adapter,
which defaults to SynthEval (Lautrup et al., 2024)
and is followed by saving the output in a chosen for-
mat. The parameter eval target col passes the ar-
gument to the evaluation adapter, due to the prefix
eval , which, when using the adapter SynthEval, al-
lows evaluation where predictions are required. In the
example in Figure 5, the argument "has survived",
corresponds to an attribute name in the dataset to be
used as the target variable for evaluation.
Figure 1 illustrates that the pipeline and functional
abstraction return a StateDict object with the keys
train, test, model, synth, and eval, represent-
ing all the intermediate steps of the Synthesize pro-
cess. Each of these, or all at once, can be saved
to a preferred file format using the save name pa-
rameter to set the file name and type (determined
by the extension) and the save key representing the
StateDict object key for the relevant data. Fig-
ure 3 illustrates an example where the synthetic
data (save key="synth") is saved as an Excel file
(save name="synthetic titanic.xlsx").
1 from synthesizers import Load
2 Load(r"data/titanic.csv").Synthesize(
3 split_size=0.8,
4 train_plugin="bayesian_network",
5 gen_count=1e4,
6 eval_target_col="has_survived",
7 save_name="synthetic_titanic.xlsx",
8 save_key="synth",
9 )
Figure 3: Call to Synthesize for Use Case 1.
4.2 Use Case 2: Multiple Generation
Methods
The objectives behind creating synthetic data can
be many, including data augmentation and balanc-
ing (Strelcenia and Prakoonwit, 2023), introduc-
ing fairness (van Breugel et al., 2021), and provid-
ing privacy to individuals (Hernandez et al., 2022).
The common feature of all objectives is that the ef-
Synthesizers: A Meta-Framework for Generating and Evaluating High-Fidelity Tabular Synthetic Data
181
ficacy of the generation methods can vary with the
dataset and objective. Take, for example, the privacy
objective: the generation of synthetic private data has
a natural trade-off between quality and privacy (Yoon
et al., 2020), which can be affected by the chosen gen-
eration methods.
Methods. To address the common scenario that a
user is unfamiliar with what generation method best
suits the given dataset and objective, Synthesizers im-
plements the ability to pass multiple generation meth-
ods to the same function call as an iterable of strings
containing the method names. The workflow in Fig-
ure 4 illustrates how the same Load object, and thus
the same dataset, is used to train, generate, and eval-
uate using all the specified generation methods. The
complete code presented in Figure 5 is similar to Use
Case 1 with the main difference being a list of method
names passed to the train plugin parameter as op-
posed to a single string. Accordingly, it is not nec-
essary to perform multiple calls to the Synthesize
method.
Load
Synthesize
Synthesize
. . .
Synthesize
Save
Figure 4: Use case 2: The same dataset (Load object) is
passed to the Synthesize module which runs an instance
for each generation method. A StateDict object is created
for each synthesis and combined as a single list or output
directory.
Results. The code in Figure 5 does not specify a
save name nor a save key resulting in no file output.
Instead, the method returns a list of StateDict ob-
jects, one for each generation method. If a name and
key are specified, a directory is created containing the
files corresponding to the specified key.
