
Innovative Hospital Exploration and the Evolving Role of Virtual
Reality Tours in the Learning Process of Medical Students During
Clinical Clerkship
Hery Dian Septama
1,* a
, Lukmanul Hakim
1b
, Meizano Ardhi Muhamad
1c
, Fidha Rahmayani
2d
and Siska Lania
3
1
Department of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, University of Lampung, Bandar Lampung, Indonesia
2
Department of Medicine, University of Lampung, Bandar Lampung, Indonesia
3
Education and Training Installation, Abdul Moeloek General Hospital, Bandar Lampung, 35145, Indonesia
Keywords: Hospital Tour, Clinical Clerkship, Virtual Reality.
Abstract: One of the stages in the process of implementing clinical clerkship is the activity of visiting hospital facilities.
The medical students are divided into groups and visit various clinical facilities that are available. The process
of physical visits requires time and expenses. Additionally, the crowded condition of the clinic facilities often
poses a problem when trying to find a suitable visiting time. For this reason, a new method is needed that is
efficient and cost-effective, which can facilitate this activity. The purpose of this research is to design a virtual
reality-based virtual tour of a hospital. With this technology, students will still be able to experience virtual
tours of healthcare facilities that are comparable to or even as good as physical tours. Since it is virtual-based,
there will be no issue with visit time as it can be done anytime. This research will utilize the Multimedia
Development Life Cycle (MDLC) development model. There are a total of six steps in its development,
namely Concept, Design, Material Collection, Assembly, Testing, and Distribution. The hospital's virtual
reality tour facility has been constructed effectively after all the stages of the MDLC approach have been
completed. The test results indicate that all functional requirements have successfully met expectations. Users
can utilize virtual reality headsets for a more immersive experience. The concept of a virtual tour of hospital
facilities based on virtual reality has been successfully developed. The presence of virtual tours will facilitate
medical education students during their clinical clerkship to observe the available facilities without being
limited by time.
1 INTRODUCTION
The implementation of clinical clerkship is a crucial
stage in the medical education system. This process is
an important moment when aspiring medical students
transition from theoretical learning to gaining
practical experience (Konsil Kedokteran Indonesia,
2012). During this transformative journey, there are
several components, and one of them involves
visiting hospital facilities. This activity is important
because it enables medical students to gain a
comprehensive understanding of the actual processes
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4032-8831
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6868-7134
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9421-4207
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1088-4159
involved in healthcare. In the traditional approach to
clinical education, students are typically organized
into groups and assigned to visit different clinical
facilities. These facilities function as the crucibles of
medical practice, where students observe the practical
application of theoretical knowledge in real-life
scenarios. However, the traditional practice of
conducting in-person visits is not without its
difficulties, which poses a dilemma that requires a
thoughtful and subtle approach. First and foremost,
the process of conducting physical visits requires a
substantial investment of both time and resources.
During times of high demand, the hospital clinic
340
Septama, H. D., Hakim, L., Muhamad, M. A., Rahmayani, F. and Lania, S.
Innovative Hospital Exploration and the Evolving Role of Virtual Reality Tours in the Learning Process of Medical Students During Clinical Clerkship.
DOI: 10.5220/0013672100003873
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical Science and Health (ICOMESH 2023), pages 340-346
ISBN: 978-989-758-740-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

services may experience a high volume of activities.
Management and students frequently encounter
difficulties in coordinating their schedules to align
with the operational hours of the clinical facilities.
Participating in this time-consuming endeavor not
only places an additional burden but also stretches the
already limited resources of educational institutions.
Moreover, the cost of these in-person visits should not
be disregarded. The costs related to transportation,
accommodation, and other logistical factors.
Given these challenges, it is evident that there is a
clear necessity for a paradigm shift. This shift should
involve the adoption of a new approach that surpasses
the constraints of conventional clinical clerkship
implementation. The request is for a method that is
not only efficient but also cost-effective, relieving the
burdens placed on both students and educational
institutions. The experience during the Covid-19
pandemic, where there were physical contact
restrictions, was a valuable lesson that we need to
prepare alternative processes with less physical
contact (Hassan et al., 2022).
