
Reducing Bias in Pre-Trained Models by Tuning While Penalizing
Change
Niklas Penzel
a
, Gideon Stein
b
and Joachim Denzler
c
Computer Vision Group, Friedrich Schiller University, Jena, Germany
Keywords:
Debiasing, Change Penalization, Early Stopping, Fine-Tuning, Domain Adaptation.
Abstract:
Deep models trained on large amounts of data often incorporate implicit biases present during training time.
If later such a bias is discovered during inference or deployment, it is often necessary to acquire new data
and retrain the model. This behavior is especially problematic in critical areas such as autonomous driving
or medical decision-making. In these scenarios, new data is often expensive and hard to come by. In this
work, we present a method based on change penalization that takes a pre-trained model and adapts the weights
to mitigate a previously detected bias. We achieve this by tuning a zero-initialized copy of a frozen pre-
trained network. Our method needs very few, in extreme cases only a single, examples that contradict the
bias to increase performance. Additionally, we propose an early stopping criterion to modify baselines and
reduce overfitting. We evaluate our approach on a well-known bias in skin lesion classification and three
other datasets from the domain shift literature. We find that our approach works especially well with very few
images. Simple fine-tuning combined with our early stopping also leads to performance benefits for a larger
number of tuning samples.
1 INTRODUCTION
There are many biases present in datasets used to train
modern deep classifiers in part for sensitive applica-
tions, e.g., in skin lesion classification (Mishra and
Celebi, 2016). The models trained on such datasets
learn to copy, i.e., reproduce these harmful biases.
This behavior leads to biased predictions on unseen
data points and worse generalization. In other words,
applying such biased models in the real world leads
tangible harm, e.g., racial biases in medical applica-
tions (Huang et al., 2022).
In this work, we tackle the question of how we can
reduce such harm by correcting biases in trained mod-
els. Toward this goal, we propose a tuning scheme to
reduce bias, relying on very few examples that specif-
ically contradict the learned bias. However, directly
utilizing standard finetuning on such data would lead
to overfitting, and performance would deteriorate.
Hence, we propose to penalize changes in the model
weights harshly. We achieve this by directly tuning a
zero-initialized complementary change network with
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8002-4130
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2735-1842
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3193-3300
Figure 1: Architecture of the proposed method. We tune a
zero-initialized change network (light grey) that is added to
a frozen pre-trained model (black).
strong regularizations. An overview of our approach
can be seen in Figure 1.
Additionally, we modify our baselines, and ana-
lyze whether an alternative early-stopping approach
can help to improve performance. We find that it is
often enough to perform fine-tuning with small learn-
ing rates until the model corrects its behavior on the
tuning data to increase performance on an unbiased
test set. This early stopping also falls in line with our
motivation of minimum change. Our work is based on
the hypothesis that models trained on a biased train-
ing distribution still learn features related to the ac-
tual problem, which are sometimes overshadowed by
biases found in the training data. Reimers et al. give
90
Penzel, N., Stein, G. and Denzler, J.
Reducing Bias in Pre-Trained Models by Tuning While Penalizing Change.
DOI: 10.5220/0012345800003660
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 19th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2024) - Volume 2: VISAPP, pages
90-101
ISBN: 978-989-758-679-8; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

some evidence for this hypothesis in (Reimers et al.,
2021). They find that skin lesion classifiers learn bi-
ases as well as medically relevant features.
We use their work as a starting point and test our
approach first on a well-known bias from the skin le-
sion classification domain. Additionally, we evaluate
our methods on multiple other debiasing and domain
shift datasets contained in (Koh et al., 2021). We find
that penalizing change generally leads to improved
performance on a less biased test set, especially if
only single samples are used during the debiasing pro-
cess. Additionally, we find that our early stopping ap-
proach combined with baseline methods also leads to
improvements for larger numbers of tuning samples
and prevents overfitting in our evaluations.
2 RELATED WORK
Many previous works propose debiasing approaches
during train time, e.g., (Rieger et al., 2020; Reimers
et al., 2021; Tartaglione et al., 2021). In (Reimers
et al., 2021), Reimers et al. propose a secondary de-
biasing loss term L
db
during training to penalize any
conditional dependence between the learned repre-
sentation and a bias term given the labels. They show
that such a conditional approach is beneficial com-
pared to previous unconditional approaches.
Rieger et al. propose a similar secondary loss
term in (Rieger et al., 2020). However, they penal-
ize explanation errors instead. If the model learns the
right decisions but produces wrong explanations for
its behavior, the loss term forces the model to cor-
rect the explanations by not relying on biases. Roh et
al. present FairBatch in (Roh et al., 2021), a sam-
pling method that lowers biases during training by
adaptively changing the data point sampling during
stochastic gradient descent (SGD), formalizing SGD
as a bilevel optimization problem. However, this ap-
proach needs access to the training data, unlike our
strategy of penalizing change. Roh et al. note that
FairBatch can also be used to increase the fairness of
pre-trained models simply by finetuning.
Furthermore, Tartaglione et al. (Tartaglione et al.,
2021) propose to use a regularization technique dur-
ing training to prohibit the model from focusing on
biased features. They do this by introducing an infor-
mation bottleneck where they employ a term entan-
gling patterns corresponding to the same target class
and a second term disentangling patterns that corre-
spond to the same bias classes.
In contrast, our approach does not rely on changes
in the training process but can instead be used to re-
move or lessen bias from pre-trained models directly.
This application is especially useful in the case that
a new bias is later detected. Related to this post hoc
approach for debiasing is the work of Gira et al. (Gira
et al., 2022), where they show that it is possible to
reduce biases in pre-trained language models by fine-
tuning on debiased data. They mitigate catastrophic
forgetting by freezing the original model and adding
only less than 1% of the original parameters. This
approach is conceptionally related to our idea of min-
imal change. However, we do not need to add addi-
tional parameters during the tuning process. Instead,
we penalize the change itself. Savani et al. (Savani
et al., 2020) propose three methods of a class of de-
biasing they call intra-processing. Our method is also
part of this debiasing class because we need access to
the pre-trained model weights. They propose a ran-
dom perturbation, a layerwise optimization, and an
adversarial debiasing approach. However, in contrast
to our approach, they directly try to optimize very spe-
cific fairness criteria.
Our definition of bias is closely related to do-
main shifts. Hence, related to our work is the field
of source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) (Yu et al.,
2023). Similarly to SFDA, we also do not need ac-
cess to the source domain, only target, in our case
less biased, domain. However, SFDA specifically
focuses on adaptation without target domain labels.
Hence, SFDA approaches often rely on self-training,
e.g., (Liang et al., 2020; Qu et al., 2022; Lee and Lee,
2023), or constructing a virtual source domain, e.g.,
(Tian et al., 2021; Ding et al., 2022). In contrast, we
rely on the labels of the tuning data and consider only
scenarios with very few examples. We refer the reader
to (Yu et al., 2023) for more information about SFDA.