The evaluation results can be accessed through the
StateDict objects and used for comparison of the
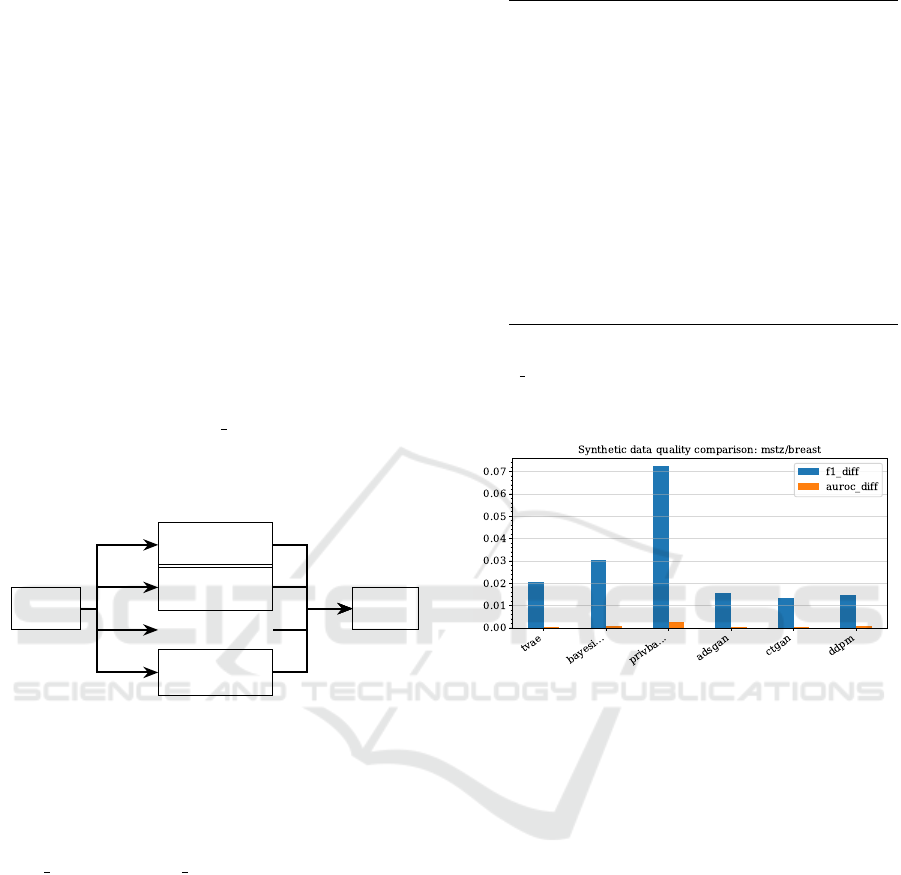
selected generation methods. Figure 6 illustrates an
example of the variance in data quality between gen-
eration methods with respect to the F1 and AUROC
differences between the real and synthetic data. While
all methods in this example show reasonable quality
results, it is clear that not all methods produce equal
quality data, highlighting the importance of compar-
ing methods.
1 from synthesizers import Load
2 state = Load("mstz/breast").Synthesize(
3 split_size=0.8,
4 train_plugin=[
5 "tvae",
6 "bayesian_network",
7 "privbayes",
8 "adsgan",
9 "ctgan",
10 "ddpm",
11 ],
12 gen_count=1e4,
13 eval_target_col="is_cancer",
14 )
Figure 5: The code used for Use Case 2. Instead of a single
train plugin, a list of plugins are selected. The input for
the Load module corresponds to a dataset on the Hugging
Face Hub.
Figure 6: Example comparison of generation methods on
utility metrics (AUROC and F1 differences between real
and synthetic data).
4.3 Use Case 3: Benchmark to Compare
Models
In this subsection, we show how Synthesizers can be
used for comparing a selection of models. This kind
of benchmark is illustrative of how a company or re-
search group may work to select which models they
should use for some particular task or how a newly
proposed generative model can show its competitive-
ness with other state-of-the-art models. Essentially,
we extend the above discussion across several more
datasets and tally up how often each model outper-
forms its peers. This approach is inspired by state-
of-the-art approaches to compare generative meth-
ods (Yan et al., 2022). In the interest of keeping ev-
erything concise in the paper, we here use far fewer
datasets than what would be advisable for a real-world
comparison, but the approach generalizes to larger
benchmarks.