The advancement of information technology
enables us to develop technologies that can assist in
that matter. The incorporation of contemporary
technological tools offers the potential to transform
the manner in which medical students interact with
clinical facilities. Virtual clinical experiences, which
are facilitated through innovative platforms, provide
a feasible alternative to in-person visits (Dinh et al.,
2020). This transformative approach utilizes the
potential of digital connectivity to bridge the divide
between theory and practice, without being limited by
time and space constraints.
There are numerous benefits to virtual hospital
tours. One of the most significant advantages is found
in its inherent flexibility. In contrast to traditional in-
person visits, virtual experiences have the advantage
of not being bound by operational hours (Satrya,
2023). This means that students can engage with
clinical facilities visit whenever it is convenient for
them. This flexibility not only empowers students to
balance their educational pursuits with other
commitments but also addresses the perennial
challenge of finding suitable visiting times amidst the
chaotic schedules of clinical facilities. Furthermore,
the significance of the cost-effectiveness of virtual
hospital tours cannot be emphasized enough. The
financial barriers that hinder access to practical
experiences are eliminated, as students no longer
struggle with the economic burdens associated with
physical visits. The elimination of travel and
accommodation expenses democratizes access to
quality medical education. This ensures that every
aspiring medical professional, regardless of their
financial background, can benefit from immersive
clinical experiences.
In order to address these concerns, a potential
solution could be to adopt a hybrid approach that
leverages the advantages of both virtual and physical
experiences. The thoughtful incorporation of virtual
platforms into the current structure of hospital or
clinical tours enables students to take advantage of
the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of virtual
experiences. The advancement of virtual reality
technology enables the creation of virtual visits to
healthcare facilities. The purpose of this research is to
design a virtual reality-based virtual tour of a hospital.
2 RELATED WORKS
Virtual reality (VR) refers to a technologically
simulated experience that utilizes pose tracking and
3D near-eye displays in order to provide users with an
immersive sensation of being present within a virtual
world. Virtual tours using VR technology have
emerged as a new and innovative way to explore and
experience remote places and educational
institutions. VR technology allows users to create
their own customized reality and provides a realistic
and immersive experience. It has been applied in
various industries such as education, tourism, and
hospitality. VR virtual tours have been found to
enhance visualization, understanding, and learning
quality in students (Kishor et al., 2023). Kishor et al
discusses the concept of using extended reality,
specifically virtual reality, to create a virtual tour of a
college campus with a voice assistant service based
on IoT technology. Leshchuk et al (2023) discusses
the use of virtual tours in education, specifically using
VR technologies. It explores the advantages,
disadvantages, and skills that can be developed
through virtual tours. It also provides instructions on
creating virtual tours using the Panotour Pro program
(Leshchuk et al., 2023).
In other works, Firmansyah et al discusses the use
of virtual reality technology for virtual tour training,
which aims to promote school media and shape
visiting patterns (Firmansyah et al., 2023). While
Shuta et al presents a Web-based multi-user Virtual
Reality system for a virtual tour of remote places,
supporting 360-degree images and live 360-degree
videos (Shuta et al., 2023). The exploration of virtual
tourism and the potential of virtual reality (VR) to
enhance the tourism industry is presented by
Polishchuk et al. It mentions the use of VR
technologies to immerse people in a virtual
Innovative Hospital Exploration and the Evolving Role of Virtual Reality Tours in the Learning Process of Medical Students During Clinical
Clerkship
341
environment that recreates touristic destinations and
experiences. However, it does not specifically
mention the concept of a virtual tour using virtual
reality (Polishchuk et al., 2023). Ferbangkara et al
also explore the usability of the Lampung Heritage
Virtual Reality Tour, which is a virtual reality tool for
educating about Lampung's historical heritage
(Ferbangkara et al., 2023). The work of Arago et al
also show that the development of a virtual tour
system using virtual reality technology to offer an
immersive user experience of selected tourist spots in
Manila (Arago et al., 2022).