Our work is also related to the area of transfer
learning, and finetuning (Perkins et al., 1992; Zhuang
et al., 2020). Here we want to mention the approach
of side-tuning (Zhang et al., 2020). Zhang et al.
continuously adapt networks using additive side net-
works. These networks can be useful when encoding
priors or learning multiple tasks with the same back-
bone architecture. They combine the side network
outputs with the pre-trained output using alpha blend-
ing. In contrast, our approach considers changes for
all individual trainable weights. Hence, even if our
implementation via a change network is similar, we
combine the weights in each layer respectively lead-
ing to an intertwined computational graph. We em-
pirically compare our approach to side-tuning in our
experiments.
Also related are works that similarly to ours in-
troduce regularization with respect to a given set
of weights. In (Chelba and Acero, 2006) and
(Xuhong et al., 2018) the authors respectively intro-
Reducing Bias in Pre-Trained Models by Tuning While Penalizing Change
91

duce distance-based regularizations for transfer learn-
ing. Both works focus on ℓ
2
regularization with re-
spect to the pre-trained weights. Xuhong et al. ad-
ditionally investigate the ℓ
1
norm. In contrast, we
also investigate a combination of both norms and find
improvements compared to the individual variants.
In (Gouk et al., 2021) the authors utilize the maxi-
mum absolute row sum (MARS) norm ||.||
∞
and addi-
tionally introduce hyperparameters corresponding to
the maximum allowable distances to the pre-trained
weights. They apply their approach to transfer learn-
ing tasks, while we specifically focus on reducing bias
in a very few tuning samples scenarios. Furthermore
in (Barone et al., 2017) the authors introduce tune-
out for machine translation tasks, where the training
is regularized by randomly exchanging weights in the
network against the pre-trained versions during tun-
ing similar to the popular dropout.
Another work related to ours and originating
from the area of continual learning is memory aware
synapses (MAS) (Aljundi et al., 2018). MAS esti-
mates importance weights for each parameter in the
network given the training data. They then regular-
ize changes in parameters correspondingly. Hence,
for new continual tasks, parameters that encode lit-
tle information about previous tasks are tuned more.
In contrast, we want to change also the parameters
that encode the bias. Therefore, we penalize change
in general. Similarly to side-tuning, we empirically
evaluate MAS in our described scenario and compare
it against our approach.
3 METHOD
This section describes our approach and what we
mean by penalizing change. We first describe how we
define bias before deriving our updated loss function.
To start, let f be a model parameterized by some
pre-trained parameters θ. Given some problem space
X ×Y , with inputs x ∈X and labels y ∈Y , we assume
that f
θ
was trained on a biased sample from this space,
i.e., on (X,Y ) ⊂X ×Y . In other words, we do not see
the whole distribution during train time.
However, we assume that f
θ
works reasonably
well on the correctly distributed test data (
ˆ
X,
ˆ
Y ) ⊆
X ×Y . To be specific, we assume that our model f
θ
is applied to data that correctly represents the latent
distribution.
Given these data samples, we are interested in ex-
amples (x , y) ∈ (
ˆ
X,
ˆ
Y ) that are wrongly classified by
f
θ
presumably because they are part of the distribu-
tion not covered by (X,Y ). In other words, we are
interested in examples where
f
θ
(x) ̸= y, (1)
applies. More specifically, we are interested in the
necessary changes to the parameters θ that correct the
mistake, i.e.,
f
θ+θ
′
(x) = y. (2)
For a given problem, it is possible that multiple such
θ
′
s exist. This is especially true given the non-convex
loss surfaces of neural networks.
However, we are interested in the specific changes
θ
′
that are minimal in some sense, i.e., that change the
original parameters θ the least, to preserve pre-trained
knowledge. This change could either be minimal with
respect to some norm, e.g., ||θ
′
||
2
, or the number of
parameters changed.
Without loss of generality with respect to the norm
used, we are interested in the loss function L
mc
com-
posed of two terms: First, the original loss function L
is used to train the original set of parameters θ, and
second, the minimization constraint for some norm of
the parameter change ||.||. We define L
mc
as
L
mc
= L( f
θ+θ
′
(x),y) + λ||θ
′
||, (3)
where λ is a hyperparameter similar to the standard
weight decay parameter that describes how strongly
we constrain the change in parameters.
To optimize L
mc
, we are using the gradient with
respect to θ
′
∇
θ
′
L
mc
=
∂
∂θ
′
L( f
θ+θ
′
(x),y) + λ
∂
∂θ
′
||θ
′
||. (4)
Equations (3) and (4) can easily be adapted to
multiple wrongly classified examples, i.e., batches of
data, by utilizing the standard notation for stochastic
gradient descent.
Our derivation of the objective function L
mc
is
similar to the classical formalization of parameter
norm penalties. See, for example, Section 7.1 in
(Goodfellow et al., 2016). However, we penalize the
parameter change for some fixed θ. Intuitively, we de-
tach the original model from the computational graph
for automatic differentiation and instead add a zero-
initialized change network of the same architecture.
On this change model, our statements are equivalent
to standard parameter norm penalization.
In our experiments, we use ℓ
1
and ℓ
2
norm or com-
binations thereof. These two norms realize two differ-
ent notions of “small” change. The ℓ
2
norm leads to
changes with small Euclidean norm, while ℓ
1
norm
can lead to sparse solutions, i.e., change in fewer pa-
rameters (Goodfellow et al., 2016).
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
92

3.1 Implementation Details and
Stopping Criterion
Following the observation that we can model our ap-
proach non-destructively as a change network, we
give some implementational details in this section and
propose a stopping criterion as additional regulariza-
tion. For reference, we use the framework PyTorch
(Paszke et al., 2019).
The part of Equation (3) that is interesting dur-
ing implementation is the parameter sum in f
θ+θ
′
. To
simplify the implementation of this parameter sum for
many neural network architectures, we utilize the fol-
lowing observation.
Let g
1
,g
2
be two linear transformations given by
g
i
(x) = W
i
·x + b
i
, (5)
with parameters W
i
and b
i
. Then, g
1
(x) + g
2
(x) =
(W
1
+ W
2
) ·x + (b
1
+ b
2
) applies. This observation
holds equivalently for the convolution operation used
in many architectures because it is a linear transfor-
mation. Furthermore, batch normalization (Ioffe and
Szegedy, 2015) is linear with respect to the scaling pa-
rameters. Hence, this observation holds also for batch
normalization layers.
Using this decoupling of the sum of weights, we
can calculate the necessary output of a combined
layer by calculating the output of both the pre-trained
and the change layers separately. However, this only
applies to layers that perform a linear transforma-
tion. Hence, we have to add the outputs together be-
fore propagating them through the non-linearity to the
next layer. Nevertheless, this enables us to circum-
vent error-prone editing of the computational graph
by simply performing a layerwise output sum. The
proposed implementation is related to the idea of side
networks in side-tuning (Zhang et al., 2020). How-
ever, while side networks are combined on the output
level of the whole network, we introduce the learned
changes in the layer-wise fashion described above.