ICSOFT 2024 - 19th International Conference on Software Technologies
182
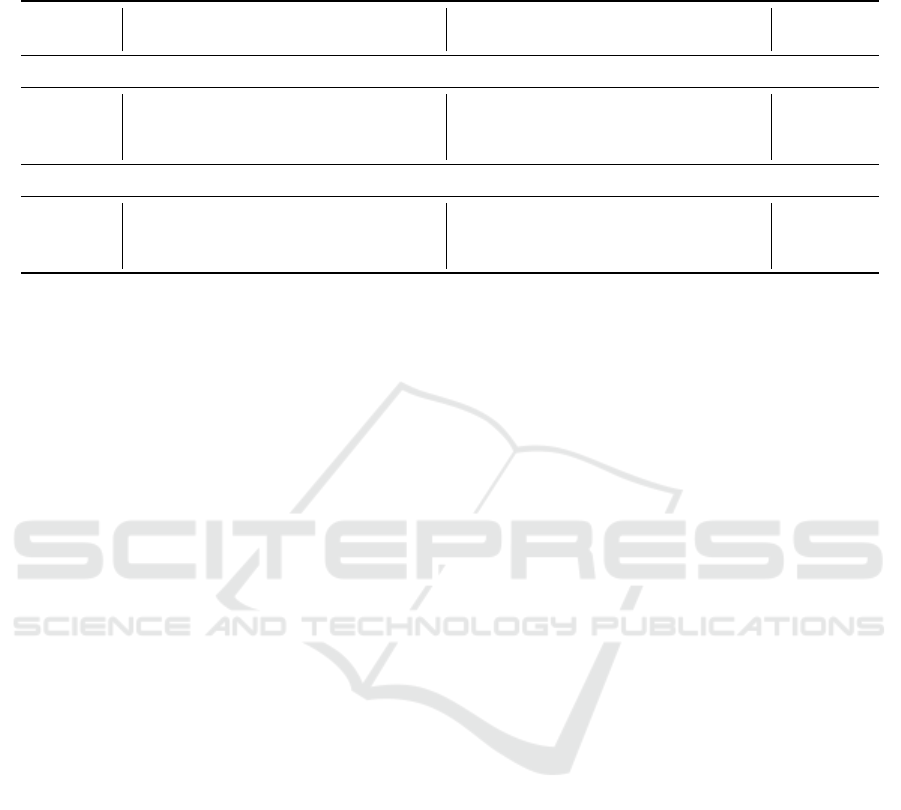
Table 3: Model Comparison Benchmark Results. The table shows the overall normalized performances on utility and privacy
metrics of each of the models on each of the datasets. In the bottom half the results are min-max normalized to make the
columns comparable and the results are summed in the bottom right.
UTILITY PRIVACY RANK
model D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 U P
Aggregated Metric Scores
ADSGAN 0.82 0.81 0.82 0.77 0.88 0.76 0.73 0.64 0.74 0.55 0.61 0.76 - -
tVAE 0.76 0.84 0.76 0.80 0.80 0.76 0.74 0.66 0.76 0.55 0.73 0.86 - -
nflow 0.82 0.81 0.79 0.79 0.92 0.83 0.77 0.72 0.76 0.54 0.63 0.77 - -
Ranked Metric Scores
ADSGAN 1 0 1 0 0.67 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 2.33 1
tVAE 0 1 0 1 0 0 0.25 0.25 1 1 1 1 2 4.5
nflow 1 0 0.5 0.67 1 1 1 1 1 0 0.17 0.1 4.17 3.27
Methods. For constructing this experiment, we se-
lect six datasets from Hugging Face; all classical UCI
datasets (see Table 2). We then proceed to load them
into a pipeline with multiple generative model plu-
gins enabled. In particular, we choose to compare
the ADSGAN (Yoon et al., 2020), tVAE (Xu et al.,
2019), and a neural spline flow (nflow) (Durkan et al.,
2019) models in SynthCity. For evaluation we use
SynthEval with the full evaluation configuration en-
abled, amounting to a total of 22 points of compari-
son. By aggregating normalized utility (privacy) met-
rics, we arrive at a utility (privacy) score for each
model on the particular dataset. Min-max scaling
of the inter-dataset scores yields a simple ranking
scheme that we combine for utility (privacy) across
all the datasets. The code is similar to the previ-
ous example, but performed iteratively. The exam-
ple involves some post-processing, why we invite the
reader to look at the notebook for the details.
