
Endophytic Bacteria from White Cambodia Stems (Plumeria
acuminata) Have Strong Inhibition Against Escherichia coli
Debie Rizqoh
1,* a
, Alvi Jalilul Hakim
2
, Novriantika Lestari
3
, Sipriyadi
4b
and Oktoviani
3c
1
Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Bengkulu,
WR. Supratman Street, Bengkulu City, Indonesia
2
Undergraduate Student, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Bengkulu,
WR. Supratman Street, Bengkulu City, Indonesia
3
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Bengkulu,
WR. Supratman Street, Bengkulu City, Indonesia
4
Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, University of Bengkulu,
WR. Supratman Street, Bengkulu City, Indonesia
Keywords: Endophytic Bacteria, Plumeria acuminata, Escherichia coli, Antibacterial Compounds.
Abstract: The health issues caused by Escherichia coli are a primary trigger for infectious diseases in Indonesia.
Bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics, leading to an increase in their usage. The rising use of
antibiotics has led to irrational usage, resulting in the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Therefore,
there is a need for new antibiotic sources that can combat bacterial infections, especially from various
biological resources. Due to its antimicrobial compound properties, white cambodia (Plumeria acuminata) is
a biological resource with potential as an antibiotic. One way to utilize this potential is by isolating endophytic
bacteria. The stem of the white cambodia provides a suitable environment for endophytic bacteria. Thus, this
study aims to determine the antibacterial potential of endophytic bacterial isolates from the stem of white
Cambodia to inhibit the growth of E. coli. This research uses a qualitative data collection method with
laboratory experimental research. In the first stage, endophytic bacteria were isolated from the stem of P.
acuminata using the serial dilution method. Subsequently, the characteristics of the colonies were observed
based on their shape, edges, elevation, texture, pigmentation, and the result of Gram staining. In the final
stage, the antagonistic test of the endophytic bacterial isolates against E. coli was conducted using the double-
layer agar method. The isolation of endophytic bacteria from P. acuminata resulted in 3,817 colonies. Based
on the observation of colony morphology, 93 isolates have different colony morphologies due to the diverse
characteristics of the colonies and bacterial shapes. The Gram staining test showed that 83 endophytic
bacterial isolates were Gram-positive, and ten were Gram-negative. The antagonistic test revealed that seven
positive endophytic bacterial isolates could inhibit the growth of E. coli. Endophytic bacterial isolates from
P. acuminata can produce antibacterial compounds that can inhibit the growth of E. coli.
1 INTRODUCTION
Infectious diseases still cause health problems in
developing countries like Indonesia. Based on
Indonesia's health profile in 2021 still has infectious
diseases are the reason death is most frequently post-
neonatal. In 2021, pneumonia and diarrhea still
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0327-5881
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1042-2576
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9195-0321
became the reason for death most during the post-
neonatal period 14.4 % of deaths were due to
pneumonia, and 14% were because of diarrhea. The
leading causes of death in the group of child toddlers
(12-59 months) are diarrhea by 10.3% and pneumonia
by 9.4% (Ministry of Health RI, 2021). Most of these
infectious diseases are caused by bacteria.
Rizqoh, D., Hakim, A. J., Lestari, N., Sipriyadi, and Oktoviani,
Endophytic Bacteria from White Cambodia Stems (Plumeria Acuminata) Have Strong Inhibition Against Escherichia Coli.
DOI: 10.5220/0013671700003873
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical Science and Health (ICOMESH 2023), pages 303-310
ISBN: 978-989-758-740-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
303

One of the most common bacteria that causes
infection in the ducts digestion is Escherichia coli,
which has been diagnosed by personnel health as one
reason diarrhea is the highest in Indonesia, reaching
10% (Ministry of Health RI, 2018). E. coli is a bacil
Gram-negative bacteria with a size range between 1.0-
1.5 μm x 2.0-6.0 μm. E. coli are many opportunistic
bacteria found in the large intestine of humans as a
microbiota. Most E. coli strains are commensal
bacteria that help, but some strains are pathogenic and
can cause disease. The disease that E. coli can cause is
diarrhea, which is caused by consuming contaminated
food or water. It also causes stomach cramps, malaise,
and fever (Joeginjantoro R, 2019).