In the field of healthcare, VR tours have recently
emerged as an innovative tool in the learning process
of medical students during their clinical clerkship
(Nguyen et al., 2023). Virtual reality (VR)-based
learning modules have demonstrated their efficacy in
enhancing pharmacology knowledge among medical
students, as evidenced by previous studies (Vignaraja
et al., 2022). Moreover, these modules have garnered
positive feedback from undergraduate medical
students. Virtual clerkship curricula in anesthesiology
have effectively integrated video-recorded
simulation-based scenarios to offer trainees a
simulated clinical experience (Wang, 2021). The
paper concluded that the virtual format provides a
valuable and informative learning experience. Roni
work shows that most undergraduate medical
students are receptive to VR as a learning tool (Roni
et al., 2023). The COVID-19 pandemic has expedited
the implementation of virtual platforms for medical
education, encompassing the utilization of virtual
reality (VR) technology (Shrivastava & Shrivastava,
2023). The work by Tyastuti et al even advise
community medicine clerkship modules need to be
redesigned for the COVID-19 pandemic. The work
concluded that modifications and variations in
learning methods and coordination are necessary
(Tyastuti et al., 2023).
Based on the aforementioned related works, the
utilization of virtual reality holds immense promise in
revolutionizing the delivery of medical education.
This is because it provides a platform for dynamic and
adaptive learning experiences. The utilization of
virtual induction programs, specifically through the
implementation of video tours, has been discovered
to significantly improve the confidence and
orientation of medical students within hospital
settings. The evolving role of virtual reality tours in
medical education shows promise, as it offers
immersive and experiential learning opportunities for
students during their clinical clerkship.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This research will utilize the Multimedia
Development Life Cycle (MDLC) development
model depicted in Figure 1 (Luther, 1994; Rickman
Roedavan et al., 2022). This method offers a well-
organized framework that aims to assist multimedia
developers in navigating the intricate process of
developing interactive and captivating multimedia
content. This type of material may encompass a blend
of textual information, visual graphics, auditory
elements, video clips, animated sequences, and
various other interactive components. The
Multimedia Development Life Cycle (MDLC) plays
an essential role in ensuring the successful execution
of multimedia projects that align with the intended
objectives and user expectations.
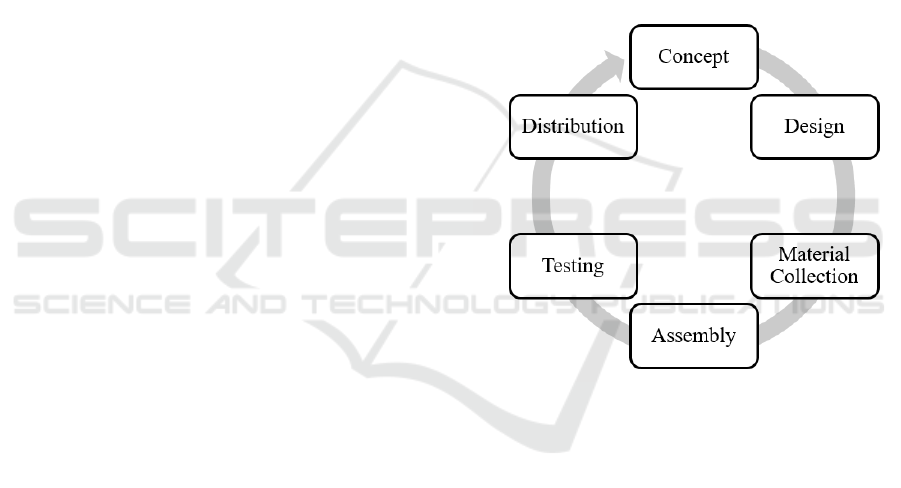
Figure 1: Multimedia Development Life Cycle (MDLC)
There are a total of six steps in its development,
namely Concept, Design, Material Collection,
Assembly, Testing, and Distribution (Luther, 1994).
The Concept phase is the initial stage of the project,
where goals and audience are defined. Design
involves the creation of a comprehensive project
blueprint. The Material Collection is responsible for
gathering the necessary assets, such as text, graphics,
and media. Assembly incorporates these elements
through the utilization of authoring tools and
programming. Testing ensures the functionality of a
system or product by identifying and addressing any
potential issues or problems. Finally, Distribution
releases the multimedia project through a variety of
channels. These stages collectively serve as a guide
for the systematic development, ensuring both quality
and effective delivery to the target audience through
an iterative process.
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
342

4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Concept
In the Concept phase, there is a plan to create a virtual
tour media for hospital facilities based on virtual
reality. The main objective is to improve medical
education through delivering a fully immersive
experience for students learning medicine. The target
audience comprises of medical students and
healthcare professionals who are looking for a
thorough understanding of hospital environments.
