
An Example of Personalized Pathway in Medical Device Evaluation
for a Master Student in Clinical Research
Guy Carrault
1,7 a
, Thierry Chevalier
2,3,7 b
, Bruno Laviolle
4c
, Lionel Pazart
5,7
and Sylvia Pelayo
6,7 d
1
Univ. Rennes, CHU Rennes, INSERM, LTSI - UMR 1099, CIC 1414, F-35000 Rennes, France
2
CHU Nîmes, Department of Biostatistics, Epidemiology, Public Health and Innovation in Methodology,
30029 Nîmes, France
3
Univ. Montpellier, INSERM, UMR 1302, Institute Desbrest of Epidemiology and Public Health, Montpellier, France
4
Univ. Rennes, CHU Rennes, INSERM, IRSET - UMR 1085, CIC 1414, F-35000 Rennes, France
5
Univ. Franche-Comte, CHU de Besançon, INSERM, UR LINC "Neurosciences & Cognition",
CIC 1431, Besançon, France
6
Univ. Lille, CHU Lille, ULR 2694 - METRICS, INSERM CIC-IT 1403, F-59000 Lille, France
7
Tech4Health-FCRIN, France
sylvia.pelayo@univ-lille.fr
Keywords: Pedagogic Personalized Pathway, Reverse Training, Medical Device Regulatory Diploma.
Abstract: The aim of this paper is to explore the possibility of combining several training lessons to offer students a
personalized pathway in the field of medical device regulation. Feasibility is demonstrated through an
experiment currently being conducted between the universities of France-Comte, Lille, Montpellier and
Rennes.
1 INTRODUCTION
For several years now, with the advent and
democratization of the use of communications and
distance training tools, the idea has been to design
personalized lessons for students. With the help of a
tutor, students can build their own pathways and
specialize in the area of their choice, while
maintaining the coherence of their training. This
article summarizes the experiment currently being
conducted by the universities of France-Comte, Lille,
Montpellier and Rennes. This experiment is intended
to serve as an anchor for the AMI-CMA project
named ARCliMeD which proposed the structuration
of a Training Pathway for Regulatory and Clinical
Affairs in the Medical Device Industry. After an
initial description of the general framework and
objectives of the ARCliMeD project, the two training
diploma are briefly introduced. The difficulties
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1482-2067
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5110-6273
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9541-6708
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2830-2548
encountered during the experimentation are then
presented and some conclusions are drawn.
2 GENERAL CONTEXT
Recent European regulations on medical devices
require the identification of people responsible for
ensuring compliance with regulations within
companies and notified institutions (which issue CE
markings for medical devices). A recent survey by
France's leading medical device trade union,
SNITEM (Snitem, 2020), showed that ¾ of
companies find difficulties to recruit such regulatory
executives. This sector, constituted of 93% of start-
ups and small and medium companies, urgently needs
support to meet the regulatory requirements. The
need for training was defined in 2020 by a national
working group (Medical Devices Coordination
Carrault, G., Chevalier, T., Laviolle, B., Pazart, L. and Pelayo, S.
An Example of Personalized Pathway in Medical Device Evaluation for a Master Student in Clinical Research.
DOI: 10.5220/0012590500003657
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2024) - Volume 1, pages 837-841
ISBN: 978-989-758-688-0; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
837

Group, 2020), led by the national research and
teaching ministry, with numerous stakeholders
(SNITEM, biomedical engineering school,
EUROPHARMAT, Tech4Health network, …). The
aim is to train 1,000 regulatory affairs executives for
the medical device industry over 5 years. This
objective meets companies' needs in terms of training
and new skills for the professions of the future. It is
fully in line with the France 2030 re-industrialization
plan (France 2030, 2022), to create the tomorrow
medical devices in France and to support companies
in their market access initiatives.
With the rapid evolution of digital health, every
medical device company already has, or will soon
have, digital products in its medical device portfolio.
The qualification criteria for regulatory affairs are
generic. It is then important to train staff able to
manage digital products and on all the aspects of the
company's products such as risk, quality
managements and clinical evaluation.