Antibiotics are the primary choice for treating
bacterial infections due to their significant benefits in
reducing pain and death consequences of infectious
diseases. Its practical usage of antibiotics has rapidly
improved in overcoming and preventing infectious
diseases. Unfortunately, its high demand for
antibiotics has caused its use to be inappropriate and
excessive. The cause is the availability of easy
antibiotics obtained by society without instructions or
recipes from medical personnel, especially doctors.
Improper use of antibiotics can result in the
development of resistant bacteria to antibiotics, which
later becomes a severe issue in treating bacterial
infections (Andiarna et al., 2020).
Resistance to antibiotics is a problem that society
needs to handle seriously. When bacteria become
resistant to antibiotics, medicine has lost its
effectiveness in treating human infections and
diseases. Resistance to antibiotics can happen due to
mutation or transfer of resistance genes through a
horizontal process. Resistance genes can inherited or
acquired from an element genetically mobile, like a
plasmid that can transferred between bacteria.
Mutations known as single-step mutations cause
appearance resistance levels quickly and in a short
time (Nurjanah et al., 2020). Incident resistance in
Indonesia is sporadic, selective, and impossible to
overcome fully (Lia Yunita et al., 2021). Based on the
problem above, it is vital to research new antibiotics
from various sources that are effective in treating
bacterial infections.
One example of source life that can utilized is the
plant white cambodia (Plumeria acuminata), which is
frequently used as a source of traditional drugs. P.
acuminata is a plant originating from Central America
that belongs to the Apocynaceae family. P. acuminata
are often found in Indonesia. Apart from being an
ornamental plant, P. acuminata also has compounds
that have antimicrobial properties. P. acuminata is one
of the plants with potential as an alternative antibiotic
to treat infections caused by bacteria (Zulkifli et al.,
2022).
Endophytic bacteria reside and live inside network
plants and then form colonies without harming the
host plants (Tangapo et al., 2018). The connection
between endophytic bacteria and host plants own
mutual relationship, beneficial or symbiotic
mutualism. In this connection, plants supply nutrients
for bacteria, while bacteria protect plants from seed
disease, help produce phytohormones, and stimulate
the absorption of minerals, especially nitrogen. P.
acuminata stems provide a suitable environment for
endophytic bacteria that can do nitrogen-fixing. This
ability is beneficial in a biological way because it
helps plants obtain nitrogen (N). The N elements
comprise essential proteins in photosynthesis,
increasing plant resistance (Koomnok et al., 2007).
The presence of endophytic bacteria in plants is
significant because these bacteria can produce
bioactive compounds with characteristics similar to
those produced by host plants. This is because there is
an evolutionary genetic exchange between host and
microbe endophyte (Hasan Basri et al., 2021). This
compound provides profit for the plant and has
potency benefits, especially in matter health.
One of the uses of endophytic bacteria is research
conducted by Zulkifli (2022), showing that
endophytic bacteria in the bark of P. acuminata plants
have the potential to be a source of antibacterial
substances against the growth of Staphylococcus
aureus, Bacillus cereus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa,
and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Further research was
carried out by Hidayati (2019), where the results of
phytochemical tests showed that endophytic bacteria
in white Cambodia stems had secondary metabolites
in the form of alkaloids.
Based on the background above, research on the
isolation of endophytic bacteria in stems of P.
acuminata is critical because there is still limited
scientific information about the existence of P.
acuminata endophytic bacteria and their benefits as
agents producing potential antibacterial compounds to
inhibit the activity of E. coli.
2 METHODS
The type of research used by researchers is
experimental research. The data collection method
used by researchers was qualitative to determine the
antibacterial activity of the endophytic bacteria of P.
acuminata stems against E. coli. This research was
conducted at the Microbiology Laboratory, Faculty of
Medicine and Health Sciences, Bengkulu University.
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
304
The P. acuminata plant used in this research was
taken from Bengkulu City. The samples needed are
three stems from three P. acuminata plants.
2.1 Isolation of Endophytic Bacteria
Isolation of endophytic bacteria was carried out using
dilution methods. The samples that must be prepared
are three P. acuminata stems from three plants. The
P. acuminata stems were cut with a size of 2-5 cm,
then sterilized surface with running water, and peeled
the skin stem. The piece sample was sterilized by
soaking in alcohol 70% for 1 minute, then moving it
into 5.25% Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl) for 5
minutes, then moving it back inside 70% alcohol
three times with an interval of 30 seconds (Hidayati,
2019). After that, the sample is crushed or crushed
using a sterile mortar and pistil by adding 3-5 ml of
sterile distilled water. Prepare 5 test tubes filled with
9 ml of sterile distilled water, then take 1 ml of
solution from the first tube containing the sample that
has been ground with a micropipette and put it in the
second tube, then homogenized using a vortex mixer.