Our zero-initialization of θ
′
is related to how Control-
Net models are attached to the pre-trained networks
in (Zhang et al., 2023).
Another practical consideration is the duration of
the tuning process. In other words, how many up-
date steps are necessary to correct the bias but pro-
hibit overfitting? To tackle this problem, we propose
an early stopping regime (Yao et al., 2007) inspired
by our problem motivation (see Equation (2)). Our
heuristic is to generally stop the training once the net-
work correctly predicts the examples in the tuning
batch. This is different from standard early stopping
approaches in two ways: First, the stopping metric is
not the loss function, and second, we evaluate the cri-
terion on the tuning data itself.
Early stopping is another form of regularization to
reduce overfitting (Goodfellow et al., 2016). How-
ever, note that given the zero-initialization of our
described change network, our penalization of the
change in the first update step is zero. If the batch
of data we use to tune the network is small, it can
happen that the first step would be enough to correct
the network behavior for all tuning samples. Hence,
stopping when the network corrects the predictions
could remove the influence of our change penaliza-
tion. Therefore, we introduce a parameter ε, which
determines the minimum amount of steps to train af-
ter the model correctly classifies the tuning data. In
other words, ε > 0 ensures that even if the model
overshoots after the first update step, the change can
be penalized correctly in the successive steps leading
to small changes in the parameters. This early stop-
ping scheme enables us to extend arbitrary baselines
and reduce overfitting. Hence, we also report updated
fine-tuning, side-tuning (Zhang et al., 2020) and MAS
(Aljundi et al., 2018) in our experiments.
4 EXPERIMENTS
We evaluate our approach empirically on different
problems. Toward this goal, we selected different data
sources that fit our definition of bias defined above. In
other words, for each of the following classification
problems, we can clearly specify a difference between
the training and testing distribution with a measurable
decrease in network performance. However, first, we
detail our general experiment setup and hyperparame-
ter settings before describing the selected datasets and
results.
4.1 General Setup
Our general experiment setup is as follows: First,
we draw a batch of b samples from our set of bias-
contradicting images, i.e., images that are part of the
test distribution and wrongly predicted by the net-
work. Second, we tune the model using our proposed
change penalization, fine-tuning, side-tuning (Zhang
et al., 2020), or MAS (Aljundi et al., 2018). We adapt
our baselines using our early stopping scheme and
setting ε to zero. See Appendix 5 for larger ε values
simulating standard tuning.
In all our experiments, we perform five runs
per trained model using different non-overlapping
batches of tuning data. We investigate number of tun-
ing samples b between 1 and 32. Furthermore, for
each dataset, we repeat this tuning process for three
different models trained on the corresponding biased
Reducing Bias in Pre-Trained Models by Tuning While Penalizing Change
93

training distribution and report results averaged over
both these sources of randomness. Where applicable,
we also redraw the train-val-test split before initially
training our models. In our experiments, ImageNet
(Russakovsky et al., 2015) pre-trained ResNet18 (He
et al., 2015) models are used to train the initially bi-
ased models. In our evaluation, we report the differ-
ence in balanced accuracy on the unbiased test set af-
ter the tuning process if not stated differently. Here
balanced accuracy means the average of the accuracy
scores calculated per class, e.g., (Brodersen et al.,
2010), and we use it to ensure an accurate estimation
of model performance in the presence of dataset im-
balances Given that we report the difference before
and after the tuning, values larger than zero indicate
an increase in performance, while values below zero
represent a decrease. In all our figures, we report the
mean and standard deviation.
For the initial biased training process, we train the
models using SGD with a learning rate γ set to 1e-
3, a momentum of 0.9, and standard ℓ
2
weight decay
of 5e-4. As mentioned above, we compare our ap-
proach to three other approaches adapted to our prob-
lem setting. For side-tuning, we follow the best setup
described in (Zhang et al., 2020), and initialize the
side-network with as the pre-trained network. Simi-
larly, for MAS (Aljundi et al., 2018), we follow the
author’s suggestion and use their ℓ
2
approximation
of the importance weights Ω and set the correspond-
ing regularization parameter to 1. For standard fine-
tuning and also for the other comparison methods, we
use a reduced learning rate of 1e-5 together with the
otherwise unchanged parameters of the pre-training.
However, we adapt all three baselines to use ε = 0
to stop the tuning process early. Note that this adap-
tion is already a form of change regularization and,
therefore, encapsulates some of our intuition about
minimum change. We apply this early stopping for
two main reasons: Firstly, it ensures that the methods
fit closely to the problem we are trying to solve. Sec-
ond, without this adaptation, classical fine-tuning is
prone to overfit on the 1 to 32 tuning examples lead-
ing to a degradation in performance. We show this
behavior in Appendix 5.
For our approach, we report results for the follow-
ing hyperparameter setting: First, we select a combi-
nation of the ℓ
1
and ℓ
2
norms as our change penal-
ization norm of choice to encode the two intuitions
of small change discussed in Section 3. Specifically,
we use 0.5 ·(ℓ
1
+ ℓ
2
). Additionally, we set λ to 1.0
and use ε = 0 to ensure comparability with our se-
lected baselines. Appendix 5 includes a limited ab-
lation study of different parameter settings for our
approach and the melanoma classification task de-
scribed in Section 4.2.
4.2 ISIC Archive: Melanoma
Dataset: The ISIC archive (isi, ), a public collec-
tion of skin lesion data from various sources, includes
the SONIC dataset (Scope et al., 2016). In this study,
Scope et al. analyzed benign nevi in children. How-
ever, they used large colorful patches to cover neigh-
boring skin lesions, which are often included in the
images. This practice results in a colorful bias in skin
lesion image classification. All ∼10K images of the
original study that contain colorful patches are of the
same diagnosis - benign nevi. We utilize this fact to
construct a simple binary dataset for melanoma clas-
sification from the ISIC archive containing the diag-
noses of melanoma and benign nevi. Some of the se-
lected nevi images contain the described patches. Ad-
ditionally, we balance the two classes, melanoma and
benign nevi, to focus on the colorful patches bias. We
use this dataset to train our initially biased models.
On a test set following the training distribution, the
model achieves an average accuracy of 0.865.
We then construct an unbiased distribution by ran-
domly pasting previously extracted colorful patches
on images of the melanoma class. To achieve this,
we use patch segmentations created by Rieger et al.
(Rieger et al., 2020). Figure 7 in Appendix 5 shows
some examples from our biased training and less bi-
ased testing distribution. On the latter distribution,
our biased models drop to an average accuracy of
0.801, i.e., a decrease of 6.4 points. We then use the
setup described in Section 4.1 together with images
containing melanomata and colorful patches to per-
form debiasing.