2.1 The ARCliMeD Project
The ARCliMeD project purpose, funded by ANR, is
to elaborate individual pathways for students and
professionals in activity, who want to specialize in the
3 domains of Quality, Regulatory Affairs, clinical
evaluations for the Medical Device industry. The
project targets professionals already working in the
health products industry, and to students who have
completed a Master 1 degree. The diploma will
enable them to meet regulatory requirements and to
apply for positions as regulatory affairs managers,
particularly in digital health, but also in notified
institutions or health authorities (ANSM, HAS, …).
The proposal is based on existing, complementary
training lessons at national level, which already have
close links with manufacturers and their
representatives. A computerized coordination
platform will serve as a shared resource for defining,
with applicants the personalized training path. These
actions will be offered both in initial training and in
continuing education as part of a professionalization
or apprenticeship contract. The teaching methods
used (e-learning, streaming, visio, webinars, reverse
training, Masterclasses, in-company and hospital
internships, ...) will determine the optimum path for
the learner, with the necessary modules.
2.2 Objectives and Target Groups
The need expressed by medical device companies is
to train qualified staff in regulatory affairs. To reach
this main objective, the ARCliMeD project will
deploy the following actions:
i) Draw up a detailed map (content, hourly volume)
of the offerings proposed by the project partners,
and recompose the training offering based on
feedback from previous learners, updating the
existing offering in line with changing skills
requirements,
ii) Create a 3D skills matrix, based on job profiles
and proposed training units,
iii) Submit these proposals: for consultation
(healthcare competitiveness cluster, student
networks, and so on),
iv) Adapt lessons/skills/trades to the needs and
constraints (size, structure, organization) of
companies or organizations.
v) Accelerate the training process by combining
several master's degrees
vi) Increase the number of student trained, by raising
awareness among students in initial training.
Three target groups are involved:
i) staff performing this function within companies
(around 1,440 companies),
ii) staff of competent authorities (ANSM, HAS) (30
students are expected before 2024),
iii) students in initial training.
3 THE EXPERIMENTATION
To demonstrate the feasibility of the ARCliMeD
project an experimentation was conducted. The
experimentation is based on the DIU (Inter-
University Diploma) EvalDM: Evaluation des
dispositifs Médicaux dans le contexte du Règlement
Européen (Montpellier, Franche Comté and Lille
Universities) and the Master II Biology and Health
from Rennes University, Pathway clinical research
(Master BS ReClin, 2023).
The aim of the DIU EvalDM is to describe the
regulatory context and provide the basis for
understanding and designing clinical evaluation
methods for medical devices throughout their
development and life cycle (from proof of concept to
post-market clinical follow-up including CE marking
and reimbursement applications in the context of
European regulation 2017/745-2017/746). The skills
acquired are multiple and concern knowledge of i) the
general basics of the life cycle of a Medical Device
(MD), ii) methodologies specific to the clinical
evaluation of MD in pre-CE marking or CE marking,
iii) the basics of usage studies, iv) the principles of
post-marketing studies (Moreau, 2019). It also covers
ClinMed 2024 - Special Session on European Regulations for Medical Devices: What Are the Lessons Learned after 1 Year of
Implementation?
838

the importance of Economics and Epidemiology
training. Indeed, the notion of materioepidemiology
is an integral part of Post Market Clinical Follow-up.
Materioeconomics (or medical device economics)
and materioecology are new disciplines in which
expertise is important. Both should be developed and
taught in future years. Finally, it provides the tools
needed to fulfill a clinical evaluation document in line
with European regulations, to critically analyze the
scientific literature on the MD clinical evaluation and
to propose appropriate investigation schemes.
It is open to students in initial training (residents
in medicine studies, students in biomedical
engineering or Masters) and continuing education
(engineers, doctors, pharmacists, odontologists), as
well as industrial project managers who manufacture
medical devices (regulatory affairs managers, R&D
teams) and assessors from notified authorities. The
course has been running since 2018, with one session
per year, and has continued to evolve in terms of
content and format. Twelve students follow in
average the DIU every year representing a total 60
students already trained.
Today, it is organized in 2 main blocks: general
methodology from September to November and
specific methodology from December to March. Each
block is organized in 3 stages: i) knowledge
acquisition via asynchronous videoconferencing; ii)
3-day face-to-face seminar with practical courses
illustration previously seen; iii) summative
assessment. A dissertation on a topic of interest, with
oral defense, closes the course.