Please do the same thing; take another 1 ml sample in
the second tube filled with 9 ml of sterile distilled
water and put it in the third tube, then homogenize.
The same step is done until the fifth tube. After
dilution, take 0.1 ml of the suspension from each
dilution and distribute it in King's B medium
aseptically, then spread it evenly using a spreader,
then incubate the isolate for 24 hours in an incubator
(Rizqoh et al., 2021).
2.2 Colony Characteristics and
Morphology of Endophytic
Bacteria
The characterization of bacterial morphology is done
in macroscopic and microscopic ways. Macroscopic
observation involves elevation, edges, shape, and
bacterial colony formation. Meanwhile, microscopic
observations were done using Gram staining (Oktavia
& Pujiyanto, 2018).
2.3 Antagonist Test
Escherichia coli are cultured into Nutrient Broth
media. The media was incubated at room temperature
for 24 hours. Then, spectrophotometry will measure
turbidity (OD = 0.3 concentration 10 6 – 10 7 cells
/mL).
Antagonist tests of endophyte isolates against
target microorganisms are carried out using the
double-layer technique. This procedure involves the
use of semi-solid nutrient media and solid nutrient
media. E. coli put into NB medium. Furthermore, E.
coli culture is mixed into semi-solid NA media, then
placed on previously solid NA media as a layer first
on the plate. Isolate endophytic bacteria dotted atop
the layer, then incubated for 24 hours at room
temperature. Bacterial isolates are said to be positive
and produce compound antibacterial if an inhibition
zone is formed in the test. The inhibition zone then
measured the diameter of the inhibition zone based on
Morales category (2003) (Table 1).
Table 1. Inhibitory Power Categories (Morales, 2003)
Inhibition Zone Diamete
r
Cate
g
or
y
≥ 20
–
30 m
m
Ver
y
stron
g
10-20 m
m
Strong
5-10m
m
Moderate
≤ 5m
m
Wea
k
3 RESULTS
3.1 Isolation of Endophytic Bacteria
The results of calculating the number of endophytic
bacterial colonies that grow in a total of 3,810
bacterial colonies (Table 2) and after viewing based
on characteristics colony 93 isolates were found to
have characteristics different colonies.
Table 2: Calculation Results of the Number of Endophytic
Bacterial Colonies
Plant Code Dilution Number of Colonies
K
1
E 10
-1
Plate 1 209
Plate 2 181
K
1
E 10
-2
Plate 1 122
Plate 2 253
K
1
E 10
-3
Plate 1 267
Plate 2 273
K
1
E 10
-4
Plate 1 269
Plate 2 217
K
2
E 10
-1
Plate 1 137
Plate 2 15
K
2
E 10
-2
Plate 1 26
Plate 2 165
K
2
E 10
-3
Plate 1 33
Plate 2 56
K
2
E
10
-4
Plate 1 265
Plate 2 271
K
3
E 10
-1
Plate 1 TMTC
Plate 2 226
K
3
E 10
-2
Plate 1 TMTC
Plate 2 159
Endophytic Bacteria from White Cambodia Stems (Plumeria Acuminata) Have Strong Inhibition Against Escherichia Coli
305
K
3
E 10
-3
Plate 1 115
Plate 2 178
K
3
E 10
-4
Plate 1 259
Plate 2 114
Total Number of Colonies 3,810
*TMTC: too many to count
3.2 Characterization Colonies and
Morphology of Endophytic
Bacteria
From growing colonies of endophytic bacteria
screening between colonies, characteristics between
different colonies were observed by looking at the
colony's shape, edges, elevation, texture, and pigment
(Table 3). Based on the results of observations of the
characteristics of the colony, 93 isolates of
endophytic bacteria were obtained, which were
grouped into 14 different colony groups.
Gram staining is done to determine the
morphology of the bacteria by determining the cell
morphology and the Gram type (Table 4). The
observation results of microscopic Gram stain show
that there were 80 isolates of endophytic bacteria in
the coccus Gram-positive bacteria, four isolates of
endophytic bacteria were coccus Gram-negative
bacteria and nine isolates of bacillus Gram-negative.