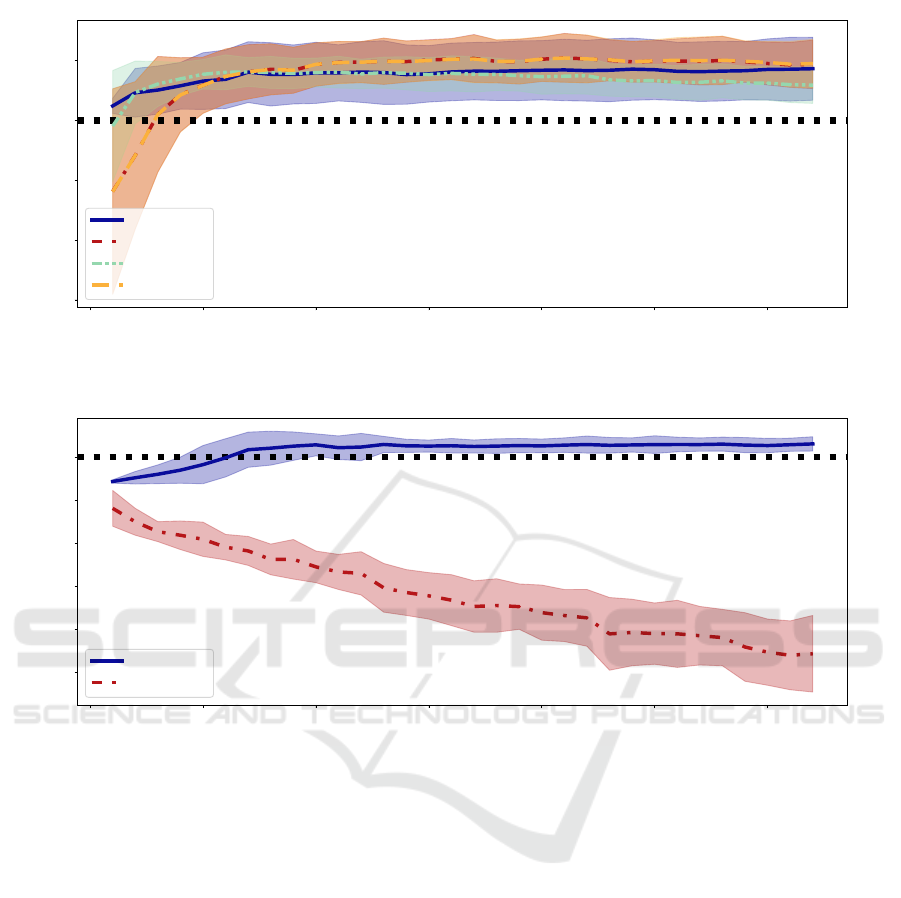
Results. Figure 2 visualizes the results of our de-
biasing experiments. We can see that for very small
numbers of tuning samples, our approach of param-
eter change penalization is beneficial and leads to an
improvement in performance on the less biased test
distribution given as few as a single image. However,
for larger batch sizes, the baselines combined with our
stopping scheme reach similar and even slightly better
results on average.
To investigate the similar performance further, we
additionally visualize ||θ||
2
−||θ + θ
′
||
2
, i.e., the dif-
ference in the Euclidean norm of the model param-
eter vectors before and after the debiasing for our
approach and fine-tuning. Figure 3 shows that even
though both methods achieve a similar increase in
performance for larger numbers of tuning samples,
they strive towards different optima. In fact, using
our approach, the Euclidean norm of the parameter
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
94
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.15
−0.10
−0.05
0.00
0.05
Balanced Accuracy Improvement
our method
fine-tuning
side-tuning
MAS
Figure 2: The difference in accuracy after debiasing using our approach versus three baseline methods combined with our
stopping scheme on the melanoma classification task.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.0005
−0.0004
−0.0003
−0.0002
−0.0001
0.0000
Norm Difference
our method
fine-tuning
Figure 3: Difference of the Euclidean norm of the model parameter vectors before and after the debiasing. Note that side-
tuning (Zhang et al., 2020) and MAS (Aljundi et al., 2018) lead to larger changes and overshadow the difference between our
approach and fine-tuning. Hence, they are omitted here.
vector increases, which is possible because we penal-
ize change and do not perform classical weight decay.
We can also observe that our approach leads to, on av-
erage, smaller changes in the parameters θ due to our
regularization.
4.3 CelebA: Haircolor
Dataset. The second dataset we chose is the celebA
dataset (Liu et al., 2015) consisting of over 200K im-
ages picturing the faces of celebrities and annotated
with facial attributes. We use the implementation
from (Koh et al., 2021) and construct a simple bi-
nary classification problem where the task is to decide
whether the hair color in an image is blond. However,
in our training distribution, all people with blond hair
are annotated as female in celebA, while we balance
not blond people between male and female celebri-
ties. Our biased models achieve, on average, a bal-
anced accuracy of 0.947 on this training distribution.
This performance drops to 0.779 on our test distribu-
tion, where no correlation between hair color and an-
notated sex exists. For debiasing, we only use images
of celebrities labeled as male with blond hair color.
Appendix 5 contains additional information and ex-
ample images of our data distributions.
Results. The second task posed by the described
celebA (Liu et al., 2015) subset is conceptionally sim-
ilar to the first problem we analyzed. Again we in-
vestigate a one-sided binary bias. Figure 4 visualizes
our results. Similar to our observations in Section 4.2,
here, our approach of change penalization leads to im-
provements as well, especially for smaller numbers of
tuning samples. Given larger batch sizes, the change
regularization implemented by our stopping criterion
Reducing Bias in Pre-Trained Models by Tuning While Penalizing Change
95

0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.10
−0.05
0.00
0.05
0.10
Balanced Accuracy Improvement
our method
fine-tuning
side-tuning
MAS
Figure 4: The difference in accuracy after debiasing using our approach versus three baseline methods combined with our
early stopping scheme on the celebA (Liu et al., 2015) classification task.
combined with the baseline methods also results in
a performance increase. MAS and fine-tuning per-
form near identical and lead, on average, to the high-
est increases for a number of 32 tuning samples. In
contrast, side-tuning is outperformed by the other ap-
proaches. Nevertheless, it still leads to an increase in
balanced accuracy.
4.4 Waterbirds: Bird Type
Dataset. Following the observation for the last two
datasets, i.e., that heavy change penalization can help
to improve simple one-sided binary biases, we now
investigate a two-sided bias. Toward this goal, we use
the waterbirds dataset (Sagawa et al., 2019) with the
implementation from (Koh et al., 2021). This dataset
is constructed by combining CUB200 (Wah et al.,
2011) birds together with Places (Zhou et al., 2017)
backgrounds. The task is to classify whether a dis-
played bird is a land or water-based species. However,
in the training distribution, there is a high correlation
between the label and a corresponding background
containing either land or water. Note that this means,
in contrast to the previous datasets we analyzed, that
there is still an overlap, i.e., some land birds are com-
bined with water images. Nevertheless, in the unbi-
ased test distribution, this correlation vanishes. The
balanced accuracies of our biased models, therefore,
decrease from 0.931 to 0.786 on average. See Ap-
pendix 5 for example images from this dataset. Note
that neither the training nor test data is class-wise bal-
anced. Hence, we compare the results for standard
accuracy and balanced accuracy. This comparison en-
ables us Finally, for debiasing, we use images from
the validation set, which follows the test distribution.