The Master's degree in Biology and Health at
Rennes University provides training in research: in
Cancerology, in Pharmacology, in Health Nutrition,
in Clinical research. This is this last pathway that has
been selected for experimentation and denoted
ReClin Master in the following. The courses alternate
theoretical sessions and personal homework projects.
The various training units are briefly presented in
Figure 1 below. Two options Units (10 ECTS) are
proposed for traditional students (Students who do
not participate to the experimentation). The year ends
with a research internship. Evaluation is based on a
continuous assessment and a dissertation.
The aim of the Master's program is to train high-
level clinical research professionals capable of
supervising the practical implementation of a trial.
The courses cover clinical research methodology, the
organization and regulatory aspects of academic and
private clinical research, pharmacology and
preclinical studies. The ReClin Master’s degree
prepares students more specifically for careers in
clinical research, professions at the interface between
research and health, and the pharmaceutical industry.
The ReClin Master has been running since 2017.
Fifteen students follow in average the ReClin Master
every year representing a total 108 students already
trained.
The idea of a personalized pathway between the 2
trainings diploma is to provide students in the
Master's degree in Biology and Health in Rennes a
specialization in MDs. In the context of the
experiment, it was decided then that students in the
Biology-Health Master's program in clinical research
could follow the DIU instead of the two optional UEs
(since these skills are already part of the DIU but
MDs-oriented).
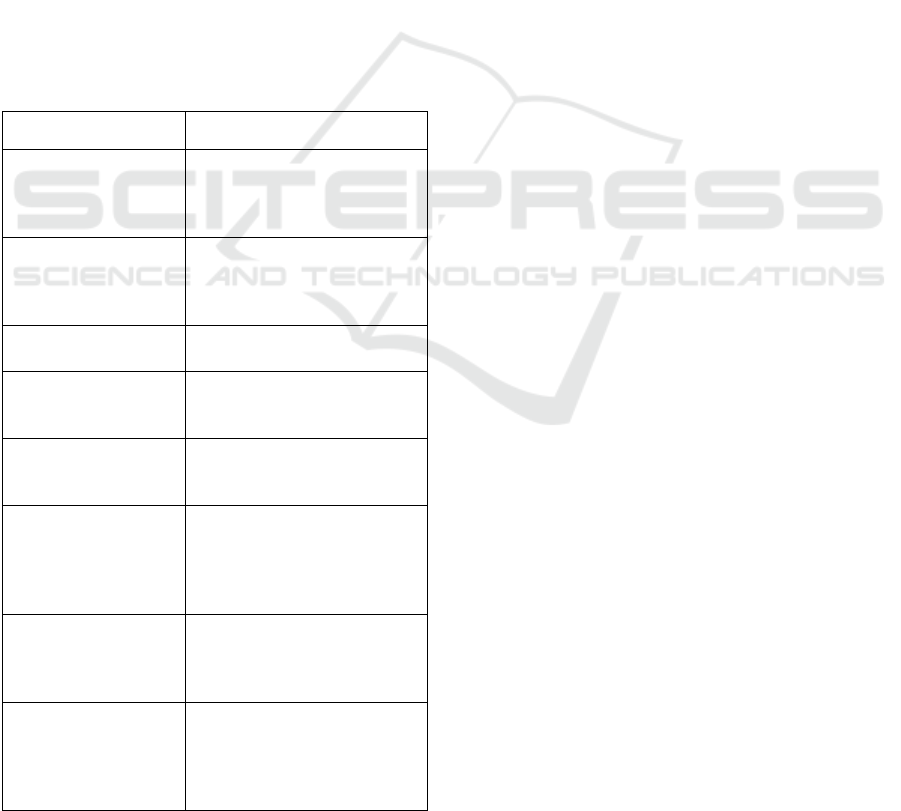
Figure 1: The different UE of the Biology and Health
Master. ECTS stands for European Credit for Transfert
System and UE for Training Unit. The two optional UE are
replaced by the DIU training Courses.
4 EXPERIMENTATION RESULT
Thirteen students were enrolled for the DIU EvalDM,
and 4 students over 20 students from the Master 2
Biology-Health chose to follow the DIU. It should be
emphasized that, like the other candidates, the
Master's students were selected on the basis of an
interview and a motivation letter.