Results. The results of the benchmark are shown in
Table 3. In the top section, the overall normalized
performance from running the utility and privacy met-
rics on each dataset is shown. In the bottom section,
the results are translated into ordinal rankings, which
are summed on the right. The ranking shows that on
these smaller datasets, the neural spline flow model
achieves the best balance of utility and privacy, while
the tabular variational autoencoder performs worst on
utility, but also best on privacy. ADSGAN seems to
struggle to improve privacy on these smaller datasets,
claiming the bottom privacy rank.
In the case of selecting one of these models for
another similarly sized dataset, selecting the neural
spline flow might be the preferred model. However,
this is an exaggerated example and more testing is
needed to verify this conclusion.
5 CONCLUSION AND OUTLOOK
In this paper, we have presented the design philos-
ophy and demonstrated the capabilities of the Syn-
thesizers meta-framework through three use cases.
In hopes of fostering a collaborative environ-
ment where ideas meet and thrive, the Synthesiz-
ers meta-framework draws on the Hugging Face
transformers library, enabling cross-framework
generation and evaluation of tabular synthetic data
through an intuitive interface that includes loading
and saving datasets and models.
The design goals of Synthesizers are ambitious,
and while the current version shows promising re-
sults, further work is needed to expand the applica-
tion range and make the framework more robust and
elegant, further improving the user experience. In the
future, more adapters, both for training and evalua-
tion, should be integrated into Synthesizers, alongside
additional type checking and better error handling.
Furthermore, Synthesizers can be improved to
allow combining generation methods from multiple
train adapters in the same function call. Similarly,
multiple evaluation adapters might be combined for
specific evaluation methods. While this addition will
improve the user experience, Synthesizers can already
be used to compare methods across adapters. Specifi-
cally, multiple instances of the synthesis pipeline can
be created and analyzed in parallel due to the isola-
tion of synthesis results into individual StatDict in-
stances. Furthermore, a range of evaluation adapters
can be applied to the same Generation object using
the method chaining functional abstraction presented
in Section 3.
The Synthesizers meta-framework is an important
step towards consolidating the contributions of the
tabular synthetic data community into open and ac-
Synthesizers: A Meta-Framework for Generating and Evaluating High-Fidelity Tabular Synthetic Data
183

cessible tools. Synthetic data generation is becoming
increasingly important across a variety of domains.
Facilitating a collaborative environment, where state-
of-the-art tools are available through a simple Python
interface, is crucial for fostering the growth of the
community, including the less technologically profi-
cient domains where there is a growing interest and
adoption of synthetic data.
The success of Synthesizers will largely depend
on the community taking an interest in the develop-
ment. Therefore, we encourage input and requests for
improvements and contributions from all sources. In-
tegration of other training and/or evaluation adapters
is of special importance to help the meta-framework
grow, and we look forward to collaborating with other
active research environments and users.
REFERENCES
Abadi, M., Agarwal, A., Barham, P., Brevdo, E., Chen, Z.,
Citro, C., Corrado, G. S., Davis, A., Dean, J., Devin,
M., Ghemawat, S., Goodfellow, I., Harp, A., Irving,
G., Isard, M., Jia, Y., Jozefowicz, R., Kaiser, L., Kud-
lur, M., Levenberg, J., Man
´
e, D., Monga, R., Moore,
S., Murray, D., Olah, C., Schuster, M., Shlens, J.,
Steiner, B., Sutskever, I., Talwar, K., Tucker, P., Van-
houcke, V., Vasudevan, V., Vi
´
egas, F., Vinyals, O.,
Warden, P., Wattenberg, M., Wicke, M., Yu, Y., and
Zheng, X. (2015). TensorFlow: Large-scale machine
learning on heterogeneous systems. Software avail-
able from tensorflow.org.
Durkan, C., Bekasov, A., Murray, I., and Papamakarios, G.
(2019). Neural spline flows. In Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems 32: Annual Confer-
ence on Neural Information Processing Systems 2019,
NeurIPS 2019, December 8-14, 2019, Vancouver, BC,
Canada, pages 7509–7520.