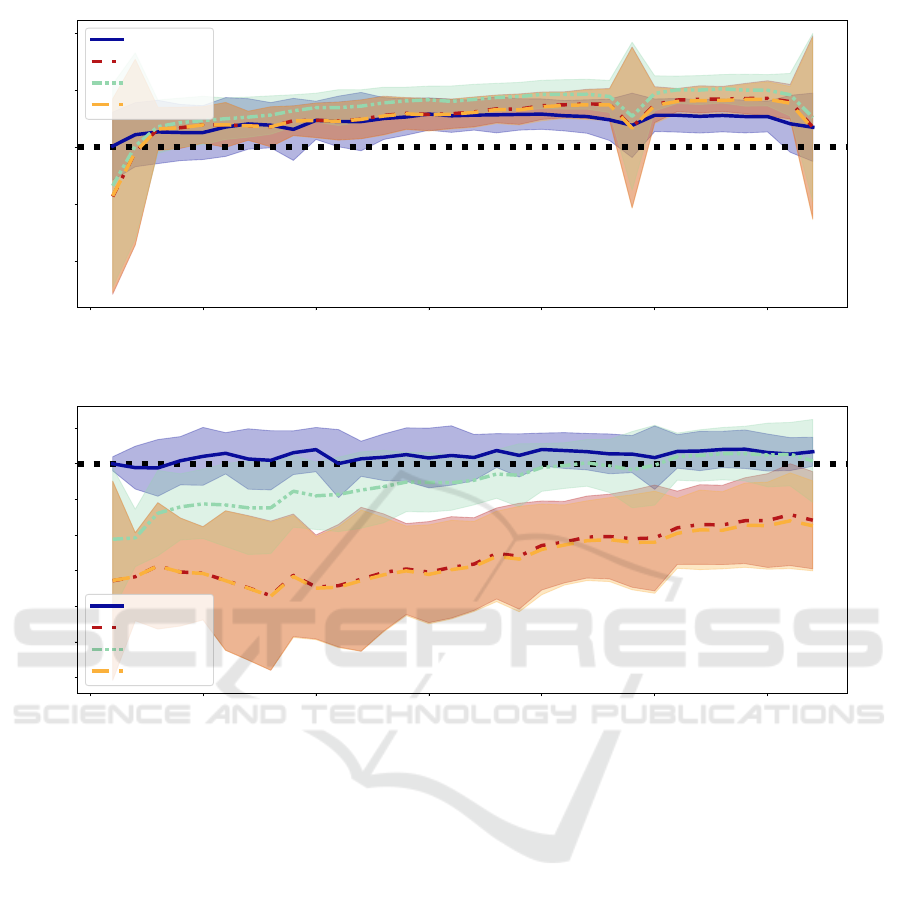
Results. For the more complicated two-sided bias
of the waterbirds dataset (Sagawa et al., 2019), we
analyze both the difference in accuracy and balanced
accuracy. Figure 5a shows that all methods lead to a
similar increase in standard accuracy. However, our
approach seems to perform slightly worse for larger
numbers of tuning samples. Yet, Figure 5b shows that
our approach does not degrade the balanced accuracy.
In contrast, while fine-tuning and MAS lead to im-
provements in the unbalanced accuracy metric, they
drop the balanced accuracy by as much as 0.1. Both
methods perform worse for smaller amounts of tuning
samples. Side-tuning still drops the performance for
nearly all numbers of tuning samples but performs in
between our approach and the other two baselines.
4.5 Camelyon17: Cancer Tissue
Dataset. The last dataset of our analysis is the
camelyon17 dataset (Bandi et al., 2018). We select
this domain shift dataset given the similarity of our
definition of bias and domain shift in general. We use
the implementation from (Koh et al., 2021), where the
task is to classify whether images of tissue slides con-
tain cancerous tissue in the image center. However,
while the training data is collected from four different
hospital sites, the test data is captured in a disjunct in-
stitution leading to a clearly visible domain shift. See
Appendix 5 for examples. Given this domain shift,
the performances of our pre-trained models deterio-
rate from 0.996 on the train distribution down to 0.786
on the test distribution. For debiasing, we use held-
out images from the test split.
Results. Figure 6 visualizes the results for our last
set of experiments. Here our approach of change
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
96
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.10
−0.05
0.00
0.05
0.10
Accuracy Improvement
our method
fine-tuning
side-tuning
MAS
(a) Difference in accuracy.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.150
−0.125
−0.100
−0.075
−0.050
−0.025
0.000
0.025
Balanced Accuracy Improvement
our method
fine-tuning
side-tuning
MAS
(b) Difference in balanced accuracy.
Figure 5: The differences in accuracy and balanced accuracy after debiasing using our approach versus three baseline methods
together with our early stopping scheme on the waterbirds dataset (Sagawa et al., 2019).
penalization performs best on average for all tested
numbers of tuning samples. Given only one tuning
sample, we can increase performance by around 0.05.
In contrast, the baselines decrease performance for
such little data. However, for a larger number of tun-
ing images, all methods increase the model perfor-
mance on the less biased test distribution. Again we
observe that MAS and fine-tuning combined with our
stopping scheme lead to similar results.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we motivate the idea of debiasing pre-
trained image classification models using heavy pe-
nalization of weight changes coupled with tuning
data contradicting learned biases. This approach fol-
lows the observation that models learn a combina-
tion of biases and meaningful features (Reimers et al.,
2021). To penalize change, we propose two methods
of change regularization: one based on an additional
loss function term and one early stopping scheme.
The latter of which can easily be added to existing
transfer learning approaches to lessen overfitting.
Our approach of adding a regularization term
leads to increased performance on less biased test
distributions of varied classification tasks in our ex-
tensive empirical evaluation. This observation holds
true for as little as one image from the test sets.
Nevertheless, for larger numbers of tuning samples,
we conclude that it is often enough to utilize simple
fine-tuning together with our early stopping scheme,
which leads to similar or better performance benefits.
A future research direction is other penalization
metrics that could lead to further benefits, e.g., the
spectral norm to force low-rank parameter changes.