Table 3 Characteristics Colony of P. acuminata Endophytic Bacterial Isolates
No
Characteristics colony
Isolate code
Number of
isolates
Shape Margin Elevation Texture Pigment
1. Circular Entire Convex Moist Shiny
white
KE 1, KE 5, KE 6, KE 9,
KE 10, KE 11, KE 21, KE
29, KE 30, KE 31, KE 32,
KE 33, KE 34, KE 35, KE
36, KE 37, KE 38, KE 49,
KE 50, KE 39
20
2. Circular Entire Convex Moist Yellow KE 2, KE 8, KE 17, KE
20, KE 78, KE 48, KE 51,
KE 53, KE 54, KE 81, KE
69
11
3. Circular Entire Convex Moist Shiny
white
KE 3, KE 18, KE 19, KE
22, KE 25, KE 62, KE 63,
KE 64, KE 65, KE 70, KE
71, KE 72, KE 60, KE 82,
KE 84, KE 85
16
4. Circular Entire Convex Moist Shiny
white
KE 4, KE 23, KE 74, KE
75, KE 52
5
5. Irre
g
ular Undulate Convex Moist White KE 7 1
6. Circular Entire Convex Moist Shiny
white
KE 12, KE 13, KE 14, KE
25, KE 26, KE 27, KE 41,
KE 42, KE 43, KE 57, KE
58, KE 61
12
7. Irregular Undulate Flat Moist White KE 15, KE 28, KE 66, KE
83, KE 89, KE 90
6
8. Circular Entire Flat Moist White KE 16, KE 45, KE 46, KE
55, KE 59, KE 67, KE 68,
KE 80
8
9. Irregular Undulate Flat Moist Shiny
white
KE 40 1
10. Irregular Undulate Flat Moist Yellow KE 44, KE 47, KE 76 3
11. S
p
indle Entire Convex Moist White KE 55 1
12 Circula
r
Undulate Flat Moist Yellow KE 73 1
13. Irre
g
ular Undulate Convex Moist Yellow KE 77, KE 79 2
14. Irregular Undulate Convex Moist Shiny
white
KE 86, KE 87, KE 88 3
Information : KE 1= Endophytic bacterial isolate 1
st
Cambodia and so on
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
306
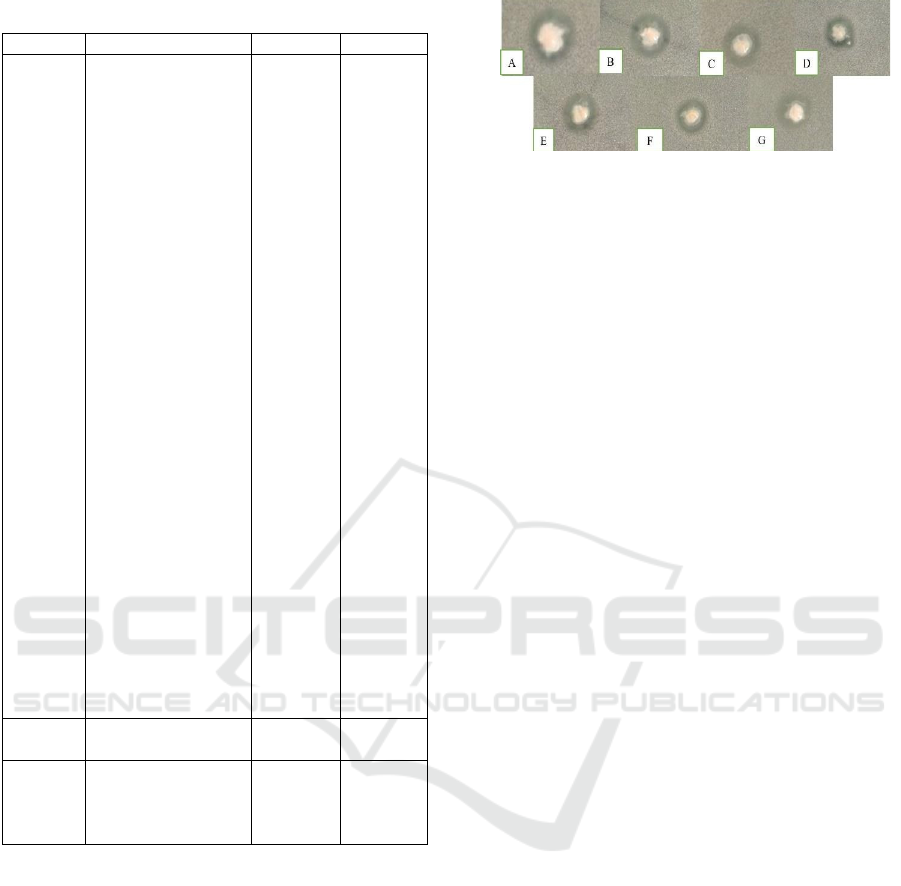
Table 4: Grouping Isolate Based on Gram Stain
Form Isolate Gram Amount
Cocci KE 1, KE 2, KE 3,
KE 4, KE 5, KE 6,
KE 7, KE 8, KE 9,
KE 10, KE 11, KE
12, KE 13, KE 14,
KE 15, KE 16, KE
18, KE 20, KE 23,
KE 24, KE 25, KE
26, KE 27, KE 28,
KE 29, KE 30, KE
31, KE 32, KE 33,
KE 34, KE 35, KE
36, KE 37, KE 38,
KE 39, KE 40, KE
41, KE 42, KE 43,
KE 44, KE 45, KE
46, KE 47, KE 48,
KE 49, KE 50, KE
51, KE 52, KE 53,
KE 54, KE 55, KE
56, KE 57, KE 58,
KE 59, KE 60, KE
61, KE 62, KE 63,
KE 64, KE 65, KE
66, KE 67, KE 69,
KE 70, KE 71, KE
72, KE 73, KE 74,
KE 75, KE 76, KE
80, KE 86, KE 87,
KE 88, KE 89, KE
90, KE 91, KE 92,
KE 93
Positive 80
Cocci KE 22, KE 17, KE
79, KE 78
Negative 4
Bacil KE 21, KE 19, KE
68, KE 77, KE 84,
KE 81, KE 82, KE
83, KE 85
Negative 9