The 4 students selected came from a variety of
backgrounds: Master 1 Biology and Health, Master 1
Integrative Biology and Physiology, Master 2
Biotechnology. The choice expressed by the students,
through a quiz, to follow the DIU EvalDM was
motivated by the fact that they would benefit from
comprehensive training in clinical research and thus
meet the requirements of the new European directive.
They also want to participate in the development of
new knowledge on innovative technologies. They
would like to take advantage of the career
opportunities offered by this field and the possibility
of contributing to the development of innovative
treatments or medical devices.
UE TRAINING LESSONS IN THE MASTER RECLIN ECTS
DBT Biotechnology in Therapeutic and Diagnostic Research
EN English
RISP or TAC
COM Communication, Management
MPP Management and Planification
MR1 Methodology for Clinical Research 1
MR2 Methodology for Clinical Research 2
RPT Precinical and Translational Research 5
SPT Monitoring and Treatment individualization 5
Intership InternShip 30
MANDATORY
OPTIONAL
Professional Insertion or Advanced Technics in life
sciences
20
An Example of Personalized Pathway in Medical Device Evaluation for a Master Student in Clinical Research
839
As described previously, the reverse training
proposed by the DIU EvalDM, with the acquisition of
prior knowledge based on documents and video clips,
represents real pedagogical potential and fits in
perfectly with the logic of a Master degree with
differentiated courses. In addition, the face-to-face
sessions enable students to reinforce and consolidate
their skills.The DIU EvalDM teaching volume is 60
hours, fully compatible with the two clinical research
master's lessons that students will not follow. It is
important to mention -and this is a crucial point of the
experimentation- that the two face to face session do
not alter the students' Master's training insofar as the
chosen date for the first face to face session coincides
with a dedicated week focused on orientation,
insertion and entrepreneurship and the second date is
proposed during the students' long study internship.
The experiment also highlighted several critical
points. Solutions were proposed to solve them and are
summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Synthetic presentation of all critical points and
solutions provided.
Critical points Proposed solutions
Distinct back-to-
university dates
between the two
diplomas
The two back-to-university
dates were synchronized at the
beginning of September
Access to courses in
different geographical
sites and temporal
constraints
Asynchronous video courses
were proposed
Registration at
University level.
Registrations were proposed in
both university
Managing official
student e-mail
addresses
A generic official student e-
mail address was used
Registration fees at the
university in charge of
the DIU
The ARCliMeD Project
covered the additional costs
Extra costs introduced
by the two 3 days face
to face seminars
(travel, hotel, ...)
Additional costs were covered
by the Montpellier University
and Lille University through the
ARCliMeD project, depending
on the seminar location.
Internship sites
The 4 students took an active
part in finding internships. This
is a critical point to look
forward to in the next years.
Dissertation defense
date
Examination dates were
differentiated to take account of
the longer internship in the
clinical research master's
degree
In summary, the analysis of the above table
illustrates the points to keep in mind and to take care
when building courses across several universities. A
deeper analysis is reported in the discussion section.
From the students' point of view after a quiz, they felt
that the implementation was effective, that the video
capsules were clear and that the face to face seminar
was very well organized. Only small difficulties were
encountered concerning the reimbursement of travel
expenses.
5 DISCUSSION
The first critical point was to know what selection
process would be used for students volunteering to
follow a combined course of this kind between the
ReClin Master degree and the DIU EvalDM. Would
they have to go through both selection processes, as
each diploma has its own recruitment criteria? The
two teaching teams agreed that the Master's selection
process alone was sufficient for admission. But
students who were interested and volunteered for this
combined pathway would benefit from a specific
question and answer information session followed by
written confirmation from the students. These
confirmation letter should have expressed their
motivation to follow this combined pathway. Five
students had initially expressed an interest in this
blended pathway and four of them confirmed and
justified their choice to pursue this pathway.