Feasibility is evaluated by taking into account
technological requirements, budget limitations, and
the potential for collaboration with hospitals. The
scope has been defined, which outlines the specific
hospital areas that will be included. This ensures that
the project remains focused and manageable.
Collaborating with stakeholders, such as hospital and
university management, medical students and VR
developers, ensures that a wide range of perspectives
are taken into account. The conceptual framework is
of greatest significance as it defines the essential
characteristics and interactive components, including
360-degree views, informational overlays, and
interactive simulations. The Concept phase plays an
essential part in ensuring that the VR project is in line
with educational objectives. After discussing with
every stakeholder involved, it has been agreed upon
that there are two levels of user role for this system,
namely administrators and users shown in Table 1.
Table 1: User role and requirement.
Role Re
q
uirement
Administrator The administrator is able to manage
the virtual tour effectively by
adding spots, reducing them, and
u
p
datin
g
the s
y
stem.
User Users can view the virtual tour that
has been developed.
4.2 Design
During the complicated design phase of developing a
virtual hospital tour for medical education, a thorough
analysis is conducted. This analysis explores various
aspects such as visual aesthetics, user interface
design, information architecture, navigation
strategies, interactive elements, and the alignment of
storyboarding with educational objectives. Visual
aesthetics serve as a canvas for innovation, as
designers properly create an immersive and visually
captivating environment that goes beyond simple
simulation. Their goal is to elevate medical education
to unparalleled levels.
The design of the user interface takes center stage,
requiring a seamless blend of functionality and user
engagement. The strategic positioning of interactive
elements and the development of an intuitive
interface are intended to empower users to
effortlessly navigate the virtual hospital tour. At the
same time, information architecture is carefully
organized, ensuring that the flow of medical
information is logical and easy to navigate within the
virtual realm. Storyboarding serves as a dynamic
blueprint, aligning the narrative flow of the virtual
tour with educational objectives. The visual roadmap
serves as a guide for the progression of the
experience. It helps refine the structure and pacing to
ensure that each interaction contributes meaningfully
to the overarching educational goals. The design
phase, in essence, involves a meticulous orchestration
of creativity and purpose.
4.3 Material Collection
During the Material Collection phase, an image-
taking activity is conducted at each predetermined
location. A 360-degree image is a photograph with a
2:1 aspect ratio. The length of the X-axis is twice that
of the Y-axis, resulting in an equirectangular shape
for the photo. It is essentially a 360-degree fully
immersive photograph. The capturing of a 360
Equirectangular Image is carried out by team
members using a 360 camera depicted in Figure 2.
Another camera is also used to capture images that
will be used as icons for each location. The results of
the graphic that is collected in this phase will be
analyzed and stitched in the subsequent phase. The
photo shoot is scheduled during non-peak hours at the
pre-determined location to ensure optimal photo
taking and minimal disruption to the clinic's
activities.
Figure 2: 360 Equirectangular panoramic image taking
Innovative Hospital Exploration and the Evolving Role of Virtual Reality Tours in the Learning Process of Medical Students During Clinical
Clerkship
343

4.4 Assembly
The subsequent stage is Assembly, which involves
the connection (stitching) of the collected images to
produce a wide panoramic image and its integration
into the virtual tour application. The assembly phase
for a virtual hospital tour in medical education is a
complex process with multiple facets. The process
includes integrating multimedia assets, programming
interactivity, implementing user controls, fine-tuning
visual and audio elements, creating interactive
simulations, iteratively refining, and integrating
assessment mechanisms. This phase plays an
essential role in converting the gathered materials into
a unified and engaging educational experience that
aligns with the overall objectives of the hospital
virtual tour in relation to medical education during
clinical clerkship. The sample of original 360
equirectangular image, taken from the 360 camera
depicted in Figure 3, was processed as shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 3: 360 Equirectangular image
Figure 4: The result of processing a 360 equirectangular
image
4.5 Testing
The Phase Testing is conducted to test the virtual tour
system that has been created, ensuring that every
feature functions as intended. After conducting
testing on the created virtual tour system, all
navigation menus within the system are functioning
properly. According to black-box testing shown in
Table 2, all features are working properly. This
system can be used as a virtual tour medium for
students during clinical clerkship to convey
information about existing health facilities. Through
this virtual tour system, students can see the health-
care facilities that the hospital has, such as clinic
rooms, administration areas, laboratories, and other
common facilities.