Hernandez, M., Epelde, G., Alberdi, A., Cilla, R., and
Rankin, D. (2022). Synthetic data generation for tab-
ular health records: A systematic review. Neurocom-
puting, 493:28–45.
Lautrup, A. D., Hyrup, T., Zimek, A., and Schneider-Kamp,
P. (2024). Syntheval: A framework for detailed util-
ity and privacy evaluation of tabular synthetic data.
Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.15821. Code
available on GitHub v1.4.1.
Lightning AI (2024). Pytorch lightning. https://doi.org/10.
5281/zenodo.3530844.
Nowok, B., Raab, G. M., and Dibben, C. (2016). synthpop:
Bespoke creation of synthetic data in r. Journal of
Statistical Software, 74(11):1–26.
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J.,
Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N.,
Antiga, L., Desmaison, A., K
¨
opf, A., Yang, E., De-
Vito, Z., Raison, M., Tejani, A., Chilamkurthy, S.,
Steiner, B., Fang, L., Bai, J., and Chintala, S. (2019).
PyTorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep
learning library. In Proceedings of the 33rd Interna-
tional Conference on Neural Information Processing
Systems, Red Hook, NY, USA. Curran Associates Inc.
Ping, H., Stoyanovich, J., and Howe, B. (2017). Data-
synthesizer: Privacy-preserving synthetic datasets. In
Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on
Scientific and Statistical Database Management, SS-
DBM ’17, New York, NY, USA. Association for Com-
puting Machinery.
Qian, Z., Davis, R., and van der Schaar, M. (2023). Syn-
thcity: a benchmark framework for diverse use cases
of tabular synthetic data. In Advances in Neural Infor-
mation Processing Systems, volume 36, pages 3173–
3188. Curran Associates, Inc.
Strelcenia, E. and Prakoonwit, S. (2023). A survey on
gan techniques for data augmentation to address the
imbalanced data issues in credit card fraud detec-
tion. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction,
5(1):304–329.
van Breugel, B., Kyono, T., Berrevoets, J., and van der
Schaar, M. (2021). Decaf: Generating fair synthetic
data using causally-aware generative networks. In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
volume 34, pages 22221–22233. Curran Associates,
Inc.
Wolf, T., Debut, L., Sanh, V., Chaumond, J., Delangue, C.,
Moi, A., Cistac, P., Rault, T., Louf, R., Funtowicz,
M., Davison, J., Shleifer, S., von Platen, P., Ma, C.,
Jernite, Y., Plu, J., Xu, C., Le Scao, T., Gugger, S.,
Drame, M., Lhoest, Q., and Rush, A. (2020). Trans-
formers: State-of-the-art natural language processing.
In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empiri-
cal Methods in Natural Language Processing: System
Demonstrations, pages 38–45, Online. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Xu, L., Skoularidou, M., Cuesta-Infante, A., and Veera-
machaneni, K. (2019). Modeling tabular data using
conditional GAN. In Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems 32: Annual Conference on Neural
Information Processing Systems 2019, NeurIPS 2019,
December 8-14, 2019, Vancouver, BC, Canada, pages
7333–7343.
Yale, A., Dash, S., Dutta, R., Guyon, I., Pavao, A., and
Bennett, K. P. (2020). Generation and evaluation of
privacy preserving synthetic health data. Neurocom-
puting, 416:244–255.
Yan, C., Yan, Y., Wan, Z., Zhang, Z., Omberg, L., Guinney,
J., Mooney, S. D., and Malin, B. A. (2022). A mul-
tifaceted benchmarking of synthetic electronic health
record generation models. Nature Communications,
13(1).
Yoon, J., Drumright, L. N., and van der Schaar, M. (2020).
Anonymization through data synthesis using gener-
ative adversarial networks (ADS-GAN). IEEE J
Biomed Health Inform, 24(8):2378–2388.
Zhang, Z., Yan, C., and Malin, B. A. (2022). Membership
inference attacks against synthetic health data. Jour-
nal of Biomedical Informatics, 125:103977.
ICSOFT 2024 - 19th International Conference on Software Technologies
184