3.3 Antagonist Test Endophytic
Bacterial Isolate to Escherichia coli
Of the 93 isolates obtained, an antagonist test was
carried out. The antagonist test was carried out using
a 2-layer agar method consisting of solid and semi-
solid nutrient media. Antagonist test results can be
seen in Table 5.
Antagonist test gets that result endophytic
bacterial isolates tested on E. coli. Seven isolates can
inhibit the growth of E. coli. Inhibiting activity
growth of E. coli bacteria can be seen from the clear
zone formed around the tested endophytic bacterial
isolate (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Clear zone formed around endophytic bacterial
isolates tested (A) KE 19, (B) KE 44, (C) KE 76, (D) KE
77, (E) KE 78, (F) KE 79, (G) KE 81
Calculating the zone of inhibition and endophytic
bacteria that grow using a compass tool shove. The
calculation method is by calculating the diameter of
the isolate and the zone of inhibition, subtracting the
diameter of the isolate, then obtaining a mark of the
diameter of the inhibition zone. The value of the
diameter of the inhibition zone formed is categorized
based on classification Morales (2003). Table 6
shows that isolates with codes KE 19 and KE 44 have
power activity hampered by categories strong against
E. coli bacteria. Isolate others with codes KE 76, KE
77, KE 78, KE 79, and KE 81 have power activity in
the moderate category of inhibition against E. coli
bacteria.
4 DISCUSSIONS
Endophytes are microorganisms in the form of
bacteria that live well in the tissues of the plant host.
In the network, plant endophytes do not give rise to
damage to plants. During co-evolution, endophytic
bacteria estimated origin from outside the
environment plants, then enter the network plant
passed various pathways, such as stomata (pores
small on the surface leaves), lenticels (holes in the
skin wood), lenticels (holes in the skin stem), wound
plant, area of emergence of shoots, roots side (root
shoots) and sprouts (Siregar et al., 2020). The number
of endophytic bacteria generally ranges between 10 3
-10 5 cfu /g network plants (Tangapo, 2018). In this
research, the results of the isolation of endophytic
bacteria from stem White Cambodia on King'B agar
that has been incubated for 24 hours, 3,810 colonies
of endophytic bacteria that grew, are presented.