Table 2: Testing scenario and results
No. Scenario Expected Results Result
Functional Feature
1 Explore virtual
hospital locations.
User visit hospital
spot in Virtual
Reality
Pass
2 Access
information
regarding virtual
hospital facilities.
Information
displayed on
hospital facilities
spot
Pass
3 Choose a virtual
hospital location
using the
location panel..
User teleport to a
chosen location.
Pass
Non Functional
4 Can make a
selection by
using the view
option,
specifically
through Gaze
Control.
Processed in 1,5
seconds
Pass
5 User may use
stereoscopic
display
Display in
stereoscopic
Pass
6 Place switching
can occur
instantly.
(Teleport)
Teleportation Pass
7 Can return to the
home menu from
any screen
Home menu button
and functional
Pass
8 Can exit the
application
Exit button and
functional
Pass
4.6 Distribution
Once the virtual tour has been refined and is ready for
deployment, the next step is to consider strategies for
widespread dissemination. This task entails
determining the most efficient channels and platforms
for reaching medical students and management. One
potential distribution avenue could be online
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
344

platforms, which would ensure convenient access for
students in various locations. The presentation of
each location is in the form of a 360-degree
panoramic photo depicted in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Web-based 360 Hospital Virtual tour
The Distribution phase also takes into account the
technical requirements for end-users, ensuring
compatibility with a wide range of VR devices. Clear
documentation and support mechanisms have been
established to assist users in accessing and navigating
the virtual hospital tour effortlessly. Figure 6 depicts
the final product that was delivered to the medical
students, who are the users.
Figure 6. Final product of hospital tour by using VR
5 CONCLUSIONS
The concept of a virtual tour of hospital facilities
based on virtual reality has been successfully
developed. According to black-box testing, all
features are working properly. The presence of virtual
tours will facilitate medical education students during
their clinical clerkship to observe the available
facilities without being limited by time. Users can
access the virtual tour either through web access on a
computer device or by using a VR device.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to express our sincere appreciation to
the Higher Education for Technology and Innovation
(HETI) Project Unila for their support in funding this
research through the Innovation and Domestic
Collaboration Research Scheme for the year 2023.
We would also like to express our gratitude to Abdul
Moeloek General Hospital and the Faculty of
Medicine at the University of Lampung for their
collaboration in this research project.
REFERENCES
Arago, N. M., De Guzman, D. V., De Leon, N. A., Esteves,
R., Pepino, T. L. F., Socorro, L. D., Amado, T. M.,
Amon, V. M., Fernandez, E. O., Quijano, J. F. C., &
Galido, E. A. (2022). MNLTour: A Web and Mobile
Application for Virtual Tour System of Select Tourist
Spots Around Manila Using 360-degree Imagery and
Virtual Reality Technology. 2022 IEEE 14th
International Conference on Humanoid,
Nanotechnology, Information Technology,
Communication and Control, Environment, and
Management (HNICEM), 1–5.
https://doi.org/10.1109/HNICEM57413.2022.1010953
8
Dinh, A., Furukawa, L., & Caruso, T. J. (2020). The virtual
visit: Using immersive technology to visit hospitals
during social distancing and beyond. Pediatric
Anesthesia, 30(8), 954–956.
https://doi.org/10.1111/pan.13922
Ferbangkara, S., Mardiana, M., Arinto, F. X., Sulistiyanti,
S. R., Khairudin, K., Sulistiono, W. E., & Muhammad,
M. A. (2023). Usability of Lampung Heritage Virtual
Reality Tour. Journal of Engineering and Scientific
Research, 4(2). https://doi.org/10.23960/jesr.v4i2.107
Firmansyah, H., Budiraharjo, E., & Sofyan, A. (2023). The
Virtual Reality Socialization and Training: Virtual
Tour. ASEAN Journal of Empowering Community,
2(2), 74–83.
https://doi.org/10.24905/ajecom/vol2issue2.38
Hassan, A. B., El-Agroudy, A., Shehata, M. H., Almoawda,
M. A., & Atwa, H. S. (2022). Adaptations of Clinical
Teaching During the COVID-19 Pandemic:
Perspectives of Medical Students and Faculty
Members. Advances in Medical Education and
Practice, Volume 13, 883–892.
https://doi.org/10.2147/AMEP.S371201
Kishor, I., Kumar, K., Sharma, A., & Bansal, H. (2023).