Reducing Bias in Pre-Trained Models by Tuning While Penalizing Change
97
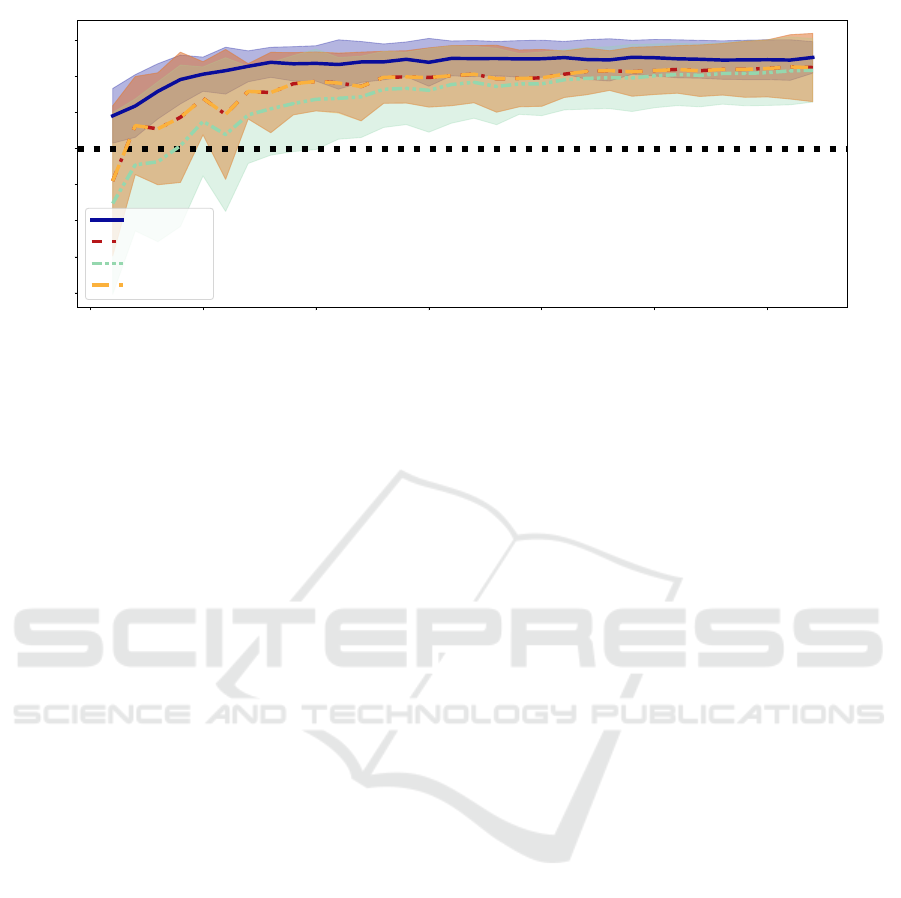
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.20
−0.15
−0.10
−0.05
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
Balanced Accuracy Improvement
our method
fine-tuning
side-tuning
MAS
Figure 6: The difference in accuracy after debiasing using our approach versus three baseline methods together with our early
stopping scheme on the camelyon17 dataset (Bandi et al., 2018).
REFERENCES
International skin imaging collaboration, ISIC Archive.
https://www.isic-archive.com/.
Aljundi, R., Babiloni, F., Elhoseiny, M., Rohrbach, M.,
and Tuytelaars, T. (2018). Memory aware synapses:
Learning what (not) to forget. In Proceedings of
the European conference on computer vision (ECCV),
pages 139–154.
Bandi, P., Geessink, O., Manson, Q., Van Dijk, M., Balken-
hol, M., Hermsen, M., Bejnordi, B. E., Lee, B., Paeng,
K., Zhong, A., et al. (2018). From detection of indi-
vidual metastases to classification of lymph node sta-
tus at the patient level: the camelyon17 challenge.
IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 38(2):550–
560.
Barone, A. V. M., Haddow, B., Germann, U., and Sen-
nrich, R. (2017). Regularization techniques for fine-
tuning in neural machine translation. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1707.09920.
Brodersen, K. H., Ong, C. S., Stephan, K. E., and Buhmann,
J. M. (2010). The balanced accuracy and its posterior
distribution. In 2010 20th International Conference
on Pattern Recognition, pages 3121–3124.
Chelba, C. and Acero, A. (2006). Adaptation of maximum
entropy capitalizer: Little data can help a lot. Com-
puter Speech & Language, 20(4):382–399.
Ding, Y., Sheng, L., Liang, J., Zheng, A., and He, R. (2022).
Proxymix: Proxy-based mixup training with label
refinery for source-free domain adaptation. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2205.14566.
Gira, M., Zhang, R., and Lee, K. (2022). Debiasing
pre-trained language models via efficient fine-tuning.
In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Lan-
guage Technology for Equality, Diversity and Inclu-
sion, pages 59–69.
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., and Courville, A. (2016). Deep
Learning. MIT Press. http://www.deeplearningbook.
org.
Gouk, H., Hospedales, T. M., and Pontil, M. (2021).
Distance-based regularisation of deep networks for
fine-tuning.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2015).
Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition.
arXiv:1512.03385 [cs]. arXiv: 1512.03385.
Huang, J., Galal, G., Etemadi, M., and Vaidyanathan, M.
(2022). Evaluation and mitigation of racial bias in
clinical machine learning models: Scoping review.
JMIR Med. Inform., 10(5):e36388.
Ioffe, S. and Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch normalization: Ac-
celerating deep network training by reducing internal
covariate shift. In International conference on ma-
chine learning, pages 448–456. PMLR.
Koh, P. W., Sagawa, S., Marklund, H., Xie, S. M., Zhang,
M., Balsubramani, A., Hu, W., Yasunaga, M., Phillips,
R. L., Gao, I., et al. (2021). Wilds: A benchmark of in-
the-wild distribution shifts. In International Confer-
ence on Machine Learning, pages 5637–5664. PMLR.
Lee, J. and Lee, G. (2023). Feature alignment by uncer-
tainty and self-training for source-free unsupervised
domain adaptation. Neural Networks, 161:682–692.
Liang, J., Hu, D., and Feng, J. (2020). Do we really need
to access the source data? source hypothesis transfer
for unsupervised domain adaptation. In International
conference on machine learning, pages 6028–6039.
PMLR.
Liu, Z., Luo, P., Wang, X., and Tang, X. (2015). Deep learn-
ing face attributes in the wild. In Proceedings of In-
ternational Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).
Mishra, N. K. and Celebi, M. E. (2016). An overview of
melanoma detection in dermoscopy images using im-
age processing and machine learning. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1601.07843.
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J.,
Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N.,
Antiga, L., et al. (2019). Pytorch: An imperative style,
high-performance deep learning library. Advances in
neural information processing systems, 32.
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
98

Perkins, D. N., Salomon, G., et al. (1992). Transfer of learn-
ing. International encyclopedia of education, 2:6452–
6457.
Qu, S., Chen, G., Zhang, J., Li, Z., He, W., and Tao, D.
(2022). Bmd: A general class-balanced multicen-
tric dynamic prototype strategy for source-free do-
main adaptation. In European Conference on Com-
puter Vision, pages 165–182. Springer.
Reimers, C., Bodesheim, P., Runge, J., and Denzler, J.
(2021). Conditional adversarial debiasing: Towards
learning unbiased classifiers from biased data. In
DAGM German Conference on Pattern Recognition
(DAGM-GCPR), pages 48–62.
Rieger, L., Singh, C., Murdoch, W., and Yu, B. (2020).
Interpretations are useful: penalizing explanations to
align neural networks with prior knowledge. In In-
ternational conference on machine learning, pages
8116–8126. PMLR.
Roh, Y., Lee, K., Whang, S. E., and Suh, C. (2021). Fair-
batch: Batch selection for model fairness. In Interna-
tional Conference on Learning Representations.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh,
S., Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A.,
Bernstein, M., Berg, A. C., and Fei-Fei, L. (2015).