There are differences in endophytic bacteria
colony numbers from the stem. It is in line
according to Afzal et al., which exists influencing
factors diversity of endophytic bacteria something
plants, besides competent with bacteria to colonize
plants as endophytic bacteria, plants host and factors
Endophytic Bacteria from White Cambodia Stems (Plumeria Acuminata) Have Strong Inhibition Against Escherichia Coli
307
the environment also has an influence on the diversity
of endophytic bacteria from something plant (Afzal et
al., 2019). Afzal et al. also mentioned that the total
population of endophytic bacteria in plants can vary
depending on the type of growth medium used for
isolation and the level of dilution when doing
isolation. In this study, endophytic bacteria were
isolated using King's B media. King's B media
consists of glycerol, peptone, dyspotassium
phosphate, magnesium sulfate, and agar, which
supports the growth of bacteria. King's B media was
selected because it has content similar to the situation
inside plants and is also non-selective, so it is possible
for endophytic bacteria to live and grow (Rizqoh et
al., 2021).
Table 5. Antagonist Test Results Endophytic Bacterial
Isolate to Escherichia coli
Results Isolate Code Number of
isolates
Positive (+) KE 19, KE 44, KE 76, KE
81, 78, KE 79, KE 77
7
Negative (-) KE 1, KE 2, KE 3, KE 4,
KE 5, KE 6, KE 7, KE 8,
KE 9, KE 10, KE 11, KE
12, KE 13, KE 14, KE 15,
KE 16, KE 17, KE 18, KE
20, KE 21, KE 22, KE 23,
KE 24, KE 25, KE 26, KE
27, KE 28, KE 29, KE 30,
KE 31, KE 32, KE 33, KE
34, KE 35, KE 36, KE 37,
KE 38, KE 39, KE 40, KE
41, KE 42, KE 43, KE 45,
KE 46, KE 47, KE 48, KE
49, KE 50, KE 51, KE 52,
KE 53, KE 54, KE 55, KE
56, KE 57, KE 58, KE 59,
KE 60, KE 61, KE 62, KE
63, KE 64, KE 65, KE 66,
KE 67, KE 68, KE 69, KE
70, KE 71, KE 72, KE 73,
KE 74, KE 75, KE 76, KE
80, KE 82, KE 83, KE 84,
KE 85, KE 86, KE 87, KE
88, KE 89, KE 90, KE 91,
KE 92, KE 93
86
Note: Positive (+) = potentially produce compound
antibiotics by forming an inhibition zone, Negative (-) = no
potentially produce compound antibiotics
Endophyte isolates of this research have various
types of colonies, including shape, edges, elevation,
texture, pigment, and cells. Diversity colonization
endophytes are formed and influenced by several
factors related to the environment, plants, and
bacteria. In addition to the ability of bacteria to
colonize plants as endophytes, the plant's host and the
environment in which bacteria grow can influence the
growth and size of endophytic bacterial cells in
certain plants. The age of the plant host, genotype,
location, geographic location, and even analyzed
network can determine the type of endophytic
bacteria it contains. Apart from that, the growth
stages of the host can also determine the diversity of
endophytes. Nutrient availability tends to experience
enhanced bacterial diversity where the plant stage is
enriched. Not only that, but the climate can also
influence the colonization of endophytes in plants
(Afzal et al., 2019). The isolates obtained were then
observed characteristics of the colony. Observation
morphology Bacterial colonies are needed to
facilitate the identification process of the type of
bacteria (Wardhani et al., 2020).
Table 6. Inhibitory Power Category Endophytic Bacterial
Isolate
No. Isolate
code
Inhibition
zone diameter
(
mm
)
Category
1. KE 19 13 ± 1.65 Stron
g
2. KE 44 10, 55 ± 0.05 Stron
g
3. KE 76 7.05 ± 0.4 Moderate
4. KE 77 7.3 ± 0.6 Moderate
5. KE 78 7.5 ± 0.6 Moderate
6. KE 79 7.35 ± 0.6 Moderate
7. KE 81 6.15 ± 0.7 Moderate
This result of the Gram stain also showed various
types of cell morphology. The type of endophytic
bacteria found in one plant host is not limited to only
types of endophytic bacteria, but consists of various
genera and types. Based on the results of research
conducted by Zulkifli (2022), skin stem P. acuminata
produces endophytic bacteria from the genus
Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and Alcaligenes. This is in
line with the statement Tangapo (2018) stated that the
genera Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Agrobacterium, and
Enterobacter are the most abundant genera found
(Tangapo, 2018).