Virtual Tour with Voice Assistant using Extended
Reality. International Journal of Engineering and
Advanced Technology, 12(5), 1–6.
https://doi.org/10.35940/ijeat.E4127.0612523
Konsil Kedokteran Indonesia, K. K. I. (2012). Standar
Kompetensi Dokter Indonesia (Competence standards
of Indonesian doctors). Konsil Kedokteran Indonesia.
Innovative Hospital Exploration and the Evolving Role of Virtual Reality Tours in the Learning Process of Medical Students During Clinical
Clerkship
345

Leshchuk, S., Struk, O., Hrynkiv, N., & Overko, Y. (2023).
USING VIRTUAL TOUR DEVELOPMENT
TECHNOLOGIES IN SCHOOL EDUCATION. The
Scientific Issues of Ternopil Volodymyr Hnatiuk
National Pedagogical University. Series: Pedagogy,
1(1), 14–23. https://doi.org/10.25128/2415-
3605.23.1.2
Luther, A. C. (1994). Authoring interactive multimedia. AP
Professional.
Nguyen, W., Fromer, I., Remskar, M., & Zupfer, E. (2023).
Development and Implementation of Video-Recorded
Simulation Scenarios to Facilitate Case-Based Learning
Discussions for Medical Students’ Virtual
Anesthesiology Clerkship. MedEdPORTAL, 11306.
https://doi.org/10.15766/mep_2374-8265.11306
Polishchuk, E., Bujdosó, Z., El Archi, Y., Benbba, B., Zhu,
K., & Dávid, L. D. (2023). The Theoretical Background
of Virtual Reality and Its Implications for the Tourism
Industry. Sustainability, 15(13), 10534.
https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310534
Rickman Roedavan, Bambang Pudjoatmodjo, & Aprianti
Putri Sujana. (2022). MULTIMEDIA DEVELOPMENT
LIFE CYCLE (MDLC).
https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.16273.92006
Roni, M., Kim, K., Xie, N., Hammersmith, L., & Berrocal,
Y. (2023). Can Virtual Reality Improve Pharmacology
Education in Medical Students? ASPET 2023 Annual
Meeting Abstract - Pharmacology Education, 192.
https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.122.149020
Satrya, I. D. G. (2023). Village Tourism Promotion
Through Virtual Tour. Ilomata International Journal of
Management, 4(2), 223–232.
https://doi.org/10.52728/ijjm.v4i2.745
Shrivastava, S., & Shrivastava, P. (2023). Virtual reality in
medical institutions: Innovative tool to strengthen the
process of delivery of medical education. Journal of the
Scientific Society, 50(1), 23.
https://doi.org/10.4103/jss.jss_159_21
Shuta, A., Shouta, S., & Nguyen, D. (2023). Design and
Implementation of a Web-based Multi-user Virtual
Reality System for Virtual Tour of Remote Places.
Proceedings of the 15th International Workshop on
Immersive Mixed and Virtual Environment Systems,
34–36. https://doi.org/10.1145/3592834.3592878
Tyastuti, D., Kunarisasi, S., Azwar, A., Fadhillah, M.,
Risahmawati, R., & Ekayanti, F. (2023). Community
medicine clerkship amidst COVID-19 pandemic: Re-
designing, implementation, and evaluation.
International Journal of Practice-Based Learning in
Health and Social Care, 11(1), 47–61.
https://doi.org/10.18552/ijpblhsc.v11i1.760
Vignaraja, V., Creese, J., Phillips, S., & Vusirikala, A.
(2022). Virtual Hospital Induction for Medical
Students: A Novel Approach. Cureus.
https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.28244
Wang, Y. (2021). Influence of Virtual Reality Technology
on Clinical Thinking Cultivation of Medical Students.
Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2021, 1–8.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8004883
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
346