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge.
International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV),
115(3):211–252.
Sagawa, S., Koh, P. W., Hashimoto, T. B., and Liang, P.
(2019). Distributionally robust neural networks for
group shifts: On the importance of regularization for
worst-case generalization. In International Confer-
ence on Learning Representations.
Savani, Y., White, C., and Govindarajulu, N. S. (2020).
Intra-processing methods for debiasing neural net-
works. Advances in Neural Information Processing
Systems, 33:2798–2810.
Scope, A., Marchetti, M. A., Marghoob, A. A., Dusza,
S. W., Geller, A. C., Satagopan, J. M., Weinstock,
M. A., Berwick, M., and Halpern, A. C. (2016). The
study of nevi in children: Principles learned and im-
plications for melanoma diagnosis. J. Am. Acad. Der-
matol., 75(4):813–823.
Tartaglione, E., Barbano, C. A., and Grangetto, M. (2021).
End: Entangling and disentangling deep represen-
tations for bias correction. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 13508–13517.
Tian, J., Zhang, J., Li, W., and Xu, D. (2021). Vdm-da:
Virtual domain modeling for source data-free domain
adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Sys-
tems for Video Technology, 32(6):3749–3760.
Wah, C., Branson, S., Welinder, P., Perona, P., and Be-
longie, S. (2011). The Caltech-UCSD Birds-200-2011
Dataset. Technical Report CNS-TR-2011-001, Cali-
fornia Institute of Technology.
Xuhong, L., Grandvalet, Y., and Davoine, F. (2018). Ex-
plicit inductive bias for transfer learning with convolu-
tional networks. In International Conference on Ma-
chine Learning, pages 2825–2834. PMLR.
Yao, Y., Rosasco, L., and Caponnetto, A. (2007). On early
stopping in gradient descent learning. Constructive
Approximation, 26:289–315.
Yu, Z., Li, J., Du, Z., Zhu, L., and Shen, H. T. (2023). A
comprehensive survey on source-free domain adapta-
tion. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11803.
Zhang, J. O., Sax, A., Zamir, A., Guibas, L., and Malik, J.
(2020). Side-tuning: a baseline for network adaptation
via additive side networks. In European Conference
on Computer Vision, pages 698–714. Springer.
Zhang, L., Rao, A., and Agrawala, M. (2023). Adding con-
ditional control to text-to-image diffusion models. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Confer-
ence on Computer Vision, pages 3836–3847.
Zhou, B., Lapedriza, A., Khosla, A., Oliva, A., and Tor-
ralba, A. (2017). Places: A 10 million image database
for scene recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence.
Zhuang, F., Qi, Z., Duan, K., Xi, D., Zhu, Y., Zhu, H.,
Xiong, H., and He, Q. (2020). A comprehensive sur-
vey on transfer learning. Proceedings of the IEEE,
109(1):43–76.
APPENDIX
Colorful Patches Examples
Figure 7 displays examples of the original biased
training data and the melanomata with inpainted col-
orful patches we added to the test distribution. The
resulting less-biased test distribution contains benign
nevi and melanomata images with colorful patches.
(a) Original images of class nevus.
(b) Artificially inpainted melanoma images.
Figure 7: Some examples from biased training and less bi-
ased test distribution.
CelebA Examples
Figure 8 displays examples from the celebA dataset
(Liu et al., 2015) described in Section 4.3. We use
the implementation provided by (Koh et al., 2021) but
rebalance and resplit the dataset. Hence, the resulting
dataset is classwise balanced.
Reducing Bias in Pre-Trained Models by Tuning While Penalizing Change
99

Figure 8: Examples contained in the celebA dataset (Liu
et al., 2015). All examples of class blond are female in the
train split (first row). The row titled “val” contains tuning
examples, i.e., men with blond hair. The final row contains
the test distribution, where men and women are uniformly
distributed in both classes.
Figure 9: Examples contained in the waterbirds dataset
(Sagawa et al., 2019). In the training distribution, birds
typically found in water-based environments correlate more
with water backgrounds, while land birds are often seen in
front of land-based backgrounds. For the validation, i.e.,
our tuning split and the test distribution, this correlation is
nearly zero.
Waterbirds Examples
Figure 9 contains examples of the waterbirds dataset
(Sagawa et al., 2019) described in Section 4.4. This
dataset is constructed with birds from the CUB-200
dataset (Wah et al., 2011) and backgrounds from the
Places dataset (Zhou et al., 2017). In the training-
split water and land-based birds correlate highly with
corresponding backgrounds. In contrast, the test dis-
tribution is more balanced, and the backgrounds and
birds are uncorrelated. We use the implementation
provided by (Koh et al., 2021).
Camelyon17 Examples
Figure 10 visualizes images contained in the came-
lyon17 dataset (Bandi et al., 2018). This dataset is
composed of similar images from different hospital
sites. These different capturing sites ensure a promi-
nent domain shift between training and test distribu-
tion. To ensure our tuning examples contain informa-
Figure 10: Examples from the camelyon17 dataset (Bandi
et al., 2018). The first row contains images from the train-
ing distribution, which consists of images from four hos-
pital sites. The validation and test splits are composed of
images from disjunct hospitals, therefore, introducing a do-
main shift. We additionally split the test data to obtain our
tuning examples.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.20
−0.15
−0.10
−0.05
0.00
Balanced Accuracy Improvement
fine-tuning, = 50
side-tuning, = 50
MAS, = 50
Figure 11: Baseline methods trained for 50 update steps
longer than our stopping criteria indicates. The black dotted
line indicates no change in balanced accuracy. All methods
lead to a decrease in performance.
tion about the test distribution, we split the original
test split provided by (Koh et al., 2021) to generate
our tuning batches. We provide more details about
our specific setup in Section 4.5.
Baseline Overfitting
In addition to our change penalization, we propose a
simple early-stopping scheme. We use this stopping
criterion to reduce overfitting on the tuning data for
our baseline methods. Here we now report what hap-
pens if we train the baseline approaches for ε = 50
update steps longer. For this comparison, we use the
dataset and setup described in Section 4.2.
Figure 11 shows the results for the amount of tun-
ing samples between 1 and 32. We see that the per-
formances of the pre-trained models on the test dis-
tribution deteriorate instead of increase. Hence, we
conclude that training for too long leads to overfitting
and reduces model performance significantly. How-
ever, we can see that both side-tuning and especially
MAS, work better than classical fine-tuning. MAS
already implicitly penalizes change to some parame-
ters, and side-tuning adds parameters and leaves the
original parameters untouched.