This antagonist test stage tests between
endophytic bacterial isolates that have been obtained
in the isolation process with the target bacteria, E.
coli. The purpose of this antagonist test is to see the
ability of isolates of these endophytic bacteria to
inhibit pathogenic bacteria, namely E. coli. Results
from the antagonist test of endophytic bacterial
isolates to E. coli showed that seven positive isolates
of endophytic bacteria inhibit the growth of E. coli.
Seven isolates of this bacteria are KE 19, KE 44, KE
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
308

76, KE 77, KE 78, KE 79 and KE 81. These isolates
have different cell types; KE 44, KE 76, KE 78, and
KE 79 have cocci form, and KE 19, KE 77, and KE
81 have basil form. Every bacterias has a different
genetic composition, metabolism pathway, and
biochemical ability, so each has produced different
compounds and metabolites (Afzal et al., 2019).
Endophytic bacterial isolates that showed positive
results can be observed by forming a clear zone
around the colony of endophytic bacterial isolates. A
clear zone is formed because target microorganisms
cannot grow around the isolate. This can be
interpreted that the isolate from P. acuminata can kill
and inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
Endophytic bacteria benefit indirectly; bacteria as
biocontrol can role against or as controller microbe
pathogen through the production of antipathogen
compounds, one of them being antibiotics. Endophyte
microbes generally can produce compounds with
structures similar to those produced by plant hosts
with the help of enzyme activity. Some endophytes
also can produce compound antibiotics that can
oppose pathogen microbes. Compound antibiotics in
the form of metabolites Secondary bacteria, created
by endophytic bacteria, act as active substances,
antibiotics, or products that help protect plants from
attacking insects or pathogen microbes. Hence,
endophytic bacteria have the potential to be utilized
as biological agents or biocontrol agents to protect
plants from pathogens (Tangapo, 2018).
The formation of an inhibition zone around the
endophytic bacterial isolate that was inoculated on the
test medium indicates that endophytic bacteria from
P. acuminata have antibacterial activity. This finding
is in accordance with the results of research by Yuli
(2019), which states that fraction test ethanol from
flower P. acuminata has an antibacterial effect on E.
coli. Based on research conducted by Hidayati
(2019), endophytic bacteria from P. acuminata stems
produce secondary metabolites in alkaloids.
Additionally, P. acuminata stems have content in the
form of tannins, flavonoids, alkaloids, and
triterpenoids. An alkaloids compound in endophytic
bacteria present in P. acuminata stem have an
antibacterial effect. The alkaloid compound works
with mechanisms inhibition that interferes with
components shaper peptidoglycan inside bacterial
cells, resulting in the layer from bacterial cell wall no
longer forming correctly, resulting in cell death.
Apart from that, Alkaloids can also prevent protein
synthesis, which can influence bacterial metabolism.
This alkaloid compound can also prevent the
development of Gram-negative bacteria (Anggraini et
al., 2019).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research, the following
conclusion is derived. Results of isolation of P.
acuminata endophytic bacteria obtained as many as
3,810 colony endophytic bacterial isolates from stem
of P. acuminata. Result of observation of
characteristics colonies and morphology of
endophytic bacteria of 93 samples of P. acuminata
endophytic bacterial isolates get various type shapes,
edges, elevations, textured, bacterial pigments and
also shape bacterial cells. The result of the Gram stain
shows that there were 80 isolates in the Gram-positive
group and 13 isolates in the Gram-negative group.
Antagonist test results of the 93 endophytic bacterial
isolates tested against E. coli bacteria showed seven
endophytic bacterial isolates in P. acuminata have the
potency to inhibit the growth of E. coli.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thanks for the support from the Faculty of Medicine,
Universitas Bengkulu, laboratory staffs, and all
parties who have helped this research process. A grant
from the Non-tax Revenue of the Faculty of
Medicine, Universitas Bengkulu, supports this
research.
REFERENCES
Afzal, I., Shinwari, Z. K., Sikandar, S., & Shahzad, S. 2019.
Plant beneficial endophytic bacteria: Mechanisms,
diversity, host range and genetic determinants.
Microbiological Research, 221 (April 2018), 36–49.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2019.02.001
Andiarna , F., Irul , H., & Eva, A. 2020. Health Education
on Use Antibiotics in a way Appropriate and Effective
as an Effort to Overcome Drug Resistance. Journal of
Community Engagement and Employment, 2 (1), 15–
22.
Anggraini, W., Nisa, SC, Da, RR, & Ma, B. 2019.