A second critical point in the experiment was also
not to overload the students with a simple
accumulation of the expectations of two existing
training programs. The training teams try to optimize
and to adapt a training transformation of the existing
lessons. This critical point can be illustrated in
particular with the dissertations that students were
required to produce during their year. For ReClin
Master, the expected dissertation was a placement
covering clinical research activities around 6 month
in a professional environment. The dissertation
required to validate the DIU EvalDM is of a different
nature. It has to attest a reflective skill in applying
specific regulatory and methodological knowledge
focused on medical devices and/or in vitro diagnostic
medical devices. The ReClin Master and DIU
EvalDM teaching teams were agreed that students
should not have to complete two dissertations (a work
placement dissertation and a cognitive dissertation),
which would overload the students. A solution has
been found so that students have to write one
dissertation that meets the criteria expected by both
courses. As a result, the orientation of the internship
ClinMed 2024 - Special Session on European Regulations for Medical Devices: What Are the Lessons Learned after 1 Year of
Implementation?
840

(only offered in the ReClin Master program) has been
adapted to also meet the criteria of a cognitive
dissertation as expected for the DIU EvalDM. Thus,
the ReClin master dissertation would propose a
section on the design of a clinical investigation study
within the meaning of the European Regulation on
Medical Devices. The work placement itself had to
include, at least in part, activities geared towards such
a design. This training transformation was approved
for ReClin Master students wishing to complete and
validate the course with the DIU EvalDM. Other
logistical issues then arose, which were also resolved
by the two teaching teams, in particular concerning
the procedures and dates for dissertations defense.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This initial experiment showed that, for a small
number of students, a personalized training program
offering a double diploma could be offered, with a
few adaptations. The experiment clearly
demonstrated the difficulties to be overcome, such as
registration, but also the advantages of offering a
training program based on existing, complementary
training courses at a national level. The DIU EvalDM
and ReClin Master's degrees were used as an
experimental resource to define, with students, a
personalized training pathway for the acquisition of
identified skills. The sharing of content, via Moodle
for example, can be considered as a success and a
guarantee of completion for the future. The next step
will be to fuse several degrees from several
universities and to offer a truly personalized course
pathway.
Even if it is, at this stage of the experimentation,
too early to draw more specific clues to this particular
double training approach dedicated to the MD
industry, it could be interesting to mention that the
students participating in both programs develop new
skills and competencies compared to traditional
students. As examples among others, we can cited:
Knowledge of the life cycle of a Medical device,
Knowledge of specific methodologies to the Medical
device clinical evaluation before CE marking, Basis
for usage studies, Know how to establish evaluation
document, Propositions of investigation plans
adapted to Medical device.
In terms of training, and from the industrial point
of view, the two degrees combined here enable the
students to meet regulatory requirements and apply
for regulatory affairs managers or regulatory focus
position within digital health companies but also in
notified health authorities (ANSM, HAS, ...).
Next steps will be to enlarge to any European
equivalent initiatives and establish any bridge
possible between different training from different
countries and identify abilities of the students that
will be trained to match expectations not only in
France but also in Europe.
FUNDINGS
This publication takes part to the ARCliMeD ANR-
23-CMAS-0002 project funded by the France 2030
program "Skills and Professions of the Future" with
the support of the Agence Nationale de la Recherche.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This article would not have written without the
contribution of the 4 students who agreed to take part
in the experiment. We hope that this article will
reflect their feelings. The authors would like to thank
them. The authors also express their gratitude to the
administrative staff of the various universities taking
part in the experimentation.
REFERENCES
Camus D, Thiveaud D, Josseran A, (2019). Nouveau
règlement européen des dispositifs médicaux :
comment l’écosystème français doit saisir l’opportunité
d’EUDAMED et du système IUD, tout en dépassant les
contraintes. Therapie. 2019 Feb;74(1):59-72
France 2030, (2022).10 objectifs pour répondre aux grands
défis de notre temps https://www.economie.gouv.fr/
france-2030
Master BS ReClin, (2023). https://formations.univ-ren
nes.fr/master-mention-biologie-sante-parcours-recherc
he-clinique-reclin
Medical Devices Coordination Group (2020).
https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/default/files/md_secto
r/docs/md_mdcg_2020_guidance_classification_ivd-
md_en.pdf
Moreau-Gaudry A., Pazart L., (2010). Development of
innovative technologies in health: The CREPS cycle,
Concept – Research – Experiment – Product – Safe
Care, Volume 31, Issue 1, February 2010, Pages 12-21
Snitem, (2023). https://www.snitem.fr/fiches_metiers_dm/
responsable-affaires-reglementaires/
An Example of Personalized Pathway in Medical Device Evaluation for a Master Student in Clinical Research
841