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
100
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.25
−0.20
−0.15
−0.10
−0.05
0.00
0.05
Balanced Accuracy Improvement
`
1
, λ = 10.0
`
1
, λ = 1.0
`
1
, λ = 0.1
`
1
, λ = 0.01
(a) ℓ
1
norm penalization.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.20
−0.15
−0.10
−0.05
0.00
0.05
Balanced Accuracy Improvement
`
2
, λ = 1000.0
`
2
, λ = 10.0
`
2
, λ = 1.0
`
2
, λ = 0.1
`
2
, λ = 0.01
(b) ℓ
2
norm penalization.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
−0.15
−0.10
−0.05
0.00
0.05
Balanced Accuracy Improvement
`
1
+ `
2
, λ = 10.0
`
1
+ `
2
, λ = 1.0
`
1
+ `
2
, λ = 0.1
`
1
+ `
2
, λ = 0.01
(c) ℓ
1
+ ℓ
2
norm penalization.
Figure 12: Results for different parameter change norms.
For each norm, we visualize varying settings of the change
penalization parameter λ. For this evaluation, we set ε = 5
to ensure that the change penalization is larger than zero,
following the observations made in Section 3.1.
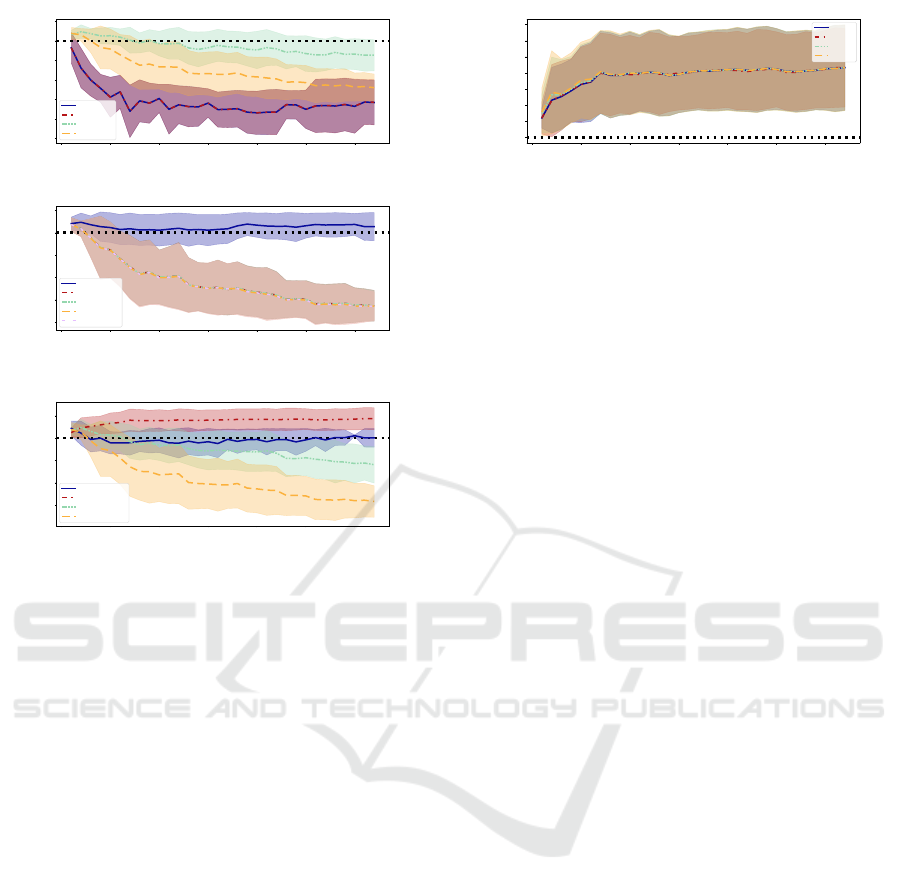
Hyperparameter Selection
Given computational constraints, we select the hy-
perparameters for our penalization approach on the
melanoma classification problem described in Sec-
tion 4.2. Here, we describe the results of our small
ablation study and discuss the influence of the three
hyperparameters for our method: penalization norm,
penalization intensity λ, and stopping parameter ε.
First, we analyze the first two hyperparameters first.
For this, we set ε to five following the observation
made in Section 3.1. We test our approach for the ℓ
1
,
ℓ
2
, and 0.5 ·(ℓ
1
+ ℓ
2
) norms. Henceforth, we abbrevi-
ate the latter with ℓ
1
+ ℓ
2
.
Figure 12 shows varying settings of the parameter
λ for each of the three norms. First, we can see that
for the ℓ
1
norm and higher λ values, the tuning dete-
riorates completely. Remember that ℓ
1
regularization
leads to sparse solutions (Goodfellow et al., 2016),
i.e., the optimum for many parameters is zero. Hence,
only tuning a small number of parameters (for large
settings of λ) seems to be counterproductive. In con-
trast, it works better for smaller λ settings, especially
for smaller numbers of tuning samples, e.g., b = 1.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of Tuning Samples
0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
Balanced Accuracy Improvement
= 0
= 5
= 25
= 100
Figure 13: Different settings for the stopping parameter ε.
Here we investigate our approach using the ℓ
1
+ ℓ
2
norm
together with λ = 1.0.
Nevertheless, for larger amounts of tuning samples,
performance still decreases. Using the ℓ
2
norm also
results in an increase in performance for smaller num-
bers of tuning samples given λ settings of 10 and
lower. In fact, all of these runs lead to very similar
parameters and, therefore, performance differences.
We argue that this behavior is overfitting similar to
the overfitting of long tuning observed in Appendix 5
indicated by the similar performance drop. Hence, we
additionally ran a set of experiments with λ = 1000.0
for ℓ
2
norm. For this setting, the models, on aver-
age, increase in performance. However, this setting
leads to convergence without correcting all tuning ex-
amples for large b, given the strong change penaliza-
tion. We, therefore, stop the tuning after 500 update
steps. Finally, Figure 12c visualizes the behavior of
our change penalization approach for the combined
ℓ
1
and ℓ
2
norms. Here we see that for very high pe-
nalization (λ = 10), the model performance for larger
batch sizes stays nearly constant compared to the pre-
trained model. Hence, penalization prevents change.
Values for λ lower than 1.0 deteriorate the model per-
formance, especially for larger b. For λ = 0.01, our
approach is closely related to standard fine-tuning.
Here the setting ε = 5 could already lead to overfit-
ting on the tuning batches as observed in Appendix 5.
In contrast, λ = 1.0 leads to an improvement in the
performance metric for all analyzed numbers of tun-
ing samples. This effect is more pronounced for batch
sizes 7 and up.
To conclude: In this first hyperparameter ablation,
we observe that in our setup for the melanoma classi-
fication task described in Section 4.2, the ℓ
1
+ℓ
2
norm
works best overall. Here we select λ = 1.0 as the pe-
nalization parameter. For this setup, we now investi-
gate different settings of the stopping criterion ε. Fig-
ure 13 visualizes results for ε values between 0 and
100. Our chosen set of hyperparameters is robust for
all settings of ε. All runs converge to indistinguish-
able performance increases. Hence, we select ε = 0
for our main experiments to increase comparability
with the extended baseline methods.
Reducing Bias in Pre-Trained Models by Tuning While Penalizing Change
101