Antibacterial activity of 96% ethanol extract cantaloupe
fruit (Cucumis melo l. Var. Cantalupensis) against
Escherichia coli bacteria. Pharmaceutical Journal of
Indonesia, 5 (1), 61–66.
Awaluddin Prihanto, A., Dwi Laksono Timur, H., Abdul
Jaziri, A., Nurdiani, R., & Pradarameswari , KA. 2018.
Isolation and identification of mangrove endophyte
bacteria Sonneratia alba producing gelatinase enzyme
from Sendang Biru Beach, Malang, East Java.
Indonesian Journal of Halal, 1 (1), 31.
https://doi.org/10.14710/halal.v1i1.3114
Endophytic Bacteria from White Cambodia Stems (Plumeria Acuminata) Have Strong Inhibition Against Escherichia Coli
309

Basri, M.H., Zulkifli, L., & Syukur, A. 2021. Isolation of
Endophytic Fungi from Vitex trifolia L and
Antagonism Test against Sclerotium rolfsii and
pathogenic bacteria. Journal of Biology Tropical, 21
(1), 72–80. https://doi.org/10.29303/jbt.v21i1.2340
Hidayati, MN. 2019. Isolation and characterization of
endophyte bacteria from the sticks of white cambodia
plant (Plumeria acuminata). Journal of
Pharmacopolium, 2 (1), 30–36.
https://doi.org/10.36465/jop.v2i1.469
Ministry of Health. 2018. 2018 Basic Health Research
Results. Indonesian Ministry of Health, 53 (9), 1689–
1699.
Ministry of Health. 2021. Indonesian Health Profile. In
pusdatin.kemenkes.go.id.
Koomnok, C., Teaumroong, N., Rerkasem, B., &
Lumyong, S. 2007. Diazotroph endophytic bacteria in
cultivated and wild rice in Thailand. Science Asia, 33
(4), 429–435. https://doi.org/10.2306/scienceasia1513-
1874.2007.33.429
Lia Yunita, S., Novia Atmadani, R., & Titani, M. 2021.
Influencing Factors Knowledge and Behavior Use
Antibiotics in UMM Pharmacy Students.
Pharmaceutical Journal of Indonesia, 6 (2), 119–123.
https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.pji.2021.006.02.7
Nurjanah, GS, Cahyadi, AI, & Windria, S. 2020.
Escherichia Coli Resistance to Various Kinds of
Antibiotics in Animals and Humans: a Literature Study.
Indonesia Medicus Veterinus, 9 (6), 970–983.
https://doi.org/10.19087/imv.2020.9.6.970
Oktavia, N., & Pujiyanto, S. 2018. Isolation and
Antagonism Test of Endophytic Bacteria Tapak Dara
(Catharanthus Roseus, L.) Against Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. J. Periodic
Biotechnology, 1 (1), 6–12.
Rizqoh, D., Kumala, WO, Sipriyadi, S., Sinuhaji, B., &
Oktoviani, O. 2021. Potential of Endophytic Bacteria
Andaliman (Zanthoxylum Acanthopodium DC.)
Inhibits bacteria that cause infections in humans.
JUMANTIK (Scientific Journal of Health Research), 6
(3), 194. https://doi.org/10.30829/jumantik.v6i3.8866
Siregar, B., Kasim, N., & Farida, N. 2020. Isolation and
characterization biology of endophytic bacteria,
phyllosphere and rhizosphere from plant sago. 335–
340.
Tangapo, AM, Astuti, DI, & Aditiawati, P. 2018. Dynamics
and diversity of cultivable rhizospheric and endophytic
bacteria during the growth stages of cilembu sweet
potato (Ipomoea batatas L. var. cilembu). Agriculture
and Natural Resources, 52 (4), 309–316.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anres.2018.10.003
Wardhani, AK, Uktolseja, JLA, & Djohan. 2020.
Identification Morphology and Growth of Padapada
Bacteria Fluid Fermented Fish Feed Silage. Fifth
National Seminar on Biology and Science Education
(SNPBS), 5 (1), 411–419.
Zulkifli, L., Rasmi, DAC, Sukarso, A., Andayani, Y., &
Jekti, DSD. 2022. Isolation, Molecular Identification
and Antibacterial Activity of Endophytic Bacteria from
Bark of the Plumeria acuminata. Journal of Science
Education Research, 8 (3), 1158–1165.
https://doi.org/10.29303/jppipa.v8i3.2249
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
310
